Varieties
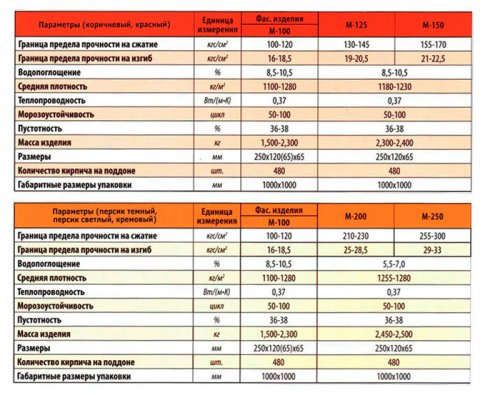
The popularity and huge demand for double brick is due to its high performance. It can differ in texture, size, number of slots and shapes of voids. There are two types of blocks depending on the raw materials used for manufacturing.
Silicate
Their main feature is that the production is carried out from a mixture of 90% sand and 10% water. In addition, the product also contains additives that increase its quality. This is an absolutely environmentally friendly material that looks like natural stone. The process of making double silicate bricks is carried out by pressing a moistened mixture of lime and sand, after which various pigments are added to it, and sent for steam treatment. It can be either hollow, slotted or porous. By strength, silicate blocks are divided into grades from 75 to 300.
These blocks are most often used for laying out internal and external partitions. It is impossible to use silicate brick for the construction of basements and foundations of buildings, since the product is not resistant to moisture, and in the absence of a waterproofing layer, it can be subject to destruction. It is not recommended to make double silicate bricks and laying pipes, ovens. It will not withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
As for the advantages, this product has excellent sound insulation and has the correct geometric shape. Despite the large weight of such bricks, their laying is quick and easy. In terms of their density, silicate products are 1.5 times higher than ceramic ones, therefore they provide durable and high-quality masonry. In addition, silicate double blocks are 30% cheaper than other types.
Ceramic
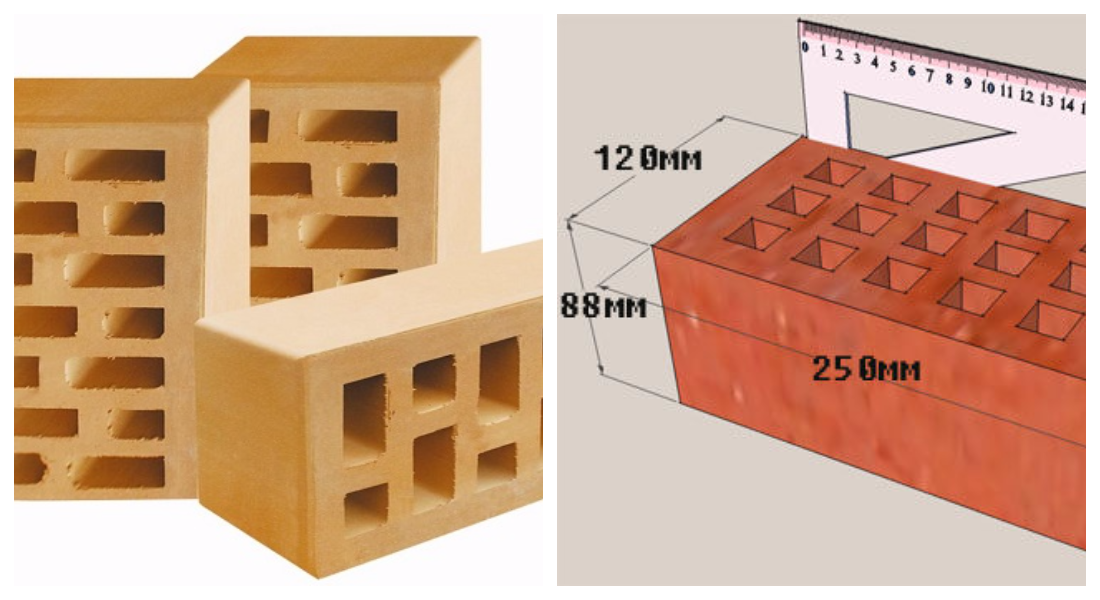
They are a modern building material that is used in almost all types of construction work. Its feature is considered to be large, which is usually 250 × 120 × 138 mm. Thanks to such non-standard dimensions, construction is accelerated, and the consumption of concrete pouring is significantly reduced. In addition, double ceramic bricks are in no way inferior in strength to conventional blocks, so it can be used when erecting load-bearing and self-supporting structures in buildings no more than 18 m high.The product is also characterized by high thermal insulation, the buildings laid out of it are always warm, and they are constantly maintained optimal microclimate.
The main advantage of double ceramic bricks is its affordable cost, while many manufacturers often make good discounts when purchasing blocks for the construction of a large object. These blocks, in addition to high quality, also have an aesthetic appearance. Usually brick is red in color, but depending on the additives, it can also acquire other shades. The product is environmentally friendly, and even with prolonged use and exposure to the external environment, it does not emit harmful substances.
These blocks are transported on pallets, where they usually fit up to 256 pieces. As for the marking, it can be different, more often everyone chooses M-150 and M-75 bricks for the construction of objects. In addition, double ceramic blocks are subdivided into solid and hollow; not only their price, but also their heat capacity depends on this parameter. Hollow bricks cannot be used for the construction of load-bearing walls, in this case only solid bricks are allowed. Despite the fact that the first is lightweight and significantly reduces the overall load on the foundation, the inherent cracks in it affect the thermal conductivity.
In addition, double bricks are subdivided into the following types.
- Private.These blocks are ideal for laying stoves, fireplaces and foundations. The only thing is that the front layout requires additional finishing.
- Facial. It is produced in clinker and hyper-pressed versions. It can be either solid or hollow bricks. Unlike ordinary blocks, face blocks are produced in curly, trapezoidal, rounded and twisted shapes. As for the color, it is dark brown, gray, red, yellow and brown.
Where are the different types of bricks used?
All of the above points form a variety of functions and configurations, which significantly expands the variability of the offer on the building materials market.
And the experience of the builders has formed a number of "rules" that everyone tries to follow so as not to lose face. For specific types of buildings, it is customary to use specific types of bricks. Therefore, you should dwell on the main points:
- For the construction of the furnace, it is customary to use ceramic, solid bricks.
- For the construction of a foundation, basement or basement, it is customary to use ceramic, solid brick. The dimensions of the bricks vary depending on the configuration of the foundation: 250x120x65 mm, 138x288x165 mm, 250x120x88 mm.
