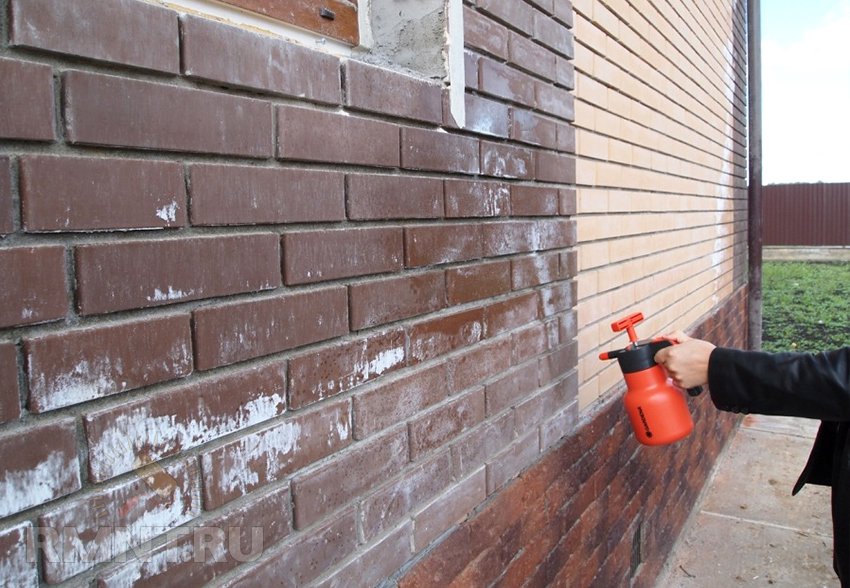
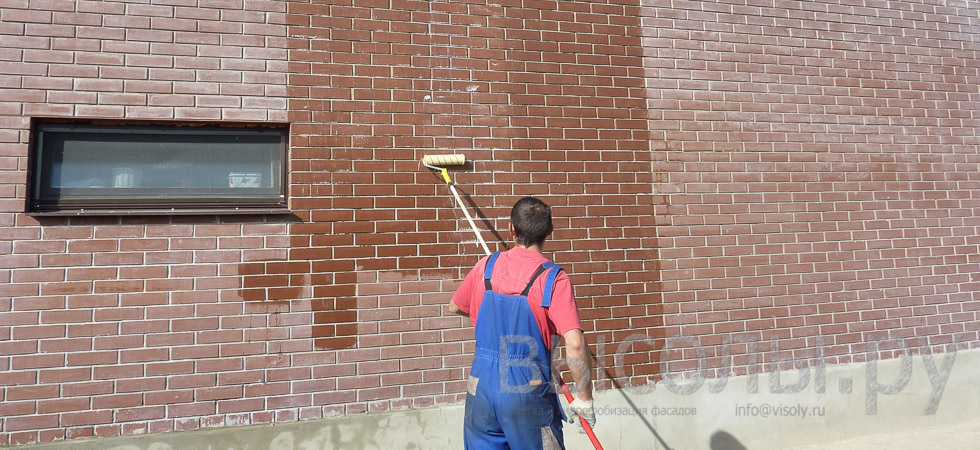
Prevention is the best method of protecting against efflorescence
It is easier to prevent any problem than to deal with its consequences later. This statement is completely true in relation to efflorescence and dark spots on the surface of paving slabs. It is much easier to properly care for the coating than to remove such visual defects from its surface.
The first step is to choose the right tile itself: it must be made of concrete grades of at least M200, M250 or M300. Such grades are characterized by increased strength and low porosity, due to which the tiles from them are characterized by a long service life and increased resistance to external atmospheric factors.
If we talk about caring for the material, then I would like to draw your attention to the fact that paving slabs should not be washed with saline solutions and other chemicals. With their help, you will not be able to remove efflorescence, because such agents, penetrating deep into the structure of the material, lead to the appearance of a new portion of salts on its surface, and also destroy the structure and color of the material.
When cleaning from ice or snow, it is better to use wooden counterparts instead of metal tools (scrap, shovel and others).
Why do efflorescence appear

Cleaning paving slabs
How to clean paving slabs from various contaminants, chemical and mechanical methods

Why paving stones are crumbling
Why are paving stones crumbling on the sidewalk, the main reasons and solutions to problems
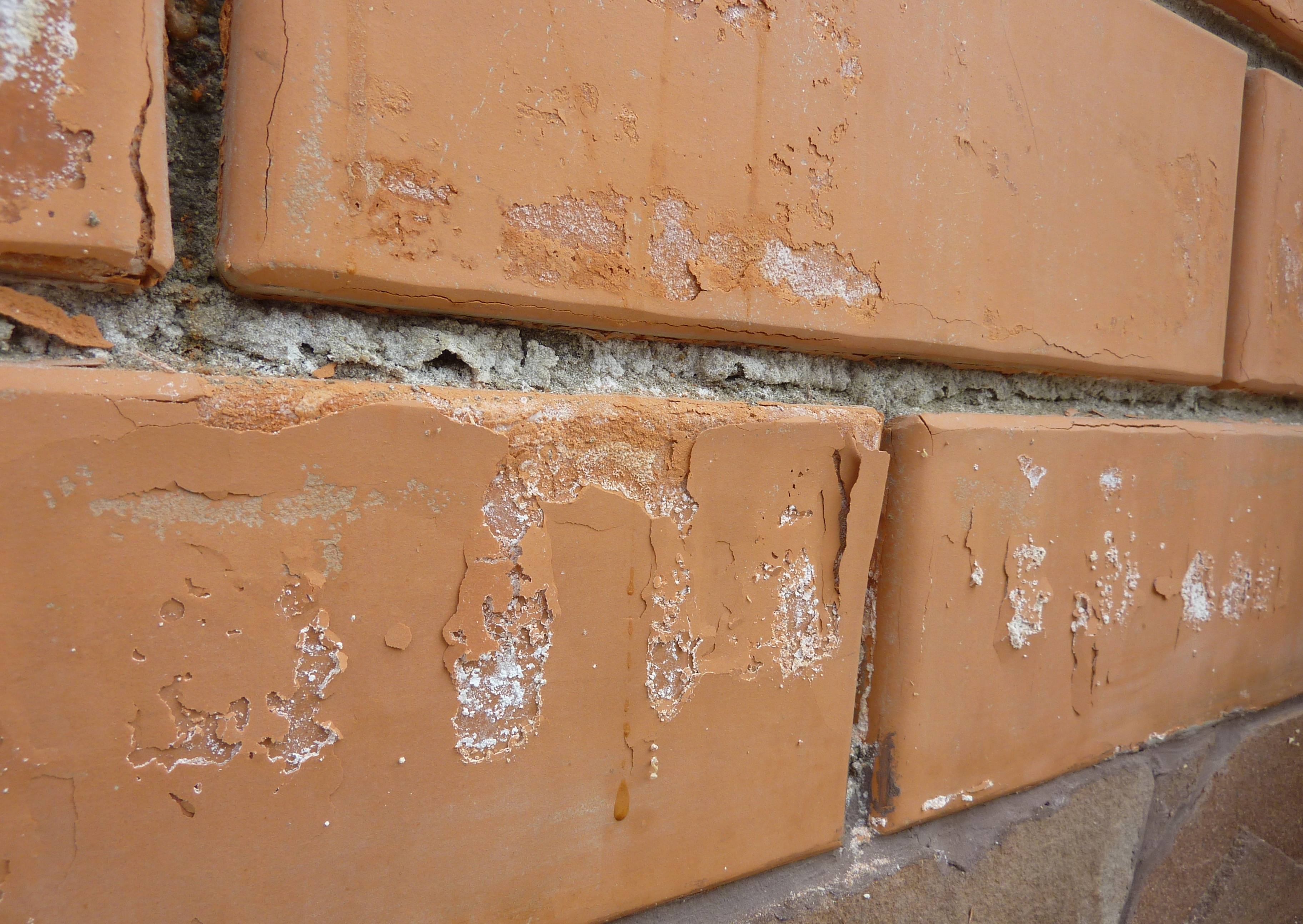
The reason for the appearance of efflorescence on the paving slabs is often the poor quality of the concrete mixture, which is used in the production of paving stones. The fact is that many manufacturers are cunning in production, and in order to speed up the production of paving stones, they add hardeners to the concrete mixture, which then have a bad effect on the durability of the material.
The cause of white bloom can be a marriage when the production technology is violated and the product has not fully received the desired characteristics. Usually on such tiles, the appearance of salt is observed shortly after installation. Hard water can also cause salt deposits to form on the surface of the paving stones.
