Outdoor fire escapes along with roof barriers are used to ensure the safety of rescuers and firefighters when carrying out measures aimed at preventing the consequences of accidents, fires and other emergencies. And also for the evacuation of residents and employees of buildings in the emergency zone.
That's why requirements for outdoor fire escapes are strictly regulated by state standards, norms and rules, the implementation of which is mandatory.

Technical norms and requirements
General Provisions

The article deals with metal welded structures, which are vertical and mid-flight stairs installed permanently outside residential, public, technical and industrial buildings and structures. (see also article Testing outdoor fire escapes: tips and tricks)
The purpose of such structures is to provide access for the personnel of firefighters and rescue teams to the roofs of buildings, transport equipment and means of extinguishing fires, rescue equipment, as well as evacuate residents and workers of these structures in the event of a threat to their life and health.
At the same time, special attention is paid to the characteristics and parameters of such structures, including checking:
- Compliance with the arrangement of elements and entire structures adopted in the design drawings relative to the building, taking into account its number of storeys, perimeter, height and other dimensions;
- Compliance with the accepted in standards and norms of the linear dimensions of all elements, their relative position, geometry and other parameters;
- Reliability of fastening structures to the wall and roof;
- The quality of protective coatings taking into account the corrosive aggressiveness of the environment and climate;
- The quality of welds, joints and fasteners of all structural elements of the staircase;
- Correspondence of angles, shapes, parallel and perpendicular elements, diagonals and distances to accepted norms and standards within the limits of permissible deviations;
- The strength of the steps of vertical and mid-flight stairs by testing them with a static load;
- The strength of the elements of the fences of vertical and mid-flight stairs by testing them with a static load;
- The strength of the sites of the marching structures by testing them with a static load;
- Strength of beams and fastenings of stairs to the wall, roof and ground by testing them with a static load;
- Dimensions, configuration and design of steps, platforms and flights of flight stairs;
- Distance from the bottom step of vertical and marching structures to the ground;
- Parameters of the platform for the exit to the roof.
Important!
The measuring tool used for inspections and tests must also be certified according to GOST 7502-89 (for tape measures), GOST 427-75 (for rulers), and GOST 166-89 (for calipers).
All test work and inspections must be carried out by specialized organizations that have permission to do such work.
Tests and checks are carried out when the structure is put into operation, as well as at least once every five years. In addition, a visual inspection of the integrity of the structure, welds, protective coatings and fasteners is carried out at least once a year. If defects are found, the damaged areas are repaired, after which the structure must be tested without fail.
As a result of a successful check, the facility receives a permit for operation, according to the data of tests and inspections, an act of checking external fire escapes is drawn up, confirming these data, and the person in charge (owner, manager or tenant of the building) receives a sample of the act of visual inspection of external fire escapes, on the basis of which further operation of the facility. (see also the article Testing fire escapes and roof barriers: necessity and basic criteria)
Structural elements

The designs we are considering can be divided into two types:
- Vertical fire escapes (P1) installed permanently outside buildings and structures;
- Marching fire and escape ladders (P2), installed permanently outside buildings and structures.
Vertical structures are also of two types: without a fence (P1-1) and with a fence (P1-2). The former are allowed to be used with a building height or height difference of no more than 6 meters, the latter - at heights exceeding 6 meters. As a rule, vertical structures are intended for fire brigades and rescuers, as well as for the delivery of fire fighting equipment and rescue equipment to the site.
Important!
The evacuation of citizens using vertical fire escapes is dangerous and occurs in extreme cases.
Marching stairs make it possible not only to deliver the personnel of the Ministry of Emergency Situations to the facility, but also to evacuate the population with a relatively low risk of human casualties and harm to the health of the injured. Therefore, it is customary to install marching structures in structures with an increased fire hazard.
Let's consider the construction of stairs in more detail.
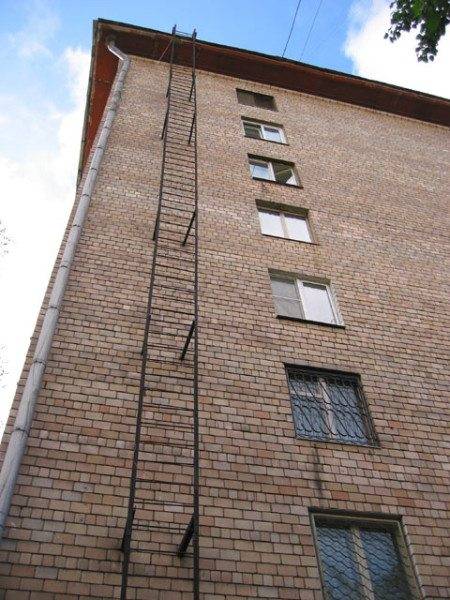
Vertical stairs
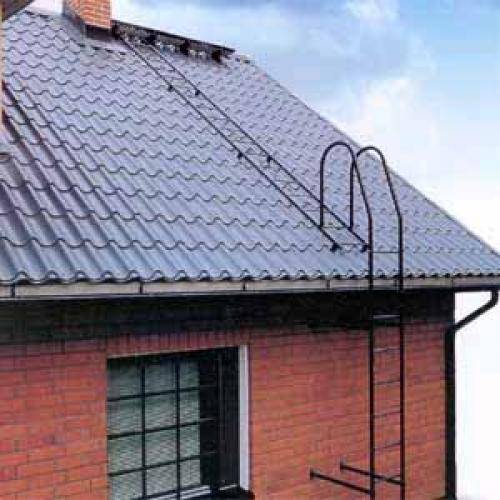