Read about the types of foundation in our article.
For the construction of internal walls and fences, it is customary to use silicate or ceramic, hollow bricks.
These "rules" should be used to avoid structural destruction.
Everything about the red brick in this video:
Features of production
Red brick can be called a strategic material, therefore the production process is strictly regulated by national standards. Today they are guided by GOST 7484-78 and GOST 530-95. According to regulatory documents, clay with a minimum content of marl and sulfates is used as raw material. Open pit mining is carried out, and brick factories are mainly located near deposits. As a rule, clay has a reddish tint, so the finished material is called red brick, although its official name is ceramic brick. During the production process, colored pigments may be added to the mass, and then the finished brick will not have the usual terracotta color. The shade of the product strongly depends on the characteristics of the raw material, therefore, bricks of different colors are obtained from the clay obtained in different deposits.
The clay mass is formed on belt presses, and the uniformity of the composition and the absence of voids is achieved through the use of vibration stands. This is followed by drying and firing. Raw bricks are dried using a chamber or tunnel method. The first option involves drying the workpieces in a room where the temperature and humidity parameters change in the required sequence. Tunnel drying method involves the passage of trolleys with raw material through zones with different microclimate. The result is almost the same.
The mass is fired in furnaces at temperatures of 950-1050C until a part of the glassy phase in the product reaches 8-10%. It is with these parameters that the brick acquires the best strength indicators. Correctly fired brick gives a ringing sound on impact and has a reddish-brown tint. If you do not burn it, then the color will be closer to mustard, and the sound upon impact will be muffled. Burnt brick can be recognized by its melted edges and dark core.
The properties of the finished brick also depend on which method of formation was chosen:
- the plastic method of formation involves the manufacture of bricks from a clay mass with a moisture content of 15-30%. The product is obtained by extrusion. For the production of hollow samples, vacuum installations are used. Blanks are dried in a chamber and fired in ovens or tunnels. Such a brick is more frost-resistant and is recommended for building a house;
- dry and semi-dry method of formation.In this case, a clay mass with a lower moisture content is used (about 7-12%, it all depends on the characteristics of a particular production), a raw brick is made from it by pressing under pressure up to 15 MPa. Drying is absent altogether or is present in an abbreviated version. The final stage is firing. In terms of performance, such a brick is slightly inferior to a plastic molded brick, but it has a more accurate geometry. In this way, facing ceramic bricks are usually produced.
Ceramic bricks are used when laying the foundation, in private construction when erecting load-bearing walls and partitions, outbuildings and garages. The facing type of brick has found wide application in the decoration of facades, and is also sometimes used for interior decoration.
Dimensions of silicate bricks
Silicate brick is made from quartz sand (9 parts) and lime (1 part), a certain amount of additives. This building material has better thermal conductivity characteristics (less heat conduction), less weight. The technology is such that it is easier to maintain the geometric dimensions, so there are usually no problems.
But it is not as hard as red brick, besides, it is afraid of moisture - with prolonged contact with moisture, it begins to crumble. Because of this, the main area of use is for the construction of walls and partitions. It can not be used for the foundation, basement, or chimney masonry.

Silicate brick can be colored In this case, it is used as a finishing material
The second area of application is as a finishing material. The basic composition has a white, slightly grayish color. You can add any dye to it and get a colored brick.
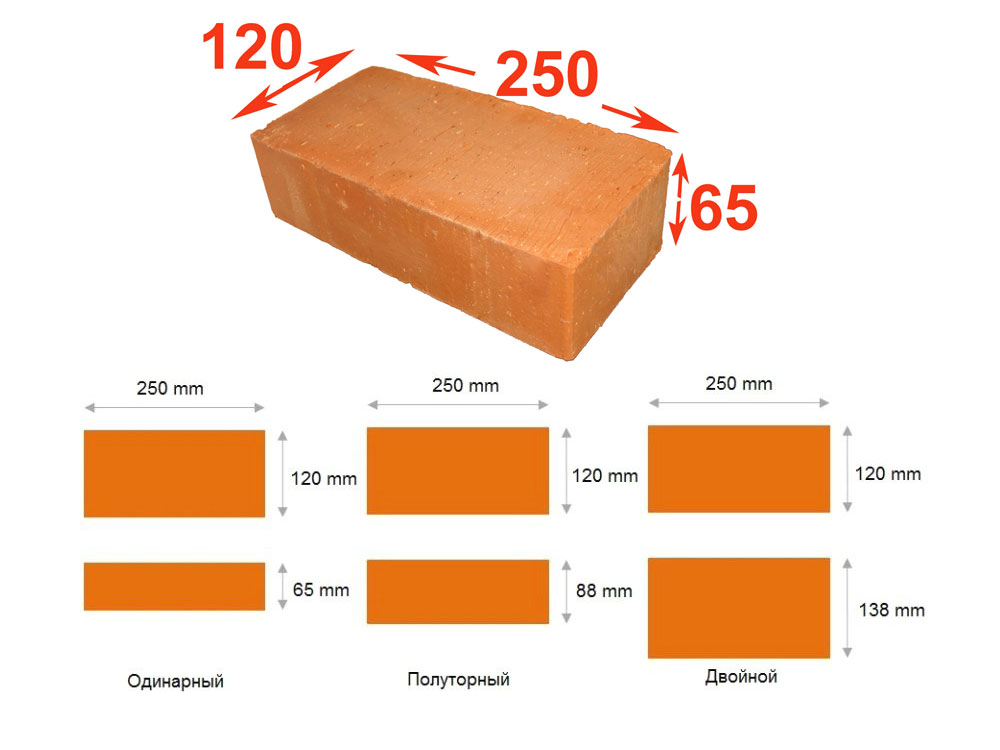
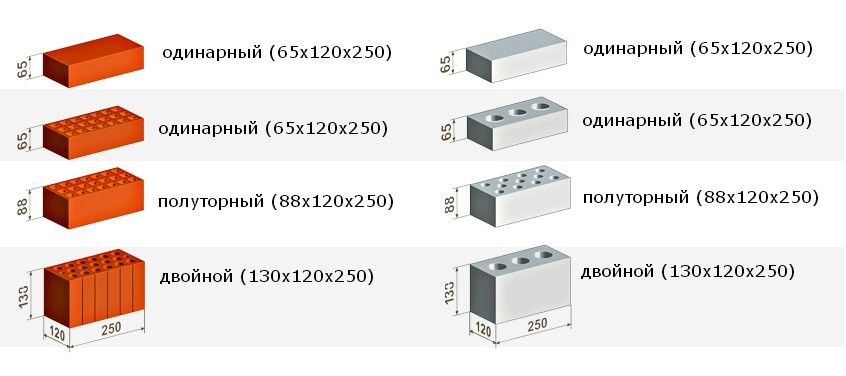
The dimensions of building silicate bricks are the same as those of ceramic: single has a height of 65 mm, one and a half - 88 mm, double - 138 mm.

