Application
Geotextiles have appeared recently, but are already used in various fields: in construction, landscape design, horticulture and gardening, in the construction of footpaths, roads and runways. Hygiene products, disposable medical clothing and underwear are made of the same material, only of low density, and used as a rough upholstery for upholstered furniture. In general, the field of application of geotextiles is very wide, and it is worth knowing which type is suitable for what purposes.
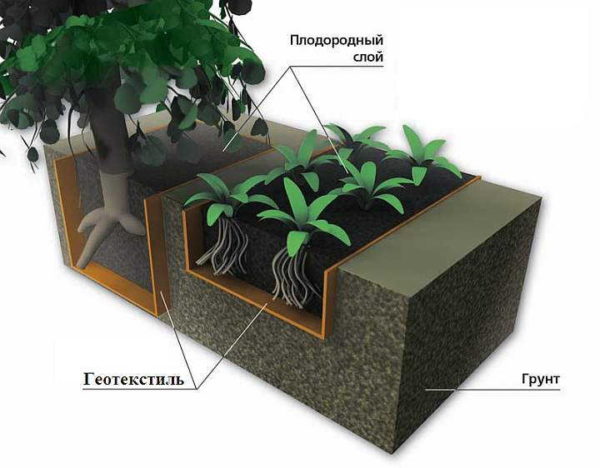
One of the uses - when arranging a site
Depending on the density
The cost of geotextiles can vary significantly. As you already understood, the price is formed depending on the material and method of production. But density also plays an important role. The same materials, but with different densities, have different prices. How do you know which geotextile is needed in a particular case? You can roughly navigate by this density division:
- Up to 60-80 g / m2 - agrotextile or covering material. Can be used to protect against germination of weeds (geotextiles against weeds). Non-woven polyester is usually used. To avoid confusion, they usually write this way - agrotextile.
- Density about 100 g / m² - for drainage, but geotextile is undesirable, as it quickly "silts up".
-
150 g / m² and more - for separation of fractions: sand and gravel. You can take more dense, but less - not worth it.
- Geotextiles with a weight of 100 to 200 g / m² are used for the construction of footpaths, under paving slabs, under lawns, to create alpine slides, etc.
- With a density of 200 to 300 g / m², they are placed under general-purpose roads, under a parking area for cars.
- Above 300 g / m² - for motorways, runways, etc.
These are only approximate boundaries. It is always worth choosing geotextiles, paying attention to specific conditions. For example, for hard and rocky ground, elongation at break will be important. The better the material stretches, the less the possibility of rupture when "fitting" irregularities and protrusions.

When arranging ponds, swimming pools
When choosing geotextiles for construction work and under roads / paths, parking lots, sites, look for a high breaking load (breaking strength). This characteristic can be neglected if you form relief irregularities, but there will be no load on them.
Depending on raw materials and production method
Thermally bonded geotextiles have high tensile strength, but drain water only in the transverse direction. That is, it can be used in areas with low groundwater levels, in well-drained soils. It is good as a separator of different fractions and materials when arranging sites, for footpaths made of various materials, and is suitable for changing the landscape. But all this is in areas with good drainage. It is not very suitable for drainage systems - water is not drained well enough.
Needle-punched is less durable, but water passes both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. It is suitable for laying on heavy soils that do not drain water well - loams, clays. The lack of strength can be compensated for by placing a geogrid underneath - another type of geosynthetics. It will take on the main loads, and geotextiles will not allow fractions to mix. This type can be used in drainage. The optimal density of drainage geotextiles in terms of price / quality ratio is 200 g / m².
