Varieties of solutions and their applicability
The connecting link between brick blocks is a mixture of a binder component with filler and water. The most common are 4 types of solutions.
- Cement-sandy. It is diluted with water, its proportions depend on the brand of cement, the method of masonry. When solidified, this option is the most durable, but when deviating from the technology, it is prone to cracking;
- Limestone - in it the cement is replaced by quicklime; plastic, but washed out by rains, therefore, it is suitable only for the installation of internal walls;
- Mixed - cement and sand are diluted with liquid slaked lime (milk of lime). The combination combines the best qualities of the first two options;
- With a plasticizer - a polymer additive is mixed with cement and sand (fraction 2 mm) to increase the plasticity of the mixture. It is easier to make such a solution from a dry building mixture by adding water according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Despite the composition, the requirements for the quality of the mixture are almost the same. All ingredients are cleaned of lumps, sand is sieved, liquid lime is filtered. To prepare the solution, first thoroughly mix the powder components, then slowly pour in cold liquid (20 ° C) and mix thoroughly so that setting does not occur. The process is accelerated using a concrete mixer or a rotary hammer with a whisk attachment.
Consumption of mortar per cube of brickwork
How much to prepare mortar for masonry walls? This is determined by several conditions:
- the skill of a bricklayer;
- the structure of the brick block - products with voids take more mortar mixture;
- type of brick - hyper-pressed and face silicate absorbs mortar less than ceramic or ordinary silicate with a rough surface;
- the thickness of the wall.
The average consumption of mortar per 1 m3 of brickwork with a standard joint thickness (12 mm) is approximately 0.23 m3. More accurate information is given in Table 1.
Consumption of cement for brickwork
The composition of the mixture for the construction of a brick wall varies depending on the quality of the initial components, weather conditions, and the number of storeys of the building. To mix the ingredients correctly, you need to know: a 10-liter bucket holds 14 kg of cement or 12 kg of sand.
- The cement slurry is flexible in terms of proportions. It is characterized by the degree of strength: the less it is, the lower the required grade of cement and the lower its percentage (1 part per 2.5 - 6 parts of sand). For cement M400 is characterized by a ratio of 1.3, for M500 - 1. 4. The volume of water (on average 0.5 - 0.7 liters per 1 kg of cement) depends on the desired density of the mixture, the type of brick, air temperature - in the summer heat, the solution should be more fluid. To increase its plasticity, experienced bricklayers add a little washing powder or dishwashing liquid to the water. For 1 cube of the finished solution 1.4, 410 kg of M500 cement and 1.14 m3 of sand are needed. Knowing that 0.24 m3 of mortar is consumed per 1 cubic meter of an ordinary wall in one brick from a silicate block 250 x 120 x 65, the consumption of cement per cube of brickwork is determined as follows: 0.24 x 410 = 98 kg. Accordingly, when using cement M400 (proportion 1. 3) a cubic meter of the mixture contains 490 kg of cement, and 117 kg is consumed per 1 m3 of masonry.
- The cement-lime mortar is suitable for use within 5 hours, and in summer at +25 o - no more than an hour, therefore, a calculation is also desirable for it. 1 cubic meter of the mixture requires 190 kg of cement M400 - M500, 1.5 m3 of sand, 106 kg of hydrated lime and 475 liters of water. For a cubic meter of masonry, an average of 46 kg of cement will be needed.
Cement consumption for brickwork during cladding
In this case, the developer is interested in how much the binder mixture will be consumed per square meter of the wall.It depends on the water absorption of the building material, the season of work, the voidness and porosity of the blocks. The norms are laid down in SNiP 82-02-95, but the real numbers are always higher, so you should buy a ready-made mortar or cement with a margin.
To save on consumables, 2 factors should be noted:
- the larger the dimensions of the brick, the less mortar will go;
- the higher the% of voids and pores, the higher the consumption of the mixture will be.
From this point of view, it is optimal to use ceramic or silicate double bricks of sufficient strength grade. This choice will allow you to achieve savings of 20% mortar mixture. Table 2 shows comparative data on the consumption of mortar per square meter of the wall.
Calculation of the amount of building material
When calculating, two methods are often used. In one, calculations are carried out taking into account the mortar seam, and in the second they are not taken into account. Typically, its thickness ranges from 5 to 10 mm.
It's important to know! If the second method is used in the calculation, there is a chance of getting an excess of building material, about 30%. The first method is more economical, but it also has its own pitfalls.
Add 10-15% to the resulting number of material. These percentages take into account possible brick scrap during construction.
Example. For a better understanding, consider an example. It is necessary to build a one-story brick house with the following dimensions:
- Length - 12 m;
- Width - 10 m;
- Height - 4 m.
The calculation is carried out only taking into account the external walls. They have one door (1x2 m) and three window (1.2x1.5 m) openings. Brick type: ordinary single. Masonry method: two bricks. Mortar joint: 7 mm.
So, the calculation of the amount of building materials for the construction of the specified house according to the first method should look like this:
First, you need to determine the perimeter of the outer walls (1). Then you can calculate their area (2). Next, you need to calculate the area of the openings (3). Now you can calculate the area of the masonry itself (4). The next step will be to determine the amount of building material by 1. To do this, you need to calculate the area of the frontal surface of the brick (5) and divide the resulting value by 1 (6), and then multiply by 2, since in our case the laying is carried out in two bricks (7). Total: 256 bricks per 1.
Result: to build the walls of a house according to the above parameters, 31,898 bricks are needed.
To calculate the amount of building material in a different way, the thickness of the seam must be added to the size of the brick, in our case it is 7 mm (9). From this it turns out that the number of bricks per 1 will be 219 pieces (10). Now we multiply this amount by the total masonry area (11), additionally adding the amount of scrap material (1500-2000 pieces) and we get about 28,800-29,300 pieces.
Calculations:
- Rn = (12 + 10) x2 = 44 m.
- Sc = 44x3 = 132 m ^ 2.
- Sп = (1x2) + (1.2x1.5) x3 = 7.4.
- Sk = 132-7.4 = 124.6.
- 0.12x0.065 = 0.0078.
- 1/0,0078=128.
- 128x2 = 256.
- 124.6x56 = 31897.6
- (0.12 + 0.007) x (0.065 + 0.007) = 0.009144.
- 1 / 0.009144x2 = 218.723.
- 219xSk = 219x124.6 = 27287.4.
Having examined both calculation options by example, you can make sure that the first method is more economical.
Calculation using an online calculator
In the event that you do not want to boggle your head with a large number of numbers or you are simply afraid to make a mistake in the calculations, then you can use special online calculators. With their help, you can quickly calculate the required amount of bricks. You just need to enter the required parameters in the appropriate fields and the calculator will immediately give you the result. In addition to calculating the number of bricks with an online calculator, you can determine other parameters necessary for construction. The main advantage of these calculators lies in their convenience and accuracy. Using this calculation method, the chance of making a mistake is reduced to zero. Plus they are completely free.
Classification of structures: levels of difficulty
It is customary to divide the laying of walls according to the following parameters, presented in the table:
| Categories | Characteristic |
| Architectural decor | Simple (20% of the total wall area) and medium architectural design (30%) |
| The expense for the construction of large parts, such as loggias and bay windows, is included in the total volume of building materials, and small elements with a height of up to 25 cm are not included. | |
| Varieties of external design | Divided by types of slabs: ceramic and concrete |
| This parameter takes into account the jointing and facing | |
| Masonry construction | There are the following types: lightweight, solid, with thermal insulation plates |
| Building type | Types of decorative structures: gazebos, columns, pillars |
| Depends on the construction project | |
| Width | 250, 380, 510, 640 mm |
| Wall height | Determined from the base, i.e. from the upper border of the foundation to the upper line of the last row |
The volume is also influenced by the way in which the mason will lay the masonry. You can put it using the following 3 technologies:
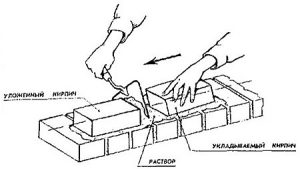
- We will press. The hard mortar lays down at a distance of up to 15 mm from the final part of the future wall. The mixture is leveled with a trowel, and the stone lies tightly to the base. Then you should collect the excess solution. And put the next stone, firmly fixing it near the first, but between them all this time there will be a metal part of the trowel. After that you need to pull it out.
- Inspired. The mixture is plastic, lays down at a distance of up to 30 mm from the outer wall.
- Undercut. It combines 2 previous types. But after completing each step, you need to trim the seams.
Peculiarities
In order to correctly calculate the need for a brick for building a house, you need to know its dimensions. Usually, newcomers to construction make mistakes and receive significantly more building material than they actually need.
The mistake is that mortar joints are not taken into account. Meanwhile, the layer of mortar between the bricks is a considerable volume. If you omit the volume of the seams, the result will differ by at least 20 percent.
As a rule, the seams are at least 5 mm and not more than 10 mm thick. Knowing the dimensions of the main material, it is easy to calculate that in one cubic meter of masonry, from 20 to 30 percent of the volume is occupied by masonry mortar. An example for different types of bricks and the average thickness of the mortar joint. Practice shows that for one cubic meter of masonry there are 512 single bricks, 378 thickened or 242 double bricks.
Taking into account the solution, the number is significantly reduced: single bricks are required 23% less, that is, only 394 pieces, one and a half, respectively, 302, and double bricks - 200 pieces. The calculation of the required number of bricks for building a house can be done in two ways.
In the first case, you can take a brick not of a standard size, but with allowances equal to the thickness of the mortar joint. The second method, in which the average consumption of building material per square meter of masonry is taken into account, is more preferable. The problem is solved faster, and the result is quite accurate.
The deviation in one direction or another is no more than three percent. Agree that such a small error is quite acceptable. Another example, but now not by volume, but by the area of the wall - calculation taking into account the method of laying in 0.5, one, one and a half, two or two and a half bricks.
Half-brick masonry is usually laid out using beautiful facing marks.
For 1 m2, taking into account the seams, it is required:
- single - 51 pcs;
- thickened - 39 pcs;
- double - 26 pcs.
For masonry of 1 brick per square meter, you must:
- single - 102 pcs;
- thickened - 78 pcs;
- double - 52 pcs.
A wall thickness of 38 cm is obtained when laying one and a half bricks.
The need for material in this case is:
- single - 153 pcs;
- thickened - 117 pcs;
- double - 78 pcs.
For 1 m2 of masonry in 2 bricks you will have to spend:
- single - 204 pcs;
- thickened - 156 pcs;
- double - 104 pcs.
For thicker walls of 64 cm, builders will need for every square meter:
- single - 255 pcs;
- thickened - 195 pcs;
- double - 130 pcs.
General information on the results of calculations.
- The total length of the tape is the perimeter of the foundation.
- Sole area of the tape - The area of support of the foundation on the soil. Corresponds to the required waterproofing.
- External lateral surface area - Corresponds to the area of the required insulation for the outside of the foundation.
- Concrete Volume - The volume of concrete required to fill the entire foundation with the specified parameters. Since the volume of concrete ordered may slightly differ from the actual one, as well as due to compaction during pouring, it is necessary to order with a 10% margin.
- Concrete Weight - Indicates the approximate weight of concrete based on average density.
- Soil load from foundation - Distributed load over the entire support area.
- Minimum diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars - Minimum diameter according to SP 52-101-2003, taking into account the relative content of reinforcement from the cross-sectional area of the tape.
- Minimum number of rows of reinforcement in the upper and lower chords - The minimum number of rows of longitudinal bars in each chord, to prevent deformation of the belt under the action of compressive and tensile forces.
- Minimum diameter of transverse reinforcement bars (stirrups) - Minimum diameter of transverse and vertical reinforcement bars (stirrups) according to SP 52-101-2003.
- Pitch of transverse reinforcement bars (stirrups) - The pitch of the stirrups required to prevent movement of the reinforcement cage when pouring concrete.
- Reinforcement overlap - When overlapping bar segments.
- Total reinforcement length - The length of all reinforcement for tying the frame, taking into account the overlap.
- Total Rebar Weight - The weight of the reinforcement cage.
- Formwork board thickness - The design thickness of the formwork boards in accordance with GOST R 52086-2003, for the given parameters of the foundation and for a given pitch of the supports.
- Number of boards for formwork - The amount of material for the formwork of a given size.
What you need to know when starting a calculation
In order to calculate the quantity, we do not have to be a professional builder (you can even just watch the video in this article).
The simplest basics are enough (we will talk about this below), the ability to read a drawing and take measurements from it, as well as school knowledge of geometry (at the level of 6-7 grades). Let's start with building knowledge.
Brick types
Not all bricks are the same. It is divided by material (ceramic and silicate), hollow and solid, brands, as well as types (facing, facade, refractory, etc.).
This is absolutely unimportant to us for calculating the amount of material. But we just take into account that even if silicate is used on all structures of the house, you will still have to buy ceramics for the basement, since silicate is not moisture resistant enough for this building element
We are interested in its size. It happens.
- Single - 250x125x65 mm.
- One and a half (or thickened) - not 65, but 88 mm high.
- Double - height 138 mm.
Ceramic single solid brick
Masonry thickness
In the drawings, dimensions are usually given in millimeters, but builders use a different designation tied to the number of bricks in one row.
Masonry happens:
- in half a brick - the brick is laid in one row with the long side along the axis of the wall;
- into brick - the wall thickness is equal to the long side of 250 mm;
- one and a half bricks alternating (depending on the method of dressing) styling with both the long side and the short side. The thickness turns out to be 375-385 mm (from the fact that the size of the seams can be added);
- in two bricks;
- two and a half bricks;
- three bricks, etc.
Note that in our climate, for the construction of a house, and almost any structure (except perhaps for ancient fortifications), masonry is thicker than two and a half bricks is rarely used. To achieve the required thermal insulation of the walls, it is more economical not to increase the thickness of the wall, but to use air gaps and materials with better insulating properties than ceramics or silicate.
Examples of masonry in thickness (moreover, the dressing of the seams may be different)
Masonry mortar
Twenty or thirty years ago, almost exclusively cement-lime mortar was used for brickwork - the thickness of the joints was 10-15 mm. Today, glue is increasingly used (especially for silicate).
When using it (depending on the type), the seam will be minimal, and its thickness can be completely neglected when calculating the number of bricks in the masonry.

Glue-on ceramic stone
The number of bricks per unit of masonry
You can, of course, independently, based on the geometric dimensions of the brick, calculate how many pieces of brick are in a cube or their number per square meter of wall area. But it is easier to do this if there is a table for calculating the number of bricks.
I give ready-made data, they differ from different sources, but by no more than 2-3 units:
Per cubic meter of masonry:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 510395 One-and-a-half 380 300 Double 240 200
Number of bricks per square meter, masonry in half a brick:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 6050 One-and-a-half 4540 Double 3025
Per square meter, brickwork:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 130 100 One-and-a-half 9580 Double 6050
The number of bricks in the masonry is one and a half bricks per square meter:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 190 150 One-and-a-half 140 115 Double 9080
Per square meter, two brick masonry:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 255 204 One-and-a-half 190 155 Double 120 105
How many pieces of bricks in 1m2, laying in two and a half bricks:
Brick thickness Quantity excluding seams, pcs Quantity including seams, pcs Single 315 255 One-and-a-half 235 195 Double 150 130
It is worth noting that it is better to use the calculation per cubic and not per square meter. Then it is easier to avoid mistakes at the corners, where you can accidentally take into account the volume of the masonry already calculated for the adjacent wall.
Varieties of bricks
For cladding a residential building, different types of facing brick material are used. Most often, the choice stops on the following options:

- Flexible cladding. An unnatural product made from polymers. The material looks like a flexible plate that is mounted directly to the wall or on plaster, sip panels, porous concrete.
- Ceramic. It is made from natural bases - clay, concrete. To add decorative effect, different pigments are added to the mixture, so the range of colors is varied - from light yellow to dark brown. The advantage of the material is reliability, frost resistance, beautiful appearance.
- Clinker. The product is based on a clay solution with a small amount of water. A brick or log house, lined with clinker bricks, is distinguished by moisture resistance, durability, since the material can withstand sudden temperature changes, precipitation, and mechanical stress. Such a product is an ideal option for cladding private houses, but the only drawback is the high price.
- Hyper-pressed. It is made from a cement-mineral mixture, it is not fired, but it is strongly compressed. Moisture-proof, heat-conducting, but unstable to temperature extremes, therefore, without waterproofing, it begins to crack.
- Silicate brick. In the composition - lime, sand, water. Differs in durability, reliability, environmental safety. A residential building lined with silicate bricks will last for more than a dozen years.
Instructions for the brick fence calculator
Specify the parameters of the fence section and fill in the dimensions in millimeters:
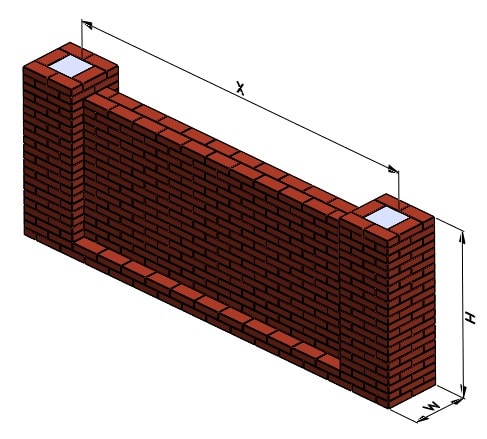
X - The span length is selected as a multiple of the brick length within 2500-6000 mm.
H - The height of the post is determined based on the overall design of the fence.
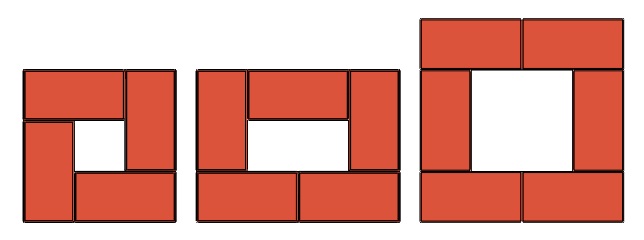
T - Pillar masonry. Here you should choose one of the proposed masonry options 1.5x1.5, 1.5x2 or 2x2.
Y - The height of the fence is selected taking into account the recommendations of SNIP 30-02-97 * "Planning and development of territories of gardening associations of citizens, buildings and structures" (as amended on 12.03.2001). The height of the fence from the side of the street and public areas should not exceed 2200 mm for the organization of normal illumination of streets, driveways, sidewalks. For fences in adjacent areas of the year, the maximum fence height is 1500 mm. Fence heights can also be set by the local government in your area. In any case, a too high fence can cause inconvenience to neighbors, even if at the stage of its construction they did not show dissatisfaction, it is better to agree on everything in advance (in paper form if possible).
Z - The thickness of the fence depends on the method of masonry (120-500 mm).
S - The height of the plinth is chosen for aesthetic reasons.
W - The thickness of the base is selected at the marking stage and is equal to the thickness of the pillar, depending on the type of its masonry.
N - Foundation width: determined by the width of the pillar.
P - The depth of the foundation depends on the type of soil, its bearing capacity, and the height of the fence. To prevent the forces of heaving, the depth of the foundation is often chosen below the level of freezing of the soil, but this is quite costly and does not guarantee the longevity of your fence. A shallow strip foundation (P = 150-400) is considered optimal, which can be arranged in the presence of good soil with a low groundwater level, having previously prepared a base of sand and crushed stone.
R - The height of the filling is selected within the range of 100 -300 mm.
Specify the masonry parameters and fill in the dimensions in millimeters:
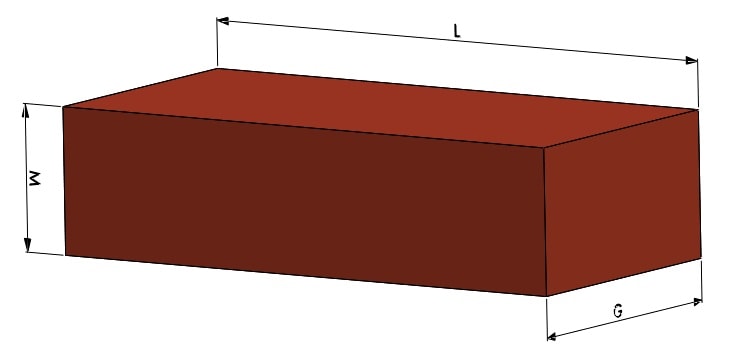
L - The value of the length of the brick depends on the material you are using. The standardized GOST 530-2007 length of ceramic bricks is 250 mm.
G - The width of the brick, depending on its type, can be different. The standard G value for bricks is 120 mm.
M - Brick height. According to the above-mentioned GOST, the height of a single ceramic brick is 65 mm, one and a half 88 mm, double 140 mm.
Q - The thickness of the seam, ranges from 8-15 mm, the optimal value is 10 mm.
Mark the sides of the fence for which you need to calculate based on the characteristics of your site.
Indicate the length of each side in meters.
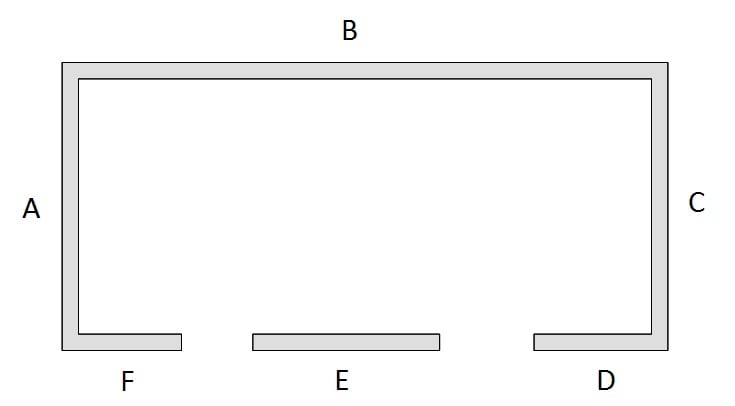
Side: A
Side: B
Side: C
Side: D
Side: E
Side: F
Check the item "Black and white drawing", so you will get a contrast drawing close to the requirements of GOST and you can print it without wasting color paint or toner.
Click Calculate.
An online calculator for calculating bricks for a fence will also help determine the height of the post and span (taking into account the height of the basement), find out how many rows of bricks are required for their construction. And also the volume of one fence post in m³ and how many bricks are needed for its construction. Find out the width of the span, taking into account the thickness of the post. How many bricks are needed for one span and its volume in m³, the height of the basement and the number of brick rows.
In addition to the calculated amount of bricks for the fence, it is recommended to make a small margin (up to 10%) for scrap and battle during unloading. It is quite difficult to build a brick fence on your own without the skill of masonry, however, knowing how much material is needed for this and a little preparation, it is quite possible.
Necessary information for calculating the number of bricks
For a correct calculation, the following information is required:
The area of the entire masonry. It should be calculated from the outside.
Wall thickness. The thickness of the mortar joint is taken into account. The final value may differ from the final result, since it directly depends on the type of masonry.
Wall length.
The amount of bricks required for construction.
The volume of mortar for masonry.
The weight of the equipment required. The parameter is determined without additional characteristics: mortar, masonry mesh.
Counting rows, taking into account the seams. When performing calculations, the height of the wall, the size of the materials used, the thickness of the solution are taken into account, but the gables are not taken into account.
The amount of mesh. Calculate the value in meters. A mesh is used to reinforce the masonry and increase the solidity of the structure.
The presence of flexible connections that are needed for facing work. The length of the indicator depends directly on the wall thickness, the insulation is also taken into account.
Foundation load. When calculating this parameter, the weight of floors, roofs is not taken into account.
Wall weight. Calculations are performed taking into account the solution, the required material, mesh
Cladding and insulation are not taken into account.
In this video, we will consider the calculation of a brick:
