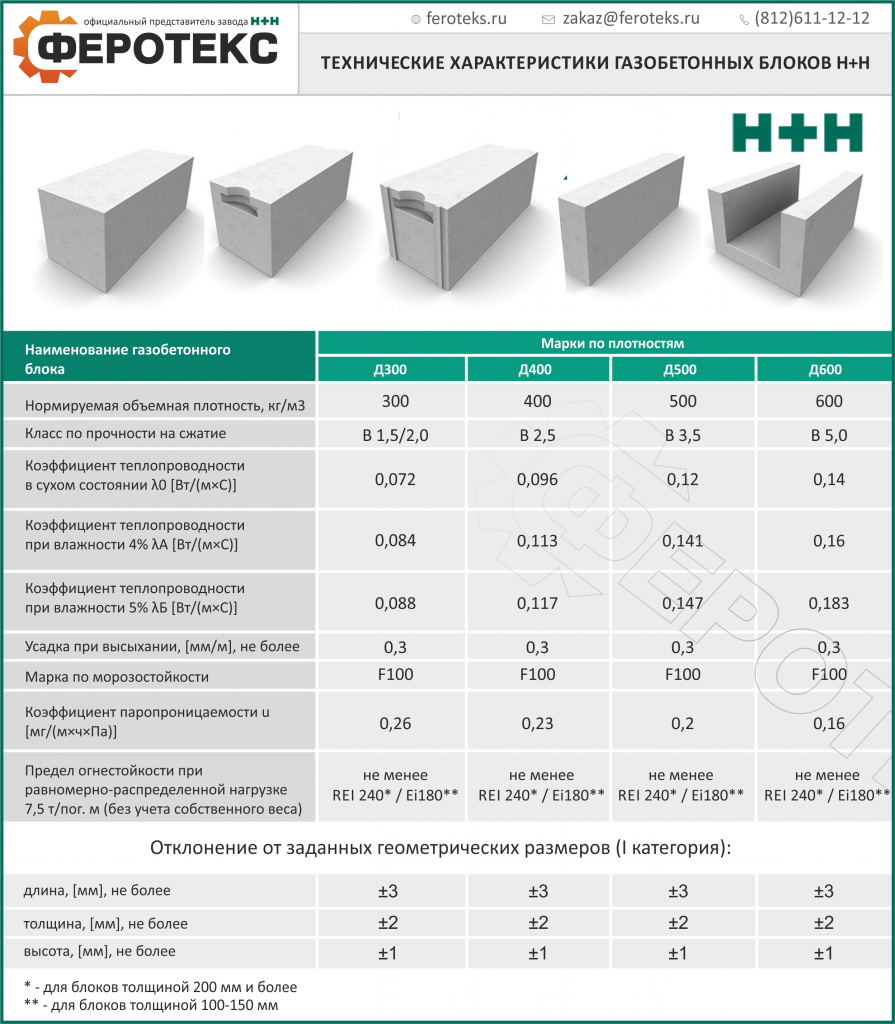
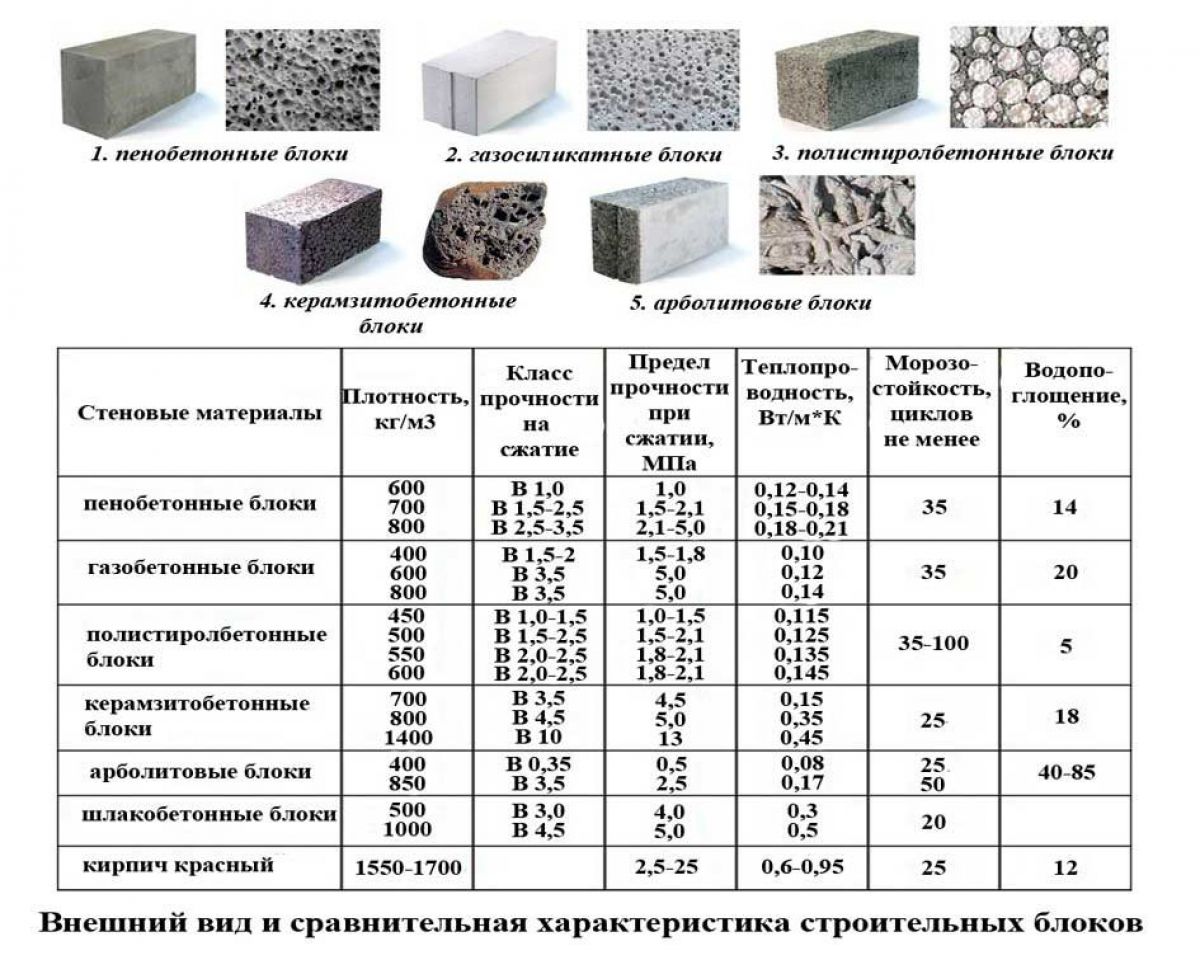
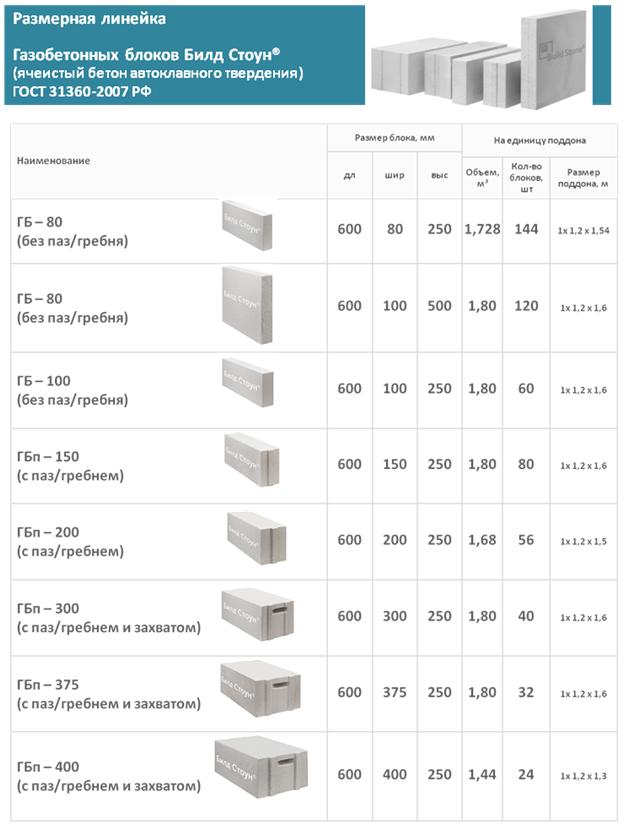
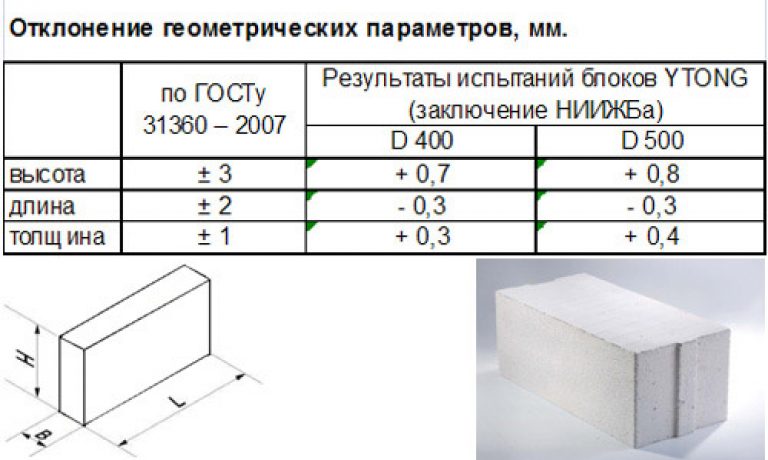
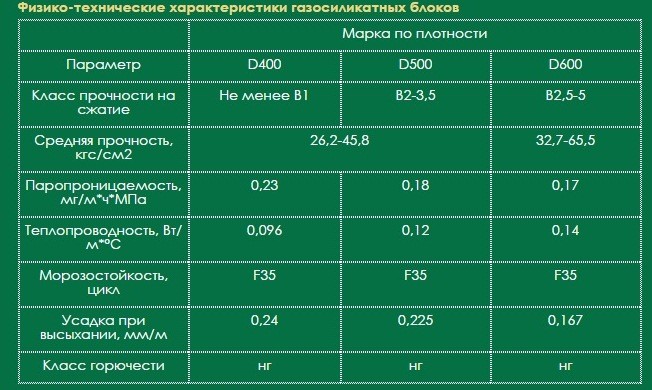
Gas silicate blocks - the pros and cons of the material
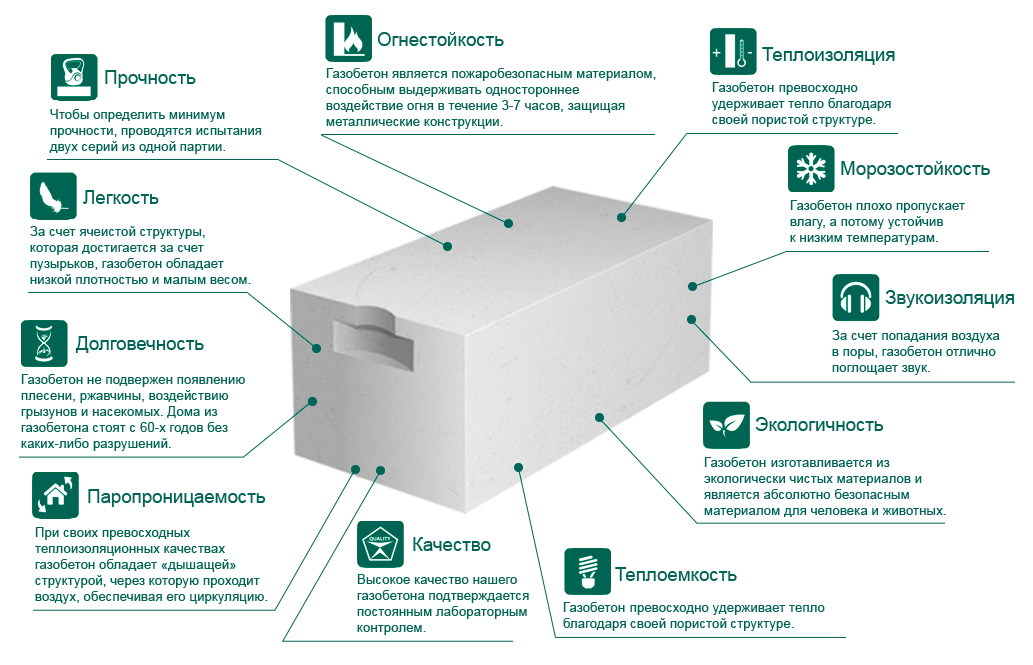
Gas silicate products have a complex of serious advantages. The main advantages of gas silicate blocks:
- reduced weight with increased volumes. The density of gas silicate material is 3 times less compared to brick and about 5 times lower when compared to concrete;
- increased safety margin, allowing to perceive compressive loads. Strength index for gas silicate block marked D500 is 0.04 t / cm³;
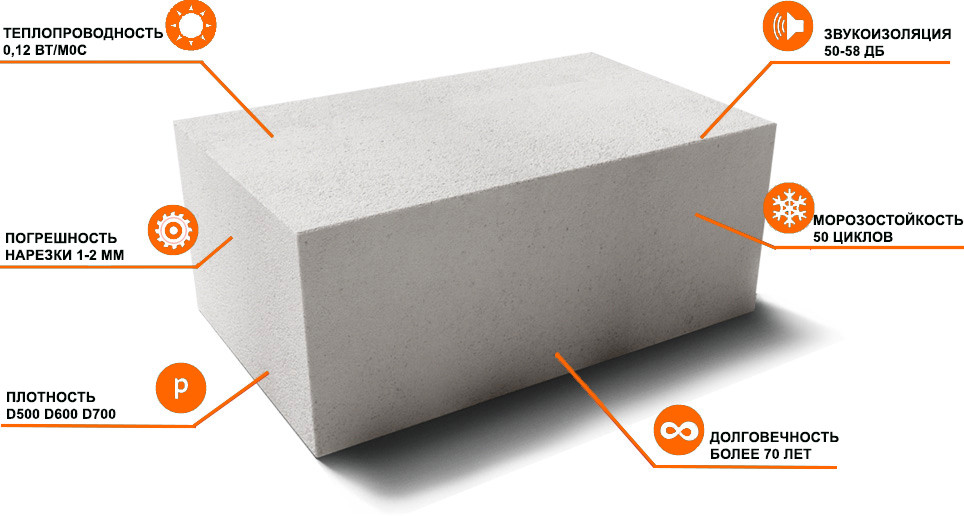
- increased thermal insulation properties. The material successfully competes with annealed brick, the thermal conductivity of which is three times higher than that of gas silicate;
- the correct shape of the blocks. Due to the reduced dimensional tolerances and clear geometry, the blocks are laid on a thin layer of adhesive mortar;
- increased dimensions. The use of large-sized silicate blocks with a low weight for the construction of walls of buildings allows to reduce the duration of construction;
- good workability. If necessary, it is easy to give the gas silicate block a given shape or cut the block material into separate blanks;
- acceptable price. Using block gas silicate for the construction of a cottage, private house or summer cottage, it is easy to significantly reduce the estimated cost of construction activities;
- fire safety. Blocks do not ignite when heated and exposed to open flames. They belong to low-combustible building materials included in the flammability group G1;
- high sound insulation properties. They are provided due to the porous structure. In terms of their ability to absorb external noise, the blocks are ten times superior to ceramic bricks;
- environmental friendliness. In the manufacture of the gas silicate mixture, toxic ingredients are not used and components harmful to health are not released during operation;
- vapor permeability. Air exchange takes place through the air cells inside the gas silicate massif, creating a favorable microclimate inside the building;
- frost resistance. Gas silicate blocks preserve the structure of the massif and operational characteristics, withstanding more than two hundred cycles of prolonged freezing with subsequent thawing;
- heat storage properties. Gas silicate blocks are an energy-saving material that is able to accumulate thermal energy and gradually release it to increase the room temperature.
 The area of application depends on the density of the material
The area of application depends on the density of the material
Despite many advantages, gas silicate blocks have weaknesses. The main disadvantages of the material:
- increased hygroscopicity. Porous gas silicate blocks gradually absorb moisture through an unprotected surface, which destroys the structure and reduces strength;
- the need to use special fasteners to fix hanging furniture and equipment. Standard fasteners do not provide reliable fixation due to the cellular structure of the blocks;
- insufficiently high mechanical strength. Block material crumbles under load, therefore, requires careful handling during transportation and laying;
- the formation of mold and the development of fungal colonies inside and on the surface of the blocks. Due to the increased moisture absorption, favorable conditions are created for the growth of microorganisms;
- increased amount of shrinkage. In real operating conditions, under the influence of loads, the blocks gradually shrink, which after a while causes the formation of cracks;
- reduced adhesion to sand-cement plasters.It is necessary to use special finishing compounds for plastering gas silicate.
Despite the existing drawbacks, gas silicate blocks are actively used for the construction of capital walls in the field of low-rise construction, as well as for the construction of heat-insulated walls of multi-storey buildings and for thermal insulation of various structures. Professional builders and private developers prefer gas silicate blocks due to the significant advantages of the material.
What it is?
Simply put, gas silicate brick is one of the varieties of porous concrete. At the exit, the material turns out to be rather porous, but at the same time its strength characteristics fully correspond to the parameters of concrete. The main difference is weight. Gas silicate blocks are less heavy - a decrease in the parameter is achieved due to voids inside the pores.
In the 18th century, builders often added the blood of a bull or a pig to concrete and obtained a kind of prototype of modern aerated concrete: when mixing the components, the blood protein entered into a chemical reaction with other substances, and as a result, foam appeared, which, when solidified, was transformed into a durable building material.
One of the most famous engineers in the Soviet Union, M.N.Bryushkov, back in the 30s of the last century, noted that when a plant called "soap root", growing in the republics of Central Asia, was added to the cement, the mixture immediately began to foam strongly and increase in size. During solidification, the porosity was retained, and the strength increased significantly. However, the most significant role in the creation of gas silicate was played by the Swedish technologist Albert Erickson, who created a unique technology for the production of the material by adding gas-forming chemical components to the cement.
Today, gas silicate bricks are made from cement with the addition of sand and slaked lime. Then the mixture is passed through autoclaves and subjected to foaming with the addition of special magnesium dust and aluminum powder.
The finished substance is poured into molds, subjected to drying and hardening, which is achieved in two main ways:
- in vivo;
- in an autoclave under high temperature and strong pressure.
Higher quality blocks are obtained by autoclaving. In this case, they become more durable and resistant to external adverse conditions.
Thus, it can be seen that the gas silicate block is a rather uncomplicated composition of inexpensive and widely sold components, so the material is quite profitable for housing construction.
Characteristics and composition
The gas silicate material contains the following components.
- Portland cement of the highest quality, which is produced in accordance with applicable GOSTs. It is composed of calcium silicate (its share is at least 50%), as well as tricalcium aluminum (6%).
- Sand that is compliant with regulatory requirements. This brand is characterized by a minimum amount of silty and all kinds of clay inclusions, the content of which should be no more than 2%. It also contains quartz, approximately 7-8%.
- Process water.
- Calcium lime, which is called "boiling pot", to create porous concrete requires a composition of at least the 3rd grade category. The rate of extinguishing of such a component is 10-15 minutes, while the proportion of burnout does not exceed 2%. The boiling pot also contains calcium and magnesium oxides, the total share of which reaches 65-75% and more.
- Aluminum powder - added for increased gassing, materials such as PAP-1 and PAP-2 are used.
- Sulfonol C is a surfactant component.
The composition and features of the technology determine the properties of the material, among which both positive and negative are noted.
The advantages of gas silicate bricks include the following characteristics.
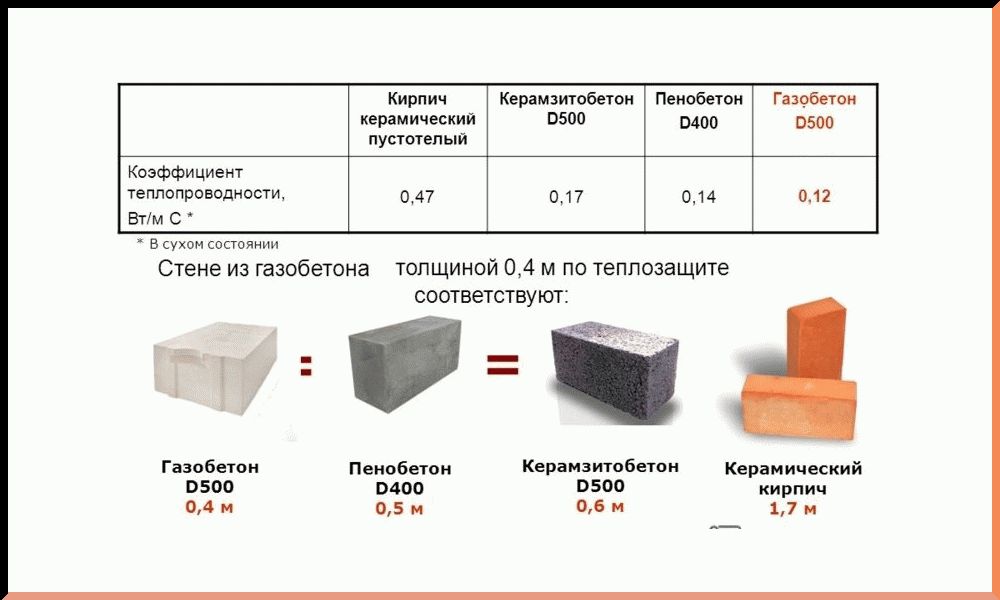
Reduced thermal conductivity. During the production of the material, the initial mixture is saturated with a large number of bubbles due to the content of aluminum powder; when solidified, they are transformed into pores, which significantly affects the thermal conductivity. That is, the more pores, the better the material retains heat.
Let us explain with simple examples. If you live in northern regions with harsh winters, then a wall 50 cm thick is quite enough to keep the heat inside the living space. You can get more, but, as a rule, a half-meter barrier is enough. In places with a warmer climate, the thickness can be 35-40 cm, in this case, even on cool nights, a favorable microclimate and a cozy atmosphere will remain in the rooms.


An equally important feature of aerated concrete is good vapor permeability. If the humidity level in the room is higher than outside the house, then the walls begin to absorb excess moisture from the air and send it outside.
If the situation is the opposite, then everything happens exactly the opposite: gas silicate bricks absorb moisture from the outside and transfer it to the room, this is especially true when the heating is turned on, when the air in the heated room becomes too dry.
For residential buildings, the fire resistance of the material is of fundamental importance. Gas silicate walls can withstand contact with the flame for about 3 hours, as a rule, this time is quite enough to extinguish the fire, so in the event of a fire, the chances of saving the house are quite high.

- The low weight of the bricks is also one of the undoubted advantages of the material. It is easy to transport, raise to a height, in addition, the structure does not create a large load on the foundation, and this significantly increases the service life of the house.
- Gas silicate blocks are made from natural components, so the material is environmentally friendly. It is quite possible to use it in the construction of preschool and educational institutions, clinics, residential areas and other buildings, where the absence of toxic emissions is of fundamental importance.
- Well, excellent sound insulation, which is possible due to the same porosity of gas silicate, will be a pleasant addition.


To get the most complete picture of the properties and characteristics of the material, it will not be superfluous to mention its shortcomings.
- The material has a rather low resistance to low temperatures. Without additional surface treatment, the composition can withstand no more than 5 freeze and thaw cycles, after which it begins to lose its strength rather quickly.
- Gas silicate complicates the repair work, for example, it is impossible to screw a dowel into such a material, it starts to fall out right there, and accordingly, even hanging a shelf in a house with gas silicate walls becomes a difficult task.
- In addition, gas silicate does not adhere to sand-cement plaster, therefore, it is unrealistic to decorate the wall with such material, it will fall off in a very short time.
- The pores absorb moisture rather intensively and retain it inside themselves. This leads to the gradual destruction of the material from the inside, and also creates an environment favorable for the growth of fungi, mold and other bacteria hazardous to health.




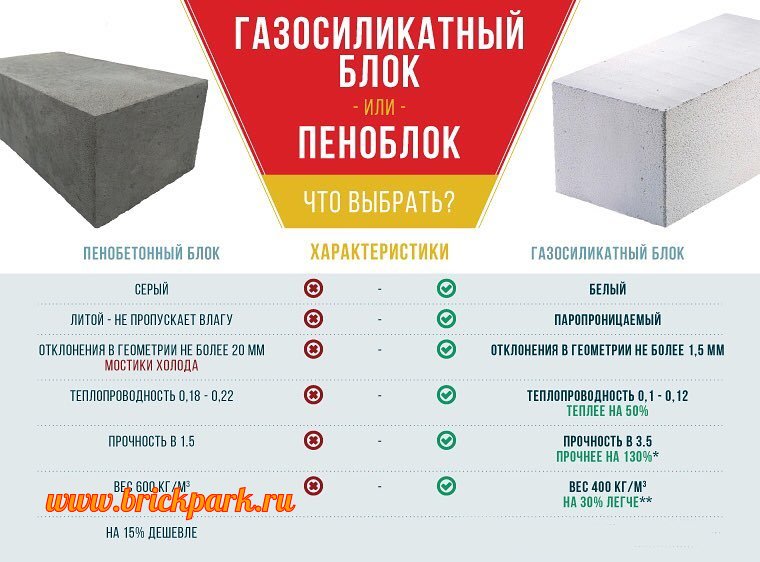
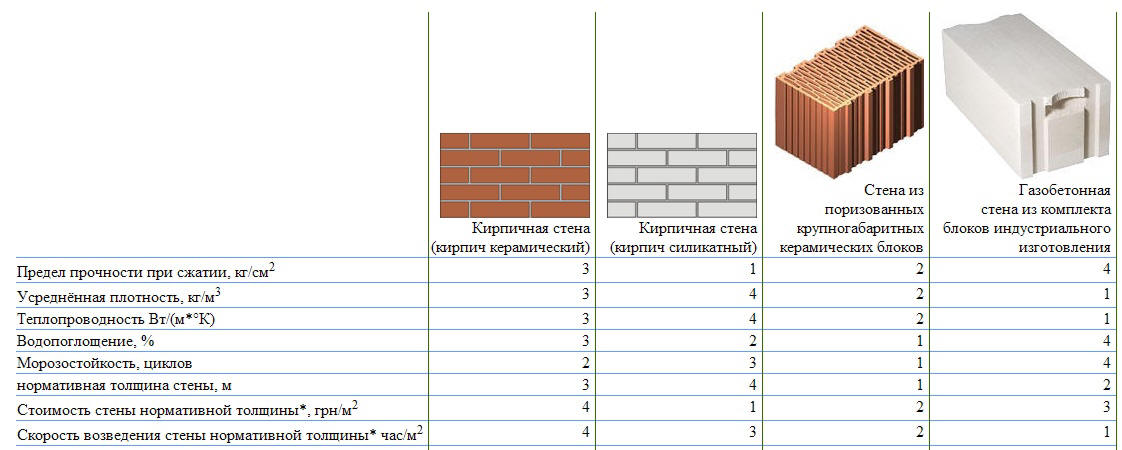
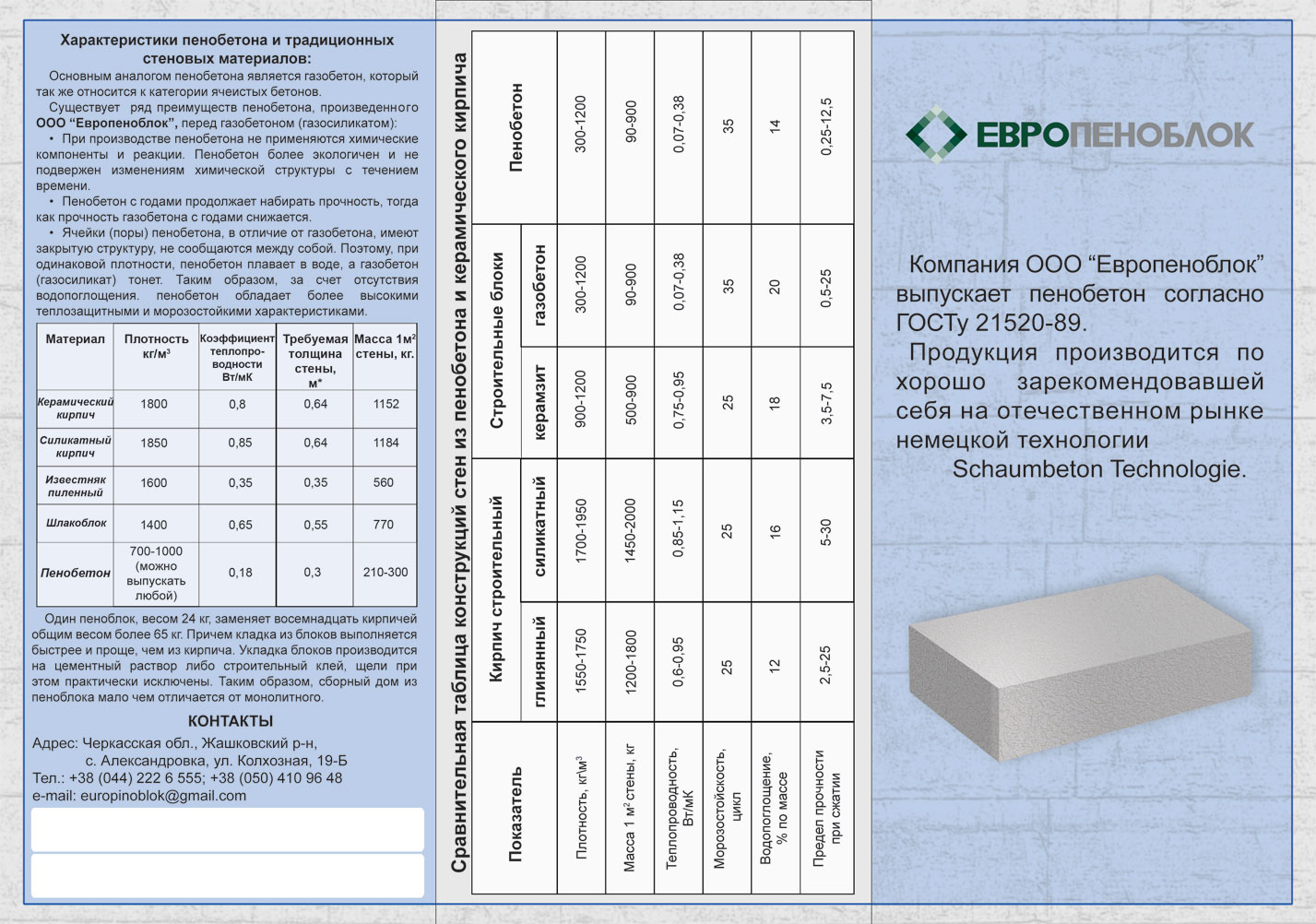
Comparison of brick and gas silicate
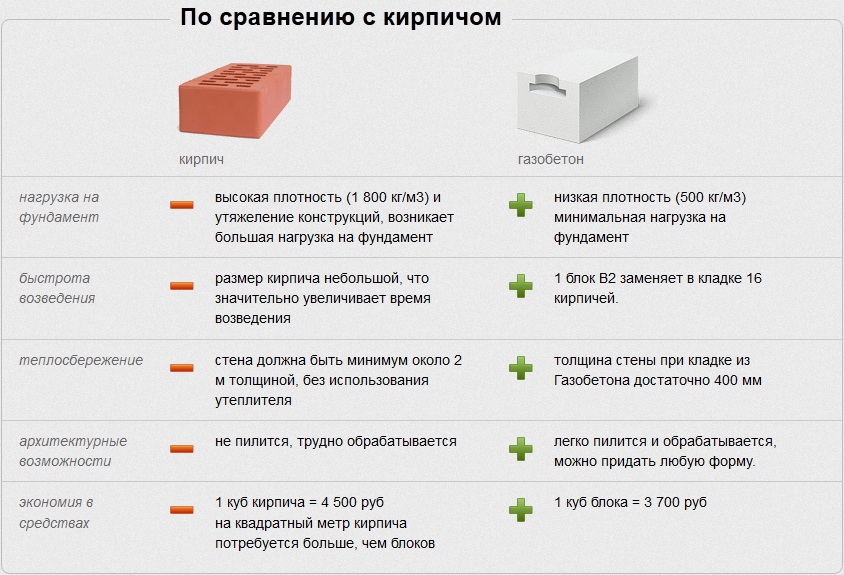
If you still have not decided which material to choose, gas silicate or ceramic / silicate brick, then it is worth considering that the last version of the products is more complicated when laying. A brick master cannot make a mistake, since it is almost impossible to get rid of the error after the completion of the masonry or in the process. That is why, before starting work with bricks, you must be sure that you have masonry skills. Gas silicate is easier to lay and, moreover, much faster than when working with bricks. The price of gas silicate is more affordable.However, walls with bricks look much more aesthetically pleasing, and there is no need to process them. Protecting gas silicate after installation is a prerequisite.
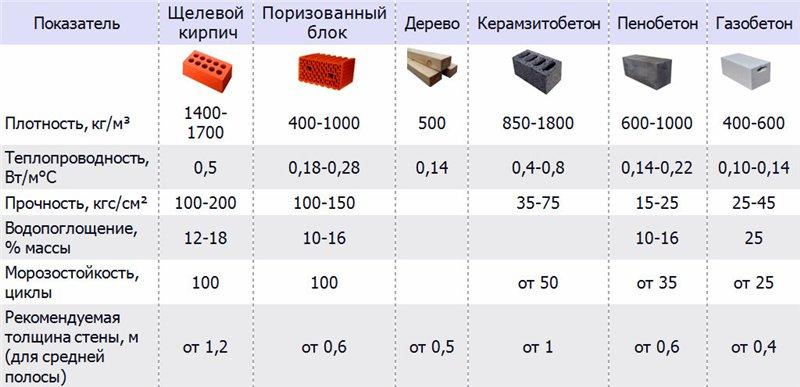
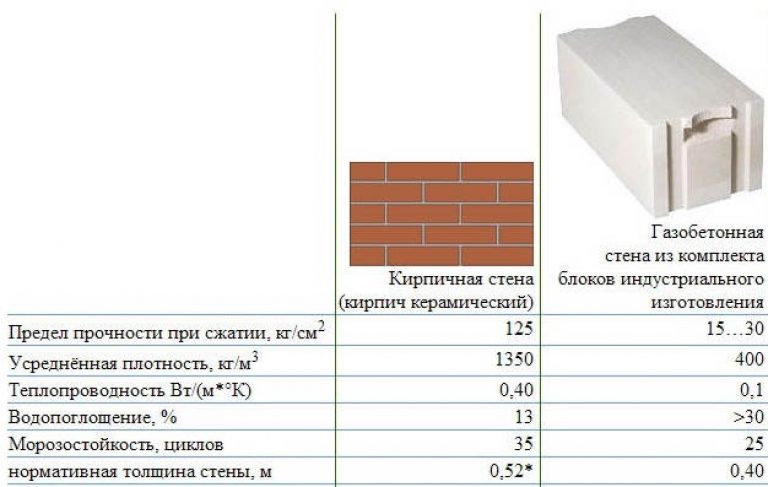
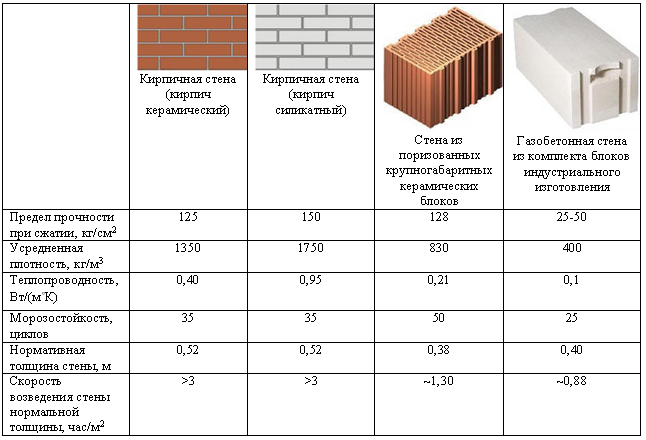
Figure 1. Table of strength of bricks and gas silicate blocks of various brands.
The complexity of working with bricks is also manifested in the fact that before starting work, it is necessary to purchase all the necessary amount of material, since the shades of products from different batches may differ.
Another comparison criterion is the possibility of redevelopment: it is permissible to transfer and dismantle internal walls made of gas silicate, with the exception of load-bearing ones, while redevelopment, where brick walls will be used, must be agreed upon in the relevant organizations.
Gas silicate can fit in any weather, but brick is more whimsical in this respect, it must be sheltered from precipitation and the sun.
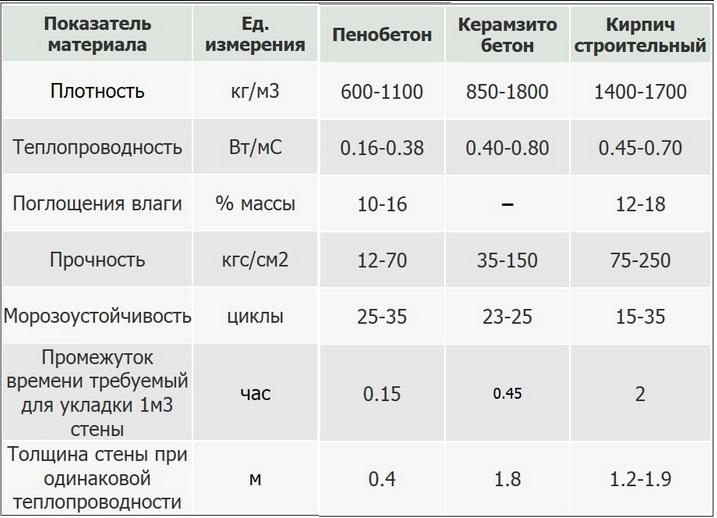
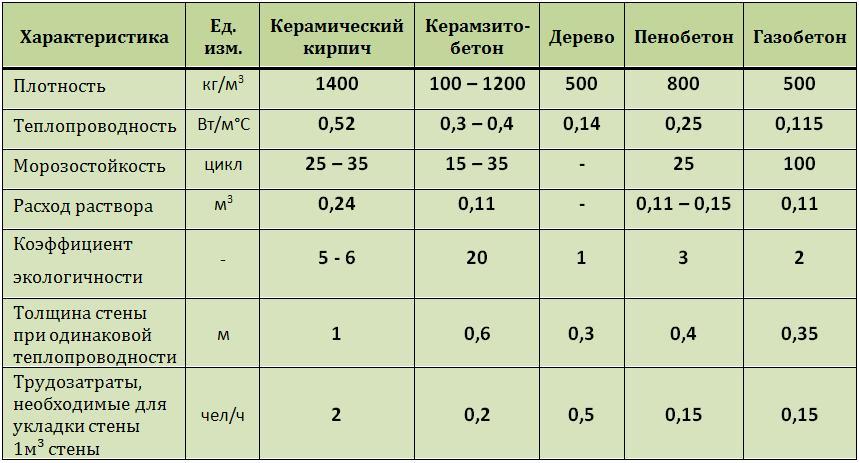
The table in Fig. 1 you can see the strength indicators of bricks and gas silicate blocks of different brands, as well as frost resistance and thermal insulation characteristics of these products.
The accuracy of the dimensions of the described products can be disregarded when choosing, since building materials are most often made using modern foreign equipment. But it is worth paying attention to the bearing capacity indicator, the brick has more outstanding
Thus, brick is used in multi-storey construction, while gas silicate can be used in the construction of low-rise buildings.
When choosing a wall material, it is important to pay attention to the indicator of its thermal conductivity. The gas silicate block does a better job of keeping the house warm in winter. In order to obtain a brick wall, the characteristics of thermal insulation of which will be equal to the corresponding characteristics of gas silicate, it is necessary to make it more massive, and this makes the cost of construction higher
In favor of lightweight concrete, it can be clarified that the porous structure excludes the presence of "cold bridges", which are bridges between voids that increase the ability to conduct heat
In order to obtain a brick wall, the characteristics of thermal insulation of which will be equal to the corresponding characteristics of gas silicate, it is necessary to make it more massive, and this makes the cost of construction higher. In favor of lightweight concrete, it can be clarified that the porous structure excludes the presence of "cold bridges", which are bridges between voids that increase the ability to conduct heat.
In view of the fact that there is a significant difference in dimensions between a brick and a gas silicate block, an analogy can be drawn between the number of products and the mass of masonry in a volume of 1 m3.
So, the consumption of bricks for the specified volume will be 513 items, which is equal to 1700 kg, while 22.2 pieces of gas silicate blocks will be spent on this volume. and their total weight will be only 625 kg.
For internal walls, undoubtedly, it is preferable to choose gas silicate, since drilling of a brick will be impossible due to scales on its surface, and the bearing capacity is not a determining factor here.
Which material you prefer, you choose, however, it is important to weigh all the qualities of both materials before starting work
Comparative characteristics
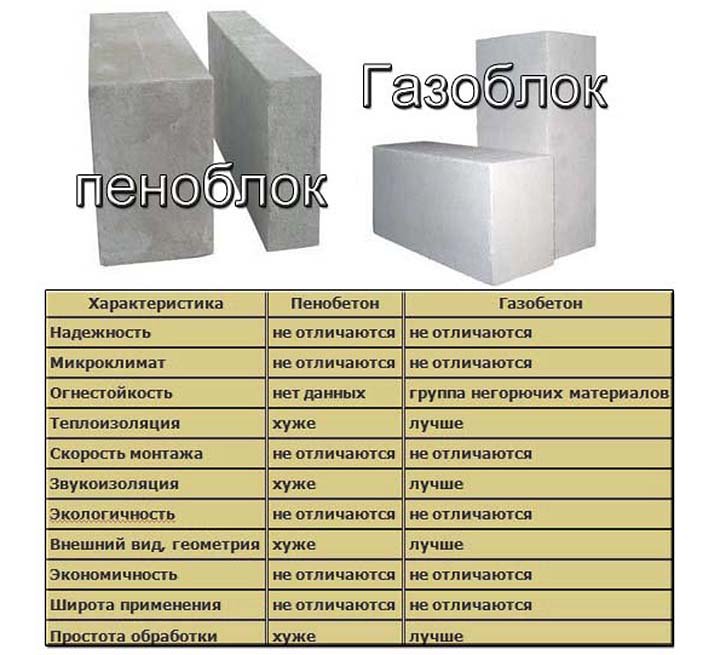
- the mass of a gas silicate block is much less than that of a brick. Therefore, its transportation is cheaper, and the load on the foundation is greatly reduced;
- gas silicate has a much lower thermal conductivity than brick. Where a wall made of gas silicate blocks is half a meter thick enough to retain heat, brickwork will have to be made one and a half meters thick;
- nevertheless, brick is better able to retain heat than gas silicate. Therefore, the heated masonry will remain in this state longer;
- the strength of brick blocks is much higher than that of gas silicate;
- ceramic bricks have been used in the construction of buildings for more than five hundred years, therefore, based on such vast experience, it is possible to predict with confidence the "behavior" of buildings made of this material. Gas silicate blocks are a relatively new invention. At the moment, we cannot say what will happen to the houses built from it in a couple of centuries.

For example, a brick does not hold heat well, but its other characteristics are higher. And gas silicate has some weaker indicators, but the thermal conductivity is remarkably low. By the way, so is the price. Brick construction is much more expensive.
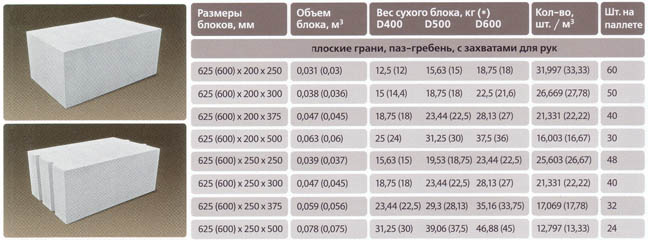
Weight and dimensions of gas silicate brick
If we compare this type of brick with the usual
... then the naked eye can see that it is much larger in size. Due to this, the speed of building houses increases significantly. Also, it is worth noting that the number of joints and seams is decreasing. This nuance allows you to reduce labor costs and the consumption of mortar for stacking blocks.
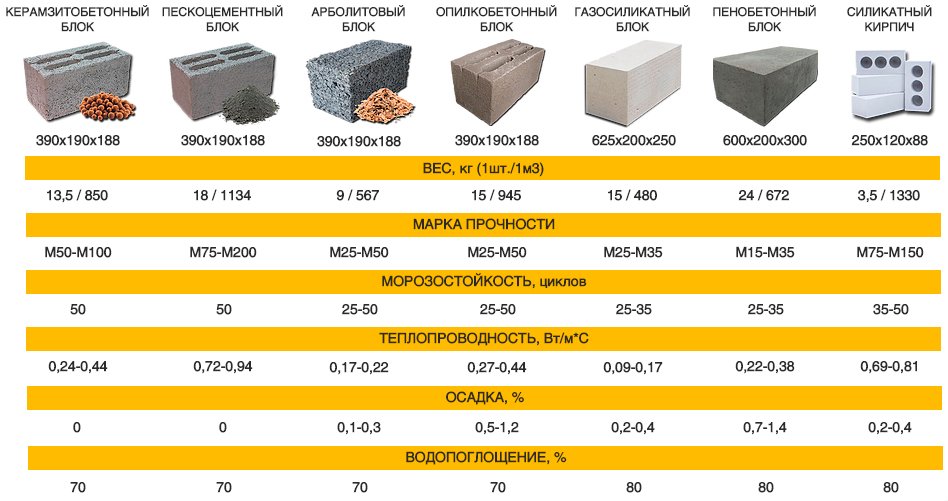
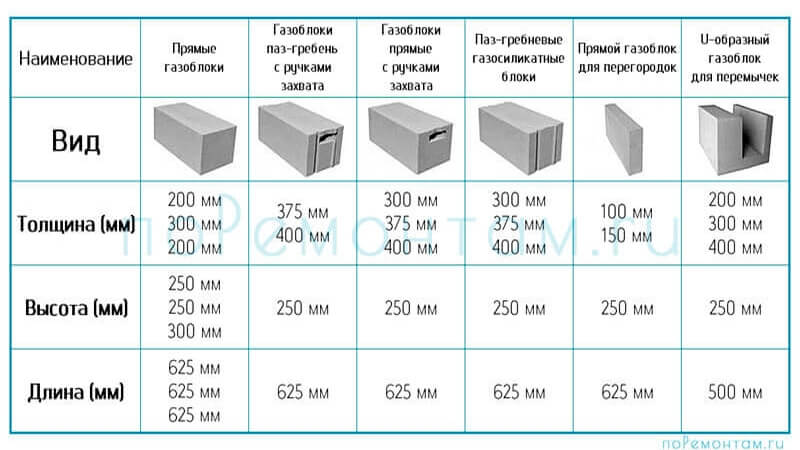
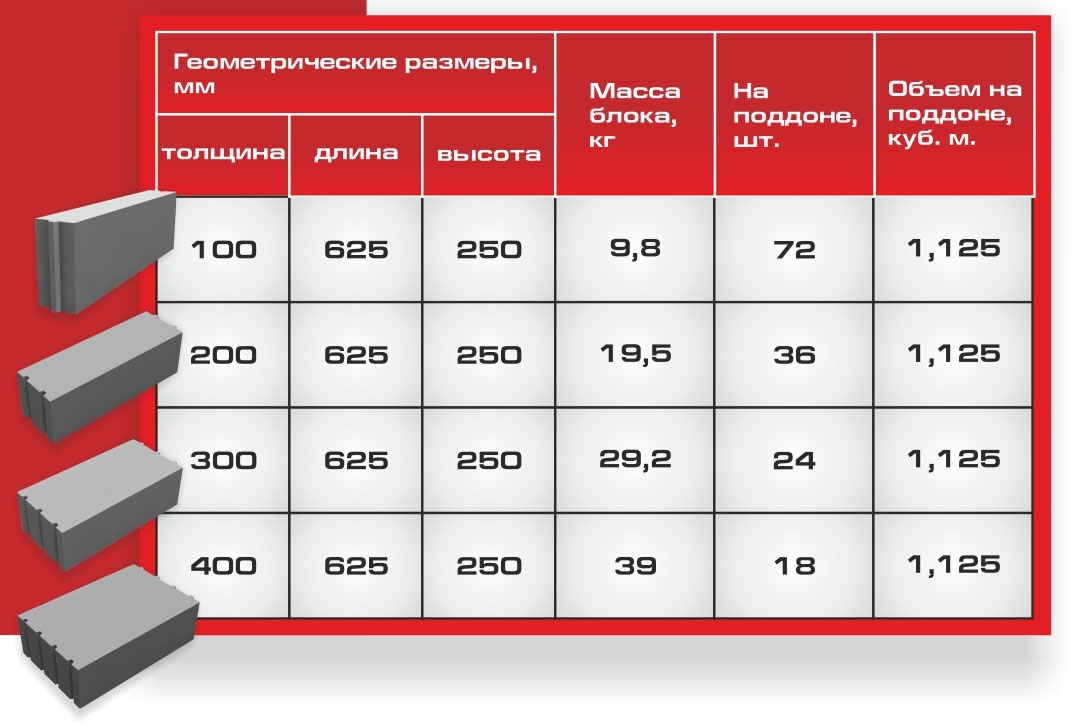
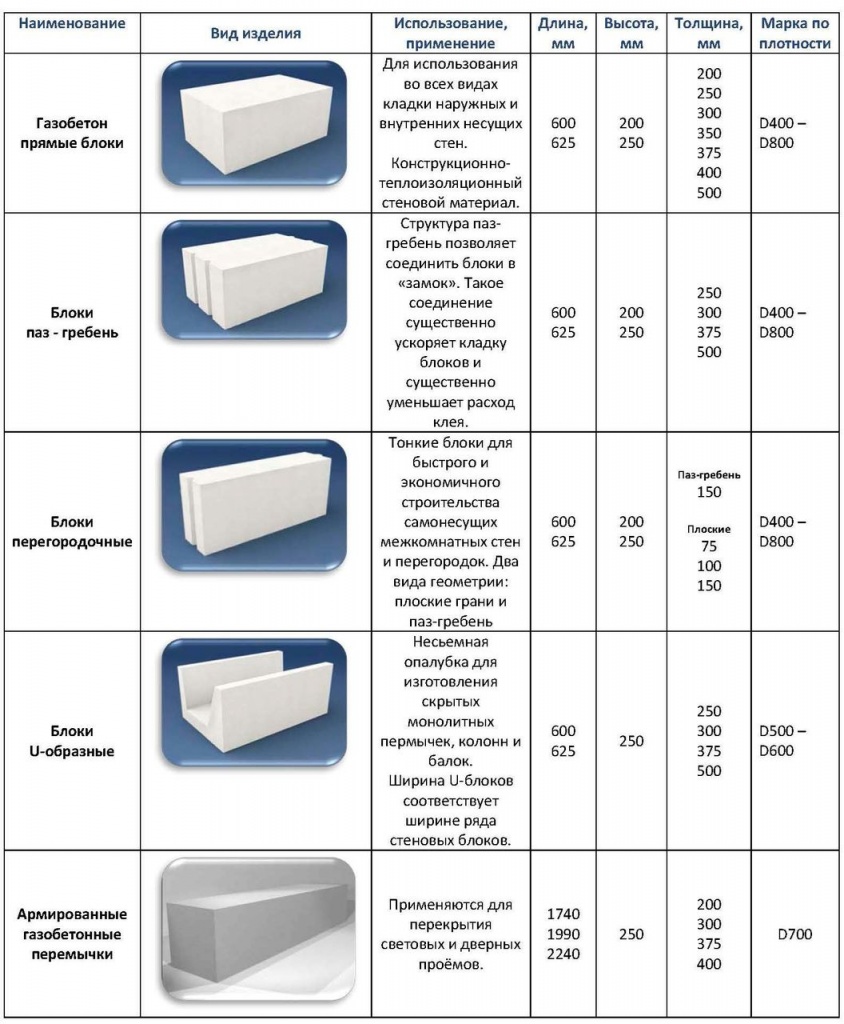
The size of a gas silicate brick has indicators of length, width and thickness. The usual size of a gas silicate brick for laying walls has a proportion of 600 × 200 × 300 mm. In addition, there is a semi-block wall brick with dimensions of 600 × 100 × 300 mm. Manufacturers produce products with various sizes, for example: 588 × 150 × 288 mm, 500 × 200 × 300 mm, etc.
As you can see, the variety of sizes is impressive, so you shouldn't have any difficulties in choosing the right one for your construction site. Knowing the thickness of the gas silicate brick, its height and length, you can make a calculation to compare the amount of ordinary brick and gas silicate brick required for building a house. With a standard brick size of 250 × 120 × 65 mm and gas silicate 600 × 200 × 300 mm, the volume of the first material will be 0.00195 m3, and the second - 0.036 m3. When dividing, we get an indicator that 1 gas silicate block is equal to the number of bricks in 1.85 pieces. Thus, for 1 m3, it is necessary to take 27.7 blocks, and 512 pieces of bricks.
The weight of a gas silicate brick depends on its size and density. The higher the numbers, the more weight. A conventional gas silicate brick weighs approximately 21 -29 kg. Compared to bricks, which have a mass per 1 m3 of bricks equal to: 512 pieces × 4 kg = 2048 kg.
Gas silicate block - how many bricks?
When using this formula to calculate 1 m3 of gas silicate, we get the result: 27.7 × 21 = 581.7 kg. As you can see, the difference is huge. Of course, this is largely influenced by the peculiarity of the structure of the gas silicate brick.
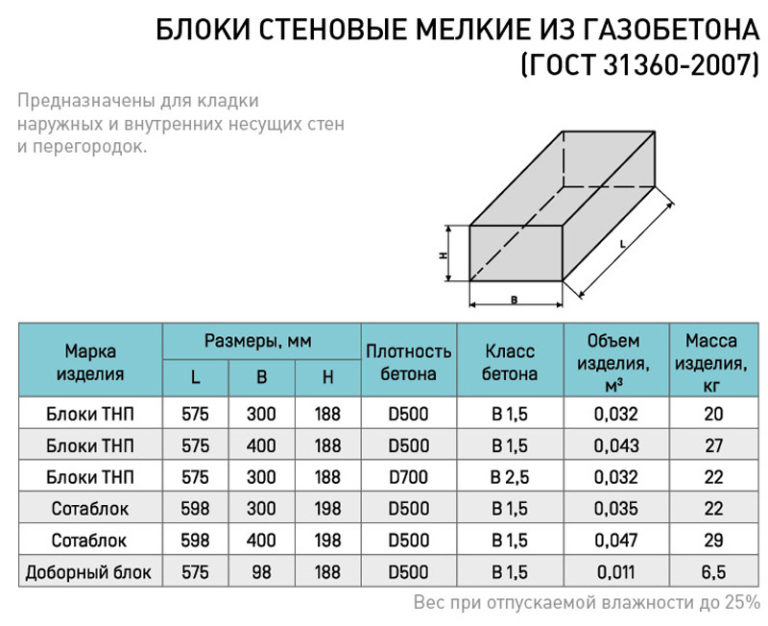
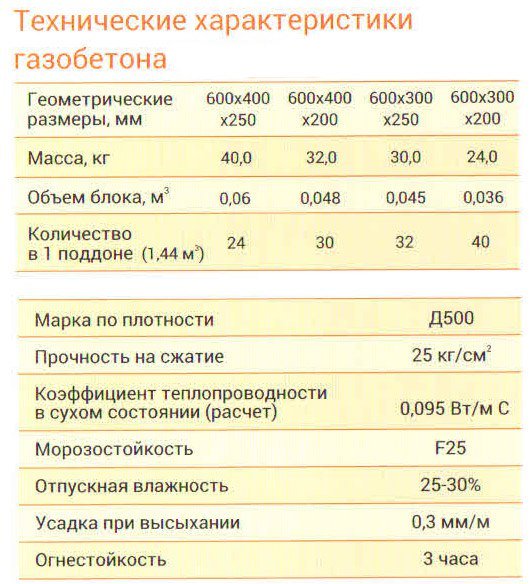
Technical characteristics of gas silicate bricks.
Distinctive features of the material are:
- Density;
- Heat conductivity;
- Resistance to subzero temperatures.
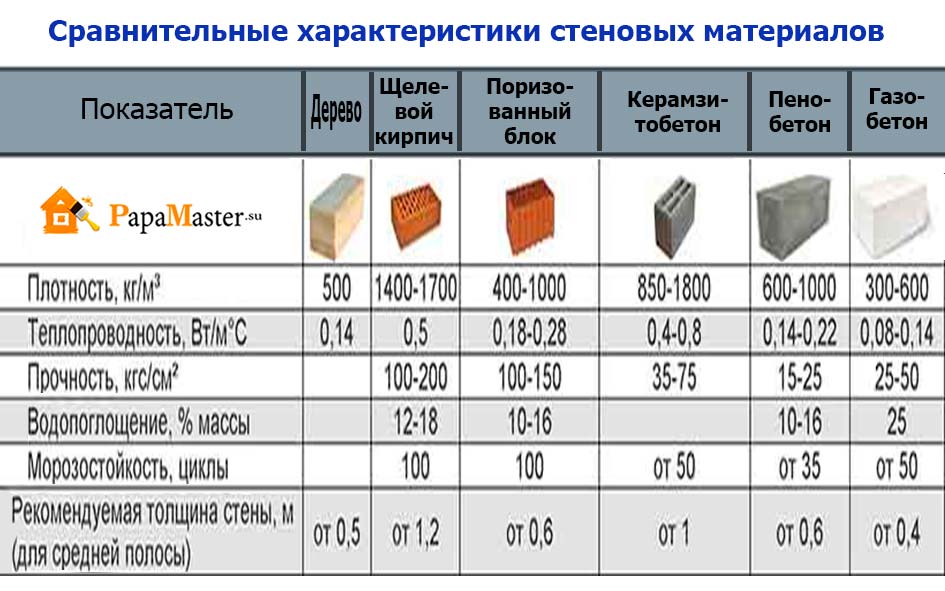
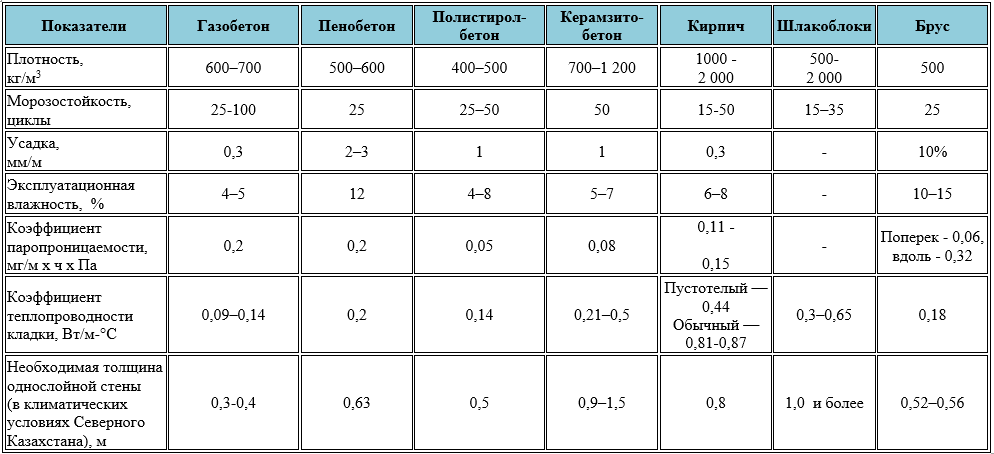
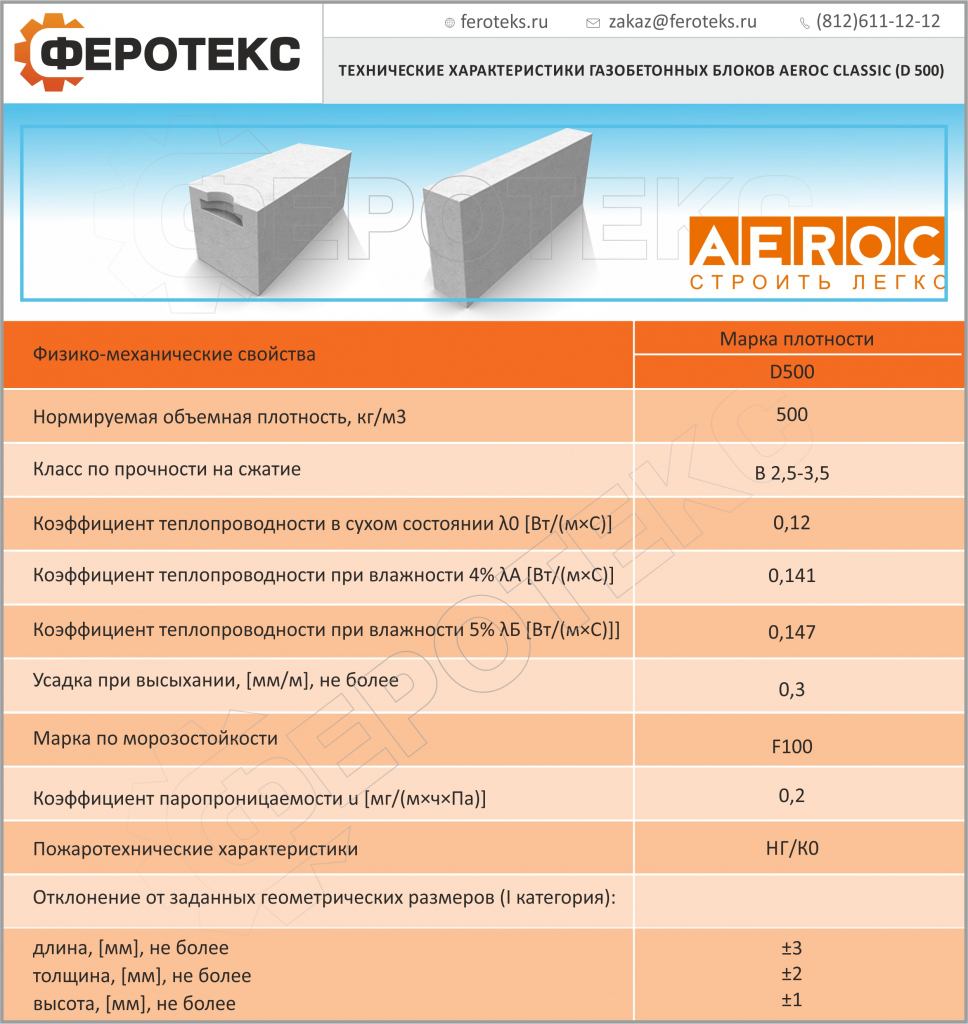
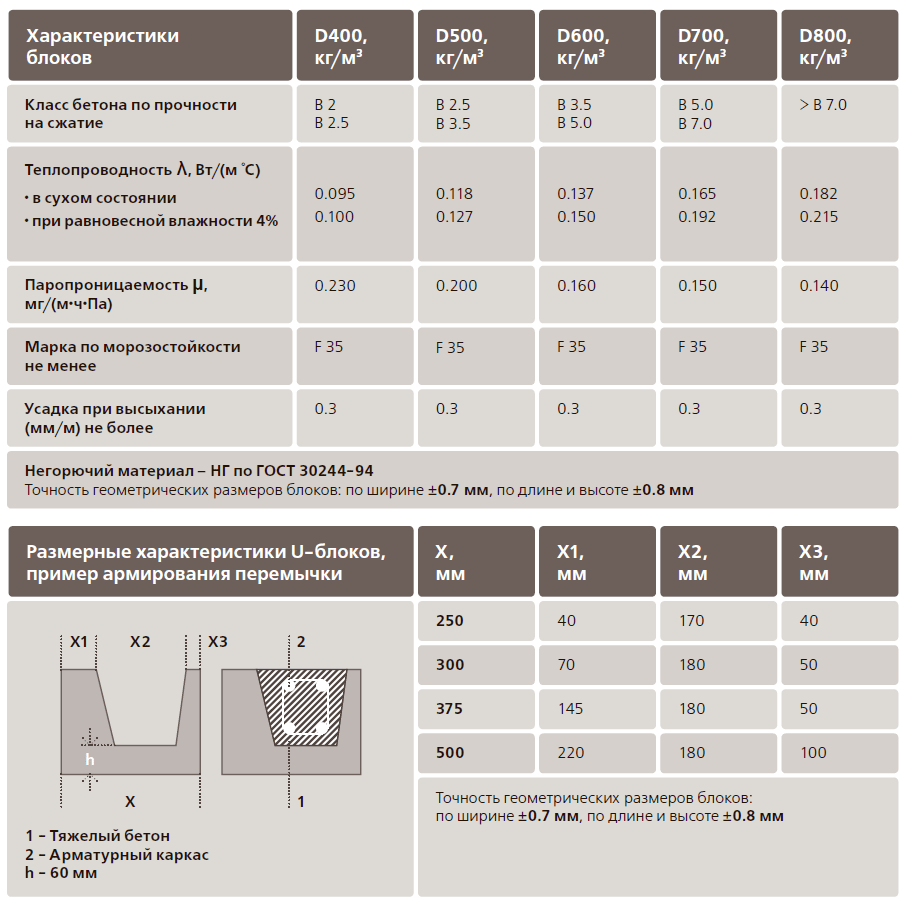
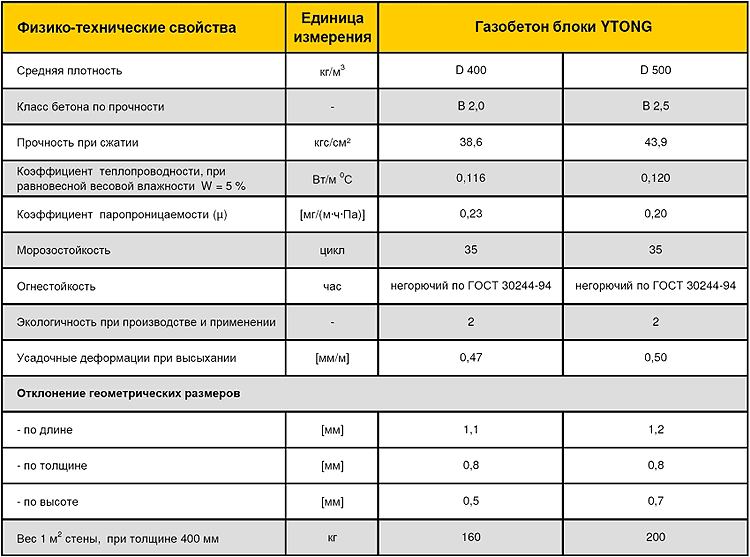
Product density marking:
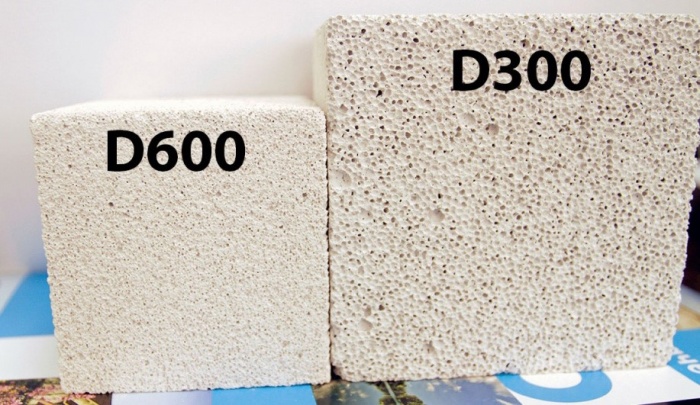
- D400 and less - products that are used as a material for thermal insulation of walls;
- D600 - D500 - indicators indicate a material with an average density, which is used for the construction of a gas silicate brick house on 1 - 2 floors and the installation of interior partitions;
- D700 is a high density material used for the construction of multi-storey buildings and buildings.
Gas silicate brick with a high level of density has indicators of 0.18 - 0.20 W / m ° C, and this is significantly lower than that of red brick. Blocks with an average density have indicators of 0.12 - 0.18 W / m ° C. And, finally, the gas silicate with the lowest density has a heat conductivity index of 0.08 - 0.10 W / m ° C.
Note. For comparison, the indicators of heat conductivity in wood are 0.11 - 0.19 W / m ° C. Gas silicate brick has a higher indicator. In addition, products of this type have the ability to breathe. These indicators refer to dry material, while in wet material, thermal conductivity increases.
Resistance to subzero temperatures is in direct proportion to the pore size in the material. Typical blocks, which are produced in natural conditions, withstand from 15 to 35 freeze / thaw cycles
Autoclaved gas silicate brick has a higher frost resistance, designed for 50 - 100 cycles
If we take into account GOST 25485-89, the average number of freeze / thaw cycles of gas silicate is not more than 35
Brick block composition

The material is produced from lime and sand.A non-fired briquette in the form of a parallelepiped is obtained from a moistened mixture of lime-siliceous binders and fillers by hyper-compression and autoclave hardening. The silicate block contains slags and ash, which partially or completely replace grains of quartz sand, reduce the density of silica building materials, improve strength characteristics and heat-insulating properties. The ingredients of the silicate mixture include the following ingredients:
- air construction lime;
- gully or river quartz sand;
- white sludge;
- ash components;
- slag;
- alkali-resistant pigments (chromium oxide);
- fine-grained ash and slag mixture;
- water.
Expert advice
Working with gas silicate blocks does not require a high level of skill, enough initial knowledge and adherence to all stages of the instructions, so you can build the necessary structure with your own hands.
Let's take a look at some tips from construction experts:
- When choosing blocks, give preference to blocks with ideal geometry - the surface is flat, smooth, uniform in color, all lines and corners are straight;
- Kneading the glue solution with a construction mixer or a drill, while manually stirring the mass does not guarantee the homogeneity of the glue;
- In summer, the surface of the blocks is wetted with water; in winter, the bricks are pre-heated;
- Construction always starts from a high angle.
Gas silicate blocks have been used for a long time in all areas of construction, they have a large list of advantages, among which stand out - thermal insulation, speed of work, ease of installation and affordable cost.
2> Composition and technology of production of gas silicate blocks
The mixture for the production of gas silicate blocks has the following composition:
- astringent (Portland cement according to GOST 10178-76, calcium boiling lime (according to GOST 9179-77);
- silicate or silica filler (quartz sand with 85% quartz content, fly ash, etc.);
- lime, with a content of magnesium and calcium oxides of more than 70%, and a slaking rate of up to 15 minutes;
- technical water;
- gas-forming additive (aluminum powder and others).
Gas silicate belongs to the class of lightweight aerated concrete. This material is a mixture of 3 main components: cement, water and fillers. Lime and quartz sand in a ratio of 0.62: 0.24 can act as fillers. Separately, it is worth talking about additives that give gas silicate its individual characteristics. Fine aluminum powder acts as an additive. All these components are thoroughly mixed, and under certain conditions observed, all these materials foaming. When aluminum powder reacts with lime, hydrogen is released. The huge amount of hydrogen bubbles released makes up the porous structure, which is the main distinguishing feature of gas silicate. Its structure resembles a concrete "sponge", since the entire volume of the block consists of cells (bubbles with a diameter of 1-3 mm).
 Gas silicate blocks
Gas silicate blocks
The cellular structure makes up almost 85% of the volume of the entire block, so this material is very light in weight. First, a mixture of components is prepared in a special mixer for 5 minutes, which includes Portland cement, fine sand (quartz), water, lime and a gas generator (most often, this is a suspension of aluminum). Hydrogen, formed by the reaction between aluminum paste (powder) and lime, forms pores. Bubbles ranging in size from 0.6 to 3 mm are evenly dispersed throughout the material.
Basic chemical reactions take place in metal containers or molds. The mixture is subjected to vibration, which promotes swelling and seizure. After hardening, all irregularities from the surface are removed with a steel string. The seam is divided into blocks, and then they are sent to an autoclave unit.The final calibration of the finished blocks is done by a milling machine.
Gas silicate blocks are made only by autoclaving. Aerated concrete blocks can be produced both by autoclave and non-autoclave method (natural hardening of the mixture):
- Autoclave treatment. This stage significantly improves the technical characteristics of the gas silicate. Here, for 12 hours at high pressure, steam treatment is carried out, the temperature of which is almost 200 ° C. This heating process makes the texture more uniform, thereby improving the strength properties (not less than 28 kgf / m²). Its specific thermal conductivity is 0.09-0.18 W (m ∙ K), which makes it possible to erect walls in one row (400 cm) in almost any climatic conditions, but excluding the northern regions.
- Non-autoclave technology. It consists in the natural hardening of the mixture: moistening and drying in natural conditions. In this case, it is quite possible to make it with your own hands, since special equipment is not required here. The strength of the blocks in this production does not exceed 12 kgf / m².
The first variety is more expensive. This is due to significant manufacturing costs, as well as the best technical characteristics of gas silicate blocks produced by this method. They are much stronger, their coefficient of thermal conductivity is lower. The pores inside such a gas silicate are distributed extremely evenly, which affects the strict compliance of the material with the specified parameters.
Positive and negative sides about gas silicate brick
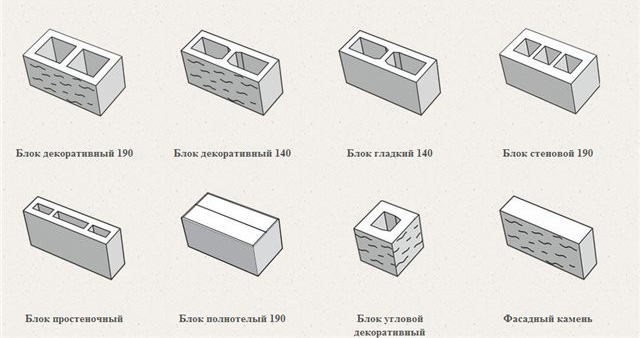 Varieties of gas silicate blocks.
Varieties of gas silicate blocks.
The undoubted advantages of a gas silicate block over ordinary building red or refractory bricks are:
- Ease and simplicity of installation.
- Convenience of machining, that is, it can be cut with the most ordinary hacksaw without much effort.
- Vapor permeability, which, due to the open structure of the cells of the gas silicate brick, makes the moisture exchange between building materials optimal.
- Reliable noise and sound insulation, which is guaranteed with a minimum thickness of the partition block of 10 cm.
In addition, it keeps heat well and has less weight than the same brick. However, one cannot do without negative aspects.
So, the disadvantages of gas silicate bricks are:
- High hygroscopicity, as a result of which, when the temperature fluctuates, the walls of the building can crack. As a result, an additional protective siding trim with a ventilation gap will be required to eliminate this problem in order to eliminate excess moisture.
- Increased bending deformation or shrinkage that occurs in places of increased stress, which can be eliminated by using reinforcing belts between floors.
- Short-lived frost resistance, equal to about 20-25 cycles.
From all of the above, we can conclude the following:
- To obtain a comfortable and economical structure from a gas silicate block, which is not inferior in durability to a brick one, it is not recommended to build private buildings higher than 2 floors.
- Outside, the gas silicate will need to be insulated with mineral wool or other vapor-permeable materials or sheathed the entire wall with siding, while on the inside of the wall it will be necessary to plaster.
- Among other things, ensure good ventilation under the insulation and build a solid foundation, and reinforce the masonry.
When working with gas silicate, it is strongly recommended to use a special glue in order to reduce the heat leakage that can occur when using a conventional solution. Good luck!
It is interesting: Projects of a bath 6x6 - setting out the question
The choice of mixture for installation work
To work with gas silicate products, several options for a binder solution are offered:
- Mortar based on cement and sand;
- Special glue.

The cement mixture is the simplest and most affordable option, the price of ingredients is quite low, the mixture can be prepared independently - 3 parts of sand and water are shaved for 1 part of cement, the mixture is thoroughly mixed until homogeneous.
But the cement-sand mixture has a big disadvantage - the appearance of "cold bridges", the room cools down quickly, so it is not worth building a residential building only with this solution, it is better to use it for the construction of garages, fences, industrial buildings, etc.
Special glue - for the installation of gas silicate blocks, it is worth giving preference to glue for deep penetration aerated concrete. It is characterized by high indicators of durability, moisture resistance, resistance to mold and the occurrence of fungal diseases.
The glue is sold in a building materials store in a tight sealed package, it contains exact instructions for preparing the solution.
When choosing a mixture, it is necessary to give preference to plastic solutions that have good moisture resistance and resistance to temperature extremes, and also have adhesive properties.

The main physical and mechanical characteristics of gas silicate bricks
Important factors that distinguish the products are the following indicators:
- Density.
- Thermal conductivity.
- Frost resistance.
As mentioned above, the weight and properties of the material directly depend on the density. Depending on this, gas silicate bricks are divided into markings:
- D700, the densest, are used for high-rise structures.
- D600 – D500, medium density, are used for the construction of low-rise buildings and partitions.
- D400 and below, an insulating material used to insulate the contour of a load-bearing wall.

The difference between gas silicate blocks is their thermal conductivity. For example, ready-made blocks of the D700 brand have an indicator of 0.18–0.20 W / m · ° С (lower than that of red bricks). If we talk about the D600 – D500 brand, then the indicators are even lower - 0.12–0.18 W / m · ° С. The lowest thermal conductivity is for D400 products, equal to 0.08–0.10 W / m · ° С.
As for frost resistance, it depends on the pore volume of the blocks. Naturally made building blocks can withstand 15–35 freeze and thaw cycles.

But, some manufacturers who manufacture blocks in an autoclave declare that their products have a frost resistance of 50-100 cycles, which is really amazing. Nevertheless, based on the information in GOST 25485-89, on average, the frost resistance of aerated concrete is not higher than 35 cycles.