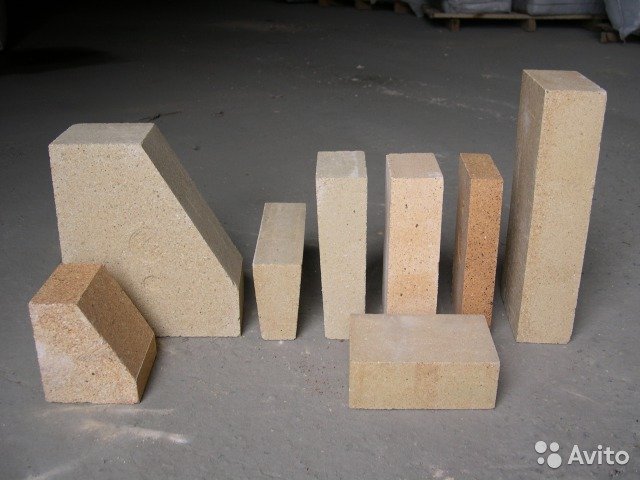
Refractory bricks
Ordinary building bricks, depending on the raw materials used in its production, are divided into:
- Ceramic - which is made from clay.
- Silicate - it uses a mixture of sand and lime, other additives.
But, these products of brick production can not be used everywhere. For example, with high-temperature technologies (up to 1800 degrees C) in the metallurgical industry, in the glassmaking (glassmaking) industries, the same ordinary clay brick (in common people, "red") will not withstand high temperatures for a long time.
With extreme heat and prolonged exposure to high temperatures, it will begin to melt, and then, cooling down, it will crumble. Although, as a masonry and finishing material, it is widely used in indoor fireplaces and stoves of baths, saunas, residential premises, where the temperature is not higher than 800 degrees C.
Variety of refractory structures and elements
Types of fire resistant building materials
In furnaces where glass is blown, porcelain is fired, in blast furnaces where steel is melted, a more resistant, fire-resistant material is used in the furnace core. Refractory bricks in accordance with GOST 8691 - 73 can withstand heat with a temperature of more than 1000 degrees C.
Refractories are produced with different properties and characteristics for different applications.
Fire-resistant material according to its physics - chemical composition, production methods and methods, temperature range is divided into four classes:
Composition and fields of application of refractories
- Quartz brick - consists of quartz (sandstone), with small additions of clay. As a result of firing, it acquires a cavity-free, full-bodied structure. In fireboxes, it is used in places where it has contact only with an open flame (for example, reflective arches in fireboxes, fireplaces, stoves). Stores accumulated heat well.
Important to remember! Quartz refractories should not have contact with alkalis, lime, iron oxides, which destroy it
- Carbonaceous - in a simplified form, it is compressed graphite or coke. It has the highest strength and fire resistance characteristics. It is used in highly specialized areas of construction (for example, in the construction of blast furnace structures).
- The main one - includes a lime-magnesian mass in its composition, which makes it possible to use this refractory for the production of Bessemer steel from phosphorous ores.
- Alumina - from its very name it is clear that in its basis clay makes up most of the structural component (about 70%). Therefore, it better (in contrast to quartz refractories) resists the destructive action of alkalis (lime). Easily tolerates rapid temperature changes.
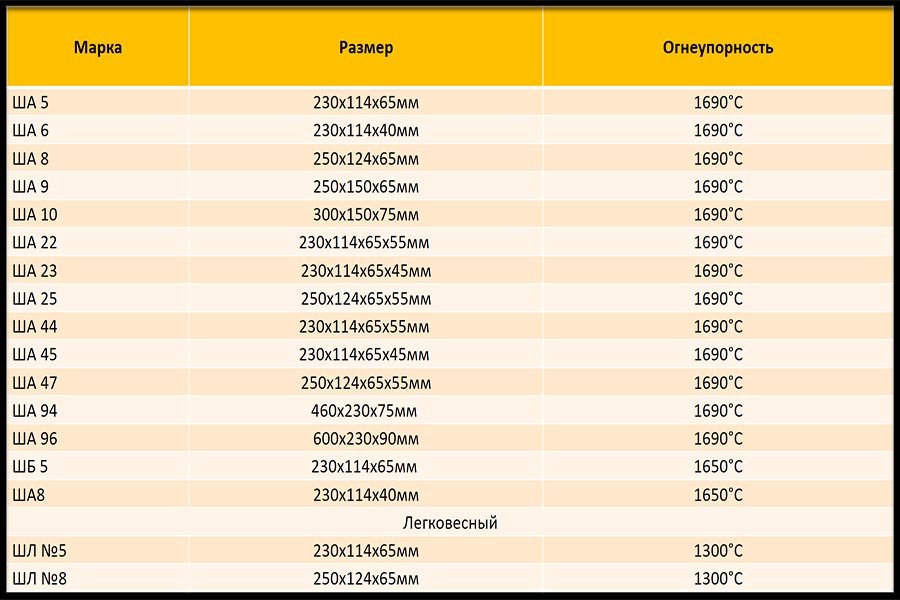
It is easy to manufacture and is less expensive than other flame retardant materials. It is widely used in the cores of furnaces, where the temperature is not higher than 1300 degrees C. Bricks of this type are also called "fireclay". It is marked with the letter "Ш", and the numbers following it carry information about its dimensions.