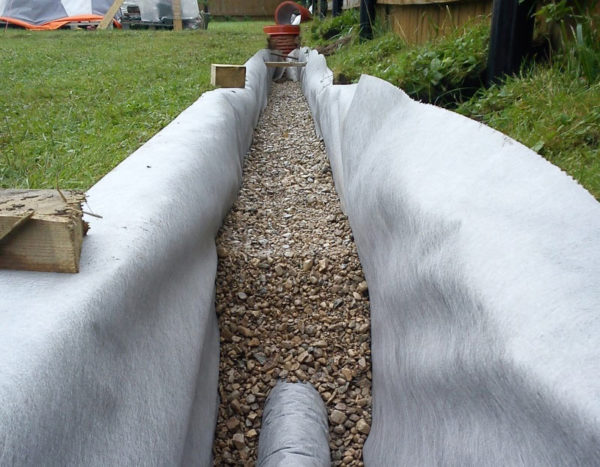

Drainage geotextiles. Properties: elasticity and strength, resistance to heavy loads and mold, long shelf life, ease of installation, fire safety and non-toxicity, resistance to ultraviolet rays
Woven geotextiles are very durable and have high tensile strength. It is ideal for embankments, landscaping, retaining walls. Moreover, it can withstand the load without question.It is not recommended to use it in drainage - the gaps between the threads are quickly clogged with small particles, which impairs water drainage.
The main characteristics of the material
Due to its properties, Agrospan is used not only by gardeners and gardeners, it is popular with farmers, they cover fields. Lightweight and durable agrotechnical fabric transmits well diffused light, as well as water and air. He is not afraid of pesticides, acid rain and pesticides. The durability of the material is ensured by the spunbond technology, which is used in its manufacture. The technology is the result of the latest developments.
Modern covering material Agrospan has a number of advantages. Thanks to the UV stabilizers in its composition, it does not disintegrate for several years. It can be used even in high altitude conditions due to its increased service life and numerous positive characteristics:
- creates an optimal microclimate for good plant development;
- protects plants from overheating and hypothermia;
- helps to reduce the rate of watering, retaining soil moisture and reducing its level of evaporation;
- averages the night and day temperature levels;
- allows you to extend the timing of harvesting;
- serves as protection from various diseases and pests;
- long service life (at least 3 seasons);
- comfortable in using;
- low cost.
Agrotechnical fabric also has some disadvantages, these include:
- weakly transmits the sun's rays, so you need to look at the marking of the canvas and the type of plants for which it is bought;
- low thermal insulation, in very early spring, certain types of plants may not have enough heat.
Covering material grades

Agrospan brands 42 and 60 are an excellent material for fixing to the frame of a greenhouse. It is fixed in the same way as a greenhouse film. Moisture and air easily penetrates the canvas. The greenhouse equipped with agrospan is easy to operate.
For the beds, Agrospan 17 and 30 are used, it is freely laid on the ground without tension. After that, in the beds with seeds or plants, it is fixed with earth. Agro-fabric does not interfere with germination of seeds and seedlings, as they grow, the edges of the material must be released.
Agrospan black mulch - this non-woven material serves as a reliable protection against weeds. The canvas is lightweight and durable, environmentally friendly. The black carbon, which is in the composition of the canvas, gives it a black color, which allows it to absorb a large amount of heat and then give it to the plants. Due to insufficient light, weeds cannot grow, they die. The structure of the fabric allows you to easily apply fertilizers in liquid form, and allows moisture to pass through.
Agrospan mulch weed protection 60 is intended for mulching the soil from weeds. It is used for the cultivation of perennial berry crops. If it is used for this purpose, then it should be in the garden all year round, until the elimination of the culture.
Many summer residents use ordinary plastic wrap according to the old tradition. Thanks to such a modern covering material as Agrospan, you can achieve better results in greenhouses or in beds if you use it there. It is more durable, easy and quick to spread and clean, dry and clean. The material is not afraid of frost. hot sun rays.
This material has long been used in agriculture to increase yields in the cultivation of cultivated plants, arrangement of greenhouses and greenhouses.
Care and storage
Fine particles of dry earth are moved by the wind along with bacteria, viruses and mycelium and are clogged between the fibers of the tissue. From this, its breathability may decrease over time.
