Is slaked lime harmful to human health?
The product can cause serious harm to health if used improperly and if in contact with it for a long time. Inhalation of dust particles or droplets of lime causes irritation of the respiratory tract mucosa, possible severe burns and the risk of developing chronic asthma. Accumulating on the surface of the skin, lime absorbs moisture and the dried skin begins to crack, small ulcers form. No less destructively slaked lime can affect the stomach and kidneys.
People who have pets and use fluff wonder if slaked lime is dangerous for a dog? An animal can eat a piece of the product from the ground on the street, and in this case it is necessary to consult a veterinarian as soon as possible. There have been cases when an animal died from poisoning and subsequent dehydration, so watch out for pets when working with hazardous substances.
Maintenance and storage tips
The cost of the finished fluff is not so great, and it is constantly on sale. But, nevertheless, if stocks remain, or the process of its application is somewhat delayed, following simple rules, you can always have access to this material.
- when density changes due to moisture evaporation - just add water;
- during use, it is necessary to constantly stir the solution;
- it is necessary to add water exactly until it is absorbed;
- for storage in a container, sand is poured from above (about 20 cm);
- when using large volumes in winter and located on open ground, so that there is no freezing, fill it with sand, and insulate it with ordinary earth on top;
- do not use in work with large grains, lumps, under-extinguished, burnt particles, because this will lead to a violation of the integrity of the treated surface;
- before using in mortars for laying bricks, blocks - an exposure is required for up to 14 days;
- for plastering work - 30 days.
The lime whitewashing process is very simple. It is recommended to dilute the solution in advance, to obtain a rich white color, it is better to use lime of the highest or first grade, dilute the composition, adhering to a 1: 1 ratio. Before whitewashing, the solution is thoroughly mixed, and the tree trunks or wooden supports are painted.
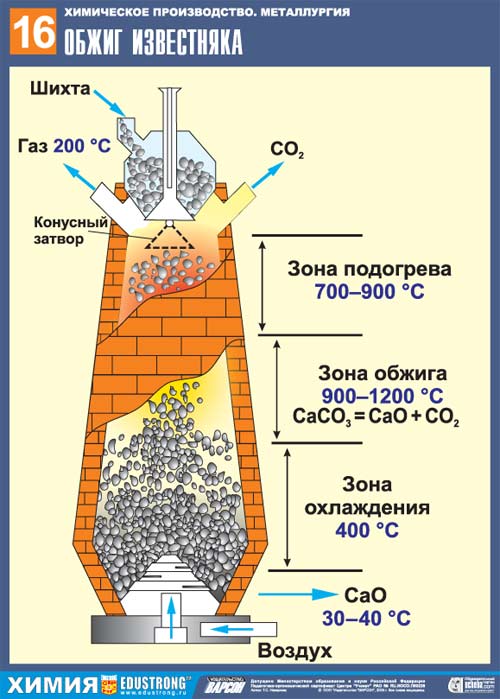
Limestone roasting is the process of heating a limestone mass, during which calcium carbonate (formula: CaCO3) decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide. The basic reaction equation looks like this: CaCO3 = CaO + CO2. This reaction is used to obtain quicklime, cement, binders, soda ash. Special industrial furnaces are used for firing. In the factory, the temperature at which the firing is carried out ranges from 1000 to 1300 degrees Celsius. Calcium oxide is the main constituent of quicklime.
If incompletely calcined, pieces of unburned material remain in the furnace. However, their presence does not affect the quality of the product formed. A more harmful effect is exerted by an increase in temperature above the maximum permissible values. In this case, the so-called burnout of the feedstock is observed, the result of which is the appearance of coarse-crystalline calcium oxide. Such lime is not suitable for slaking, since in this case the process is very slowed down, as a result of which it continues even after the lime has been used for its intended purpose.This can cause the appearance of defects in the structure, up to and including its freelance destruction.
Impurities present in limestone affect the firing process and the properties of the resulting product, often leading to a decrease in the efficiency of the process.
How and where is lime used
Each of us has come across such material as slaked lime. Its scope of application is so diverse that it can be found even during the preparation of certain dishes. But this is a rarer option.