The size of the silicate brick is the same as the standard ceramic
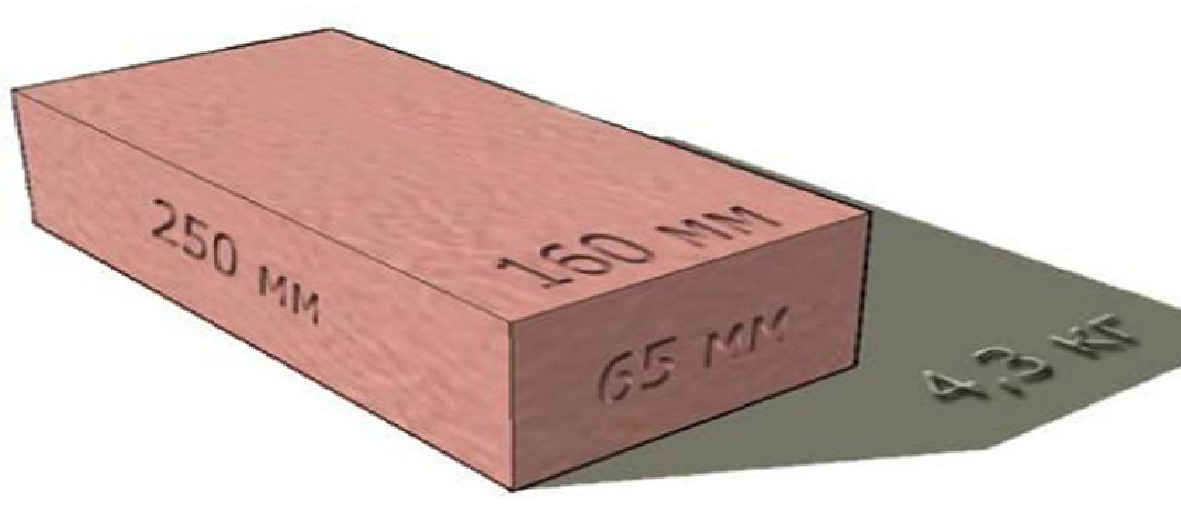
Single and one-and-a-half silicate bricks can be solid and hollow. Single corpulent weighs 3.6 kg, hollow - depending on the size of the voids 1.8-2.2 kg. A full-bodied one-and-a-half has a mass of 4.9 kg, and a hollow one - 4.0-4.3 kg.
Double sand-lime bricks are usually made hollow. Its weight is 6.7 kg. Corpulent ones are rare - because of their large mass (7.7 kg) it is difficult to work with them.
Calculation of the required quantity
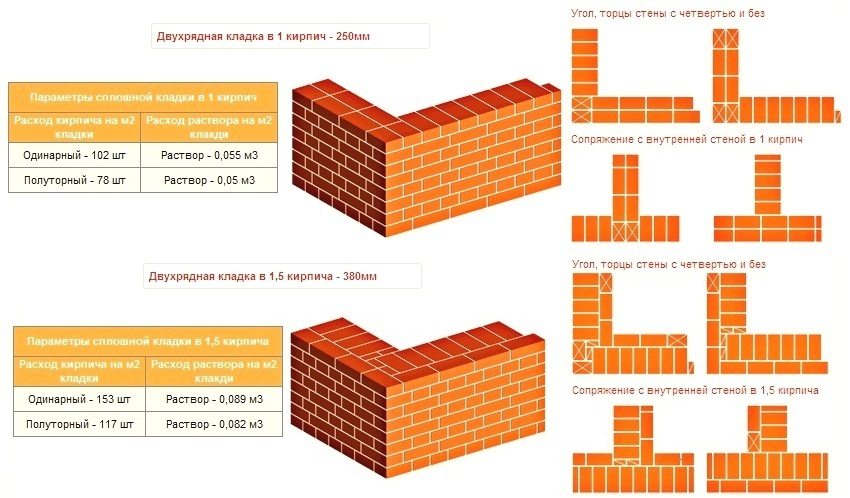
To correctly determine the amount of building material required for masonry, you should calculate how many pieces of bricks are in 1 sq. meter. It should be borne in mind which masonry method is adopted, as well as the size of the brick.
If, for example, a masonry of two bricks is required with a one-and-a-half product, then there will be 195 pieces in one square meter. taking into account the battle and not taking into account seam costs... If we count the seams (vertical 10 mm, horizontal 12 mm), then the bricks are estimated to be 166 pieces.
Another example
If the wall is made in one brick, then, without taking into account the parameter of the seams, 128 pieces are used for one square (1mx1m) of masonry. If we take into account the thickness of the seam, then 107 pieces are required
bricks. In the case when it is necessary to create a wall of double bricks, it will be necessary to use 67 pieces without taking into account the seams, taking into account the seams - 55.
Taking into account the seams
In the event of a change in the specified data in the direction of increase, material overruns or the appearance of defective connections between building elements will inevitably follow. If you make a wall or bulkhead one brick thick, then you will need at least 129 pcs. (this is excluding the seam)
If it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the seam, then 101 bricks will be needed. Based on the thickness of the seam, you can estimate the consumption of the solution required for masonry
If the masonry is made with a parameter of two elements, then 258 pieces will be needed without seams, if we take into account the gaps, then 205 bricks will be needed.
Excluding the seam
The brick can be calculated without taking into account the size of the seam, this is sometimes necessary if you make a preliminary calculation.In any case, if you make more accurate calculations, you will have to take into account the coefficient of consumption of the solution from the entire volume of the masonry (0.25).
