How to work with a calculator for calculating gas blocks for building a house?
In order to avoid errors in calculations, to avoid the problems of unnecessary costs or lack of materials, we recommend that you use the calculator of aerated concrete blocks for building a house. Our computing program is based on the data of GOST 21520-89 "Cellular blocks small wall concretes ”, GOST 25485-89“ Cellular concretes ”, GOST 31360-2007“ Unreinforced wall products made of autoclaved aerated concrete ”.
Our service has an intuitive, simple interface. For clarity, we have placed demo miniatures, which show how the elements of the structure look, as well as what is required of you.
In order to calculate gas blocks for your home, you need to decide on the format and size of the products. After you choose the most suitable option, you can start calculating.
Fill in all the fields as accurately as possible, based on the plan of your home or the recommendations of specialists.
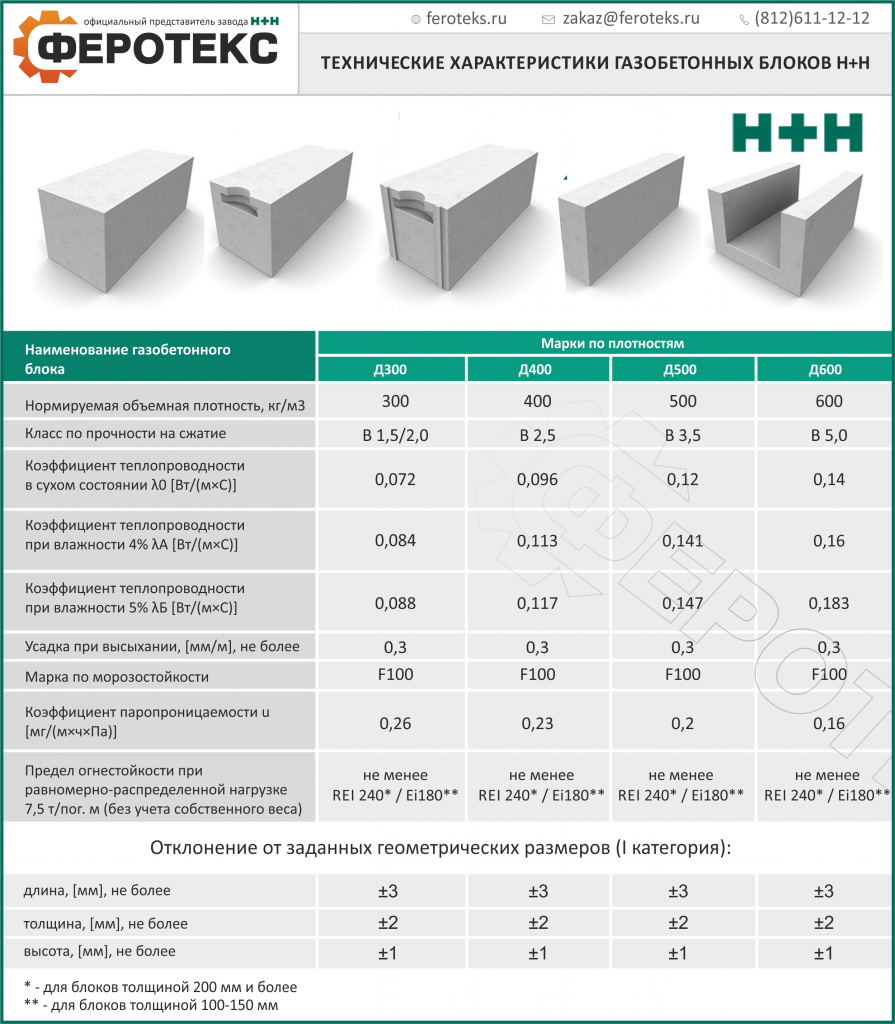
Block parameters:
- size, mm (the most popular 600x300x200);
- density, kg / m3 (D500, D600 brands are suitable for most private houses);
- price, rub.
We advise you to stock up on a small number of blocks for combat, cutting and scrap. 3-5% will be enough.
Wall parameters:
- the total length of the walls of the house of the same thickness, m (by default, you count blocks only for load-bearing walls with the same masonry thickness, if you want to find out the amount of material for partitions, use the calculator again and add up the values);
- wall height, m;
- masonry option (standard in half a block);
- the type and thickness of the mortar in the masonry (glue or foam);
- masonry mesh (at your discretion).
After you have filled in the basic elements of the calculator, you can click on the "Calculate" button. The result will be an approximate calculation of the gas block, without taking into account the openings, jumpers and armored belt.
This data can be used only for orientation, but not before starting construction.
It is highly advisable that you also include:
- number and size of windows;
- number and size of doors;
- type of pediment and its characteristics;
- for triangular:
- total height, m;
- base width, m;
- for trapezoidal and pentagonal:
- total height, m;
- height between bases, m;
- base width, m;
- for triangular:
- all used jumpers;
- armopoyas (if available).
The base is a segment that connects the opposite corners of the pediment at the same level.
Taking into account all the elements of the building structure, the reliability of the calculations will increase significantly, while the errors will become minimal. Transferring all the necessary parameters to the sheet, or printing out the calculation results, you can confidently go to the hardware store and purchase the necessary materials.
Tips & Tricks
When laying aerated concrete blocks, it must be borne in mind that the parameter of the length of the horizontal joints should be approximately 2-8 mm. If we are talking about vertical seams, then their size should not exceed the 3 mm mark. If excess mortar appeared from the seams, then they do not need to be rubbed - these elements must be removed with a trowel.
When doing work on laying aerated concrete blocks with your own hands, it is recommended to use homemade scaffolding. It will be much easier to work with them. Do not forget that the quality of the entire wall will depend on the laying of the starting block row.
That is why it is so important to use a building level at the very beginning. If you notice certain inaccuracies, then they need to be eliminated as soon as possible, and only then proceed to the installation of the next row