In order for agrofibre to serve for many years and not become a source of infection of plants with fungal diseases, you need to know the basic rules for caring for it:
- The accumulation of dust can be removed with a special soft brush or broom.
- Stubborn dirt is removed with an automatic washing machine in a delicate mode without spinning.
- Small stains and streaks can be removed with a damp cloth and detergent.
- Rinsing the fabric in a weak solution of manganese or fungicide can be a good disinfectant.
- So that the material does not lose its physical and mechanical properties, it must be stored in a dry place, where it is carefully folded in a washed and dried form.
Agrotextile tends to break with prolonged exposure to sharp or rough metal objects. During installation, it is necessary to use protective layers in the places of greatest friction and fastening. To do this, use any dense fabric or thin wooden lath.
Film or agrofiber
It is simply impossible to answer the question which of the materials is better. Each material should be used where it is more effective, or a combination of shelters. Don't get hung up on tape or spunbond. They have different properties that can be used wisely for the benefit of plants.
If you come to the dacha only on weekends, then the film will not work. Under it, the plants will simply cook if they are not opened during the day. Agrofibre in this case is preferable. Of course, the plants under the film develop faster at first than under the spunbond, but later they even out in growth.
Spunbond allows moisture to pass through itself, so there is no need to open the plantings when watering. This significantly saves the time of the summer resident. Leaves, in contact with agrofibre, will not undermine and die. However, spunbond is not suitable for use as a roof, for example, for sheltering grapes or tomatoes. The leaf apparatus of these plants must be protected from precipitation in order to avoid the development of fungal pathogens. In this situation, it is better to use a film, since spunbond will not cope with this task.
Under the film, the beds warm up faster, which means it is worth covering the greenhouse with film. To maintain a comfortable temperature inside, we use spunbond stretched over arcs or simply cover the plants with it from above. After all, you cannot throw a film on vegetative plants - they will suffocate and burn.
To protect open ground plants from precipitation, and crops in the greenhouse from overheating, we make the roof with foil, and sheathe the sides with agrofibre. So the greenhouse will be ventilated without the constant participation of a person.
How to cover the beds with covering material: rules and recommendations
An important parameter of agrofibre for mulching, which you should pay attention to when buying, is the width of the roll. It varies within 1.5-3.2 m
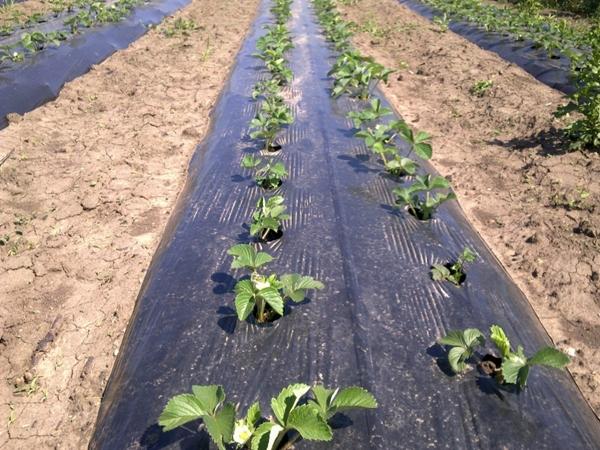
Select a width that will be enough to cover the garden bed with a ten-centimeter margin on both edges. After spreading the material to the ground, these protrusions are sprinkled with earth. This completes the styling process. The width of the bed depends on the type of plant being grown. For example, for a strawberry garden bed with a covering material, a roll of 3.2 m wide will be required.
Before covering the plants in the material, you need to make holes with the required distance.
Before laying agrofibre, small square, round or cross-shaped cuts should be made in it. The intervals between such holes should correspond to the distance at which the plants are supposed to be planted. The upper cover of a berry or vegetable crop with a material of low density can be made without any additional fasteners.
How to fix the covering material on the garden bed? It is enough just to lay the spunbond on the surface and hammer pegs along its edges so as not to be blown away by the wind. You can build a mini-greenhouse from dense agrofibre by pulling the material onto a pre-prepared frame.
