Consumption of mortar for 1m3 of brickwork
Approximate mortar consumption per 1 m2 of masonry
Most builders calculate the consumption of mortar for masonry approximately, but there are certain subtleties that are very important to consider. So, the rates of mortar consumption per 1 m3 of masonry can be different, and this is what will be discussed below.
A little about brickwork
As you know, the use of bricks in construction is an extremely widespread phenomenon. Buildings made of this material are distinguished by high reliability rates, they retain heat well and transmit much less noise compared to structures made of some other materials.
Factors affecting the costs of the cement mixture
What affects the consumption of the solution
The criteria on which the volume of mortar consumption per 1m2 of masonry depends are as follows:
- The thickness of the walls of the structure, which can be 1, 1.5 and 2 bricks.
- The type of cement used for the anchorage.
- The type of building materials used, which can be either solid or hollow from the inside.
The principle of manufacturing building anchoring material:
Depending on which components are included in it (sometimes structures such as clay, lime are used), the consumption of mortar per m3 of masonry may be different.
Professional skills of the one who mixes ready-to-install cement:
- It is believed that in such work there is nothing difficult and even an inexperienced owner can do it with his own hands.
- However, a very common reason for overspending is that, due to his inexperience, the master uses more material than the instructions require.
Based on what type of cement is used in the fixing composition, some conclusions can also be drawn.
How much dry raw material is required for 1 m3 of building mixture?
Each type of cement has its own measures.
So, studying the rates of mortar consumption for laying partitions in ¼ bricks, dry raw materials are used in the following quantities:
- Cement brand "M50" - 2.5 kg.
- Mixtures of type "M75" need 4 kg.
- For cement grade "M100" you need to apply 5 kg.
There are some other ways to take measurements:
- If the installation is carried out in 1 brick, then the mortar consumption per 1m / sq of masonry will be approximately 75 liters.
- When designing partitions of 1.5 elements, this parameter will change and will be equal to 110 liters.
The amount of cement per cubic meter
The required amount of cement for the preparation of 1 m3 of building composition:
- Professional specialists use such measures very often, since the principle of all calculations lies in the basis of the volume.
- It is believed that in order to prepare 1 m3 of the composition, at least 400 kg of cement will be required (in other words, standard bags of 50 kg).
- At the same time, the consumption of masonry mortar per 1 m3 of masonry will be about 0.25 m3 of the resulting composition.
- It is these proportions that are taken as optimal and used in construction.
Cost rate
Despite this, in certain sources, the data may differ slightly, the reason for which may be the presence of different styling options.
Previously specified rate of solution consumption per cube of masonry suitable for a standard installation procedure and may well be taken into account when building a brick building on your own.
With long-term storage, the technical characteristics of the material are significantly reduced, and the cost of such an error is very high:
For example, the cement brand "M400" after six months of its acquisition in its properties will correspond in its properties to the brand "M200" or "M100".
Tools used to calculate composition costs
When calculating the cost of the consumption of cement mixture for the installation of bricks, it is necessary to take into account the list of tools required for this procedure.
These include:
The use of a cement composition when installing shell rock
First of all, it should be noted that the consistency of the anchoring structure for mounting the shell rock must have certain viscosity parameters.
Varieties of solutions and their applicability
The connecting link between brick blocks is a mixture of a binder component with filler and water. The most common are 4 types of solutions.
- Cement-sandy. It is diluted with water, its proportions depend on the brand of cement, the method of masonry. When solidified, this option is the most durable, but when deviating from the technology, it is prone to cracking;
- Limestone - in it the cement is replaced by quicklime; plastic, but washed out by rains, therefore, it is suitable only for the installation of internal walls;
- Mixed - cement and sand are diluted with liquid slaked lime (milk of lime). The combination combines the best qualities of the first two options;
- With a plasticizer - a polymer additive is mixed with cement and sand (fraction 2 mm) to increase the plasticity of the mixture. It is easier to make such a solution from a dry building mixture by adding water according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Despite the composition, the requirements for the quality of the mixture are almost the same. All ingredients are cleaned of lumps, sand is sieved, liquid lime is filtered. To prepare the solution, first thoroughly mix the powder components, then slowly pour in cold liquid (20 ° C) and mix thoroughly so that setting does not occur. The process is accelerated using a concrete mixer or a rotary hammer with a whisk attachment.
Consumption of mortar per cube of brickwork
How much to prepare mortar for masonry walls? This is determined by several conditions:
- the skill of a bricklayer;
- the structure of the brick block - products with voids take more mortar mixture;
- type of brick - hyper-pressed and face silicate absorbs mortar less than ceramic or ordinary silicate with a rough surface;
- the thickness of the wall.
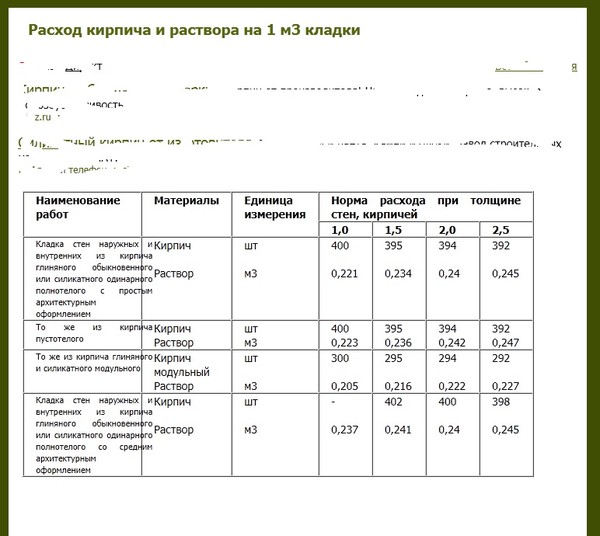
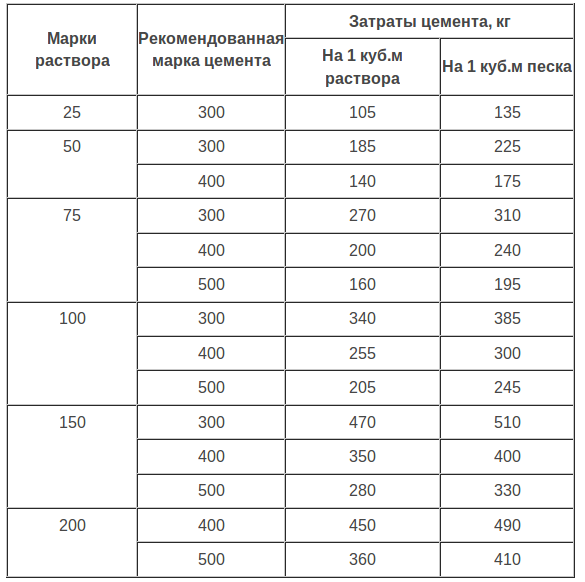
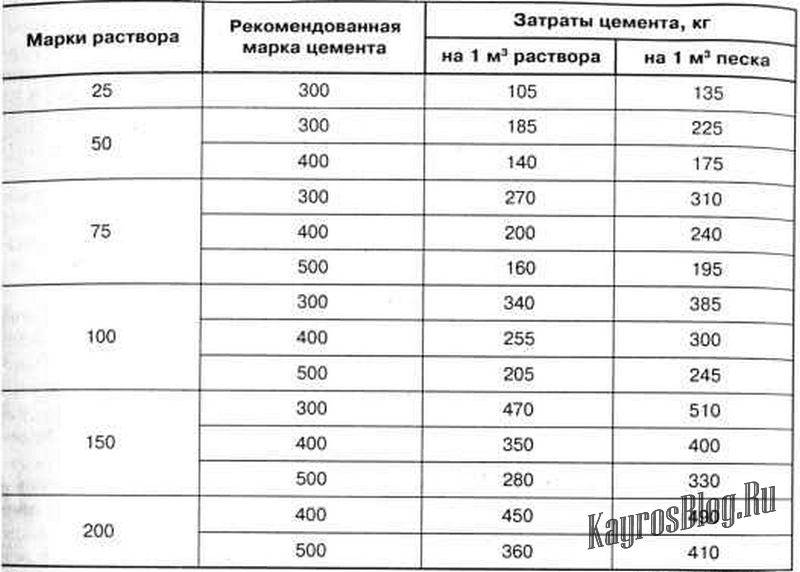
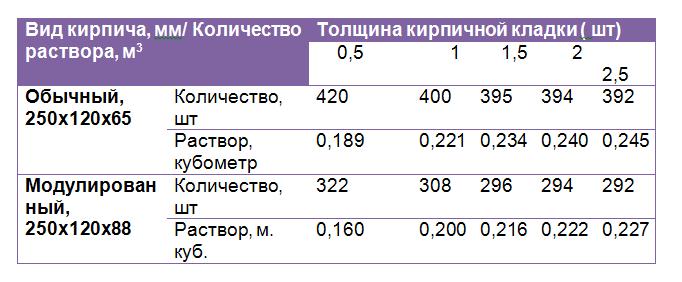
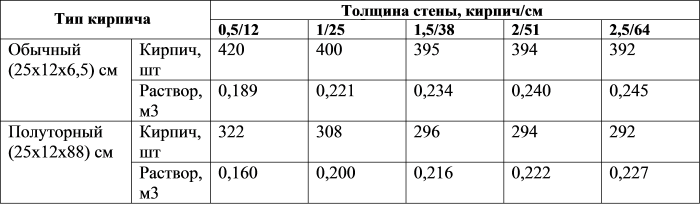
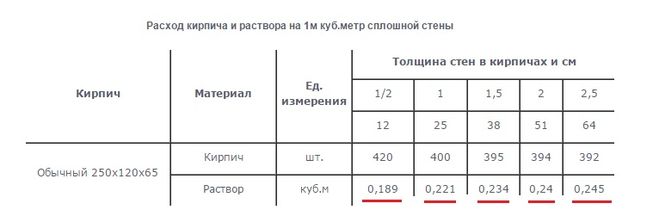
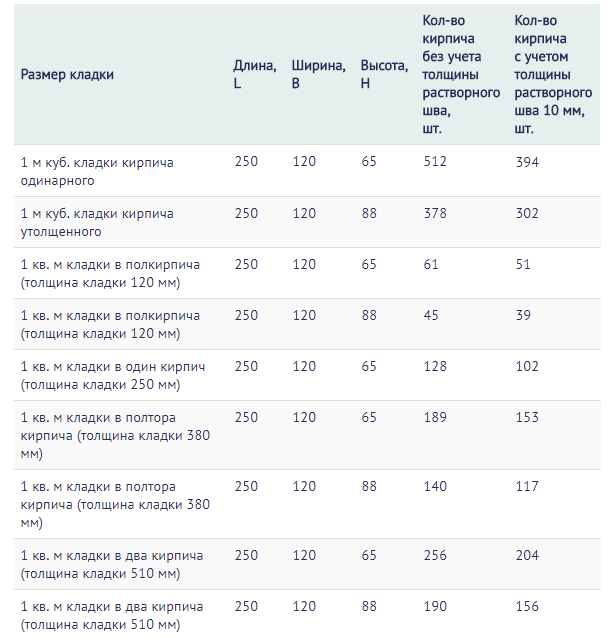
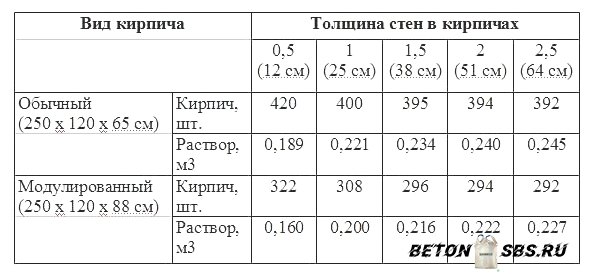
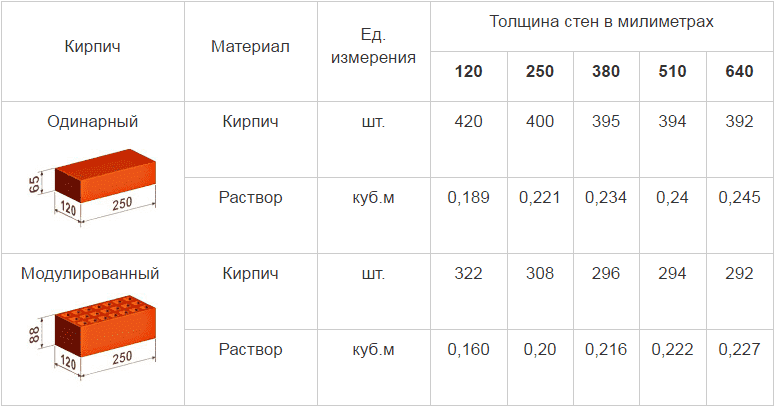
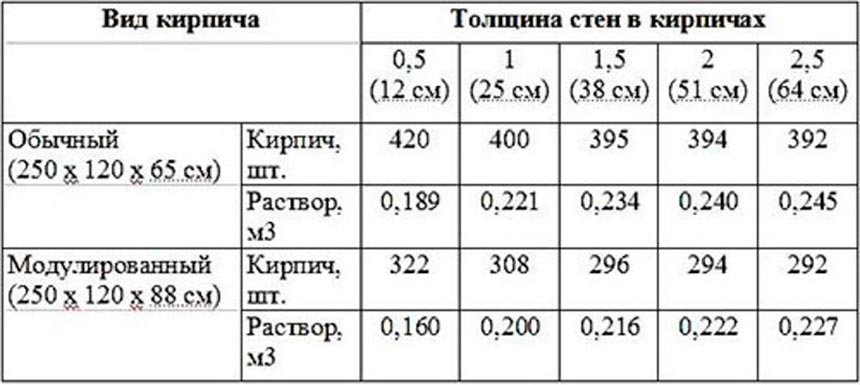
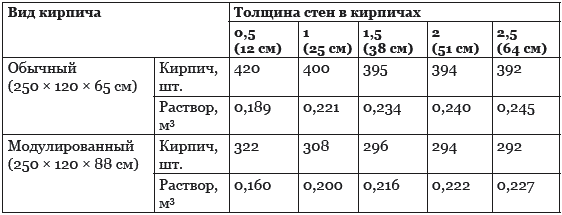
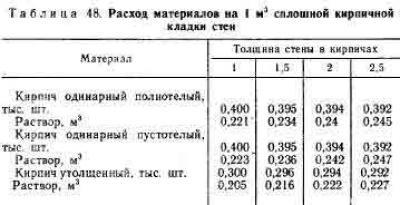
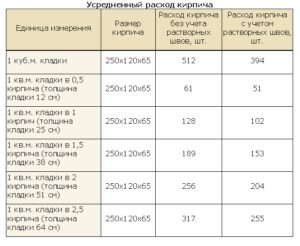
The average consumption of mortar per 1 m3 of brickwork with a standard joint thickness (12 mm) is approximately 0.23 m3. More accurate information is given in Table 1.
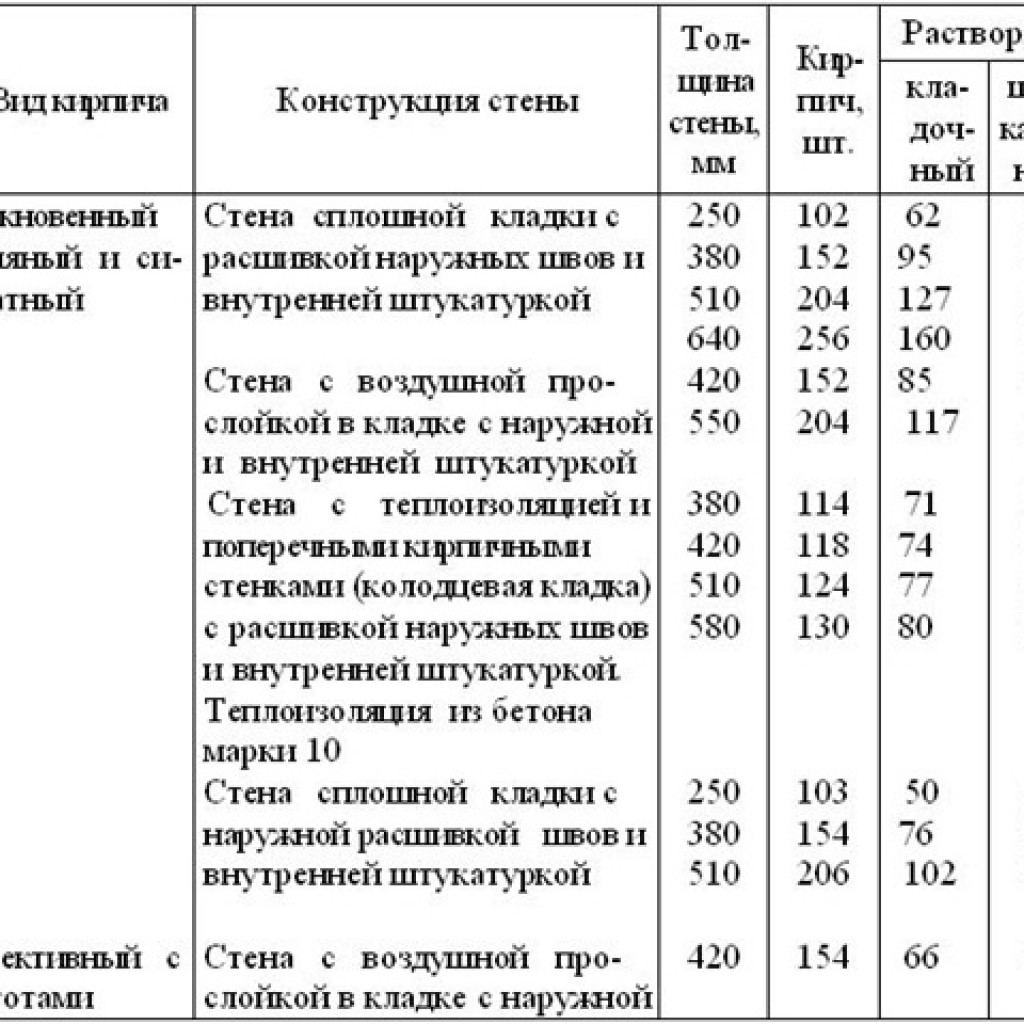
Consumption of cement for brickwork
The composition of the mixture for the construction of a brick wall varies depending on the quality of the initial components, weather conditions, and the number of storeys of the building. To mix the ingredients correctly, you need to know: a 10-liter bucket holds 14 kg of cement or 12 kg of sand.
- The cement slurry is flexible in terms of proportions. It is characterized by the degree of strength: the less it is, the lower the required grade of cement and the lower its percentage (1 part per 2.5 - 6 parts of sand). For cement M400 is characterized by a ratio of 1.3, for M500 - 1. 4. The volume of water (on average 0.5 - 0.7 liters per 1 kg of cement) depends on the desired density of the mixture, the type of brick, air temperature - in the summer heat, the solution should be more fluid. To increase its plasticity, experienced bricklayers add a little washing powder or dishwashing liquid to the water. For 1 cube of the finished solution 1.4, 410 kg of M500 cement and 1.14 m3 of sand are needed. Knowing that 0.24 m3 of mortar is consumed per 1 cubic meter of an ordinary wall in one brick from a silicate block 250 x 120 x 65, the consumption of cement per cube of brickwork is determined as follows: 0.24 x 410 = 98 kg. Accordingly, when using cement M400 (proportion 1. 3) a cubic meter of the mixture contains 490 kg of cement, and 117 kg is consumed per 1 m3 of masonry.
- The cement-lime mortar is suitable for use within 5 hours, and in summer at +25 o - no more than an hour, therefore, a calculation is also desirable for it. 1 cubic meter of the mixture requires 190 kg of cement M400 - M500, 1.5 m3 of sand, 106 kg of hydrated lime and 475 liters of water. For a cubic meter of masonry, an average of 46 kg of cement will be needed.
Cement consumption for brickwork during cladding
In this case, the developer is interested in how much the binder mixture will be consumed per square meter of the wall.It depends on the water absorption of the building material, the season of work, the voidness and porosity of the blocks. The norms are laid down in SNiP 82-02-95, but the real numbers are always higher, so you should buy a ready-made mortar or cement with a margin.
To save on consumables, 2 factors should be noted:
- the larger the dimensions of the brick, the less mortar will go;
- the higher the% of voids and pores, the higher the consumption of the mixture will be.
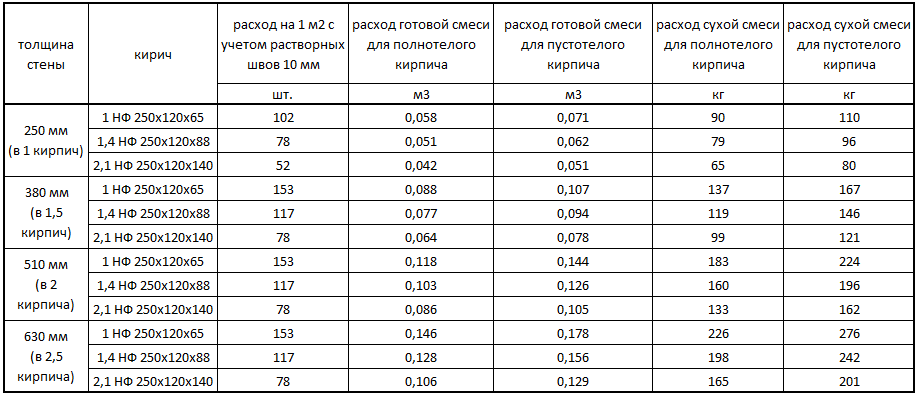
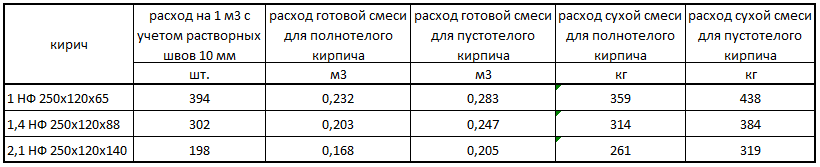
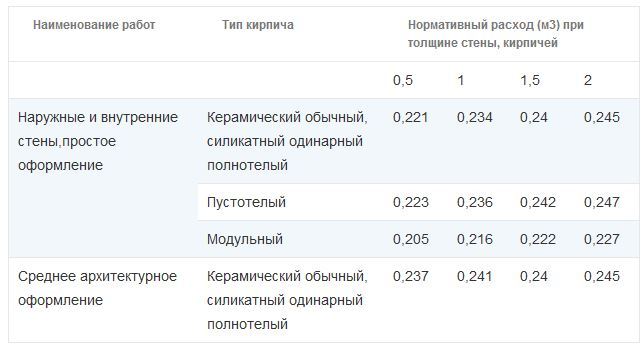
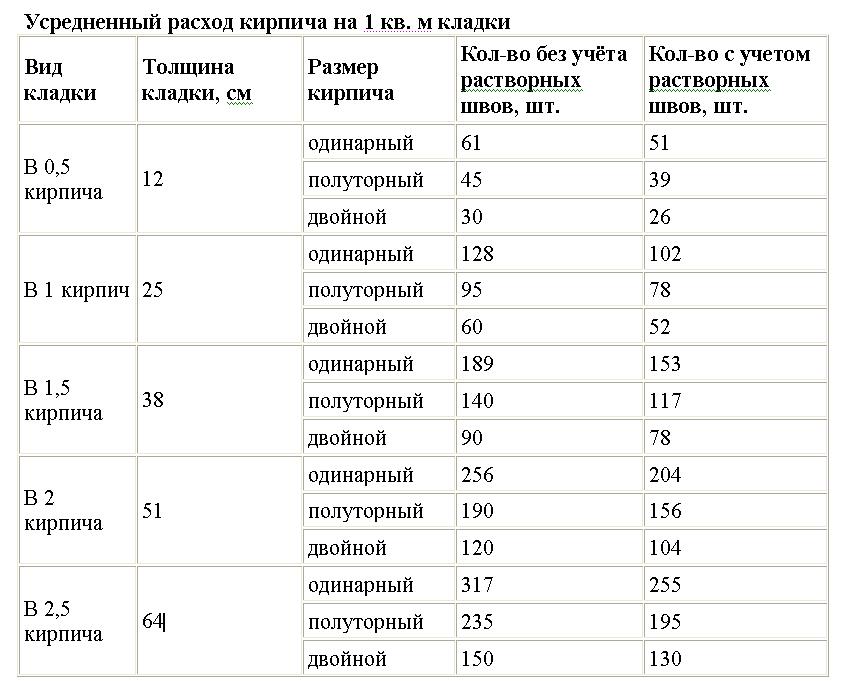
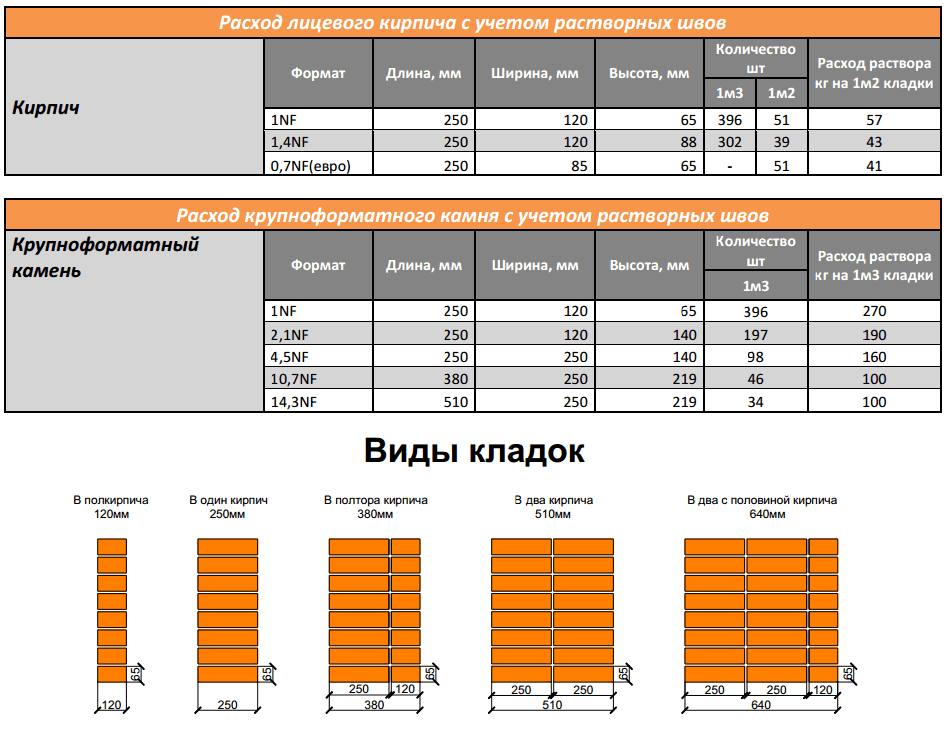
From this point of view, it is optimal to use ceramic or silicate double bricks of sufficient strength grade. This choice will allow you to achieve savings of 20% mortar mixture. Table 2 shows comparative data on the consumption of mortar per square meter of the wall.
What formulations are used
The most famous and demanded mixtures:
- Traditional universal building compound made of sand and Portland cement. The standard ratio of ingredients is three to one or four to one;
- Working mixture of sand and quicklime. Applicable only for interior masonry work;
- Mixed composition for brickwork. These are quartz sand, cement and hydrated lime;
- Cement mixes with plasticizer additives.

General norms according to SNiP II-22–81: the sand must be washed and sieved, the milk of lime must be strained, the cement must be fresh and free of lumps. All formulations are mixed with clean industrial water. In dry mixed components, water is added in portions, until the required consistency is set.
Solution costs per cubic meter of partition
The following process parameters affect the rates of solution consumption per 1 m3:
- Base thickness and quality of brick blocks;
- A kind of brick - it can be solid or hollow;
- Climatic conditions - temperature and humidity, sunny or cloudy day.

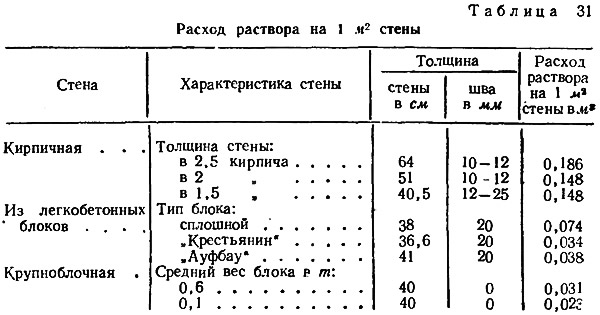
Practice shows that for 1m2 of an ordinary brick structure, it is necessary to prepare 75 liters. The construction of one and a half bricks will require the preparation of 115 liters of the working mixture, the base in half a brick will take 40 liters of cement composition per 1 m2.
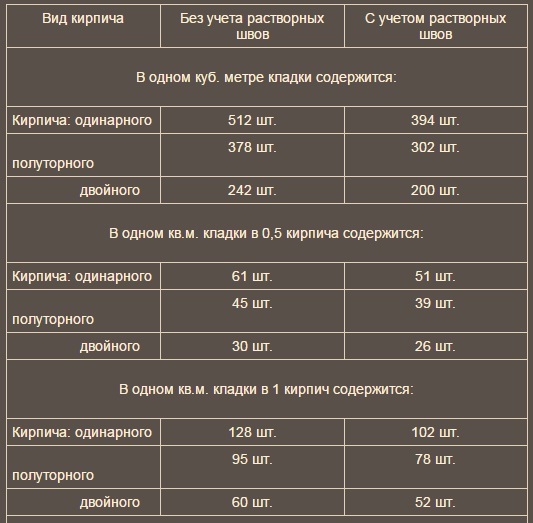
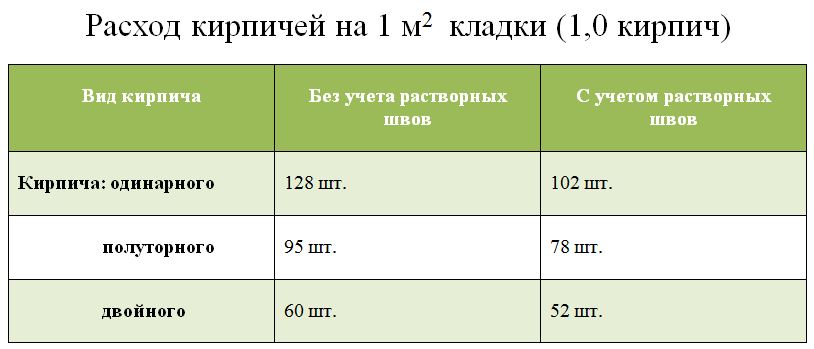
According to SNiP 82-02-95, which show that the rates of mortar consumption per 1 m3 of brickwork are as follows:
- 0.19 cubic meters for half-brick masonry;
- 0.22 cubic meters for one brick masonry;
- 0.235 cubic meters for one and a half blocks;
- 0.24 cubic meters for two brick masonry;
- 0.25 cubic meters for masonry in two and a half blocks.
More accurate and extended data are contained in SNiP II-22–81.
Mortar for the wall - how much is needed for 1 m2
How to find out the consumption of mortar per 1 m2 of brickwork? In order not to engage in calculations, there is a table of all the components included in the composition.

It takes into account the consumption of mortar for laying bricks from different materials:
| Variety | Composition | The proportions of the components for the layer | ||
| Splashing | Priming | Covering | ||
| Slaked lime or quicklime | Milk of lime and quartz sand | 1,0:(2,5-4,0) | 1,0:(2,0-3,0) | 1:(1,0-2,0) |
| Portland cement | Portland cement and quartz sand | 1,0:(2,5-4,5) | 1,0:(2,0-3,5) | 1,0:(1,0-1,5) |
| Clay | Quartz sand and clay | 1,0:(3,0-5,5) | 1,0:(3,0-5,5) | 1,0:(3,0-5,5) |
| Lime-cement | Portland cement, lime milk and quartz sand | 1,0:(0,3-0,5): (3,0-5,0) | 1,0: (0,7-1,0): (2,5-4,5) | 1,0:(1,0-1,5):(1,5-2,5) |
| Gypsum-lime | Milk of lime, gypsum and quartz sand | 1,0:(0,3-1,0): (2,0-3,5) | 1,0:(0,5-1,5):(1,5-2,5) | 1,0:(1,0-1,5): (1,5-2,5) |
| Clay-lime | Milk of lime, clay and quartz sand | 0,2-1,0:(3,0-5,0) | 0,2-1,0:(3,0-5,0) | 0,2-1,0:(3,0-5,0) |
| Clay-cement | Portland cement, clay and quartz sand | 1,0:4,0:12,0 | 1,0:4,0:12,0 | 1,0:4,0:12,0 |
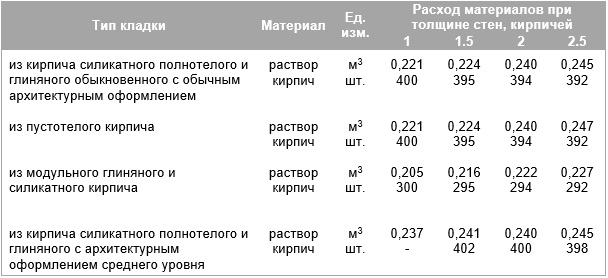
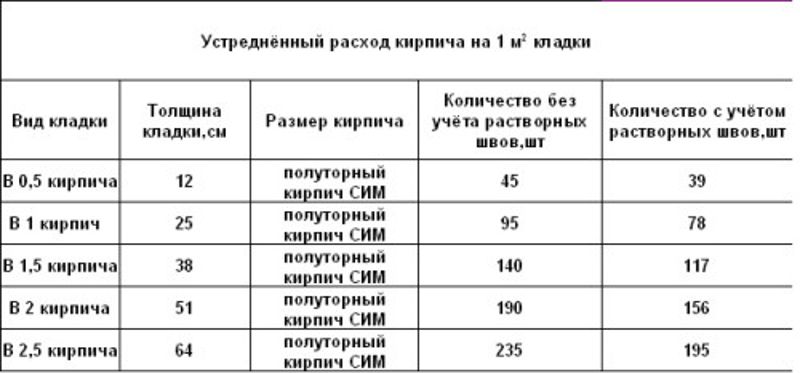
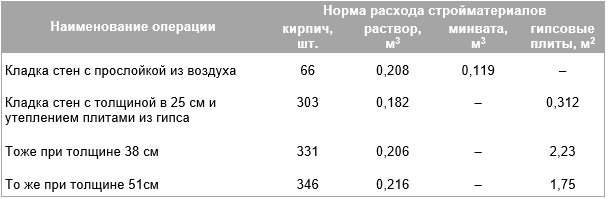
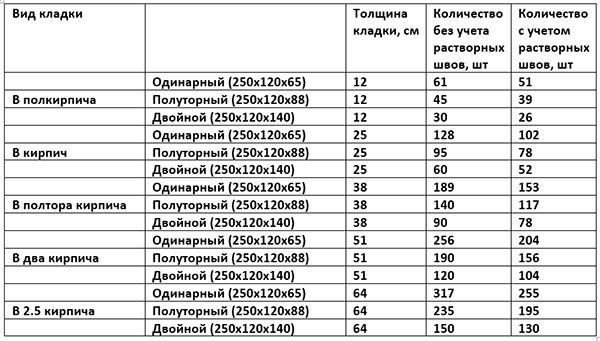
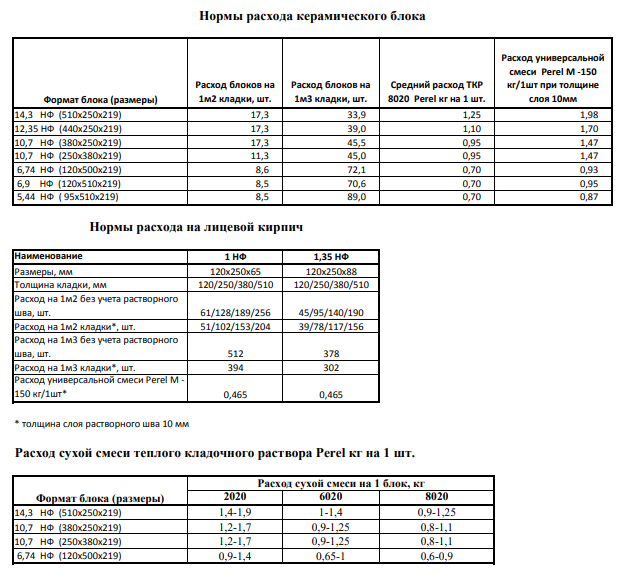
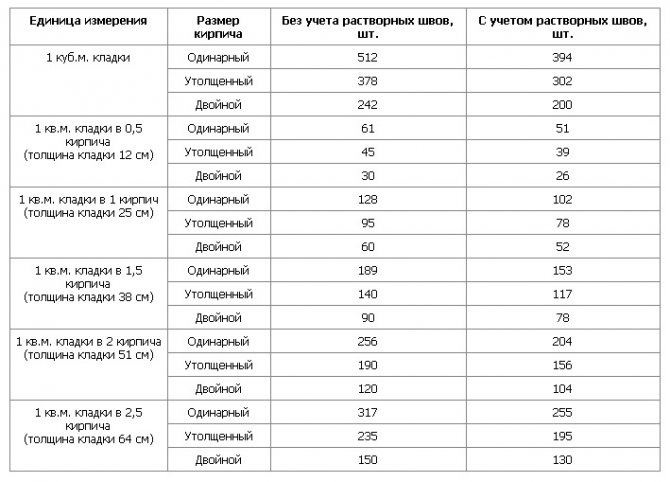
Consumption rates of the building mixture for different types of building blocks
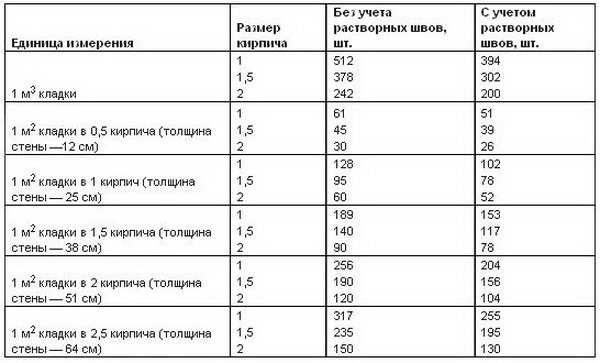
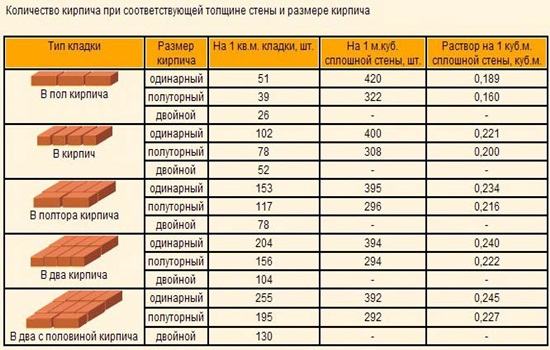
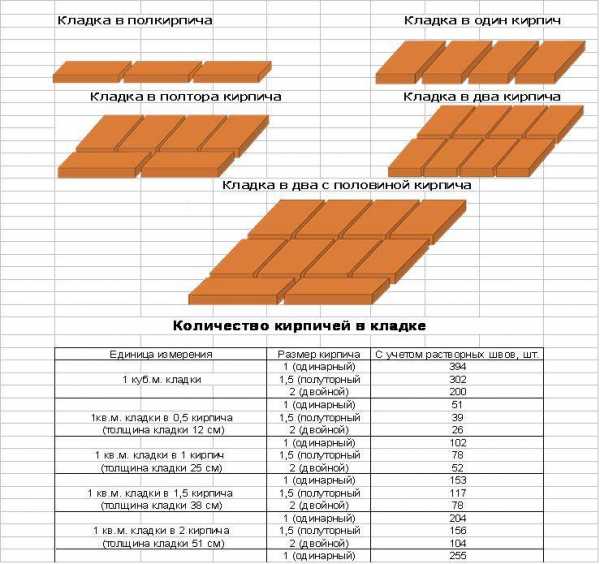
About 0.0108 m3 of the composition is consumed per unit, and 0.054 m3 of the mixture will be used to cover 50% of the seam. The arithmetic mean of these two values is 0.08 m3. This value determines the consumption of mortar per 1 m2 of brickwork.

For different clutches, this parameter will be equal to:
- When erecting a partition in half a brick - 0.04 m3;
- Private - 0.82 m3;
- One and a half - 0.125 m3;
- Double - 0.164 m3.
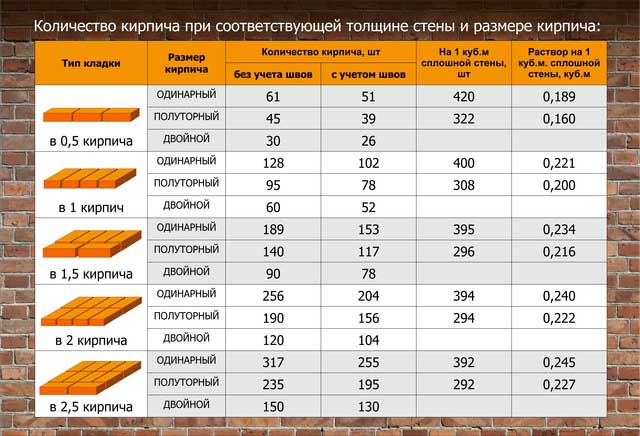
The table shows the rates of mortar consumption for brickwork from blocks of different sizes for partitions of different thicknesses:
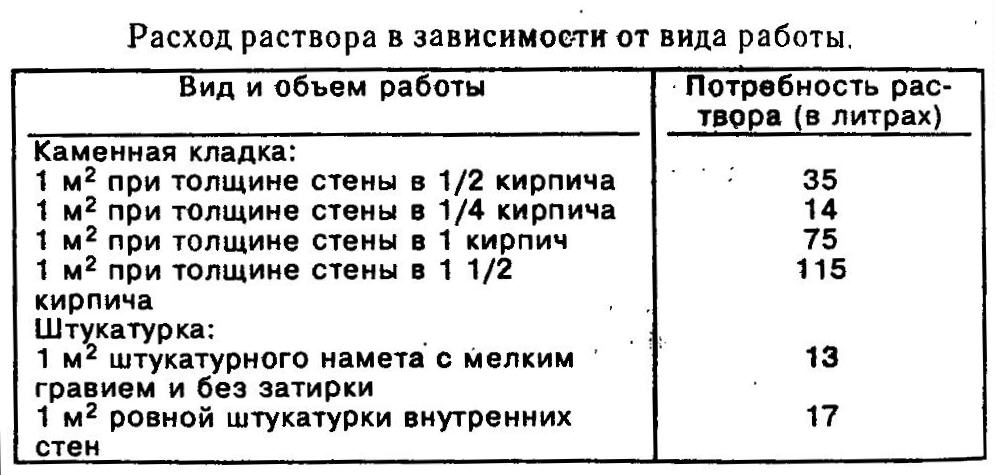
| Variety of works | Construction volume | Volume |
| Masonry work | 1 m2 with a base thickness of a quarter of a briquette | 14 liters |
| 1 m2 with a base thickness of half a brick | 35 liters | |
| 1 m2 with a thickness of one brick | 75 liters | |
| 1 m2 with a wall thickness of one and a half bricks | 115 Liters | |
| Plastering | 1 m2 basting without grouting with fine gravel | 13 liters |
| 1 m2 of internal plaster | 17 liters |
In this case, the flow rate of the solution per 1 m3 will be equal to:
- When working in half a brick for 53 building units - 0.19 m3;
- With single masonry for 102 blocks - 0.22 m3;
- One and a half for 153 units - 0.23 m3;
- Double for 204 blocks - 0.24 m3.
Cement consumption during construction work
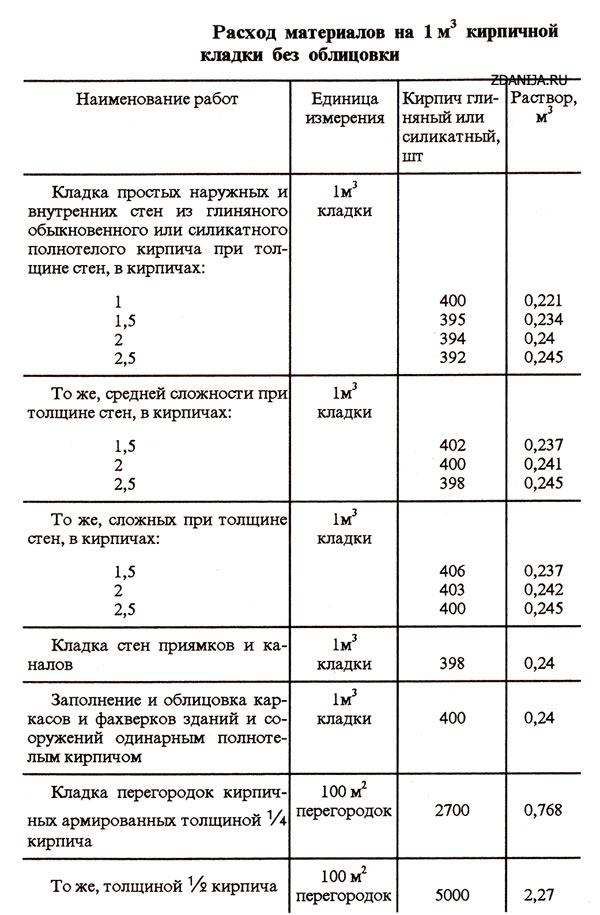
The use and consumption of this binder depends on its viscosity, density, and drying time. The material is used for the preparation of mortars used for arranging the foundation, brickwork and other purposes. Also, the consumption depends on the grade of the material:
- for laying 1m3 of bricks, you will need about 250 kg of the mixture. The amount of cement depends on the brand, the requirements for the solution (the ratio of cement, sand). If you need a M100 grade mortar, which is most often used for masonry, then the cement consumption will be 75-100 kg. Much here also depends on the professionalism of the builders;
- when arranging a cement screed, the consumption of cement is approximately 575 kg per "cube" of the mixture when using grade 400, if grade 500, then 460 kg is enough;
- for the construction of the foundation, provided that grade 300 cement is used, the consumption will be 320 kg per "cube" of the mixture;
- for plastering an area of 1 "square" 0.005 cubic meters is enough. m of cement, provided that the layer thickness does not exceed 1 cm. Consumption will also depend on the amount of added lime or plasticizers.
Carefully selected components that make up the mixture are the key to preparing a good solution. The durability of any structure directly depends on its quality, be it a house, a fence post or a garage. Building recommendations should be taken into account and the appropriate type of mortar should be drawn up for each type of construction work.
Calculation of cement for brickwork
The need for cement is determined as follows:
Compositions of mortars for brickwork.
- the total volume of brickwork is calculated;
- the total volume of the required mixture is determined;
- taking into account the selected ratio of components, the amount of cement is calculated.
For example, you need to find out how much cement is required for the construction of the external walls of a one-story house of 10x12 m with a ceiling height of 3.2 m, if ordinary bricks and 2 bricks are used.
The first step is to find out the total volume of the masonry. To do this, the length of the walls is multiplied by the height and thickness of the masonry: (10 + 10 + 12 + 12) * 3.2 * 0.51 = 71.808 m 3. From Table 1 it can be seen that 1 m 3 requires 0.240 m 3 mortar. Therefore, for the given example, you will need: 71.808 * 0.240 = 17.233 m 3 of cement-sand mixture. To prepare a mortar for masonry in a ratio, for example, 1: 3, you need to buy: 17.233 / 4 = 4.308 m 3 of cement.
Since the hardener is sold in 50 kg bags, this value must be converted to kg. To do this, you need to know the density of the cement. Usually, the average density value is used, which is 1300 kg / m 3. That is, for the construction of walls you need to buy: 4.308 * 1300 = 5600 kg, or 5600/50 = 112 bags of cement.
When purchasing cement, it should be noted that it is not recommended to choose material in simple two-layer packages. They poorly protect the cement from moisture, so its quality will be much lower than that declared by the manufacturer. In this case, you will not be able to achieve the required structural strength, which will reduce its operational life.

Consumption of mortar for 1m3 of brickwork

Approximate mortar consumption per 1 m2 of masonry
Most builders calculate the consumption of mortar for masonry approximately, but there are certain subtleties that are very important to consider. So, the rates of mortar consumption per 1 m3 of masonry can be different, and this is what will be discussed below.
A little about brickwork
As you know, the use of bricks in construction is an extremely widespread phenomenon.Buildings made of this material are distinguished by high reliability rates, they retain heat well and transmit much less noise compared to structures made of some other materials.
Factors affecting the costs of the cement mixture
What affects the consumption of the solution
The criteria on which the volume of mortar consumption per 1m2 of masonry depends are as follows:
- The thickness of the walls of the structure, which can be 1, 1.5 and 2 bricks.
- The type of cement used for the anchorage.
- The type of building materials used, which can be either solid or hollow from the inside.
The principle of manufacturing building anchoring material:
Depending on which components are included in it (sometimes structures such as clay, lime are used), the consumption of mortar per m3 of masonry may be different.
Professional skills of the one who mixes ready-to-install cement:
- It is believed that in such work there is nothing difficult and even an inexperienced owner can do it with his own hands.
- However, a very common reason for overspending is that, due to his inexperience, the master uses more material than the instructions require.
Based on what type of cement is used in the fixing composition, some conclusions can also be drawn.
How much dry raw material is required for 1 m3 of building mixture?

Each type of cement has its own measures.
So, studying the rates of mortar consumption for laying partitions in ¼ bricks, dry raw materials are used in the following quantities:
- Cement brand "M50" - 2.5 kg.
- Mixtures of type "M75" need 4 kg.
- For cement grade "M100" you need to apply 5 kg.
There are some other ways to take measurements:
- If the installation is carried out in 1 brick, then the mortar consumption per 1m / sq of masonry will be approximately 75 liters.
- When designing partitions of 1.5 elements, this parameter will change and will be equal to 110 liters.

The amount of cement per cubic meter
The required amount of cement for the preparation of 1 m3 of building composition:
- Professional specialists use such measures very often, since the principle of all calculations lies in the basis of the volume.
- It is believed that in order to prepare 1 m3 of the composition, at least 400 kg of cement will be required (in other words, standard bags of 50 kg).
- At the same time, the consumption of masonry mortar per 1 m3 of masonry will be about 0.25 m3 of the resulting composition.
- It is these proportions that are taken as optimal and used in construction.
Cost rate
Despite this, in certain sources, the data may differ slightly, the reason for which may be the presence of different styling options.
The previously indicated rate of mortar consumption per cube of masonry is suitable for the standard installation procedure and may well be taken into account when building a brick building on your own.
With long-term storage, the technical characteristics of the material are significantly reduced, and the cost of such an error is very high:
For example, the cement brand "M400" after six months of its acquisition in its properties will correspond in its properties to the brand "M200" or "M100".
Tools used to calculate composition costs
When calculating the cost of the consumption of cement mixture for the installation of bricks, it is necessary to take into account the list of tools required for this procedure.
These include:
The use of a cement composition when installing shell rock

First of all, it should be noted that the consistency of the anchoring structure for mounting the shell rock must have certain viscosity parameters.
Calculation tolerances
The calculator is designed to calculate walls made entirely of bricks. For this reason, structures that have voids or are filled with insulation must be calculated by other methods, since the result will be greatly overestimated. Another factor that influences the result is the thickness of the seams. Let's say a 10 mm gap is included in the calculation, but in practice the builders slightly reduced or increased it.In this case, the error in the calculation will be the greater, the larger the volume of the masonry.
It is recommended that the number of bricks obtained during the calculation be multiplied by a factor of 1.05 - 1.07, adding 5 - 7 percent to the original amount. So you can insure yourself in case of detection of marriage, battle or your own mistake.
"Grandfather's method" or the current SNiP?

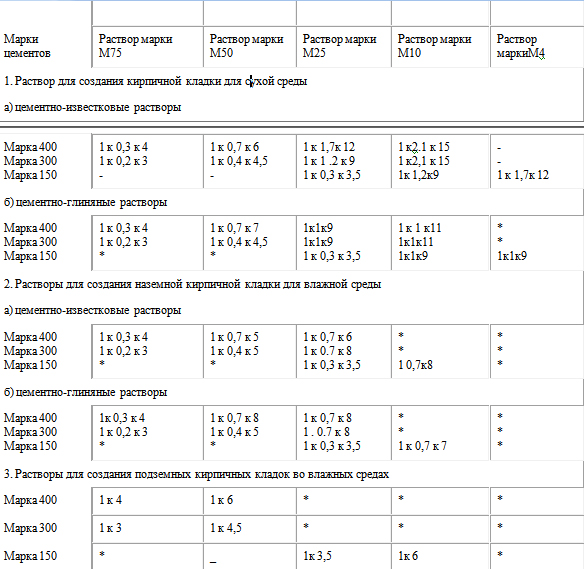
Experience is a good thing, but building codes should not be forgotten either. They take into account all the factors accompanying the preparation of mortars and concrete (purity, size, moisture content of sand and gravel, cement activity and water quality).
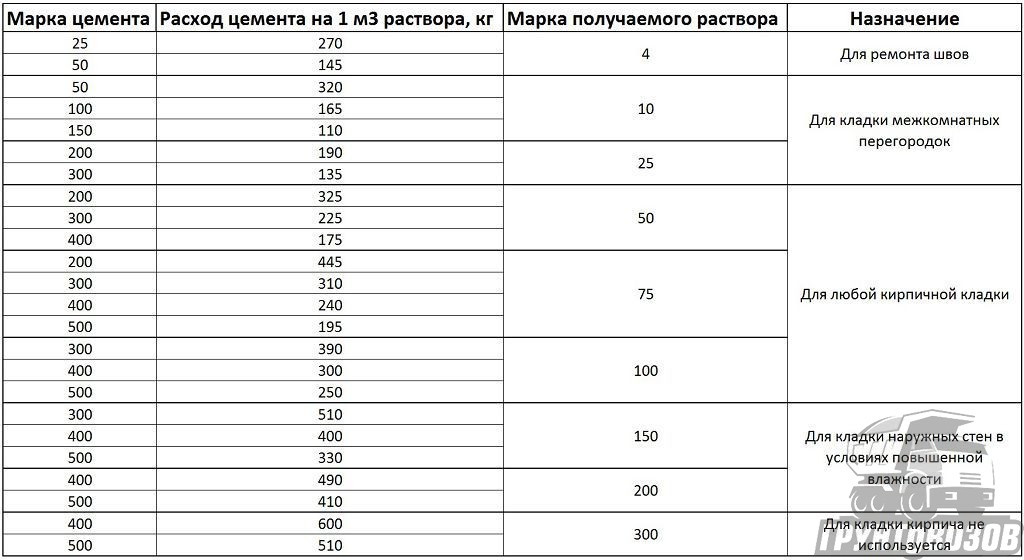
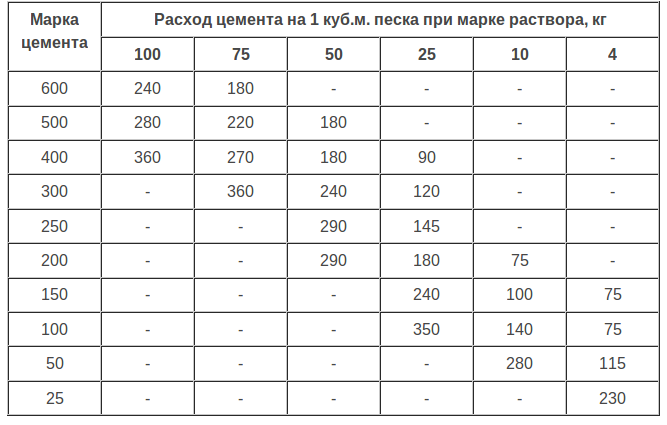
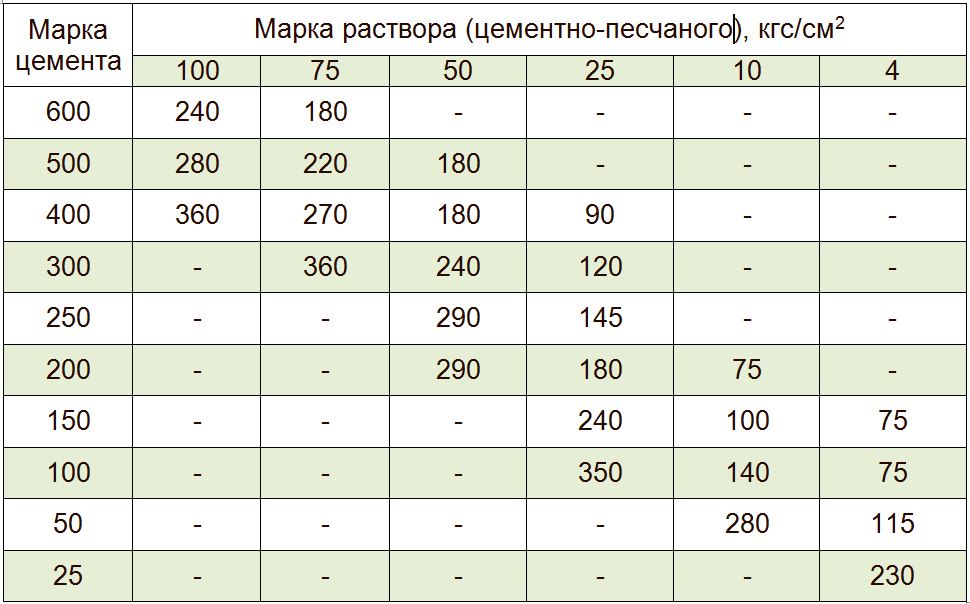
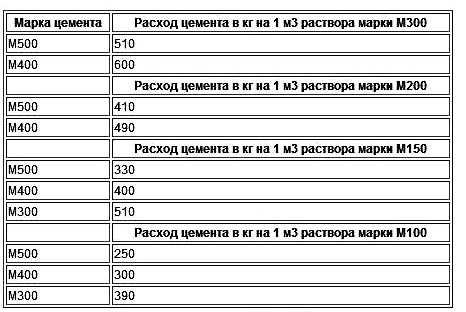
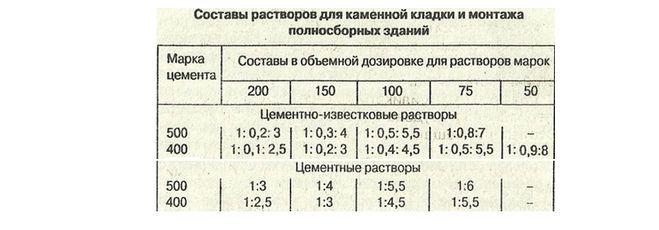
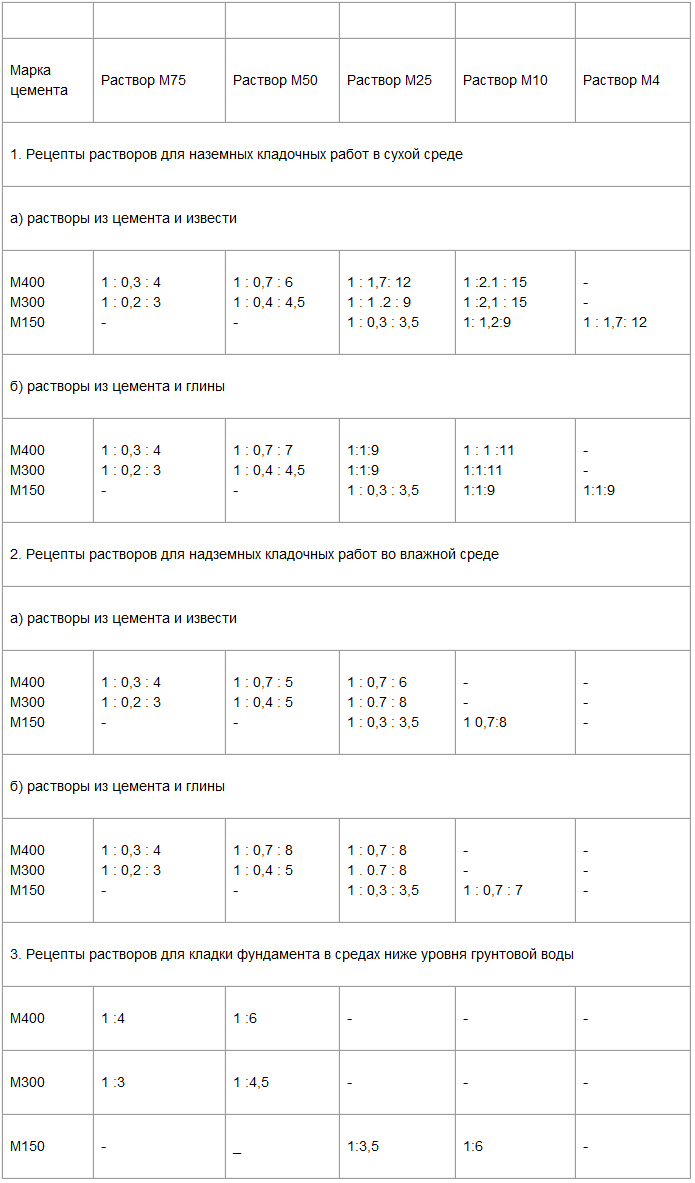
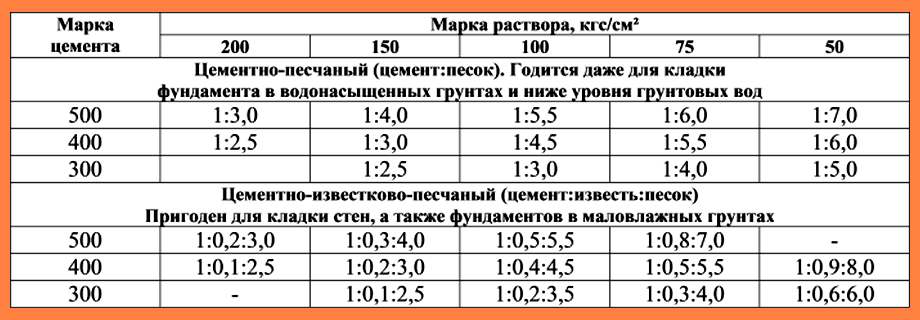
Therefore, when preparing for work on pouring the foundation, screed or laying walls, do not be lazy to look at the gost tables. You only need one or two lines in them. They clearly describe what should be the consumption of cement per cube of mortar to obtain the required strength (grade).
|
Cement grade |
Solution grade |
Consumption rate of cement for the manufacture of 1m3 solution |
|
M400 |
M200 |
490 kg |
|
M500 |
M200 |
410 kg |
|
M400 |
M150 |
400 Kg |
|
M500 |
M150 |
330 kg |
Here is a simple "extract" from SNiP, which will help prepare a high-quality mortar for masonry and screed. After reading it, remember that the given consumption rates differ slightly from the practical values.
The reason is that they are derived from standard cooking conditions (air temperature + 23C, sand of medium grain size, perfectly clean, its moisture content is no more than 7%, etc.).
It is not realistic to provide the standard parameters for batching at a construction site, therefore it is better to purchase cement with a small margin (10-15%).
The answer to the question of how much cement and sand is needed per cube of concrete will be given by the following standards:
|
Concrete grade |
Cement consumption M500 kg / 1m3 |
|
M100 |
170 |
|
M150 |
200 |
|
M200 |
240 |
|
M250 |
300 |
|
M300 |
350 |
|
M400 |
400 |
|
M500 |
450 |
When making concrete, it is important to know not only the amount of cement, but also the standard volume of sand and gravel. For calculations, the following table will be useful
Volume proportions for different grades of concrete
|
Concrete, brand |
Ratio cement / sand / crushed stone in liters |
|
|
cement M 400 |
cement M 500 |
|
|
100 |
1,0 : 4,1 : 6,1 |
1,0 : 5,3 : 7,1 |
|
150 |
1,0 : 3,2 : 5,0 |
1,0 : 4,0 : 5,8 |
|
200 |
1,0 : 2,5 : 4,2 |
1,0 : 3,2 : 4,9 |
|
250 |
1,0 : 1,9 : 3,4 |
1,0 : 2,4 : 3,9 |
|
300 |
1,0 :1,7 : 3,2 |
1,0 : 2,2 : 3,7 |
|
400 |
1,0 : 1,1 : 2,4 |
1,0 : 1,4 : 2,8 |
|
450 |
1,0 : 1,0 : 2,2 |
1,0 : 1,2 : 2,5 |
The required consumption of sand per 1m3 of the solution is 1 cubic meter. Some developers are mistaken in believing that the volume of cement increases the volume of the finished mixture. This is not true.
The cement has a very fine grinding, therefore it is distributed in the voids between the sand, without increasing the total volume of concrete and mortar. Therefore, for 1m3 of sand, we can add 200 and 400 kg of cement, getting the same 1 cubic meter of mortar.
Water is added to the mixture in a simple proportion - half of the total weight (not volume!) Of the cement. In this case, you need to take into account the actual moisture content of the sand and pour water in small portions so that the mortar or concrete does not turn out to be too liquid.
The consistency of the mortar according to the standards is determined by the amount of sediment of a standard metal cone dipped into the mixture. At a construction site, you are unlikely to be able to carry out such a test.
Therefore, just remember that the density of the masonry mortar should be such that it is not too hard, but rather plastic and does not flow out of the seams.
For a screed, mortar and concrete should be of medium density so that they can be easily compacted and leveled with a rule.
Varieties of solutions and their applicability
The connecting link between brick blocks is a mixture of a binder component with filler and water. The most common are 4 types of solutions.
- Cement-sandy. It is diluted with water, its proportions depend on the brand of cement, the method of masonry. When solidified, this option is the most durable, but when deviating from the technology, it is prone to cracking;
- Limestone - in it the cement is replaced by quicklime; plastic, but washed out by rains, therefore, it is suitable only for the installation of internal walls;
- Mixed - cement and sand are diluted with liquid slaked lime (milk of lime). The combination combines the best qualities of the first two options;
- With a plasticizer - a polymer additive is mixed with cement and sand (fraction 2 mm) to increase the plasticity of the mixture.It is easier to make such a solution from a dry building mixture by adding water according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Despite the composition, the requirements for the quality of the mixture are almost the same. All ingredients are cleaned of lumps, sand is sieved, liquid lime is filtered. To prepare the solution, first thoroughly mix the powder components, then slowly pour in cold liquid (20 ° C) and mix thoroughly so that setting does not occur. The process is accelerated using a concrete mixer or a rotary hammer with a whisk attachment.
Consumption of mortar per cube of brickwork
How much to prepare mortar for masonry walls? This is determined by several conditions:
- the skill of a bricklayer;
- the structure of the brick block - products with voids take more mortar mixture;
- type of brick - hyper-pressed and face silicate absorbs mortar less than ceramic or ordinary silicate with a rough surface;
- the thickness of the wall.
The average consumption of mortar per 1 m3 of brickwork with a standard joint thickness (12 mm) is approximately 0.23 m3. More accurate information is given in Table 1.
Consumption of cement for brickwork
The composition of the mixture for the construction of a brick wall varies depending on the quality of the initial components, weather conditions, and the number of storeys of the building. To mix the ingredients correctly, you need to know: a 10-liter bucket holds 14 kg of cement or 12 kg of sand.
- The cement slurry is flexible in terms of proportions. It is characterized by the degree of strength: the less it is, the lower the required grade of cement and the lower its percentage (1 part per 2.5 - 6 parts of sand). For cement M400 is characterized by a ratio of 1.3, for M500 - 1. 4. The volume of water (on average 0.5 - 0.7 liters per 1 kg of cement) depends on the desired density of the mixture, the type of brick, air temperature - in the summer heat, the solution should be more fluid. To increase its plasticity, experienced bricklayers add a little washing powder or dishwashing liquid to the water. For 1 cube of the finished solution 1.4, 410 kg of M500 cement and 1.14 m3 of sand are needed. Knowing that 0.24 m3 of mortar is consumed per 1 cubic meter of an ordinary wall in one brick from a silicate block 250 x 120 x 65, the consumption of cement per cube of brickwork is determined as follows: 0.24 x 410 = 98 kg. Accordingly, when using cement M400 (proportion 1. 3) a cubic meter of the mixture contains 490 kg of cement, and 117 kg is consumed per 1 m3 of masonry.
- The cement-lime mortar is suitable for use within 5 hours, and in summer at +25 o - no more than an hour, therefore, a calculation is also desirable for it. 1 cubic meter of the mixture requires 190 kg of cement M400 - M500, 1.5 m3 of sand, 106 kg of hydrated lime and 475 liters of water. For a cubic meter of masonry, an average of 46 kg of cement will be needed.
Cement consumption for brickwork during cladding
In this case, the developer is interested in how much the binder mixture will be consumed per square meter of the wall. It depends on the water absorption of the building material, the season of work, the voidness and porosity of the blocks. The norms are laid down in SNiP 82-02-95, but the real numbers are always higher, so you should buy a ready-made mortar or cement with a margin.
To save on consumables, 2 factors should be noted:
- the larger the dimensions of the brick, the less mortar will go;
- the higher the% of voids and pores, the higher the consumption of the mixture will be.
From this point of view, it is optimal to use ceramic or silicate double bricks of sufficient strength grade. This choice will allow you to achieve savings of 20% mortar mixture. Table 2 shows comparative data on the consumption of mortar per square meter of the wall.
How do I use the table?
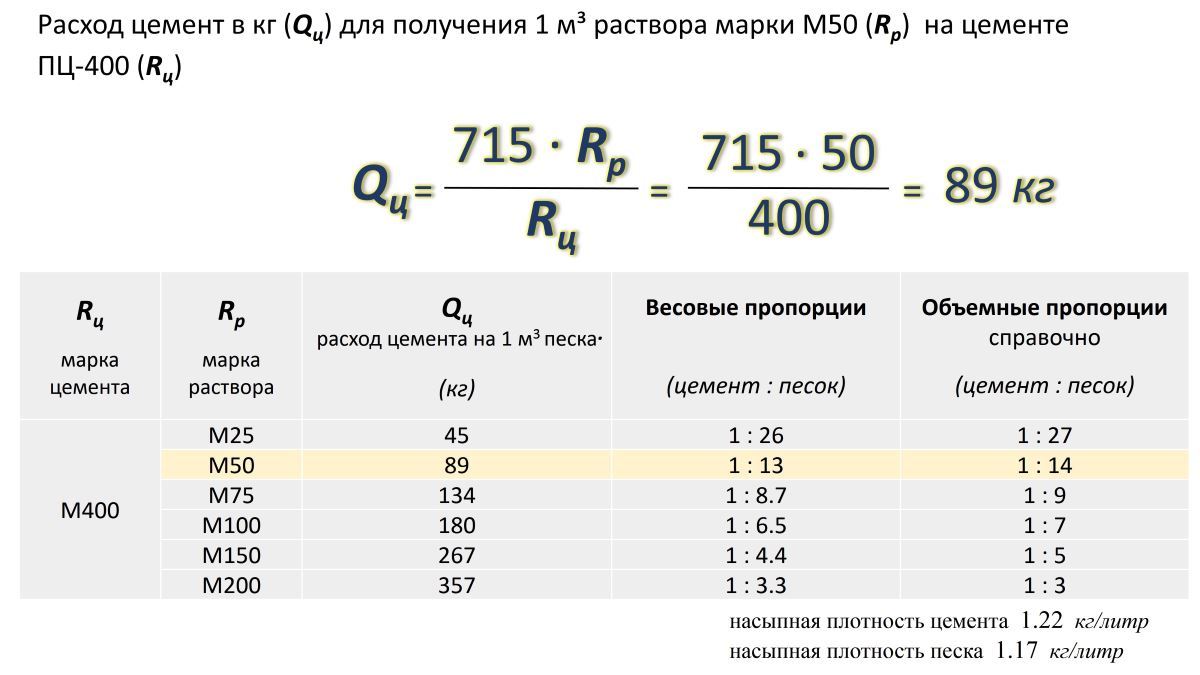
Since when preparing concrete and masonry mortars, it is generally accepted to operate with the volumetric characteristic "1 m3", we calculate (reduced to 1 m3) the amount of cement for preparing 1 m3 of mortar with the ratio "cement-sand" - 1: 3 and 1: 4.
In practical calculations of the amount of cement, novice developers make a gross mistake.They believe that if it is required to prepare a solution from 1 part of cement and 3 parts of sand, then the weight of 1 m3 should be divided by 4 and thus the number of components should be obtained. In fact, this is not the case. Since the particles of cement are much smaller than grains of sand, it fills the voids between grains of sand, so more cement is needed. For any calculation of the components of cement and sand, we will take the following assumptions:
- One "cube" - 1000 liters;
- The volume of a bag of cement weighing 50 kg - 36 liters;
- The weight of one "liter" of cement is 50/36 = 1.4 kilograms;
Option of the ratio "cement: sand" 1: 3
To prepare the solution, you will need 1 m3 of sand and 1.3 m3 of cement, which corresponds to 333 liters of cement. 333x1.4 = 466 kilograms of cement will be required to mix 1 m3 of masonry mortar.
Option of the ratio "cement: sand": 1: 4
To prepare the solution, 1 m3 of sand and 1.4 m3 of cement are required, which corresponds to 250 liters of cement. 250x1.4 = 350 kg of binder is required to mix 1 m3 of masonry mortar.
Using the calculated data and the data in the table, as an example, we calculate the amount of cement required to mix the amount of masonry mortar per cubic meter of brickwork from a single brick of normal format with a thickness of "1.5 bricks".
For 1 m3 of the specified masonry, you will need to spend 0.234 m3 of mortar (table). Therefore, the amount of cement mortar with a ratio of 1: 3 is 466x0.234 = 109 kg; for a ratio of 1: 4 - 350x0.234 = 82 kg.
Using the given technology and tabular data, you can calculate the required amount of cement for masonry mortars of any ratio of components - just substitute your data.
You can also use a calculator to calculate the right amount of bricks for your house, garage or utility block.
Consumption of mortar for 1m² of masonry
Construction work using a cement-based mortar involves the advance purchase of all the components that make up the mixture.
Brick laying scheme.
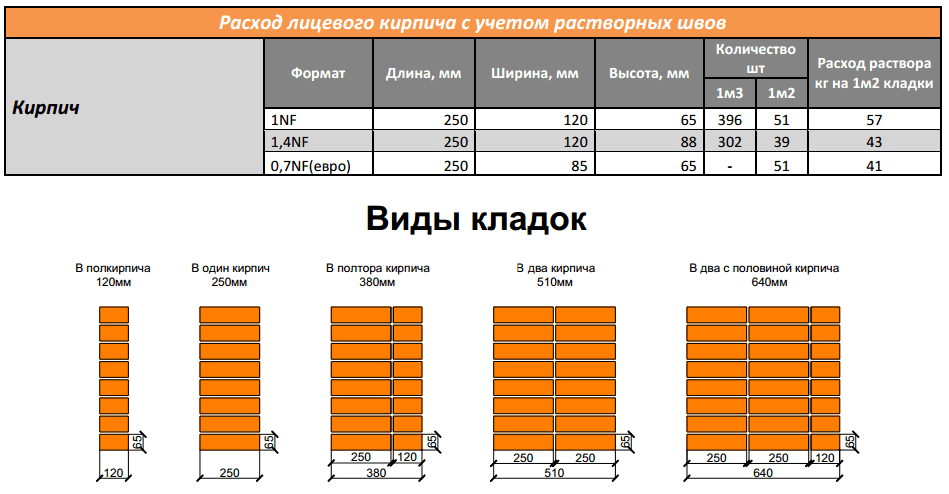
Particular attention is paid to such an indicator as the consumption of cement, and its preparation, since this material cannot be procured for future use due to increased hygroscopicity and, as a result, a rapid transition to a state of unusability. First of all, you need to decide on the brand of material that corresponds to your type of work, since certain types of mortars are required for certain purposes (cement-sand, slag-cement, concrete and others)
The type of brick used is determined according to the project. For example, a plastic pressed ceramic product is popular for masonry walls due to its frost and moisture resistance. Hollow ceramic bricks have low thermal conductivity, however, they can reduce the weight of the structure by 25% and the thickness of the walls by 20-25%. Ceramic material cannot be used for ovens, chimneys and chimneys. When laying the foundation, solid pressed bricks or concrete heavy blocks are used, and for the outer walls - silicate hollow bricks or lightweight concrete blocks
First of all, you need to decide on the brand of material that corresponds to your type of work, since certain types of mortars are required for certain purposes (cement-sand, slag-cement, concrete and others). The type of brick used is determined according to the project. For example, a plastic pressed ceramic product is popular for masonry walls due to its frost and moisture resistance. Hollow ceramic bricks have low thermal conductivity, however, they can reduce the weight of the structure by 25% and the thickness of the walls by 20-25%. Ceramic material cannot be used for ovens, chimneys and chimneys. When laying the foundation, solid pressed bricks or concrete heavy blocks are used, and for the outer walls - silicate hollow bricks or lightweight concrete blocks.
The strength of the structure directly depends on the brand.For example, if you make a floor screed, you need a mixture from M200 to M300, for laying walls made of bricks or foam blocks it is best to use a mixture with a hardness of M50 to M100, for foam blocks - from M50 to M100, and making a foundation requires strength from M200 to M300.
Scheme of a masonry masonry using a solution.
After the grade of material, mortar and type of work are determined, it is necessary to select a suitable grade of cement. When making a cement-sand mixture, it is necessary that the grade be two to three times higher than the grade of the solution. For example, for the M200 composition, M400 or M500 cement will be required, and for concrete blocks it is necessary that its grade is six to eight times higher than the grade of the mixture.
Of course, the consumption of materials depends on many different factors, for example, such as: the size of the structure, the thickness of the seams between the rows, the size of the block, and many others. However, the average values of consumption indicators per 1m2 can be calculated using the tables below.