Most often we encounter her in the country, at a construction site. Here we are talking not only about large construction projects, but also in private construction sites.
Application in construction
Slaked lime is used in construction in such cases:
the most common and well-known case is the whitewashing of walls and ceilings. Here about mdf for the ceiling;
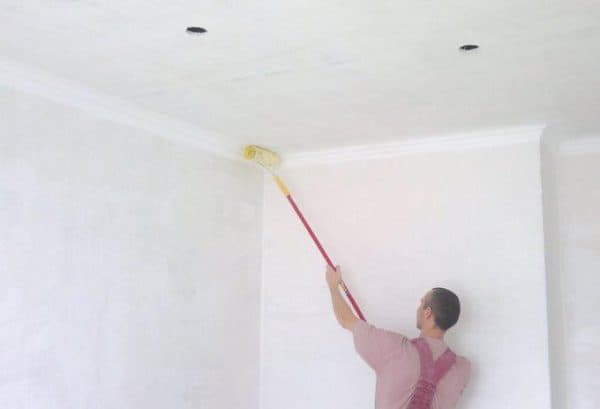

Whitewashing walls and ceilings
- also lime can be used to protect wooden buildings from fire and decay. To do this, it is enough to simply process the object itself with diluted lime;
- slaked lime is used for joint cement mortars. Here are the proportions of cement-lime mortar for plaster;

Joint solution
you can meet it in the preparation of silicate concrete. Here is the consumption of cement for 1 cubic meter of concrete;

Silicate concrete
also, such material is used during the installation of the furnace, namely, when laying the inner part of it. Here about the solution for plastering the stove.
You need to understand that lime must be prepared according to a specific recipe.
Is it possible to use and how is it used in gardening and in the garden
Slaked lime has found its application in horticulture:
lime takes part in the production of fertilizer, which is used in the garden and horticulture;

Fertilizer
garden. A special solution is made from such material, with which the beds are whitened in order to protect the plant from various kinds of diseases, as well as in order to fence the beds from parasites;

Sadovaya
for whitewashing trees. This procedure not only guarantees the protection of the tree bark, but also gives it a beautiful appearance.

Whitewashing trees
But this is far from all where such material can be used. It can be used by:
- in the process of tanning leather;
- add lime to the connecting systems, to clean the drainage pipes;
- interestingly, lime is added to the production process of E 526, which in turn is used in the food industry;
- even in dentistry, you can find this material. It has found its application in simple disinfection of root canals (passage canals).
There are quite a few branches and spheres of human life, they use it only in a slaked version, but again, in order to get the desired result, it is necessary to deliver lime in the correct proportion.
Lime is also used in the process of disinfecting garden tools. The process is carried out only by fresh quenching of the material. The process is simple - the material is neutralized in a one-to-one ratio, after which it is allowed to dry, after which the milk of lime is prepared.
Read the material about bleach for disinfection.
Material preparation scheme:
- one kilogram of lime is one liter of water;
- let the material cool and dry;
- add more liters of water.
For more information on the use of lime, see the video:
Application
-
Lime fertilizers
since ancient times they have been used in agriculture to increase soil fertility and for liming, that is, to lower acidity. Solid lime fertilizers, such as chalk, limestone, dolomite, are ground or burned before being introduced into the soil. Soft lime fertilizers work more efficiently and are introduced into the soil without preliminary treatment - natural dolomite flour, lake lime (drywall), lime tuff, marl.Lime fertilizers include rock processing products: quicklime burnt lime (ground or lumpy) and fluff (slaked lime), as well as industrial waste such as cement dust, white flour, blast furnace slag, shale and peat ash, defecation mud, etc. -
Painting of trees.
Dissolve 1 kg of lime in 4 liters of water. After a couple of days, the solution is ready for use. -
Spraying plants.
Copper sulfate is added to lime water and sprayed two hours after preparation. -
Whitewashing ceilings and walls.
Here the proportion will be different: 1 kg of lime per 2 liters of water. Then add water until the desired consistency is obtained. Let the solution stand for a couple of days and strain it. -
Fluff
(or dry calcium hydroxide) perfectly copes with the functions of protecting against moisture, disinfecting and improving the binding qualities of cement and concrete mortars.