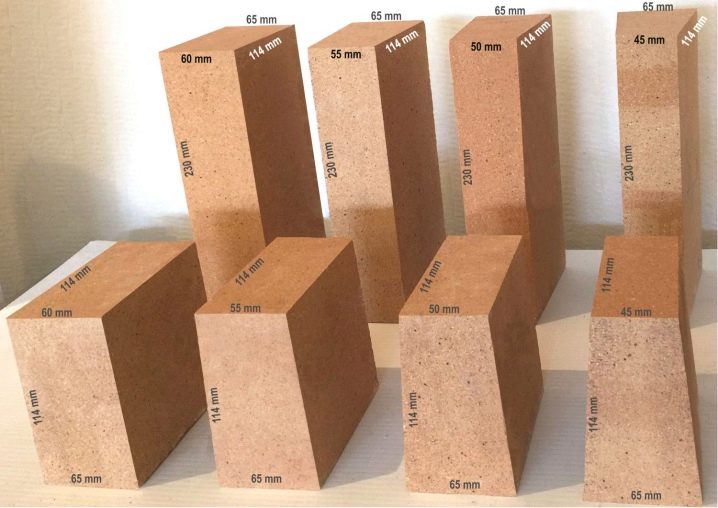
Designation, shapes and sizes of fireclay products (GOST 390-96, GOST 8691-73)
The size and shape of the refractory brick can vary. According to GOST alone, there can be more than a hundred such standard sizes.
Therefore, we will present only the most used products in private furnace construction. The rest can be found in the standards themselves.
The brand of building material depends on the maximum temperature of its application during operation.
Table: Limiting temperatures for the use of fireclay products
Refractory grade
Tables: Wedge chamotte
Thus, chamotte products for standardization are divided into:
- wedge or straight (normal sizes),
- large or small formats;
- shaped large-block, especially complex, complex, simple;
- special fireclay products for industrial and laboratory use.
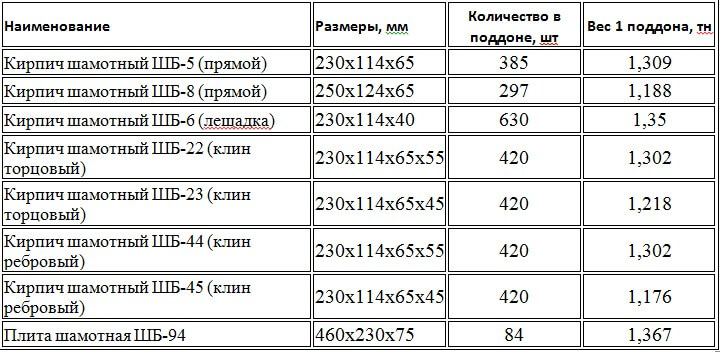
Weight characteristics of refractory (fireclay) brick GOST 390 - 96
The weight of refractory bricks depends on the raw materials from which it is made, on its shape and size. How much does the fireclay brick of the most popular brand (ША, ШБ) weigh, and its packaging (cages) without taking into account the mass of the pallet 30 - 40 (kg), see the table below
Views
Chamotte bricks differ for a number of reasons:
- by molding;
- by the type of already finished product;
- by porosity.

Depending on the variant of the formation of raw materials, there are several types of fireclay bricks:
- semi-dry molded;
- molten;
- thermoplastic extruded;
- cast;
- hot pressed.

By the type of brick, there are shaped, figured, wedge, as well as arched and trapezoidal types. The most popular is considered to be chamotte in the shape of a rectangle, but when installing arched structures, it is better to use wedge material. Depending on the level of porosity, there are:
- high-density brick - with a grain size not higher than 3%;
- high-density - in this case, the graininess is differentiated from 3 to 10%;
- dense - with a porosity parameter from 10 to 16%;
- refractory compacted - with a porosity parameter of about 16-20%;
- medium-dense - differs in grain size at the level of 20-30%;
- highly porous - in this case, the grain size corresponds to 30-45%;
- lightweight - with increased grain size of 45-85%;
- ultra-lightweight - in this case, the graininess exceeds 85%.
Separately, it is necessary to dwell on such a variant of fireclay bricks as quite popular lightweight products. These bricks are usually used instead of insulation. They consist of special oily clay, as well as peat, shavings or sawdust and some other organic components. During heat treatment, they completely burn out, leaving pores of various sizes in their place. As a result of this technology, a porous material with high energy efficiency is obtained.

Lightweight bricks are made entirely of organic substances, therefore, they are considered environmentally friendly, they do not emit harmful and toxic substances, and therefore are suitable for use in residential premises. By the way, the special structure does not affect the heat resistance of the material in any way: lightweight bricks can withstand even extremely high impacts up to 1800 ° C.

Lightweight bricks are generally used to form a layer of thermal insulation when equipping electric furnaces, as well as evaporators and heaters. Quite often, it is purchased for lining heat exchange boilers and steam pipelines. At the same time, such protection can significantly reduce heat losses (by 25-75%) and thereby reduce the dimensions of heating devices. Experts note that if you take fireclay materials for lining furnaces, then the heating and cooling period will decrease by 5 times, while all heating costs will be reduced by 10-15% in continuously functioning furnaces and by 45% in those that work from time to time ...

