Golden potato nematode: signs of a pest and control methods
Often all the problems associated with growing and storing potatoes, attributed to insufficiently fertilized soil, seed degeneration or negative weather conditions. However, this is not always the case. All these factors, of course, affect the yield of potatoes, but the main harm is caused by pests, one of which is the nematode. There are four types of pest: pallid nematode, stem nematode, root nematode, and golden potato nematode.
Content:
- Characteristics of the golden potato nematode
- The harmfulness of the parasite
- Potato infestation symptoms
- Pest control methods
- Prevention of infection
Characteristics of the golden potato nematode
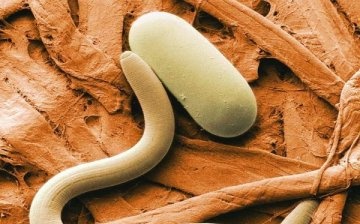
Potato nematodes are tiny worms that feed on the juice of tubers potatoes and are the causative agents of brown bacterial rot. They are ranked among the most dangerous quarantine pests. Due to its size, about 1 mm, the nematode is very difficult to identify. Under the microscope, you can see that the female worms have a rounded body, and the males have a worm-like body.
Digging up an infected bush after finishing flowering and carefully shaking off the soil from the tubers, you can see small rounded blotches on them - these are female nematodes. Initially, they appear as milky-white, rounded larvae, which later become covered with a wheat-brown shell. By this time, the female nematodes had already fattened their own and the larvae and became containers for storing offspring - cysts.
Cysts, being in the soil, are able to withstand the most severe winters, droughts, floods and even radiation. Nematodes are able to multiply rapidly, especially in sandy loamy moist soils, and destroy almost the entire crop. The danger of a nematode is that at first it is not possible to identify whether the soil is infected.
Parasites manifest themselves when the affected area has become extensive and threatens almost the entire planting.
After wintering, the first batch of young nematodes is selected from the cysts and, finding potato tubers, they penetrate inside and there they go through all stages of maturation. They suck the sap from the plants, as a result of which the leaves and stems are deformed. The rapid growth of soil infection occurs due to the fact that the larvae are selected from the cysts in stages. This process can take 3-6 years.
If the soil was infected with a golden potato nematode and the necessary control measures were not taken, then this soil is capable of remaining a carrier of this harmful insect for 10 years, even without the presence of their food source - plants of the Solanaceae family. If such plants are planted, then insect metamorphosis begins, that is, the passage of development stages. The larvae that emerged from the cysts change their shell several times as they grow. After a month of such transformations, a division into females and males occurs. A fertilized female is capable of carrying from 50 to 1200 eggs, which remain viable even after the death of her mother's body. The danger lies not only in the emergence of a huge population pests, but also in the ease of their distribution. The soil and any plants planted on it become carriers and carriers of this infection.
The harmfulness of the parasite
Golden nematode causes globoderosis potatoes, a tomato and eggplant... But most of all he loves potato tubers, destroying the crop by 30-90%. The losses depend on the degree of soil contamination and the resistance of the potato variety.
In addition to destroying the crop, the nematode:
- Deteriorates the taste characteristics of potatoes, there is a shrinkage of root crops or their absence.
- In addition to direct losses, it also causes indirect losses - in the form of a ban on restricting the export of a product from contaminated areas.
The main carrier is potatoes, less often tomato and eggplant are infected. The nematode does not disdain weeds and with pleasure inhabits henbane and nightshade: winged, bittersweet and black.
When cultivating potatoes in one place, without observing crop rotation and over-saturating the site with nightshade crops, as well as weed infestation of the plantation, contributes to nematode infection and accelerates the rate of spread, increasing the harmfulness.
Lack of water and micronutrients (organic and mineral) activates the activity of parasites.
Introducing nitric acid feeding, pest infestation of the plantation can be suppressed. However, you should not get carried away with nitrogen, because an excess of this fertilizers is often the cause of the development of cultural diseases.
Potato infestation symptoms
Often times, the presence of the golden potato nematode is noticed when the soil is critically infested. First alarms:
- The appearance on the potato plantation of areas with sluggish, yellowing and inhibited bushes in development. The foliage curls and dries from the bottom.
- Affected plants form only 1-3 shoots. In potatoes, shoots are deformed, the color is weak or absent altogether. Bushes die before harvesting.
- The development of roots also slows down. They turn brown, stunted and form many adventitious roots.
Potatoes and soil are infected with nematodes through mechanical transport:
- planting infected planting material
- storage infected tubers together with healthy ones at high humidity
- use of garden tools without pre-treatment
- planting potatoes in infected soil
- contaminated garden shoes
The reason for the appearance pests in the ground - planting horticultural crops in the wrong sequence or not alternating at all. Golden potato nematode is able to populate the entire plantation, appearing on one bush. In this regard, it is necessary to regularly inspect the plantings, identify and remove plants with signs of the disease.
Pest control methods
There are 2 important rules to follow when starting to fight a nematode:
- War is declared on the pest when at least one infected bush is found.
- The blow is applied comprehensively and with the use of all methods of struggle.
Today there are many methods, the application of which at a certain stage, allows you to effectively fight the parasite:
- The mechanical method is the digging up and destruction of infected specimens. The bushes are removed along with the earthen lump - the place of residence of the cysts. The extracted plants must be burned or placed in a container or ditch with bleach, and the place of excavation must be abundantly covered with urea.
- Application of biological methods - alternate landing potatoes with plants harmful to nematodes: marigolds, rye, beans, calendula or fragrant sweet clover; to populate the soil with natural enemies of the nematode: by introducing into each planting hole a special soil with the presence of predatory nematodes and provoking the appearance of earthworms, abundantly fertilizing the soil organic in the springtime.
- Chemical attack - the treatment of seed and planted bushes with chemicals. Pre-planting treatment of tubers with a growth stimulant, they can increase the immunity and resistance of potatoes to pests. With large areas of infection, it is effective to use systemic nematicides, which accumulate in plant cells, poisoning the sap of plants that parasites feed on. With contaminated soil in autumn and spring, arable work is carried out with the simultaneous introduction of urea. With the subsequent removal of the infected bushes, carbamide is poured into the holes.
Prevention measures
Agrotechnical techniques:
- compliance with crop rotation - re-planting of potatoes and other nightshade crops is carried out no more than once every four years
- maintain the immunity of potatoes, timely introducing a complex of microelements. These can be balanced purchased formulations or properly selected organics in combination with superphosphate or wood ash and urea.
- planting of parasite-resistant varietal species potatoes (Red Scarlet, Carlina, Impala, for example). When trying to eat the tubers of such plants, nematodes die or lose their ability to reproduce. However, to prevent adaptation of the pest, it is recommended to plant ordinary potatoes every fourth season or change resistant varieties every season.
- planting fresh seeds purchased from verified farms, and not imported from quarantine zones
- before planting dubious seed material, you need to rinse the tubers with heated water and treat with a manganese solution
- after harvesting, all tops and weeds should be burned, and garden tools should be disinfected with formalin solution
The golden potato nematode is very insidious and it is possible to get rid of it using a whole range of techniques. Effective and harmless to humans methods of complete extermination of the parasite have not yet been invented.
On an infected site, observing all preventive measures and control methods, it is possible to grow a high-quality crop.
But it should be remembered: if the site is in the quarantine zone, then it cannot be exported. Potatoes must be consumed or processed within this zone.
To finally lime the golden nematode will take tens of years of painstaking work, systematically applying all kinds of methods of control and prevention. However, the number of these parasites will rapidly decline from year to year.
More information can be found in the video: