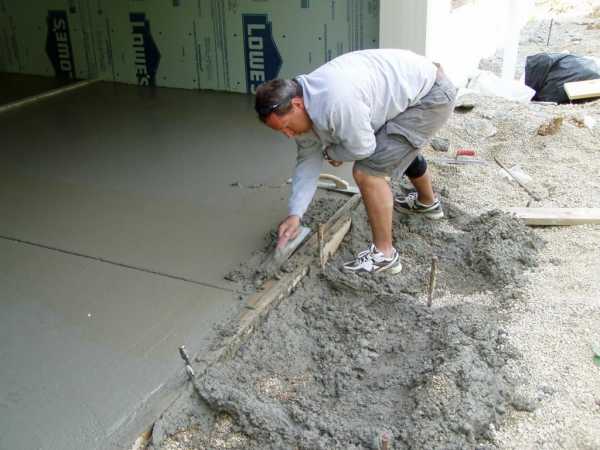
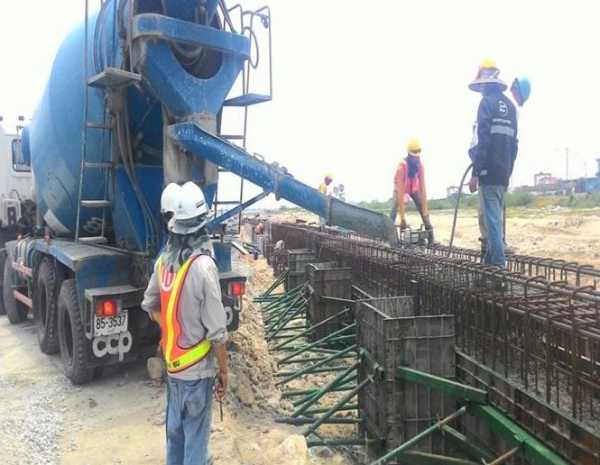
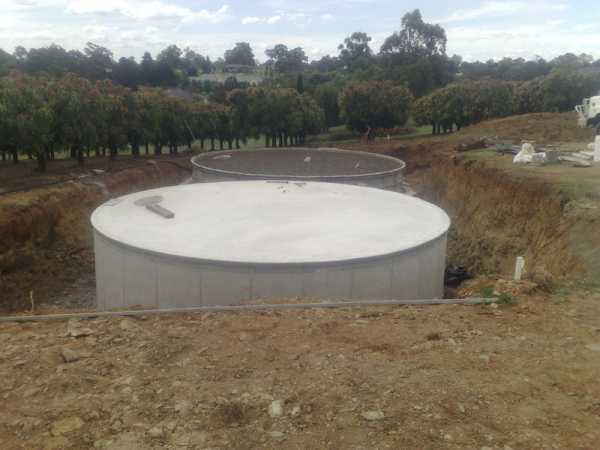
Production and composition
The manufacturing technology of sulfate-resistant Portland cement and ordinary cement differs very slightly, but more stringent technical control is required. These binders are obtained after the simultaneous fine grinding of gypsum and Portland cement clinker. As the mineral additives used, electrothermophosphoric and garnulated blast-furnace slags are used, the volume of which is 10-20%, and for sulfate-resistant slag Portland cement from 40 to 60%. Sedimentary rocks with a volume of 5 to 10% are used as active additives.
The composition of the clinker used in production is of great importance. It should contain no more than 50% tricalcium silicate, no more than five - tricalcium aluminate. The alumina module must be 0.7 or more. It should be noted that the amount of C3A + C4AF in the clinker should be no more than 22%. The composition includes magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide 5% each. Requirements for raw materials are predetermined by the need to prepare clinker with a standardized chemical and mineralogical composition. As part of the clay component, it is recommended to use a flask or tripoli.

Active additives are not used, and only upon reaching an agreement between the customer and the supplier and in the presence of favorable working conditions, it is possible to add a small amount of them during the production of grinding. All additives must meet the requirements of GOST. Active mineral additives - 6269-54, and slag additives - 3476-60. To increase the resistance of sulfate-resistant types of cement, surfactants are introduced into their composition. According to the recommendations of GOST 970-61, soap or sulfite-alcohol stillage is used for this purpose, and after that it is called hydrophobic or plasticized.
Application in construction
 It is recommended to use it for the production of monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures for the construction of hydraulic structures and structures that are exposed to sulphate aggression and work underwater under the influence of sea and ocean water.
It is recommended to use it for the production of monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures for the construction of hydraulic structures and structures that are exposed to sulphate aggression and work underwater under the influence of sea and ocean water.
It is advisable to use in the manufacture of concrete and reinforced concrete structural elements, including prestressed ones, which will later become part of the structures of breakwater supports, sea and river breakwaters, as well as any types of building structures that are subject to alternating moisture and drying. Due to the reduced content of fuel components and reduced exotherm, it is allowed to use high-weight hydraulic structures in the construction of the outer zone.