Manufacturing technology
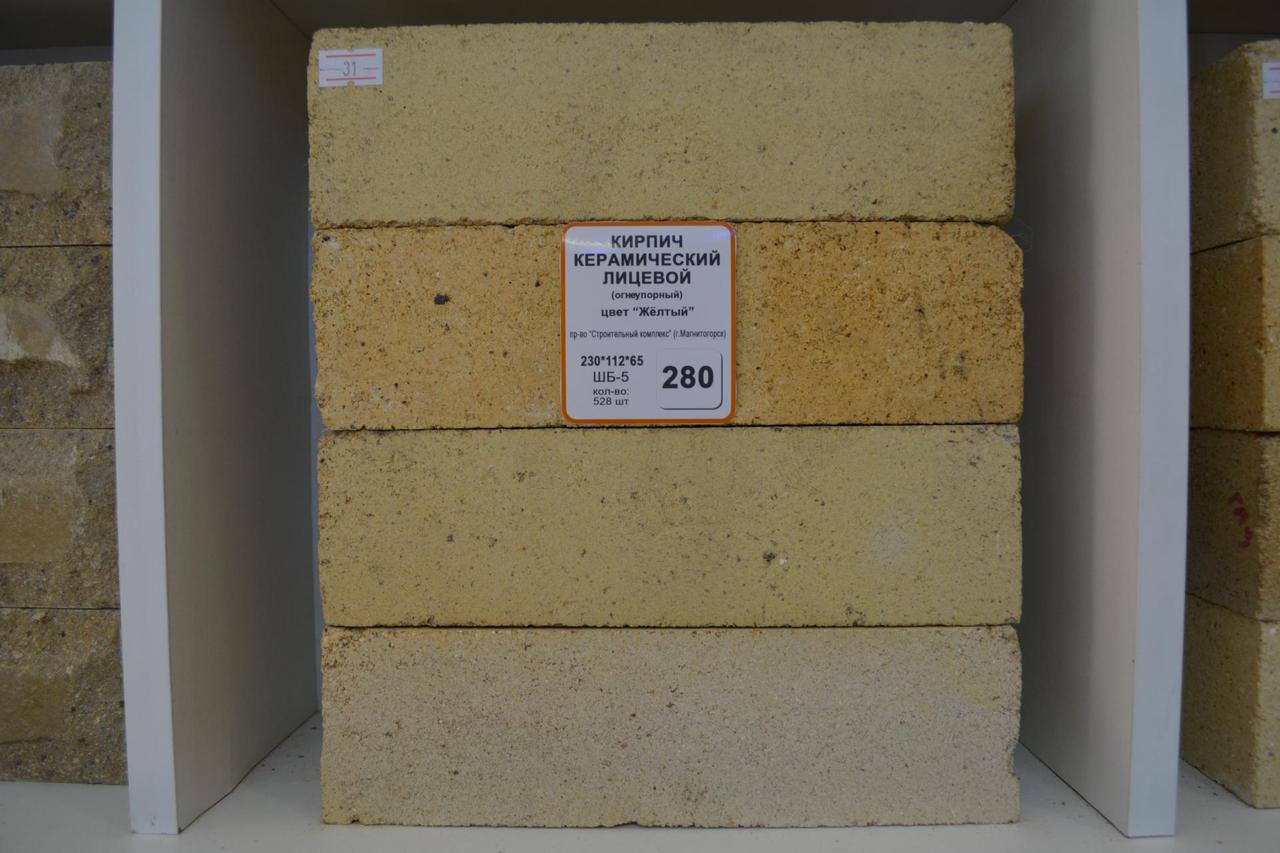
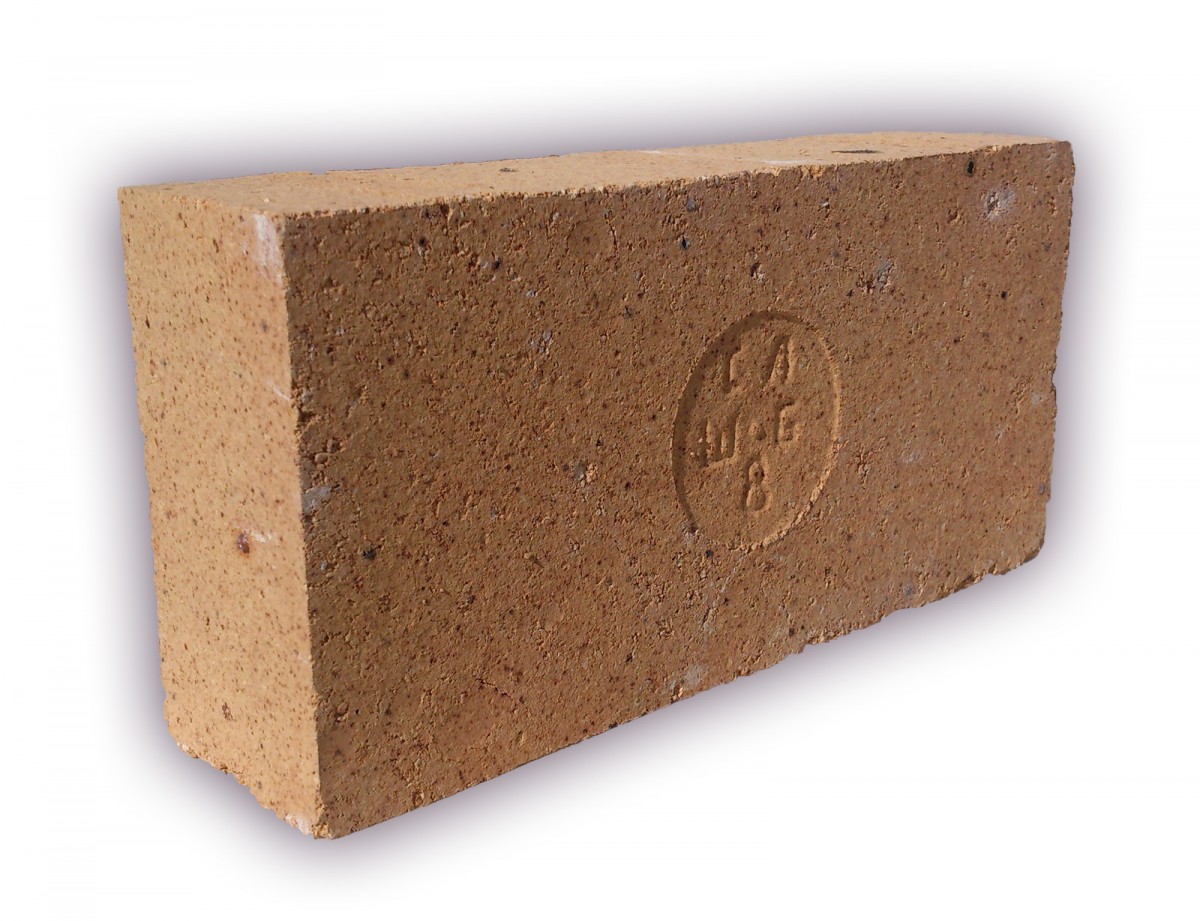
Among all types of bricks, fireclay is the most durable and resistant to strong heat and temperature extremes. The material owes these qualities to its composition and specific manufacturing technology, which consists in firing a clay mixture with the addition of chamotte powder. As a result of exposure to high temperatures, the brick acquires a characteristic gray-brown or yellowish color, by which it is easy to distinguish it from other varieties.
