The staircase is the staircase itself with flights, platforms and fences, plus walls with openings in them (window and door), as well as the ceiling and floors that enclose it. Everyone understands that the stairs serve us to move to different levels of the building.
But not every man in the street thinks, looking at the staircase, that in the event of a fire, it may or may not become a saving corridor to fresh air and safety. In this case, one might say, human health is being decided, and possibly life.

Useful information
We strongly recommend all developers not to lose sight of this critical aspect of construction, especially those who design and build with their own hands. Perhaps, the article will look like a boring instruction below, but after reading it carefully, you can easily figure it out and get what you need for your case.
However, one should not forget that theory and practice often differ, therefore, before embarking on any types of work, you should make sure that the data, measurements and information received are accurate. We will not describe detailed instructions for the installation of each type of cage; further, complete information on the purpose and classification of structures will be provided.
Staircase classification
The basis of the difference is fire safety and unhindered evacuation of people in case of fire and smoke generation in a building, as a result of which the following types of stairs and staircases are formed:
- Ladders.
- Internal - type 1.
- Internal open - type 2.
- Outdoor open - type 3.
- Common types:
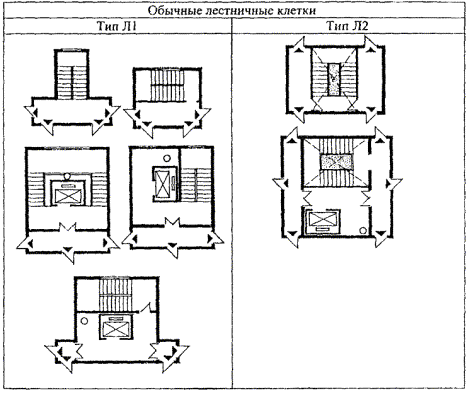
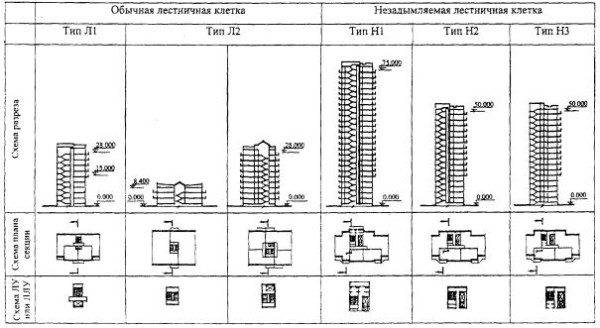
- Staircase type L1 - must have glazed or non-glazed (open) openings on each floor in the outer walls.
- Staircase type L2 - with natural light through glazed or open openings in the roof.
Smoke-free structures:
- Staircase type H1 - with an entrance to it from the floors of the building through the street part of the structure along an open passage, provided with no smoke. Usually used in administrative and educational institutions for the safe evacuation of people.
- Staircase type H2 - with a backpressure (supply) of air in case of a possible fire, which allows people to receive oxygen.
- Staircase type H3 - equipped with an entrance from the floor through a vestibule with air pressure during a fire or constant supply.
This is how the type of stairwells is classified according to SNiP for fire safety of buildings and structures. As you can see, the main factor in breaking down into types of structures is the degree of smokeiness of the structures in the event of a fire.
Note! This does not apply to home stairs installed in country houses for the transition between two or three levels.
Requirements for stairs and stairwells
Since staircases serve as an escape route in case of fire, SNiP 21-01-97 * "Fire safety of buildings and structures" regulates the fire-technical parameters of stairs, marches and platforms:
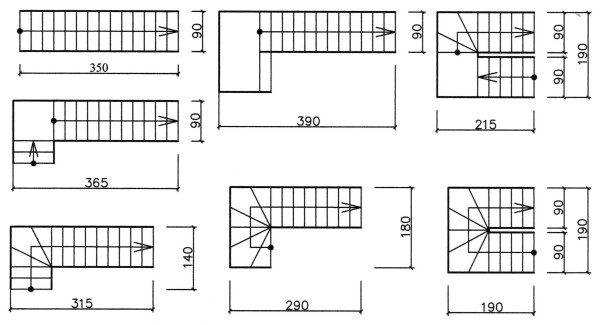
- The width of the flight of stairs, along which the evacuation of people is planned, must be no less than the calculated one, or equal or more, the width of any exit (door) to it intended for evacuation. At the same time, comply with the permissible dimensions:
- Buildings of class F 1.1 - the size should be 1350 mm.