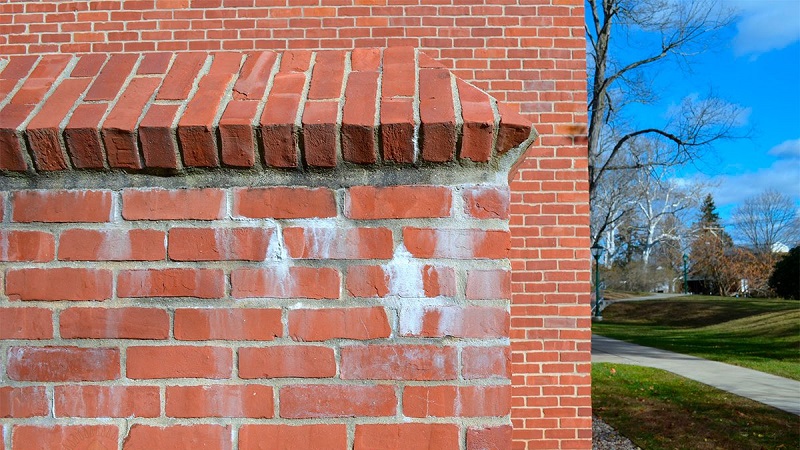
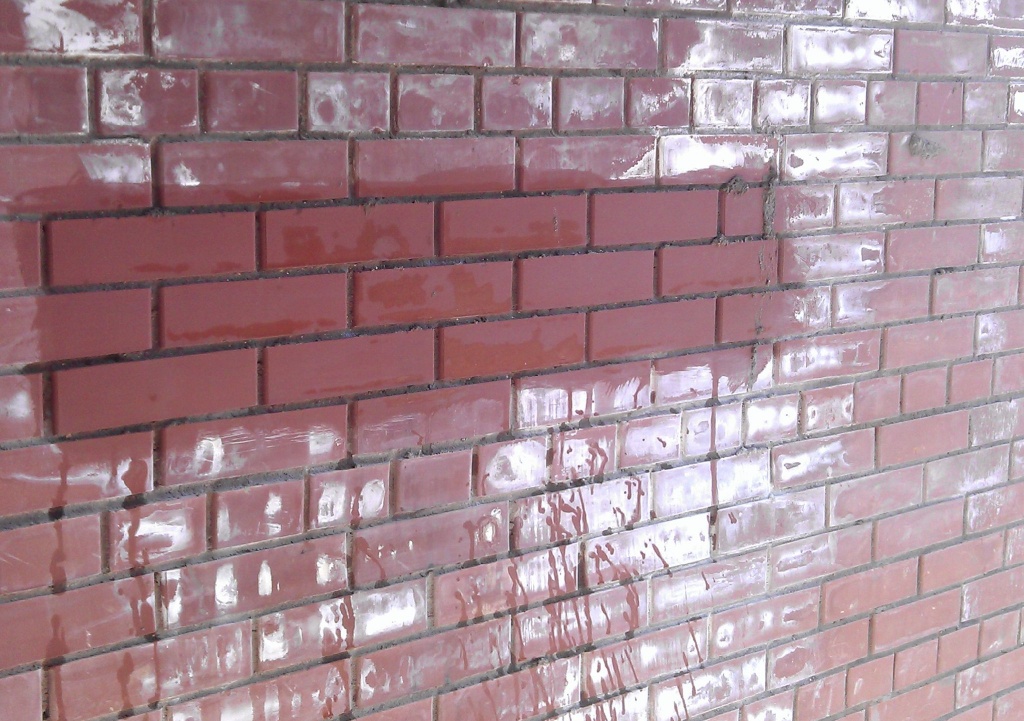
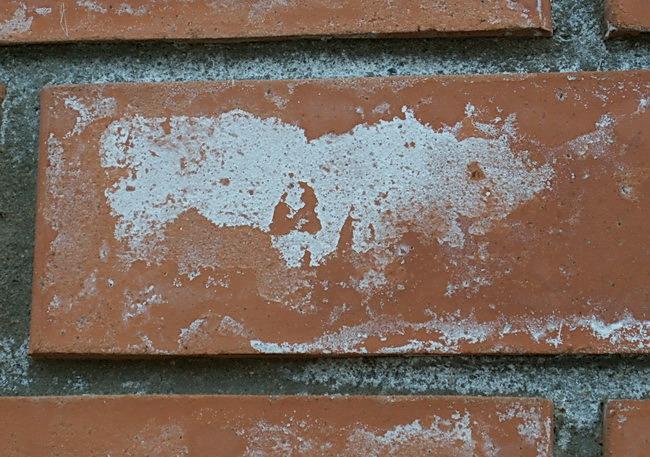
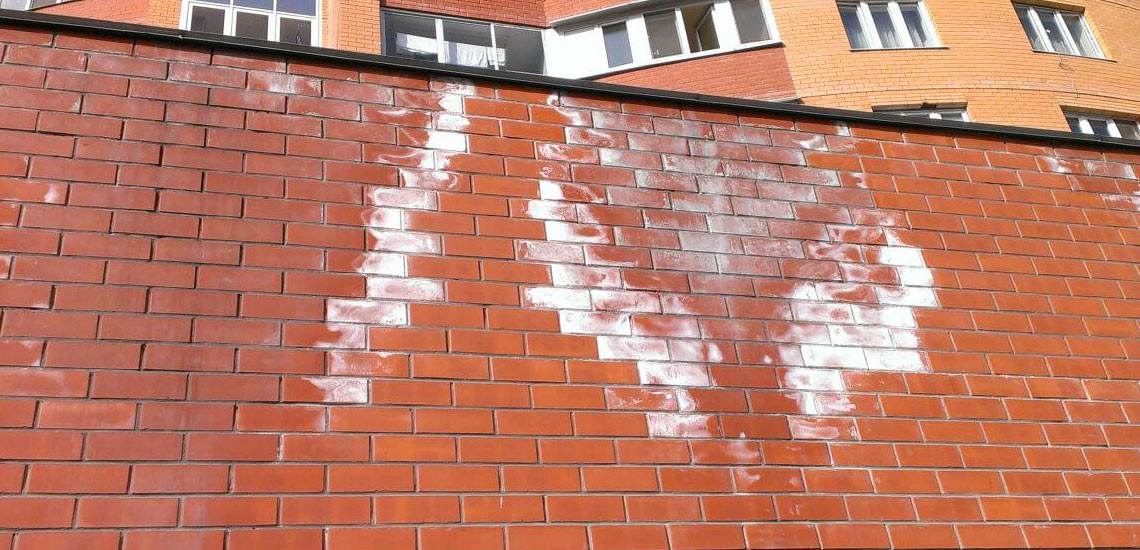
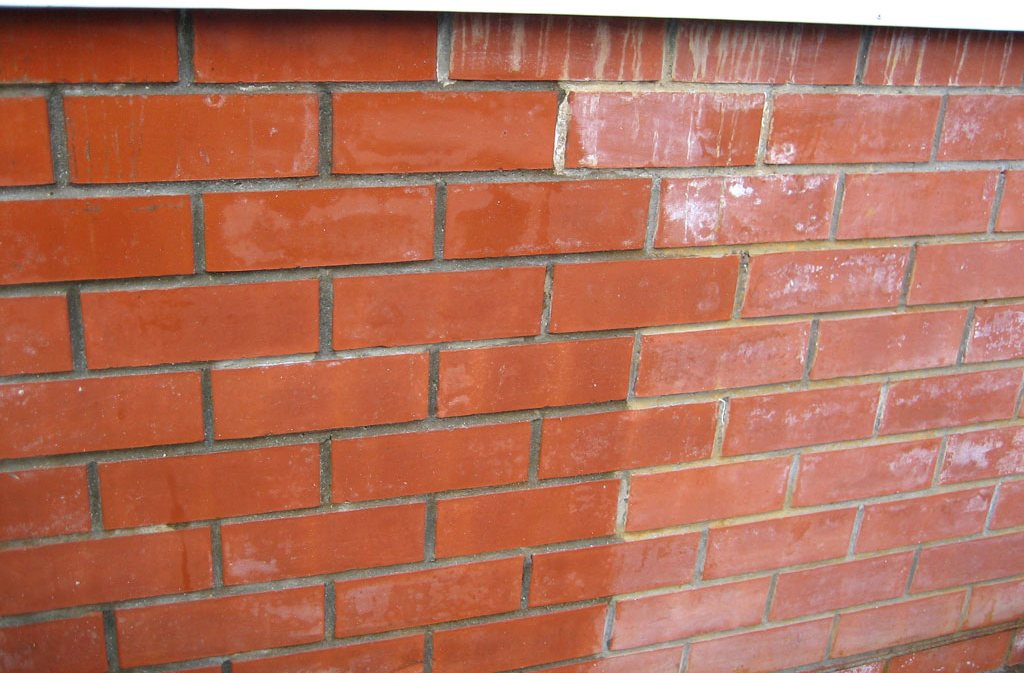
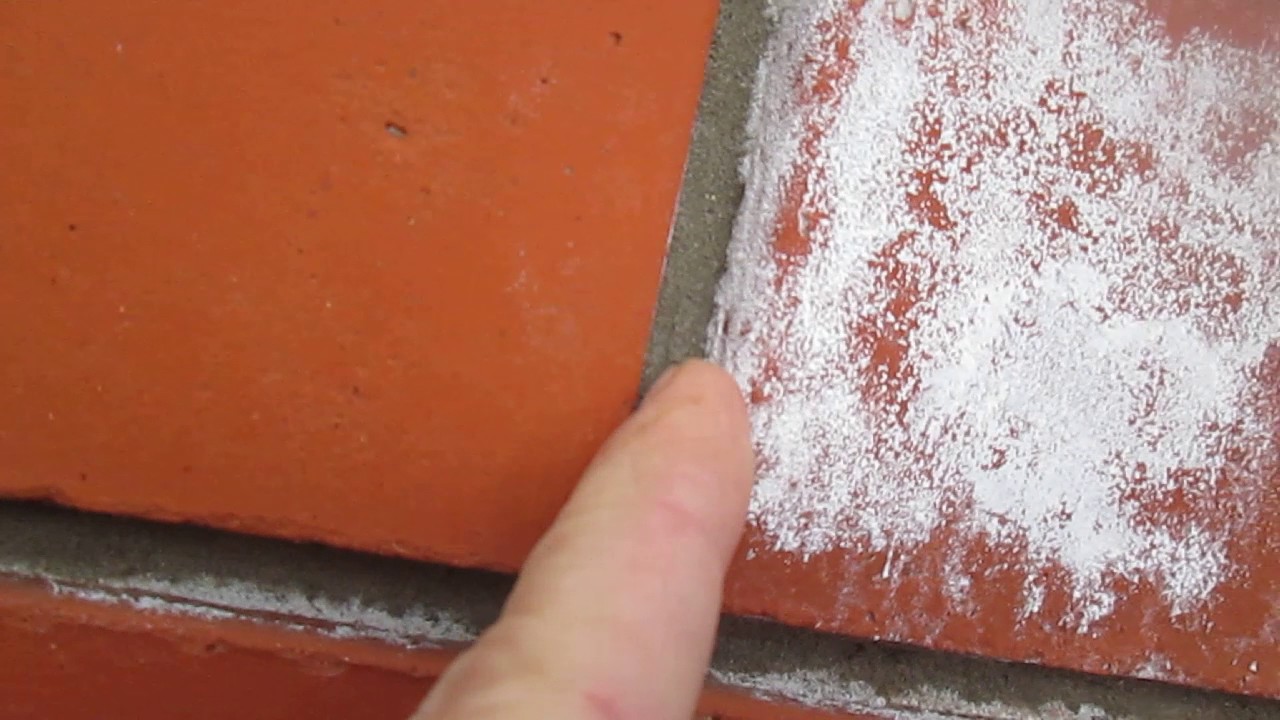
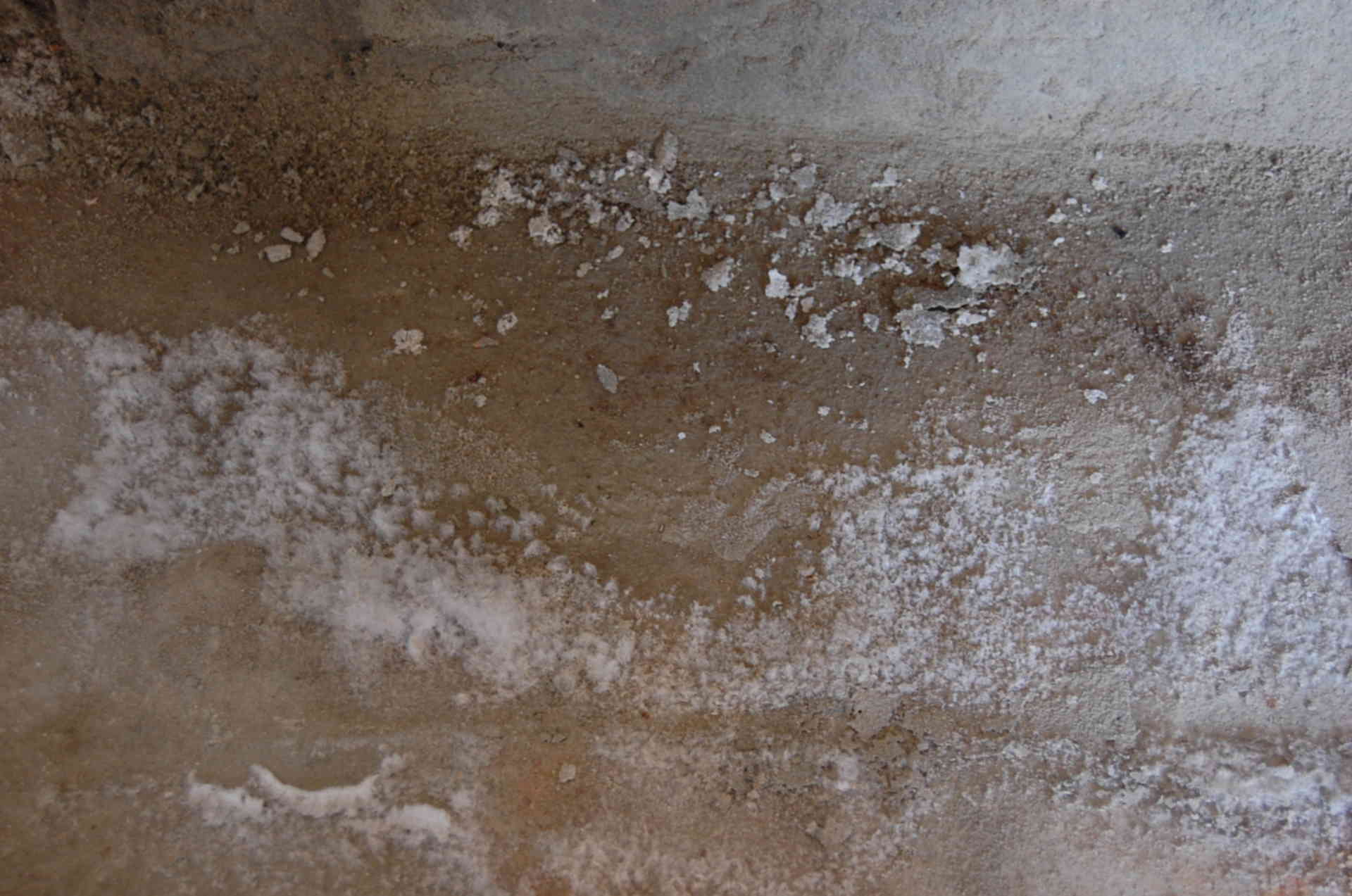
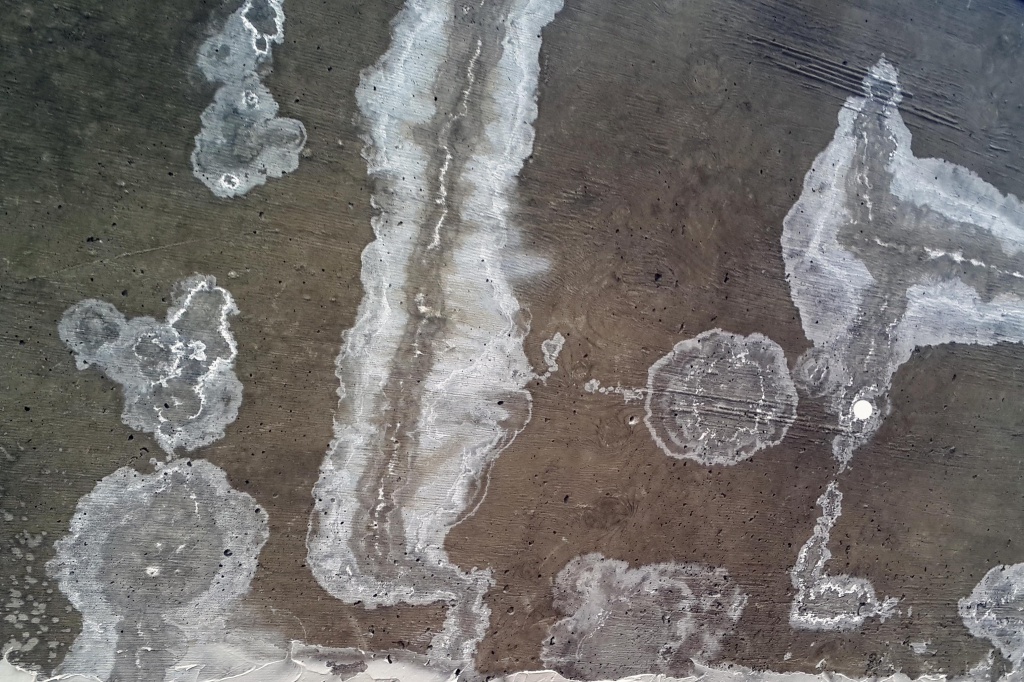
 White bloom on the surface of the material
White bloom on the surface of the material
Such spots can appear and disappear on their own during rain, but after a short time, salt deposits appear on the coating and spoil the appearance.
It is important to solve the problem in time, so that later it does not become larger.
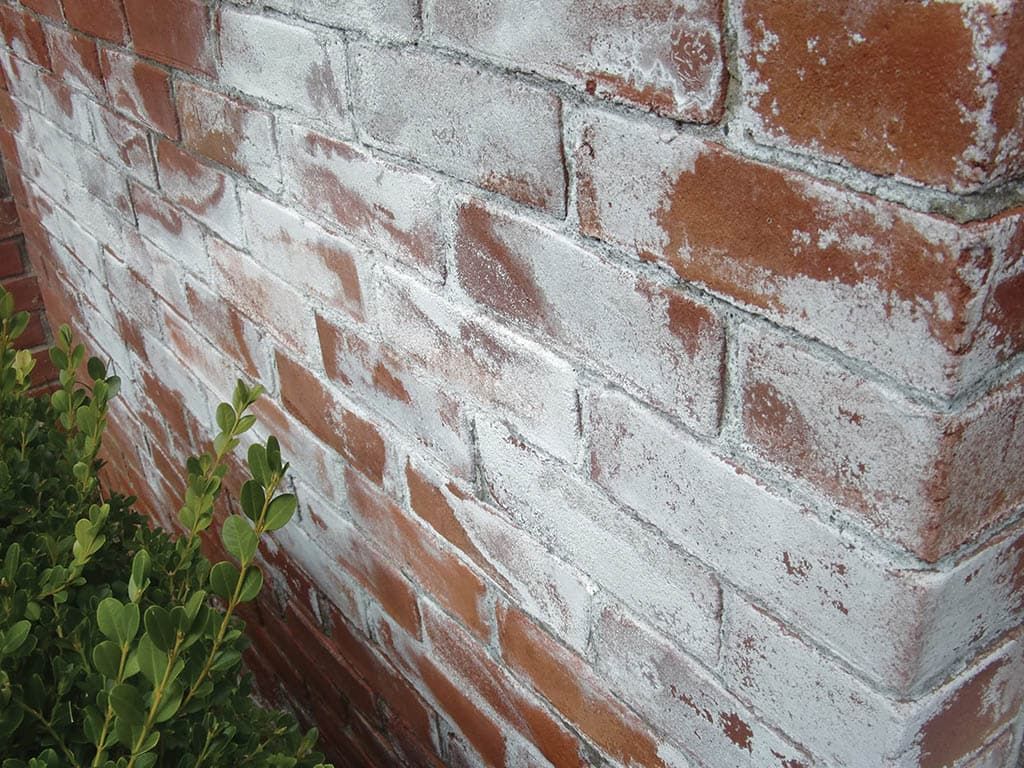
There are different ways to do this, but not all will provide a result. Paving slabs are covered with a white coating when the concrete contains mineral salts, which appear on the surface through the porous structure of concrete, and this is facilitated by external factors:
- Temperature drops.
- Precipitation.
- Incorrectly selected cleaning agents.
If you try to remove efflorescence from the paving stones with plain water, you run the risk that more such spots will appear on the surface later. If you wash off the white bloom from the surface of the sidewalk, then the water will also saturate the paving stones, after which it will evaporate and bring new salt deposits to the surface of the material. This process of removing efflorescence is endless - you remove stains, and after a short time the surface of the tiles is again covered with them, only in larger quantities.