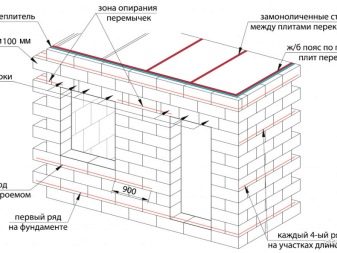
Please note that if the blocks contain parts such as gripper handles, then when installing them, the consumption of adhesive can significantly increase. The reason for this is that the technology for laying aerated concrete provides for the filling of absolutely all cavities in the course of work.
Transport aerated concrete blocks carefully so as not to damage their surface. It is recommended to cover this material with plastic wrap, which will protect them from negative external factors. If, in the course of laying window or doorways, you did not manage to get into the length of the whole aerated concrete block, then you can take a hacksaw or saw and cut off the excess part of the part. This work will not take much time and effort, since aerated concrete is a pliable material.

If you are going to use aerated concrete for the construction of a private house, then you need to be as responsible as possible in choosing a reliable and strong foundation. This is due to the fact that this material does not withstand the movement of the base. Because of this, the type of foundation should be selected based on the characteristics of the soil and the characteristics of the gas block itself.
Experts do not advise to lay aerated concrete blocks, starting from two corners towards each other. As a result of such actions, it will be problematic for you to bandage the rows and adjust the finishing element to the required size. Before buying aerated concrete blocks, you need to carefully examine them. The materials should not show the slightest damage, chips or cracks. If you notice such, then it is better to refuse the purchase.
In the next video, you will find the laying of aerated concrete blocks.
Material characteristics
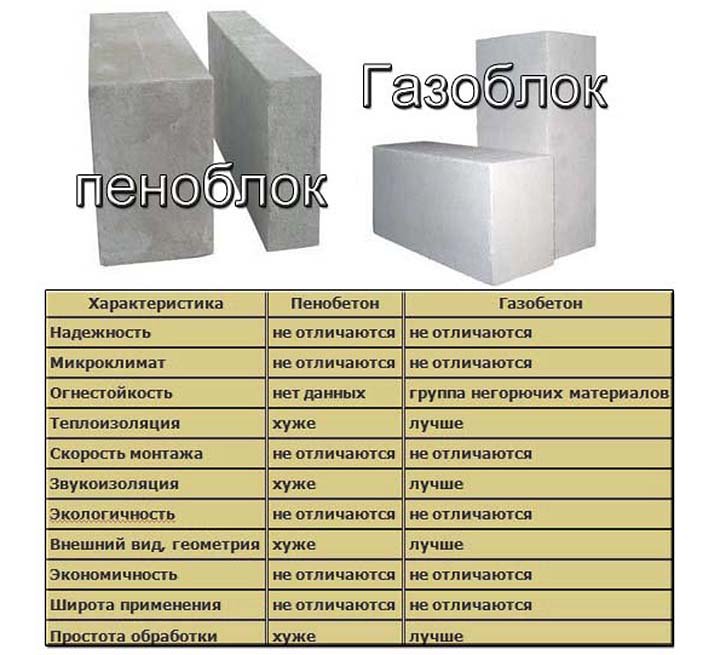
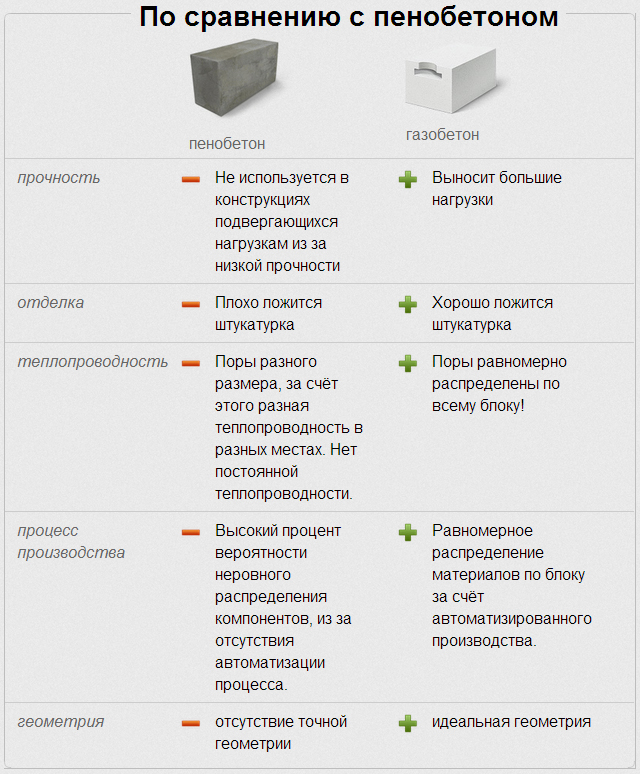
The presence of cellular voids provides high heat capacity and sound insulation. A wall of aerated concrete 30 cm thick retains heat as much as 1 meter of brickwork (more about brick houses), this is an indisputable advantage of both aerated concrete and foam concrete. However, the presence of through or non-through pores forms a different moisture absorption capacity of materials and their ventilation properties.
Aerated concrete with a structure of through pores "breathe" like wooden walls. There is no need to build a forced ventilation system for them. A traditional hood above the stove and ventilation ducts from the kitchen and bathroom are enough. On the contrary, foam concrete with insulated cells "does not breathe". A building with such walls requires mandatory ventilation even in living rooms.
Moisture permeability of aerated concrete and foam concrete
Similarly, due to the different cellular structure, aerated concrete is able to absorb moisture, condensate, and get wet when exposed to atmospheric precipitation. This minus of aerated concrete makes it necessary to finish the facade of the house as soon as possible, spending additional funds on this during the main construction.
In general, the durability and service life of aerated concrete houses directly depends on its protection from external atmospheric influences. If you approach this issue competently, then such a house will serve no less than a brick house without problems.
Foam concretes, in turn, do not absorb atmospheric moisture and remain dry, therefore they are often used where there is a fairly humid climate. However, the gray appearance of buildings made of foam blocks, one way or another, obliges the owners to make the exterior of the house.