These models are quite simple and represent vertical bowstrings connected by horizontal steps.
The bowstrings are attached to the wall with steel beams. At the point of exit to the roof, the bowstrings are bent in the form of handrails for convenience and safety, and at the point of transition to the roof, a special platform or additional ladder is installed, as in the photo.
Vertical models can have full or partial protection in the form of fences to prevent a person from falling; on low buildings, this protection may not be available.
The lower section of the vertical structure is allowed to be retractable, with a strong and reliable fixation in the working position. The roof exit platform must be at least 0.8 meters in length.

The steps are made of steel and are rigidly attached to the bowstrings, usually by electric arc welding. Each step must be able to withstand a static load of 180 kg. The load is applied to the middle of the part and directed vertically downward.
Important!
Vertical models are used in conditions of height differences from 1 to 20 meters.
At high altitudes, marching structures should be used.
The exit to the roof from the platforms of the stairs should not be obstructed by roof fences.
The main advantage of vertical structures is their low price. However, from the point of view of safety, convenience and speed of movement, such models are inferior to marching stairs.
Advice!
Simple vertical models can be made by hand, but it is better to trust the manufacture of outdoor fire escapes to professionals, otherwise the very strict test instructions will not allow you to successfully pass certification and verification, as a result of which you will have to redo or completely reassemble the product.
Marching stairs
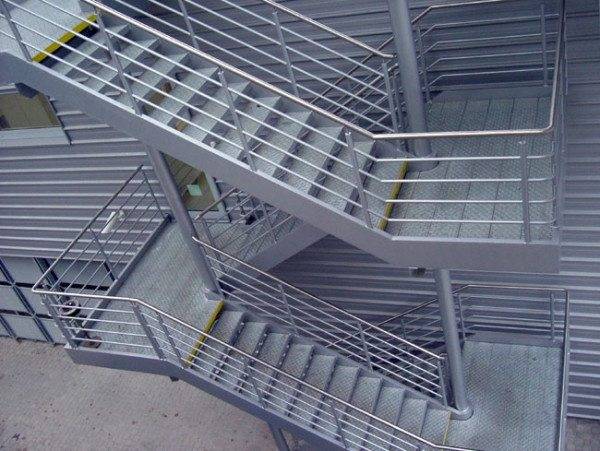

Marching structures are somewhat more complicated than vertical ones. They consist of a system of inclined flights of stairs connecting horizontal platforms.The system can be anchored to the wall using steel beams, and it can also be supported on the ground using metal columns, pipes or stringers.
Platforms and marches should be securely fenced off with strong steel railings with handrails to ensure safe stair climbing. The height of the handrail must be at least 120 cm (for evacuation models). Civilian evacuation structures are carefully regulated and inspected.
The width of the step for such models must be at least 25 cm, the width of the stairs must be at least 90 cm, and the height of the railing must be at least 120 cm.
In this case, the steps can be performed in various configurations:
- solid corrugated steel (F);
- lattice from stamped elements (W);
- lattice from strips on the edge and steel round timber (P);
- lattice of stripes on the edge, laid in one direction (C);
- lattice made of expanded steel (B).
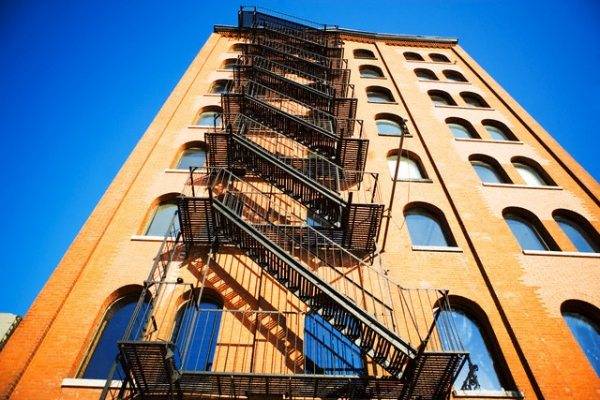

