Are there any GOSTs for outdoor fire escapes? What exactly do these normative documents regulate? What requirements do they contain? Let's figure it out.

Why is it needed
During the construction of apartment buildings, industrial, public and administrative buildings, one of the mandatory requirements is to ensure the possibility of evacuation in case of fire.
However, let's leave the bureaucracy and formulate the problem in simple language.
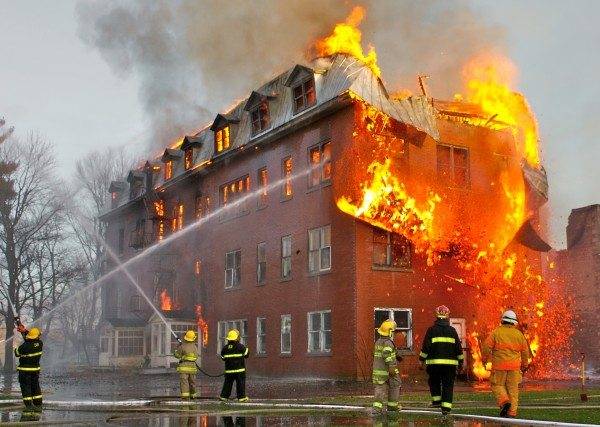
There is always food for fire in any home. Curtains, hardwood floors, furniture can all burn beautifully. As soon as the fire flares up - and the thrust arising in all vertical mines, ventilation and interfloor openings turns a small flame into a raging fire storm, devouring all combustible materials. Including those capable of igniting at very high temperatures.
If at the initial stage of a fire it is possible to defend a burning room using a fire extinguisher, then literally a few minutes later the situation can only be changed by the use of heavy fire fighting equipment. There is only one thing left for the inhabitants of the house - an urgent evacuation.
An important detail: when extinguishing a fire in the initial stages, you can use only and exclusively a fire extinguisher. An attempt to pour a bucket of water into the hearth of a fire very often leads to an electric shock: the insulation drains from the wires already at 200 degrees.
In multi-storey buildings, the flame always spreads from bottom to top - thanks to the notorious draft. Indoor staircases very quickly turn out to be smoky, with unbreathable air; moreover, this air soon heats up to dangerous temperatures. The only escape route is outside stairs.

Regulations
Currently, there are two documents in force that regulate the requirements for outdoor fire escapes:
- Fire safety standards NPB 245-97, introduced by the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia in 1997.
- The current GOST for fire ladders by number R 53254-2009 was adopted 12 years later and duplicates the previous document on almost all points. In the standard, the requirements are expanded and set out in more detail, so in the future we will consider just its text.
Standard requirements
Application area
The standard regulates the production and installation of metal stairs intended for evacuation in case of fire - marching and vertical; platforms for these stairs and fences to them. We are talking about all fixed staircases installed outside residential, public and industrial buildings; in addition, roof fencing has been standardized for the safety of people during evacuation or firefighting activities.
The standard specifies the types of fire escapes, their dimensions and other parameters, the general requirements for them and the test procedure for compliance with these requirements.
The norms of the standard are applied at the stage of design and commissioning of a building. In addition, the GOST requirements for testing fire escapes are applicable during periodic inspections.