Calculation table for the required number of bricks.
| P / p No. |
Type and size of masonry |
Length |
Width |
Height |
Number of bricks per piece (excluding seams) |
Number of bricks per piece (taking into account seams of 10 mm) |
| 1 |
1 sq. m masonry in half a brick (masonry thickness 120 mm) |
250 |
120 |
65 |
61 |
51 |
| 2 |
1 sq. m masonry in half a brick (masonry thickness 120 mm) |
250 |
120 |
88 |
45 |
39 |
| 3 |
1 sq. m of masonry in one brick (masonry thickness 250 mm) |
250 |
120 |
65 |
128 |
102 |
| 4 |
1 sq. m of masonry in one brick (masonry thickness 250 mm) |
250 |
120 |
88 |
95 |
78 |
| 5 |
1 sq. m masonry in one and a half bricks (masonry thickness 380 mm) |
250 |
120 |
65 |
189 |
153 |
| 6 |
1 sq. m masonry in one and a half bricks (masonry thickness 380 mm) |
250 |
120 |
88 |
140 |
117 |
| 7 |
1 sq. m masonry in two bricks (masonry thickness 510 mm) |
250 |
120 |
65 |
256 |
204 |
| 8 |
1 sq. m of masonry in two bricks (thickness 510 mm) |
250 |
120 |
88 |
190 |
156 |
| 9 |
1 sq. m masonry in two and a half bricks (masonry thickness 640 mm) |
250 |
120 |
65 |
317 |
255 |
| 10 |
1 sq. m masonry in two and a half bricks (masonry thickness 640 mm) |
250 |
120 |
88 |
235 |
195 |
Masonry features
In the process of laying bricks, it is most often laid on the largest face, and so that the load is distributed over at least 2 underlying parallelepipeds. At the same time, in order for the walls to come out strong and durable, the masonry is made with an offset, called dressing. A brick in a wall can be positioned both along and across it, that is, to address the wall surface with the smallest edge (poke) or narrow long (spoons).
0.5 brick masonry is defined in square meters. If the wall is laid out in brick or thicker, then the volume, expressed in cubic meters, is used for measurement.
When calculating the wall, the width should be a multiple of 0.5 bricks. During the design period of the surface, the thickness of the vertical masonry joint is taken into account, taking it as 10 mm, although in fact it fluctuates within 8-12 mm. Two bricks laid with a poke, taking into account the width of the masonry joint (120 + 10 + 120 = 250 mm), make up a module equal to the length of a whole single product. In each row (when using a single product placed on the bed), vertical seams can be placed every 120 or 250 mm. If laying on the edge, the seams will pass through 65 mm.
If the walls are erected without additional air gaps and insulation, then their vertical dimensions will correspond to the sum of the vertical edges of the used building materials plus the thickness of the masonry joints (12 mm for horizontal joints). To calculate the vertical dimensions of brickwork, there is a special formula: N × R + (N-1) × T, in which the designations correspond to the following values:
- R is the vertical parameter of the brick (65 mm for a single size or 88 for one and a half);
- N - row number;
- T - seam thickness.
In order not to make calculations for each row, you can use a ready-made table of the vertical multiplicity of masonry:
| Row number | Row number | Row height with masonry mortar (mm) | |||
| 1NF | 1,4NF | 1NF | 1,4NF | ||
| 1 | 77 | 100 | 19 | 1463 | 1900 |
| 2 | 154 | 200 | 20 | 1540 | 2000 |
| 3 | 231 | 300 | 21 | 1617 | 2100 |
| 4 | 308 | 400 | 22 | 1694 | 2200 |
| 5 | 385 | 500 | 23 | 1771 | 2300 |
| 6 | 462 | 600 | 24 | 1848 | 2400 |
| 7 | 539 | 700 | 25 | 1925 | 2500 |
| 8 | 619 | 800 | 26 | 2002 | 2600 |
| 9 | 693 | 900 | 27 | 2079 | 2700 |
| 10 | 770 | 1000 | 28 | 2156 | 2800 |
| 11 | 847 | 1100 | 29 | 2233 | 2900 |
| 12 | 924 | 1200 | 30 | 2310 | 3000 |
| 13 | 1001 | 1300 | 31 | 2387 | 3100 |
| 14 | 1078 | 1400 | 32 | 2464 | 3200 |
| 15 | 1155 | 1500 | 33 | 2541 | 3300 |
| 16 | 1232 | 1600 | 34 | 2618 | 3400 |
| 17 | 1309 | 1700 | 35 | 2695 | 3500 |
| 18 | 1386 | 1800 | 36 | 2772 | 3600 |
If building material of other parameters is used, then according to the above formula, you can easily draw up your own table, according to which, during the masonry process, control is carried out using the ordering - slats with divisions corresponding to the masonry rows.
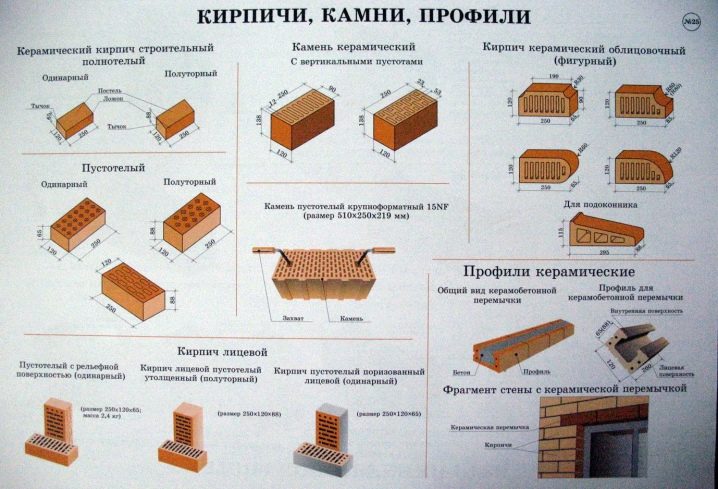
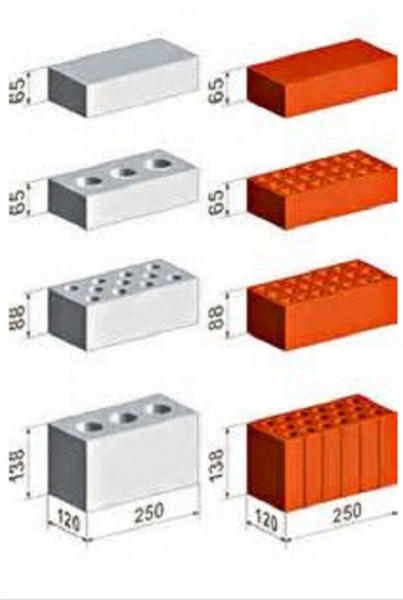
The difference between solid and hollow products
Full-bodied products are a solid bar, without through holes. It is a good soundproofing material with good heat retention ability. It is resistant to moisture and other aggressive influences. The weight of one product is about 4 kg.
Building solid single material is used for the following purposes:
- laying of foundations, basement walls, plinths;
- the device of stoves, rude, fireplaces;
- production of interior partitions;
- construction of load-bearing walls and other high-strength structures that make up the house.