Acquisition
It is not difficult to buy sulfate-resistant cement: manufacturers sell it through exchanges, through wholesale trade organizations, and purchasing through exchanges, for example, the Moscow Stock Exchange, can significantly save on the cost of the purchased material, especially if the buyer is ready to purchase in bulk and in a batch of 300 tons or more. The price in this case ranges from RUB 3,030 to RUB 3,730 per ton. Purchase of packaged or smaller lots will increase the price.
Composition and properties
Portland cement is made from clinker. Due to the fact that it is almost impossible to find ready-made granules in nature, clinker chips are created artificially from a mixture of clay and carbon mixtures. The finished clinker is mixed with gypsum (its proportion does not exceed 5%) to make the mortar mobile.
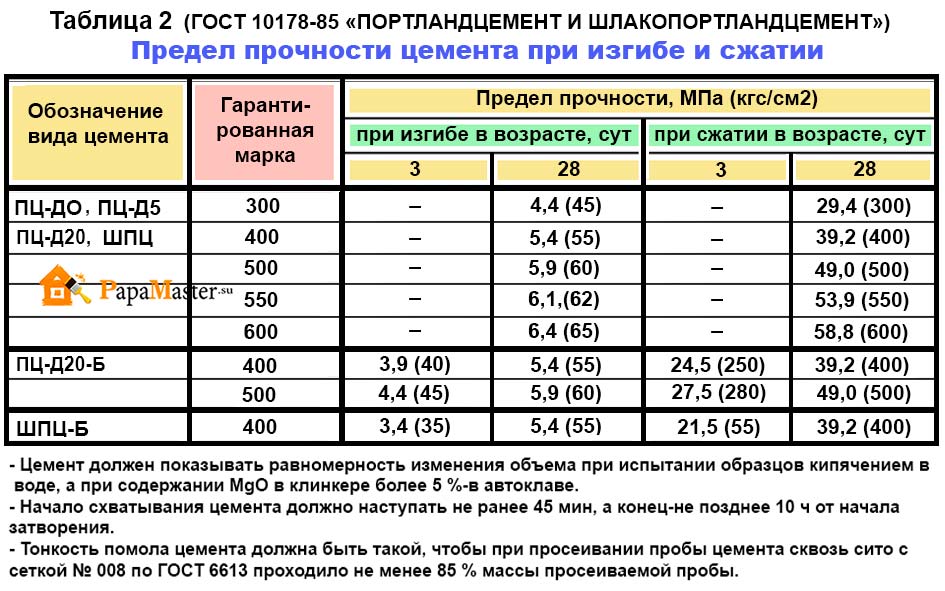
High operational and technical characteristics are determined by the proportion and type of components introduced into the composition of Portland cement. This aspect is regulated by GOST 10178-85 "Portland cement and slag Portland cement".The packaging with the powder must indicate the features of production, compliance with GOST.
If TU (technical conditions) is indicated on the container instead of GOST, this indicates that the properties of the material may differ from the regulated ones.
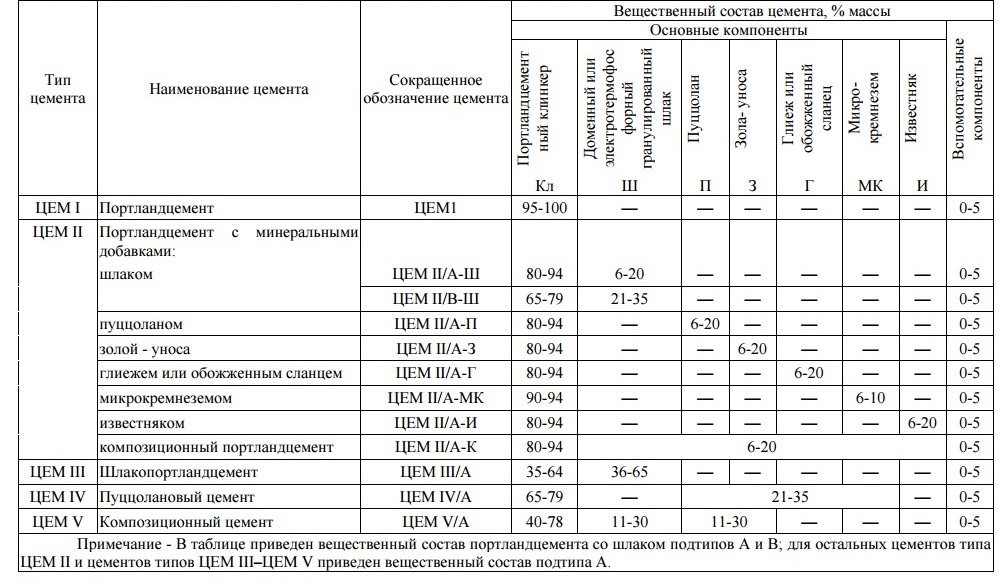
To give the cement certain properties, various mineral additives are added to the powder (in a volume equal to a maximum of 20-25% of the total weight). Their interaction affects the chemical composition of Portland cement, largely determines the characteristics and parameters.
Most Popular Mineral Supplements:
- Aluminate - prolongs the setting time, but demonstrates low strength, and therefore it is introduced into the mixture in a volume not exceeding 15%.