The composition of fireclay bricks determines its performance characteristics. Depending on the proportions of clay and powder, several types of material are distinguished.A colossal role is played by the method of processing, or rather, the time of baking the bricks. So, if you overexpose it in an oven, then a strong glassy film forms on the surface, which will make the brick incredibly strong, but less refractory. If it is not fired for a long time, then such a material will absorb and retain moisture well, but it will completely lose its strength. Only if you adhere to the "golden mean", you can make a brick, ideal for laying stoves and fireplaces.

So that the products do not crack during the firing process, a certain amount of special refractory clay - chamotte - is added to them. Sometimes coke powder, graphite or coarse quartz are put instead. The result is different types of bricks with individual characteristics. Moreover, the result depends not only on the raw material and the processing method, but also on the characteristics of the fuel for burning and the resulting ash.
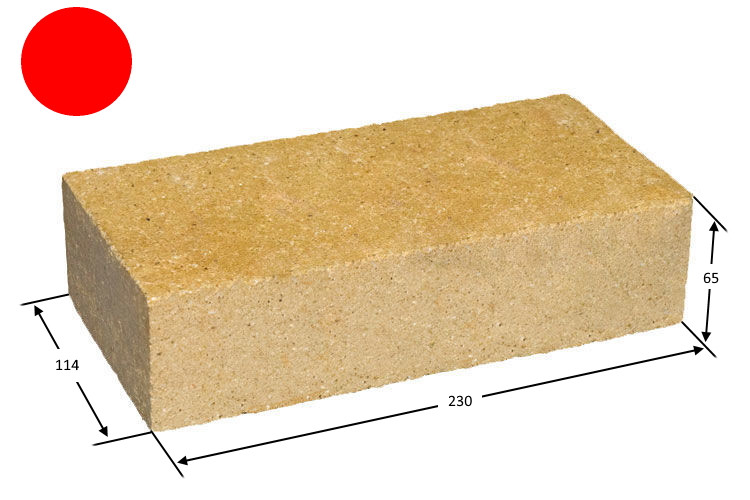
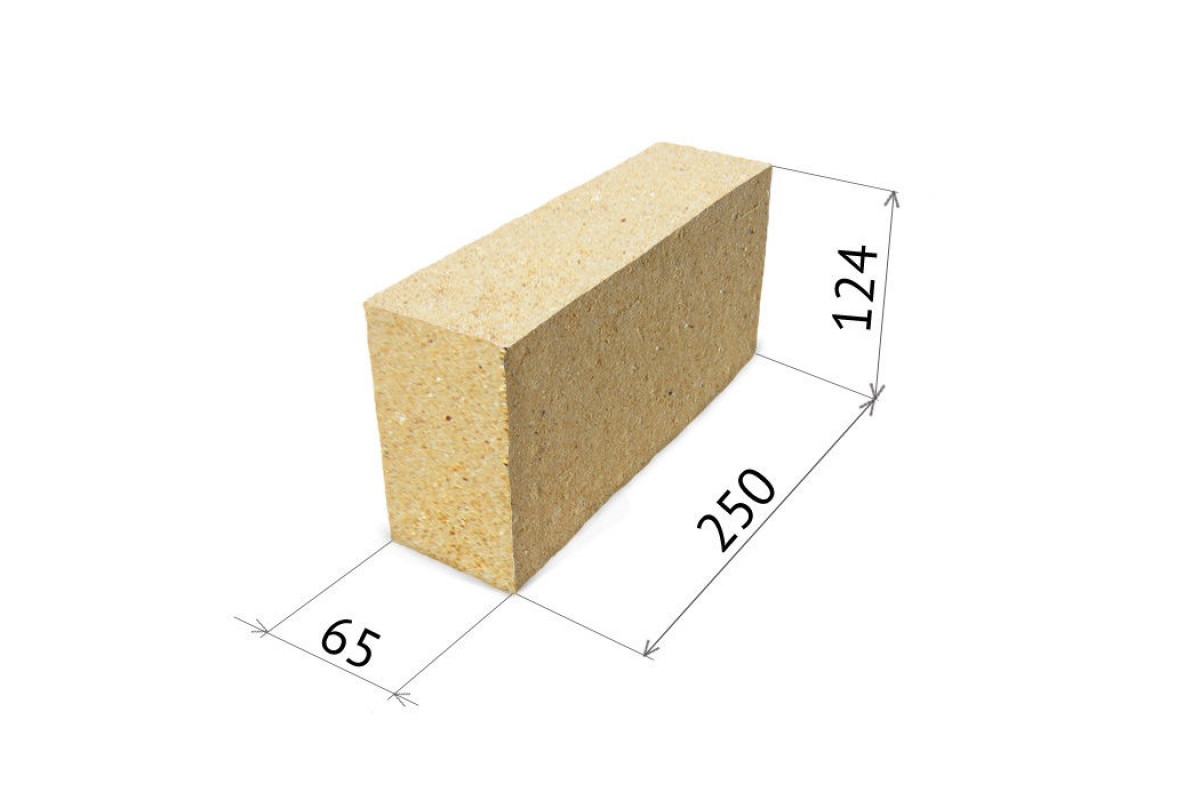
The production of fireclay bricks is carried out in accordance with GOST 390-69, and depending on what it will be used for, the production technology, weight and dimensions of the material differ. So, the mass of fireclay bricks can vary from 2.5 kg to 6 kg. Differences also lie in the density, porosity and composition of the bricks. There are uniform size standards that most manufacturers adhere to: 230x113x65 mm, 250x123x65 mm and 300x150x65. These are the most convenient dimensions for construction and transportation.

