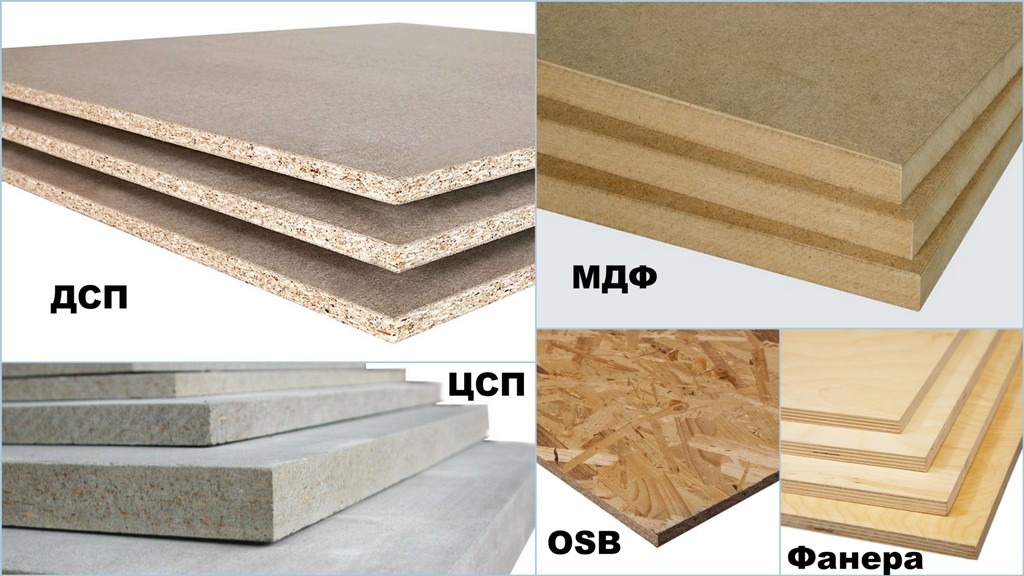
What's better
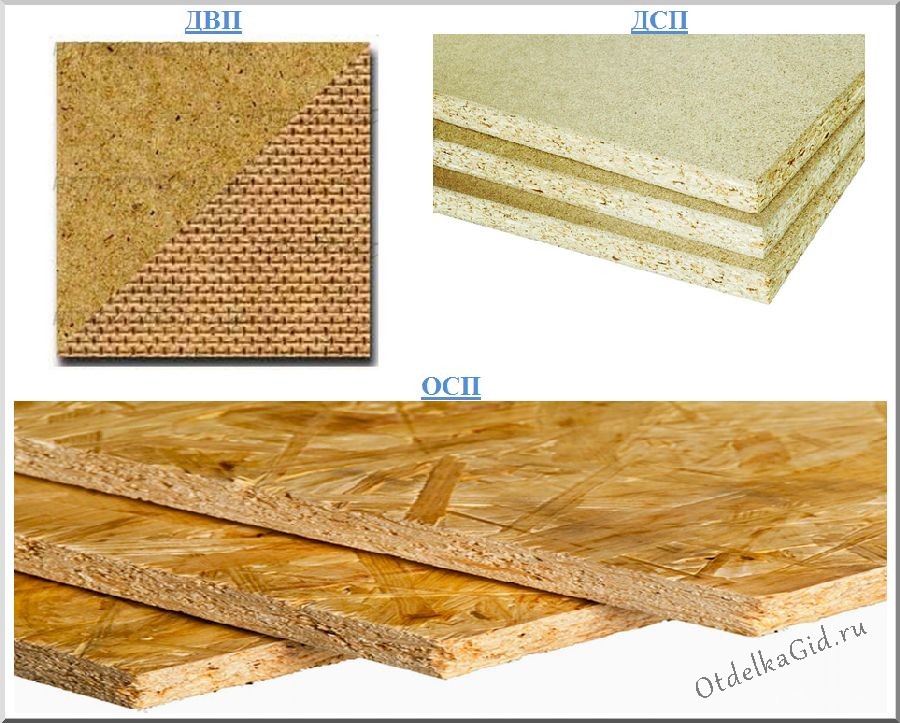
Plywood and chipboard can be used for flooring. The choice depends on the specific case: the floor, the surface on which the floor is laid and the functional purpose of the floor. Plywood differs not only in thickness, but also in grade, you can easily choose the best option for a special project:
Since plywood is made up of layers going in different directions, it is a very durable wood-based construction material. The panel holds the screw tightly, is shock-resistant, less exposed to water, relatively lightweight and easy to cut. Higher grades of the product have a smooth sanding surface, woody texture free of knots and other serious defects.
Lower grades are used in the construction of subfloors. Such a surface is hidden from view - you can choose a cheap material. For the subfloor, plywood with a thickness of 12-18 mm is needed, for the final surface 10-12 mm. A wide variety of board formats are on sale in terms of grades, thicknesses and sizes. Plywood comes from different types of trees: oak, ash, maple or softwood. The assortment is wide. The more noble the tree, the more expensive it is.
Chipboard is made from wood residues of lower varieties of trees - slabs made from such material are cheaper and more often used for subfloors. Chipboard has shrinkage properties like wood, but is less durable. Plates are indispensable for leveling uneven floor surfaces. When laying boards on logs, chipboard boards with a thickness of 16 mm or more are recommended. Chipboard sheet weight 16 mm 3500 x 1750 - 63.7 kg. Therefore, it is more convenient to cut the plates and work in tandem with a partner. Lags should be 30 mm high or more. Particleboard is widely used due to the low cost of the material and good sound and thermal insulation.
If your budget is very modest, and you do not have problems with dampness, then chipboard can be used as flooring material. If dampness is a problem, thick plywood is best. Both products come in sheet form and are equally easy to install. However, particle boards are more tolerant of small errors than plywood.
Subfloor technology from sheet materials
Sheet materials can be laid on an old floor (plank floor, linoleum), on ceilings leveled with a screed, or on logs. In the first two cases, in addition to fastening with screws, glue is used.
Screed flooring
A cement screed is used to level the surface. To do this, using a level around the perimeter of the room, a line is drawn on the walls, which will serve as a guideline for the height of the screed.
Then the bars are laid on the base, forming a grid of squares with a side length of about 1 meter. Their thickness should be slightly less than the thickness of the future screed.
Next, a cement-sand mortar is prepared in a ratio of 1: 3, which is poured into the mesh cells and smoothed.  Leveling screed device
Leveling screed device
Note. To prevent the screed from cracking, it is necessary to maintain a certain level of humidity during drying.
To do this, cover it with plastic wrap and leave it for 7-10 days.
After the solution has dried, the instruction requires priming the surface with bitumen mastic and letting it dry. After that, you can start laying the sub-floor.