- Alumoferrite - has identical properties to aluminate, but its composition should not exceed 10-18%.
- Belite - knits, prolongs the hardening time, but in large volumes reduces strength (add no more than 37%).
- Alite - is most often introduced into the compositions of liquid grades to accelerate hardening (up to 60%).

The main properties of Portland cement are determined by its composition. When choosing a powder for preparing a solution, it is necessary to immediately determine the scope and the required (desired) characteristics, optimal parameters.
The main criteria for choosing Portland cement:
- Setting speed - the standard time is considered to be 40-45 minutes. This indicator is influenced by the fineness of grinding, the composition of mineral additives, and the temperature at the facility.
- Water demand - the volume of water required for mixing (usually no more than 25% of the total mass of the solution). To reduce the required volume of water, plasticizers, sulphite-yeast brew can be used.
- Frost resistance is determined by the number of freeze / thaw cycles that a stone can transfer without loss of quality and deformation. In order to increase the level of frost resistance, washed wood pitch or sodium abietate, special additives are often introduced into the mixture.
- Water separation is the extraction of water in a mixed solution, which appears due to the settling of heavy cement particles. To lower the indicator, mineral additives are used.
- Heat release - during hydration (hardening). If the composition gives off heat very quickly, it may deform. To avoid this, use active mineral supplements.
- Corrosion resistance - determined by the degree of porosity of the solidified monolith (the fineness of the grinding of the mixture).

Briefly about the main
- The sulphate aggression of sea, river, waste and ground waters is resisted in two ways: • the use of sulphate-resistant Portland cement, slag Portland cement and pozzolanic cement; • the use of modifying additives that improve the quality of the concrete or mortar mixture, increasing the durability of the final product - reinforced concrete structures. Such additives can be hydrophobic, which ultimately gives concrete water-repellent and plasticizing properties, which makes it possible to reduce the water-cement ratio W / C during the molding of products and structures and, as a result, increase the density of the concrete stone.
- The most aggressive salts that have a destructive effect on concrete are magnesium and sodium sulfates. It is not for nothing that the tests for the sulfate resistance of cement are carried out on a 5% sodium sulfate solution.
- The main danger of sulfate corrosion is from the reaction of tricalcium aluminate with sulfates from the environment and the formation of calcium hydrosulfoaluminate (HACA), which expands in pores and cracks in volume (by 227%) and creates pressure on the concrete stone. This effect, together with the washing out of these formations by water, leads to type III concrete corrosion.
- Sulfate resistant cements are those with a low C3A or tricalcium aluminate content. Let us recall the content of the main minerals in the cement clinker, the main component of the cement: • Alite, tricalcium silicate - C3S. The main mineral influencing the quality of the cement.Alite possesses the properties of a fast-hardening hydraulic substance of high strength. Cements of high grades and fast-setting cements are made with a high content of tricalcium silicate. The content in the cement is 37-60%. • Belite, dicalcium silicate - C2S. Medium strength slow hardening hydraulic binder. Cements with a high content of belite harden slowly, but their strength builds up over a long period of time. The content in cement is 15-37%. • Tricalcium aluminate - C3A. Fluid mineral, the main task of which is to lower the sintering temperature of the raw mixture. It hardens quickly, but has low strength. The content in the cement is 5-15%. • Tetracalcium alumoferrite - C4AF. Fluid mineral. It hardens faster than silicates, but slower than aluminate. The content in the cement is 10-18%.
Hydroconcrete composition
When selecting components for the composition of hydraulic concrete, it is important to take into account all the functions that it must perform, namely: frost resistance, water resistance and strength. Depending on the requirements, a special composition is selected
How concrete will cope with its responsibilities depends on many factors such as: the ratio of water to cement, vibration compaction, quality, time during which the mixture is kept, the quality of the added components, etc.
Video application of a hydraulic additive in concrete
Let's consider the components that make up concrete in more detail. Cement is the main component used in the manufacture of this type of concrete. There are several types of such cement:
- Sulfate-resistant cement is used when the washed area of the building will come into contact with hard water.
- Portland and plasticized cement is the basis of mixtures, which is used for the construction of buildings located in a place where the water level is constantly changing, and the temperature is always below zero.
- Hydrophobic cement is used to create concrete that will be used in the construction of a structure that will be constantly exposed to water.
- Slag and pozzolanic cements have chemical characteristics that are capable of resisting water damage to the structure. Hard water has its destructive properties due to the presence of minerals in it.
Important! The required concrete density is achieved precisely due to the presence of cement in the mixture. Hydroconcrete includes, in addition to cement, many other components
One of them is quartz sands, they serve as aggregates. Sand significantly increases the level of water resistance. Quartz sands are obligatory for use, as without them the level of water resistance drops.
The sand used for hydro-concrete must be of high quality, and also there must be almost no impurities in it. The density of sand, according to GOST, should be 2t / m3. The grain size should be no more than 2 millimeters. Neglecting this factor threatens to make the mix's mobility level undesirable. All hydraulic structures, be they dams, piers or bridges, must be very strong and reliable. To obtain these qualities, the large components to be filled must be selected very carefully. Quite often, granite is used for these purposes because of its ability not to let water through and not collapse under heavy loads.