The technology for the production of concretes and mortars provides for the use of burnt lime of the crushed fraction. In the process of processing, almost all components of natural material are used, which makes its use profitable and preferable.
Products containing lime are durable, water-resistant and high-density. The valuable qualities of quicklime raw materials allow the component to be added to the composition of strengthening and stabilizing solutions used in road construction.
It is difficult to imagine the production of sand-lime bricks without lime. But the scope is not limited to the construction direction. The material is often used in fishing, poultry farming, agriculture due to its purifying and disinfecting properties.
Lime is produced from carbonate rocks by burning them until carbon dioxide is completely released. The main raw materials are often used:
- limestone;
- dolomite;
- shell rock.
Technical properties
There are special requirements for the production of slaked and quicklime, regulated by the state standard (GOST 9179-77):
- In the production of lime, only carbonate rocks and a certain amount of mineral additives are used. The amount of additives should not exceed the amount specified in the standards for a particular type of lime.
- Quicklime is subdivided into three grades and should not contain additives, powdered lime with additives is available in two grades, slaked lime may or may not have additives and is divided into two grades.
- In calcium lime, the main component is calcium, the percentage of MgO should not be more than 5.
- Dolomitized lime contains MgO up to 20%
- Dolomite up to 40% MgO.
- The hydraulic can include silica, iron oxides, a small amount of clay.
The properties of lime are determined by the rocks used for firing and by the manufacturing process itself. As a result of the heat treatment of limestone, solid pieces of quicklime come out of the furnaces, its color depends on the additives present, the more snow-white the shade, the higher the grade of the material. Dolomite and hydraulic lime have a grayish tint.
Upon contact with water, carbon dioxide is released and lime turns into a liquid state, the concentration of which depends on the amount of water. Depending on the technological process of firing and temperature, it is possible to obtain lime of different strength - hard-fired, intermediate version and soft-fired.
As a building material, softly fired is more common, it differs in the following characteristics:
- Smallest grain size.
- Lower density.
- The shortest blanking period. Firmly fired turns into a liquid state in 10 minutes, softly fired in three minutes.
In the process of slaking lime, heat is generated, therefore, if safety precautions are not followed, you can get a severe burn.
The density of the quicklime depends on the temperature used in the kilns.Lime, calcined at 800 degrees, has a density of 1.6, an increase in temperature to 1300 degrees makes it possible to obtain pieces of raw material with a density of 2.9 g / cm3.
According to the hazard class, lime is classified as a low-hazard substance. But certain requirements are imposed on its storage and transportation. The quicklime must be protected from moisture, as moisture ingress and heat escaping can cause a fire.
The certificate of conformity of lime must contain information about its grade, percentage of impurities, condition. The certificate is issued to certain organizations that comply with GOST for the manufacture of this building material.
Lime is considered an environmentally friendly and clean material. Slaked lime disinfects premises well, prevents fungi from developing and negatively affects parasites. Whitewashing the walls and ceiling provides microscopic air penetration, so the humidity in such rooms will always be at a normal level.
Lime is well tolerated by people with allergic respiratory diseases. But at the same time, one should not forget that when extinguishing the material, burns are possible, and the vapors released at this time are dangerous for the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and eyes. Subject to safety measures when working with lime, it is completely safe and not harmful to health.
How to slake lime: tips and tools
When quicklime interacts with a small amount of water, a lime dough is obtained, to which sand and other materials are added. The resulting substance is used in construction to hold bricks together as a binder.
If the mass is diluted with a large amount of water, you get a lime suspension or milk of lime. In agriculture, the suspension is used to treat the bark of fruit trees from sunburn and to destroy the embryos of parasitic organisms that cause disease. A solution in a mixture with other substances is also sprayed on fruit trees and shrubs, whitewash curbs, walls of buildings.
To extinguish lime, do not forget about safety precautions and follow these tips:
- During slaking, lime gives off heat. To prevent the container from melting, use an enamel cookware.
- The vapors released are toxic to the body and can also cause airway atrophy, so wear a respirator.
- When slaking lime, an ebullient reaction occurs, accompanied by splashing of the substance. To avoid burns, wear goggles, rubber gloves, and work clothes that cover exposed areas of the body.
- Extinguish lime outdoors. If there are windows in the room, open them, creating conditions for ventilation.
- During the procedure, keep away from the container until the vaporization ends.
- Use a wooden spatula when preparing the substance.
The method of extinguishing depends on the purpose of use.
Whitewashing the walls.
Lime paste is used during this procedure. It is obtained by mixing lump lime with tap water.
The solution is prepared in a 1: 4 ratio. Water is added in small, even portions. After stopping boiling, the substance should be well stirred and filtered. After 1 hour, the solution should be left in a dark room for 1-2 weeks.
Whitewashing trees.
To whitewash the trees, a lime suspension is prepared. For this purpose, the lime dough is diluted with water. For 1 kg of lime, take 10 liters of water. The solution is used immediately.
During lime slaking, the following tools are used:
- enameled container;
- wooden spatula;
- a bucket or watering can for water.
Make sure that no lumps remain during the extinguishing process, and the substance of the ball is homogeneous. For the treatment of walls, trees, shrubs, you can use a spray. In this case, remember to wear a respirator.
About slaked lime

A practical, simple product of the construction industry, which is deservedly in demand among both professionals and ordinary people. Let us consider in detail the features and properties of this substance.
Manufacturing method
Slaked lime is called calcium hydroxide and is formed when water gets on it. In the process of transformation of the substance, a large amount of vapor is released. After slaking the primary product, milk of lime, water or hydrated lime in dry equivalent is obtained. The process of "extraction" of calcium hydroxide or its dehydration is usually carried out in an open space of a large area or in a special creation (box, pit, etc.).
Depending on the rate of quenching, there are 3 types of calcium hydroxide:
Slow quenching (over 25 minutes).
The slaking time is determined from the moment lime is combined with water until the reaction temperature stops rising (usually this period of time is indicated on packages with raw materials).
Using lime and water, you can get a lime dough and a hydrated type substance (fluff). In the first case, water with lime powder is taken in a 3: 1 ratio. To obtain a plastic composition, it is necessary to withstand it for a couple of weeks in a special pit. Fluff is obtained exclusively in industrial conditions: for its manufacture in factories, special hydraulic motors are used.
The process of "extraction" of slaked lime is accompanied by the release of a large amount of heat, therefore, in order to avoid a decrease in temperature, water is added gradually. The density of calcium hydroxide can be adjusted by kneading while gradually adding water. As soon as the initial product stops absorbing water, it is necessary to immediately stop adding it.
ON A NOTE... Quicklime can have different initial properties, so it is better to choose a longer amount of time for the slaking process. This will help to avoid the formation of steam on the walls plastered with lime mortar when moisture gets on their surface. The slow-extinguishing composition must be poured with water several times, the fast / medium-extinguishing composition must be poured until the steam release stops.
Application and storage
Slaked lime is a highly demanded product used as an effective fertilizer, whitewash, water softener and even for dental purposes. Undoubtedly, the main field of application of calcium hydroxide is construction. Lime dough is a constant "participant" in many building mixtures, which is primarily due to its useful properties: immunity to fungus and mold, the ability to "resist" rodents and insects.
ON A NOTE... Immediately after receiving slaked lime, it must be filtered through a special sieve to make the composition more homogeneous, and then gypsum / cement is added to it (otherwise the lime solution will harden for a very long time).
If slaked lime is obtained in large quantities for the purpose of repeated use, in order to avoid deterioration of the composition, it should be properly stored. To do this, unused lime dough is placed in a specially prepared pit and covered with a 20-centimeter layer of fine sand. If we are talking about the cold season, it is necessary to additionally lay out an earthen layer with a thickness of at least 0.7 m in order to avoid freezing of the composition. The storage place is fenced off with marks that are removed only after the slaking of the smallest particles of lime is completed.
If it is planned to use slaked lime in building mixtures for masonry, it is enough to withstand the composition for 14 days, if the component is added to the mixture for plastering, it should be kept for at least a month.
Specifications
Lime is a substance that is often found in nature (mainly in rocks), and the product is manufactured in full compliance with established standards, because mixtures on such a basis must perform protective functions at a high level.
The finished lime should consist only of carbonate rocks (limestone) with a small amount of clay.
Various additives and impurities are allowed in the composition of the material based on GOSTs, depending on the field of application.
Limestone is very similar in appearance to chalk or coke, but they have different properties and are not interchangeable. To distinguish limestone from chalk, you can drip water on them. Chalk will not give any reaction, but limestone will begin to foam and generate heat. If you use chalk to whitewash the walls, it will leave marks on clothing and surfaces in contact with the wall. Lime does not leave any traces, so it is most often used to whitewash walls.


Quicklime is divided into three grades (1, 2 and 3), and slaked lime is subdivided into 1st and 2nd grade. The exception is powdered quicklime, it is divided into two grades and has additives. The rest of the types are made without impurities.
By external physical indicators, for example, by color, you can determine the grade of the material.
After heat treatment of limestone, quicklime is obtained, and if it has a white color, this means that the material does not contain additives and belongs to a high grade. In other cases, the material has a grayish color, most often it is dolomite and hydraulic lime.


The production of lime material consists of the extraction of the rocks themselves, their crushing to the required size and subsequent firing in special furnaces. Nowadays, shaft and rotary tube furnaces are most commonly used because they provide a uniform temperature effect on the material and a continuous firing process.
The strength of raw materials is influenced by the temperature during firing and the production process itself. There are three options for the strength of the finished product: hard-fired, medium-fired, and soft-fired lime.

Softly calcined lime is very popular in construction, due to the following properties:
- the quenching process occurs quickly, within about 3 minutes;
- such material has a small size and low density.
Lime belongs to a low hazard class, but safety precautions must be observed during transportation and storage. Since quicklime reacts violently with water, you must make sure that moisture cannot get on the material.
The composition of lime most often includes various mineral additives that improve the properties of the material: granulated blast-furnace slags, quartz sands and other substances.


Scope and features of the use of lime
- The use of slaked lime. It is a popular material for whitewashing, plastering, and other finishing tasks performed during repairs. Depending on the type, work is carried out with a spatula, spray, and other painting tools.
- The use of quicklime. Lime cement is produced from it. It can be used for a wide range of construction work, with the exception of the construction of fireplaces and stoves, since when heated, such a substance releases carbon dioxide, toxic to humans. You can also buy lime for the production of wall
With air lime
called the astringent obtained
burning carbonate rocks
(limestone, chalk, dolomite), with
the content of clay impurities is not higher
8% by mass. Lime production
consists in crushing and firing
raw materials. At the heart of the process
firing is a thermal reaction
dissociation of the main component
limestone - calcium carbonate - at
temperature 1000 0 С
according to the scheme
.
Roasting of raw materials
produced in furnaces of various designs.
At the optimum firing temperature
clean limestone until completely removed
carbon dioxide (theoretically 44%)
the mass is reduced by almost 2 times, and the volume
product - by 10-12%. Obtained in the form
pieces of lime (lumpy) is
is a porous material consisting of
mostly small oxide crystals
calcium CaO
and partly magnesium oxide MgO.
calcium ();
magnesian
();
dolomite ().
In construction
air lime is used in
powdered with mineral
additives or without them. For use
lump lime is crushed either by slaking,
or by grinding.
Quicklime
- anhydrous calcium oxide, which
actively interacts with water
reactions
with the formation of hydrated (slaked)
lime Ca (OH) 2.
At the same time, a large number of
heat, which leads to the transition of a part
water into a vaporous state, loosening
lime into fine powder and enhance
temperatures up to 100 0 С.
Quicklime
happens: lumpy and ground. Quicklime
powdered lime is obtained
lump grinding. Heat generated
heats the mortar with quicklime
mixture, improves the initial process
hardening and drying, especially in winter
conditions, but with long-term storage
quickly loses activity due to
hydration due to moisture contained
in the air.
Hydrated lime
used in construction in the form
powder, dough and milk of lime.
When slaking lime with a small amount
water (60-80% of the mass) is formed
powdered hydrated lime. By
appearance is a loose powder
white with bulk density
300-600 kg / m 3.