This design can be opened on one side for ventilation and ease of watering. Frame shapes are either arched or rectangular.
Which side to cover the beds with covering material
There is no fundamental problem in this matter in the case of plastic wrap. It is the same on both sides. Covering material such as agrofibre should be laid with the top side up, and the bottom side down. Some difficulties arise only in terms of how to distinguish one side from the other on a roll. Visually, they are very similar. This must be done by touch. Smooth surface - lower, rougher - upper.
If the fiber is monochromatic, then it must be laid with the rough side down, and the smooth side up.
If the material is black and white, the black side is definitely the bottom. It must absorb heat to keep weeds from growing.
How to use covering material for beds
Any type of agrofibre is designed in such a way that the gardener pays as little attention as possible to the material itself after laying it. It is necessary that he cares exclusively about his seedlings.
Problems with the operation of non-woven polypropylene coating can arise only if it has been blown away by the wind (usually due to poor adhesion).
In areas with strong winds, the use of reinforced agrofibre is recommended. Inside, such a material is equipped with a rigid mesh, which allows it to be firmly fixed to the frame, for example, using a wire. Covering material for weed beds can not be touched after installing it for several years. Especially when it comes to planting perennial plants in a garden bed. Agrofibre will pass water well and retain sunlight until holes appear on it from wear.
If the covering material is dense enough, then a small greenhouse can be made from it.
Nonwovens in the garden have another use. With their help, you can equip paths along the beds. On the one hand, additional weed protection is obtained. On the other hand, the base of such a track will absorb water well, which will prevent the structure from deforming. In its lower layer there is crushed stone, above it is geotextile, then there is a layer of sand. At the very top there is a tile or stone cladding.
As you can see from the above, there is no problem in which covering material for the beds to choose
It is only necessary to take into account the climatic zone in which the vegetable garden is located, the size of the beds, the type and variety of plants grown, as well as the season planned for farming. Taking into account the listed factors, you can get a guaranteed increase in yield from each hundred square meters of land with a simultaneous decrease in labor costs
How to lay {q}
The easiest method of using a cover sheet is to simply spread it out on the garden bed. Recently, a method of growing strawberries and other crops on a covering material has become popular. The beds should be properly covered. When buying, you need to remember that the width of the canvas should be greater than the width of the bed, since the edges must be fixed to the ground.
Before laying a single-color canvas, you need to determine where its top and bottom are. A nonwoven fabric has one side smooth and the other rough and fleecy. It should be laid with the fleecy side up, as it allows water to pass through. You can conduct a control test - pour water on a piece of canvas: the side that allows water to pass through is the top.
First, the soil in the garden bed is prepared for planting. Then the canvas is laid, straightened and securely fixed to the ground. The type of soil affects the way it is fixed. On softer soil, it should be fixed more often than on hard soil, after about 1-2 m.
For fastening, you can use any heavy objects (stones, logs), or just sprinkle it with earth. However, this type of fastening has an unaesthetic appearance and, moreover, does not allow the web to be pulled evenly. Better to use special pegs.
Having covered the bed, on the covering, they determine the places where the plants will be planted and make cuts in the form of a cross. Seedlings are planted in the resulting slots.
On arc temporary greenhouses, the covering material is fixed with special clamping holders, and is fixed to the ground using special pegs with rings.
A large and varied assortment of covering materials allows you to make the best choice in accordance with specific purposes.
You can find out visual information about the covering material in the video below.
About the author: admin4ik
What is spunbond?
Most people associate this material with the beds. And for good reason: for more than 10 years it has been sold in gardening stores and is very popular with owners of summer cottages or backyards. However, agriculture is not the only area where spunbond products can be found.
Covering material
Spunbond is used as a covering material in several cases:
- to protect crops from birds;
- to reduce the likelihood of cross-pollination of different crops;
- to protect plants from frost;
- to protect delicate leaves and flowers from excessive amounts of ultraviolet radiation.