Crushed stone and gravel are used in the composition of hydro-concrete to ensure frost resistance. The structural features of gravel and crushed stone make it possible to withstand sudden temperature changes.
Flakiness is a very important factor in the construction of hydraulic structures. It flattens the components. The presence of crushed stone in the composition of concrete has a very positive effect on its strength due to its shape. The flat edges of the grains allow for a more even distribution of the load throughout the structure, since they fit quite tightly to each other.These characteristics allow you to save cement and sand, because their consumption in this situation is significantly reduced.
Important! When hydro-concrete is laid, it is compacted using deep vibrators. Such operations are carried out in order to increase the required indicators.
Also, the composition of concrete includes various microfillers. Their presence in the mixture prevents deformation of the structure. Micro-fillers significantly increase the level of thermal conductivity, which has a very positive effect on the durability of the structure. The composition of hydraulic concrete contains a lot of different chemical components that make the mixture very high quality. Nowadays, chemists are working on the development of a component CMID - 4. This component will allow the construction of buildings that will constantly be in contact with drinking water. One of the very significant advantages of microfillers is the fact that when they are added, the cement diverges much less.
Important! When selecting a composition for hydro-concrete, it is imperative to take into account the ratio of the proportions of the components in accordance with GOST 26633 2012
Video: Protection of concrete surfaces of hydraulic structures
Hydrophobic Portland cement
A distinctive characteristic of hydrophobic Portland cement is its increased water resistance. It is made by joint grinding of Portland cement clinker, gypsum and a special hydrophobic additive that makes the cement hydrophobic. The hydrophobic additive contains bottoms of synthetic fatty acids, asidol mylonft, oleic acid, oxidized petrolatum and others. The additive is introduced into the cement in a ratio of 0.1-0.3% of the mass of the entire solution. In the process of cement setting, they form monomolecular hydrophobic films on its surface, which reduce the hygroscopicity of the cement. Thanks to this, the cement can be stored for a long time in humid conditions. Concretes and mortars made with the use of a hydrophobic additive have increased water resistance and lower water absorption. In addition, they are more resistant to low temperatures.
Thanks to the additive, Portland cement becomes hydrophobic, while retaining all the other advantages of conventional Portland cement, but only if the optimal additive has been introduced into the composition. If too little hydrophobic additive was added to the cement composition, then it will not have hydrophobicity, while other qualities will not be affected. If too much additive is added to the composition of the cement, then the solution will be too porous, since it will contain too much air, due to which the strength is significantly reduced.
This type of cement is used in cases where the material has to be transported over long distances or stored for a long time before use.
What is sulfate resistant cement

Sulfate-resistant cement is a material that significantly expands the possibilities of using concrete solutions in construction for aggressive conditions. The need for it is dictated by objective circumstances, when ordinary concrete is destroyed during operation. Material requirements are standardized by state and international standards.
What is the material
Sulfate-resistant cement is a corrosion-resistant material, which contains special additives (aluminates and silicates) to increase resistance to aggressive influences. It has a specific field of application when waters with a high content of sulphates are present and cyclical effects of water in large quantities are noted.
A high concentration of sulfates in a humid environment provokes sulfate corrosion. In this process, concrete components enter into a chemical reaction, which leads to the formation of a cement stone inside and to the precipitation of salt crystals on the walls.The structure of the concrete is broken and it collapses. Cyclic moisture also has a destructive effect on concrete - constant cycles of drying and abundant moisture, freezing and thawing. This is why sulphate corrosion resistant cement was developed.
Types of material
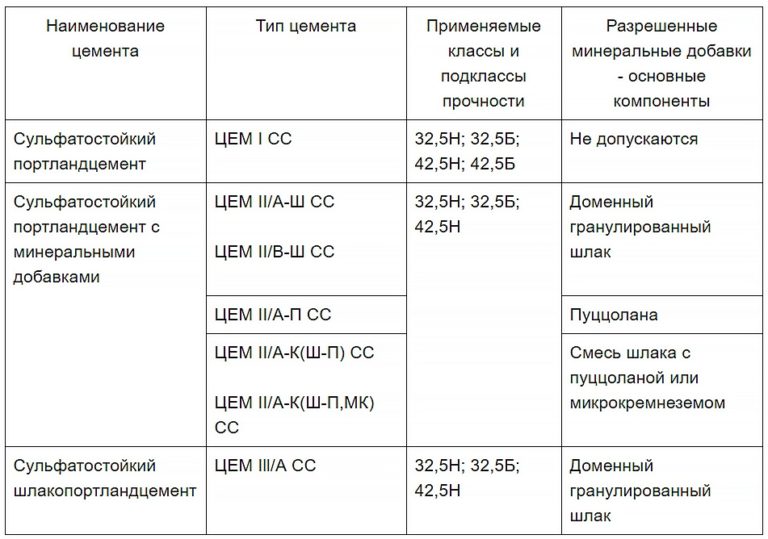
Pozzolanic cement. It is based on blast-furnace slag and volcanic rocks (pozzolans). Among the latter components are tuff, pumice, volcanic ash. These are active mineral additives that provide sulfate resistance. This material is not intended for cyclic humidity conditions.