Lime dough is obtained by adding
200-300% water by weight, and milk of lime
- with significantly higher water consumption.
Particle formation
hydrated lime is accompanied by
an increase in their volume by 2-3.5 times
compared to quicklime. It gives her
good water retention capacity
and plasticity.
Depending on the
lime slaking time is subdivided
on:
fast-extinguishing
(less than 8 minutes);
medium damping
(8-25 minutes);
slow-extinguishing
(more than 25 minutes).
Lime slaking
produced in hydrators. On small
on construction sites lime is preliminarily quenched
in creations and finally withstand
at least two weeks in extinguishing pits.
It is necessary to completely extinguish the lime, otherwise
unextinguished CaO particles
will lead to their belated extinguishing in
mortar and its cracking.
Depending on the
content of active CaO + MgO
hydrated lime is subdivided into
two varieties.
Lime hardens
in air with simultaneous flow
two processes: crystallization Ca (OH) 2
from a saturated aqueous solution and
carbonation CaCO 3
by reaction
After 28 days
air hardening construction samples
slaked lime solutions reach
ultimate compressive strength 0.5-1 MPa, and
on quicklime powder - up to 4-5
MPa. The lime hardening process can
accelerate by drying.
During transportation
and storage lime must be protected
from moisture and pollution
foreign impurities. Store lime
should be separated by type and grade.
Mining and production technology
Lime production basically consists of two stages:
- Extraction of limestone and other used rocks. For the production of lumpy lime can be used and waste products that use limestone for other purposes.
- Roasting of prepared rocks.
Limestone is mined in open pits using explosives. Selective mining of rocks makes it possible to prepare raw materials that are homogeneous in their density and chemical composition, which affects the quality of later produced lime.
Preparation of raw materials is carried out by crushing it.Since the temperature is set in advance in furnaces, the use of fractions that differ greatly in size leads to the fact that small pieces can burn out, and large pieces do not completely undergo heat treatment.
Calcination of limestone is the main technological stage in the manufacture of air lime. Different temperature conditions are used depending on the content of impurities. All technological conditions must be met, since the burning of limestone leads to the formation of a material with low quality characteristics. Burnt lime is poorly soluble in water, has a high density and has a negative effect on concrete solutions.
The firing of the starting material is carried out in different furnaces. Shaft furnaces are widely used, they are characterized by a continuous cycle of operation, efficiency, ease of control. Rotary kilns produce the highest quality soft-calcined lime.
Installations have been developed and are used, which allow firing material in a fluidized bed or in a suspended state. Such installations are good for firing the smallest fractions of rocks, but they are characterized by low efficiency.
Educational film about lime, how it is made, what and where it is used:
How is quicklime produced?
Previously, limestone was processed by the thermal method to obtain lime, now this method is practically not used, since this produces carbon dioxide. A replacement for this method is the decomposition of calcium salts, which contain oxygen, during heat treatment.
First, limestone is mined from a quarry, then it is crushed, sorted, and fired in special furnaces. Mainly for such work, shaft-type gas furnaces are used; their furnaces can be overflow or remote. Overflow furnaces run on anthracite or other coal, which leads to significant savings. Such furnaces are capable of producing large quantities of material, up to 100 tons per day. The only drawback is ash clogging.
A remote firebox gives a cleaner kind of lime, it works on coal, wood, peat or gas, but the power of such a furnace will be much lower. The highest quality lime comes from a rotary kiln, but is rarely used.
Hydraulic lime production
The production of hydraulic lime includes the following main operations: extraction and preparation of marly limestone, roasting of raw materials, quenching of the roasted product, separation of unquenched particles and their grinding, mixing of crushed grains with quenched material and packaging. Marly limestone is mined, crushed and sorted in the same ways and using the same mechanisms as in the production of air lime. Marly limestone is fired, depending on its composition and structure, at 900-1100 ° C. The firing temperature is the lower, the more clay and magnesian impurities in the raw material. When firing marly limestones, as well as firing air lime, calcium and magnesium carbonate decompose, and there is also an interaction between these compounds and calcium and magnesium oxides and sandy and clay impurities. These reactions take place mainly in the solid state.