 Hollow briquettes have through holes in their bed. They come in round and square shapes. The presence of voids provides products with improved thermal insulation properties and reduced weight. But at the same time, the strength characteristics deteriorate.The voidness in different brands ranges from 15-45%. The weight of one block is 2-2.5 kg.
Hollow briquettes have through holes in their bed. They come in round and square shapes. The presence of voids provides products with improved thermal insulation properties and reduced weight. But at the same time, the strength characteristics deteriorate.The voidness in different brands ranges from 15-45%. The weight of one block is 2-2.5 kg.
From ordinary bricks with voids, they are made:
- external walls in buildings up to 3 storeys high;
- structures that need to withstand high temperatures or their differences;
- structures made of bricks, laid "ruba".
Solid blocks are more often used when building a house, for the construction of external walls, and partitions in it are made of hollow products.
Brick dimensions according to GOST - height, length and width
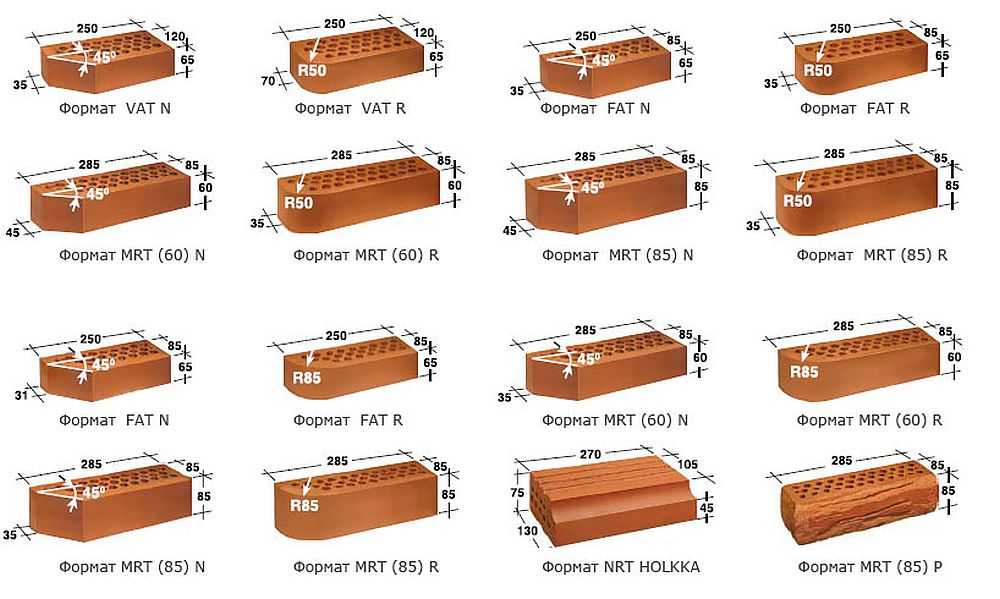