The sheets are laid on a surface greased with glue with a small indent from the walls and with a gap between each other of 2-3 mm, which is necessary for temperature and humidity expansion. They should be laid out with an offset of the joints: at one point the corners of the four sheets should not be joined.  Chipboard fixing
Chipboard fixing
After laying chipboard or plywood on the floor, it is drilled and screwed to the base, first in the center, then along the perimeter.
Laying on logs
This method is less labor intensive and more environmentally friendly. If necessary, insulation or soundproofing material is laid between the logs.  Floor insulation
Floor insulation
However, thicker and stronger sheets should be placed on the logs to avoid deformation. Which is stronger - chipboard or plywood? It depends on the thickness of the sheet and the distance between the lags.
For example, 12 mm plywood can be laid on a solid base, and at least 20 mm on the logs, provided that the distance between them is no more than 40 cm. The chipboard thickness should also be 18-22 mm.
- Draw a scheme for laying the logs depending on the size of the sheet material (see also the article Plywood flooring on logs - a simple technology that requires a thoughtful approach). The joints of the sheets should fall on the axial lines of the log. At the same time, take into account the shift of the sheets to offset the seams. You should have a grid with a mesh size of 30-50 cm.
- Lay the longitudinal logs on the floor and level them using shims. Secure.
Attention! The distance between the wall and the extreme lags should be no more than 30-40 mm
- Mark the position of the transverse logs and attach them to the longitudinal nails driven in obliquely.
 Photo of the finished frame
Photo of the finished frame
- Lay the first sheet in the corner of the room, stepping back from the walls by 10-15 mm. In order not to stray off the center line when attaching to intermediate lags, mark the edges of the sheet with pencil marks corresponding to the middle of the bars, and connect them with a straight line. Along these lines, with a pitch of 100-150 mm, screw in the self-tapping screws, sinking the caps into the body of the material. Then secure the sheet around the perimeter. It is best to use an electric screwdriver.
- Mount the rest of the sheets in the same way, leaving a gap of 2-3 mm between them. If it is not there, the floors may begin to creak over time.
 Fastening sheets to logs
Fastening sheets to logs
- When using grooved sheets, there is no need to leave a gap. In this case, tongue-and-groove joints are lubricated with glue and sealed by tamping to each other with a mallet.
- Do not forget to shift the sheets to prevent the four seams from crossing at one point, and to leave a gap between them and the wall. Subsequently, they will be covered with a plinth.
It remains to say that when laying in rooms where humidity may increase, sheet materials must be coated with linseed oil or other protective agents before laying. If the room is dry, then from the point of view of cost savings and ease of processing chipboard on the floor is better than plywood.
Plywood or chipboard on the floor: advice on what to choose
For the construction of the subfloor, sheet materials are often used, which are made from wood. But in the process of choosing a suitable type of building material, the question often arises "what to give preference to: veneer or chipboard?" In this article, we will try to understand this issue and find out what is better to use for finishing the floor: plywood or chipboard.

