Variety
Any type of material has unique distinctive characteristics, since it is used for the construction of various objects.
The beginning of construction is preceded by the calculation and acquisition of the necessary building materials. A well-executed calculation will eliminate material deficiencies or surpluses during construction.
Experts advise to buy material from one batch so that the product does not differ in color.
To perform the calculations, you will need the following data:
- material type;
- the method of masonry, established by starting from the suitable thickness of the walls of the upcoming house;
- the zone of partitions from the inside and external walls is calculated separately;
- the scale of windows, doors.
Depending on the purpose of the structure, weather conditions, they prefer to select the type of product.
Considering the production, the material has subspecies:
ceramic, which include clay raw materials and inclusions. Here are its pros and cons;
silicate brick. You can see its weight here.
the compressed product contains lime and cement. In the manufacture of this brick, cement GOST 31108 2003 is used;
refractory clay is the basis for the production of fireclay products. Here are its dimensions.
Considering the application, the brick product is divided into types:
an ordinary building product is suitable for the construction of internal and external walls of buildings. Here are the dimensions of an ordinary brick;
the facing material belongs to a perfect plane without damage. Here is its size.
Considering the filling, there is a corpulent / hollow product. For the walls of buildings with a large number of floors, only solid brick is used. Hollow building materials are suitable for interior work, including soundproofing.
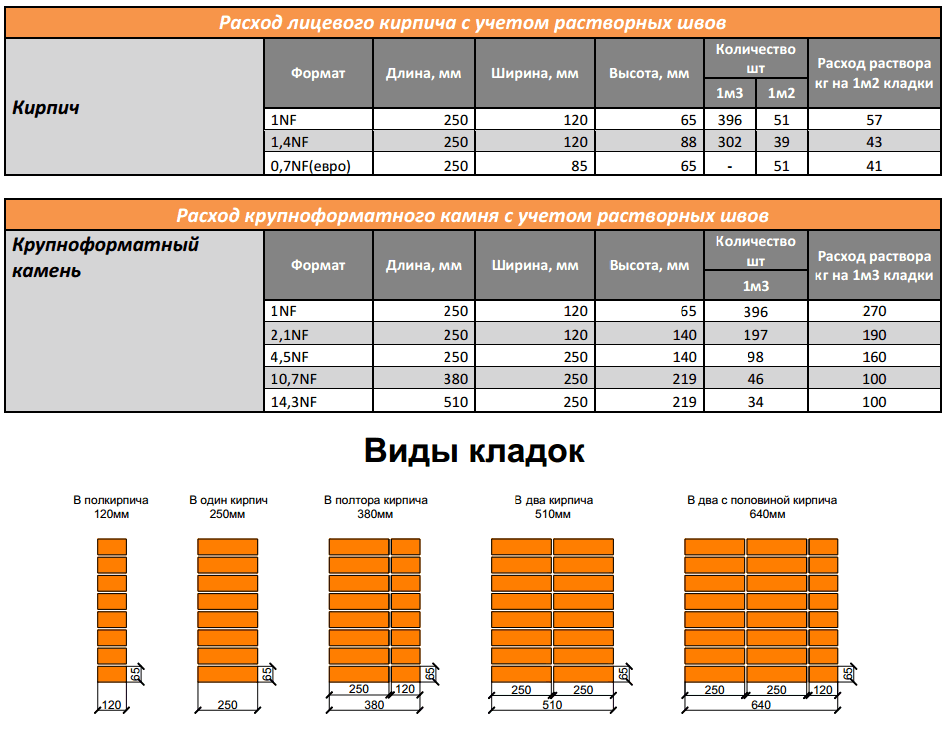
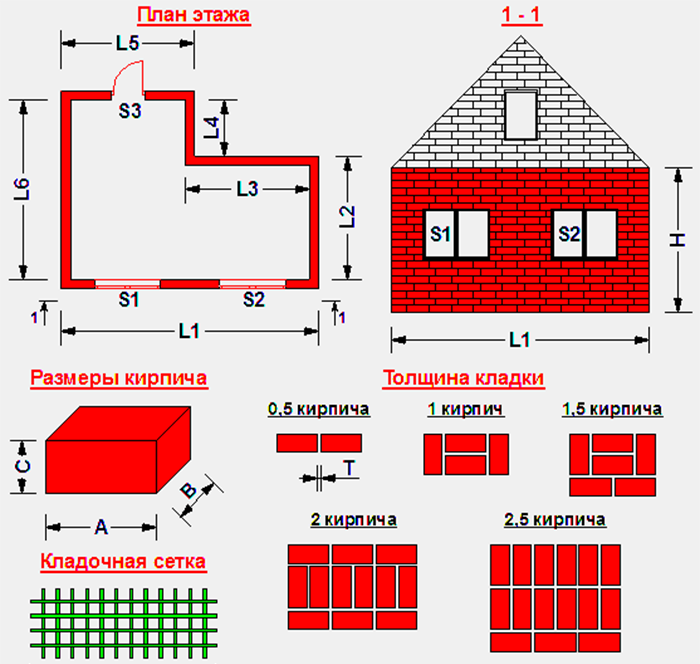
Measurement units and standard sizes
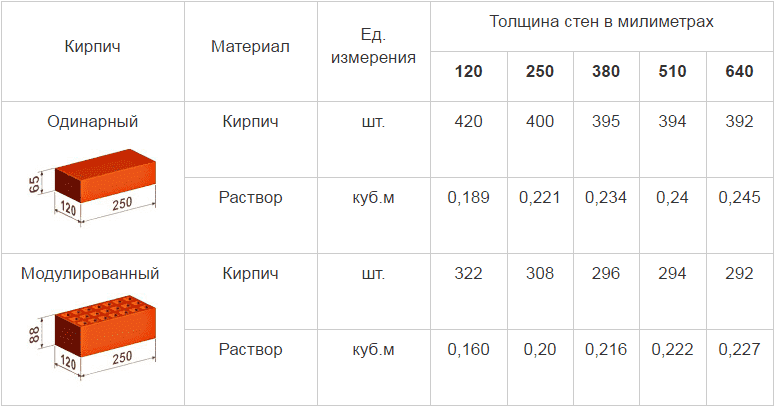
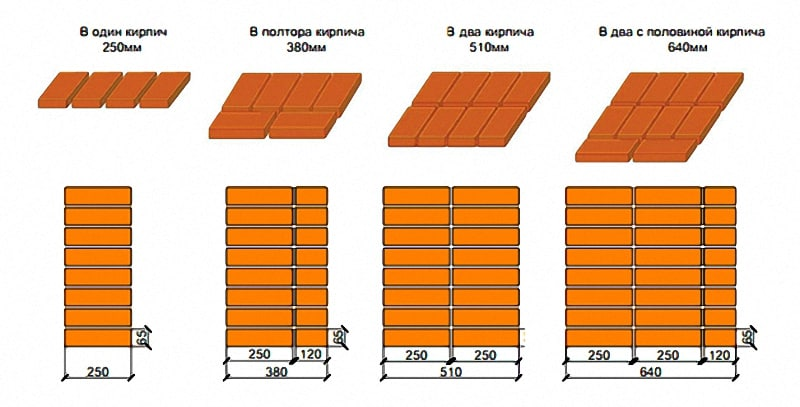
Brick is a standardized product. GOST 530-2012 defines the dimensions of each of its types. An ordinary parallelepiped has side dimensions: 250 mm - length, 120 mm - width, 65 mm - height. For the construction of residential buildings, thickened bricks can be used: one and a half - with a height of 88 mm and double - with a height of 138 mm.
Requirements are calculated in different ways depending on the task. Usually you need to know the volume of building materials - m 3. These units determine the amount of sand, cement, concrete for the entire object. If you need to calculate how many bricks will be required for laying the walls, use the units of area - m 2. The calculation of the amount of material in the masonry is carried out taking into account the volume of the seams - the inter-brick space, which is filled with mortar during the work. Usually it is 0.1 cm.
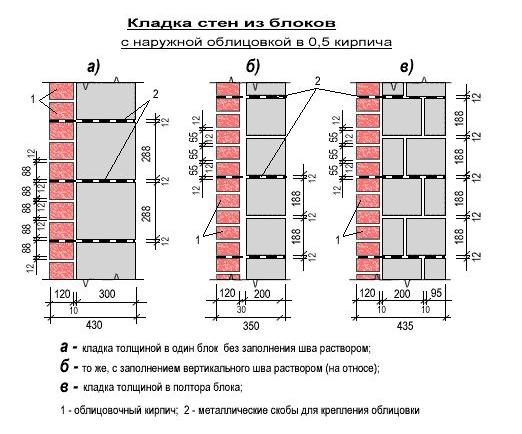
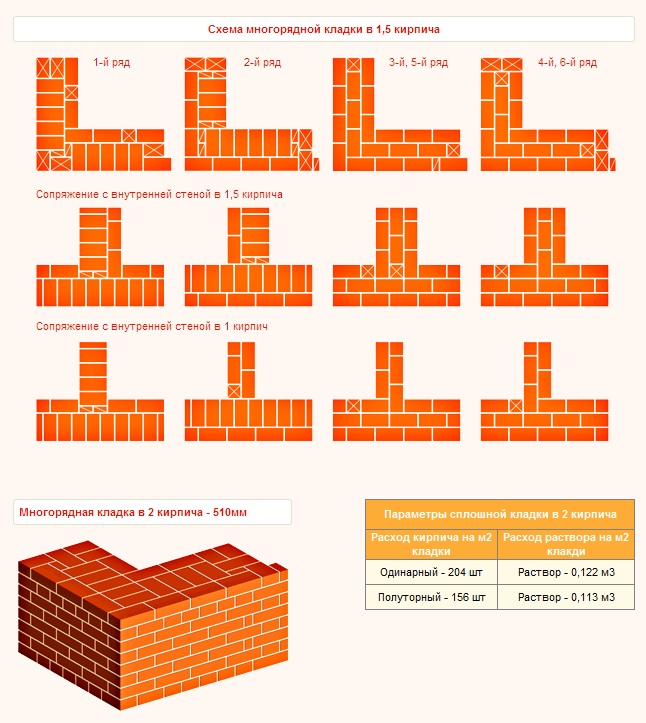
The calculation of materials is carried out taking into account the thickness of the masonry. The cross-section of the outer walls must be at least 40 cm. To lay out such a structure, one and a half bricks must be placed in each row: two with a poke and one with a spoon. The thickness of the masonry in old houses is 60-80 cm. To build such a structure, two-three-row masonry is used.
They order the production and delivery of bricks in pallets or pallets - in packing units, which are used to account for the release and transportation of products. The general conclusion is this: there is a theoretical consumption of materials per unit of masonry (in pieces) and practical (in pallets).
How many bricks are in 1 m2 of masonry: necessary parameters, options for calculating the required amount
It is possible to determine how many bricks are in 1 m² of masonry under certain conditions, on which the desired figure depends.
Therefore, before tackling the calculations, you should decide on the design features of the barrier being erected. The calculation itself will not cause any particular difficulties.
The number of bricks in 1 m² of masonry walls and partitions is the basis for determining the need for ceramite for the entire volume of construction.
note
When it comes time to plan the procurement of materials for the construction of summer cottages, their characteristics are usually already known: if it is a ceramite fence or an internal partition of a room, the masonry will be half a brick, a household shed is made thick as a whole block, and for the outer wall of a residential building no less than in one and a half ceramite. Depending on the purpose, the following main types of the main element of the masonry are distinguished:
- Red brick is the most durable, it is used in the construction of load-bearing structures and in terms of volume it can be single, one and a half, double.
- White silicate block is used for non-critical structures: internal partitions and gazebos, to give the facade an attractive look. This kind in the form of a double volume is not released.
- Facing ceramite is used to decorate individual structures of architectural objects, and can be single in size with deviations in one direction or another.
To determine how many bricks are in 1 m² of masonry, one must take into account the factors that affect the desired result: the first is the thickness of the walls. It was mentioned above, measured by the length of standard ceramite: ½ part, in a whole block, one and a half, two or more bricks.
The thickness of the mortar joints between the individual elements in the masonry is the third condition for the successful solution of the problem. In the full volume of the wall, approximately one fourth of the gaps are accounted for.
Dimensions of bricks and gaps
There is a state standard - GOST 530–2012 Ceramic bricks and stones, where the nominal dimensions of products and their designations are given. Ceramites are in the greatest demand:
| Dimensions, mm | Normal or single - 1NF | One and a half - 1.4NF | Double - 2.1NF |
| Length | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Width | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Height | 65 | 88 | 138 |
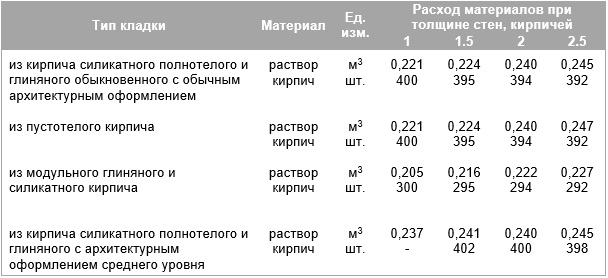
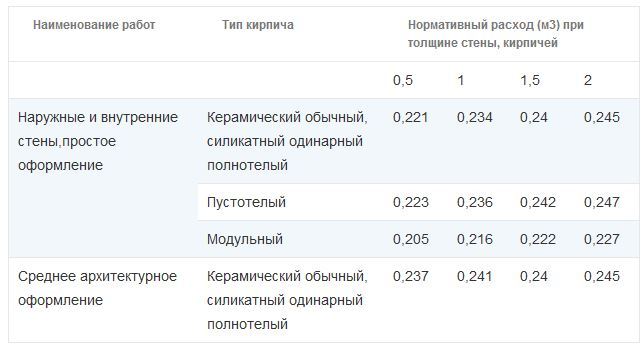
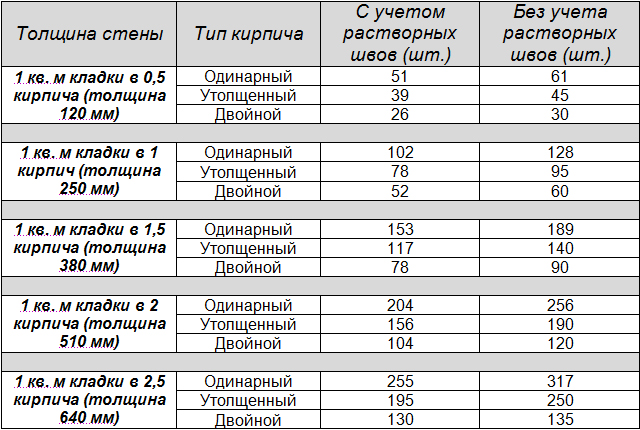
The inter-brick space is filled with cement mortar, the average joint size is taken as 1 cm.Standards for the thickness of brickwork, taking into account the filling of the gaps:
| Type of | 0,5 | 1 | 1,5 | 2 | 2,5 |
| Size, mm | 120 | 250 | 380 | 510 | 640 |
Calculation of the number of ceramites
Obviously, in one square meter of masonry of 1.5 bricks, the number of elements will be greater than with a wall thickness of one length of ceramite.
Therefore, several calculations are performed if the structure will include partitions with different characteristics, including the shape of individual blocks.
For example, you can calculate how many one and a half bricks in 1 m² of masonry in one ceramite. Sequencing:
- The size of the one-and-a-half element is fixed - 250x120x88 and the wall thickness - 250 mm.
- Along the length of one meter, taking into account the filling of the seams, (1000/260) * 2 = 7.69 pieces are placed.
- The number of blocks in height is 1000/98 = 10.20. Here it is not multiplied by 2 - this was taken into account by the previous action.
- The desired result is 7.69 * 10.20 = 78 pcs.
Alternative way
It is based on determining the surface area of a single masonry element and further shifting towards establishing the quantity depending on the wall thickness. The initial data remains the same as in the previous calculation. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- The area of the lateral surface of one element is determined as 0.26 * 0.098 = 0.02548 m².
- For a half-brick wall, the number of blocks will be 1 / 0.02548 = 39 pieces.
- The required value according to the condition of the problem - the number of ceramites in 1 m² of brickwork with a thickness of brick will be 39 * 2 = 78 pcs.
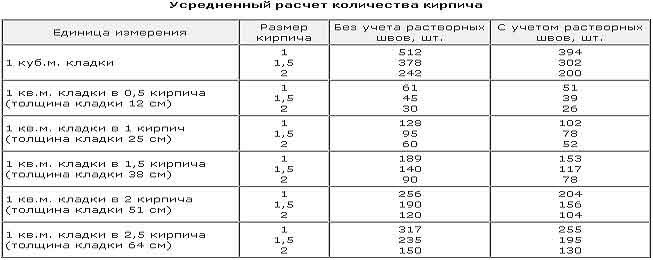
As you can see from the result, both methods gave the same answer. To simplify the use of data when determining the need for the purchase of materials, special tables are compiled, in which quantitative indicators are summarized for all options for ceramite masonry.
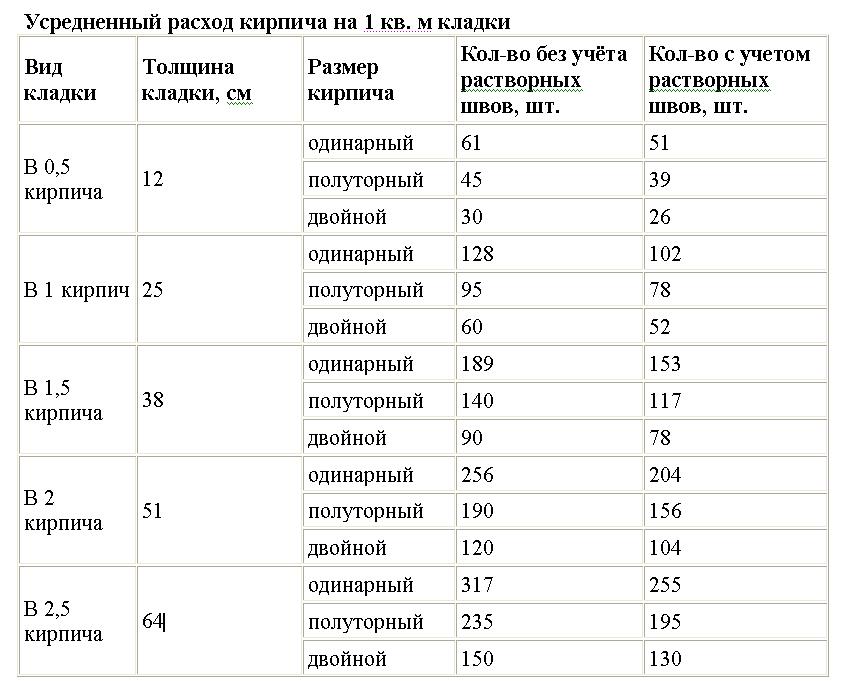
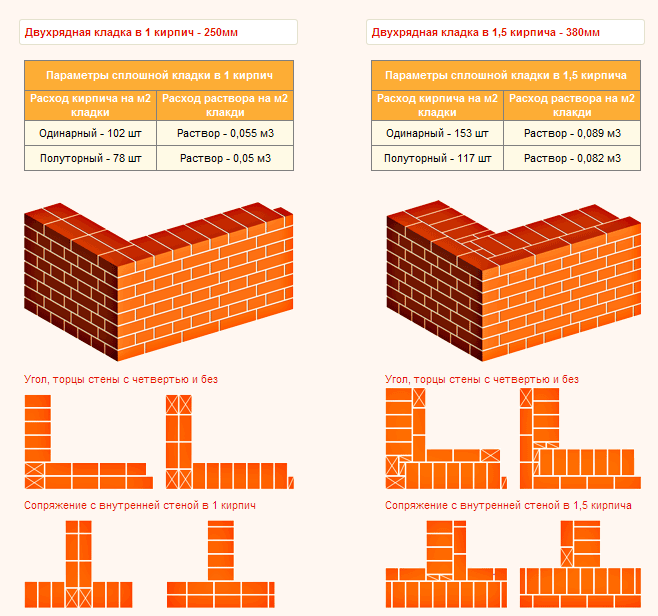
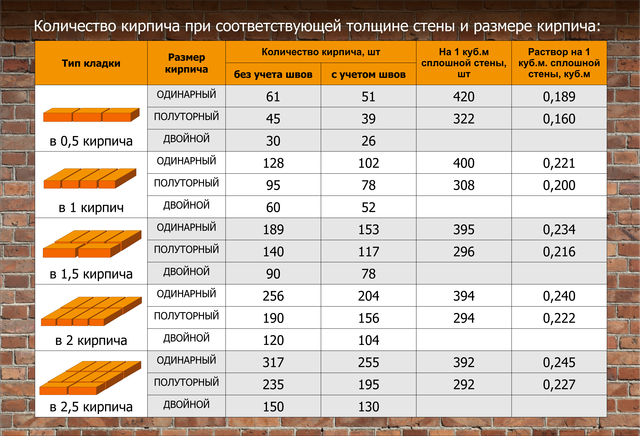
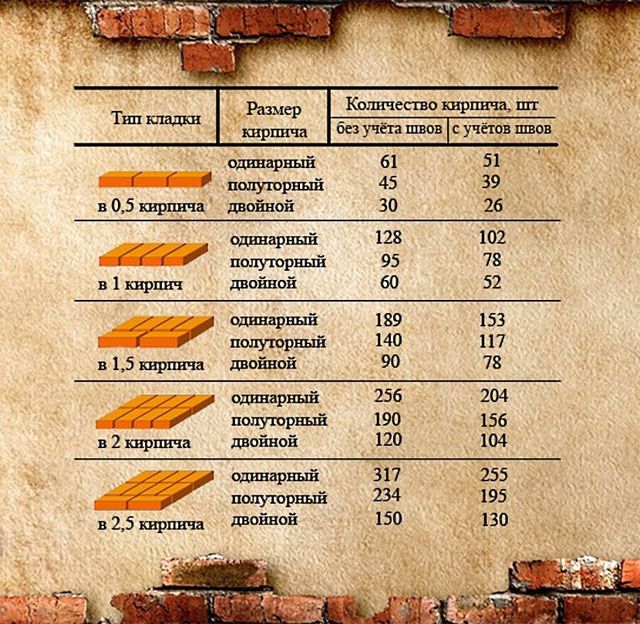
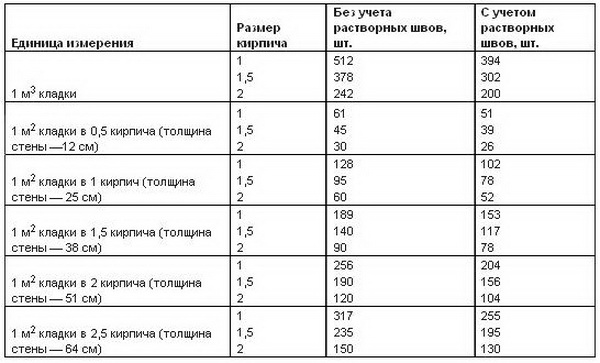
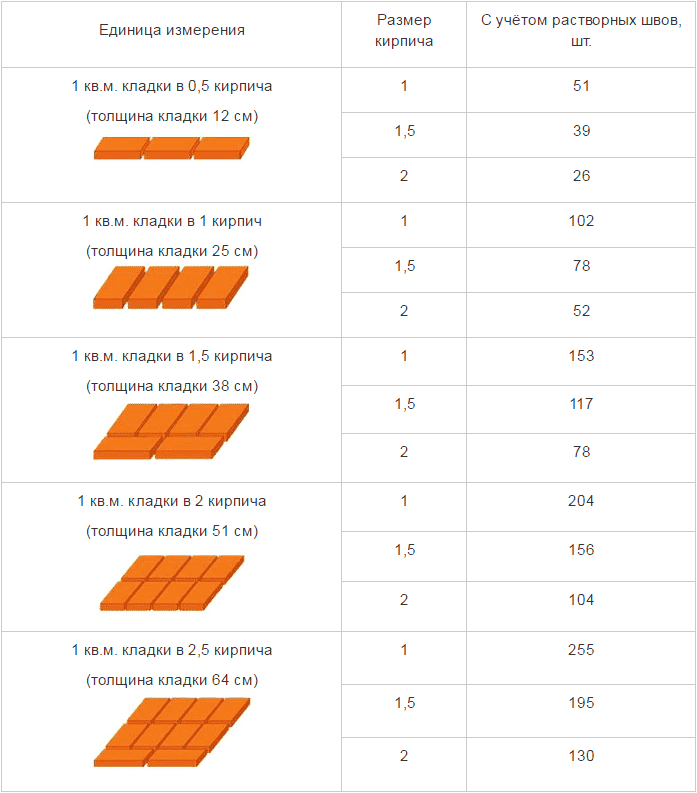
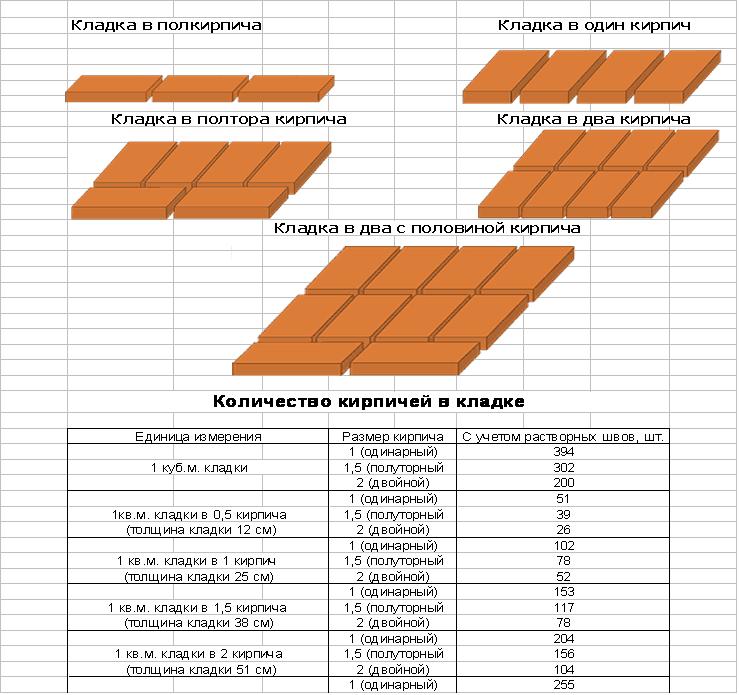
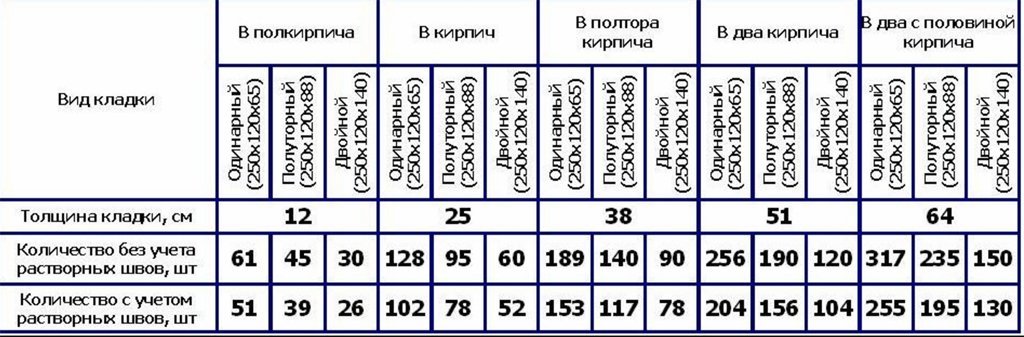
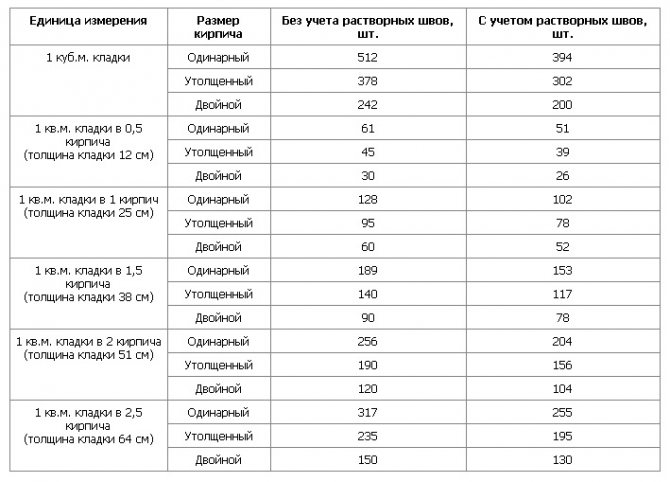
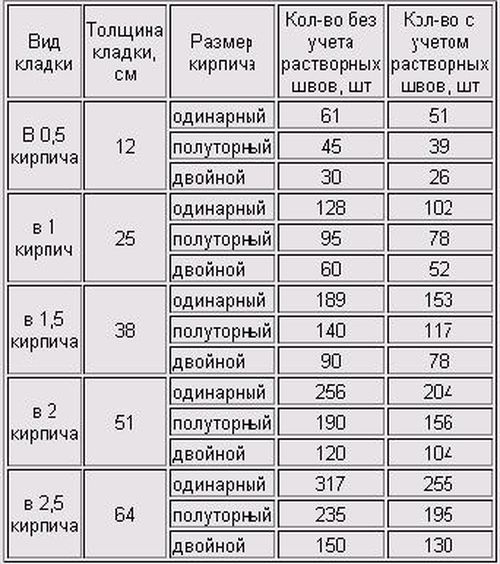
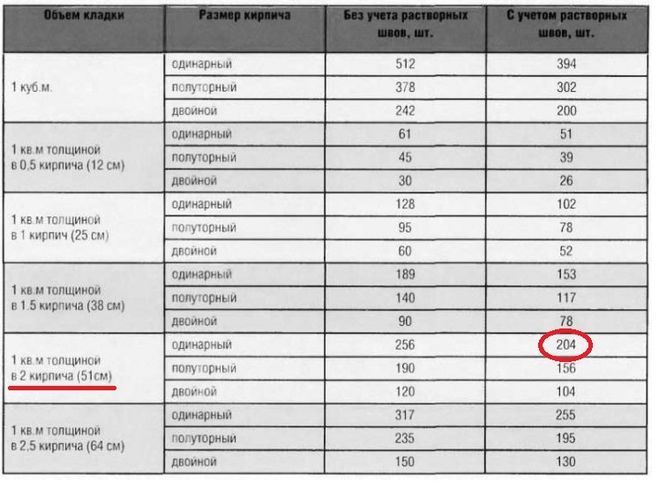
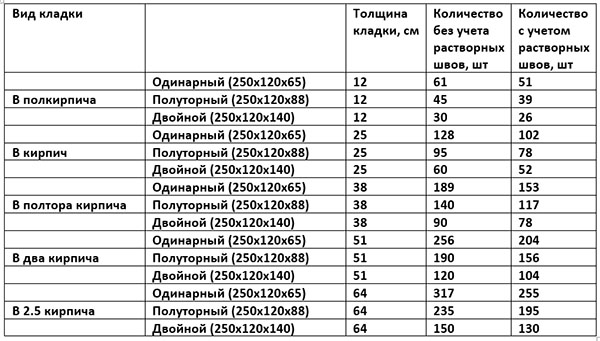
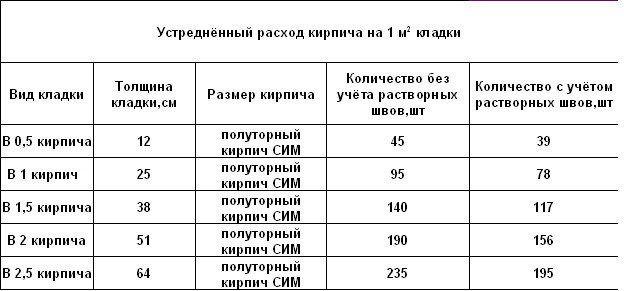
Table for determining the number of blocks in 1 m² of partitions
| Wall thickness in bricks | 1NF - single, pieces per 1 m² of masonry: close / with a seam | 1,4NF - one and a half, pieces per 1 m2: close / with a seam | 2.1NF - double, pieces in 1 m2: close / with a seam |
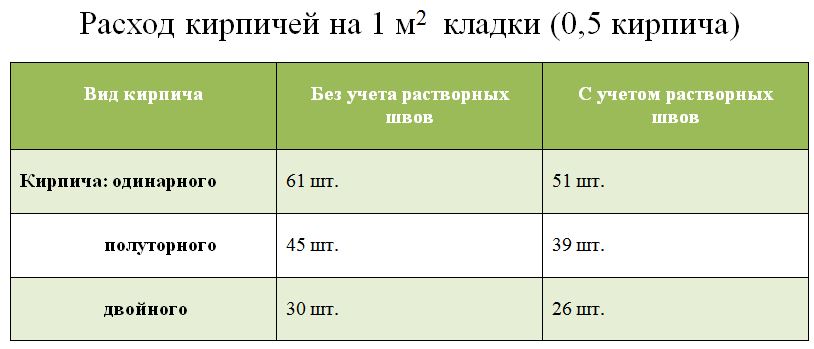
| 0,5 | 61/51 | 45/39 | 30/26 |
| 1 | 128/102 | 95/78 | 60/52 |
| 1,5 | 189/153 | 140/117 | 90/78 |
| 2 | 256/204 | 190/156 | 120/104 |
| 2,5 | 317/255 | 235/195 | 150/130 |
Using the table is simple: choose a value suitable for the conditions of the brickwork and multiply by the calculated area of the walls to be built with a given thickness.When determining the volume of the purchase, it is necessary to take into account that the amount of scrap in the purchased ceramite reaches 5% of the total number of bricks.
The principle of determining the consumption of bricks based on the volume of the walls
The methodology is based on the determination of the quotient from dividing the total volume of the walls (adjusted taking into account the deduction of openings for windows and doors) by the volume of one brick. The result is the required amount in pieces for brickwork.
In practice, the problem is solved with the passage of several stages:
- determination of the areas of internal walls and partitions, external load-bearing walls, differing in thickness;
- calculation of the areas of window and door openings;
- subtracting the size of the openings from the value of the area of the walls;
- calculating wall volumes by multiplying their corrected area by thickness;
- calculation of bricks for laying external, internal walls and partitions by dividing the obtained wall volumes by the volume of one brick.
The task is complicated by the fact that there are grout-filled joints between the bricks. Their standard thickness is taken equal to 10 mm, but it can be smaller if the brick has an ideal geometry. A few millimeters of mortar between bricks on the scale of the entire building grows into a rather impressive value, reducing the consumption of bricks.
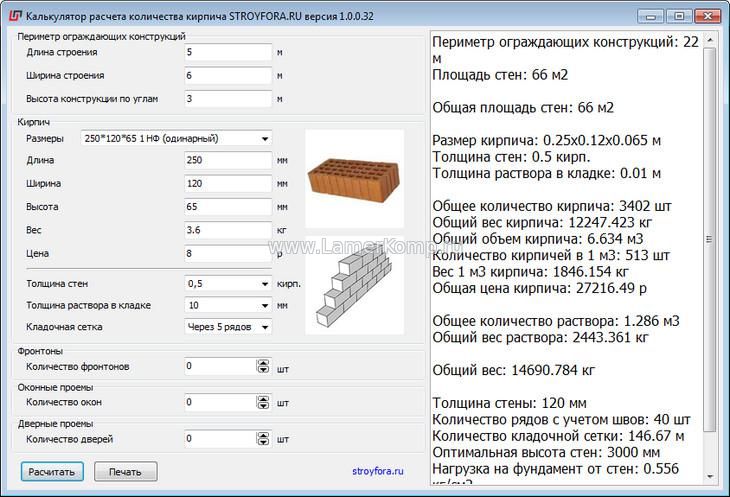
The simplified calculation is based on the standard dimensions of a single brick "normal shape" (1NF) - 250 x 120 x 65 mm (length, width, height). In a cubic meter of masonry such bricks fit exactly 512.82 pieces. Taking into account the seams (10 mm), the difference is 118 bricks, which for the entire object represents a mountain of unnecessary material. Using an online calculator, the purchase of unnecessary building materials will be excluded.
Any batch of bricks initially has a certain percentage of rejects. Losses are inevitable during loading, transportation and unloading. This damage increases the calculated amount by 5 - 8%.
What does it depend on?
If we talk about what the number of bricks in brickwork depends on, then it should be said that there will be a lot of factors in general. To begin with, the calculation for a start is carried out depending on the thickness of the brick wall. She usually happens:
- in half a brick;
- into a brick;
- one and a half bricks;
- in two bricks.
This is the first factor. Another factor is the volume and physical dimensions of the material as such. But to say about them, first it must be said that a brick has three sides. The first of them is called the bed and is the largest, the second is called the spoons and is the side. And the end of the brick is called a poke. If we talk about domestic standards, then usually such material has dimensions of 25x12x6.5 centimeters. Only the height of the poke will change. For a single solution, it is, as already mentioned, 6.5 centimeters, for one and a half - 8.8 centimeters, and for a double - 13.8 centimeters.
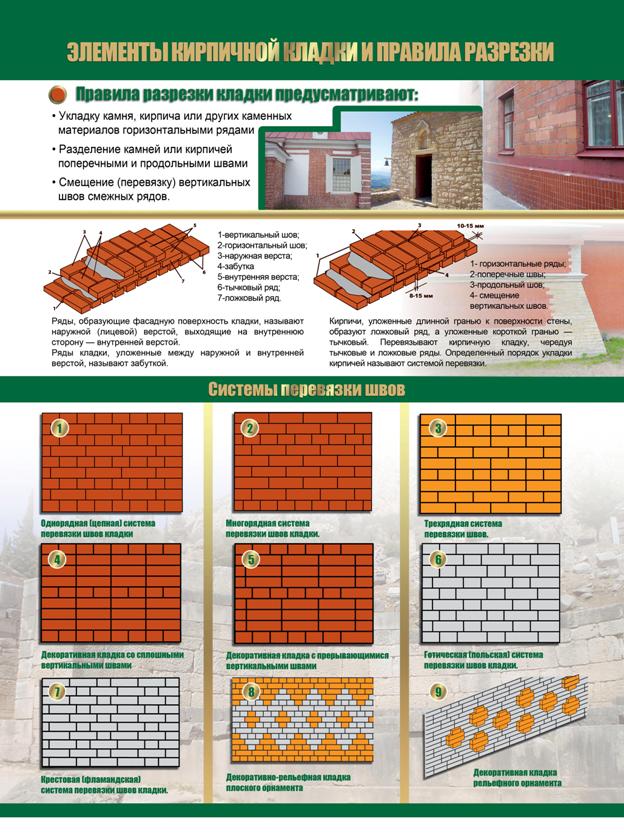
Types of brickwork
In modern construction, several types of brickwork are used, differing in their width. The standard thickness of the walls of a building can be from 1 to 2 or more bricks. In this case, the term “bricked” means the length of a brick, which is 25 cm. The standard size of a “single” brick is fixed in the provisions of GOST and is:
- Length - 25 cm (brickwork).
- Width - 12 cm. ("Half brick" masonry)
- Height - 6.5 cm.
Brickwork width
From the point of view of economic feasibility for low and medium-rise construction, the most effective is the thickness of the outer walls of 38 - 51 cm - two or one and a half bricks thick. This type of masonry can easily withstand the weight of two or three floors above, as well as the load from the roof. At the same time, the mass of the structure remains relatively small, so that the developer does not have to additionally strengthen the foundation of the house. Another plus of such masonry is that this type of masonry can significantly save on building material.
Walls thicker than 2 bricks are practically not used in modern construction. This is due to the fact that, firstly, their bearing capacity is clearly excessive - a wall of 2 bricks can also cope with the necessary load.
The increased dimensions of the masonry only lead to unreasonably high estimated costs for building materials, without any benefit in terms of the strength of the building. Secondly, it is much more effective to improve the thermal insulation of a building thanks to the use of insulation materials, rather than by increasing the thickness of the bearing walls made of bricks. Thinner walls for supporting structures, according to SNiP standards, are not recommended. So, a load-bearing wall in a half-brick will not be able to provide sufficient strength of the building and the durability of its operation.
For internal partitions, masonry in half a brick (12 cm) is most often used. This is the most optimal option, both from the point of view of the financial component, and taking into account the strength characteristics of the structure. Much less often, masonry is used in brick (25 cm) and 6.5 cm when the bricks are placed on the edge.
How to calculate the wall masonry with a calculator?
Bricklaying methods
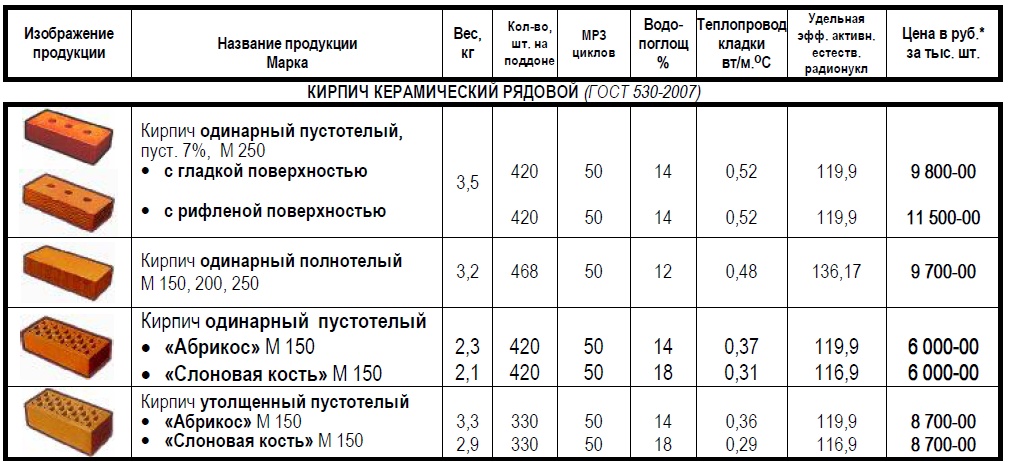
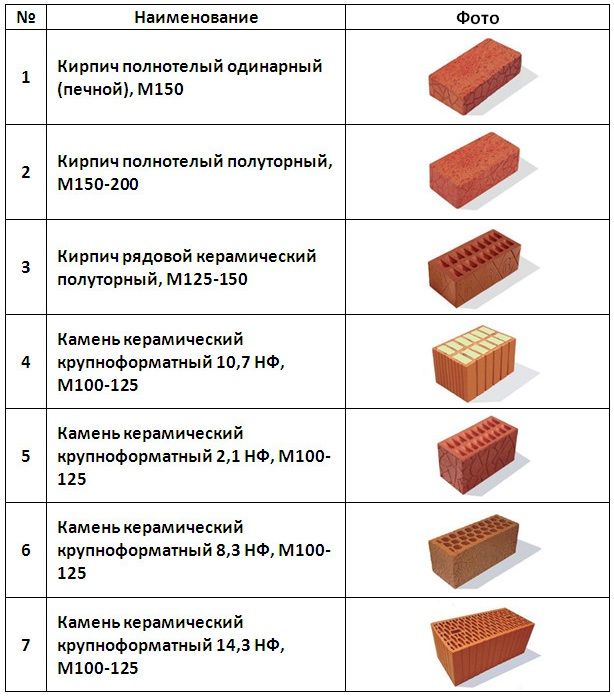
Brick is the most demanded and widespread building material, it serves for a long time and pleases with a neat appearance. Today there are several types of bricks for the construction of buildings:
- a brick made of clay and other fillers is called adobe;
- ceramic, the most used, of fired clay;
- silicate made from sand and lime;
- with the addition of cement - hyper-pressed;
- clinker, from a special composition;
- refractory.
Such materials are used both for laying a house and for building additional finishes in the future, creating a facade, and interior structures. Fireclay bricks can withstand high temperatures and various heating and cooling cycles without loss of strength.
Bricks can be hollow, porous, the most common standard size of this product is 250-120-65 mm, with preliminary calculations of brick consumption, brick dimensions increase by 10 mm for each parameter.
Algorithm for calculating the material for the construction of a building

masonry calculation table
For correct calculations you need:
You need to start with such important points as calculating the cubic capacity of brickwork:
- First, answer for yourself the question about the thickness of the brickwork. It can be half a brick and be 12 cm. In a brick with a thickness of 25 cm. In one and a half bricks and a thickness of 38 cm. In two bricks 51 cm and two and a half bricks 64 cm. The calculation takes into account the width of the seam - 1 cm. Taking into account climatic conditions, the best option would be to choose masonry 510 mm or 640 mm.
- Count the number of walls, their length, width. To do this, use a tape measure and write down the measurements with a small margin. For calculation, you can use the information from this article.
- Calculate the area of each wall taken separately. Multiply the length by the width. After that, calculate the area of the window openings. doors, other places that do not require material consumption during laying.
- Determine the entire area of the brick luggage. by subtracting the area of windows and door openings from the calculated area of the walls.
- For a final understanding of how to calculate the volume of brickwork, you should calculate the brick in pieces, in accordance with its dimensions. For the construction of a brick building, a single (250 * 120 * 65), double (250 * 120 * 138) or one and a half (250 * 120 * 88) stone is used. More often, a single brick is used when building a house.

calculation of brick volume
The main question is how to calculate the cubic capacity of a brick. For a single brick, the consumption of building material per square meter is 51 pieces of bricks, for one and a half - 39 pieces, for double - 26 pieces. To know exactly the required number of bricks, you need to multiply the amount at the rate of 1 square meter by the calculated area.These calculations are correct for half-brick masonry.
More about the technology for calculating the number of bricks here. If the masonry is planned in one brick, the figure obtained in the calculations must be multiplied by 2, if it is one and a half bricks, then it must be multiplied by 3, and multiplied by 4 if the masonry is in two bricks.
- After the received quantity, add a safety stock in case of unforeseen expenses of building materials.
If you decide to start building a brick house, any outbuilding on your site, then purchasing the main building material in advance is the right decision.
In an unstable economy, there is no certainty that the price of building materials will not rise or that their price will remain unchanged. Of course, the existing calculations are nowhere near as accurate as you would like. There is a chance that the brick may not be enough, and you will have to buy the missing amount. It is to prevent such incidents that a safety stock is taken.
It is necessary not only to protect yourself from a lack of material, but also to insure against a possible break of material.
After the calculations of the necessary bricks for the construction are over, do not forget about the necessary tools for masonry. They can also be purchased in advance and with the onset of heat, start construction work.
An important point! When calculating the amount of required building material, keep in mind that the sizes of imported bricks differ from domestic ones. Therefore, before starting the calculations, check the dimensions of the brick, this will help make accurate calculations. For a better disclosure of the topic and if you still have questions, we recommend watching this video:
Our recommendations:
- Brickwork quality
- Brickwork of channels, ledges and niches
- Making jumpers
- Technology for the construction of a frame house from OSB slabs
Material features
Brick is one of the most technologically advanced building materials. Due to its excellent operational and technical qualities, it has long been used by man for the construction of both small one-storey buildings and in the construction of massive multi-storey structures.
Building brick successfully withstands loads thousands of times greater than its own weight, and if all masonry technologies are followed, the load-bearing walls of a brick house can easily serve for more than a dozen or even hundreds of years. Meanwhile, the durability of the service depends on such technical indicators of the material as the coefficient of strength and frost resistance.
The frost resistance index of the material gives an idea of the ability of a load-bearing brick wall to withstand freeze / thaw cycles when the seasons change. The frost resistance coefficient directly affects the terms of "accident-free" operation and depends on the density and porosity of the material. The higher the moisture absorption coefficient, the lower the resistance of brick walls to seasonal temperature changes. According to the requirements of GOST, the minimum cyclicity of the building material should not be lower than 20 - 25 seasons.

Types of building bricks
The strength factor is calculated depending on what kind of load the material can withstand without destruction and deformation. Marking is done in increments of 25-50 units and can range from M-75 to M-200. Each of these varieties has its own area of use.
Standard sizes of masonry material Among the disadvantages of brickwork, high hygroscopicity should be noted. Burnt clay, which is the main raw material for this building material, is able to easily absorb from the atmosphere and retain water inside. The dampness contained in micropores and cracks gradually leads to the destruction of the brick, the loss of its strength properties. In this regard, the external masonry should, if possible, be protected from the effects of precipitation by waterproofing or moisture-repellent primers.
Another disadvantage of brick as a material is its high thermal conductivity. Thanks to this, the brick itself is an excellent "cold bridge", contributing to the penetration of frost into the building from the outside. Previously, this negative property was fought by increasing the thickness of the load-bearing brick wall.
In Soviet times, with the relative cheapness of bricks and the lack of effective insulation, this was the easiest way out. A few decades ago, the thickness of the walls of a brick house in the central regions of the country could be 64 cm, and in the northern regions - 1 m or more. However, now, when there is a huge selection of building thermal insulation on the construction market, such a thickness of a brick wall is becoming an unnecessary waste.
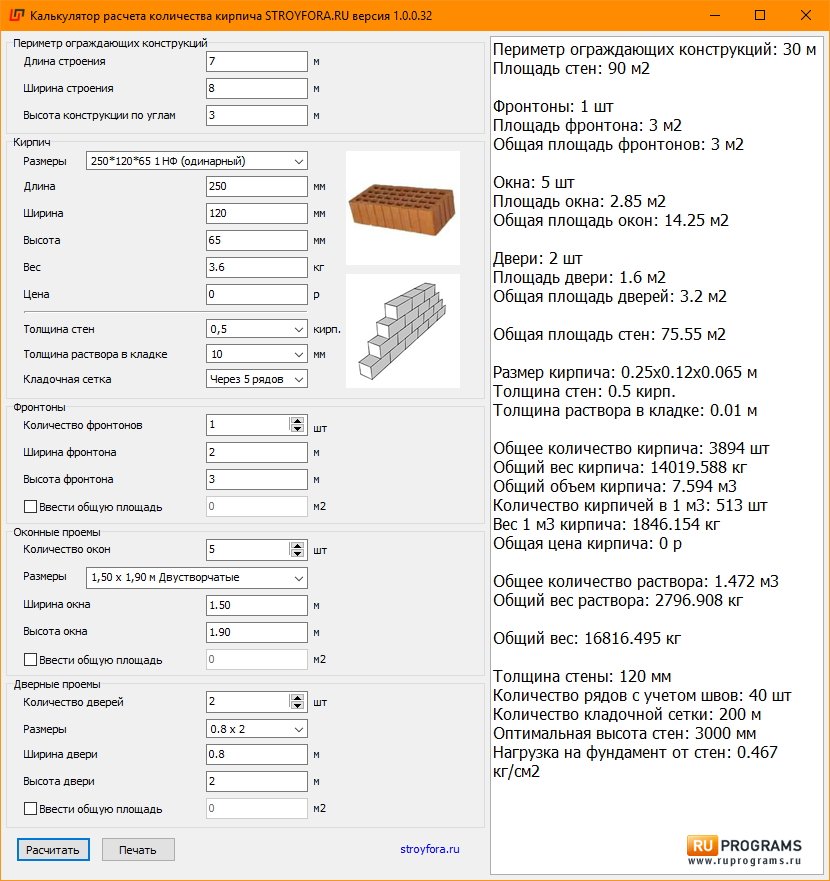
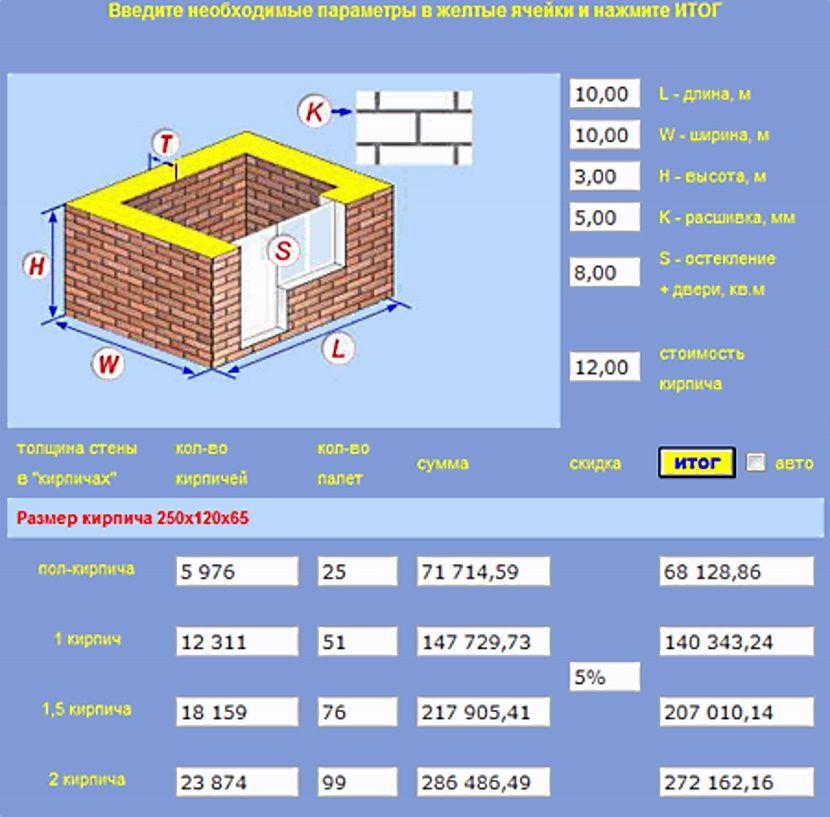
Calculator Purpose Information
K irpic online calculator is designed to calculate the number of building and facing bricks for a house and a basement, as well as related parameters and materials, such as the amount of masonry mortar, masonry mesh and flexible ties. Also, in the calculations, the dimensions of the gables, window and door openings of the required number and size can be taken into account.
When filling in the data, pay attention to the additional information with the Additional information sign
For a long time, irpich has been the most demanded, widespread and familiar building material for the construction of durable and reliable structures. This situation persists for a number of reasons, despite the emergence of new, modern and cheaper building materials. There are several of the most common types of bricks for any building needs:
- Adobe - made of clay and various fillers
- Ceramic - (most common) from fired clay
- Silicate - from sand and lime
- Hyper-pressed - from lime and cement
- Clinker - made of special fired clay
- Refractory - (fireclay) from refractory clay
Ceramic brick (clay), according to their purpose, are subdivided into facade, ordinary and clinker. Ordinary bricks (backing bricks) may not have ideal geometry and in most cases are used for laying rough walls of houses, basements, garages, which are subsequently plastered, painted and protected with facing materials and coatings. Its color has various shades of red.
About blitz (front) is used for the construction of walls without any additional finishing in the future. There are also various special types of facade bricks that can withstand high mechanical loads and adverse weather conditions, and are usually used for paving paths, building all kinds of retaining fences, stairs, walls.
Linker has an ideal smooth surface, various shades of red and black colors and has a high density.
With orkatny is a light-colored calcareous-silicon artificial stone. Silicate brick differs from ceramic brick in that it is not fired during the manufacturing process. It is quite hygroscopic, and, accordingly, is not used for the construction of objects that will be operated in humid environments, such as basements and basements.
Likewise, silicate brick is not used in the construction of furnaces, pipes, chimneys and foundations, since it can withstand external destructive loads rather weakly.
Oh refractory It is divided into several types and is used for the construction of structures exposed to high temperatures, such as stoves, fireplaces, chimneys and smelters. The most common is fireclay brick, has a yellowish tint, made of special refractory clay (fireclay) and, unlike ordinary clay brick, can easily withstand high temperatures (up to 1400 grams), as well as numerous heating and cooling cycles without loss of strength.
Irpichi are full-bodied (the volume of voids is not more than 25%), hollow and porous-hollow. It is believed that indentations and voids in the material not only reduce weight, but also significantly increase the overall strength of the masonry by increasing the contact area between the brick and the masonry mortar.
The most common standard brick size: 250 - 120 - 65 mm (length - width - height), the so-called first "normal form" (1NF).
When calculating the number of bricks required for work, a rule called "format" is usually used, in which the dimensions of the brick itself are increased by 10 mm (this is the standard seam thickness), that is, it turns out: 260x130x75 mm.
The following is a complete list of calculations performed with a brief description of each item. If you did not find the answer to your question, you can contact us by feedback.
Calculation of bricks for a house
Calculate amount of material per houseusing 1 of 2 ways:
- Considering the mortar joint. The standard thickness is 5-10 mm.
- Calculation without taking into account the seam.
When counting seamlessly, the number is higher. The increase is 25-30%. Counting taking into account the seam, requires an increase of 10-15%, in case of a possible battle during construction.
How to calculate the number of bricks manually?
To calculate manually, you need to know the dimensions, types of bricks, the method of laying the building material. The following describes how to do this on your own.
Types of bricks for construction
Building material is divided into two groups:
- Silicate brick.
- Ceramic brick.
According to the fullness of the product, they are divided into:
- Corpulent.
- Hollow.
Solid material, no cavity inside. It is used in the construction of load-bearing walls.
The next group helps to determine the size of the product:
- Single - 65 mm.
- One and a half - 88 mm.
- Double - 140 mm.
During construction, there is no difference in what kind of laying is carried out. The difference is in aesthetic appeal.
How to choose the thickness of the brick wall?
When calculating the required thickness, take into account the structural features of the building, height, total area. There are standard norms, the thickness should be equal to 1/20 of the height of one floor. With a ceiling height of 2.7 m, making a calculation of 2700x1 / 20 = 135 mm. If the building is two-story, the indicators are multiplied by 2.
The thickness of the wall is determined by the type of masonry:
- The wall thickness in half a brick is 120 mm.
- Masonry with material laid across is called one brick. Width - 250 mm.
- One and a half - 380 mm plus 10 mm for a seam.
- Transverse laying of two bricks - 510 mm + joint 10 mm.
- 2 across and one lengthwise - 640 mm.
 Types of masonry
Types of masonry
Note that the use of masonry thicker than 2.5 bricks is a rare phenomenon. This is due to the climatic characteristics of the region. But so that the structure does not lose its thermal insulation properties, it is more reasonable to use air channels in the masonry and thermal insulation materials.
Masonry mortar
On the amount of material for masonry, you need to know one more parameter, the type of solution. A few years ago, the only option for brickwork was a cement-lime mortar, in which the joint width varied from 10 to 15 mm.
In the current conditions, the choice of builders is somewhat increased, and it is possible to use glue instead of cement mortar. This is especially true for silicate bricks.
In this case, the seam thickness will be minimal, so it can be ignored in the calculations.
 Laying on glue
Laying on glue