A dry method of cleaning with a brush will not bring success for a long time, after the first rain the surface of the paving slabs will again “beautify” white spots.But how to remove efflorescence from the surface of the sidewalk, are there effective methods or not? There are methods that bring results, and there are many, but they all consist in the use of chemicals that are designed specifically to remove efflorescence.
They approach the choice carefully, and it is important to consider the reason for the formation of white spots. If the cleaning compositions are considered according to their functional purpose, then the products are divided into two groups: to remove minor stains that have formed not so long ago, and to combat complex obsolete plaque
Given the complexity of the fight against efflorescence, it is better to prevent the appearance.
 Remedy for the fight with a touch
Remedy for the fight with a touch
How to prevent the formation of white plaque
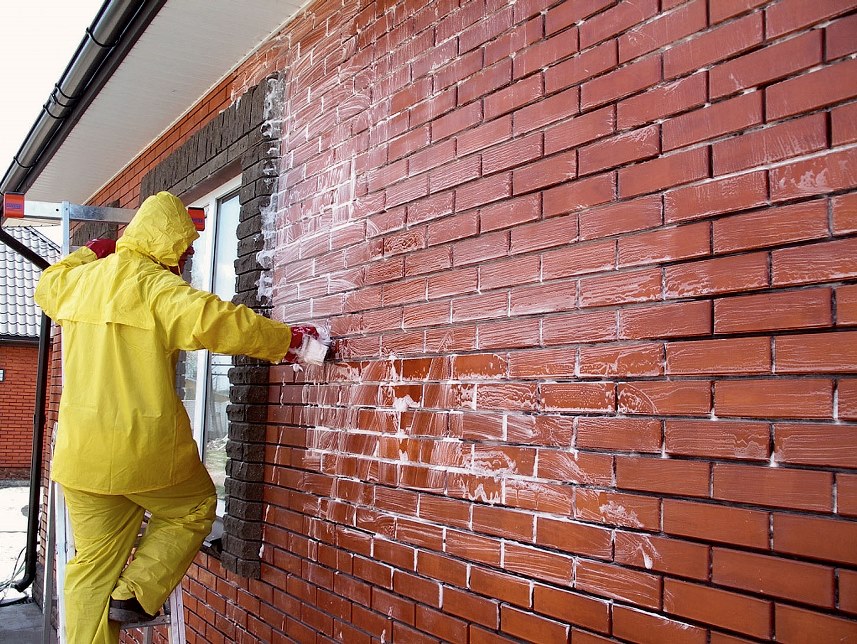
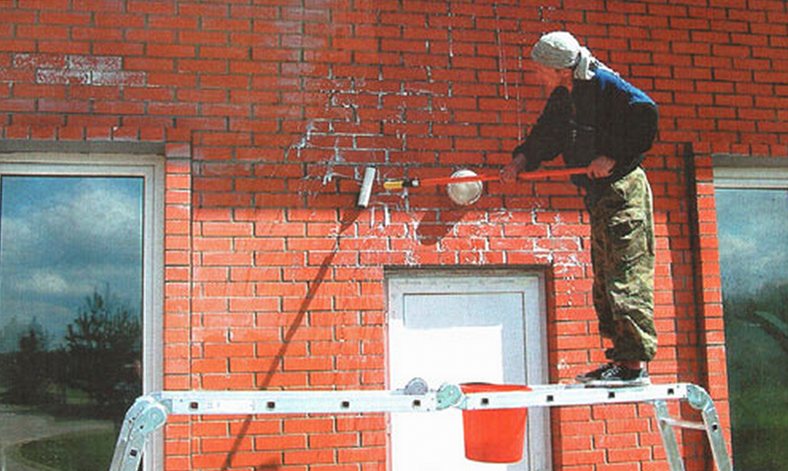
If the road is lined with tiled material, then it is better to immediately think about how to prevent the appearance of efflorescence. This can be done if moisture will not come into contact with the paving stones, the paved area is under a canopy. How to clean the paving slabs in the open air? Special compositions that are designed to treat the surface of the coating immediately after laying will help.
