A staircase is an integral part of buildings with multiple floors. In private houses, many craftsmen equip stair flights with their own hands, since the price for the services of professional companies is too high. However, along with the usual structures serving to communicate the floors, there are evacuation ones, which are called smoke-free.
The presence of smoke-free stairs is dictated by the SNIP for a number of buildings, therefore, many architects, when designing a particular structure, are obliged to provide for them. In this article, we will look at the features and types of smoke-free staircases that exist today.

Staircases
Modern stairs, based on the characteristics of their location in the building, are divided into 3 types:
- 1st, in which the staircase is in the staircase located inside the building.
- 2nd, the staircase is open, but at the same time it is located inside the building.
- 3rd - open and outside the building structure.
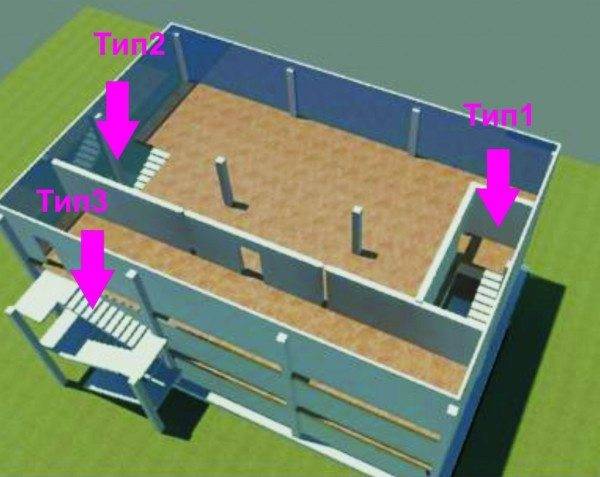
We are talking about structures designed for evacuation purposes..
In turn, they are of two types:
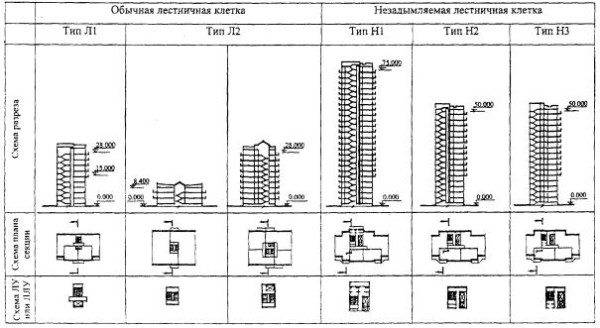
- Regular:
-
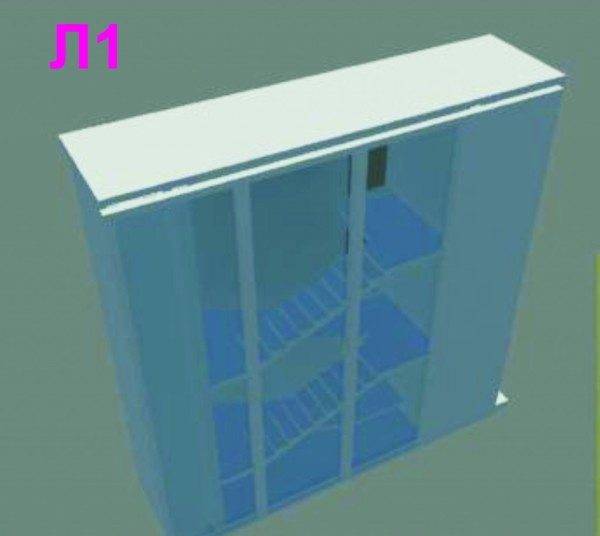
- L 1 - when the structure has open or glazed openings in the outer walls. They should be located on each floor.

