What plants get from the soil: root nutrition and additional feeding
Plants, like any living thing, must be fed for good growth, breeding, fruiting. Nutrition comes to the plant from the external environment: soil, air, sunlight. They absorb and assimilate various substances useful for their vital activity.
Content:
Plant nutrition: species
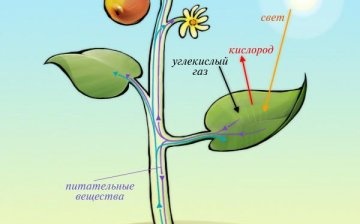
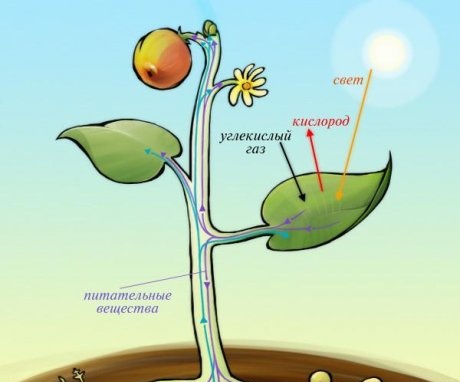
Higher plants growing on earth have 2 types of nutrition: root, through the soil and air, through air and sunlight. From the substances that plants receive from the soil, it is possible to extract the mineral substances necessary for the normal growth of the plant.
Plant nutrition:
- Air nutrition of plants. Air nutrition includes photosynthesis, the process of forming organic substances from inorganic ones with the help of sunlight. The leaves of plants contain chlorophyll, which gives them their green color. Under the influence of sunlight, a complex reaction begins in chlorophylls, as a result of which oxygen and energy are released. Then comes the next stage, in which light is no longer needed. At this stage, various organic compounds, carbohydrates, are formed, which are then distributed throughout all parts of the plant. This process is useful not only for the plant, but also for all living things, since green plants actively release the oxygen necessary for the respiration of all living things.
- Root nutrition of plants. This type of food is also called mineral. The root of the plant absorbs water and minerals from the soil, which are necessary for its growth and normal functioning. Root system plants can be so developed that it exceeds the size of the terrestrial part. The roots are able to extract nutrients from the deepest layers of the soil. The roots of the plant are equipped with special thin hairs, which, like pumps, extract water and salt from the soil. The amount and proportion of minerals required by a plant depend on its species, stage of growth, climate and even the time of day. The most active food is during the day.
Both types of plant nutrition are related to each other. The development of the root system depends on photosynthesis, and the process of photosynthesis is impossible without water obtained from the soil.
What plants get from the soil
To determine exactly what substances a plant absorbs through its roots, scientists conducted an experiment by growing a particular type of plant in water. Various substances were added to the water, and it turned out that the plant primarily sucks out potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, sulfur, phosphorus and nitrogen. If you exclude any of the above, growth or fruit formation is impaired.
There are other trace elements that are needed by the plant. For example, beets in addition to all of the above, boron is also required, as well as copper, zinc, cobalt. Each element is important and valuable in its own way for plant nutrition:
- Nitrogen. This element is necessary for the normal growth and development of the fruit. With a lack of nitrogen, plant growth slows down greatly, and with an excess, active growth of greens and tops takes place, but insufficient development of fruits.
- Phosphorus. Phosphorus is required during the period of active plant growth.It is responsible for the protective functions of the body, increases resistance to various diseases and pests, stimulates the development and ripening of fruits.
- Calcium. With a certain amount of calcium, it supports the normal metabolism of the plant.
- Potassium. Potassium helps the plant cope with environmental influences (temperature extremes, excessive moisture, soil salinity). Buds, fruits and shoots become more resistant to diseases, the harvest is stored longer.
- Magnesium. Magnesium participates in many chemical processes inside the plant, it is necessary for energy production. With a lack of this trace element, the root system of the plant begins to suffer, which is not always noticeable immediately.
- Iron. The plant needs iron in small quantities, but it is important for the synthesis of chlorophyll. If this element is not enough, the leaves begin to fade, turn yellow and fall off prematurely.
Why do you need top dressing
All minerals and salts must be contained in the soil in a certain amount, maintaining a balance. Only in this case can one count on normal plant growth and a rich harvest. If cultivated plants are grown on the same plot for many years in a row, the soil becomes poorer, loses some of the nutrients and does not have time to accumulate them. For this, there are various feeding.
Correctly and on time entered fertilizers can significantly increase yields.
Fertilizers can be organic or mineral... Both those and others perform the same function - feeding the soil, plants and increasing yields. Organic fertilizers (usually manure or litter, peat, humus) are considered more effective, but they will cost more for large areas. The main advantage of organic fertilizers is their ability to accumulate humus in the soil. Not all cultivated plants tolerate organic matter well, especially fresh manure, some can get sick, since various microorganisms and parasites often live in the manure.
There are many complex fertilizers on the market, in which all nutrients are already balanced, but experienced gardeners prefer to feed separately in different amounts depending on the stage of growth. It is worth remembering that an excess of fertilizer can also be harmful. Usually feeding is done when landingand then as needed. Plants themselves will show that they lack any trace elements.
There are also bacterial fertilizers. As you know, nodule bacteria living in the soil take some of the carbohydrates from the plant, but supply it with nitrogen. They provoke active division of root cells, as a result of which nodules are formed on it.
More information can be found in the video.












For seedlings, nitrogen is first important, and for better fruiting, a complex fertilizer is used - amofoska. Unfortunately, mineral fertilizers increase the acidity of the soil, so it should be limed.