- For buildings with the number of people simultaneously staying on each next floor, except for the first one, exceeding 200 people - the width is about 1200 mm.
- For stairs intended for access to a single workplace - not less than 700 mm.
- In other cases, an average of 900 mm.
- The permissible slope of stairs for evacuation is 1: 1; tread depth - not less than 250 mm, riser height - not higher than 220 mm.
Important! By violating the standard dimensions, you allow the possibility of people descending or climbing to knock down a step, stumble and fall.
- The slope for open stairs can be up to a 2: 1 ratio.
For your information! The slope is the ratio of the depth of the tread and the height of the step (riser).
- Open-type stairs should be made of non-combustible materials and mounted near blind (without light openings) walls, of a class not lower than K1, with a high fire resistance limit. Such stairs should be equipped with platforms at the level of emergency exits, fenced off at a height of at least 1200 mm. The distance to the nearest window opening should not be less than 1000 mm.
- In width, landings must correspond to the width of the march.
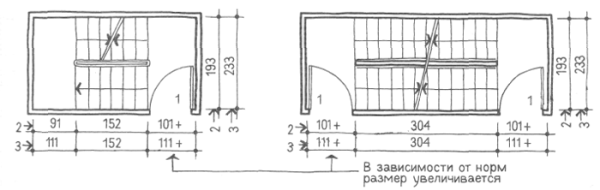
- The doors to the staircase should not, when opened, narrow the existing width of the marches and landings to which they exit. In addition, all doors should be equipped with door closers that allow the door leaf to be fixed in the desired position.
- Cluttering of staircases is not allowed:
- Built-in wardrobes. The exception is cabinets with communications.
- Equipment protruding at a height of 2200 mm from treads and platforms from the plane of the walls.
- Household items (boxes, baby carriages and much more).
- Lay gas pipelines, electrical cables. An exception is the wiring for lighting the staircase itself.
- Allowed:
- Place the heating system devices exclusively in smoke-free rooms - staircases of the H2 and H1 types.

- The location of the garbage chute and electrical wiring for lighting living quarters in ordinary stairwells of structures up to 28 m.
- Stairwells should be equipped with an exit to the outside directly, or through the lobby. The corridors adjacent to the lobby must be fenced off with a wall (partition) with a doorway. If an emergency exit is carried out by two stairs through a common area, then one, at least, should be equipped with an exit directly to the territory adjacent to the building. Stairwells of the H1 type must have an exit exclusively directly outside.
- Stairwells of type L1, H1 and H2 should be illuminated in a natural way, through special openings in the facade walls on each floor. The recommended area of light openings is 1.2 m2 or more. The number of unlit structures, therefore, should not exceed 50% of the total. This rule works for buildings:
- Classes F2, F3 and F4 - cages of type H2, H3 arranged with air access in case of fire.
- Class F5, category B (height up to 28m), - type H3 cages with the possibility of air ingress in case of fire. As for the categories D and E, the height of the structure does not matter in them.
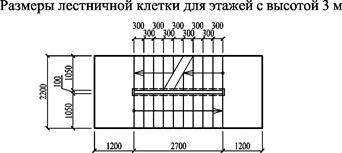
- Stairwells of type L2 must be equipped with light openings in the covering with an area of about 4 m2, provided there is a gap between the openings with a width of at least 700 mm. Or a light shaft along the entire height of the staircase, with a horizontal section of at least 2 m2.