Making a choice
Features of chipboard sheets
Chipboard is a board made from wood shavings and some types of synthetic resins by hot pressing. It can be produced with a flat edge or a thorn-groove fastening, in the photo you can see such a locking system. Such plates are suitable for arranging a black base if they are treated with moisture-resistant compounds.
The sheets are laid either on a concrete base or on logs. To enhance sound insulation, a special canvas is laid on the floor before laying the material: fiberglass or botament, which can be made of natural and synthetic materials.
Such plates are used for warming and leveling the floor, after which they install linoleum, laminate, carpets and other coverings. Since chipboard can be attributed to hygroscopic materials, it is advisable to polyline it before laying the board, and on both sides.Then, over time, they will not start to rot, so that mold does not form under the floor.

Chipboard
Features of plywood sheets
Plywood is a sheet consisting of many layers of peeled veneer, which are glued together using special resins. Due to its good strength characteristics, plywood is used not only for sound and heat insulation, but also for leveling the floor. As in the variant with chipboard, veneer sheets can come with a flat or grooved edge. Slabs with a tongue-and-groove system provide a more reliable fastening, however, they are more expensive.
When choosing plywood, you need to take into account that many technical characteristics of the material depend on its class. When buying sheets that have not been treated with moisture-resistant compounds, there is no need to prepare for a long period of use.
What is better to buy: chipboard or plywood?
To give an objective assessment of the characteristics of both types of wood-based panels, certain criteria should be highlighted. Thanks to them, it will be easier for the consumer to decide on the choice of a suitable material for the sub-floor:
- Appearance. In this case, veneer sheets are much preferable. Due to the aesthetic appeal of the plywood surface, it is often used for finishing the floor;
- Processing features. If the veneer sheets are cut well by any types of power tools, then in the chipboard version, only those that have sufficiently small teeth should be selected, otherwise the sheets will begin to crumble;
- Moisture resistance. Veneer board will have better performance than chipboard even when treated with the last varnish or paint;
- Flexural strength. Chipboard on the floor is better than plywood in this context. The sheet can be bent and it will not break;
- Body and sound insulation. And here chipboard gives odds to veneer boards, which have the worst insulating characteristics;

- Abrasion resistance. Chipboard of any quality will have worse strength than plywood;
- Price. Wood-based materials are cheaper, which is explained by the low cost of recyclable materials from which they are produced.
However, it should be noted that even processed plywood does not have sufficient moisture resistance. If laid in a damp room, over time, it will still start to rot, which will lead to deterioration of the topcoat.

Conclusion
What sheet material should be preferred? This largely depends on the purpose of use and financial capabilities. Obviously, plywood has better wear resistance, but it cannot boast the same "ductility" as chipboard. In addition, a veneer board is much more expensive, although if properly installed, it will last longer. If you want to lay wood-based panels on the floor for the purpose of insulation, then you should take a closer look at the chipboards.
What is chipboard?
The first chipboard boards went on sale in the 18th year of the last century. Of course, they were not of high quality, but in the process of subsequent years this material was significantly improved. Particleboard of this type has several stages of production:
Step one: processing of natural wood and procurement of raw materials. Chipboard is made on the basis of large wood sawdust, and then the workpiece is ground until a finer fraction is obtained.

The first step is to prepare sawdust
Step two: drying the sawdust. The resulting small chips are sent to special equipment, where they are dried under the influence of air.

Drying of raw materials
Step three: the raw material goes through the selection stage. Thus, only small shavings go into production, and large pieces of wood are crushed again.

Sorting raw materials
Step four: mixing with an additional component. At this stage, synthetic formaldehyde resin is added to the chips for better bonding.
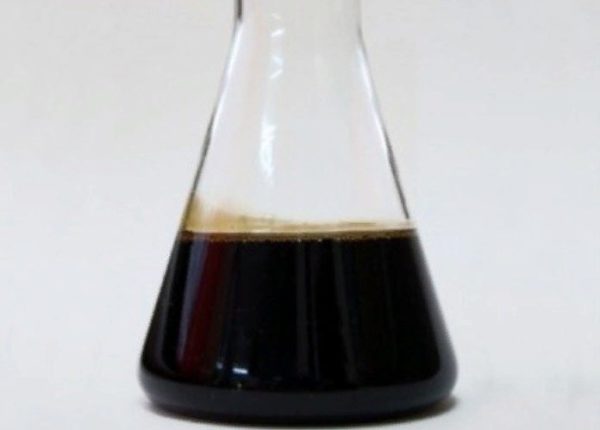

Formaldehyde resin
Step five: shaping the workpiece.The mixture of resin and shavings enters the conveyor, where the rough plates are formed in several layers by cold pressing.

This is how slab blanks look like
Step six: the surface of these slabs is carefully sanded. In order to give the material a decorative look (as is the case with MDF), a special polymer film is applied to the surface.

Film application process
Then it remains only to cut the slabs to standard sizes. Then they go on sale.
The following advantages of laminated chipboard are distinguished:
- Budgetary cost compared to natural solid wood and even MDF.
- Good resistance to temperature extremes and high humidity.
- Large selection of different colors. As in the case of MDF, chipboard has a huge variety of laminated surfaces.
- The material does not deform as a result of mechanical damage.
- If ordinary chipboard quickly deteriorates, then laminated boards are durable.
- The material has good scratch resistance. In addition, it can be cleaned with various chemicals.

Chipboard boards are sold in various shades
Of the minuses of the material, the following can be noted:
- Plates are quite tough compared to MDF, which means that they are less susceptible to processing. It turns out that it is difficult to make curly structures from such a material.
- This material often splits at the edges during sawing, so it is best not to cut it with a regular hand saw.
- The composition contains dangerous formaldehydes - it is this point that can cross out any positive qualities of chipboard.
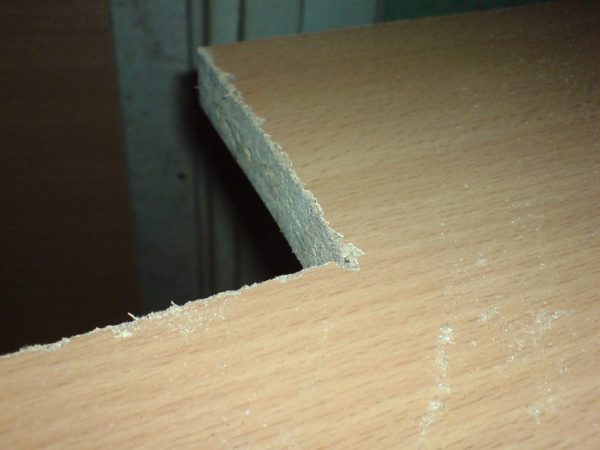

Chipping is common when sawing
Despite such significant shortcomings, not everything is so bad. After all, there are two types of laminated chipboard: with the marking E1 and E2. In the first case, 10 grams of poisonous resin is added to one hundred grams of shavings, in the second case, the amount of formaldehyde for the same mass of sawdust exceeds 30 grams.
main parameters
So, which is better for the floor - chipboard or plywood?
Let's take a look at all the characteristics in order.
- Appearance:
The wood-laminated board has an original textured pattern inherent in wood and a shade pleasant to the eye, which makes it possible to use it even for the formation of a finishing one;

The appearance of the chipboard is very specific and is usually not put on public display, since it is a compressed chip mass;

- Strength indicators.
The answer to the question of what is stronger than chipboard or plywood is somewhat ambiguous:
Plywood is a fairly hard and at the same time flexible material that can be easily processed with your own hands;

But the chipboard, although it has a higher bending strength, crumbles during its processing and holds the screwed screws worse;

- Thermal insulation properties. Here everything is decided by the coefficient of thermal conductivity inherent in these materials:
Environmental friendliness
In order to answer the question of which chipboard or plywood is more environmentally friendly, you should pay attention to the amount of glue used in the manufacture of both materials, because it is in it that harmful formaldehydes can be contained. It can be seen from the definition that the chipboard uses a much larger amount of adhesive solution, but the wood-laminated product cannot be called environmentally friendly either;
| Marking | Content of harmful substances, mg / 100 g |
| E0 | Less than 6 |
| E1 | 7-9 |
| E2 | 10-20 |
- Installation instructions. Installation of both sub-floor options is fairly easy to do on your own. The sheets are not excessively heavy, they are easy to cut and fit into a continuous covering, after which they are fixed with ordinary self-tapping screws;