-
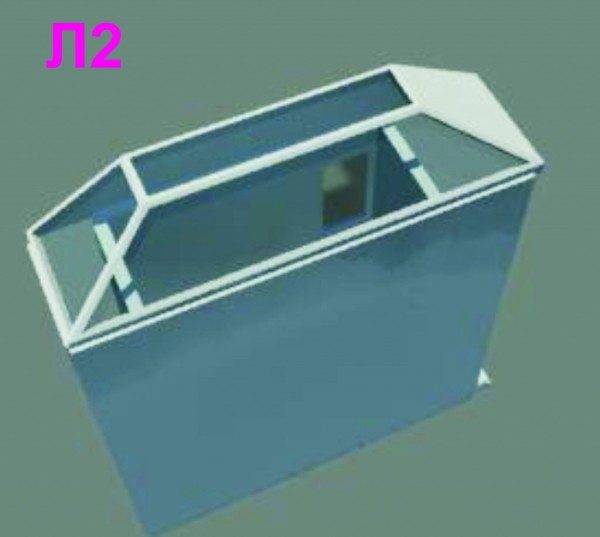
- L 2 has open or glazed openings in the roof.

- Smoke-free.
Types of smoke-free stairways
First, let's take a look at what a smoke-free staircase is. Its difference lies in the fact that in the event of a fire, OFPs (smoke, fumes, etc.) do not penetrate into it.
Types of smoke-free staircases:
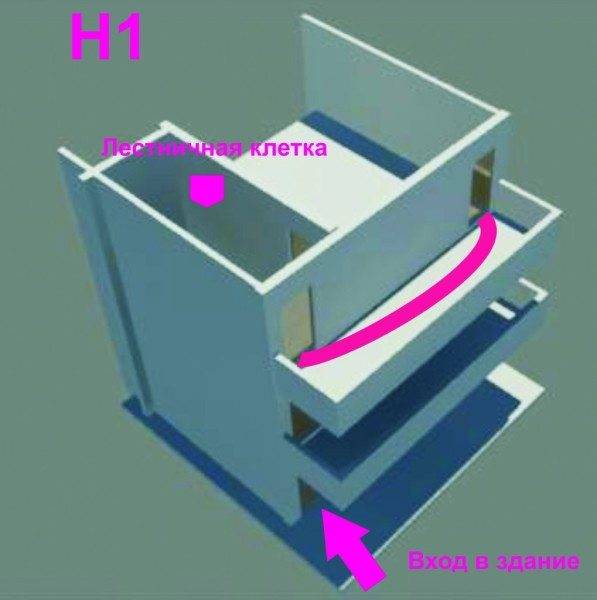
- Smoke-free staircase type H1. This design allows you to get directly into the building only through the balcony, which in this case is a smoke-free area. In other words, it will be impossible to get into the building through it. Thus, entering on any floor, a person will have to go through the balcony, which is an air zone, and only then he will get into the corridor, hall, etc.
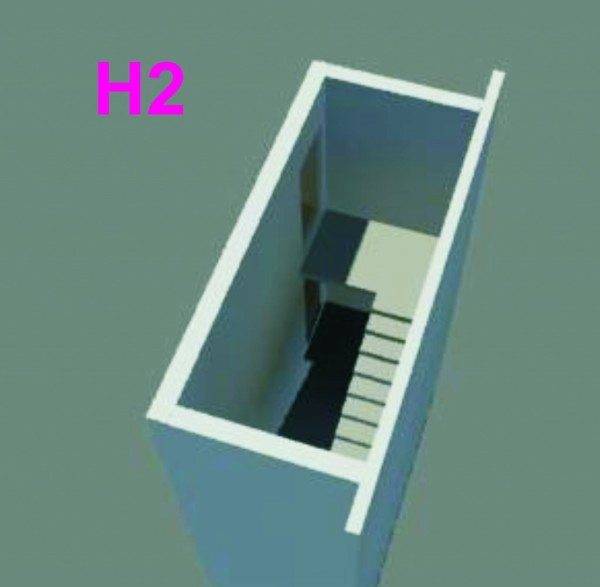
- Smoke-free staircase H2. We are talking about a room with fire walls, where by means of ventilation boxes, a continuous supply of fresh air is carried out into the structure of the H2 type.
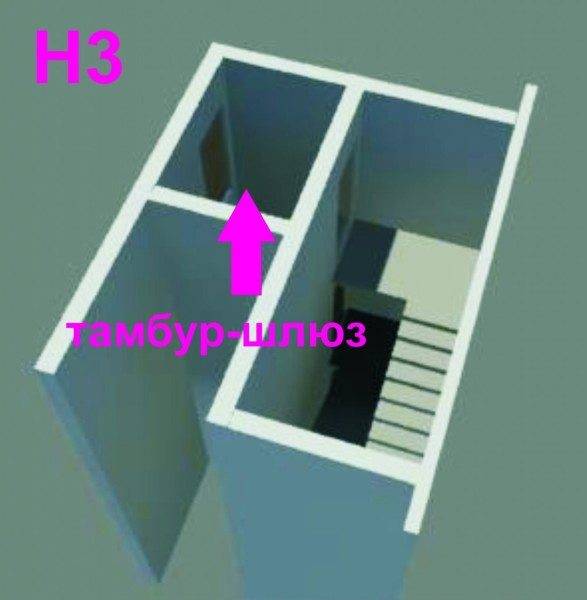
- The design of the H3 type assumes that the stairs are located in the staircase, which can only be accessed by means of a tambour-sluice with fire walls. In this room, air is pressurized by means of ventilation boxes. Doors in such systems, as a rule, are made of fire-prevention ones, equipped with an automatic doorway.
Implementation of evacuation from smokeless cages
Doors leading from such staircases are evacuation doors, and therefore they must meet all the requirements of SNIP for smoke-free staircases, in particular SNIP 21.01.97 *, which states: the emergency passage must have a width of more than 1.2 meters, its height must be more than 1.9 meters. Such parameters refer to premises A 1.1, that is, when it comes to evacuating more than 15 people at the same time.