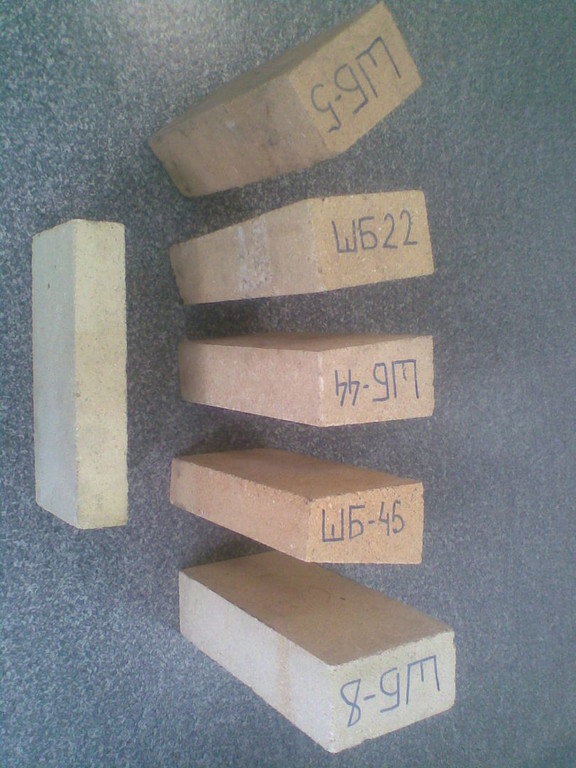
The most frequently used brands of fireclay bricks are: ШБ №5, ШБ №9, ШБ №22, ШБ №44, ШБ №47. The letters in front of the number can be different, for example, PB, SHB, SHUS, SHL and others, but for domestic use it is better to choose bricks marked "ШБ". The first letter indicates that the brick is chamotte, the second means which class of fire resistance it belongs to, and the number indicates the aspect ratio.
Lightweight brick
Lightweight fireclay brick has established itself as a good insulation. It contains peat, oily clay, sawdust and other organic components. During the firing process, they burn out, leaving behind pores of various sizes. This manufacturing technology makes it possible to obtain a very lightweight porous material with high energy-efficient characteristics.
Since lightweight bricks are made entirely from organic matter, they are environmentally friendly materials that cannot harm human health or the environment. At the same time, high refractoriness remains - the brick can withstand extremely high temperatures up to 1800 ° C.

In shape, lightweight bricks can be rectangular or wedge-shaped. In order for the material to fully retain all its operational properties, it must have the correct structure with smooth edges and perfectly right angles.
There are several types of lightweight bricks, depending on the scope of application:
- trapezoidal;
- shaped;
- straight;
- rib wedge;
- end wedge.
The marking of lightweight bricks is indicated by the letters SHL and SHTL (T is the presence of talc in the composition). It is usually used to create an insulating layer in the construction of electric furnaces, heaters, evaporators, steam pipelines, heat exchange boilers, etc. Such protection can significantly reduce heat loss by 20-70%, reduce the mass of thermal devices and their dimensions. If you buy fireclay bricks for building or lining a furnace, the heating and cooling time will be reduced by 5 times, and fuel costs will decrease by 10% in continuously operating furnaces and by as much as 45% in periodically operating ones.