Covering agrotextiles are always painted white. If it has a density of 14 to 30 g / m2, it can be laid directly on the plants. With a density of more than 30 g / m, additional supports are required, therefore, greenhouses are most often covered with such material.
Mulching material
Black spunbond is placed directly on the ground, and then holes are made in it for planting plants. Since sunlight does not penetrate the material, there is no need for weed control. At the same time, the earth "breathes", that is, mold does not appear under the spunbond.
There is also a double mulching agrofiber. One side is black and the other is white. It is laid on the ground with the black side. This achieves three goals at once:
- Berries (especially strawberries) and fallen fruits do not deteriorate for a long time, since they do not come into contact with the ground. Plus, they stay clean.
- Plants receive more light (the sun's rays are not absorbed by the soil, but "mirrored" from it).
- It is possible to avoid overheating of the soil and rapid drying of plants.
The service life of the covering and mulching cloth is up to five years. After this time, it begins to degrade as the UV protection additives lose their effectiveness.
Medical material
When nonwoven fabrics were used in medicine, the number of complications associated with infection during surgical and other manipulations significantly decreased. There are two reasons for this:
- First, the spunbond and the composites that contain it are not reused, which results in a high degree of sterility.
- Secondly, by adding special substances to polypropylene fiber, manufacturers achieve an antibacterial effect.
Medical spunbond is of different density: from 15 g / m2 (hats and shoe covers are made from such cloth) to 50-60 g / m2 (used for sewing disposable shirts and gowns). Surgical drapes and spunbond for masks usually have a density of 25–35 g / m2.
In addition, the material used in medicine falls into two categories:
- normal - used for products that hypothetically will not come into contact with the body fluids of one person and the skin of another person;
- laminated - like polyethylene, it does not allow moisture to pass through, therefore, surgical aprons are made of it, which protect doctors from blood splashes.
Insulating material
In construction, spunbond is used to insulate houses - vapor barrier and vapor-permeable membranes are produced from it. In addition, this material is laid between the wall and the finish - this helps to avoid cracking of the plaster. When building roads, it is placed under the drainage layer.
Sewing material
Spunbond is widely used in the garment industry. Its most famous variation is non-adhesive non-woven liner for sleeve cuffs, stiff collars and pocket flaps. They also strengthen the seams and corsages. In the production of bags, wallets and shoes, substrates are made of very dense material - 400–600 g / m2. Also, a solid base is cut out of spunbond for straight curtain lambrequins. In the manufacture of furniture with removable covers, the soft parts of sofas and armchairs are sheathed with spunbond.
There was a place for this material in factories where pillows and mattresses are made. It makes excellent naperniki, substrates for fillers.
Spunbond, processed using Ultrastep technology, takes on the appearance of a quilted woven material, which is why stunning bedspreads are sewn from it - strong, durable, quick-drying, wear-resistant, beautiful, silky to the touch.
Packing material
Spunbond is often used instead of polyethylene, cellophane and other packaging materials. In particular, anthers for bags and shoes, covers for outerwear, transport covers for laptops are sewn from it. There are several reasons for such a replacement:
- higher strength;
- ventilation;
- additional protection against scratches and other physical damage;
- no unpleasant sound during unpacking.
Types of nonwoven weed coverings
Agrocloth for weeds is sold on the market in a very different category of quality and price. You can choose a product according to color, density, structure and other preferences and needs.
Spunbond
The brand became so popular that summer residents began to call this word any covering material for beds. Spunbond is a special fabric production technology. It turns out to be light, airy, but we fix it. The material is environmentally friendly, it is not affected by temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress.
In color, spunbond is white and black, in density - 20-60 g / m2:
- White material up to 30 g / m2, used mainly to protect crops from recurrent spring chills and abundant sunlight in summer. They cover seedlings, berries, decorative species, flower beds. And young seedlings of spunbond fruit trees protect from harmful insects.