- Protection of staircases (for types H2 and H3) from smoke is provided in accordance with SNiP 2.04.05. If necessary, ladders of the H2 type are divided in height into separate spaces with the help of blind fire partitions. The passage from compartment to compartment is carried out outside the stairs.
- Stairwells of the H2 type are equipped with blind (non-opening) windows.
- Open passages to structures of type H1 are arranged with a width of 1200 mm, and a fence height of 1200 mm. The distance between doorways in the outdoor air zone is 1200 mm and between doorways and the window is more than 2000 mm. This ensures that the staircase is smoke-free.
- In buildings with a permissible height of up to 28 m, of practically any class of functional fire hazard, staircases of type L1 can be provided. For buildings of class F5 (with categories A and B), access to the corridor on the floors must be provided through a tambour-gate with constant air access.
- For buildings above 28 m, smoke-free staircases of the H1 type are recommended.
- It is permissible to provide staircases of type L2 in buildings with fire hazard class F1, F2, F3 and F4 with a height of not more than 9 m.
- In buildings with equipped non-smoke staircases, smoke exhaust systems with smoke detectors are installed in all common areas (halls, corridors, foyers, lobbies).
Note! Smoke detectors should be installed in any places where there is a possibility of fire, they provide almost complete safety of people in the room.
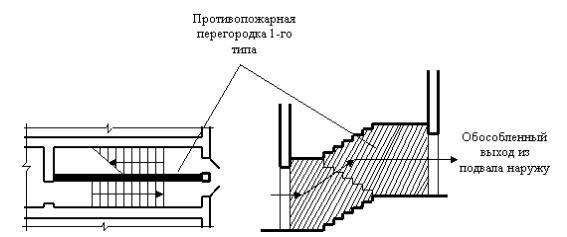
Classification of buildings and premises
A few more concepts that flashed in the text and may have raised questions. We are talking about a possible fire hazard, according to which structures, buildings and their parts - premises are divided into classes, depending on the safety measures for people in them in the event of a fire.
The classification takes into account many factors:
- Age.
- The physical state.
- The ability to stay in a state of sleep.
- The number of people constantly present.
It will become clearer if we give several classes of FPO (functional fire hazard):
- Ф 1 - premises for permanent and temporary residence.
- F 1.1 - institutions for preschool children, special disabled and elderly citizens, hospitals, buildings for sleep in boarding schools.
- F 1.2 - hotels, hostels, rest houses, boarding houses, sanatoriums.
- F 1.3 - residential apartment buildings.
- F 2 - cultural, educational and entertainment institutions.
- F 2. 1 - circuses, theaters, concert halls, sports facilities, clubs and other areas in enclosed spaces.
- F 2.3 - similar establishments to those described above in open areas.
- F 2.2 - exhibitions, museums, indoor dance halls.
- F 2.4 - the same outdoors, and so on up to F 5 (read the original source - SNiP).

The above is part of the additional information on fire safety of structures under construction and finished structures in relation to staircase structures. We tried to give as much useful information on this topic as possible so that you do not have any questions and all the answers were found.
The article also contains useful drawings and photographs that allow you to familiarize yourself with this topic visually.
Output
Arrangement of stairwells, as you already understood, requires a special approach, of course, this does not apply to those structures that are erected in country houses (see also the article Height of stair railing: from size to finished product).
Although there are some safety requirements for them:
- It is not allowed to install stairs with narrow steps and without installing railings, especially for spiral structures, when people are trying to save as much space as possible. On such structures, fences must be located on the outside, in compliance with the rules and regulations for the installation of balusters.
- All ladders should be able not only to climb them, but also to carry, in which case, various objects: strollers with children, a wheelchair for the disabled and much more.
- There is one important requirement for timber structures - the material must be properly processed to exclude the possibility of fire. Remember, you cannot use wood that is too dry, as it is it that often becomes the source of fire in the house. Price, in this case, is not an indicator.
In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic.






