4.3 Marking and packaging
Labeling and packaging
cements are produced according to GOST
22237.
5 RULES
ACCEPTANCE
Acceptance of cements is carried out
according to GOST
22236.
The quality document
the maximum value of the specific effective activity should be indicated
natural radionuclides in raw materials and additives used for
production of cement for a given batch.
6 METHODS
CONTROL
6.1 Definition
the physical and mechanical properties of cement are produced in accordance with GOST
310.1-310.4.
6.2 Chemical analysis
clinker and cement are carried out in accordance with GOST
5382.
6.3 Content in clinker
tricalcium silicate (3CaO × SiO2), tricalcium aluminate
(3CaO × Al2O3), tetracalcium
aluminoferrite (4CaO × Al2O3× Fe2O3) and the sum of alkali oxides
(R2O) are calculated based on
the results of chemical analysis according to the formulas:
3CaO × SiO2
= 4.07 (CaO - CaOsv)
- 7.6 (SiO2 - SiO2sv.)
- 6.7Al2O3 - 1.42Fe2O3;(1)
3CaO × Al2O3
= 2.65 (Al2O3 - 0.64Fe2O3);(2)
4CaO × Al2O3× Fe2O3
= 3.04Fe2O3;(3)
R2O
= Na2O + 0.658K2O. (4)
6.4 Determination of the specific
effective activity of natural radionuclides in raw materials and
additives used for the production of cements, if necessary, carried out according to
GOST
30108.
7 TRANSPORTATION
AND STORAGE
8 INSTRUCTIONS ON
APPLICATION
Cements, depending on
special requirements for concrete, it is recommended to apply in
according to table 5.
table
5
Sulfate resistant
Portland cement
Sulphate-resistant Portland cement with
mineral additives
Sulfate resistant
slag Portland cement
Pozzolanic
Portland cement
Corrosion resistance when exposed to media,
aggressive in sulphate content
All are allowed
cements
Corrosion resistance when exposed to media,
aggressive in terms of sulfate content, while at the same time systematic
freezing and thawing or moisturizing and drying
Allowed
It is allowed to use only cement grade
400 provided that surface-active substances are added to the composition of cement or concrete
additives that increase frost resistance
Not allowed
Corrosion resistance when exposed to media,
aggressive in the content of sulfates, and reduced
heat release
All are allowed
cements
9 WARRANTY
MANUFACTURER
The manufacturer guarantees
compliance of cement with all the requirements of this standard, subject to the rules
its transportation and storage when delivered in a container within 60 days after
shipment, and when delivered in bulk - at the time of receipt of cement by the consumer, but
no more than 60 days
Application
A
LIST OF STANDARDS LINKED TO
IN PRESENT STANDARD
GOST 310.1-76 Cements. Test methods. General
provisions
GOST 310.2-76 Cements. Determination methods
fineness of grinding
GOST 310.3-76 Cements. Determination methods
normal density, setting time and uniformity of change
volume
GOST 310.4-81 Cements. Limit determination methods
flexural and compressive strength
GOST 3476-74 Blast-furnace slag and
electrothermophosphoric granular for production
cements
GOST 4013-82 Gypsum stone and
gypsum anhydrite for the production of binders. Technical
conditions.
GOST 5382-91 Cements and materials
cement production. Chemical analysis methods
GOST 6613-86 Woven wire mesh with
square cells. Technical conditions
GOST 10178-85 Portland cement and slag Portland cement.
Technical conditions
GOST 22236-85 Cements. rules
acceptance
GOST 22237-85 Cements. Packaging, labeling,
transportation and storage
GOST 30108-94 Building materials and products.
Determination of the specific effective activity of natural
radionuclides
Keywords:
sulfate-resistant cement, corrosion resistance, clinker, mineral additive,
pozzolana
|
1 2 3 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 5 6 7 8 9 Appendix a List of standards for which |
Stamps
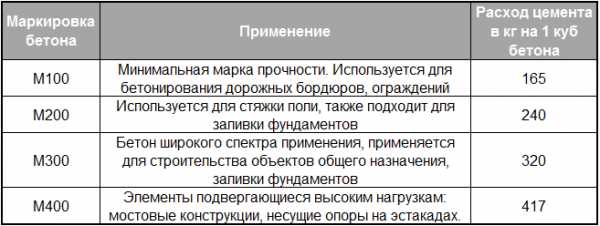
Based on the requirements of regulatory documents for a cement sample undergoing compression and bending tests, the main brands of Portland cement can be distinguished:
M700 is a particularly durable compound. The area of application is limited to the manufacture of concrete with increased strength characteristics for the construction of stressed structures. The price of such cement is high, which makes it unprofitable for conventional construction activities;

Any kind of Portland cement grade 400 is used to create conventional and standard structures that are not subject to increased loads.
- M600 is a composition of increased strength. Scope - production of critical reinforced concrete products and structures;
- M500 is a cement with sufficiently good strength characteristics, which makes it possible to use it in the reconstruction of buildings and structures after accidents, the construction of military-technical facilities, and paving;
- M400 is the most affordable and widely used brand. This is explained by the fact that the inherent indicators of frost resistance, moisture resistance make it possible to use it in the construction of objects for any purpose.
Manufacturers produce Portland cement of grades M200 and M300, but in a rather limited quantity. This limitation is natural, since the demand for these brands is low.
|
Brand (GOST |
Class (GOST |
|
300 |
22.5H |
|
400 |
32.5H |
|
400B |
32.5B |
|
500 |
42.5H |
|
500B |
42.5B |
|
550 |
52.5H |
|
600 |
52.5B |
Class
and brand are expressed in different units
measurements - in MPa and
kgf / cm2
respectively.
Differences in numerical class values
and brands when expressed in the same
units of measurement are due only
different test conditions for cement.
Application.
Portland cement - basic material
modern construction industry,
used for mortars,
concrete and reinforced concrete products and
structures, for special types
cement, as well as in the manufacture of a number
other building materials.
–
regulation of chemical and mineral
composition and structure of cement clinker;
–
change of real (component)
the composition of the cement (the introduction of additives);
–
by adjusting the fineness of grinding and
grain size composition of cement.
The grade is defined as the strength of a specimen when tested for bending and compression. For the manufacture of a sample, Portland cement and sand are used, taken in a ratio of 1: 3. A sample of 4x4x16 cm is made from this solution, which solidifies within 28 days, hardening occurs in conditions of high humidity. To accelerate solidification, it is allowed to use the sample steaming technique.
The most common today are the brands of Portland cement M 400, 500, 600:
M 400 is the most demanded cement brand. The technical characteristics (strength, frost resistance) laid down in it are suitable for the construction of most objects.
M 500 is a cement with a somewhat large margin of safety, which allows it to be used in reconstruction or restoration of facilities after an accident, to use it for road repairs, construction of military-technical facilities, asbestos-cement structures.
There are also "intermediate" cement grades, for example M 550 (in terms of their technical characteristics they are close to M500, but differ in slightly higher strength).
Clinker minerals and concrete destruction
All types of cements differ significantly in mineralogical and chemical composition, as the sources of raw materials and the ratio of raw materials are different.
Four types of minerals
Scientists from different countries have attempted to control the properties of cements in order to accurately classify them by type of purpose and to exclude the procedure of constant physical testing. But the attempt to establish the limiting ratios and quantities taken as the basis of the four clinker materials was unsuccessful. The reason for the failure is that the mineralogical composition of raw materials cannot be accurate enough, does not take into account the required properties of cement, which means that control physical tests of cement are necessary.
Basic clinker minerals
- C2S - dicalcium and C3S - tricalcium silicates;
- C4AF tetra calcium alumoferite;
- C3A - tri-calcium aluminate.
Concrete destruction mechanism
By interacting with water containing sulfates, C3A aluminate. calcium hydrosulfoaluminate is formed with further crystallization in the concrete structure. This leads to expansion of the volume with the subsequent destruction of concrete.
Such crystallization is most often observed with a large number of cycles of concrete flooding followed by drying. First of all, this applies to hydraulic structures - bridge supports, buried piles, flooded foundations.
Even crystals of efflorescence on a brick wall can lead to its destruction. Reinforced concrete reinforcement is also subject to similar processes; anti-corrosion additives are used to protect against them.
Differences from simple cement
Portland cement is the type of cement that is considered the most suitable and justified for pouring concrete. Concrete is used in monolithic / reinforced concrete construction, in the process of erecting various objects, which imply increased requirements for strength and ability to withstand loads.
Clinker granules and other additives in Portland cement make it more durable, resistant to frost, external negative factors and aggressive environments. It should be noted that such a description is suitable for almost all types of Portland cement, which makes it in demand in the process of building gas and oil industry facilities.
Also, this type of binder is suitable for pouring the foundation on unstable complex soils - it is usually chosen, which excludes shrinkage and propagation of cracks along the monolith.
When trying to determine how cement differs from Portland cement, it must be remembered that they relate as a general class of binder and one of its types. Portland cement is a stronger type of cement. And obvious differences can be determined by considering specific grades and types of Portland cement in composition. The same aspects as setting technology, mixing features, installation method, application, etc. are similar.
Cement production technology
Cement production - video
Cement production is an energy-intensive and expensive process, which consists of two stages:
- Obtaining clinker. To begin with, through the development of limestone deposits, raw materials are extracted, in particular limestone. Then the material is crushed into pieces with a diameter of 10 cm, dried and mixed with other constituent elements. After that, the raw mix is fired. The result is the so-called clinker.
- Converting clinker to powder. At this stage, the clinker and gypsum stone are crushed, the mineral additives are dried, and then all the constituent parts are ground together. However, the quality and physical and technical characteristics of raw materials (moisture, density, etc.) are different, therefore, the methods of cement production may differ.
Cement production methods
Currently, the cement industry produces cement in three main ways:
- Wet.It is used if the cement is created from clay (silicate component), chalk (carbonate product) and iron-containing additives (converter sludge, pyrite cinders, ferrous product). In this case, the moisture content of chalk should be no more than 29%, and the moisture content of clay - no more than 20%. Grinding of the raw mixture takes place in an aqueous medium, and as a result, a mixture is obtained in the form of a sludge dissolved in water with a moisture content of 30 to 50%. Then the sludge is sent for firing into a special furnace with a diameter of 7 m and a length of 200 m. During the firing process, carbon dioxide is released from the raw material and clinker balls are formed. They are ground into powder, thus obtaining the required grade of cement.
- Dry. The peculiarity of this method is that all raw materials are dried before (or during) grinding. Therefore, the raw material mixture is immediately obtained in the form of a crushed dry powder.
-
Combined. In this case, cement can be produced using two different technologies:
- The raw mixture is prepared in the form of sludge mixed with water, and then dehydrated to a moisture content of 16-18% on special filters and sent to the kiln for roasting, after which it is crushed and turned into cement.
- the raw mixture is dried and crushed, and the resulting mixture is granulated by adding 10 -14% water and fed for roasting. The pellets are then removed from the oven and ground.
Previously, cement in most cases was produced by the wet method, but nowadays the preference is given to dry technology.
How to choose a method of cement production?
1. Heat consumption increases significantly with the wet method of cement production. But the presence of water in the mills makes it easier to grind raw materials. Therefore, if the moisture content of the feedstock is more than 10%, then it is most expedient to create cement using wet technology.
2. If the raw mix consists of two soft materials, it is also preferable to produce cement by wet method, since the raw material is easily ground by ordinary stirring in water.
3. The dry method is used if the moisture content of the raw material is no more than 10%.
4. If the raw material is sufficiently plastic, then the combined method of cement production can be preferred.
Composition and properties
As already mentioned, Portland cement is composed of clinker. In nature, ready-made granules are quite rare, therefore, clinker chips are obtained by an artificial method by mixing and firing carbon and clay mixtures.
The finished clinker is mixed with gypsum, the content of which in the composition does not exceed 5%. It is introduced in order to ensure the mobility of the solution for 45 minutes, which is necessary when molding products or performing some types of work.
The composition and percentage of the components of the mixture is regulated by GOST 10178 85 "Portland cement and slag Portland cement". It is the observance of the state requirements during production that guarantees high technical and operational characteristics of the product.


To give Portland cement certain technical characteristics, mineral additives are introduced into the composition, the content of which does not exceed 20-25%.
The most popular are the following:
- Aluminate increases the setting time of cement, but has low strength indicators (the possible content in Portland cement is no more than 15%).
- Alumoferrite has the same properties as the previous additive, but its content in the finished product is reduced to 10-18%.
- Belite has an astringent effect, helps to increase the hardening time, however, excessive content can negatively affect the strength characteristics of the composition (the permissible content is no more than 15-37%).
- Alite is widely used (the percentage can reach 60%) in compositions of high grades, since it provides their quick hardening.
The properties of Portland cement are determined by its composition.The main criteria by which the quality of the product is assessed are the following:
Setting period. The setting of the mixture, subject to the technical requirements of its dilution, should occur after 40-45 minutes. Mineralogical composition, fineness of grinding and temperature at which work is carried out - these factors primarily affect the setting speed of the product.
Water demand. This term refers to the amount of water required to obtain a thick, suitable for operation of the cement paste. Typically moisture should not exceed 25% of the mix. In order to reduce the required amount of water, sulphite-yeast mash or plasticizers are used.
Water separation. This term denotes the squeezing of water in the finished solution, the occurrence of which is due to the settling of heavier cement particles. Mineral supplements can reduce this indicator.


Frost resistance - the ability of a product to endure a certain number of freeze and thaw cycles without losing its performance characteristics.


Features when working with white cement
White cement is an excellent material for the implementation of original design ideas, finishing work, pouring structures, etc. When working with white cement M600, you need to remember some important rules that will allow you to achieve maximum results.
Points to remember when working with white cement:
- All tools and mechanisms must be clean, with stainless steel working parts.
- To get a light solution, you need to add white fillers (or at least light ones) to the mixture - it can be transparent sand, white crushed stone. It is not recommended to exceed the proportions of normal sand due to the risk of discoloration.
- If white cement M600 is used to create a structure with a reinforced frame, rods and all iron parts must be covered with an anti-corrosion compound.
- this type is possible only with clean water, preferably non-rigid.
By mixing white cement with pigment and marble, granite crushed stone, you can achieve a complete resemblance of the solidified stone to natural material. Often such solutions are used to create decorative tiles, bricks, and plaster mixes.
Cement M600 is a high-quality and fairly expensive building material, the properties of which are not relevant in all areas. But in some cases, the technical characteristics of the binder help to achieve the assigned tasks quickly and reliably.
You can buy cement in Moscow and the regions in any construction supermarket, but before choosing this material, you need to carefully calculate the loads and requirements, as well as the optimality of high costs.
Views
According to its composition, sulfate-resistant cement is divided into the following types:
- pozzolanic Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant slag Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant Portland cement with the addition of minerals.




Now let's take a quick look at each of these building materials:
- Pozzolanic Portland cement contains a mixture of granulated blast furnace slag and pozzolans. The latter refers to products of volcanic origin in the form of ash, tuff and pumice. Pozzolans are active mineral additives in the manufacture of Portland cement. This building material relatively poorly tolerates the regime of alternating moistening and drying, as well as thawing and freezing.
- Sulphate-resistant slag Portland cement is made by mixing clinker with blast furnace slag in granular form (about 50-60%) and a small amount of gypsum. The slag used for production must contain a limited amount of aluminum oxide (up to about 10-12%). Sulphate-resistant slag Portland cement is assigned grades M300 and M400.It is relatively resistant to the effects of sulfates, but it does not tolerate severe frosts.


- Sulfate-resistant Portland cement has the M400 brand. It is prone to slow curing and low heat generation. It is versatile and can withstand any kind of temperature and humidity conditions.
- In sulfate-resistant cement with minerals, about 15-20% of the total cement mixture of blast furnace slag in granules or 5-10% of minerals is added. This type of building material is produced with the M400 and M500 brands. Sulfate-resistant cement with mineral additives is excellent for the construction of various structures, has increased frost resistance and resistance to strong moisture and drought.


What does the brand of cement mean?
Cement marking allows you to accurately characterize the composition of the material, its technical properties. Currently, marking is carried out in accordance with GOST 31108-2003. The full name of the material is indicated - Portland cement, sulfate-resistant or other cement. The binder component is designated below:
- CEM I - ordinary Portland cement;
- CEM II - Portland cement with additives up to 35%;
- CEM III - Portland cement with slag up to 95%;
- CEM IV - pozzolanic composition up to 55%;
- CEM V is a composite mixture.
The main additive is indicated - it can be composite (K), slag (W), pozzolan (P), limestone (I), prepared fly ash (Z), silica fume (MK). Their use allows achieving water resistance, fast setting or other desired properties.
The brand itself is designated M with a numerical index that shows the compressive strength of a particular sample according to the tests carried out. For example, M200 can withstand a pressure of 200 kg / cm³ or 15 MPa. The measurement results are entered into tables, which reflect not only the brand, but also the modern characteristic - the strength class.
| Class | Brand | Ultimate load | |
| MPa | kg / cm³ | ||
| B7.5 | M100 | 7,5 | 100 |
| B15.0 | M200 | 15,0 | 200 |
| B22.5 | M300 | 22,5 | 300 |
| B32.5 | M400 | 32,5 | 400 |
| B42.5 | M500 | 42,5 | 500 |
| B52.5 | M600 | 52,5 | 600 |
To obtain special grades, raw material additives are added to them, technologies are used that will give them the desired properties. Such materials include:
- Alumina cements. They are produced by firing aluminate slag, bauxite and limestone at a temperature of 1600 C °. After grinding, such compositions, due to the high content of calcium aluminate, react intensively with water, therefore they gain 90% of the given hardness in just a day. Two days later, the specified M400-M600 is dialed. When this type of binder is hydrated, a lot of heat is generated, which allows its use at low temperatures.
- The addition of calcium hydroaluminate, gypsum and other components makes it possible to obtain a non-shrinking, expanding or stressing material. Such mixtures harden in water, do not change the volume or expand upon setting, compact or self-tension.
- Slag-alkaline cement with a high content of granulated blast-furnace slag, ground into a fine powder. This adds frost resistance, corrosion resistance, and aggressive environments to mortars. Excellent for hydraulic structures, has an average rate of strength gain.
Methods of obtaining
Concrete with the desired characteristics is obtained in 2 ways:
- Manufacturing of mortar with the subsequent introduction of mineral additives. If the amount of added substances exceeds the norm, the strength of the concrete structure decreases. Increased fragility causes the structure to collapse. In the manufacture of such solutions, one must not deviate from the recommendations contained in regulatory enactments.
- Adding sulfate resistant Portland cement. The introduction of this component increases strength, protecting the structure throughout its entire service life. The sulfate-resistant solution acquires the desired qualities after 28 days. Portland cement contains 20% slag. In the manufacture of slag Portland cement, this component can be replaced with ash, the amount of which in the volume of the solution should not exceed 10%.
Cement production
All types of cement are produced using the same technology. The components and their proportions may differ, some mineral and other substances may be added at the end, but the production itself always involves certain stages and actions. All modern mixtures are based on Portland cement.
Simplified description of the cement production technology:
- Obtaining primary raw materials: crushed limestone and clay are mixed into slurry in a ratio of 4: 1.
- In the process of sludge firing at a temperature of +1500 degrees Celsius, the raw materials are sintered into a solid mass called clinker.
- The clinker is ground very finely to a powder.
Mineral additives, gypsum, are added to the clinker powder to obtain cement with the desired properties.
Composition
Several components work at the molecular level in the composition of cement. The material is a fine gray powder, but the components in its chemical formula are different and are responsible for certain processes in concrete.
What substances does cement contain:
- Calcium oxide - in the amount of about 67%.
- Silicon oxide - up to 22%.
- Aluminum oxides - up to 5%.
- Iron oxide - up to 3%.
- Modifying components of various types - maximum 3%.
Materials that form the basis of cement:
Clinker made of clay and lime - strength and other properties of the material depend on its quality.

- Mineral components - special additives to improve the characteristics, expand the scope of cement use. These can be crushed shale materials, granular slags, pozzolanic ingredients, lime, etc.
- Auxiliary components with calcium sulfate - to regulate the characteristics of the hydration process.
- Special additives - synthetic components that increase resistance to acids, temperatures, aggressive media, alkalis.
Portland cement differs in composition not only due to the addition of components to it during the production process, but also due to the peculiarities of the places where raw materials are extracted. So, in each region the cement is different, although the differences are insignificant.
Material composition options:
- Various types of clay (including shale and loess).
- Marl, limestone, chalk, other carbonate rocks.
- Mineral additives: silica, alumina, apatite, fluorite, fluorspar, gypsum, phosphogypsum, etc.

Strength
Strength is one of the most important properties of cement, which determines the scope, expected loads, technical characteristics of a concrete monolith structure. Cement acquires standard compressive strength after 28 days from the moment of mixing.
Strength can be viewed by brand (the most popular brands of cement are M300, M400 and M500, indicate strength in kg / cm2) and class (the indicated brands correspond to the approximate indicators of B20, B30 and B40). The prepared solution begins to harden within 1-2 hours, the process ends at least 12 hours after laying.
Then hydration heat appears and concrete gains strength within 28 days. At low external temperatures, heat allows the cement to gain a full cycle of strength, at high temperatures it can provoke an acceleration of the reaction, as a result of which cracks propagate due to the appearance of thermal stresses.
The strength of the cement is looked at on the packaging and in special tables, for each sphere and type of construction, for a certain load, an optimal indicator is sought. The strength is also influenced by the observance of the technology of mixing the solution, laying, leaving after.