Definitions
The standard uses a number of specific terminology. Some of the terms need clear definitions.
- Bowstring Is a longitudinal structural element to which the steps are attached.
Clarification: along with the bowstring, the function of the supporting element can be performed by stringerslocated under the steps; however, they are rarely used in the construction of fire and escape ladders: bowstrings are more compact with the same strength characteristics.
The vertical ladder consists of two vertical bowstrings, rigidly connected by steps.
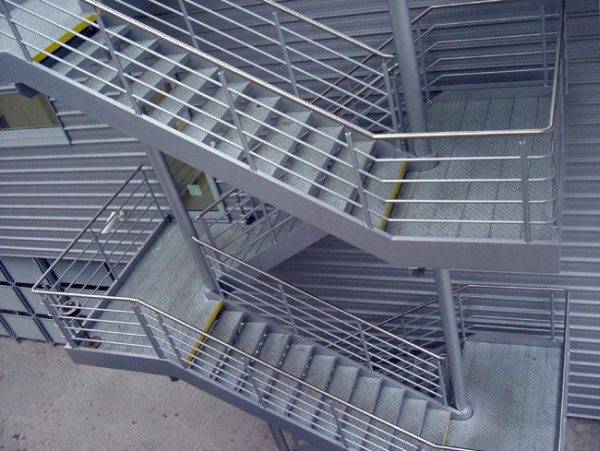
- March - construction of two parallel inclined bowstrings, rigidly connected by steps.
- Area consists of a horizontal base with a guard.
- Marching staircase - from marches and platforms rigidly fixed relative to each other (stairs can be both single-march and multi-march).
- Beam - a structural element by means of which the staircase is attached to the wall or supporting column of the building.
- Static load - constant, with a constant vector, impact on the structure from the outside.
- Permanent deformation - change in the shape of the structure after removing the load. Measured as the distance between the original position of the control point and its position after the load is removed.
Classification
GOST for outdoor stationary fire escapes and roof fences classifies them as follows:
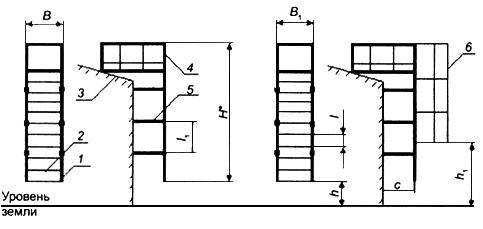
- External fire ladders are divided into two types - P1 (vertical) and P2 (marching). In turn, type P1 is subdivided into non-fenced P1-1 up to six meters high and equipped with P1-2 fencing (height 6 meters or more).
It is worth clarifying: GOST for the fire escape P1-2 was adopted relatively recently; most of the old houses (including those whose roof is at a distance of more than six meters from the ground) are equipped with ladders without fencing and will not be re-equipped in the foreseeable future.
- Fences are divided into MH, intended for mid-flight staircases, and HV for vertical ones; PN - for sites; KO - for roofs without a parapet and KP - for roofs with a parapet.
- Decks for platforms and steps are also divided into several types: F - solid corrugated; Ш - stamped; P - from steel strips, welded by an edge, and round timber; C - from steel strips welded in with an edge in one direction; В - steel expanded metal decks.

Dimensions (edit)
GOST for metal fire escapes regulates, of course, some of their dimensions and roof parameters associated with the construction of fire escape routes.
For escape stairs:
- The width of the step (tread) must be at least 25 centimeters. Of course, the requirement is relevant only for marches: with vertical structures, crossbars of such a width would interfere with the descent.
- The width of the march (the length of the step) is not less than 0.9 meters.
- The height of the fence should not be less than 1.2 meters.
For marching firefighters (type P2):
- The width of the ladder from bowstring to bowstring is not less than 500 mm, full width - not less than 600 mm.
- The width of the step is at least 200 millimeters.
- Step height - no more than 200 millimeters for a march located at an angle of 45 degrees to the horizon, and no more than 300 for an angle of 60 and 80.5 degrees.
- The fence should not be lower than one meter.
For vertical firefighters (type P1):
- The width must be at least 600 millimeters for type P1-1 and 800 for type P1-2. The instructions for a larger width for a ladder with a fence are clear: in a 60-centimeter shaft, a large person may well get stuck.
- The distance from the last step to the ground should not be more than one and a half meters.
- The length of the beams (elements connecting the bowstrings to the wall or columns) is at least 300 millimeters.
- Fencing of P1-2 type structures should end no more than 2.5 meters from the ground.

