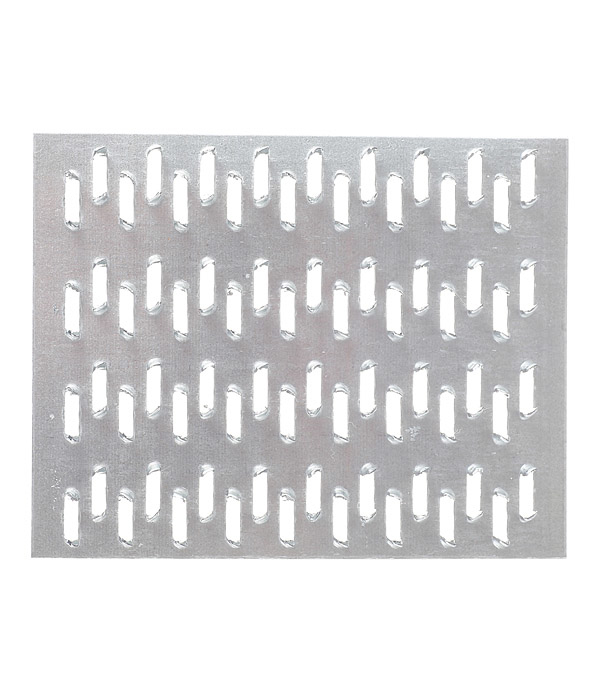
Views
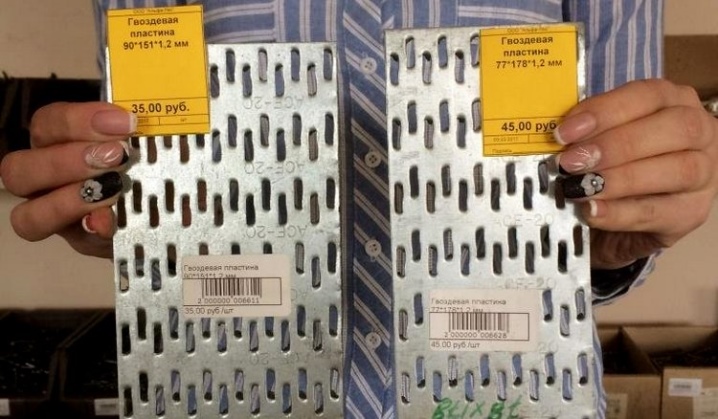
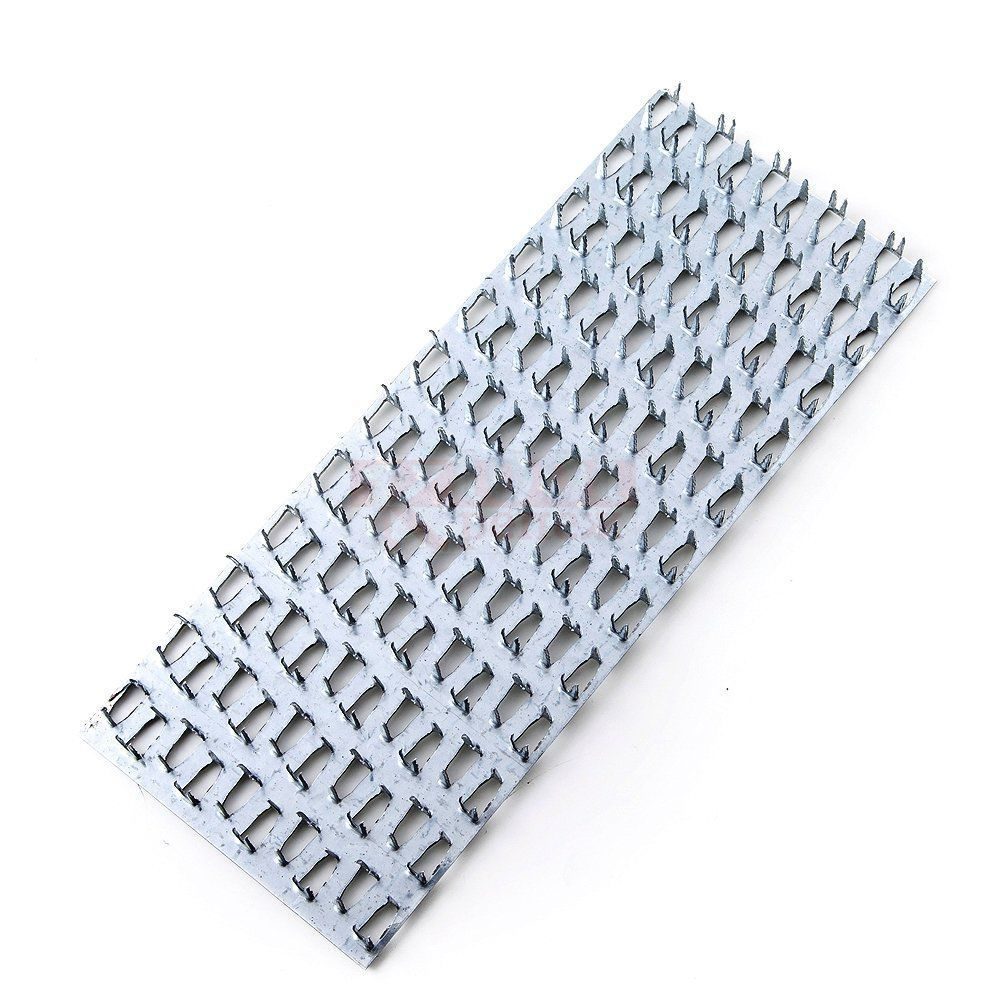
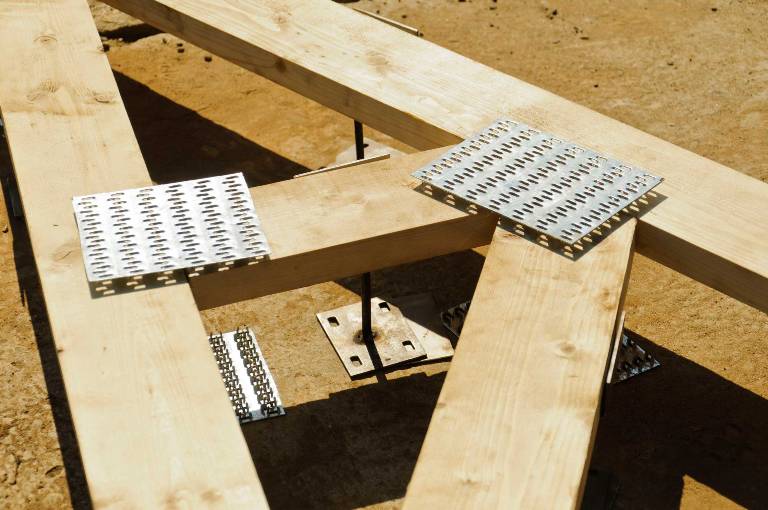
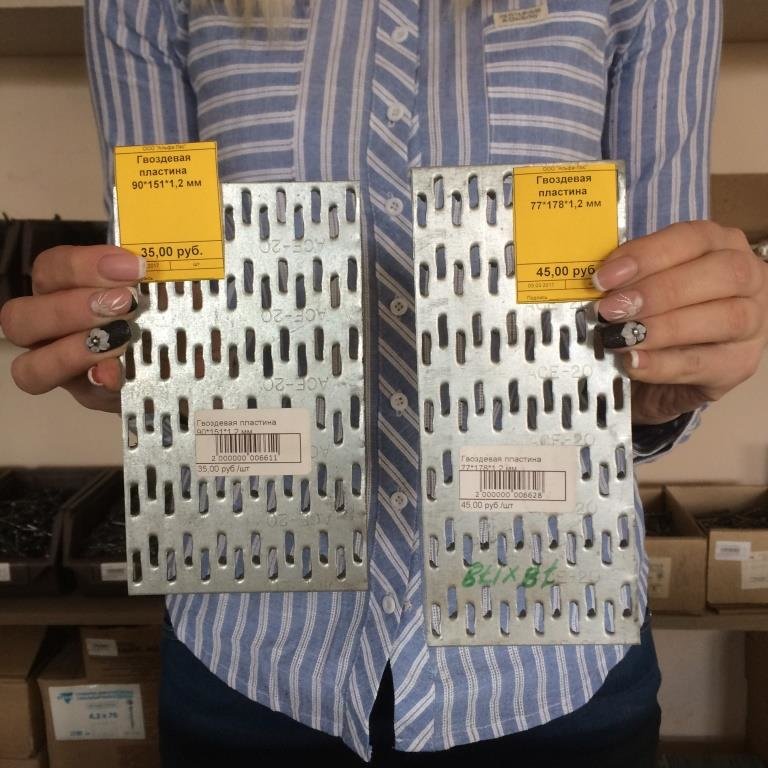
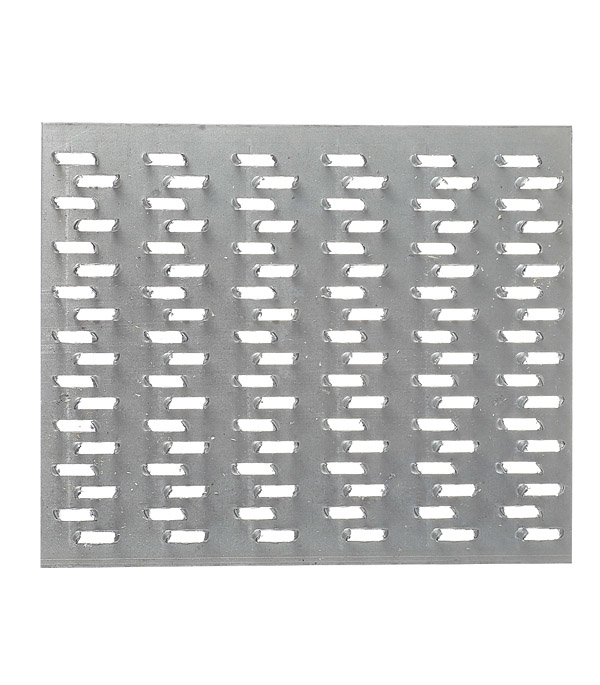
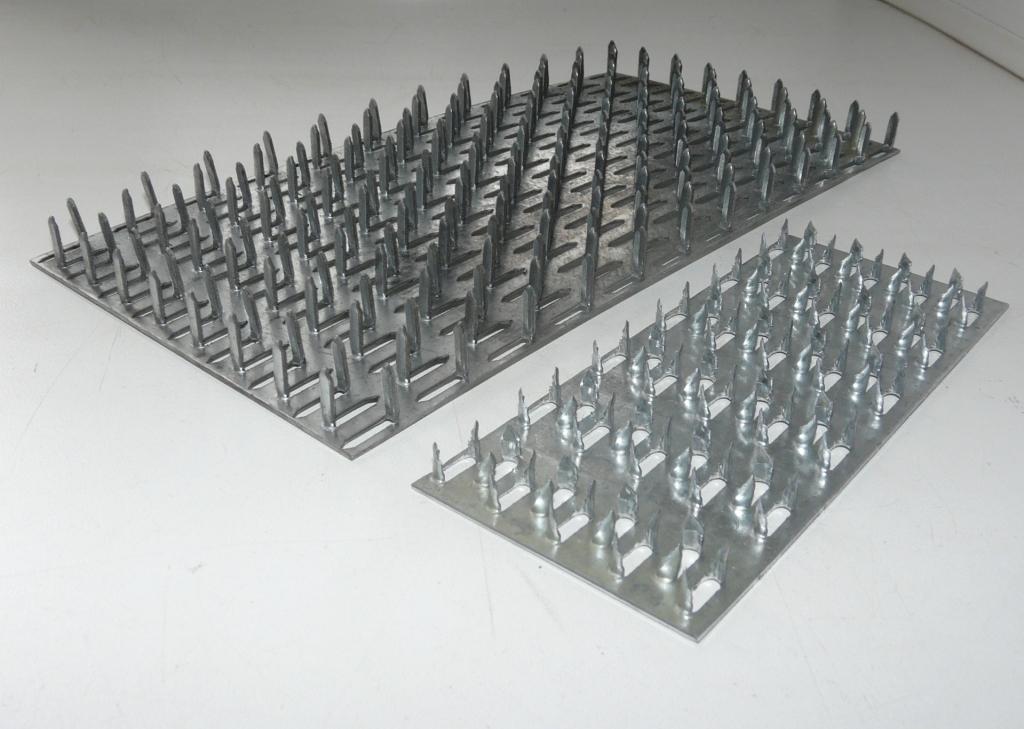
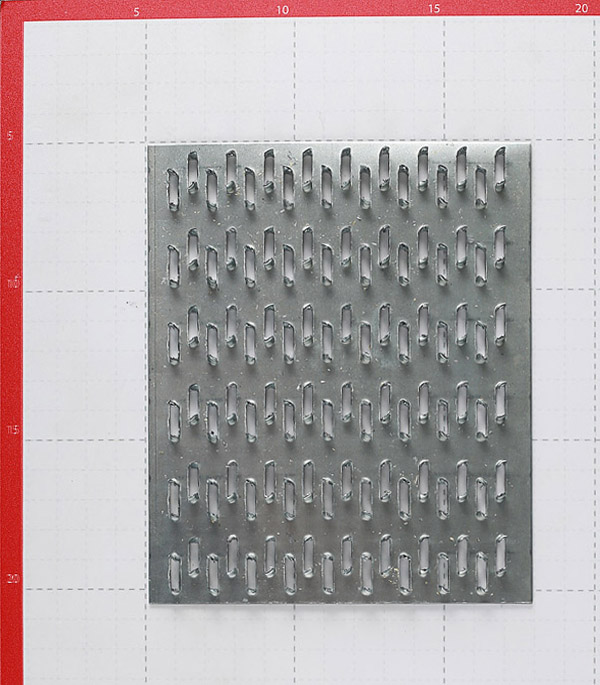
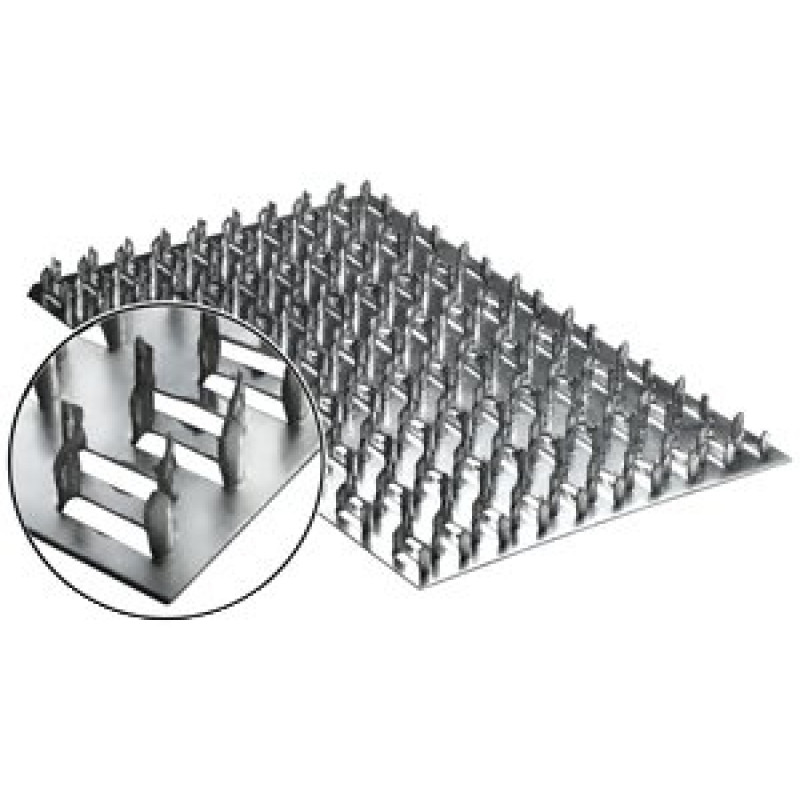
MWPs differ in their appearance. They have a different thickness of the metal base, a different number of rows with spikes, the length of which varies over a wide range. Products made from sheet steel are marked with GP (RK) symbols, and from galvanized sheet steel - GPZ.

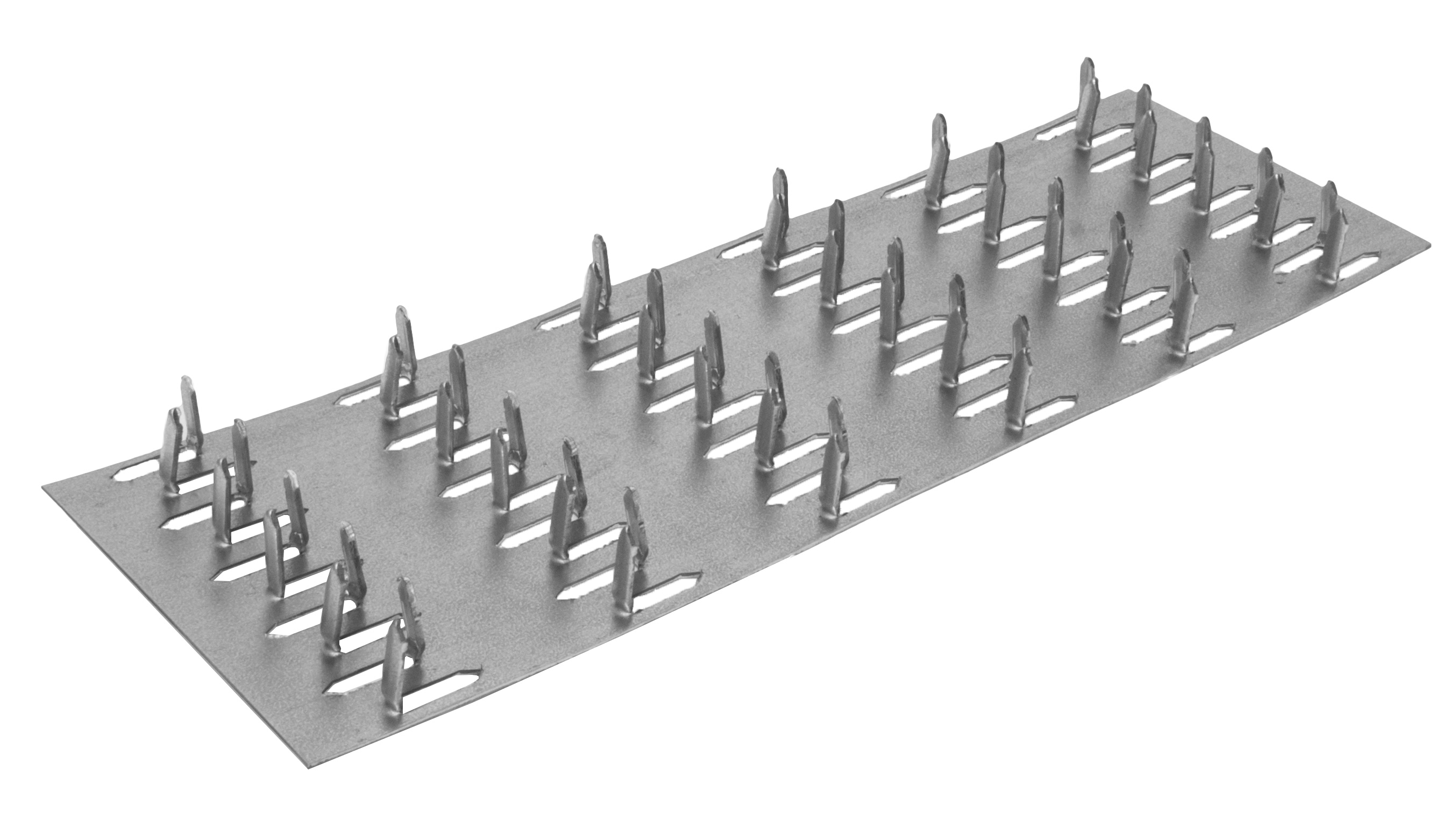
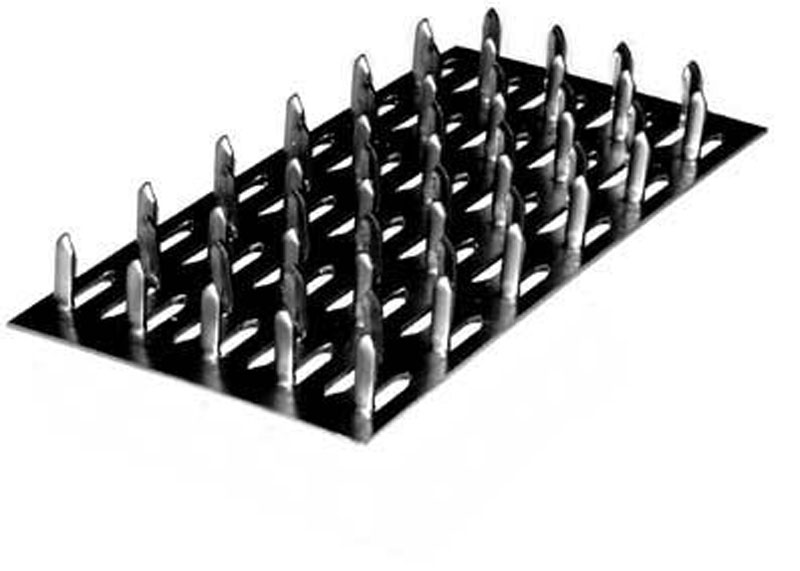
Nail plates are available with unidirectional or bi-directional pin arrangement.
- The production technology of the first fasteners is simpler and cheaper. According to it, MZP are manufactured at domestic factories. Plates with unidirectional teeth are less reliable than bi-directional pins.
- The second ones have thorns with different directions - they are located parallel to the sides and diagonals of the plate (visually, their arrangement resembles a "Christmas tree"). The production process of multidirectional nail plates is more labor intensive and financially costly. Most of these fasteners are produced in Poland, Germany and Finland.


Features of mounting metal toothed plates
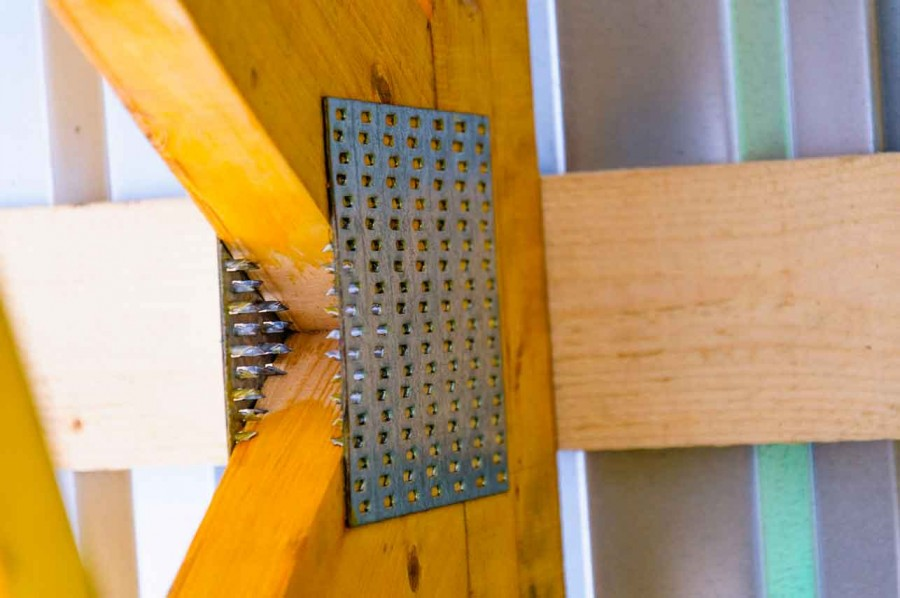
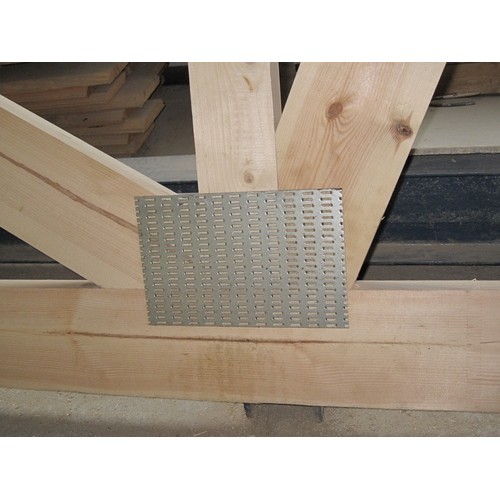
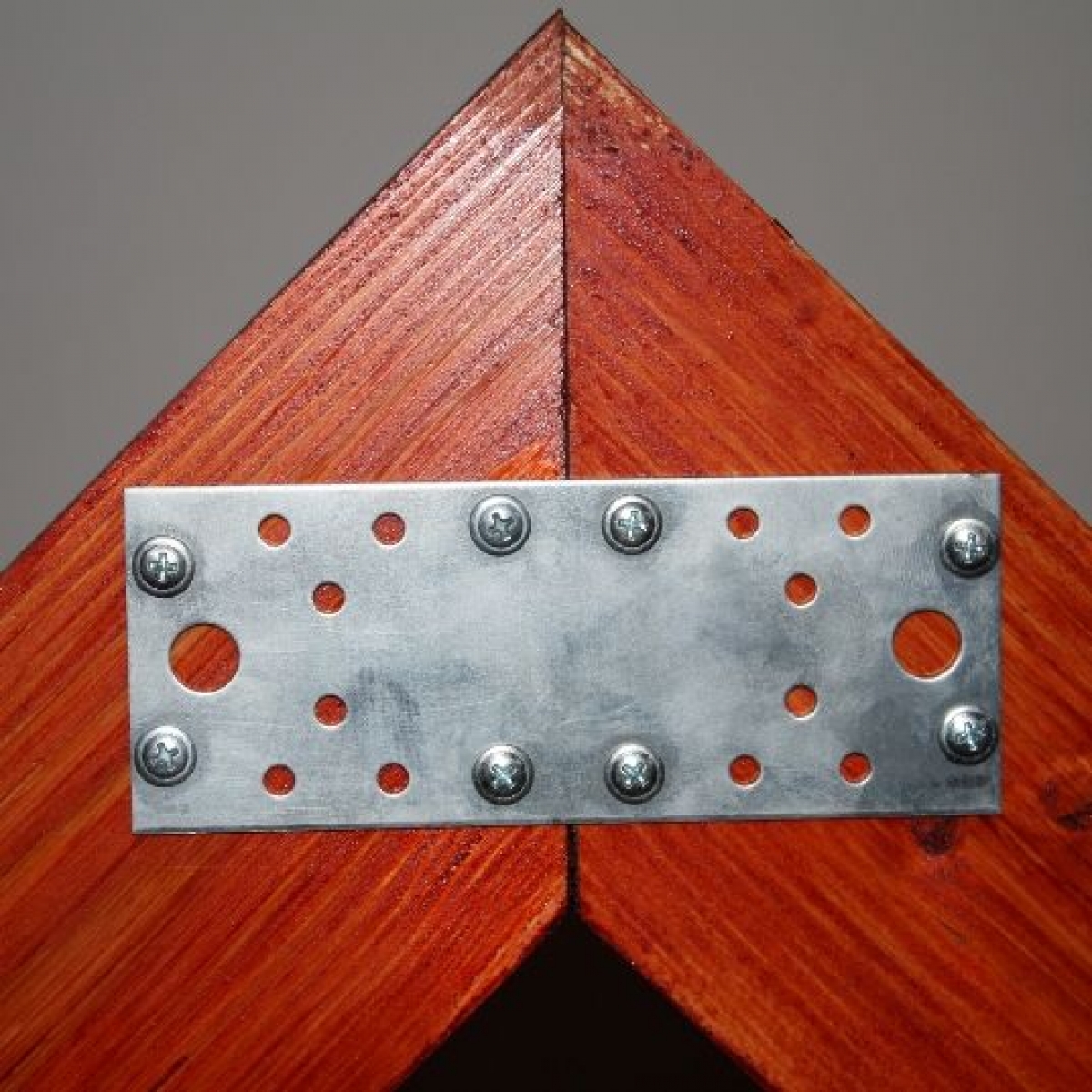
- The joint is fastened with plates on both sides.
- The installation of the MZP does not provide for the work with a sledgehammer, hammer or other percussion tool. Their use is not effective due to uneven pressure and vibration that deforms the pins.
- In ideal conditions, the MZP is fastened with the help of a rolling press at the assembly sites, and the finished part is delivered to the installation site.
- When installing the MZP directly on the construction site, a clean and even surface is equipped, and clamps or jacks are used to press the plates into the tree. First of all, the outer corners of the structure are squeezed, and then other joints.

Dimensions of metal toothed plates
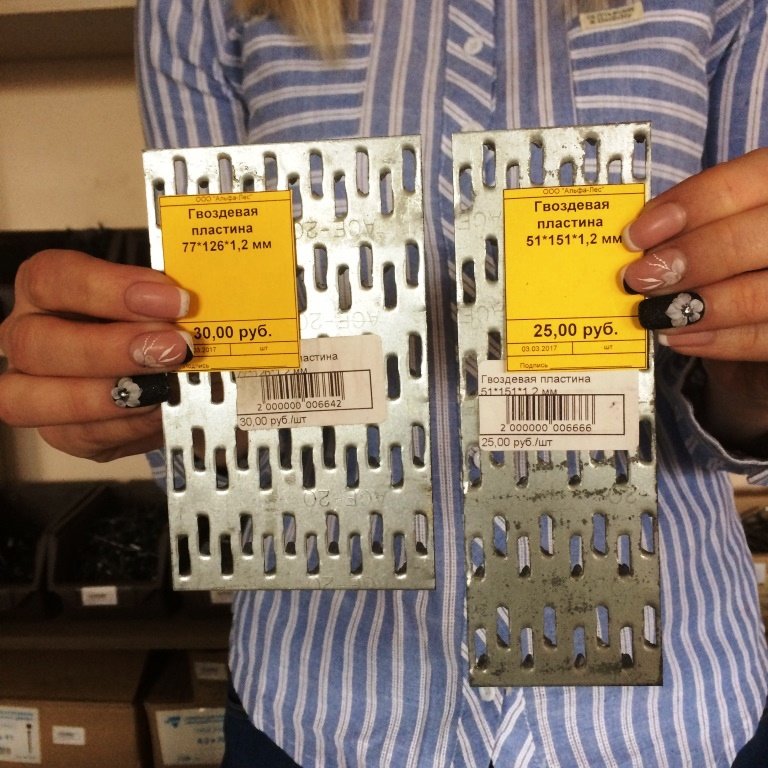
Metal toothed plates are supplied with dimensions in width from 25 to 180 mm, and the most demanded are MZP with a length of 300 mm. These dimensions can vary depending on the client's requirements and can be produced according to an individual order. The height of the thorns themselves also varies. The classic option is a tooth length of 8-10 mm. If necessary, it can reach 25-26 mm. As a rule, as the thickness of the plate increases, so does the length of the tooth.
Compared to traditional fasteners perforated for bolts, self-tapping screws, anchors or nails, the MZP has its own set of studs, obtained by extrusion on a punched-type stamping press. Their number can reach up to 80 units per square decimeter of the plate. With a competent approach and correctly set work, each thorn is pierced into the tree, and the part begins to work as a single fastening array. Even with the strongest loads on lumber products, there is a high probability of violation of integrity in the body of the structure, but not in the connecting joint made of MZP.

How to solder the carbide insert to the cutter at home

Photo No. 6: Soldering the carbide part to the P18 steel holder
Manufacturing of cutting tools with soldered carbide plates is possible in domestic conditions. For these purposes, argon-arc welding is used. The following describes a method of soldering an element onto a R18 steel blank. For work, you will need an argon-arc apparatus operating in direct current mode, a drill and a brass filler (wire).

Photo # 7: Putting a borax on the holder
Before soldering, the surfaces are degreased, flux is poured into the place of the future joint and a hard-alloy plate is exposed. It takes 15–20 seconds to fasten the parts together.

Photo # 8: Finished part before cleaning
Then the part is cleaned with a wire brush and left to harden in the open air.
Types of minimum wage
In addition to different dimensional characteristics and plate thicknesses, these fasteners have another major difference. It consists in different methods of obtaining teeth and, as a result, in their different shapes:
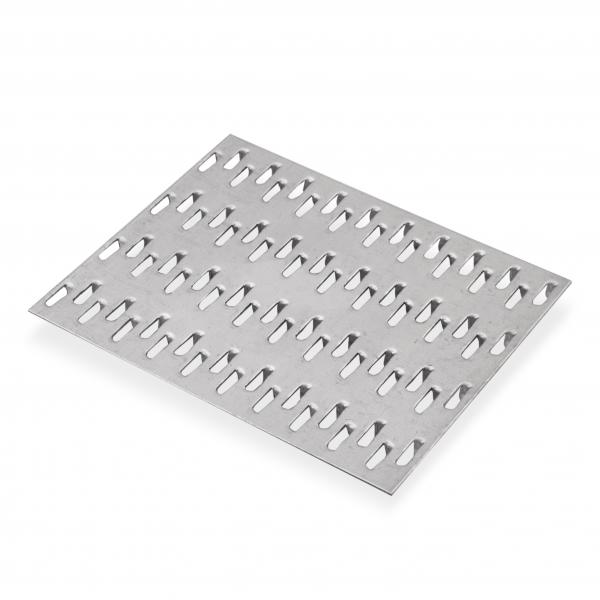
- Unidirectional tenoning. It has proven itself well in the installation of joints on which the load acts in one plane - either longitudinal or transverse. With simultaneous loading in several directions, their effectiveness decreases. It is necessary to take into account the direction of the grain of the tree during installation.
- MZP with multidirectional cutting. Such fasteners equally cope with any loads directed to the lumber and do not require a clear orientation along its fibers.

Nail plate properties
The connecting nail (toothed) plate has important advantages over other types of fasteners. For example, from separately driven nails, each of which is on its own. - * The strength of the bond to the tree is achieved by the shape of the teeth and their angle of inclination, by their arrangement in rows. At the junction of the elements of wooden structures, the nail plate forms a connection with high strength characteristics, with which no other fastening element can compete. These indicators have been verified by many mechanical tests of structures.
- * A common monolithic platform - the base on which all the teeth are attached, excludes the possibility of their mobility and swaying. The platform becomes a common, connecting base for the connected parts of the structure, due to which the connection is again given the quality of strength.
- * Metal serrated plates provide excellent strength even when splicing wood structural elements by butt-joint.
- * Details are attached extremely tightly. This has also been proven empirically. For example, a beam assembled using a plate of two butt-connected wooden beams, when exposed to a fracture, broke not at the junction of structural elements, but in the monolithic part of the beam. Thus, the monolithic platform of the nail plate completely prevents shifting or loosening of the teeth and becomes a reliable base for the joint.
- * If necessary, it is possible to apply galvanic coating - this is a possible additional service at the request of the customer. This coating will add extra durability to the steel nail plate.
- * Metal serrated plates install faster than traditional fasteners due to their unique design. This will significantly save time for construction and installation work on fastening elements of rafter and rafter systems.
- * Due to the possibility of manufacturing floor beams with specially designed "corridors" for these purposes, this method of fastening facilitates the laying of communications (ventilation ducts).
The listed qualities of nail connecting plates have become the reason for their widespread widespread use in the construction and construction of wooden structures for any purpose. The simplicity of the design of the nail plates brings exceptional strength and durability to the joint.
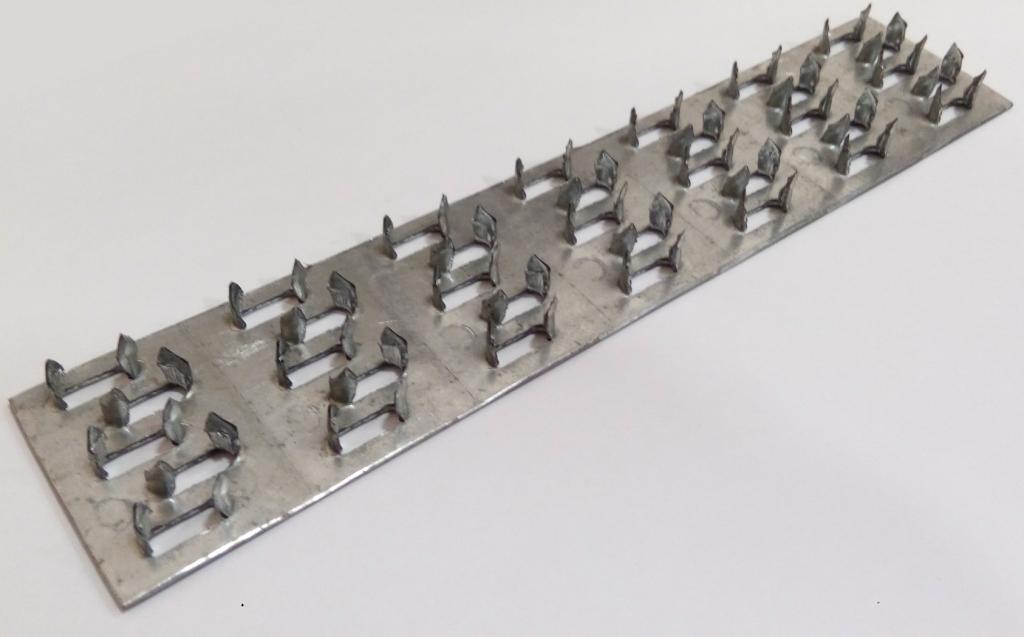
Types by tooth arrangement
Manufacturers often try to lower the price of the building material they manufacture. One way to do this is to simplify design and manufacturing techniques. In this regard, most of the nail plates used are of the simplest and cheapest type with unidirectional teeth. But there are other options that are used in critical structures: with multidirectional teeth in adjacent rows and with teeth located at an angle of 45 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the plate.These options are more difficult to produce, therefore, the price of building materials for fasteners of these types is slightly higher.
Benefits of using turning inserts
Inserts for cutting or boring cutters are made on the basis of different grades of hard alloys. This is very convenient, since it will allow you to arm yourself with a large set of cutting elements that will process workpieces from different elements.
And the use of interchangeable turning fixtures for cutting tools can be confidently called an advantageous solution from an economic point of view, since if a breakdown or wear occurs, you will not need to change the entire cutter, only its cutting part. It is best to use a tool equipped with replaceable carbide inserts when you need to automate technological processes
This is especially important for small and medium batch production of various products.
Carbide products, which are put on turning tools, have a number of their advantages:
- they are cheaper than solid cutters;
- replacing the carbide cutting element with a new one can be very quickly;
- carbide-based inserts have high reliability even under intensive operation;
- if necessary, such replaceable cutting parts can be readjusted;
- All existing models of these cutting elements for cutters are unified, so you can easily select the appropriate option for a particular type of processing, as well as the grade of material of the workpiece being processed.
And also the use of replaceable carbide inserts, equipped with a mechanical fastening, can significantly increase the service life of the turning tool holder, and you do not need to sharpen and solder its cutting part. In addition, under the conditions of use of this tool, the temperature and cutting force can be reduced by up to 40 percent. Carbide alloys have such properties that they can be used for the production of plates, and with their help it is possible to process metals, subject to changing cutting conditions.
Currently, various types of carbide products are produced. Requirements for each type are spelled out in state standards. They are presented below:
- GOST 19086–80 - implies the characteristics of support and cutting plates, as well as chip breakers;
- GOST 19042–80 - prescribes the requirements for the shape, classification, and also for the designation system of plates of replaceable type based on carbide materials;
- GOST 25395–90 - regulates the production of several types of carbide inserts, they are fixed on the tool holder by soldering. This applies to elements that are soldered to the tools of the revolving, bore or boring type.
Brazing technology for carbide inserts
The technology of brazing carbide inserts on circular saws and other cutting tools is a process of permanently joining workpieces. Parts of the future product do not melt, but dock due to the introduction of liquid solder. For this reason, in the future, the soldering point can be separated without damaging parts of the part.
The main problem in manufacturing is the difference in the coefficients of linear thermal expansion of hard-alloy products and steel, which is why the plates crack and lose their strength characteristics during cooling.
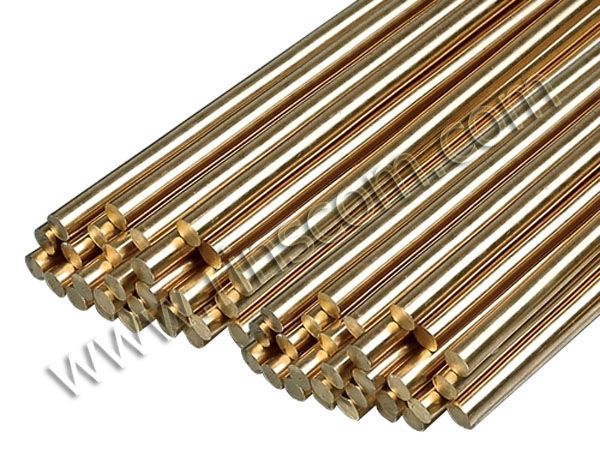

Photo No. 2: Solder TP-1M
Solder is used to reduce the internal stress by 30–50 MPa. In the metallurgical industry, good results are shown by TP-1M three-layer products. This material consists of non-melting bronze BrNB7-0.5, framed by layers of LNMts50-2-2 brass.
Surface preparation
The tungsten carbide slots are open, closed and half closed. The most convenient are open ones, which have a ratio of steel to carbide thickness of 3: 1.
To remove oxide films, mechanical and chemical tumbling is carried out. In this case, the part is treated with a free abrasive using a rotating drum.The approximate time for the procedure is 3-4 hours.
Flux selection
Flux is an intermediate material that is placed between the solder and the plate. Ideally, its melting point should be 370-400 degrees lower than that of the solder. It is widely used in the form of borax flux, otherwise sodium tetraborate. The melting point of the material is 741 degrees.

Photo No. 3: Borax (soldering flux)
Assembly order
The flux is poured into the prepared hole 0.3–0.5 mm deep, and the solder is placed on top (its edges should protrude 0.5–1 mm beyond the groove perimeter to control the soldering process). A plate is placed on top. The parts are fixed in one piece by means of wire, technological pin or glue without slag inclusions.
Soldering process on HDTV installations
Heating and soldering of parts is performed on installations with a current frequency of 60–66 kHz. First, the holder is heated to 700-800 degrees, after which heat is supplied to the rest, moving it into the inductor. A gap of 10-15 mm is maintained between the parts and the tool. The heating rate is determined depending on the thickness of the plates and the grade of the alloy.
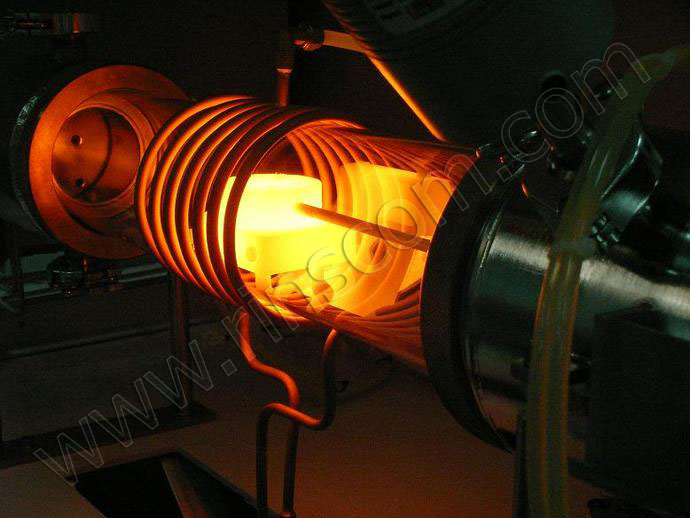
Photo No. 4: Installation of HDTV for soldering plates
During the melting process, it is observed that the surfaces are covered with brown. When it flows down, a new layer is added. After the solder has melted, it is kept for 5–10 seconds, then removed from the apparatus, the plate is fixed with a clamp and placed in an oven heated to 200 degrees for 2–4 hours.
Heat treatment and cleaning
Soldering of products is combined with hardening. This process relieves residual stress and increases the hardness of the finished blocks. Holders from steel 45 and 40X are hardened in water or oil. Tools made of metal 35ХГСА, 5ХНВ and 20ХГНМ are treated in air. Baths filled with nitrate are also used for hardening. At the end of the treatment, excess solder and borax are removed with a file and boiled in a 10% soda solution, after which they are adhered in a sandblasting chamber.
Soldering control
Soldering defects are checked by visual inspection. Products are rejected if more than 10% of the seam is not soldered, there are cracks, the sharpening allowance is shifted by a third. Cracks are checked by color flaw detection.
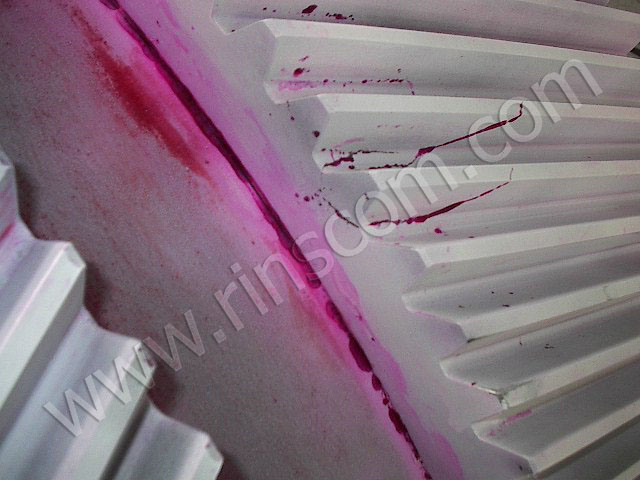

Photo No. 5: Checking the part for cracks by means of color flaw detection
In this case, the red dye is applied to a previously degreased surface, dried and removed with oil diluted 30% with kerosene. Then the plate is painted with a white compound, on which cracks appear (if any).
How plates are marked and who produces them
By marking the carbide structures for turning tools, you can determine the composition of the production material. In particular, the marking T15K6 means that the product is made on the basis of an alloy of titanium-tungsten-cobalt group. Tungsten is mandatory in these alloys. In addition to tungsten, the alloy must additionally contain:
- tantalum;
- cobalt;
- titanium and others.
In the composition of such an alloy, in accordance with the marking, there is titanium carbide in the amount of 15 percent and cobalt in the amount of 6 percent, respectively.
The most famous manufacturers of these products used for mechanical fastening to cutters are:
- Ceratizit (Luxembourg);
- BDS-Machinen and Proxxon (Germany);
- Instrument-Service and Novomoskovsk Pipe Plant (Ukraine).
Construction and material of manufacture
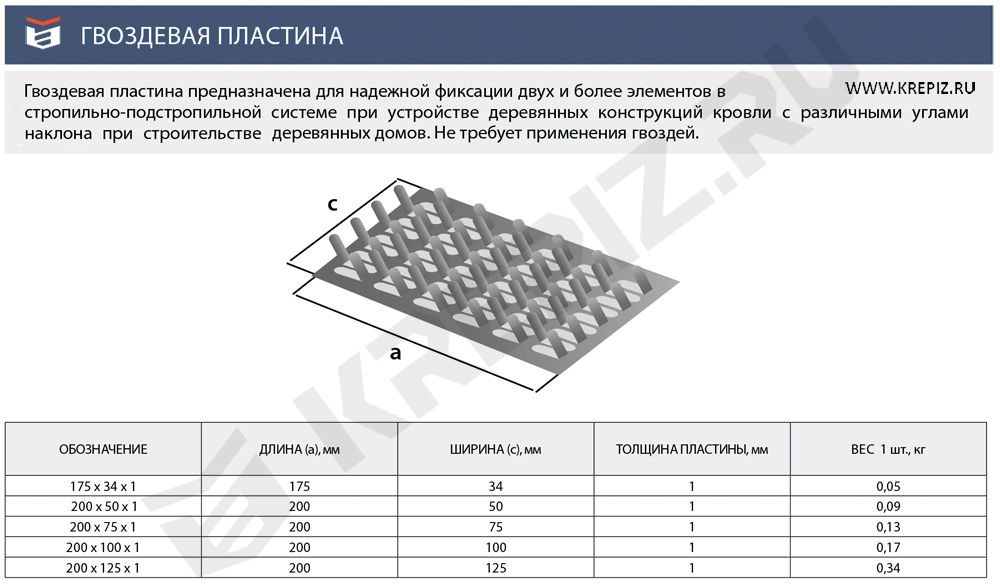
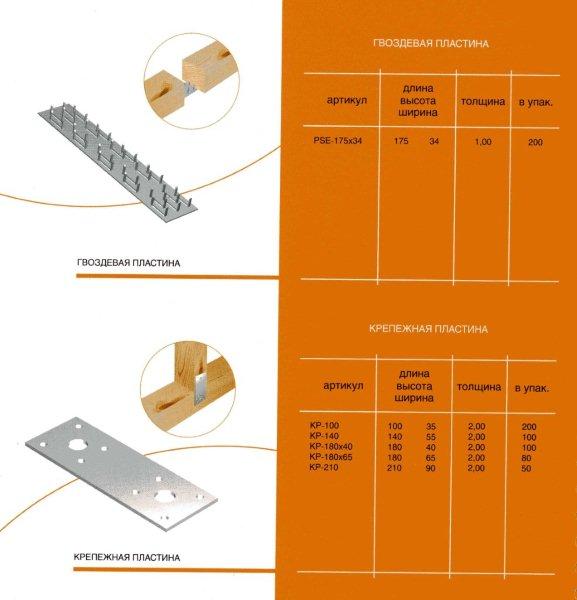
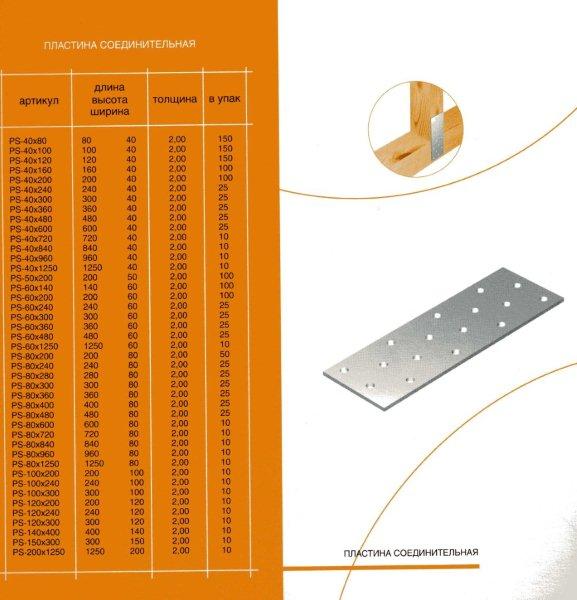
From the name it is clear that the nail plate by its design is a strip of metal with an analogue of nails. Its thickness is from 1 to 2 mm, dimensions vary from 40 to 200 mm in width, and any length can be. Different manufacturers have their own size standards. Most often, nail plates are produced with a length of 25 mm.
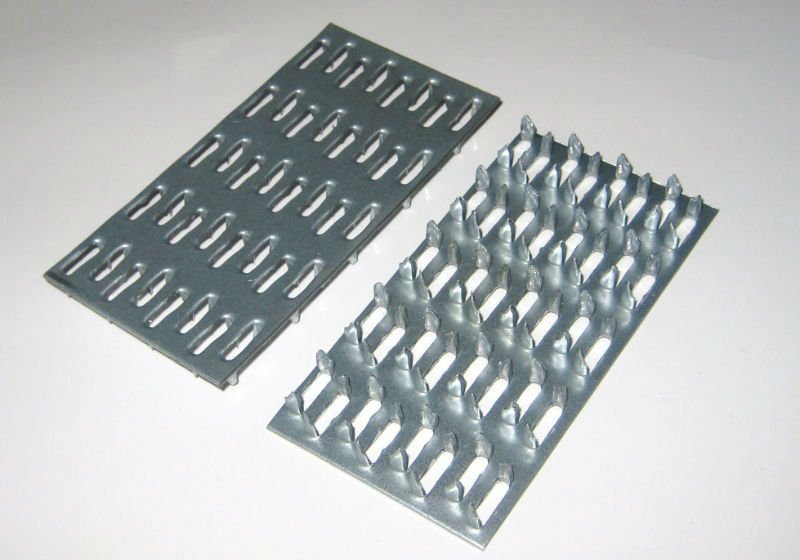
The starting material for manufacturing is high-strength alloy or galvanized steel sheet.In production, it is cut into plates of the required size, and then thin protrusions are squeezed out on a special press up to 8 mm long... They play the role of nails, firmly entering the wooden structures.
Experience in using nail plates
Steel nail plates have been used for more than twenty years in Canada and the USA, it was in North America that they began to be massively used in the construction of wooden structures. This fastening method is now widely used throughout Europe. Almost all types of roofs, attics, attics, skylights, etc. can be built using commercially available plate-based roof structures.
Roofs using nail plates are applicable in all types of structures, for example: -dwelling houses, -industrial, -agricultural, sports and commercial structures.
In addition to roof structures, this technology can be successfully used for: - reconstruction of buildings and flat roofs, where plates are considered an indispensable type of fasteners; - production of panels for walls; - the manufacture of lattice frames, - the construction of formwork for concrete structures, - the construction of large-span buildings made entirely of wood.
The possibility of creating trusses with a span of more than 30 meters without internal supports (for example, tennis courts), which has arisen in connection with the use of connecting plates, is widely used. Plates can be successfully used when splicing boards lengthwise.
Serrated (nail) plate is a strong, fast and economical connection for timber structures. Distinctive advantages and properties of this fastening contribute to its ever wider distribution in the construction of wooden houses and structures in our country. The possibility of purchasing this product is becoming more and more affordable, and those who are interested can appreciate the convenience and quality of this fastener in practice.
Why mounting can be a problem
The issue of fastening is very important due to the characteristics of the wood, its "behavior" depending on weather conditions. With a change in the degree of humidity, wooden building elements decrease or increase in size and often bend. As a result, large and long-term "stresses" arise in the places of their connections and abutments. The reason for this may also be the erection of a light foundation or its complete absence (which is possible based on the low weight and elasticity of wooden structures), leading to a change in the geometry of these structures. When using a metal plate, increased corrosion resistance of the connecting element is provided, which favors its operation in conditions of high humidity, as well as when performing external work.
Advantages of spiked mounting plates
Spike fastener connectors have gained widespread popularity due to the many advantages and benefits that their use promises.
The main one is, perhaps, that this fastener guarantees a strong and durable connection of wooden parts. At the same time, the wood does not split, its integrity is preserved.
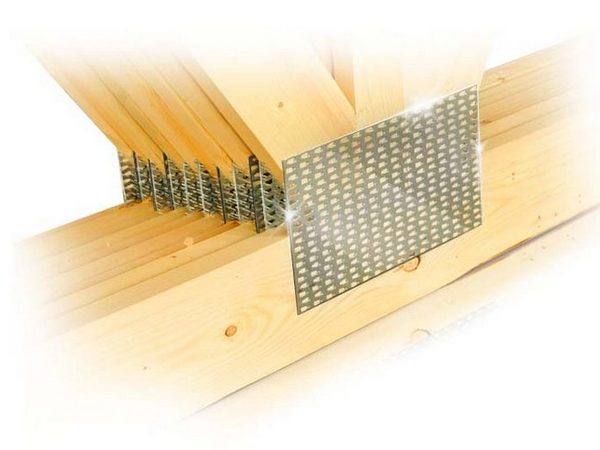
Due to the presence of a high-quality anti-corrosion coating, the nail plates practically do not rust, which is especially important for such a hygroscopic material as wood. The nail plate is used for fastening the rafter part of the house, as well as for connections in frame housing construction
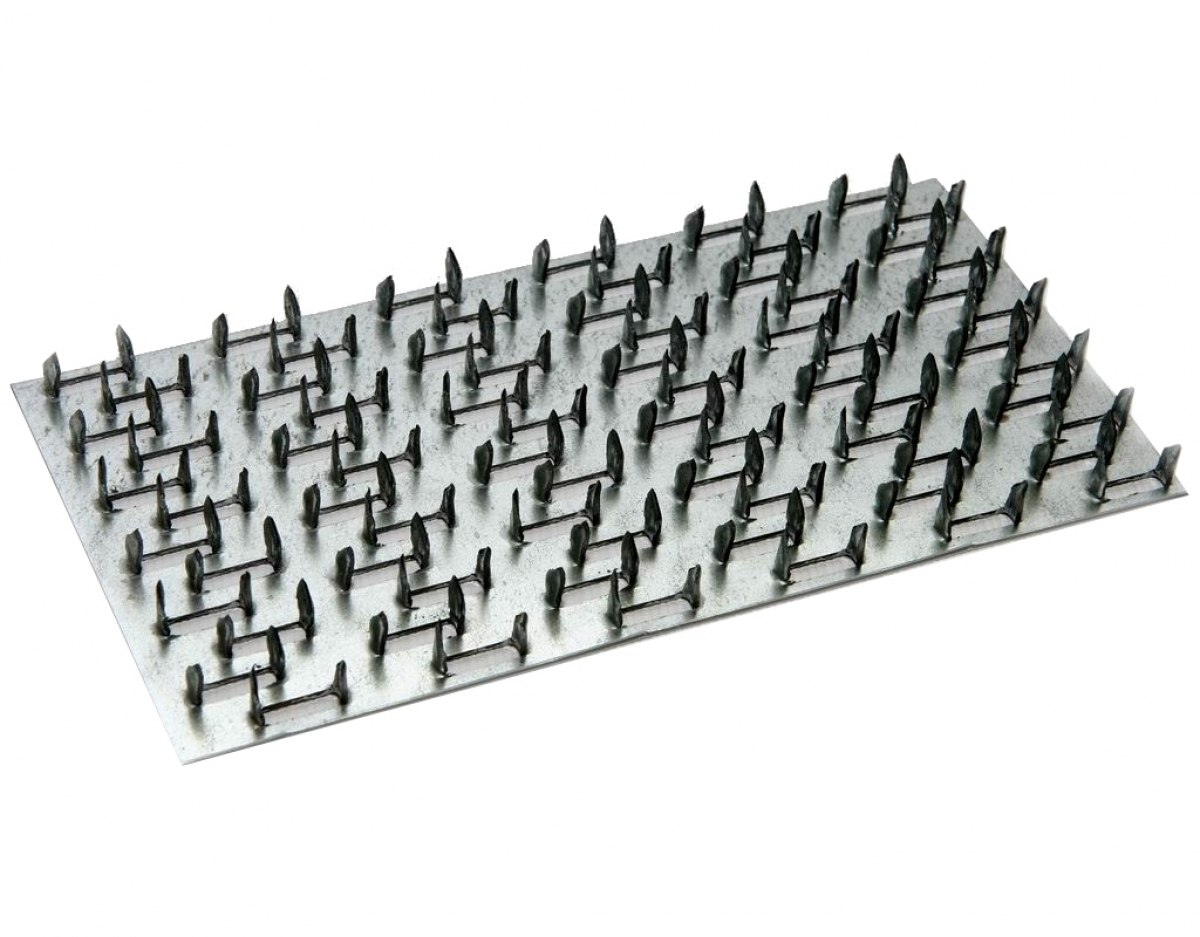
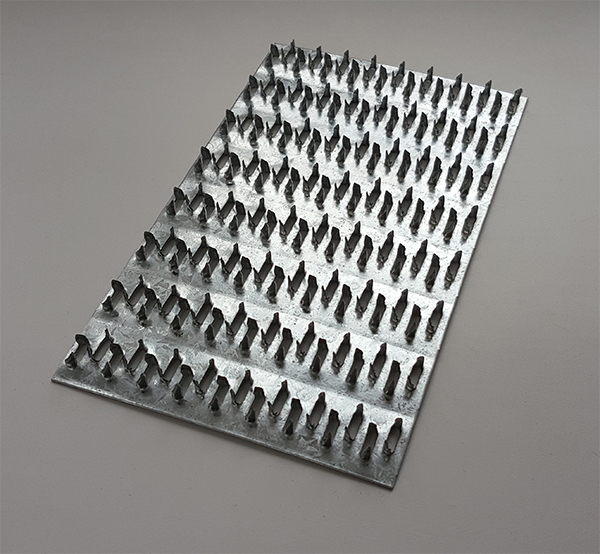
It is a strip (plate) made of galvanized sheet steel with stamped nails (teeth). The production of nail plates by cold stamping on a hydraulic press allows to obtain high-quality connecting elements. Standard insert teeth are 8 millimeters high. One nail plate can have 2 to 16 rows of teeth
The nail plate is used for fastening the rafter part of the house, as well as for connections in frame housing construction. It is a strip (plate) made of galvanized sheet steel with stamped nails (teeth). The production of nail plates by cold stamping on a hydraulic press allows to obtain high-quality connecting elements. Standard insert teeth are 8 millimeters high. One nail plate can have from 2 to 16 rows of teeth.
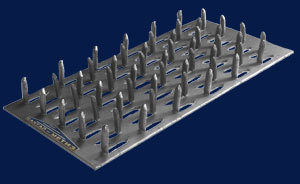 The thickness of the nail plate is from 1 millimeter, the width can be, depending on the standard size, from 20 to 132 millimeters, and the length is from 76 to 1250 millimeters. With the help of metal toothed connecting plates, such wooden structural elements as boards, beams, beams, lying in the same plane, can be connected without the use of nails, screws and other fasteners.
The thickness of the nail plate is from 1 millimeter, the width can be, depending on the standard size, from 20 to 132 millimeters, and the length is from 76 to 1250 millimeters. With the help of metal toothed connecting plates, such wooden structural elements as boards, beams, beams, lying in the same plane, can be connected without the use of nails, screws and other fasteners.
What is it and what is it for?
The nail plate is a fastener used when working with wood. It is a strip of metal with sharp teeth on the working part (analogue of nails). Depending on the type of fasteners, such pins can have different shapes and sizes. The plates have a minimum thickness, due to which such fasteners can be used at any stage of the construction of structures.

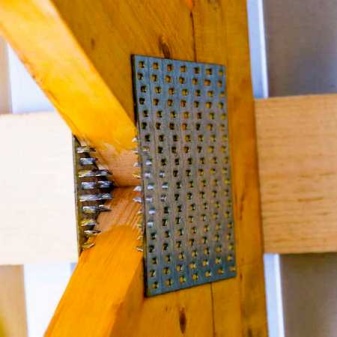
Metal toothed plates (abbreviated as MZP) are widely used in the construction of wooden structures for any purpose. They are massively used in industrial and private housing construction, when erecting timber frame structures or installing rafter systems.

In modern construction, such fasteners are very popular due to a number of advantages:
- they connect wooden elements without protrusions;
- have a low weight, due to which they do not additionally "load" the structure;
- make it possible to mount complex systems without involving large-scale special equipment;
- provide a reliable and durable connection;
- resistant to corrosion.