In addition, the gap between the flights of stairs, as well as between the handrails of the railings of stair flights, is regulated. It must be at least 75 mm.
Attention!
The parameters of marching models for children's and preschool institutions have been discussed separately.
For such objects, the flooring of the platforms should be made of solid corrugated steel (type F), and the steps - from stamped elements or expanded steel (types Ш and В).
It is also important to maintain the correct distance from the bottom step to the ground: it should not exceed the step height of the steps in the flight of stairs.
Fencing elements must be attached to the structure as rigidly as possible and withstand a static load applied horizontally, measuring 54 kg. The same requirement applies to booms of vertical models.
Primary requirements

The main technical requirements for external fire escapes installed permanently are presented in the following regulatory documents:
- GOST 23118, GOST 23120 and GOST 25772 - requirements for the construction of vertical stairs, landings, staircases and fences to them;
- GOST 23118 - installation and placement of structures on buildings and structures;
- GOST 5264 - quality and parameters of welded seams of metal structures. Seams, joints and connections should not have sharp protrusions, burrs and edges that could injure a person;
- GOST 9.032 - priming and painting of metal parts of external structures;
- Fastening of structural elements to the wall and roof, as well as the interconnection of parts must be as strong and reliable as possible, while the presence of cracks in the fixing of beams to the wall and metal breaks is strictly not allowed;
- The steps must withstand a test load of 180 kg applied to the middle of the part and directed vertically downward;
- The fastening beams are subjected to a static load, the value of which is calculated according to the formulas given in GOST R 53254.
Testing
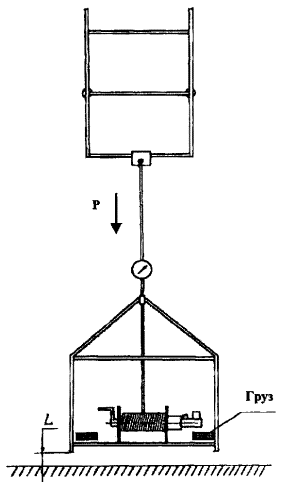
Inspection of external fire escapes is carried out by specialized certified organizations that have permission to carry out such work. The verification tool must comply with the standards, norms and rules adopted in the Russian Federation.
A group of specialists leaves for the object, which makes an external examination of all structures and their parts. At the same time, the integrity of the protective coatings, the quality and condition of the welds, the general geometry of the system and the correspondence of the attachment points and locations of the product parts to the drawings approved in the prescribed manner are checked.
On the basis of such a check, an act of visual inspection of external fire escapes is drawn up, a copy of which is provided to the owner or another responsible person.Next, they begin to conduct tests, for which a power plant is used in the form of a winch with a dynamometer or a pneumatic cylinder.
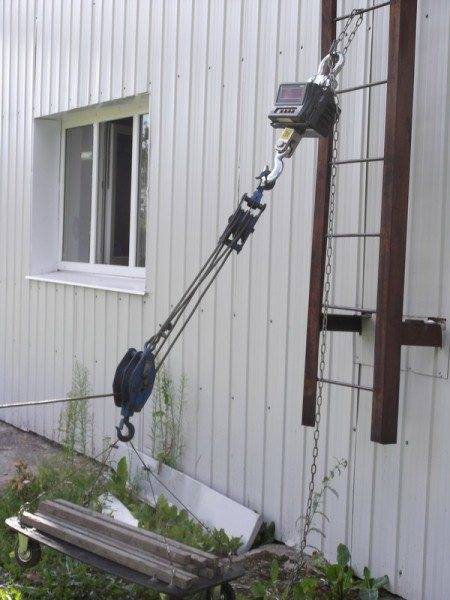

The load is applied for a period of two minutes. The load must be static and not cause acceleration and inertia. After removing the load, check the distance between the control points for permanent deformations, ruptures, cracks and other defects.
If at least one of the listed damage is noticed, the test is considered not passed. In this case, the home owner is given a number of recommendations to eliminate the causes and consequences of these damages. After repair and elimination of defects, the product is re-tested.
The steps (every fifth), flights, platforms, fences and beams of fastenings are subjected to power tests separately.
If the test is passed, then the owner of the house receives an appropriate document and permission to operate the stairs, which is valid for five years. After this period, a repeated check of the structures is required according to the same scheme.
In case of evading mandatory inspections and tests, the owner of the house can be fined in accordance with the articles of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Output
Fire escapes are an important element of fire safety and evacuation in case of emergencies and man-made disasters, therefore high requirements are imposed on these structures. The compliance of elements and systems with these requirements is checked by a special competent commission using special equipment and tools.
And the video in this article is ready to demonstrate additional information on the topic we have covered.