- White cloth 30-50 g / m2, suitable for winter protection of any ornamental and fruit crops. It is also pulled over an arc frame greenhouse or greenhouse.
- Black spunbond 50-60 g / m2 with a UV-stabilizing layer reliably protects against weeds, contributes to the receipt of more heat by cultivated plants.
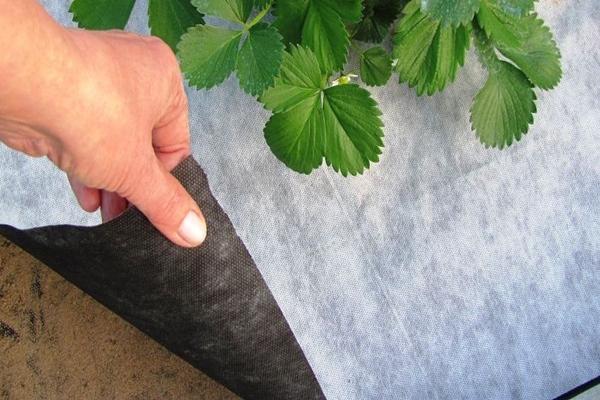

Geotextile
Geofabric, which is based on polyester fibers, woven under thermal influence, is characterized by strength and ability to breathe. The popularity of the product is due to:
- long service life;
- versatility of application;
- ease of installation on site;
- low cost.
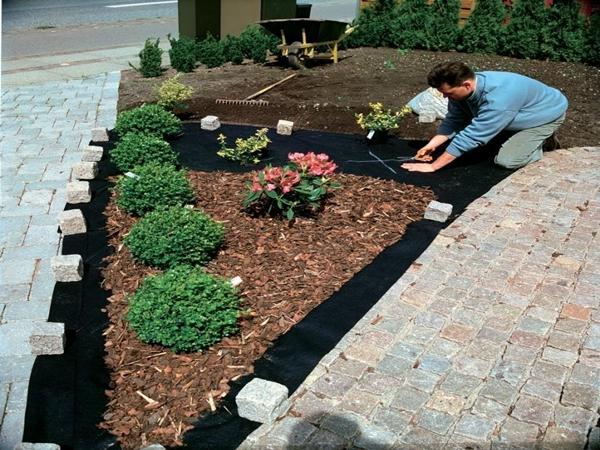

Agrospan
In fact, a kind of spunbond produced by the Russian company Ayaskom. The same high quality, durable, inexpensive. It is mainly used for sheltering strawberries, strawberries and other berries.
Agro-fabric has a UV-stabilizing layer, wears out slowly, is not susceptible to temperature fluctuations.
Agrotex
Another popular type of covering material from a Russian manufacturer. Available in two colors:
- yellow - intended for the destruction of pests on nightshade plants;
- black - a means of protection against weeds, used mainly on strawberry plantations.
The material has a perforated structure, so there is no need to cut holes for crops. It is enough to cover the plot in the garden, and the cultural plantings will not suffer from high temperatures, get dirty with soil during irrigation and precipitation. Agrotex does not wrinkle, is not afraid of temperature fluctuations, does not provoke soil damage by a bacterial infection.

Agril
Breathable fabric designed specifically for weed control. Sheltered plants do not wither from the heat, do not freeze during the cold period. The covered soil remains loose, does not undergo crust-forming and erosion processes, the biochemical component is not disturbed in it, oxygen and nutrition continue to be fully absorbed by the roots. With proper use of the material, cultivated plants give a harvest earlier. You can use agryl for mulching strawberries, vegetable beds.
For weed control, a black material with a density of 50 g / m2 is used. For the equipment of the greenhouse, a transparent fabric with a density of 20-40 g / m2 is taken.