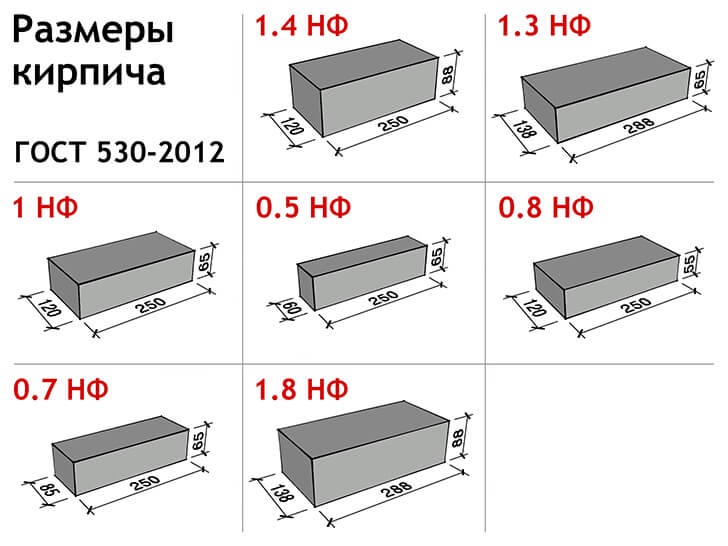
Modern construction does not stand still. With the growth of requirements for the construction of houses, the range of brick sizes has also expanded:
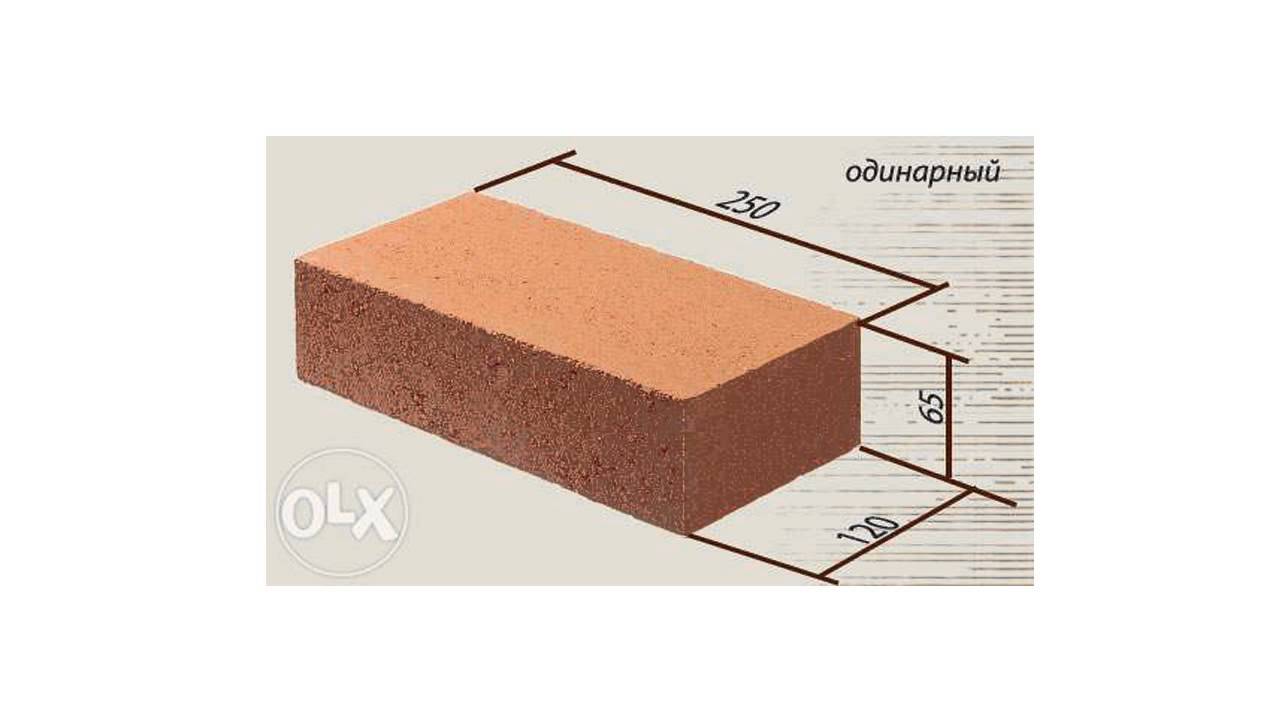
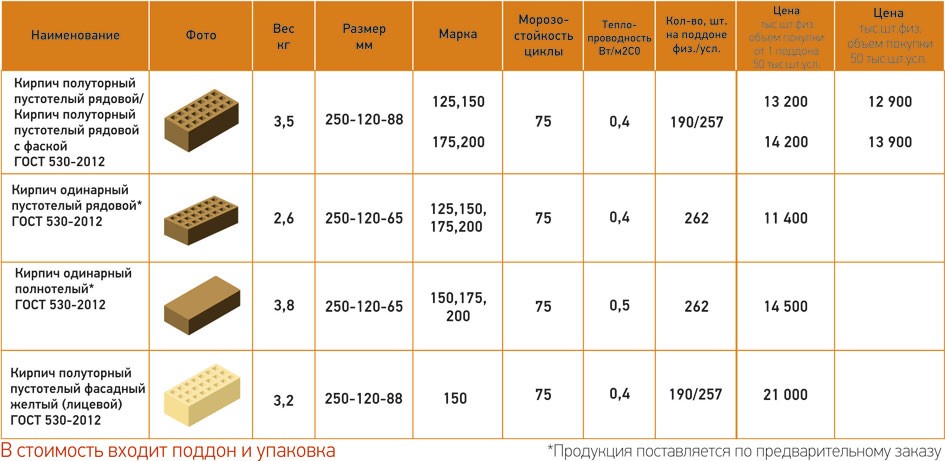
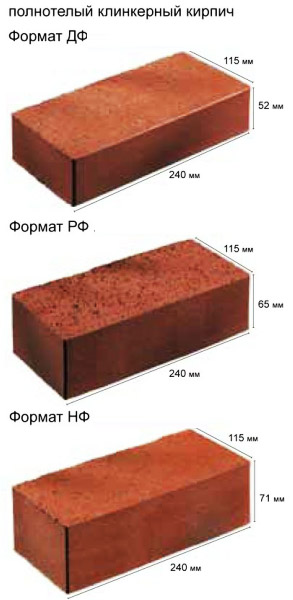
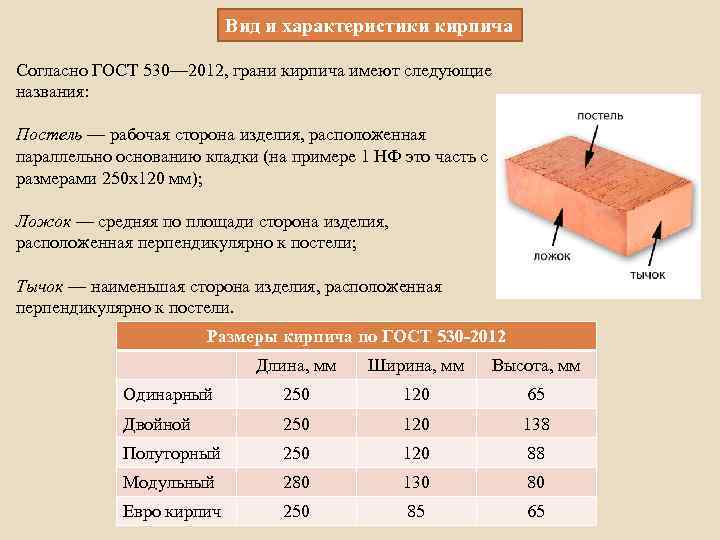
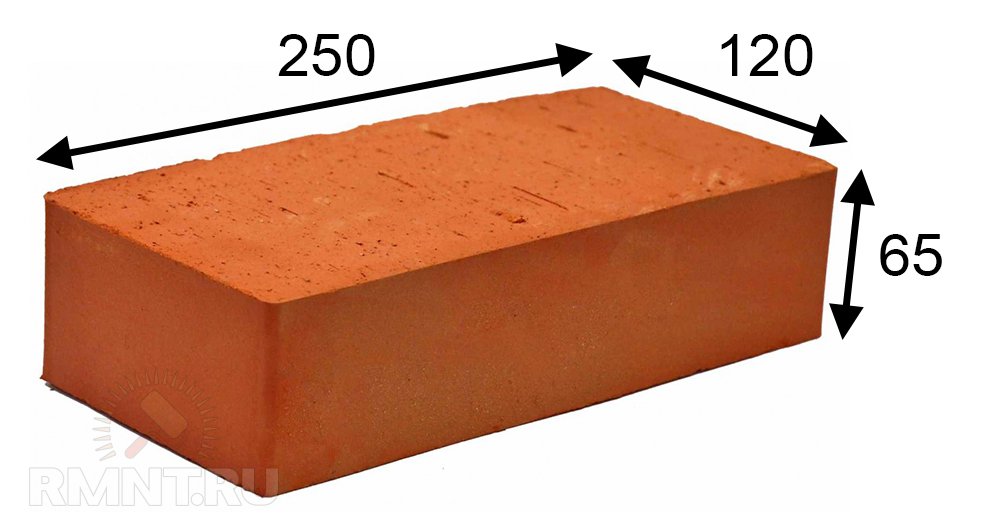
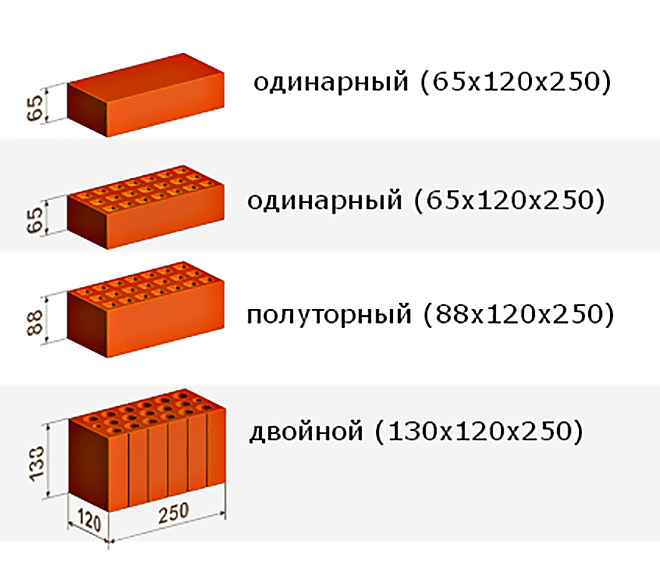
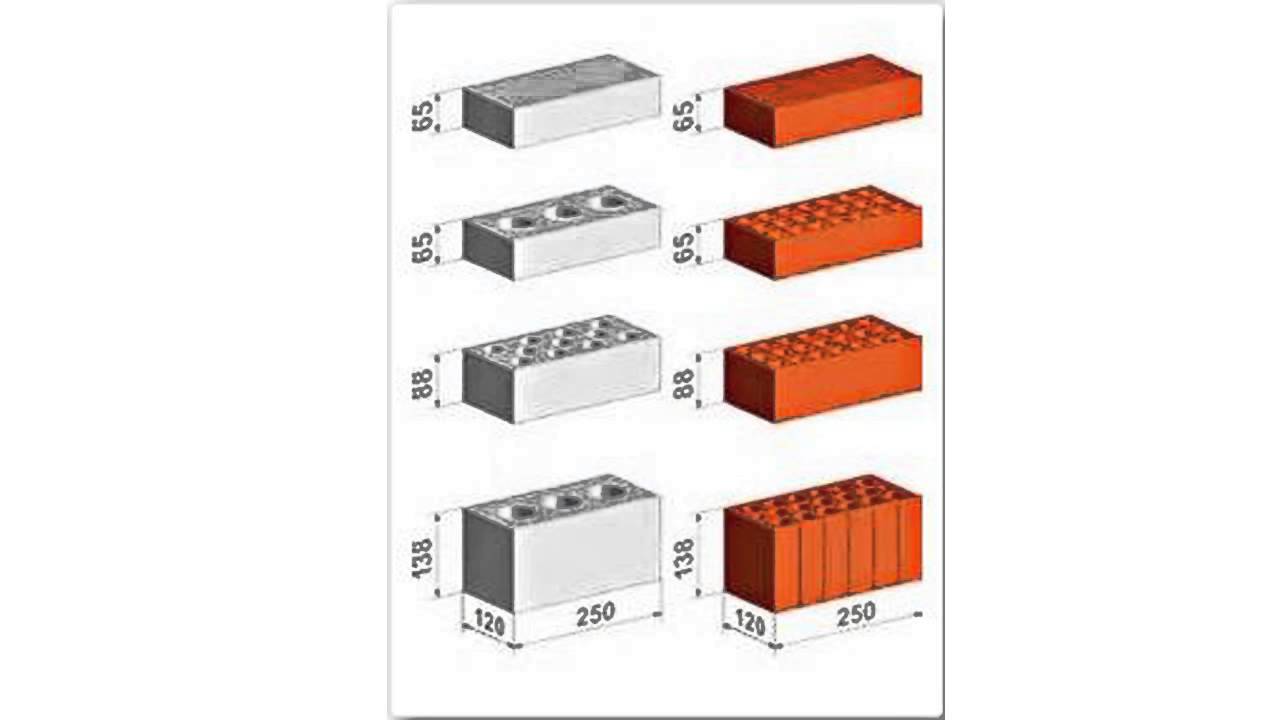
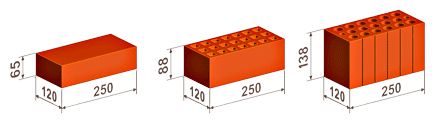
- Single - 250x120x65 mm (fixed by GOST 530-2007). According to the European marking, they have the RF designation.
- Double - 250x120x138 mm.
- One and a half - 250x120x88 mm.
- Modular - 280x130x80 mm.
- Euro bricks h - 250x85x65 mm.
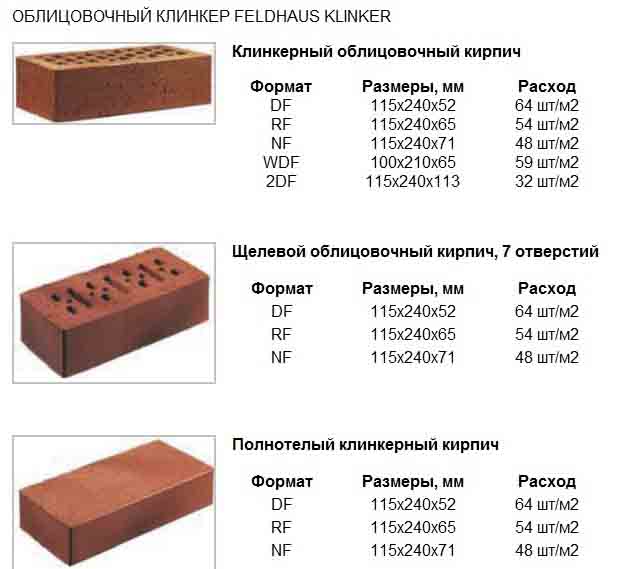
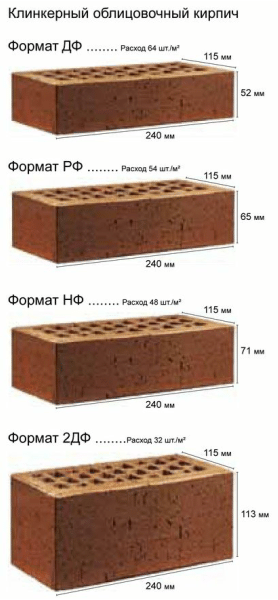
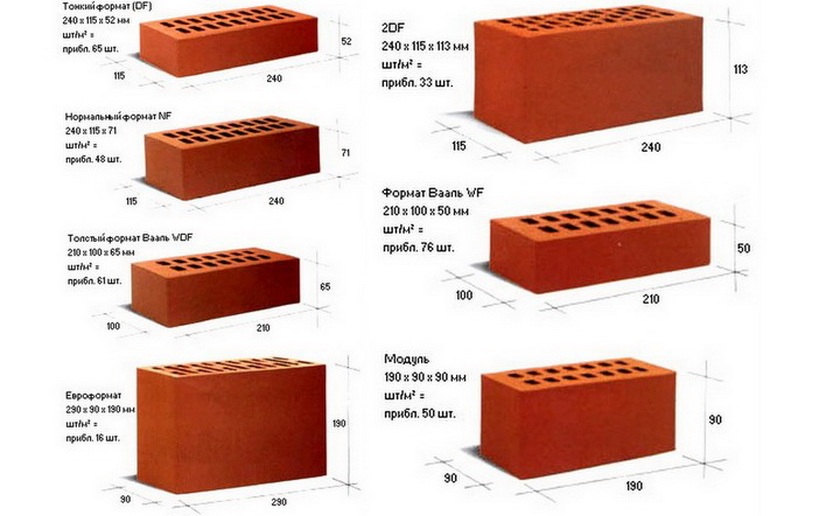
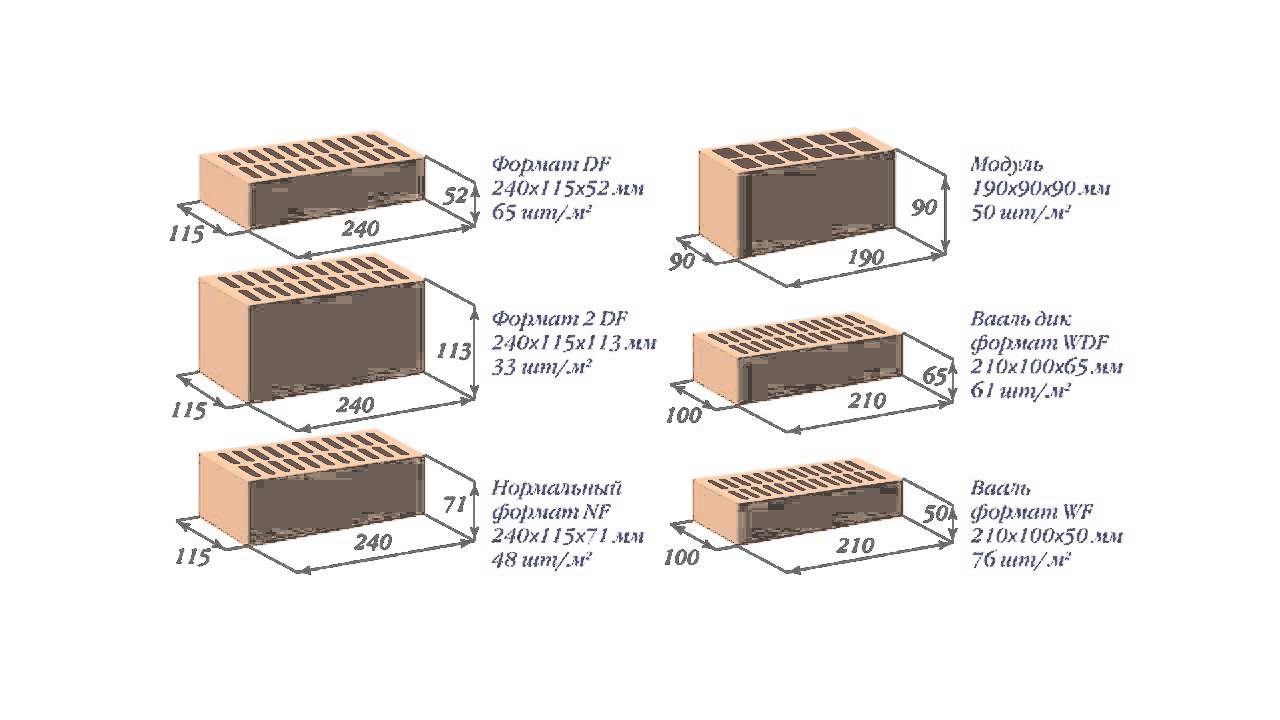
The most popular in Europe are bricks NF (normal) - 240x115x71 and DF (thin) - 240x115x52, less common sizes - 250x85x65 mm and 200x100x50 (65). Today you can buy material up to 500 mm long. The choice of standard sizes is growing every year.