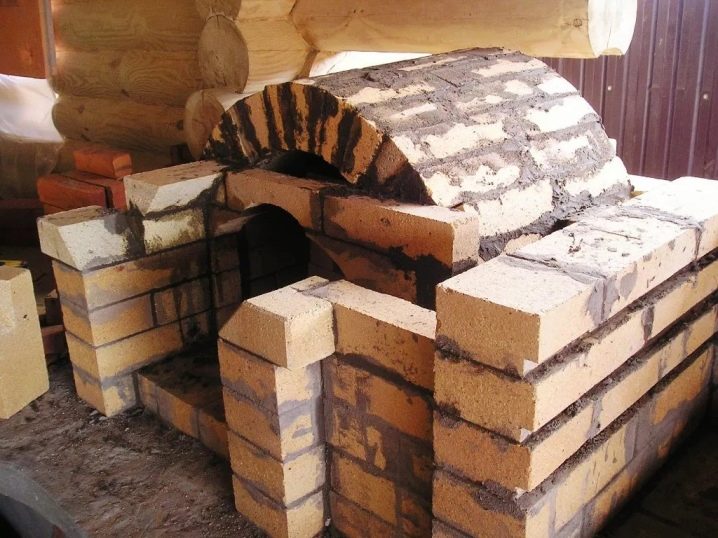
Features of fireclay brick masonry
The main feature is that the usual cement mortar for laying this type of brick is not used, since it does not have sufficient heat resistance.
Refractory brick masonry mortar
In hardware stores, you can purchase a ready-made composition that has all the necessary properties, namely:
- glue for laying fireclay blocks has sufficient heat resistance;
- after drying, the properties of the material are similar to the parameters of the brick itself;
- the material has good adhesion to fireclay blocks.
If for some reason it was not possible to buy a ready-made composition, you can make it yourself, for this you will need:
- finely ground fire-resistant clay;
- fireclay sand;
- purified water.
The solution is prepared in the following sequence:
- Fire-resistant clay is filled with water for 24 - 72 hours and mixed periodically.
- The settled clay is wiped with a mesh with a cell of no more than 3x3 mm.
- The sand is sieved and added to the clay in the ratio of 2 parts of sand to one part of clay. The resulting composition is thoroughly mixed.
- Water is added to the resulting mixture and mixed again. The ready-to-use solution should have the consistency of sour cream.
- You can improve the quality of the mixture by adding 3% water glass or salt.
Features of masonry heat-resistant blocks
There are a number of rules, the observance of which will ensure high-quality and durable masonry:
- the starting row is laid "dry", without the use of an adhesive. When laying subsequent rows, an adhesive mixture is applied to the bottom and end surfaces, so that the thickness of the finished joint after laying does not exceed 5 mm;
- as soon as the adjustment of the brick is completed, the excess mortar should be removed immediately;
- the strength of the structure is ensured by stacking blocks with overlapping (staggered);
- seams must be sealed flush with the side of the blocks. Depressions and unfilled seams will inevitably lead to cracks;
- when laying corners and decorative elements, the blocks are stacked with the front side out;
- cutting fireclay bricks should be carried out with a grinder equipped with a diamond saw blade; using a trowel or pickaxe to correct the size is highly undesirable;
- the finished structure does not need any additional processing with special compounds, primers, etc.
Strict adherence to these simple rules will ensure a long service life and reliability of the structure.
Since structures operating in conditions of high and extreme temperatures are classified as particularly critical, the correct choice of material is of particular importance. The use of fireclay bricks provides high heat resistance, resistance to mechanical stress and sufficient fire safety of the structure. In addition, one should not forget that the use of ordinary ceramic or silicate bricks when laying heat-resistant elements will not only not give the desired results, but also significantly increase the risk of fire.
Properties and technical characteristics of fireclay bricks
When choosing one or another modification of fireclay refractory blocks for the construction of a specific structure, the following characteristics must be taken into account:
|
Indicators |
Unit. |
Meaning |
Notes (edit) |
|
Specific gravity |
kg / m3 |
1500 — 1900 |
Used when calculating the static load on a supporting surface or structure |
|
Working temperature range |
WITH |
1100 — 1800 |
It is taken into account when assessing the temperature modes of operation and determining the average service life until the first repair. |
|
Thermal conductivity |
W / m * C |
0,5 – 0,6 |
Determines the amount of heat energy passing through the fireclay masonry. Necessary when assessing the temperature effect on protected elements |
|
Strength |
units |
75 — 250 |
Helps determine static compressive loads |
|
Freezing / thawing |
cycles |
50 |
Affects the duration of operation with amplitude fluctuations in temperature |
|
Porosity |
% |
up to 85 |
This characteristic affects the specific gravity of the material, its thermal conductivity and strength. |
The following are the different types of porosity in fireclay bricks:
|
Name |
Porosity,% |
|
Extra dense blocks |
3 |
|
High density blocks |
3 — 10 |
|
Dense blocks |
10 — 16 |
|
Condensed blocks |
16 — 20 |
|
Medium Density Blocks |
20 — 30 |
|
Blocks with increased porosity |
30 — 45 |
|
Lightweight blocks |
45 — 85 |
Application area
Fireclay bricks are widely used in industry, and are also often used for the construction of various types of fuel chambers and process boilers. It is in them that coal is burned.




The material is also common in everyday life, here it found its application for the construction of fireplace inserts, kitchen hearths and wood-burning stoves. For chimneys, experts also recommend taking precisely fire-resistant chamotte blocks, they can withstand not only hot air, but also adverse types of atmospheric influences.




There are a lot of rumors and myths around the features of the material. It is believed that when heated, it begins to emit harmful components and even radiation. Experts completely refute all these theories. Moreover, if the last statement is still in principle possible in theory (if the brick is made of clay mined in an area exposed to radiation contamination), then the first is impossible to believe. Most likely, the reason for the appearance of such rumors is the following: some types of fire-resistant materials, indeed, when exposed to hot air, begin to emit toxic substances. However, this does not apply to the fireclay block, since it was originally created as a material for domestic use.
