To ensure fire safety of industrial buildings and residential buildings, they must be equipped with special structures that must be kept in good condition. It is for this purpose that regular inspections, inspections and tests of fire escapes and roof fences are carried out.

It should be noted that although their direct purpose and use is fire protection, they often also serve to perform various technological works related to the maintenance of a building.
Fire escapes and fences: types and features

The main feature and requirement for stationary structures is their outdoor location. Fire escape can also be located on the balcony.
Any construction site ten meters or more must have one of two things:
- vertical ladder;
- mid-flight stairs (with an allowable, no more than 6/1, slope).
Marching stairs can be single-march, double-march and multi-march.
The variant of the device of these elements is determined by the structural features of the building:
- vertical stairs are used with a lifting height of 10-20 meters, or for buildings with a multi-level roof;
- with a building height above 20 meters, marching flights are arranged with obligatory platforms between marches.
The number of fire exits depends on the size of the building and its features: if there is an attic floor - one exit per 100 m², without it - 1 exit per 1000 m².
Requirements for compliance with the frequency of testing

When a construction object is put into operation, and then regularly, at least once every five years, it is mandatory in accordance with GOST R 53254-2009 a test of the fire escape should be carried out, and annually an inspection of the integrity of the structure, the identification of cracks and damage to the anti-corrosion coating.
If any damage, defects or destruction of elements is found, they are corrected, and then mandatory unscheduled strength checks are carried out. Then the five-year mandatory frequency of testing fire escapes will be counted from the new date.
Features of the study of fire escapes
The test of fire ladders must show that the structure is capable of withstanding the weight of the fire brigade in case of need or emergency. There are also requirements for the materials used for their construction and manufacture - they must necessarily belong to the category of non-combustible materials. It also requires compliance with the requirements for their location on the building - no closer than one meter from the windows.
Features of the study of roof fences and requirements for them
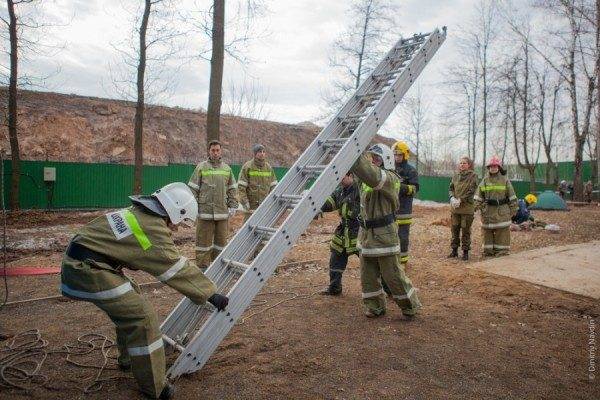

Construction sites with a slope of the roof must pass the test of fences and fire escapes, the device of which must also be carried out in accordance with existing standards.
The fence can be any structure that meets fire regulations. For example, even for a flat roof of a country house, a parapet can be built, which is an architectural element, but is not a fireproof one.
In the case of a roof with a slope, the rules and requirements for fences in accordance with SNiP 21-01-97 clause 8.11 and GOST 25772-83 begin to apply, that is, they are mandatory for:
- buildings with a height of no more than 10 meters and with a slope of the roof up to 12%;
- for objects with a height of 7 meters, but with a slope of the roof structure more than 12%.
Requirements for other building envelopes
It should be borne in mind that the requirements of this standard are relevant for:
- flat roofs, if they are in service;
- loggias;
- balconies;
- external structures (marches, platforms);
- galleries.
According to regulatory requirements, the height of the fence or parapet as a fence must be at least 1 m20 cm for operated roofs and at least 0.6 m for unexploited ones. It is allowed to increase the height of the parapet to the required installation of an additional fence.
Manual fire ladders: their varieties and features of testing
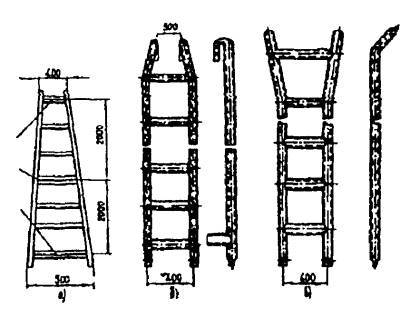
In addition to outdoor stationary, manual ladders exist and are widely used, which are of several types:
- folding or stick ladders;
- car retractable three-knee ladders;
- suspended or ground attack aircraft.
Among themselves, the types of manual fire escapes differ mainly in height. For a three-knee, it is 10 meters, and for a folding stick-ladder, only 3 meters.
Requirements for the periodicity of the study of manual fire ladders
The main procedure and timing for testing manual fire ladders is subject to the following requirements:
- mandatory - annually;
- after any type of repair;
- in case of participation in any competitions or test events, they must have certificates;
- it is strictly forbidden to use defective or damaged.
Features and conditions
Manual fire ladders are tested in accordance with the following rules:
- For retractable structures:
- install on a solid base or ground;
- extend to full height, leaning at an angle of 75 ° to the horizontal plane;
- be sure to comply with the condition - at least 2.8 m from the wall to the shoes of the structure;
- each knee is loaded with a 100 kg weight for 2 minutes;
- the rope should be without deformation after being pulled from a load of 200 kg;
- it is imperative that the structure is inspected for various damages, and the knees should be folded easily, without jamming.
- For suspended attack aircraft:
- hang from a hook;
- each bowstring at the level of the second stage is loaded by 80 kg for 2 minutes (total 160 kg);
- after loading - inspection for cracks and defects, as well as permanent deformation of the hook.
- For folding specimens, the test procedure for fire escapes (ladders-sticks) is as follows:
- install on a solid support, you can on the ground;
- lean against the wall at an angle of 75º to the horizontal surface;
- load the middle with a weight of 120 kg for 2 minutes;
- after the test load, no damage or defects should be detected, the ladder should fold tightly and without much effort.
Attention! A dynamometer is most often used as a measuring device during testing.
Testing of stationary outdoor fire-prevention staircase and enclosing elements is carried out by specialists.
Fire escape tests are carried out in compliance with certain conditions, safety measures and in strict adherence to the regulatory framework. Before starting the test, you should fence off and mark the work area with warning signs.
Testing time - only during daylight hours, in calm weather, maximum wind speed up to 10 m / s and air temperature from + 5 ° С and above. Organizations carrying out research must have the necessary and in good working order equipment for testing fire escapes and special equipment.
Basic requirements for testing
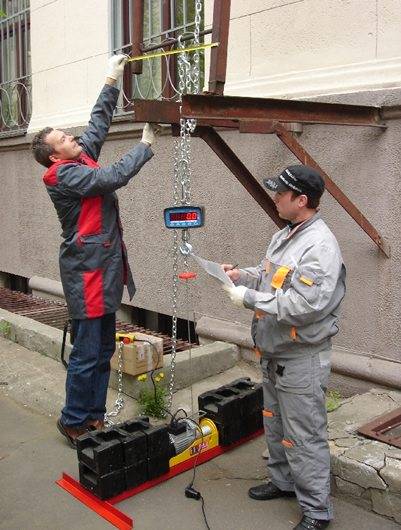

Start of testing - control of the size and quality of materials and external coating or paint.
For this, measuring devices are used, such as a vernier caliper, a tape measure and a metal ruler or a laser rangefinder.
- A visual external inspection of the quality of seams and joints is carried out. The permissible deviations are checked by GOST-25772.
- The quality of painting and priming of structures is checked, they are, in accordance with the standards (GOST-5264, GOST-53254-2009, GOST-9.302 and GOST-9.032), must belong to the V class.
- The surface is also carefully inspected for cracks or other damage.
Separate control is assigned to the steps - they must withstand a vertical load of 180 kg, which is located in the middle of the step for 2 minutes. According to the requirements of the standard, every fifth stage is checked.
The presence of any defects or problems with the load must be recorded in the reporting document - the protocol for testing fire escapes, a sample of which is in the NPB 245-2001 (Appendix No. 2).
Features of testing elements of stationary fire structures
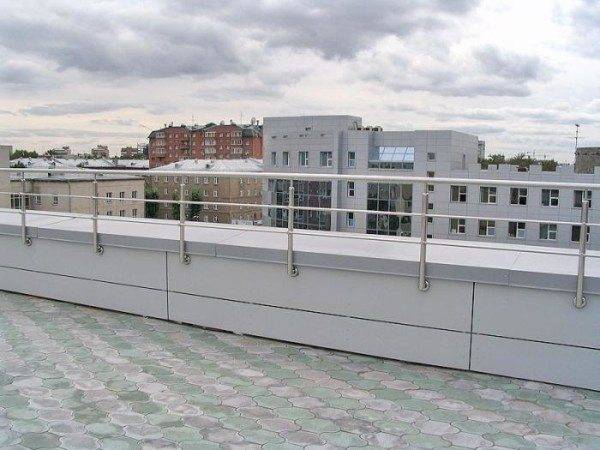

Testing of stationary structures has some peculiarities. For example, for a vertical one, the strength of fastening a beam to a wall is checked by a vertically downward load, the value of which is calculated by specialists for a specific structure individually. After testing, no signs of damage to integrity or permanent deformation should be detected to obtain a decision on further operation.
The stairway is tested for strength also by a vertical downward load located in the middle of the step. Marching platforms, fences of vertical stairs, flights and roofs are separately checked for strength.
Thus, the instruction prescribes strength studies of the following elements of ladder structures:
- ladder beams;
- marches;
- steps;
- railings of stairs and roofing structures.
Test results
If, as a result, any deficiencies or inconsistencies are revealed, as well as as a result of testing, residual deformations are found, it is considered that the structure has not passed the test, and its operation is not possible.
By concluding a test contract, the organization's specialists go to the site for an initial visual inspection, and a technical assignment for the upcoming work is drawn up. Based on the results, the customer is provided with an estimate, where the price for each type of research should be indicated.
Upon completion of the work, all the necessary documentation is provided. It should be noted that the interaction of the customer with the contractor is regulated by the okdp testing fire escapes, according to which the types of work and the quality of their performance are determined.
Constructions that have successfully passed all the tests are supplied with special plates or tags with appropriate information indicating the date and nature of the research. There are no special requirements for the design of the plates, they are determined by the organization independently, depending on the climatic conditions.
Attention! All information about objects and structures that have not passed control, except for entering into the Protocol, is brought to the attention of the fire services, which are in charge of this object.
Conclusion
The procedure for conducting research on fire escapes and other objects can be seen in the video in this article. If there is a question about testing at a private residential facility, for example, for a country house or a cottage, the owner naturally has a question about who can carry out these works. To the joy of the owner, you can do everything yourself, but in compliance with the requirements of NPB 245-2001.
Testing does not require a special license to perform such work and research. But if difficulties arise, then for help you can turn to any company or laboratory that has equipment and specialists trained to perform these works.