The presence or absence of moisture in the pores of the wall reduces or increases frost resistance. Walls made of foam concrete have a higher frost resistance index.
Heat insulation of cellular materials
The thermal insulation characteristics of aerated concrete in the technical passport are indicated by a coefficient of 0.116 (with a moisture content of 6%). For foam concrete, the range is from 0.13 to 0.16. However, these figures are for dry material. For an honest comparison, it is necessary to increase the humidity to the same 6%, then the heat capacity will slightly decrease and will be comparable to the same characteristic of aerated concrete.Thus, the thermal insulation characteristics of the materials can be considered the same.
Strength of aerated concrete and foam concrete
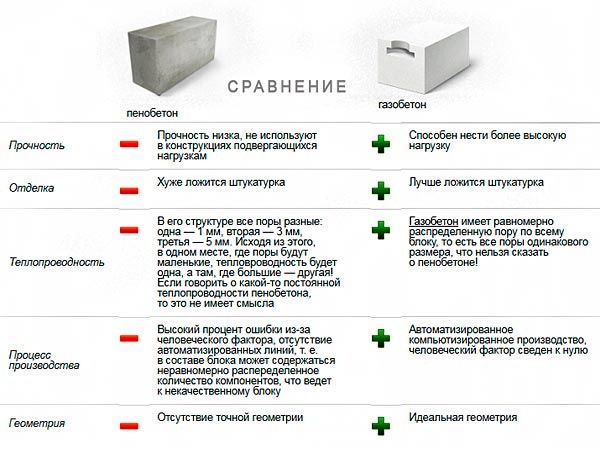
The strength of aerated concrete (30-35 kg / cm2) is higher than that of aerated concrete (about 10 kg / cm2) at the same density
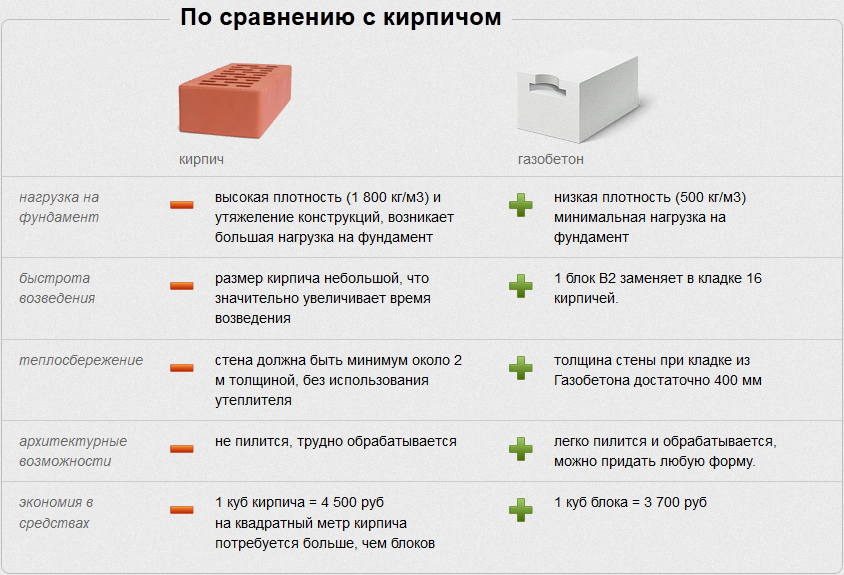
This important advantage allows you to build two-story houses with 35 cm thick aerated concrete walls.At the same time, foam concrete walls will have to be made thicker (up to 65 cm) in order to provide the structure with the necessary strength
This significantly increases the cost of materials for construction and increases the volume of construction work. Therefore, the advantage of aerated concrete will be the reduced consumption of material and money during construction.
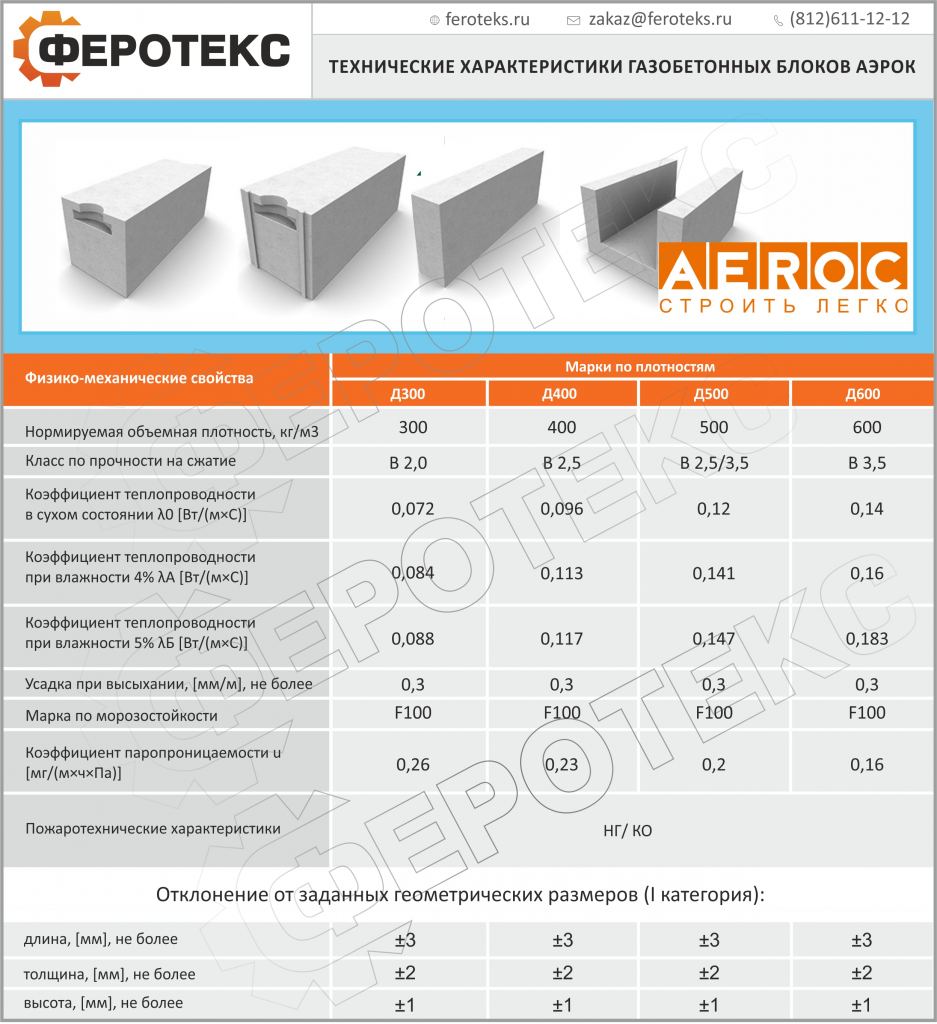
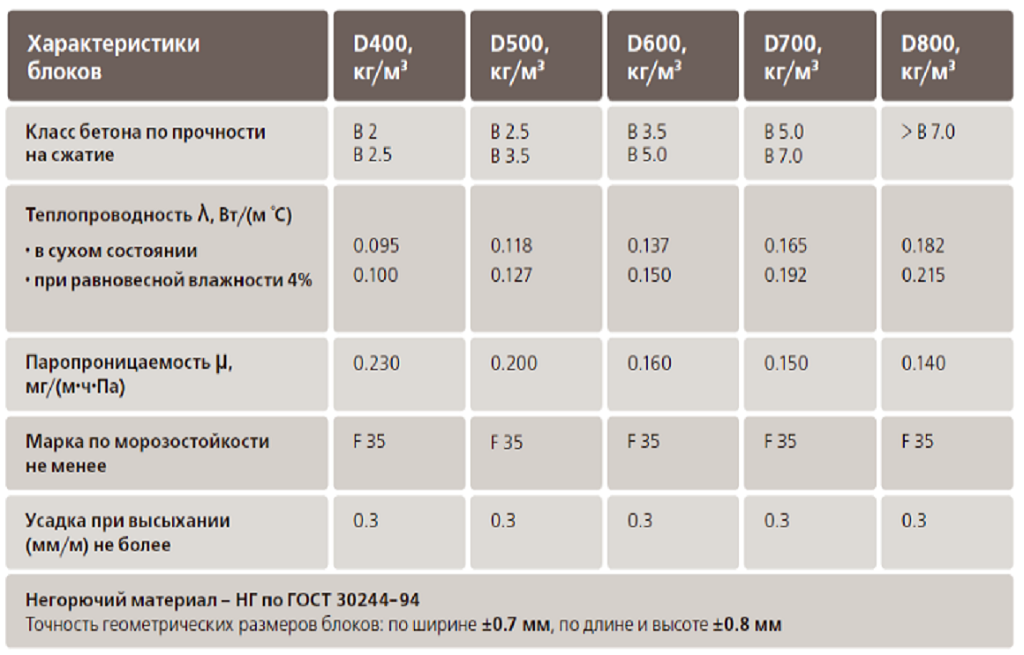
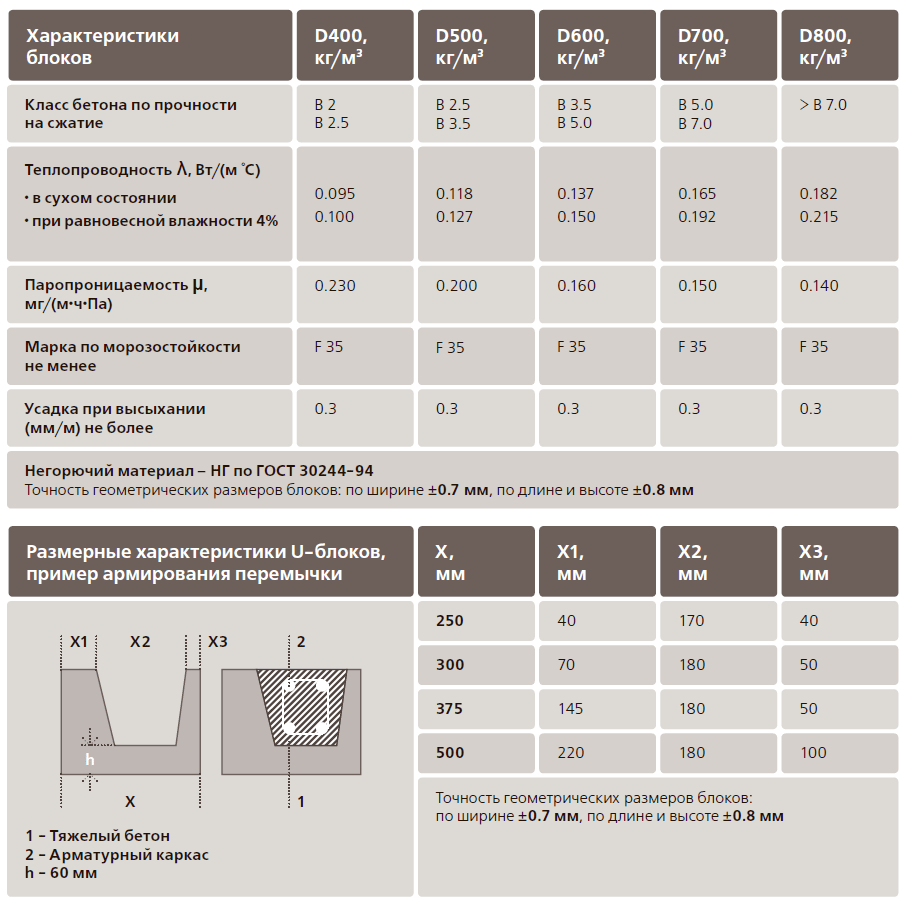
In the line of aerated concrete materials with different densities are used - from 300 to 600 kg / m3. When building a house for permanent residence, it is best to use aerated concrete with a density of about 500 kg / m3, since it is optimal in terms of price-quality ratio.
Aerated concrete is characterized by higher strength, reliability, it does not shrink. Foam concrete has lower strength characteristics and shrinkage, but at the same time its price is 20% lower. Therefore, foam concrete is used as a substitute for aerated concrete where there are no bearing loads (for the construction of partitions, additional insulation).
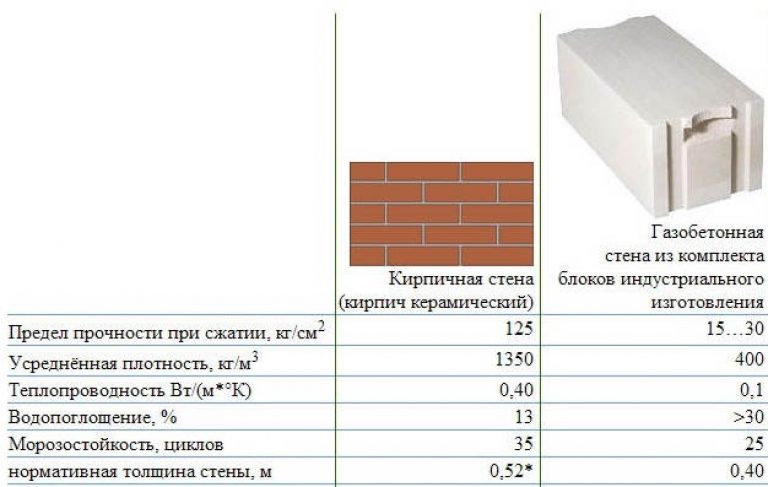
To understand what is better for building a house - foam concrete or aerated concrete, you need to take into account all the above indicators and apply them to your area, the project of the house and your financial capabilities. In any case, there are always backup options in the form of brick buildings or wooden houses.
Options
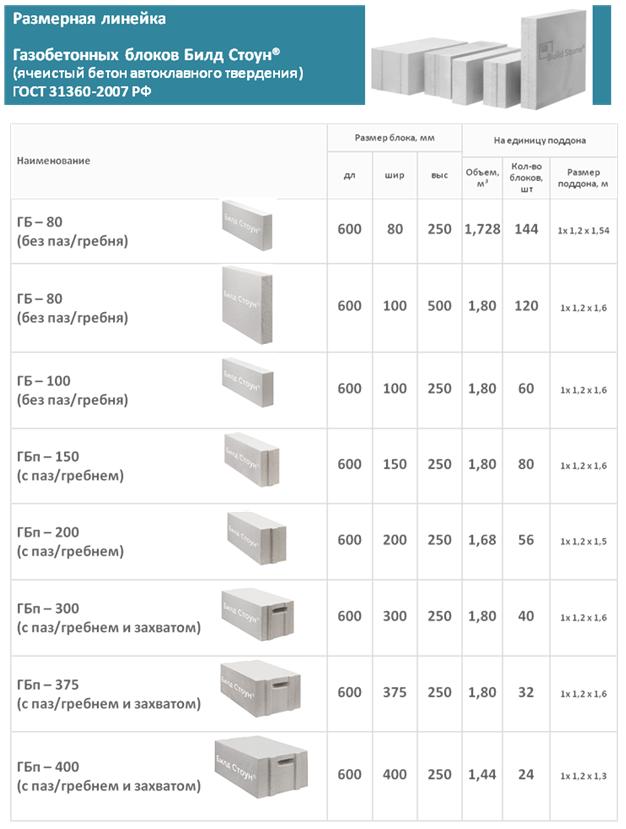
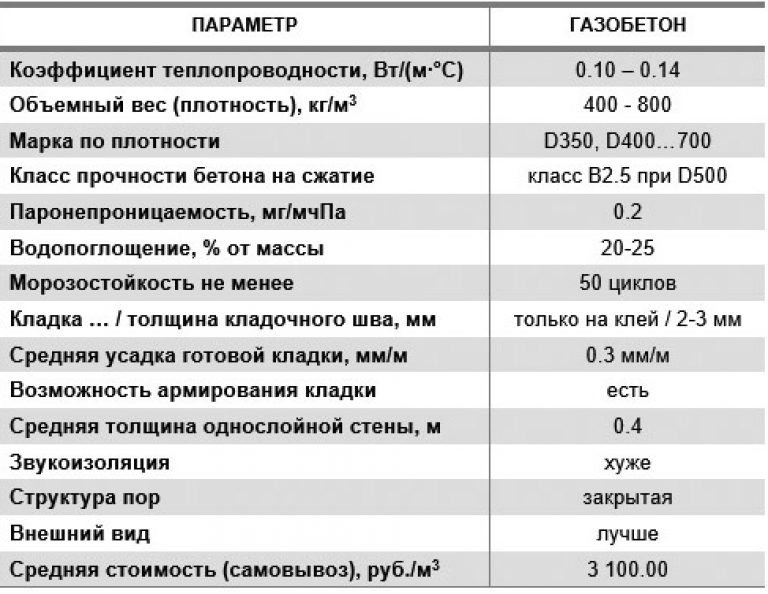
can be very different, like the shape, design. Wall blocks are usually made in the form of a large parallelepiped. An example of a standard size is 60 centimeters long, 30 centimeters high and 20 wide. Several other standard sizes are also common, but there are also blocks for internal walls (they are smaller), additional elements, products of a special design.
There are two types of gas blocks
For most tasks on construction sites, it is enough to have two types of aerated concrete blocks - ordinary rectangular and U-shaped, which are relevant for performing different parts of the structure. In addition, the shape of the blocks can be different.
What are the gas blocks by type and shape:
- Rectangular blocks - used for the construction of internal partitions, external load-bearing walls.
- Reinforced aerated concrete beams - for creating ceilings. Overlappings are mounted from T-shaped beams 60x25x20 centimeters in size, window / door openings are made of U-shaped blocks, which can significantly speed up the installation process and reduce labor costs.
- Arc-shaped gas blocks, lintels - are used to facilitate the construction process (certain parts of the structure are made of them).
When choosing blocks from aerated concrete, it is important to know the technology for the production of the material. There are two options in total, and in general they are similar, but differ in key parameters.
The mixture is prepared for pouring into a mold according to the same recipe, but in case the solution is poured into one large mold and sent to an autoclave, where it is exposed to high pressure and temperature.
Non-autoclaved aerated concrete is poured into molds and then dried under natural conditions. In this case, the material turns out to be less durable, there may be chips and delamination on it.
For construction, it is better to choose autoclaved aerated concrete, which may cost more, but demonstrates much higher performance characteristics.
Standard product sizes
The standard sizes of the blocks were indicated above (600x300x200 millimeters), and other standard sizes can also be attributed to them.
What sizes are usually used:
- Length - from 60 to 62.5 centimeters.
- Height - from 20 to 25 centimeters.
- Width - from 8.5 to 40 centimeters.
Possible options are listed below:
U-shaped products are produced with the following parameters
Products of this form are standard usually have the following dimensions: 25 centimeters in height, 50-60 centimeters in length and 20-40 centimeters in width. Before purchasing building materials, it is imperative to carefully measure everything and calculate how many and where gas blocks are needed. Calculations are carried out in the same way as in the case of conventional gas blocks.
Calculations
To perform calculations and search for the required volume of aerated concrete, you first need to correctly calculate the structure. The height and width of the walls, the dimensions of the entire building, and internal partitions are considered. Then the length of the walls is multiplied by the height and the total area in square meters is obtained. Next, they are determined with the thickness of the walls and the resulting indicator is multiplied by the thickness in meters (0.2, 0.3, 0.4, which is 20, 30, 40 centimeters, respectively) and the required volume of the gas block in cubic meters is obtained.
After that, you need to find how much cubic volume falls on the block - multiply all its sides with each other and divide the unit by the resulting figure. Then it is enough to multiply the number of cubic meters by the number of blocks in a cubic meter and get the desired value - the number of gas block pieces.
Usually, the examples do not take into account the thickness of the seam, so you can not add the classic 7-10% to the resulting indicator. Seams can be thin when using special glue or medium thickness when laying on a cement-sand mortar.
Despite the fact that glue packaging costs more than an identical volume of masonry mixture, in the end it turns out to save both due to the thickness of the seams and on heating, since the glue does not provide cold bridges.
Knowing how many aerated concrete blocks in 1m3 is desirable for everyone who starts construction. Even if all these volumes and figures can be calculated in production or in a store, there is no need to doubt the correctness and correctness of the calculations performed independently.
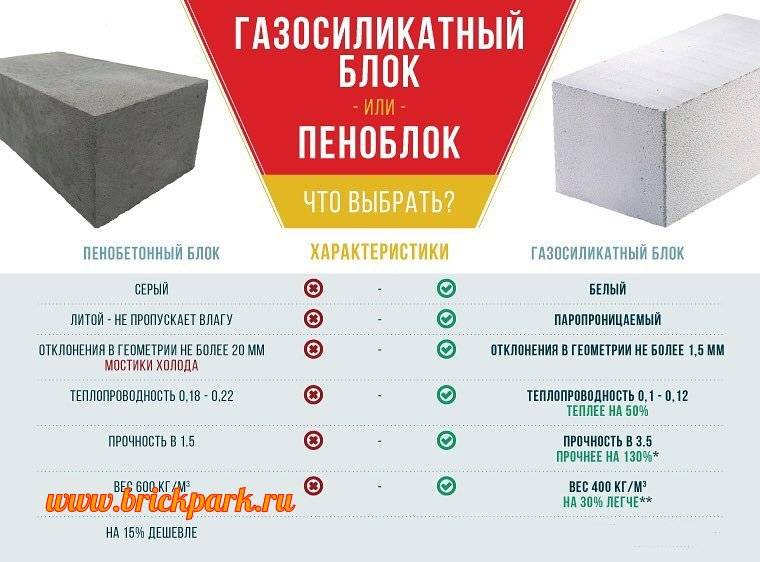
What is common between aerated concrete and gas silicate
Composition and properties of materials strengths and weaknesses
To generalize, gas silicate is aerated concrete processed in an autoclave - an apparatus for rapid hardening of the material at elevated pressure and temperature. The difference between aerated concrete and gas silicate lies in the features of the production process.
Aerated concrete, like gas silicate, is a type of aerated concrete, which has a porous structure. Thanks to this feature, the material is lightweight, but at the same time durable. Due to the presence of voids in the blocks, they have low thermal conductivity.