Advice!
It is necessary to provide for such a width of the opening that would be sufficient for convenient transportation of the stretcher with an adult.
In the event that the exits leading from the smokeless cages do not meet the requirements of SNIP, then such structures should be considered as spare, which can be used in case of evacuation.
Advice!
Those exits that do not comply with the SNIP and are considered spare are not considered as evacuation exits in the initial design, that is, in addition to them, the architect must provide full-fledged exits that meet the standards.
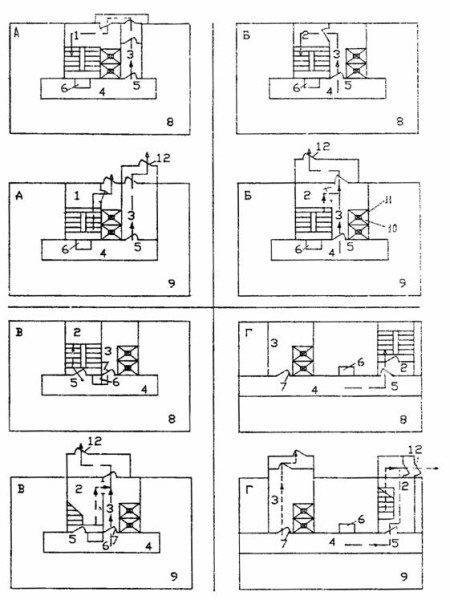
These outputs include:
- Exits to the balcony, which is open from all sides or from one side.
- To the transition that leads to the adjacent section of the building, which has class F 1.3.
- To the veranda / balcony, which are equipped with an outdoor fire escape.
In turn, exits that lead to:
- From the premises located on the first floor of the building to the street.In this case, the exit should be carried out:
- Through the foyer or lobby.
- Through the corridor.
- Through the lobby.
- Through the corridor and lobby.
- From rooms located on any floor, except for the first:
- To the stairs that lead to the street.
- To a corridor that ends with a type 3 staircase or smoke-free cage.
- In the foyer or hallway, which has an exit to the staircase or staircase belonging to the 3rd level.
- To the adjacent room, which is located on the same floor and has access to the street.