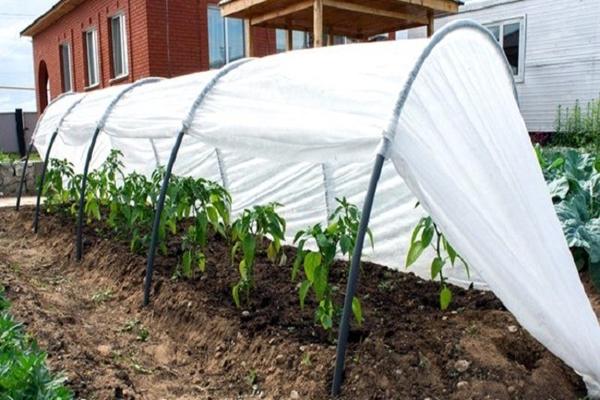

Lumitex
It is a corrugated film coating of soft structure and different colors. Due to its ability to reflect harmful and transmit the sun's rays beneficial to plants, even in cloudy weather, agrofibre is used to shelter cucumber and berry beds, does not provoke overheating and hypothermia of plants, and accelerates the ripening of fruits.
When equipping a greenhouse, you can combine lumitex with plastic wrap.
Lutrasil
Usually used for cold protection, but can be a good weed control. The material is of high quality, it costs a little more than spunbond, in quality it is actually similar to it. Available in two colors - white and black. Density - from 20 to 60 g / m2.
The coating is applied:
- low density white - to protect seedlings and seedlings from spring frosts;
- high density white - as a winter shelter (in frosts up to 8-10 ° C);
- medium to high density black - against weeds.
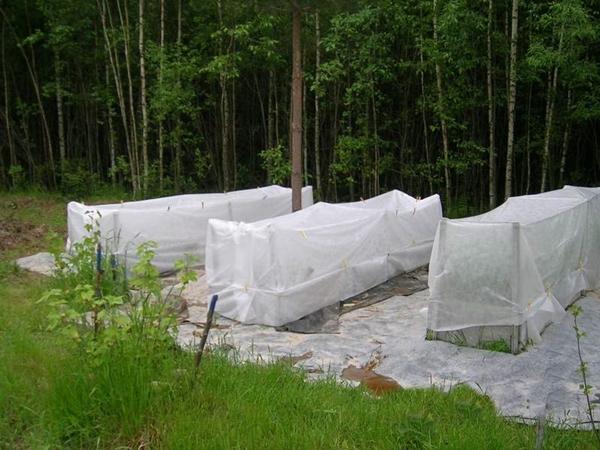

Black film
Before the advent of agrotextiles, black sheeting was the only material used to shelter the soil from weeds. It dims well. It can cover not only the beds, but the aisles.
Today, the film is significantly inferior to modern agricultural fabrics:
- does not let water through;
- creates a greenhouse effect, which increases the likelihood of a fungal infection;
- has a short service life.

Polyethylene films
The polyethylene film does not lose ground. First of all, the price attracts. Regular film will only last one season when exposed to sunlight. In order to slow down the destruction process, manufacturers add stabilizers. Light-stabilized material usually differs from ordinary polyethylene in color, which does not affect the properties, but indicates the type of film. There are such varieties:
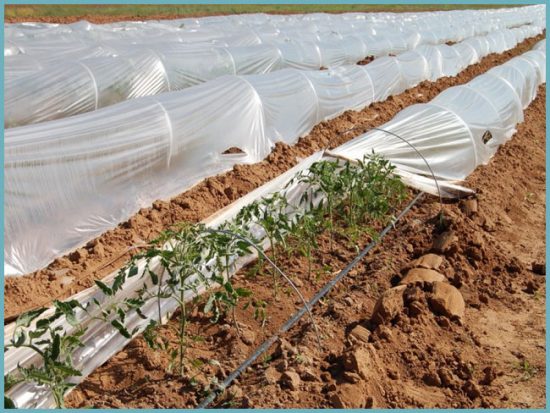


Advice. Breathable films include reinforced polyethylene with punched holes. This is a relatively new material on the market. The tunnels above the beds are covered with a transparent film.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any other agro-fabric, Agrospan has certain advantages and disadvantages. The indisputable arguments in favor of choosing this material include the following:
- perfectly copes with the main task - the creation and maintenance of the most favorable climate for uniform growth of plants;
- regulation of the degree of soil moisture due to its ability to perfectly pass water and evaporation, while condensing the required amount of moisture underneath;
- regulation of the temperature regime (smoothing out the differences between the average daily and average night air temperatures), thereby ensuring reliable protection of the future crop from overheating and sudden cooling;
- ensuring early ripening of fruits, which gives farmers a chance to get a crop throughout the season and harvest it without unnecessary haste;
- the term of use depends on how carefully the material is handled - ideally, Agrospan can last even more than 3 seasons in a row;
- reasonable price and absolute availability.