A solution of gas silicate and aerated concrete is a mixture of the following materials:
- cement;
- sand;
- lime;
- water;
- gasifier - aluminum powder or paste;
- special additives to increase the numerical values of the desired characteristics.
Since the parameters of products made of gas silicate and gas blocks are quite close, it is worth highlighting the general advantages of slightly different materials:
- A low coefficient of thermal conductivity, which, according to GOST for cellular concrete, starts at 0.09 W * ms.
- Frost resistance. The technical documentation for each material indicates the minimum number of freeze-thaw cycles - 25. In practice, this number differs from manufacturer to manufacturer. Due to high competition, this indicator usually exceeds 50, regardless of the type of aerated concrete blocks.
- Optimal density - denoted by the letter D. It is in the range of 300-1200 kg / m3. The densest products are used in the construction of walls. For insulation, blocks with a lower rate are used.
- Strength grade. According to GOST, it is B1.5 - B15.
- Environmental friendliness. According to this indicator, cellular concrete is inferior to wood by only 1 point.
- Burning resistance.
- The ease of creating masonry is due to the ease of sawing and sanding materials.When working with aerated concrete and gas silicate, there is no need to use special equipment.
- High speed of construction - due to the simple technology of stacking blocks and the optimal dimensions of the products.
The common advantage of both materials is their affordability due to the wide choice of manufacturers. Due to the popularity of materials, they are produced in the form of wall products, U-shaped elements.
General disadvantages of gas silicate and aerated concrete:
- High fragility. During the transportation of products, they are often subjected to mechanical stress, which leads to the formation of chips and an increase in the number of rejected blocks.
- High degree of water absorption. Since the materials are hygroscopic, they quickly absorb moisture, which requires careful protection. With prolonged exposure to water, products are gradually destroyed.
- The difficulty of fixing various objects on the walls of cellular material.
- Low degree of adhesion to finishing materials.
- Susceptibility to shrinkage and cracking as a result of this process.
Considering the general disadvantages of gas blocks, you can focus on construction opportunities.
Types and scope of application of both materials

Since gas silicate is a variety of aerated concrete, one classification has been developed for them:
- Structural products have high strength and the ability to withstand significant loads. The thermal conductivity of such products is higher than that of other types.
- Structural and heat-insulating gas silicate and aerated concrete are more often used by developers, since due to its use, the cost of insulation is reduced.
- Heat-insulating cellular concrete is characterized by a high degree of thermal insulation.
Gas silicate or aerated concrete blocks are more often used for the construction of the first and second floors of country houses, outbuildings. Knowing what is the difference between them, you can determine the specific construction tasks.
Properties of non-autoclaved and autoclaved aerated concrete
The resulting blocks, made using two different technologies, are so different both in appearance and in their characteristics that even an inexperienced man in the street can distinguish between them.
External indicators
The first thing the buyer faces when choosing is the appearance of the materials. It would seem, what's the difference how the wall blocks look, which subsequently still need to be plastered. However, appearance is the most accurate visual characteristic that will help weed out low-quality products.
Geometric dimensions
If we compare gas blocks by the criterion of geometry, then autoclaved products are more accurate. This is partly due to the autoclaving and, of course, the cut technology. Even GOSTs regulate deviations of linear dimensions from nominal in different ways, depending on the method of production used.
| Parameter tolerances | Autoclaved aerated concrete | Non-autoclaved aerated concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Length, mm / m | 3 | 5 |
| Width, mm / m | 2 | 4 |
| Height, mm / m | 1 | 2 |
These data only underline the fact that autoclaved aerated concrete is characterized by precise geometry of finished products, which prevents:
- freezing of walls due to thickening of the masonry seam, which compensates for deficiencies in the form of blocks;
- overspending of masonry glue, leading to an increase in costs for it.
Colour
When buying blocks, pay attention to their color. Of course, it will be gray in the case of naturally hardened products and almost white in autoclaved aerated concrete
Differences in block hues and color irregularities indicate changes in the manufacturing process, which often result in decreased performance.

Automated equipment for the production of autoclaved aerated concrete reduces any errors to zero, which is initially considered a guarantor of quality and durability.In addition, such large-scale workshops are supplemented by their own construction laboratory, the timely testing of which isolates inconsistencies in technology or recipes.
Physical and mechanical properties
Aerated concrete blocks differ not only in appearance and color, but also in physical and mechanical properties.
Strength
Aerated concrete is represented by a rich nomenclature of strength grades - from B1 to B7.5. They are widely used not only as the creation of load-bearing structures, but also for wall insulation. If we compare aerated concrete produced using different technologies, then autoclave ones are distinguished by greater strength at the same density with non-autoclave ones.
For example, blocks with a density of D600 must have a strength class of B3.5. If for autoclaved products the indicator is observed, then with naturally aged products, the strength class hardly reaches half the norm. The situation is even worse with the strength indicators of self-produced aerated concrete. If you want to see for yourself, buy a block and test it in an independent construction laboratory. The results will be obvious.
Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of aerated concrete directly depends on the density of this material. The lower the grade in terms of block density, the better its thermal capacity properties. It is wiser to purchase products of lower density, but with higher strength characteristics, thereby reducing the thermal conductivity of the walls.
Shrinkage
The weakest side of any aerated concrete is its shrinkage after the walls are erected. If the wrong construction technique is used, cracks may appear and the plaster layer will peel off. The processes of shrinkage of aerated concrete of natural aging can last up to several years, when autoclaved blocks are practically devoid of such a disadvantage, since during heat and moisture treatment they have already reached brand strength and complete drying.

In addition, aged aerated concrete blocks in natural conditions are far from ideal indicators, which is negatively manifested in the form of shrinkage. This not only leads to a violation of the linear dimensions, but also to the destruction of the structure.
Summing up, we can easily conclude that autoclaved aerated concrete blocks have undeniable advantages over natural aging products. But in any case, when buying such wall material, always ask for documents certifying its quality.
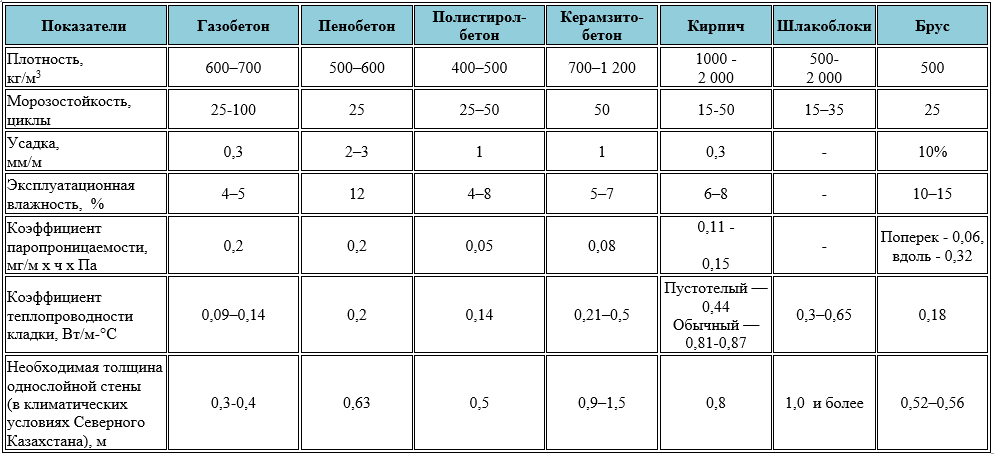
Comparative characteristics of aerated concrete and foam concrete
Despite the fact that the production of cellular concrete blocks is strictly regulated by unified state standards, the technical parameters of these materials have significant differences.

Component components
Concrete materials are produced using the technology of mixing cement with fillers, which provide it with a cellular structure.
Foam concrete is produced on the basis of the following components:
- Portland cement is a binder.
- Lime or sand of the middle fraction is a mineral filler.
- Foaming agent - a chemical additive to create a porous structure.
- Water.

The gas block includes the following components:
- Portland cement is a binder.
- Quartz sand, gypsum, lime, wood ash, slag waste - mineral fillers.
- Aluminum paste or powder is a component for the formation of pores.
- Water.

Aluminum foaming agent is a harmful component in its pure form; in the production of aerated concrete solution, it completely dissolves in water.
Structure
The difference between aerated concrete and aerated concrete blocks lies in their structure and appearance:
- Foam blocks: large closed cells with a low level of moisture absorption, excellent sound insulation and thermal insulation properties. They have a smooth gray surface.
- Gas blocks: small cells with microcracks formed as a result of gas formation.They are distinguished by good air and moisture permeability, insufficient thermal insulation and require mandatory external finishing. The material has a textured rough surface in white.

Strength
Which material is more durable - aerated concrete or foam concrete? This parameter directly depends on the density of the blocks.

The density of aerated concrete blocks ranges from 200 to 600 kg / cubic meter. m, density of foam concrete blocks - from 300 to 1600 kg / cu. m.
Modern technologies make it possible to create aerated concrete with a density of up to 400 kg / cubic meter. m, capable of withstanding the ultimate load, as well as a foam block with a density of over 600 kg / cu. m.
p> Despite the high density, foam concrete is definitely inferior to its competitor. This is due to the heterogeneity of the structure over the entire area of the material.
Frost resistance
This parameter determines the ability of the cellular material to maintain its operational characteristics during multiple cycles of freezing and defrosting.

Compared to other porous materials, autoclaved aerated concrete blocks have increased frost resistance, low thermal conductivity and excellent vapor permeability.
For example, due to its special structure, the strong structural gas block "Sibit" is able to withstand 75 full cycles of freezing and defrosting, while in the foam block this figure is only 35 cycles.
Features of use
Possessing many advantages, porous foam concrete is widely used for low-rise construction. It is also suitable for the construction of monolithic buildings and structures. In this case, it is used as an insulating or additional material.

Aerated concrete blocks are used as the main structural and heat-insulating material for the construction of objects of varying complexity. The blocks are suitable for arranging heat-resistant and other partitions, filling frame structures made of metal and concrete, restoring dilapidated buildings and erecting half-timbered structures of residential buildings. Moreover, they can be operated in any climatic conditions.
Price
What is the main difference between foam concrete and aerated concrete? At their market value. With equal technical parameters and dimensions, gas silicate will cost more than foam concrete blocks. This is due to the complexity of the technological process, the high cost of equipment and consumable raw materials, as well as significant costs for its transportation.

Foam blocks are produced on cheaper and simpler units that can be located at the construction site.
The market value of aerated concrete blocks is higher, but production costs are offset by the quality of construction. At the same time, building a warm house from aerated concrete is economically profitable due to the lower consumption of building material. In addition, less cement mortar will be spent on the facing of aerated concrete than is required to level the foam concrete blocks.