- Moisture resistance. In this matter, the difference between plywood and chipboard is quite tangible:
-
- Wood-laminated board has good resistance to excessive moisture due to the presence of adhesive interlayers;
- Chipboard, although it contains an even greater amount of adhesive solution, does not have a solid wood structure.Sawdust in contact with moisture swell and no longer return to its shape;
- Soundproofing. Chipboard is much better at absorbing unnecessary noise that hinders your peace of mind;
- Price. What is cheaper than chipboard or plywood in the case of creating a rough base? Of course, the first option, which is made, in fact, from waste that cannot be expensive. But for the production of wood-laminated products, veneer sheets are needed, which raises the cost of the finished product;
- Flammability. Both options are dangerous in the event of a fire, as they are prone to fire. In addition, during combustion, they will emit a large amount of toxic substances, which will only aggravate the situation.
Combination

The most significant advantage of chipboard over plywood is its low price. Plus, it's worth adding bending strength and sound insulation. Otherwise, it is significantly inferior. But it is also worth noting that there is also a combined version of these two materials - veneered chipboard.
As a result, we get a sample that:
- Better protected from the negative effects of excessive moisture, crumbling and abrasion by a layer of plywood;
- It is cheaper than a full-fledged wood-laminated board, since it consists of shavings inside;
- Looks aesthetically pleasing;
- Possesses excellent heat-insulating and sound-absorbing qualities.
Comparison by characteristics
Most often, either plywood or OSB is placed on the floor. But which is better? Most will say that plywood is stronger in bending and therefore it is better to lay it on the floor. It is stronger. That's for sure. But if the material is laid on a concrete base or a floating flooring is made from it, or it is laid on a sub-floor along the logs - why is there a high bending strength? More important is the tendency to delamination and warping, and these are precisely the problems of plywood. In general, it's up to you to decide which is better - plywood or OSB. Below is information for an informed decision.
The comparison is given in points and it is difficult to judge objectivity, but ...
Moisture resistance and environmental friendliness
Oddly enough, moisture resistance is directly related to environmental safety. The fact is that a synthetic binder is used in the production of materials, and it is possible to say which is more environmentally friendly - OSB or plywood, specifically for each material. Although, in general, plywood is safer: there are brands in the production of which safe substances are used. But not all. For example, FSF is one of the cheapest types. It is made using a phenol-formaldehyde binder. So this brand does not differ from OSB in terms of environmental friendliness.