Portland cement with increased sulfate resistance. It is made with the addition of mineral additives to the M400 brand. The material hardens slowly with a gradual set of strength and reduced heat generation during setting. It can be used in any operating conditions.
Portland cement with a high content of sulfate-resistant minerals. The additive content is 6-10%. The material of the M400 and M500 grades is produced. It is distinguished by increased frost resistance and resistance to cyclic humidity.
Sulphate-resistant slag Portland cement. This is a mixture of blast furnace slag with Portland cement clinker with the addition of aluminates
An important requirement - the slag should not consist of more than 10% aluminum oxide. The material of grades M300 and M400 is produced
Has a high sulfate resistance, but is afraid of frost.
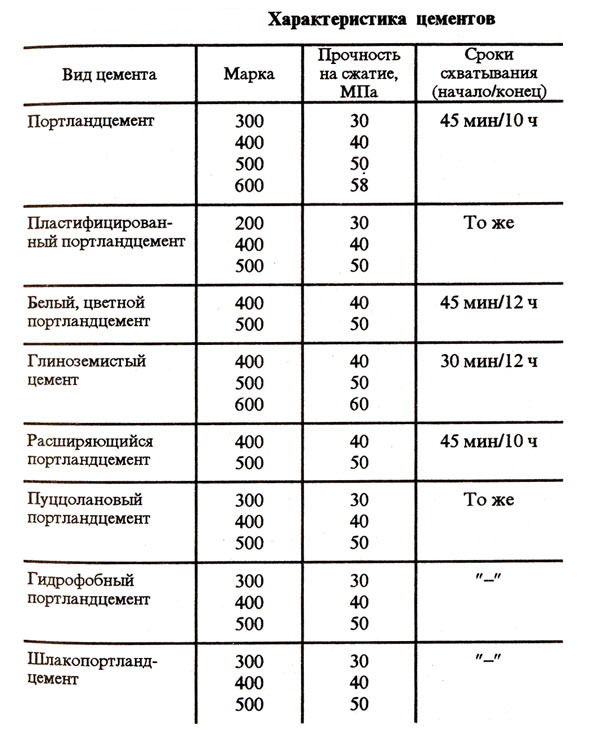
In addition to the compositional subdivision, the cement in question has a gradation in compressive strength. This indicator is entered into the marking - from M200 to M500.
Composition

According to the production technology, cement resistant to sulfates does not differ from the production of conventional cement. In fact, both materials are fine powders with astringent properties. The structure is provided by a special drying mode and thorough grinding in the bunkers of special mills. The difference is ensured by the desired composition of the mixture.
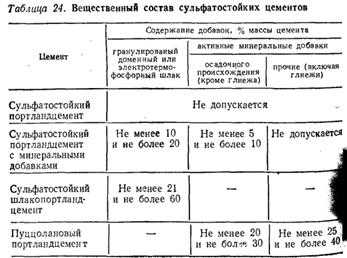
The basis of mineral additives are blast furnace slags of the electrothermophosphoric or granular type. Usually, their content fluctuates in the range of 10-22%, and for sulphate-resistant Portland slag cement - 42-55%. The active ingredients are additives from sedimentary rocks. They are introduced in the amount of 6-12%.
To ensure increased resistance to aggressive influences, special requirements are put forward for the composition of the clinker used. The content of tricalcium silicate in it should not exceed 52%, tricalcium aluminate - no more than 6%, and C3A + C4AF - no more than 23%. The composition includes oxides of aluminum and magnesium, but not more than 4-5%. The alumina modulus of the clinker exceeds 0.7. It is recommended to introduce flask and tripoli into the clay component of Portland cement.
The clinker is based on alit or belit. In the first case, accelerated hardening and rapid strength development is ensured. Belite is characterized by long-term setting, but the final strength exceeds alite.
Active additives are used with great care. Excessive content of them can deteriorate the technical characteristics of cement.
According to GOST, an increase in resistance to sulfates is achieved by the introduction of surfactants. So hydrophobic, plasticized materials have additives in the form of soap or alcohol-sulfite vinasse.
Varieties of material
In the construction industry, various types of cement materials are used, differing in the following parameters:
- composition;
- concentration of ingredients;
- the presence of special additives;
- appointment;
- properties.
On the packaging, in addition to the brand, the percentage of additives is also indicated.
There are the following types of Portland cement:
- fast hardening. Contains additives of mineral origin, which shorten the curing time. It is used for the accelerated implementation of construction activities and the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures;
- sulfate resistant.The main advantage - resistance to sulfates, is achieved by a decrease in calcium aluminates in the clinker. Used for structures operating in a humid or aggressive environment;
- hydrophobic. Contains surfactants that significantly reduce hygroscopicity. The result of the introduction of additives is an increase in mobility, the convenience of laying the solution. The material retains its properties at high humidity;
- White. It is easy to distinguish from other cementitious compounds. Has a light gray color, does not contain titanium oxides, iron and manganese salts. Used for finishing activities;
- color. Contains special pigments of organic and inorganic origin, added to the clinker material before grinding. Colored compounds, for example, yellow cement, are used in finishing activities;
- pozzolanic. Resistant to sulfates, hardens quickly at elevated temperatures. Autoclaving significantly improves the strength characteristics. Designed for use in soil, as well as in a humid environment;
- backfill. Produced exclusively for sealing wells in oil and gas fields. Provides reliable isolation from groundwater, pressure and temperature resistant. It gains strength at the initial stage of hardening.
Cement is a dry mixture that is used specifically for the preparation of concrete mortar
On the basis of lime, slag and clay, the following cement compositions are produced:
How to do it?
Getting sulfate-resistant cement is possible in two ways:
- make cement mortar with special additives from mineral substances;
- the use of a special zinc-sulphate cement-sand mixture produced by an industrial method, which is durable and guarantees the protection of the structure during the entire period of operation.
In the event that mineral additives are several times higher than the standard rate, the strength of the solution is significantly reduced, and accordingly the fragility of the buildings also increases, due to which their destruction occurs. A solution of sulfate-resistant cement must necessarily comply with the basic norms of state standards.
After all, the durability of Portland cement is several times higher than that of conventional materials. It should be noted that its main distinctive properties fully justify the high cost.
Sulfate-resistant cement reliably protects buildings and structures from the effects of moisture and frost, increases the wear resistance of structures. It can also significantly improve the quality of simple concrete mortar, as a result of which such a building material will last longer than the usual declared life.
For information on how to properly mix the cement mortar, see the video below.
Specifications
Ordinary or reinforced concrete mortar has a very weak resistance to such natural factors:
- low and high temperatures (frost and heat);
- sea, river and ground water flow;
- acidic, sulfate and salt effects.
Sulfate-resistant concrete has the following positive characteristics:
- Even at high hydrostatic pressure, it remains integral and stable, the structure does not collapse and retains its original appearance.
- The service life is significantly increased.
- Due to the composition, the corrosion process from constant contact with water is excluded.
- Does not interact with sulfate-containing substances.
Sulfate resistant cement

Recall that such cement is an artificial material that is obtained from magnesian and carbonate-silicate rocks by sintering in huge kilns (up to 180m). The clinker obtained after firing is poured into ball mills with the addition of up to 6% gypsum (CaSO4x2H2O). Further, the resulting powder is pneumatically pumped into silos.This is how ordinary Portland cement is obtained, named after the English island of Portland, where it was first obtained in 1824.
In order to impart sulfate-resistant properties to Portland cement, a certain mineralogical composition is assigned to it at the production stage. Two letters C are added to the marking, which means sulfate resistant. The table for regulating the content of minerals in clinker is taken from GOST 22266 - 2013.

This table shows that it is important to keep the tricalcium aluminate normal, which is the harmful component when interacting with sulfates. We talked about this at the beginning of the article.
The formation of calcium hydrosulfoaluminate (HSAA) leads to damage to the concrete stone from expansion during the reaction, and subsequently to the leaching of this formation from the concrete body. This is how type III concrete corrosion proceeds.
Strength grades of sulfate-resistant cement - B32.5, B42.5, B52.5.
Views
Portland cement is available pure and with additives. The binder without additives does not include minerals in the composition, only gypsum. Such material is used in the installation of underground / surface and underwater monolithic objects, precast concrete / reinforced concrete structures, operated in the absence of a pronounced aggressive environment.
Mineral additives can significantly improve certain properties of the material, which can be used in water and aggressive conditions. The most popular additives: active minerals, blast-furnace slag. They improve resistance to corrosion, water, frost, chemicals, etc.
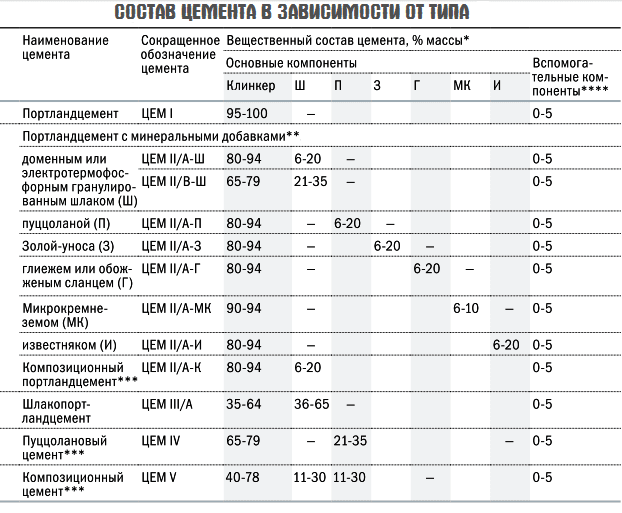
Types of Portland cement by additives (what is made of astringent):
- Normally hardening - no additives.
- Fast-drying - hardens within 3 days after pouring due to the inclusion in the composition of mineral additives and slag. The grinding of the mixture should be minimal, there are M400 and M500 grades. Thanks to the use of the substance, it is possible to speed up the performance of work, which is important for prefabricated and reinforced concrete objects.
- Plasticized - the composition contains special additives to reduce water absorption, increase mobility and heat resistance. Plasticizers are added to the powder at the grinding stage, they envelop the cement particles, preventing them from sticking together. The composition turns out to be comfortable to work with, relevant for working with complex architectural structures.
- Hydrophobic - does not absorb moisture, quickly sets due to the presence of asidols and mylonft in the composition. It is used in conditions of high humidity, at objects with a risk of flooding.
- Backfill Portland cement - protects wells from groundwater, is relevant in the gas / oil sector, as it is not afraid of temperature and pressure, it holds the structure even at the beginning of solidification. There is a lightweight grouting compound containing appropriate additives.

- Expanding - increases in volume when mixed. It is used for filling cracks and joints, in various types of repair work.
- Portland cement with slag - with the addition of blast furnace slags, which increase the volume of metal particles in the composition and make the hardened stone resistant to fire. So get, which is used when creating objects under water, land, at a considerable height. But the frost resistance of the composition is low.
- Sulphate-resistant - not afraid of sulphate waters that provoke corrosion. Most often, this type of cement is also frost-resistant and is made in the M300-M500 grades.
- - used for decorative purposes in architectural and finishing works, often colored with different pigments. White cement is obtained by the manufacturer through the use of white clays, pure limestones, as well as cooling the clinker with water.
- Slag-alkaline cement - shows even higher performance and properties in comparison with conventional Portland cement. Resistant to aggressive influences, environments, temperature extremes, heat and frost, moisture. Such characteristics can be obtained due to the introduction of alkali and ground slag, less often clay, into the composition.
- Colored - relevant for decorative work, obtained by adding pigments to white Portland cement (ocher, red lead, chromium oxide, etc.).
- Magnesian - is produced on the basis of heating magnesium oxides to a high temperature and adding an aqueous solution of magnesium chloride of 30%. The technology of creation and the components make the cement durable and well amenable to finishing (polishing, resistance to microorganisms, etc.). Often used for decoration, complex structures.

- - created from colored cement, gypsum, additives of sedimentary or volcanic origin. The solution is resistant to water, solidifies even under water, therefore it is used in the construction of hydraulic structures, for lining various types of tanks, surfaces in contact with chlorinated or seawater. The hardened stone turns out to be durable, resistant to water and chemicals, and does not give out efflorescence.
- Alumina is a strong, fast-setting cement based on clinker and limestone in molten form. The powder contains a lot of calcium aluminates (low basic). Freezes at + 25C and below, otherwise it loses half of its strength. It is forbidden to mix material with other types of cement and additives. Usually, the powder is used to create acid-resistant solutions, filling granite, beshtaunite and other acid-resistant rocks. Such a mixture is grabbed within 8 days.
4.1 Features
4.1.1 Clinker used
in the production of cements, according to the calculated mineralogical composition, it must
meet the requirements specified in table 1.
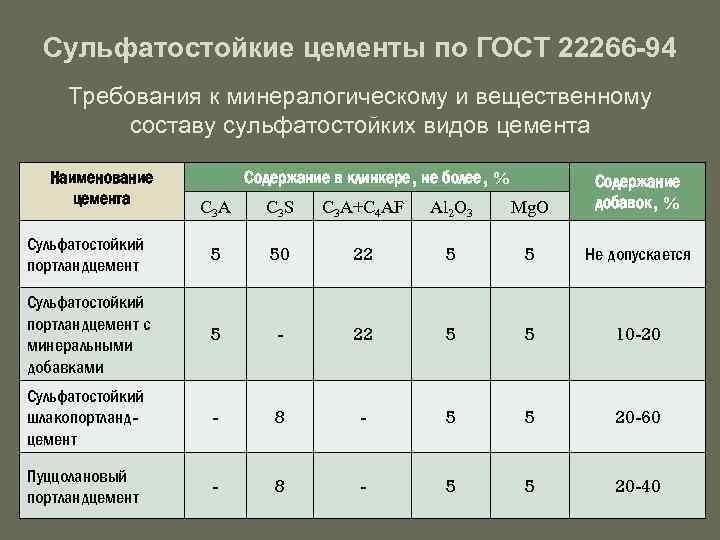
Table 1
Clinker value,% by weight, not
more, by type of cement
sulfate resistant
Portland cement
sulfate-resistant Portland cement with
mineral additives
sulfate resistant
slag Portland cement
pozzolanic
Portland cement
Tricalcium silicate content
(3CaO SiO2)
50
Not standardized
Tricalcium aluminate content
(3CaO Al2O3)
5
8
The amount of tricalcium aluminate
(3CaO Al2O3) and
tetra-calcium alumoferrite (4CaO Al2O3Fe2O3)
22
Not standardized
The content of aluminum oxide (Al2O3)
5
Magnesium oxide (MgO) content
5
4.1.2 Content of additives in
cement, depending on their type, must correspond to that indicated in the table
2.
4.1.3 In sulfate-resistant
Portland cement with mineral additives, it is allowed to use a mixture of slag and
pozzolanas, the total number of which should not exceed 20
%.
table 2
V
percent by weight of cement
Content of additives
Granulated blast-furnace slag,
electrothermophosphoric slag
Pozzolana
Sulfate resistant
Portland cement
Not allowed
Sulphate-resistant Portland cement with
mineral additives
St. 10 and no more than 20
Sulfate resistant
slag Portland cement
St. 40 and no more than 60
—
Pozzolanic
Portland cement
—
St. 20 and no more than 40
4.1.4 In sulfate-resistant
slag Portland cement it is allowed to replace slag with pozzolana or ash (acidic) in
an amount of not more than 10% by weight of cement.
4.1.5 Anhydride content
sulfuric acid (SO3) in the cement should not
exceed the values given in table 3.
table
3
V
percent, no more
Content
SO3
Sulfate resistant
Portland cement
3,0
Sulphate-resistant Portland cement with
mineral additives
3,0
Sulfate resistant
slag Portland cement
4,0
Pozzolanic
Portland cement
3,5
4.1.6 Allowed to enter into
cement when grinding, plasticizing and water-repelling surfactant
supplements in an amount of not more than 0.3% of the mass of cement in terms of dry
additive substance.
Mobility
cement-sand mortar of 1: 3 composition from plasticized cements of all
species should be such that, with a water-cement ratio equal to 0.4, spreading
the standard cone was at least 135 mm.
Hydrophobic cement should not
absorb water within 5 minutes from the moment a drop of water is applied to
cement surface.
4.1.7 During production
cement to intensify the grinding process, it is allowed to introduce technological
additives that do not deteriorate the quality of cement, in an amount of not more than 1% of the mass
cement.
Effectiveness of application
technological additives, as well as the absence of their negative impact on
the properties of concrete must be confirmed by the results of cement tests and
concrete.
4.1.8 Tensile strength
of cements under compression should be not less than the values indicated in Table 4.
table
4
V
megapascals
Cement grade
Ultimate strength at compression at age 28
days
Sulfate resistant
Portland cement
400
39,2
Sulphate-resistant Portland cement with
mineral additives
400
500
39,2
49,0
Sulfate resistant
slag Portland cement
300
400
29,4
39,2
Pozzolanic
Portland cement
300
400
29,4
39,2
4.1.9 Cement should
show the uniformity of volume change when testing samples by boiling in
water.
4.1.10 Start of setting
cement should come no earlier than 45 minutes, the end - no later than 10 hours from the beginning
mixing.
4.1.11 Fineness of grinding
cement, determined by the specific surface, should be at least 250
m2 / kg. For cements containing additives of sedimentary origin,
the fineness of grinding is determined by the residue on a sieve with a mesh No. 008 in accordance with GOST 6613. Residue
on the sieve should not be more than 15% of the mass of the sifted
samples.
4.1.12 Alkali content in
cement is established by the supply contract.
History of cement
The word "cement" comes from the Latin caementum, which translates as "crushed, broken stone." This substance was the result of a search for ways to cope with the poor water resistance of gypsum and limestone rocks. For this purpose, waterproof mineral substances were introduced into their composition. At the very beginning, they were the remains of baked clay bricks and volcanic rocks. The ancient Romans used the ash deposits of the famous Vesuvius volcano - pozzolana.
The optimal technology for the production of cement was developed many years later, when the need for large quantities of inexpensive and durable binder did not become most acute. The greatest contributions to the research were made by:
- Bricklayer John Aspind, who received a patent for Portland cement in 1824.
- Russian builder Yegor Cheliev, who wrote a book in 1825 about cement for underwater work.
The name Portland cement comes from the English island of Portland, which is composed of limestone rocks. In England, stones from this island were considered the most prestigious building material. Aspind managed to obtain an artificial stone, which was very similar in strength and color to the specified material.
Additives for improving grouting slurries
To improve the performance of the solution, you can use additional additives:
Calcium chloride and sodium carbonate accelerate the setting time of the cement. When added to a liquid, a quick setting mixture is obtained, it can be used at temperatures up to 65 ° C. For expansion properties, add up to 30% gypsum-alumina cement.
If you add gypsum, the hardening period is significantly reduced, as a result, a stone with increased strength is formed 3-4 hours after the injection of the solution
In order to prevent solidification in the borax themselves, process inhibitors are added.
Bentonite increases the initial mobility of the solution, which is especially important when pumping it.
Compositions with the inclusion of clay further improve the viscosity of the material during its punching, which allows for the subsequent hardening of the solution with an increase in plastic strength.
A cement-resinous composition with the addition of plastic substances, mainly epoxy aliphatic resins, is used if aquifers are located near the well.
If it is required to pump the solution to a depth of more than 100 m, add diesel fuel. Cement is completely inert to organic hydrocarbons, and the solution becomes much more viscous
Strength is acquired after hydrocarbons are replaced by water.