And the best solution to avoid the appearance of stains is to buy products of good quality, with low porosity, and have a water-repellent effect. The cost of high-quality paving stones is higher, but such products will save you from preventive and resuscitation work. And it will save money on compositions that are designed to remove the formed efflorescence.
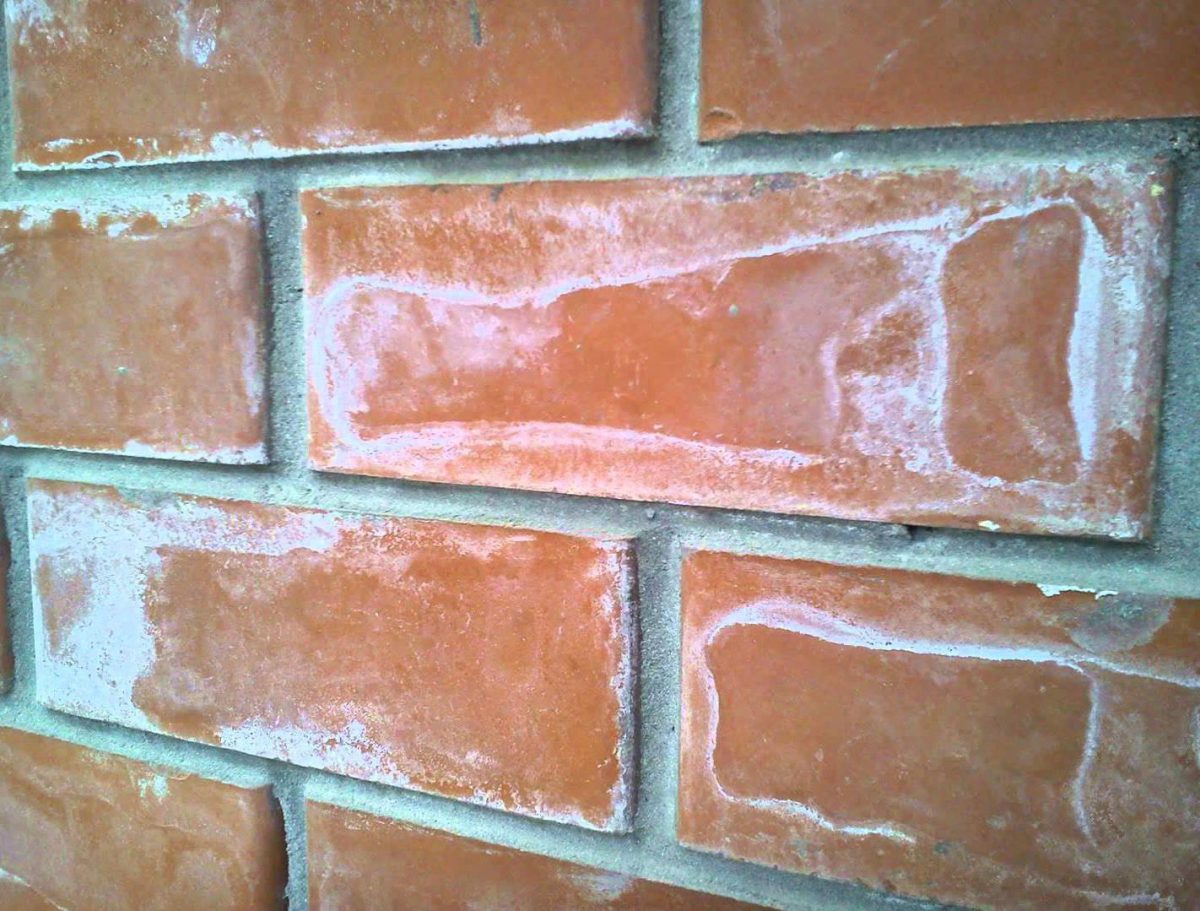
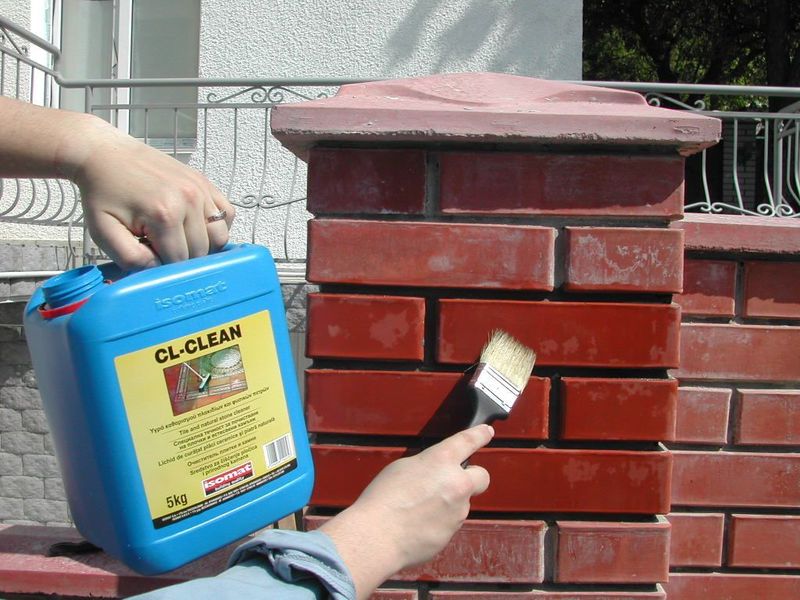
 The special composition provides a high-quality result in the fight against white formation on tiles
The special composition provides a high-quality result in the fight against white formation on tiles
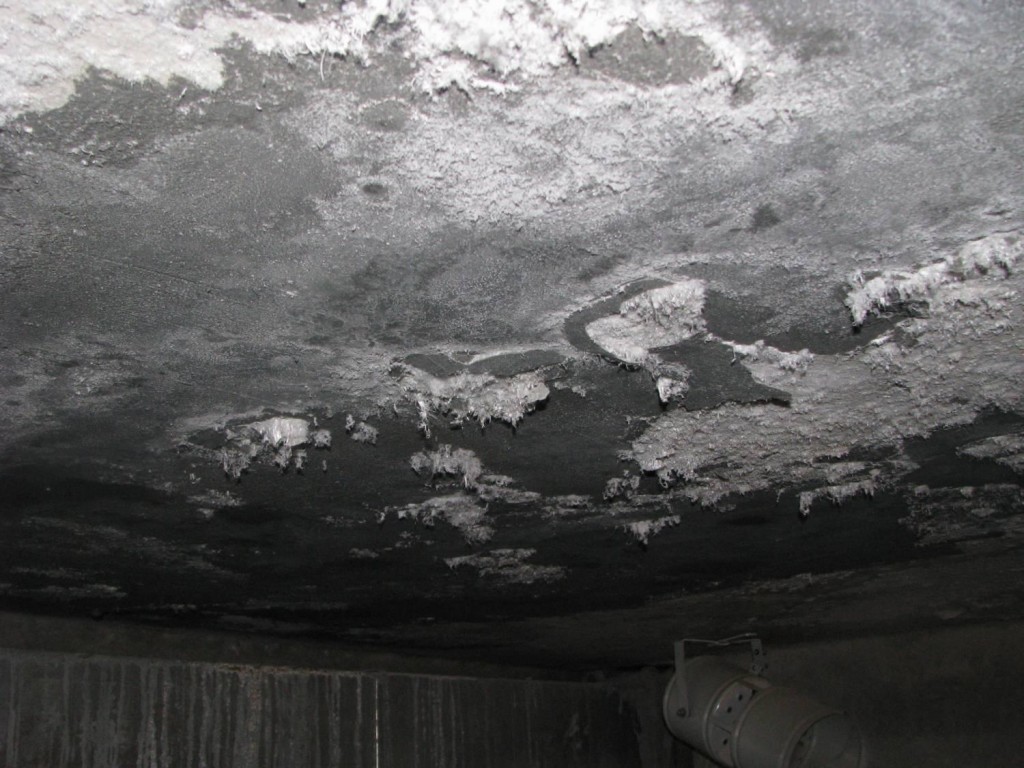
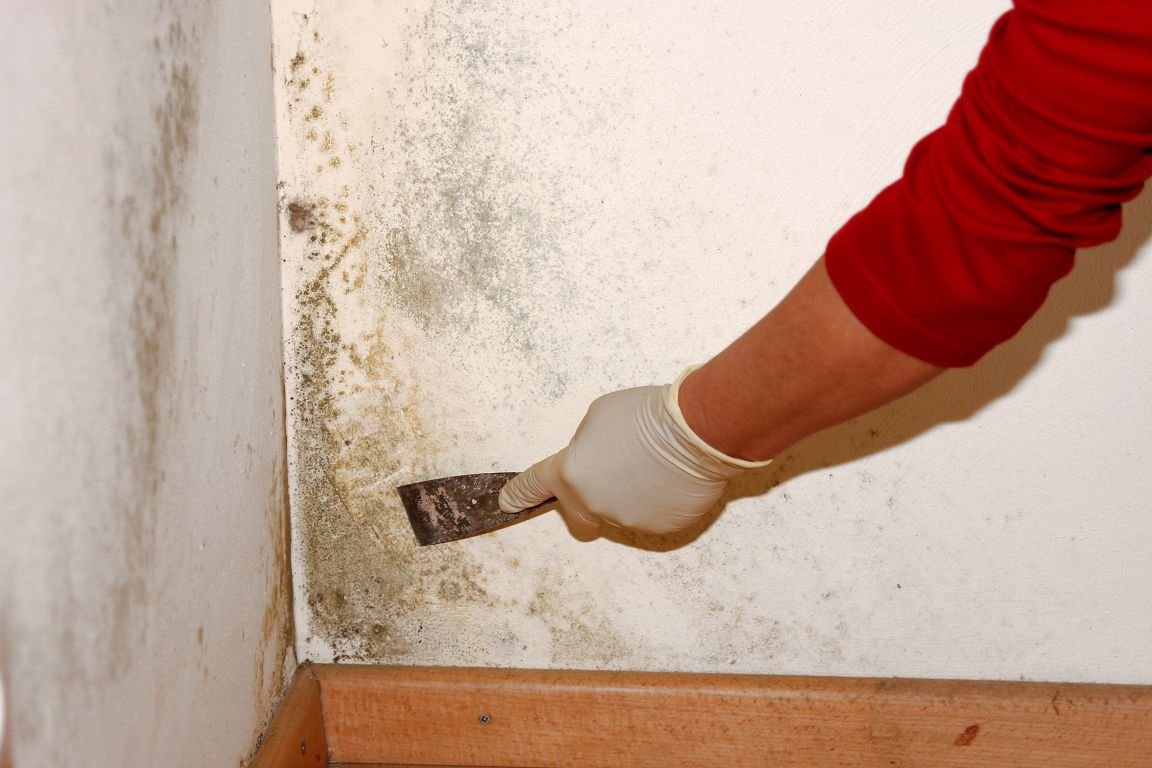
Mold
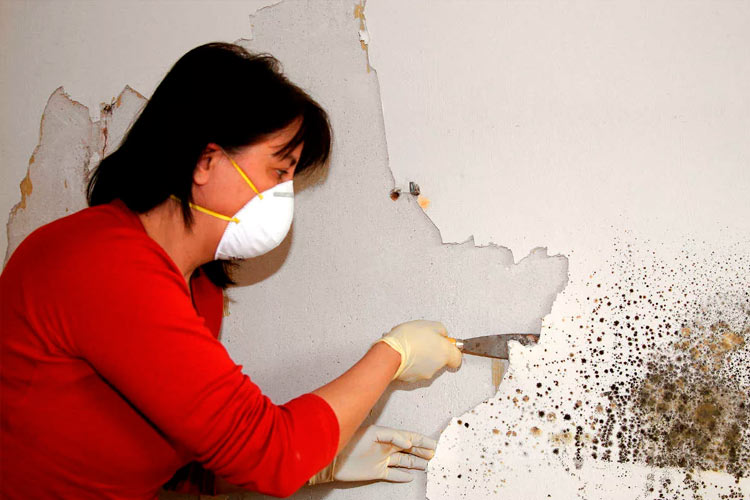

Mold on plaster
Another possible defect on the wall surface is mold. This microorganism develops on the plaster, leading to its biological damage. The reason for the appearance of mold is the creation of favorable conditions for its growth and reproduction, namely:
- air humidity in the room is above 60%;
- stagnation of air masses, i.e. poor or absent ventilation;
- insufficient heating, the fungus prefers a cool atmosphere;
- violation of waterproofing or leakage.
How to deal with a fungus
Sequencing:
-
The areas of the wall affected by mold are treated with a biocide. For more information on wall etching, see a separate article.
- The fungus is removed with a spatula along with the outer layer of plaster.
- Then the site is treated with a biocide a second time.
- As a prophylaxis, diluted antiseptic is sprayed on places where the fungus is not visible.
- The part of the wall to be repaired is primed.
- Next, the plaster layer is restored. As in other cases, the new finish should be similar in composition to the existing one.
- Sanding and grouting.
Moldy fungus is extremely tenacious, and even the conscientious implementation of all actions to eliminate it sometimes does not lead to the desired result.
Folk ways to remove efflorescence
Traditional methods of removing salt deposits from tiles or bricks have the following advantages:
- Cheap compared to traditional chemical agents;
- Ease of use;
- Safety for human health and the environment;
- Lack of surfactants and allergens.
Among such solutions are acetic acid, hydrochloric acid and ammonia. The use of acidic solutions is justified by the fact that they quickly dissolve efflorescence, without giving them a chance to form again.
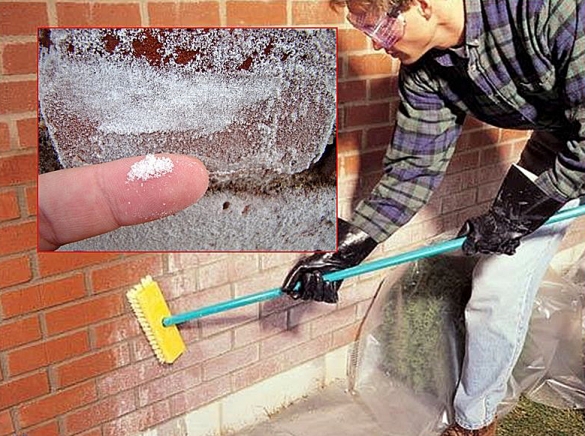
Sometimes the owners of private houses try to remove efflorescence by mechanical means. This is ineffective, and besides, the use of scrapers damages tiles or bricks. In general, a soft roller should be used to apply any efflorescence agent.
When working with acids and alkalis, be sure to use personal protective equipment. It is imperative to wear protective gloves, even if the acid solution is only five percent. The acid can corrode the code of the hands, causing blisters and foci of infection.You should never use an unknown acid.
However, some building materials can deteriorate from acid or ammonia, for example, their color may change or completely disappear. Cement also suffers from acids and alkalis, which negatively affects the strength of the wall.
Gentle cleaning of tiles from cement
In the process of most of the construction work, a cement-sand mixture is used, which falls on the tiles and hardens quickly. In addition, the paths themselves require periodic renewal of the joints with the help of the same cement mortar.
If the spray of the mixture has not yet dried, then the cement is removed from the paving slabs using a strong pressure of water. But, if you do not have a mini-sink at hand, then you can use ordinary table salt, which effectively cleanses the surface of cement deposits. To do this, moisten the tile with cold water and sprinkle some salt on it. After a while, it will eat away at the adhering stain and it can be easily removed with a stiff brush.

Old dirt can be removed mechanically, but only very carefully. It is not worth using nails, a chisel and a skein for this, since this way you damage the surface of the tile, and it will no longer look attractive