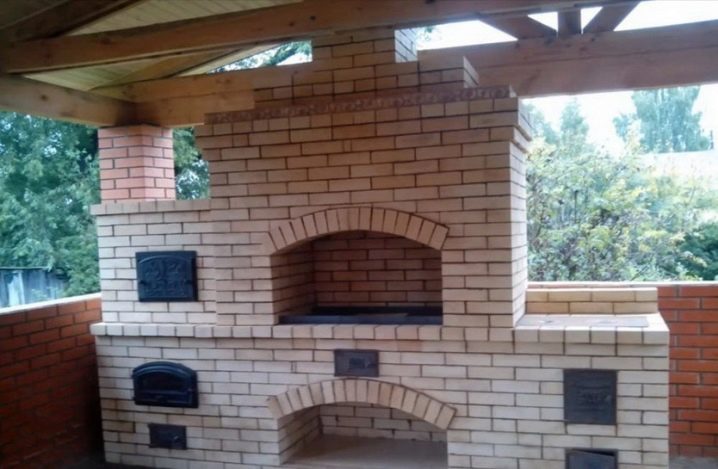

Application of fireclay bricks
Fireclay bricks withstand contact with alkalis, such as lime, better than other refractory products. Therefore, it can be used in various industrial installations where combustion products contain active chemical substances (masonry and lining of boilers, fuel chambers, blast furnaces, etc.).
The solution used is of particular importance for imparting resistance to high temperatures to thermal aggregates. Usually, the same components are used for its preparation as in the production of the brick itself. When working with brands ШБ-5 or ШБ-8, refractory clay is used, to which crushed brick is added. Such a composition is usually called "chamotte clay" or mortar.
 This is how dry mortar looks like.
This is how dry mortar looks like.
At particularly high temperatures, a thickness of less than 1 mm may be required. Such work requires a special quality of the preparation of the mixture and high qualifications of the performers. In addition, the consumption and cost of the material significantly increases (it is necessary to use only special grades with increased fire resistance, the ShB-8 or ShB-5 brick will not withstand the load), and the total weight of the finished product also increases.
With all its advantages, fireclay brick also has a number of disadvantages that limit its use:
- Hygroscopicity. It absorbs moisture well, while the weight increases and the strength decreases when heated;
- Instability to freezing. Usually, fireclay bricks of the brands ШБ-5, ШБ-45, ШБ-94, ШБ-8 are used for laying household stoves, which often crumbles with irregular use and periodic cooling of the stove;
- High density. The material is difficult to cut if necessary to ensure the required dimensions;
- Relatively high price, long heating time, the need to prepare a special solution.
Summing up, we note that the use of fireclay bricks is optimal for facing areas exposed to strong thermal effects. At the same time, its use as the main building material for household stoves is constrained by the presence of a number of disadvantages caused by the technological features of production.
Types, forms, brands and purpose

According to the method of forming brick blocks, types of fireclay stone are cast from slip, made by a semi-dry or plastic method, fused, hot-pressed and thermoplastic-pressed. According to the geometric shape, such subgroups of fireclay oven bricks are distinguished:
- Straight - rectangular with smooth edges.
- Trapezoidal.
- Wedge-shaped brick, it is also arched or arched:
- wedge rib;
- wedge end.
- Shaped - has a wide selection of shapes, allows you to erect structures of complex construction.
- Suspended - used for industrial furnaces.
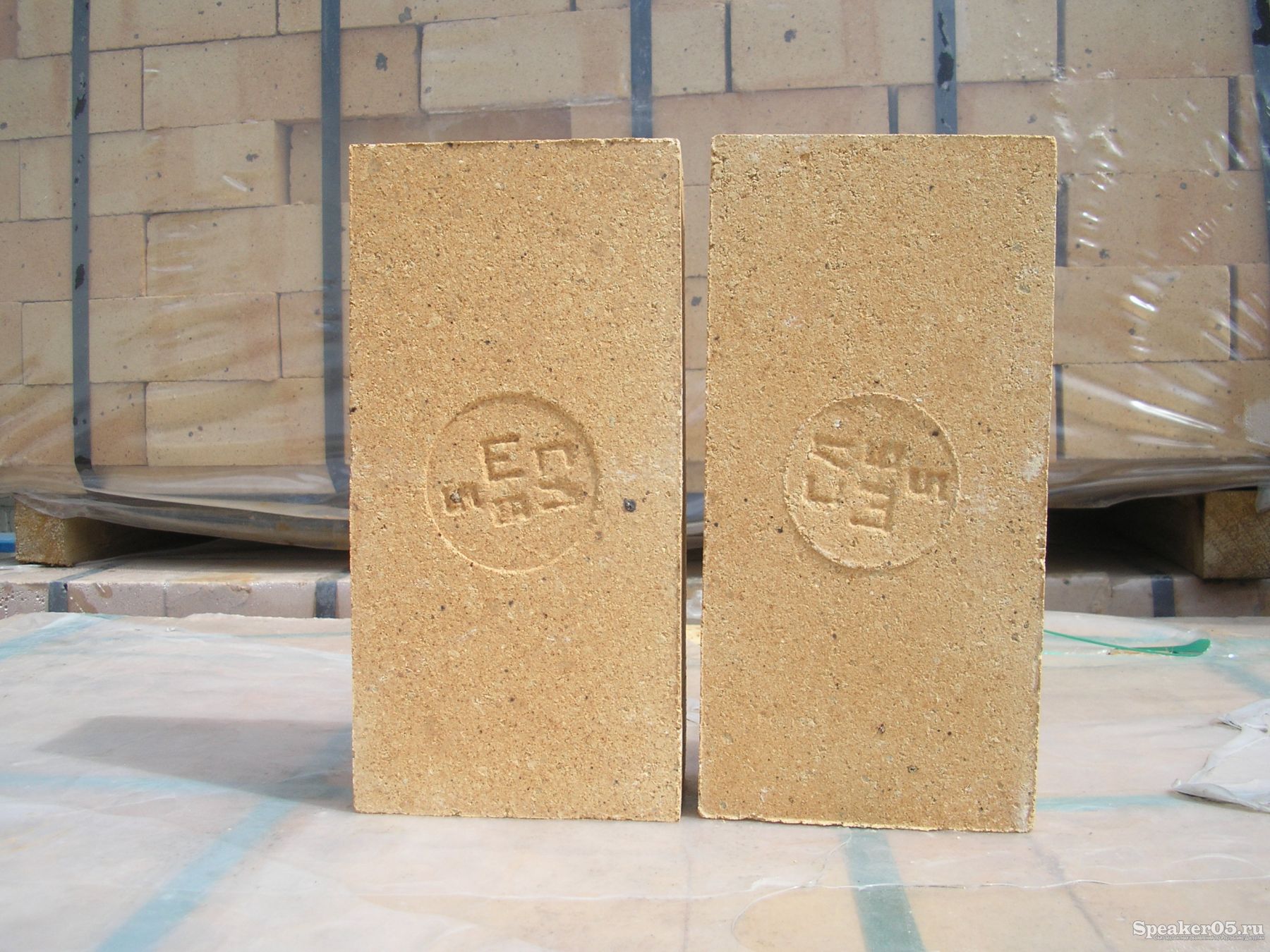
The kiln brick has a wide range of applications and, according to GOST, there is a marking on each block. The first capital letters are the designation of the material in the composition and the fire resistance class. After them there is a number that indicates the block size. For example, brick ША-5 contains 30% aluminum oxides, and the size is 230 × 114 × 65 mm. Brick ША-8 is the same in composition, the only difference is in size - 250 × 124 × 65 mm. After the designation of the dimensions, the abbreviation of the manufacturer is put.
Grades of bricks used in private construction
ША, ШБ - have a fire resistance of +1690 degrees Celsius and contain 30% aluminum oxide in the ША version, in ШБ - +1350 degrees and 28%, respectively, are quite dense. When laying the vaults of furnaces in boiler rooms, brick ШБ-8 (straight) is used for the inner lining of the furnace pipes. The SHA-10 brand has the same properties, but the size of the stone is much larger: 300 × 150 × 75, which facilitates construction on an industrial scale. Laying arches, tandoor and rounded structures will help wedge brick SHA-25 (end), SHA-44 and SHA-47 - ribbed. It has the same characteristics indicated in the marking, only differs in size.

PB and PV - semi-acid fireclay brick (PB (PV) -5 marking) with a high content of silicon oxide and with a smaller amount of aluminum oxide, which means it is slightly less durable in compression and has a lower refractoriness. Withstands a maximum temperature of 1350 degrees, full-bodied, with less ideal geometry than the SHA brand. It may well replace the brand in the lining of pipes, the construction of fireplaces, barbecues, stoves. The price on the construction market for this refractory is cheaper than the SHA brick grade.
ШЛ - lightweight fireclay block with refractoriness from +1100 to +1300 degrees. It also has a large number of shapes and sizes, a low coefficient of linear expansion. If on the marking (ШЛ-0) the numbers from 0 to 1 mean that the product is ultra-lightweight - weighing up to 1 kg. An index of 1.0 and higher indicates a lightweight stone - the weight range is 1.7-2.2 kg.
Industrial
ШВ and ШУС - fireclay material that can withstand a maximum of +1250 degrees. Used only in enterprises. The blocks are laying gas-fired shafts at heat stations, steam generators. They have a high price, but a small range. SHKU and SHK - fireclay ladle products and equipment for coke production. ШЦУ - end double-sided products, with refractoriness up to +1710 degrees. Purpose - laying of protective cladding in rotating heating facilities. Broadband - used for blast furnaces. Melting point +1750 degrees.
How to choose?
Fireclay brick is quite expensive, so you need to take it seriously. If you buy low-quality material, then you risk simply losing all your money.
If you find yourself in a hardware store with a good reputation, this does not at all guarantee that you will be offered an ideal product without external defects, therefore, when choosing, pay attention to all important details.
- The basic indicator of product quality is its color, it must certainly be straw yellow. If you have lighter, almost white blocks in front of you, most likely you see in front of you a brick that has not been fired in the oven, which absorbs moisture well and is subject to destruction from the inside. And heat accumulates in it much worse, which means that functionality will be a big question.
- The brick should have a fairly even surface and a perfect shape. Many people believe that these requirements are dictated by the aesthetic component of the project, but this is far from the case. The fact is that when arranging a fireplace or stove, the inner surface must be smooth, any relief obtained as a result of the preservation of the remains of the solution or the swelling of the brick leads to the creation of barriers to the flow of heated gas.If the defect is not eliminated, then an uneven distribution of heat begins, as a result, the level of traction will be insufficient, and the heat transfer will drop dramatically.
- The kiln masonry is distinguished by a very strong joining of fireclay bricks, a small number of seams and a tight fit. If the material used has cracks, chips and other defects, then it is impossible to ensure reliable adhesion. In this regard, when buying bricks, be sure to choose them from the same batch. Otherwise, you risk getting a completely heterogeneous material, which can have a most deplorable effect on the operational characteristics of your future thermal element.