As a result of firing the raw material at 900-1100 ° C, a product is obtained that usually consists of free calcium oxide, undecomposed calcium carbonate, as well as p-dicalcium silicate C2S, which is formed mainly by the interaction of CaCO3 with impurities of finely dispersed quartz. Establishing and maintaining the correct firing regime is of great importance: underburning or overburning reduces the quality of the hydraulic lime. Lime, calcined before sintering, is almost not extinguished, and when ground, it can give a binder that does not have a uniform volume change. In the presence of magnesium carbonate in the feedstock, firing leads to the formation, in addition to the indicated compounds, also CaO-MgO- * SiO2 and free magnesium oxide.The hydraulic activity of lime and the hardening strength directly depend on the presence of C2S, C2AS, ferrous compounds and partly calcium sulfate.
For the burning of hydraulic lime, shaft and rotary kilns are used. The consumption of equivalent fuel in the firing of hydraulic lime is lower than in the firing of air lime, and is usually 12-14% by mass of the finished product for shaft furnaces.
The burnt lime is crushed and then ground in mills, usually to a residue on a sieve No. 008 of no more than 5-7%.
Slaking of hydraulic lime is more difficult than air lime, since it contains a significant amount of non-extinguishable particles, has a dense structure, and less heat is released during slaking. The more silicate components in the hydraulic lime, the denser the calcined product and the more difficult it is to quench lime particles due to the fact that they are enveloped in non-extinguishing grains of hydraulic connections. In this regard, slaking of hydraulic lime must be carried out in appropriately equipped factories.
The amount of water required for slaking depends on the composition of the hydraulic lime. Depending on the composition of the lime, the amount of water theoretically required for slaking will be 7-17%. In practice, a certain excess of water is needed, and since when the temperature rises during the quenching process, part of it evaporates. Usually they take water in an amount 1.5 times the theoretically required. When slaked in factories, lime is moistened in dampening augers and sent to slaking silos, where the slaking process ends. It is also extinguished in extinguishing drums or other extinguishing devices. For a more complete slaking, hydraulic lime is kept in silos for quite a long time, on average about 15 days.
During the setting and hardening of ground hydraulic lime, physical and chemical processes occur that are characteristic of hardening of ground quicklime, on the one hand, and hydraulic binders, on the other. Initially, as in the case of air hardening of ground quicklime, the calcium oxide contained in hydraulic lime is hydrated to Ca (OH) 2. Then, when hardening in a humid environment, silicates, aluminates and calcium ferrites are gradually hydrated, forming the corresponding hydrates in a gel-like state. The physical processes occurring in this case, as in the hardening of other hydraulic binders, contribute to their gradual compaction and increase in strength.
The specific properties of this lime make it necessary to provide first air-dry hardening conditions, and then moist conditions (for the hydration of silicates, aluminates and calcium ferrites). In this case, the more free calcium oxide in lime, the longer should be the initial hardening in air.
Extinguishing
When limestone is mixed with water, a chemical reaction occurs with intense heat release in the form of steam, i.e. calcium hydroxide is formed. The evaporated moisture loosens the substance and converts it into powder. Depending on the quenching period, the product is divided into three types:
- Fast quenching product. The procedure continues for eight minutes.
- Moderate extinguishing product. The reaction lasts 25 minutes.
- Product obtained with slow quenching, more than 25 minutes.
The time is determined from the moment of combining water with lime, until the temperature of the mixture stabilizes. When purchasing a product, this value can be read on its packaging.
Thus, you can produce fluff or lime dough. To obtain the first, water is added to quicklime 1: 1. All options for extinguishing are carried out in production using hydraulic motors. To obtain a lime dough, powder and water are mixed 1: 3, respectively. All these actions can be performed on the construction site. To make the composition more elastic, it is kept for 14 days in a pre-equipped pit.
To obtain slaked lime at a slow process, the raw material is poured with water in small portions. Lime of the other two types is poured while heat is generated. In order not to burn steam, it is necessary to use protective equipment: goggles and gloves. The amount of water used is determined by what kind of material will need to be obtained when extinguishing.