By shape, bricks are divided into:
However, in addition to basic dimensions such as height, length and width, permissions for deviations from the norm (defects) are also used. Their size depends on the type of building material - building or facing. The latter is subject to more stringent requirements, since the aesthetics of the building depend on its characteristics.
For building solid bricks, it is allowed:
- The presence of dullness and chips of ribs and corners no more than 2 and no more than 1.5 cm along the length of the rib;
- Curvature of edges and edges up to 0.3 cm;
- On the lateral longitudinal (spoon) edges, a crack up to 3 cm long across the width of the brick is allowed.
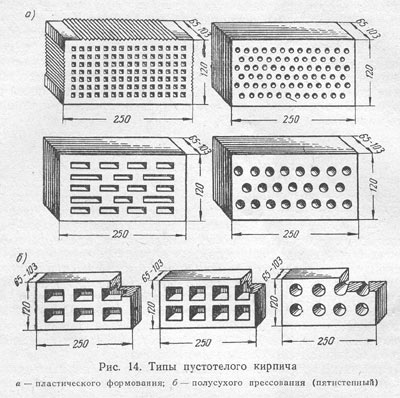
For a construction hollow version, it is allowed:
- No more than 2 bumps on corners or edges 1-1.5 cm long, provided that they do not reach the voids;
- Full thickness cracks in the bed. In width, they can reach the first row of voids;
- One crack on the butt and spoon (transverse lateral) faces.
For facing bricks it is not allowed:
- Chipped corners, the depth of which exceeds 1.5 cm;
- The presence of cracks;
- Broken ribs, the width of which is more than 0.3 cm and the length exceeds 1.5 cm.

In this case, a facing material that has:
- No more than 1 bit of corners up to 1.5 cm deep;
- Separation of handwriting, which in total does not exceed 4 cm in length;
- No more than 1 broken ribs, in depth - not exceeding 3 cm, and in length - no more than 1.5 cm.
The architectural concept often involves the use of different textures and colors. The modern choice of building materials is almost limitless. If desired, you can combine artificially aged, variegated and textured options in the masonry without compromising the durability of the house.
One-and-a-half and double bricks are mainly produced as hollow bricks. This helps to reduce the weight of the structure.
The most popular in modern construction are large-sized porous blocks. Ceramic bricks are lighter and warmer than conventional construction options. Its use allows you to simplify and speed up construction, while reducing the consumption of masonry composition.
For laying 1 m 3, 512 single-type bricks will be required, and 378 bricks are required by 26% more.