The most reliable self-test with materials intended for purchase
In the case of oriented strand board, phenolic resins are always used. They give the material high strength and moisture resistance. But it is phenol that is a substance hazardous to health. Its release is controlled by a sanitary station. A special classification has been introduced - formaldehyde emission. Each batch must be checked and an emission class must be assigned based on the measurement results. Safe are E0 or E1. And E2 and E3 can only be used outdoors. By the way, the same characteristic should be indicated in the technical parameters for FSF plywood.
OSB water resistance
Oriented strand boards are available in four water resistance categories:
- OSB1 and OSB2 - not moisture resistant, for use in rooms with normal operating conditions;
- OSB3 and OSB4 are waterproof, for use in high humidity conditions.
It's not easy to make a choice - plywood or OSB
If they make the floor, they usually take OSB3. Its water resistance is sufficient for use in any floor cake, so the material is versatile. If significant strength is required, a higher grade can be taken.
Waterproof plywood
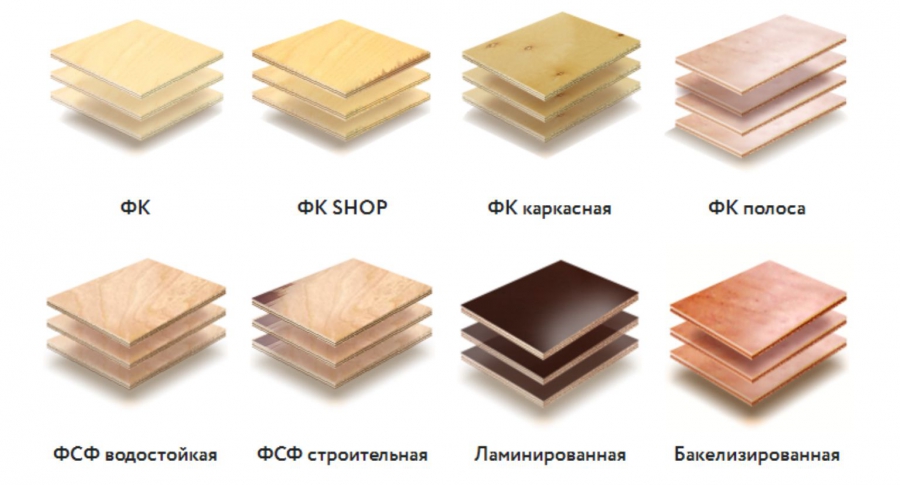
Plywood is a little more complicated. In its production, various glue is used and it is he who affects the properties of the material. The following types are used in construction:
- FC - on urea glue. Good environmental performance, but average moisture resistance. If you lay it on the floor, then in dry rooms where moisture is unlikely to come in. There is a waterproof plywood of this brand. The letter V is added to the marking - FKV, sometimes the letter G is added - hydro-resistant. But moisture resistance is achieved not due to glue, but due to additives / impregnations for wood.
-
FSF - on phenolic glue. This type has high moisture resistance, but the phenolic glue gives off formaldehyde. So you need to be sure of the safety of the material. This is one of the cheapest types, often called construction. They are used more often for temporary structures - formwork.
- FKM - on melamine glue. Waterproof but expensive.
- FB - bakelite on a water-soluble composition, BS - on alcohol-soluble glue. BS plywood is most often called aviation. Lightweight and durable, waterproof, expensive. The FB subtype is used more often in the construction of ships and railway cars, where there is less weight requirement.