It is best to use a non-rigid brush or grinder. In some situations, a hammer and a chisel help, but you need to work with these tools carefully. "Tap" the stains with a chisel so that they crack and then they can be removed in parts.
However, such methods do not always work, so you have to use aggressive chemicals.
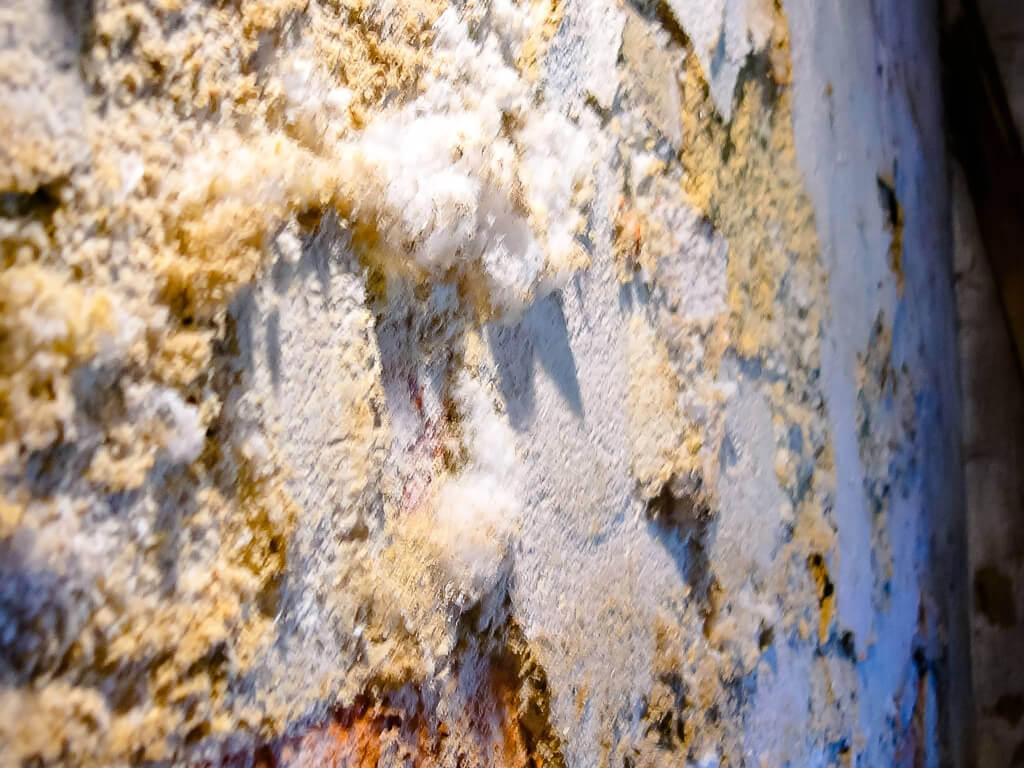
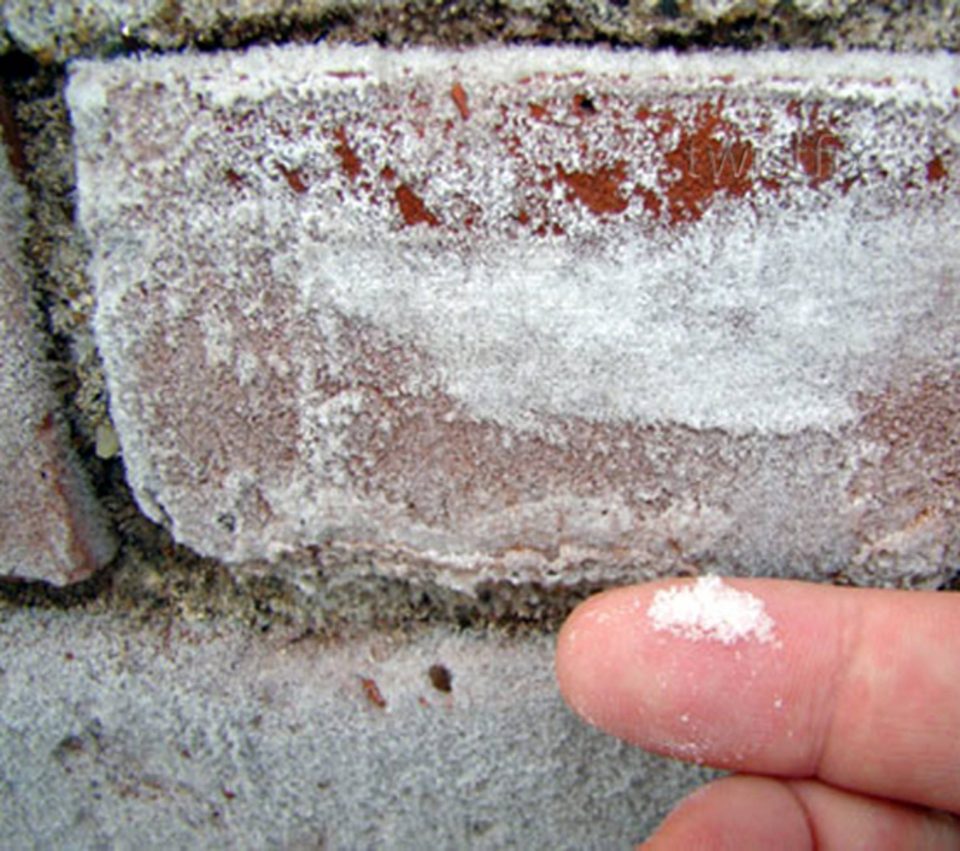
How to remove efflorescence on a brick
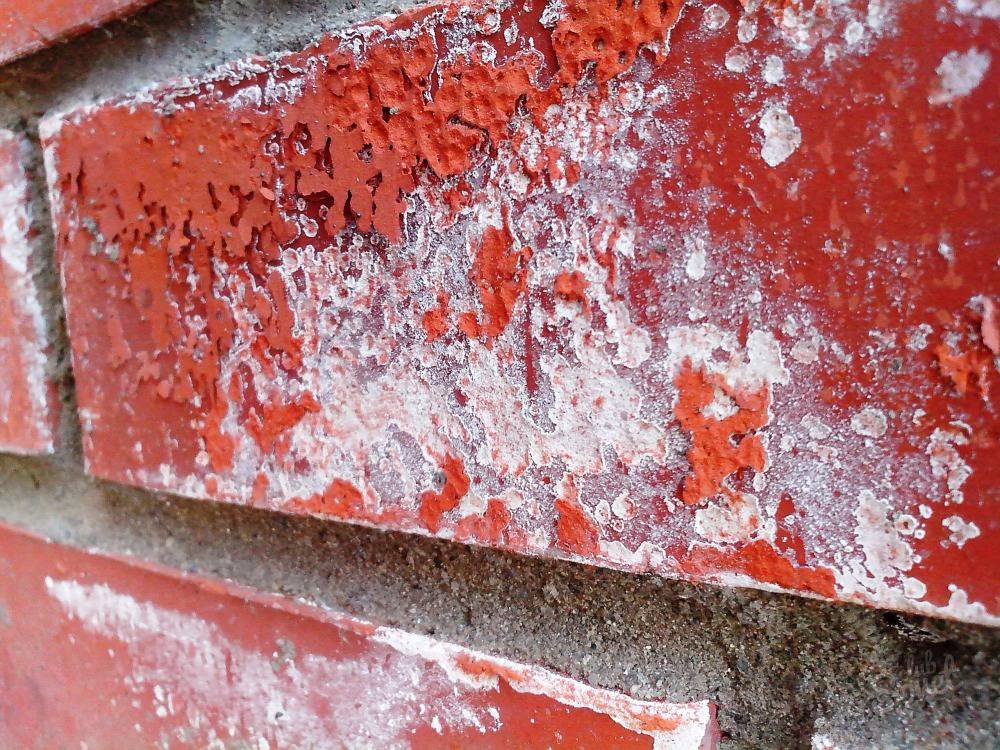
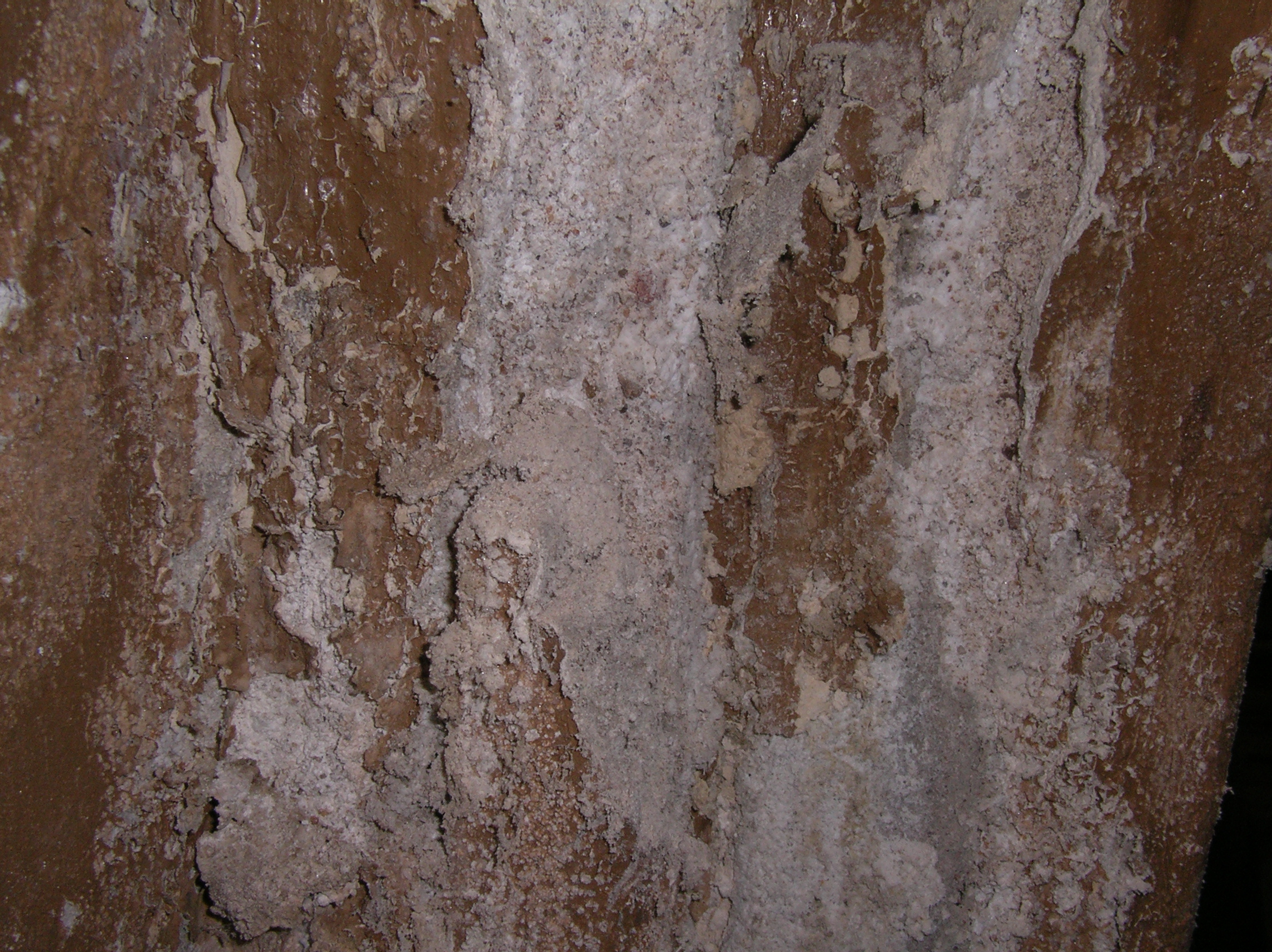
Efflorescence is a rather difficult-to-dissolve structure, since the composition of the whitish coating may contain sodium sulfate compounds, sodium carbonate, calcium carbonate. In addition, the composition of efflorescence can include aluminum, silicon, iron-containing inclusions.
As a result of exposure to atmospheric and industrial emissions, soluble salts become insoluble, which significantly aggravates their removal.
The tasks for eliminating efflorescence are:
- removal of plaque;
- preventing the release of salt from the material;
- protection of walls from further formation of efflorescence.
Technological means for cleaning walls from whitish deposits are acid solutions based on phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and others.
NOTE!
When choosing a product for removing efflorescence, it should be tested on a small surface.
Since certain preparations may not be suitable for every chemical composition, it is recommended to use universal means.
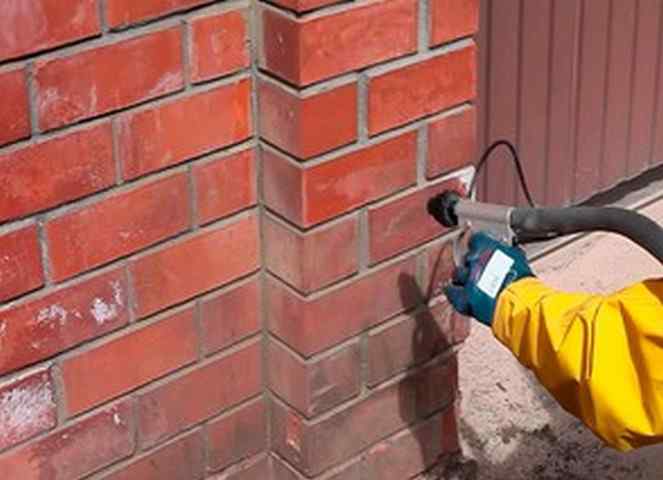
To remove efflorescence, you can use sprayers, rollers, hard brushes. Since the ready-made solutions contain active chemicals, gloves and protective masks must be worn for the safety of the skin of the hands and face.
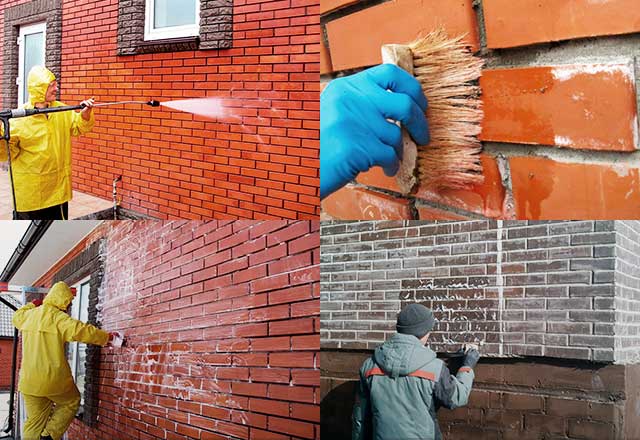
As a rule, acidic solutions are applied to the wall, and then, after a while, washed off. Previously, the wall is cleaned with a spatula, thick layers of plaque are knocked off, and then a solution is applied.
Sometimes it is possible to remove plaque with hot water and a brush, but this method is not effective enough: plaque can remain in the seams and hard-to-reach places.