The following output options are allowed:
- Evacuation basement and basement exits should be provided in the lobby.
- From the foyer, dressing rooms, sanitary and smoking rooms, the placement of which falls on the basement or basement floors, the exit should be provided to separate stairs belonging to the second type, or the lobby of the first floor.
- Evacuation exits from premises for various purposes should be provided for type 2 stairs.
- The exit to the outside from the basement or basement floor can be equipped with a vestibule, including a double one.
Requirements for the width of marches

The width of the march for the stairs, which is designed to evacuate people from the building, must be at least:
- 1.35 m, if we are talking about buildings of class F 1.1.
- 1.2 m if there are more than 200 people in the building.
- 0.7 meters for stairs that lead to single workstations.
- For all other cases, the width of the flight of stairs should be up to 0.9 meters.
The tread width must be at least 25 cm with a step height of less than 22 cm. Otherwise, during a panic, the risk of injury to evacuees increases. The steps should never be too large or too small.
Some nuances
Instructions for arranging smoke-free stairs are based on the features of each of these structures.
Let's consider them in more detail:
- H1. If we are talking about buildings exceeding 30 meters in height, then in this case all stairwells of category H1, according to the regulations, must be smokeless. Each unit must be provided with natural lighting from the windows, in addition to which the span is equipped with an emergency source of lighting for the stairs.
The H1 type is excellent for high-rise residential and public buildings. Such a flight of stairs can be accessed from the vestibule or corridor through the open outer air zone of the loggia, through the outer passage, balcony or gallery. At the same time, the width of the air zone is at least 1.2 meters, and the width of the approach to this zone should be less than 1.1 meters.

Advice!
Such structures are best placed in the inner corners of buildings.
Remember that the distance from the staircase exits to the adjacent window must be more than 2 meters, which will ensure effective smoke-free air zone.
- Based on the requirements of SNIP 31.1, it is allowed to design sites of the type H2 and N3 in large cities for buildings with a height of 28 to 50 meters.
Advice!
These types of cages are also applicable to lower buildings that are residential or public.
Cell H "can be accessed by means of a corridor or an airlock, it is also possible to pass through the elevator hall, but only if the elevator is equipped with E130 class fire doors.
Smoke-free cages of the H2 type are distinguished by a device for pressurizing the air flow, which is supplied to the territory of the stairs in the event of a fire. It is advisable to delimit such cells vertically, creating compartments every 8 floors to reduce the volume of air, as a result of which an air pressure is created.
In such areas, it is strictly prohibited:
- Blocking the passage with personal belongings of residents (boxes, sports equipment, strollers, etc.).
- De-energize the fire panel equipped with a smoke protection system in the new house after acceptance by the fire department.
- Hang cables and wires other than those required by fire safety regulations.
- Cut through doors in blind partitions (fireproof).
- Forcing furniture, locking or clogging emergency exits and balcony hatches.
Requirements for fire barriers
SNIP 21-01-97 * specifies the following requirements for fire barriers:
- Such barriers are designed to prevent the spread of fire and combustion products from the room with a fire source to other rooms of the building.
- Firewalls include walls, ceilings and partitions.
- Such barriers must be characterized by fire resistance and fire safety.
Fire resistance in this case is determined by the fire safety of such structural elements:
- Structures that are responsible for the stability of the obstacle.
- Structures that are supporting for a fire barrier.
- Fastening nodes.
- The enclosing part.
- Overlappings and partitions of the vestibule sluices should also be made fireproof.

Conclusion
Evacuation stairs are an integral part of any multi-storey building. In the event of a fire, they must ensure the safe exit of people in the building to the street, therefore, their correct arrangement is very important. You can glean all the useful information on this topic in the video in this article.