So it is difficult to compare plywood and OSB in terms of water resistance. There are different brands and the matter is in a specific choice. It's just that in terms of water resistance, OSB is more reliable, since the chips are in a layer of glue, which simply does not let moisture to the wood. With plywood it is more difficult: the outer layers are wood veneer, the veneer cuts at the edges of the sheet also remain open. So even moisture-resistant plywood often begins to warp - the top / bottom layer swells, the edges swell.
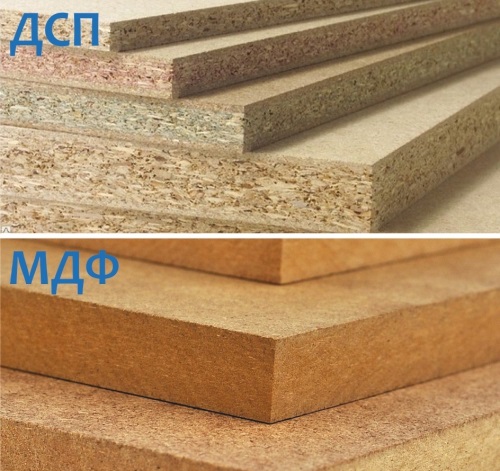
Particleboard and plywood: differences and advantages
In order to better understand the differences between board and chip materials, we will study separately their advantages and area of use, and then compare them according to the main criteria.
Plywood advantages:
- good strength characteristics due to the location of adjacent veneer sheets perpendicular to each other;
- high moisture resistance, especially in FSF and FBS. Plywood of these brands is used for exterior decoration, as well as for the construction of hydraulic structures. FC and FBA are used for interior work, arrangement of dry rooms and furniture production;
- resistance to temperature extremes. Plywood does not dry out when the weather changes;
ease of processing. Plywood is easier to cut than chipboard. Due to this, it becomes possible to produce parts of complex shapes.
Chipboard advantages:
- high strength due to the homogeneity of the material and the perpendicular arrangement of chips relative to each other in adjacent layers;
- heat and sound insulation. The use of small chips reduces the thermal conductivity of the material and increases noise absorption;
- good water resistance, resistance to wear and bioinfection;
- affordable cost compared to plywood of similar dimensions and characteristics;
- aesthetic appearance (laminated chipboard).
Chipboard laying methods
The method of laying chipboard on a concrete base is good for ensuring noise and thermal insulation properties. Chipboard floors on concrete do not creak, they do not have wave formation.
The flooring should be done in this way:
- First of all, the entire surface must be cleaned and reinforced with a special primer.
- After drying, waterproofing is spread on the floor. All joints should be sealed with special tape. Ordinary plastic wrap can be used as insulation.
- After that, fiberboard or other materials such as Botament or fiberglass should be laid on the concrete base. This will improve the sound insulation properties in the best way.
- When the first layer has been laid, you should start laying the particle sheets. Plates from 1.6 cm to 3 cm are suitable for laying. When laying, do not forget to leave a special gap under the plinth up to 20 mm. Sheets are fastened either on self-tapping screws or on PVA glue. The second method is used if the slab is mounted on a bare concrete base.