There are very few disadvantages of this covering fabric, but they still exist:
- with the wrong choice of brand, problems may arise associated with insufficient receipt of sunlight by plants that remain sheltered for a long time;
- thermal insulation, unfortunately, leaves much to be desired, since the material may be completely useless if severe frosts begin in combination with a cold squally wind.


Non-woven covering material
Spunbond, agril, agrotex, lutrasil, agrospan ... How not to get confused in front of a counter with non-woven materials and what to choose? The essence of all these materials is the same, only the manufacturers are different, so you can safely take packaging with any name, focusing only on the characteristics of the covering material.
First of all, you should be interested in density and color, because it depends on them where this shelter can be applied. The density of spunbond and similar materials is of 3 (sometimes 4) types:
- 17-30 g / m2 - the thinnest and lightest (and also the cheapest) material; protects plants from short return frosts, scorching sun, insects and birds, great for sheltering the first greens and vegetables in the open field, enveloping bushes and trees during the ripening period of the crop;
- 42-60 g / sq.m - suitable for the construction of greenhouses with arches, compact greenhouses, winter shelters for decorative and fruit crops that are afraid of frost;
- 60 g / m2 - the densest and most expensive option; serves for several seasons in a row, is used for the construction of shelters for plants, is often made using UV stabilizers, which further extends the shelf life of the material.
Spunbond - how to choose and use agrofibre correctly
Choosing the right agrofibre to protect plants from frost, hail, insects, birds and weeds.
White covering material
White non-woven covering material is widely used in the garden and vegetable garden. With its help, you can perform the following work:
- shade the first shoots from the sun's rays;
- create an optimal microclimate for greens and vegetables that do not need pollination;
- protect plants from birds and pests;
- cover the greenhouse, greenhouse, build a temporary shelter;
- organize a winter shelter for crops in need of such a measure.
Black covering material
Covering, or mulching, material from weeds is similar to its white "brother" only in the manufacturing method, but differs in characteristics and functions. It is laid on the ground in order to reduce evaporation, to increase the heating of the soil, protect plants from excess moisture and dirt, and to minimize weeding and loosening work.
The soil under such material remains moist and does not become crusty from irrigation, and pests have nowhere to hide on its surface, so it is easier to eliminate them. In fact, planting strawberries on a covering material reduces all crop care to watering, feeding and picking berries. However, the same goes for other crops grown under black nonwoven fabric.
Double layer nonwovens
If you see that the sides of the covering material differ in color, be aware that this is not done for beauty. Usually the bottom of such material is black and works as mulching, and the top is white, yellow or foil. This side reflects sunlight and illuminates the plantings from below, significantly accelerating the ripening of the crop.
Even solid color nonwoven covering materials have a front (top) and back (bottom) side. They only allow water to flow from top to bottom to ensure easy watering and reduce liquid evaporation. In order not to be confused, you need to mark the sides right at the time of purchase. If you haven't, wash a small piece of material, dry it, and then sprinkle water on one side. If the water easily seeped inside, then this is the front side, if it spreads over the surface - the wrong side. True, this only works with materials denser than 17-30 g / m2, and thinner materials let water pass in both directions.