In some cases, chemicals based on organic and inorganic acids do not help. You can try to prepare your own compositions for removing efflorescence from brick walls.

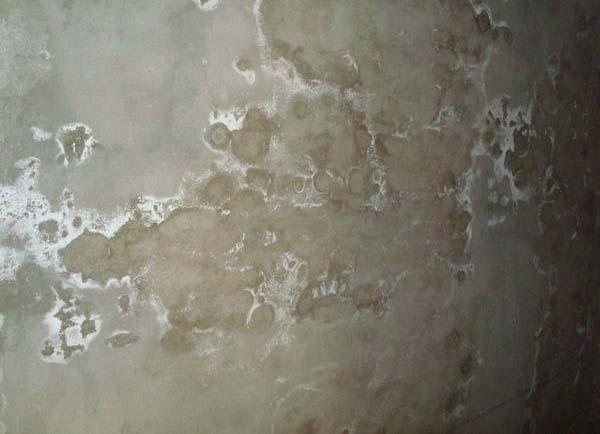
Efflorescence on internal walls
Fading on plaster can lead to white spots on interior walls and damage to paint and wallpaper.
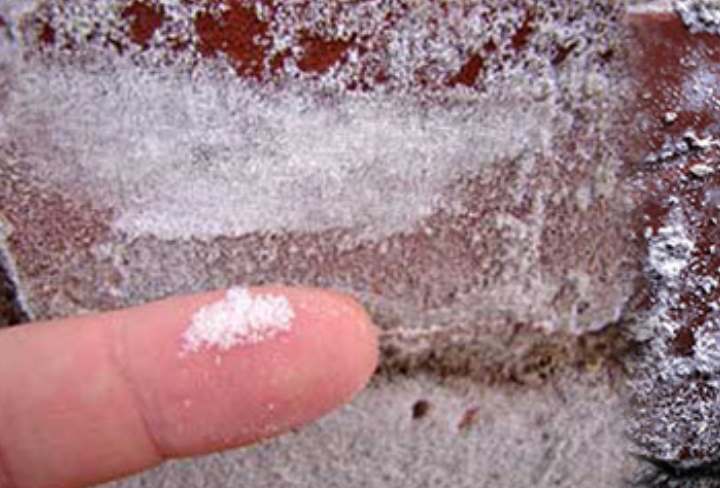
These white salts, which "crunch" to the touch, are quite durable under the wallpaper. This type of sulfate crystal accumulation can occur in any building of any age where water enters the structure. This water will find its way out of the wall through evaporation, leaving behind salts.The salts can be brushed off, but they often repeat and damage the finish again.

In this situation, you need to find the cause and eliminate it. You can buy a salt neutralizer. This will prevent salt reoccurrence, provided the root cause of the problem has been corrected. It will not go through the paint, so you will have to clean the surface before starting the treatment in order to return to bare plaster, stone or brick.
The salt neutralizer can be used after the cause of the dampness has been removed, but this will only be successful if:
There is no more water passing through the wall.
It is applied on bare plaster, plaster, stone or brick. It won't work if applied over paint or wallpaper.
Penetrating Moisture - Before proceeding with efflorescence, check for any possible building defects that may allow water to enter the building:
Damage to walls and can lead to moisture ingress
Internal Water Leak - Check for the following possible internal leaks before processing:
radiator pipes
sewer pipes
water pipes
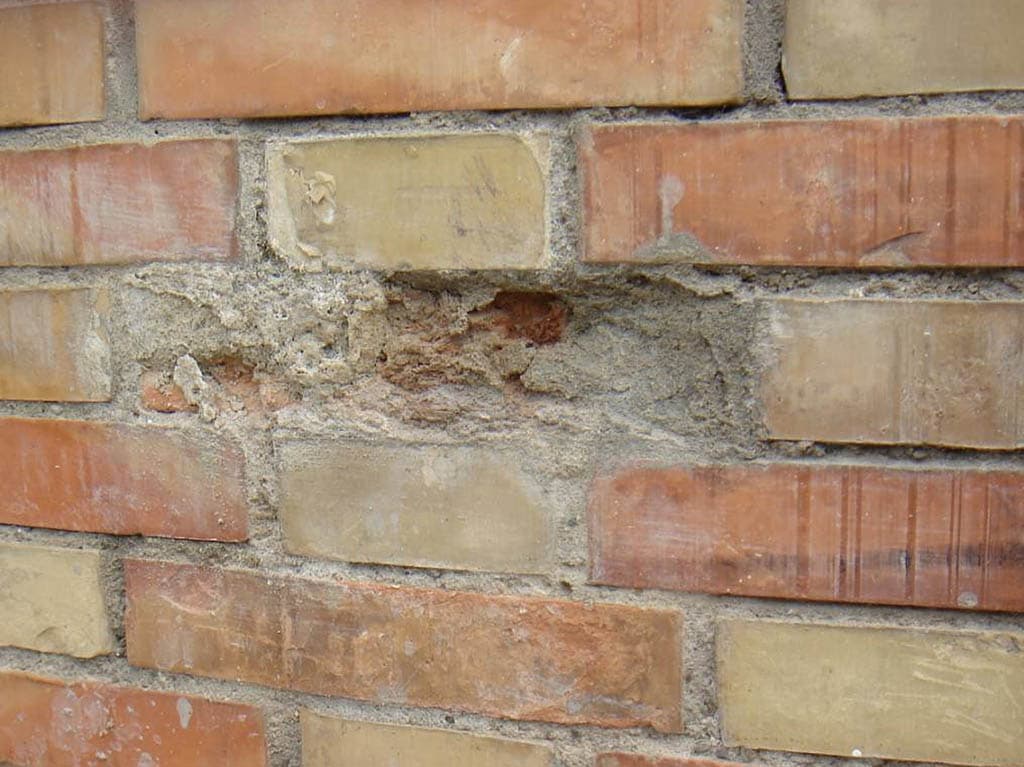
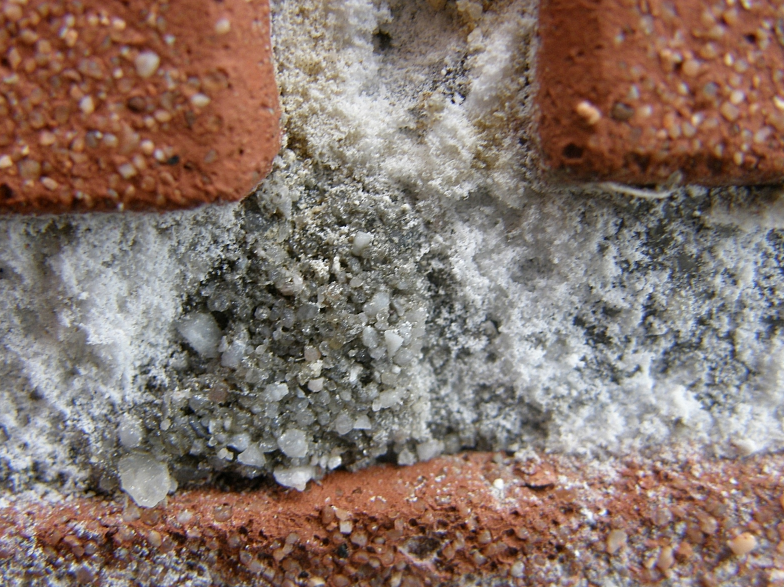
Loose lime is the result of the hardening of mortar or concrete, or from some of the clays used in the manufacture of bricks.
Remedies
It is possible to remove efflorescence inside the room or outside the facade not only by chemical, but also by folk remedies. The salts that dissolve in water include chlorides, sulfates, potassium and sodium salts. They can be removed from the walls with plain water and minimal physical effort. Poorly soluble salts are carbonate salts, as well as phosphates of calcium, iron, aluminum, barium sulfates, calcium silicates.
Often, hard-to-dissolve salt compounds can be found on brick and concrete surfaces. To eliminate them, you will need to use special cleaning agents for chemical basis. Since no one can say with certainty about the characteristics of efflorescence, the method of exclusion is often used to eliminate them. Fortunately, a wide range of substances can be found in hardware stores today that help eliminate plaque.


To conduct tests, it is recommended to buy several types of efflorescence cleaning substances in small packaging and try them in a small area facade. Application is carried out with rollers or brushes, then kept for half an hour and washed off with liquid. Further, the treated areas should be examined and determined which tool did the job better. When using special cleaners, craftsmen should protect themselves with glasses and rubber gloves. In case of contact with any part of the body, you should immediately rinse the area with clean water and thereby prevent chemical burns.
The result of removing efflorescence must be fixed - for this, the walls are treated with a special impregnation called a water repellent. This product removes the base and prevents plaque re-formation. This event should be carried out immediately after the brickwork has dried.
Quite a lot of compositions for the elimination of salt stains are known. Silicone water repellents have proven themselves well. As a result of their use, a protective siliconized film is formed, it prevents the penetration of moisture into the masonry. In addition, these substances contribute to the "breathing" of the walls and natural gas exchange. Treatment with such substances reduces the contamination of the facade and stops the formation of mildew and mold on surfaces.
The information for these products indicates that after processing, they protect the facades for about 10 years. Reapplication of the water repellent is required if the walls get wet from rain. In some cases, re-treatment is carried out 5 years after the first application. The surface must be processed until the agent is absorbed.After that, it is worth reapplying. Before applying to the masonry, the water repellent must be diluted in water, according to the instructions. It is impossible to eliminate re-plaque by increasing the concentration, as this can cause a reverse reaction.


To eliminate salt deposits from the facade, you can use the following folk methods:
- treatment with acetic acid - as a result of the work, an easily soluble plaque is obtained, which can be washed off with water;
- mechanically - using the usual detergents, brushes and a large amount of unsalted water, you can try to remove plaque;
- diluted phosphoric acid.
The industrial substance Trilon B (chelaton III) is considered a super agent for removing salt stains on masonry. It has been shown to be highly effective in combating insoluble salt from a steam boiler or heat generating plant. Trilon makes it readily soluble from a sparingly soluble salt at a high speed. After 15 minutes have passed since the application of the product, the surface will need to be rinsed with hot water.