A number of additional parameters are also regulated:
- A fire escape must be present at points where the height of the roof changes by a meter or more.
- Type P1 is intended for buildings and roof heights up to 20 meters (which corresponds to 6 floors). For higher heights, P2 are intended.
- Marches should be separated by a distance of at least 7.5 centimeters. The handrails of the marches are mounted at the same distance.
- The rectangular landing of a vertical staircase adjacent to the roof should not be less than 0.8 meters in length.
- There is even a GOST for the dimensions of the steps of the stairs. In kindergartens and nurseries, the maximum distance from the bottom step to the ground is regulated: the height should not be greater than that of the step itself. At the same time, in preschool institutions, only corrugated flooring can be used for playgrounds, for steps - stamped or expanded.
- For vertical structures, the lower section can be sliding, in the manner of a step-ladder. At the same time, it must be securely fixed in the lower position.
- The width of the flat surface of the site must be at least 500 millimeters. This width is enough for a person of any size to be able to move from march to march. The width of the platform, together with the supporting elements of the structure, should not be less than 600 millimeters.
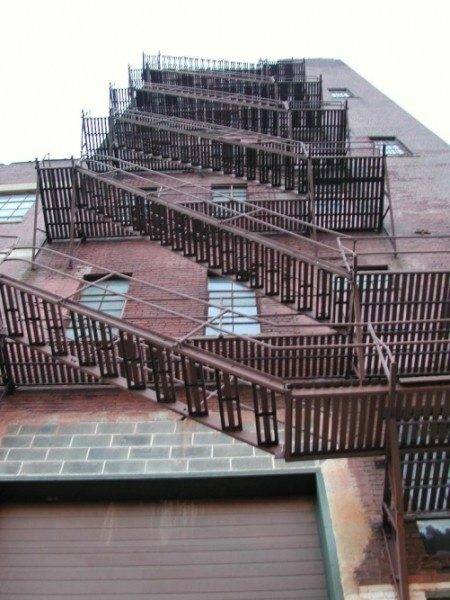

- The minimum height of the platform fencing is the same 1000 millimeters as for stairs.
- The minimum height of the roof railing without a parapet is 600 mm, for a roof with a parapet - 600 mm minus the height of the parapet itself. The fence posts must be connected with horizontal bridges; the distance from the upper edge of the fence to the lintel is not less than 300 millimeters (the distance will allow you to detain a person in case of an accidental fall from a pitched roof).
Technical requirements
GOST for an external fire escape contains a number of requirements for its design and execution.
- Weld seams, assembly and factory joints should not have protrusions, burrs and sharp edges. The seams must be free of scale; in addition, the surface must not be rusty.
Useful: the problem of corrosion is solved by periodic painting with PF-115 alkyd enamel with preliminary cleaning of problem areas with a metal brush. The price of a 3.5-kilogram can of paint does not exceed 200 rubles; work can be done with his own hands even ... how to put it politely ... a person with a purely humanitarian mindset.
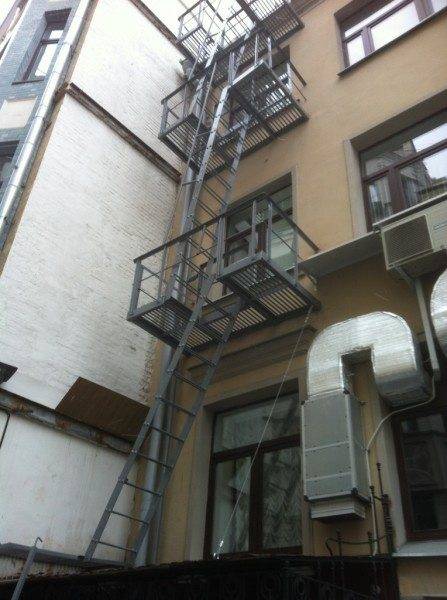

- Cracks in the embedding of beams in the wall, incomplete seams of metal structures are unacceptable.
- Each stage must withstand a static test load of 1.8 kN (which corresponds to a mass of 180 kilograms). The load vector during testing is directed vertically downward.
- Staircase and roof railings are mounted with a horizontal load of at least 0.54 kN (54 kgf).
Testing
At the acceptance stage, the following parameters are checked:
- Basic dimensions.
- Limit deviations from nominal dimensions.
- The integrity of the structures themselves and their fastenings (determined by visual inspection).
- The quality of the welds (and it is determined visually).
- The condition of the protective coating (as already mentioned, alkyd enamel most often plays its role).
- The location of the stairs and their accessibility during evacuation.
- Strength of individual steps, beams and flights. Every fifth stage is subjected to strength tests. After the load is removed, there should be no permanent deformation and signs of violation of the integrity of the structure.
It is worth clarifying: the test load is applied to the tested part of the structure for 2 minutes.
- The strength of the fences.

Output
It seems that we have provided the reader with the necessary minimum of information on the topic of interest. In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic (also learn about the benefits of dielectric stairs).
Good luck in construction!