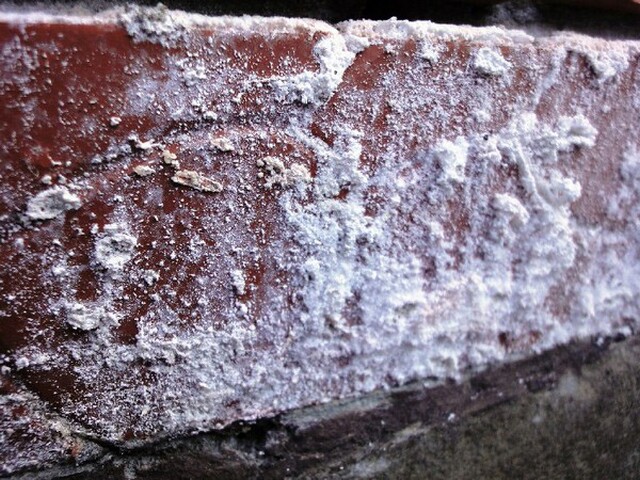
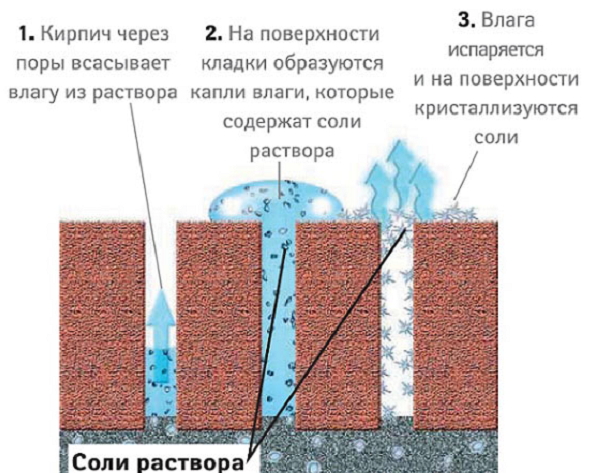
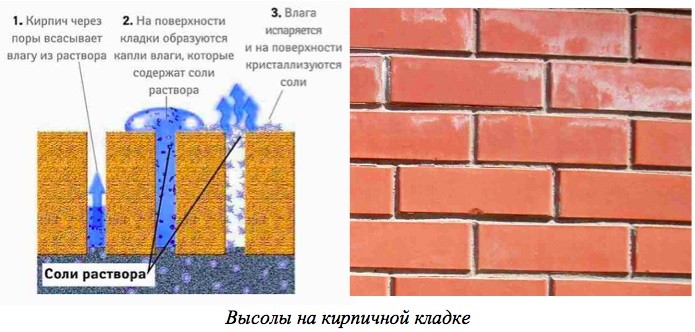
Reasons for the appearance of efflorescence on brick
Efflorescences appear from at least five different sources:
- The raw materials from which the bricks are made contain salts. Due to the fact that the brick has a porous nature, it absorbs moisture well. They dissolve the salts in the building materials and raise them to the surface. When evaporated, they leave a white trail.
- Masonry mortar also contains salts. This is due to the fact that the sand for the solution is not washed, and therefore it has an increased salt content. There are also salts in the water, sometimes their amount is also large.
- There is also a certain amount of salt in the soil on which the house is being built. As a result of capillary phenomena, it moves upward and penetrates to the brick.
- Atmospheric moisture - rain, snow, fog does not contain salts. But in this case, moisture is able to penetrate the brick and bring out the salt in a dissolved state. In addition, atmospheric precipitation can contain dissolved salts that enter the environment from various industries. So a chemical plant in the vicinity of the house is also able to paint the brick in an unwanted white color.
- Additives to concrete contribute to the appearance of efflorescence. These can be different accelerators or retarders for concrete setting. Or, for example, if construction is carried out in winter and antifreeze is added to the concrete. In this case, larger salts may appear.
Causes of occurrence
The main reason for the formation of efflorescence on brickwork is the crystallization of soluble substances that are part of the raw materials for brick and the composition of the solution. In this case, the brick can be any: ceramic, clinker or silicate.
There is a process of formation of excess salts as a result of increased water absorption of the facing material. As a result of high humidity inside the brick in cold weather, water freezes in the structure of the material, which leads to its destruction.
Efflorescences indicate that the surface of the brickwork requires measures to protect the surface from excessive influence of water. To do this, it is necessary not only to cover the surface with protective agents, but also to check the visors, roof, window sills from leaks, as a result of which water gets on the wall.
The following factors can be the causes of efflorescence beyond the control of a person:
- sand that is used to prepare the solution can be oversaturated with salts due to the lack of measures for washing it during the extraction process;
- the presence of salts in the composition of raw materials for the production of ceramic blocks contributes to a high absorption of moisture due to the porous structure of the material;
- the presence of a large amount of salts in the composition of water, which is used for the production of bricks or concrete mixtures;
- groundwater;
- finding a room next to a chemically hazardous enterprise, due to which natural precipitation carries aggressive substances.
There are other reasons why salt streaks can occur on the surface of brickwork:
- improper preparation of the solution in violation of the proportions in which excess water prevails;
- poor quality material;
- the use of cement-lime (or lime) mixtures;
- poor quality waterproofing;
- lack of protection from snow and rain.
CAREFULLY!
The low air temperature, at which the crystallization of salts occurs and the predominantly humid climate, are a comfortable environment for the formation of efflorescence.
Therefore, in the area where rain predominates, and in the autumn-winter period, the temperature drops below -5 ° C, the appearance of efflorescence is almost inevitable.
Folk remedies for removal
Some recipes are effectively used by experienced craftsmen to remove white plaque. Self-prepared solutions contain acids that can be purchased at pharmacies or hardware stores.
The most common plaque removal recipes are:
- hydrochloric acid solution (2-4%). Moisten the wall with water, apply an acidic solution, rinse off after 10 minutes with a strong stream of water;
- a solution of acetic acid is applied to the surface of a brick wall, after 10 minutes, rinse with water;
- apply ammonia to the surface, after a while rinse with a stream of water using brushes.
Some of the tips of the craftsmen are based on mechanical scraping off the plaque from the surface.
IMPORTANT!
When scraping off thick layers of efflorescence, do not use metal spatulas, so as not to damage the front surface of the brick.
For this, use wooden materials.
After the efflorescence has been removed, care should be taken to protect the walls to prevent the reappearance of saline streaks on the wall.

Ways to prevent white plaque formation
To avoid the formation of salt stains on the surface of the sidewalk, you need to treat the coating with hydrophobic compounds. Their use protects against moisture ingress. You can treat the pavement with a mixture that prevents dirt from sticking.
So that there is no need to use a salt remover, you need to carefully choose the material for the arrangement of the territory.
When choosing tiles, concrete paving stones, it is recommended to pay attention to the declared parameters
The quality of products is influenced by additional components used in production. Low porosity of the cladding, low moisture absorption coefficient indicate compliance with the technology.
Measures for the processing of shaped paving elements (FEM) to prevent salt formations can be carried out before installation. To do this, it is recommended to wipe each tile with a 5% aqueous solution of acid.
After this type of treatment, a hydrophobic agent is applied to the surface, which forms a thin protective layer that prevents moisture penetration. If, after purchasing the material, it is impossible to organize stacking in a short time, then it is recommended to store the products on pallets.
Lay the tiles so as to provide air access and protection from moisture. It is impossible to prevent the formation of whitish spots on the surface of products laid on the street. Such a coating is exposed to precipitation.
Chemical cleaning of paving slabs from cement
You can wash out old cement stains as follows:
- Prepare a cleaning agent that dissolves cement and glue (such as Sopro ZEA 703 thinner or any compound that contains phosphoric acid) with a sponge, rag, putty knife and clean water.
- Before you try cleaning your paving slabs with chemicals, put some solvent on the paving stones and make sure it won't corrode or discolor them.
- Apply the detergent to the floor with a sponge and after a while try to separate the cement from the tile.
- If excess acid has formed on the surface, apply baking soda, ammonia or lime to the tile.
- Rinse the surface with clean water.
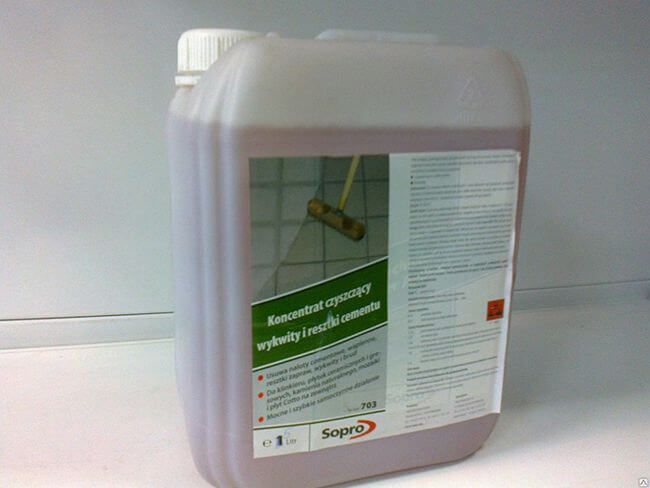

Important! If you are using a solvent, it is not recommended to apply it more than once. If phosphoric acid has not "coped" with an old stain, you can use a more aggressive substance - a solution of hydrochloric acid
For this:
If phosphoric acid has not “coped” with an old stain, you can use a more aggressive substance - a solution of hydrochloric acid. For this:
- Dilute the acid with water in the ratio indicated in the instructions.
- Prepare protective clothing and gloves.
- Apply the solution to the paving stones and leave it to dry completely (during this time, do not touch the surface with bare hands).
- Remove dissolved cement.
- Cover the tile with a neutralizer (5% solution of soda, hydrated lime or caustic soda). If acid gets on the ground, cut off the contaminated soil layer and dispose of it.
- After that, the paving stones must be thoroughly washed with water (so that the surface does not fade, use trisodium phosphate).
- Apply sealant to dry tiles.

Important! If hydrochloric acid gets on your skin, wash it off with water and see a doctor immediately. In addition to cement, spots of a different nature may form on the paving stones, we will consider them in more detail
In addition to cement, spots of a different nature may form on the paving stones, we will consider them in more detail.
What is the cause of efflorescence?
You can find efflorescence on brick, concrete, or stone walls or floors. They can also be found on fresh plaster. Efflorescence on fresh plaster can appear white and fluffy. As mentioned above, they are caused by the reaction of water with salts in plaster (or other building materials), which can occur after a water leak or in the event of severe condensation.
Preventing efflorescence on brick and plaster may not be possible if it is caused by the materials getting wet during construction, you may just need to let the surfaces dry completely and then treat the surface. If you have a high level of condensation, you can eliminate the cause of the moisture and treat the salts to neutralize them, and this is the only reliable way to effectively protect against efflorescence.

Under normal circumstances, white, salt is found in relatively new buildings because the brickwork was not weather-protected during construction. The brickwork becomes saturated during the construction of the wall, and after its completion, this water comes out of the porous bricks in the wall due to evaporation, when it evaporates leaves salt on the surface bricks.
In this case, the salts can be brushed off the wall and they should not reappear. However, in cases where efflorescence is caused by water leakage, for example, there are no masonry joints to allow water to continuously flow into the building material, then efflorescence will continue to form. In this situation, the cause must be found and eliminated, because otherwise unsightly salts will continue to form.