If in the future it is planned to install heavy furniture, safes and the like in the room, it is recommended to make the flooring structure two-layer.The first layer must be thicker than the second, and the total thickness must reach + - 30 mm.
In regions with high humidity, it is recommended to additionally treat chipboard with impregnations with fungicidal properties, and lubricate the joints with glue mastic.
Such actions are not required with plywood. This is another distinct fact in which the relevance of plywood is much higher.
Array or chipboard? Pros and cons of materials
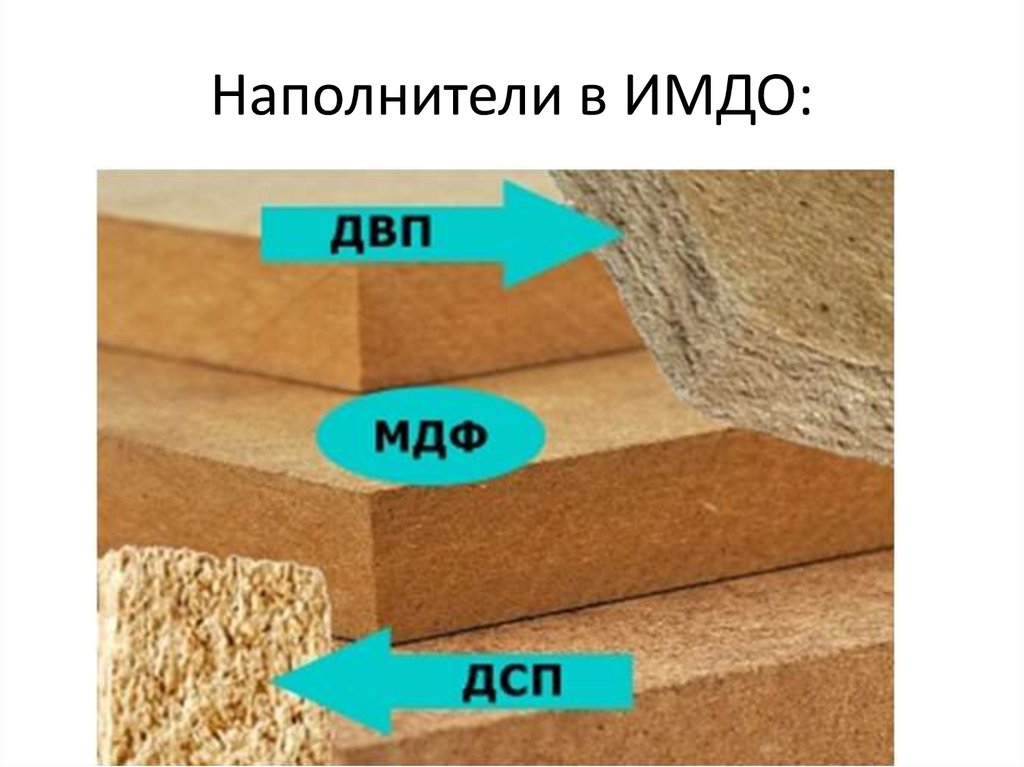
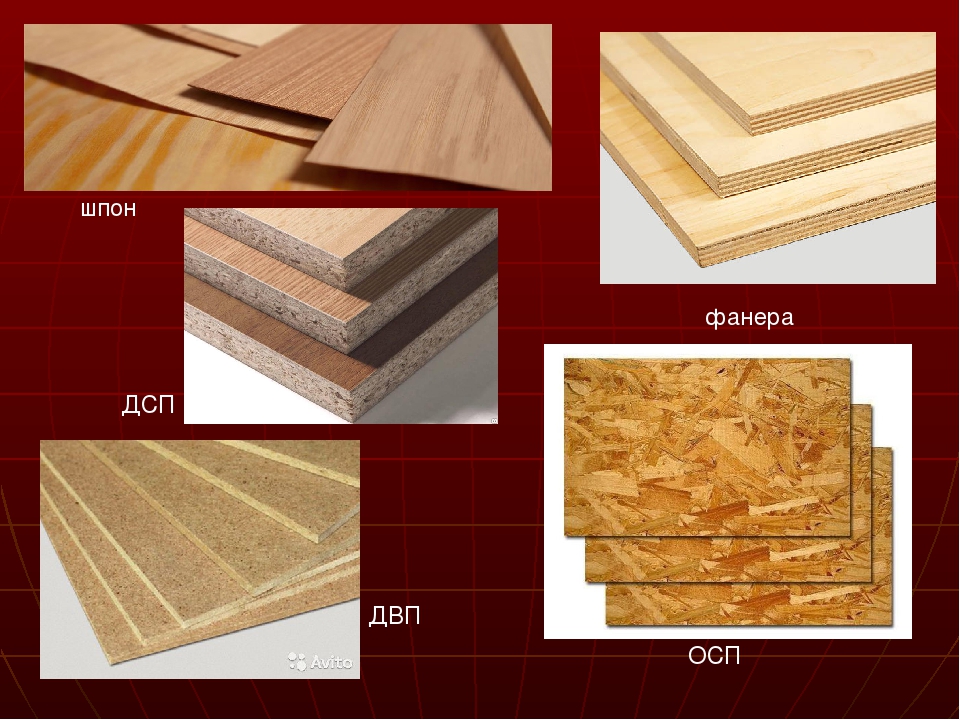
Solid wood, chipboard, MDF, fiberboard - what do these terms mean, and how not to get confused by an uneducated buyer? What is the furniture around us made of - wardrobes, dressers, cabinets, furniture for the kitchen, bathroom and bedroom?
Solid wood
Furniture made of solid wood gives a solid and noble look to the room. Often these are exclusive custom-made furniture.
+ naturalness and environmental friendliness of the material;
— natural wood is prone to darkening, sensitive to dampness and temperature extremes;
— expensive and not always affordable option.
A cheaper analogue is furniture made of wood-based panels. MDF, chipboard, laminated chipboard, fiberboard are materials based on wood, but in the form of shavings, fibers and sawdust. Most often it is woodworking waste, as well as raw materials obtained in the process of sanitary felling of trees.
A classic option in the production of furniture is considered: the front part is made of MDF, the body is made of laminated chipboard, the back wall is made of fiberboard.
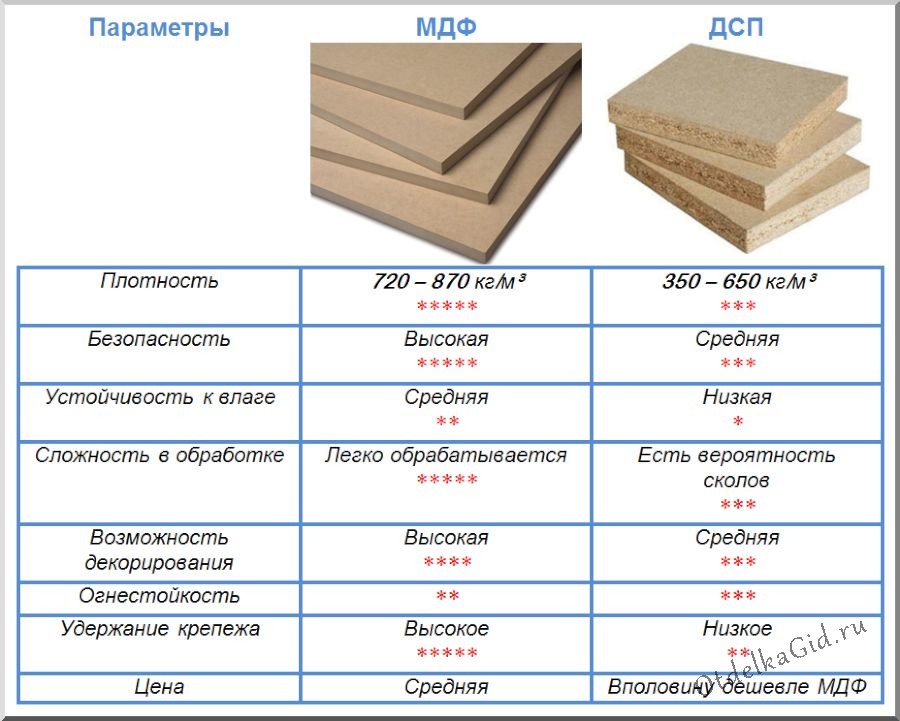
Medium Density Fiberboard (from English Medium Density Fibreboard - MDF - MDF ). In the production of MDF, the raw materials are crushed into practically dust and mixed with organic or non-toxic resins. It is a material that is easy to process, which is very much appreciated in the manufacture of furniture that requires elegance and subtlety of lines.
+ the density of the board, which almost corresponds to the density of natural wood, holds screws and other fasteners well;
+ the ability to produce bent furniture elements
+ the plate is immune to microorganisms, mold and mildew.
— reacts painfully to temperatures above 70 degrees Celsius: it swells, warps, and the decorative coating bubbles and peels off, which is why it is not recommended to place furniture made of MDF near heating devices;
— furniture made entirely of MDF is quite expensive, therefore such plates are most often used only in the production of facades.
Chipboard and chipboard
Chipboard (official abbreviation is Particleboard , in common parlance chipboard) is made by hot pressing of large shavings mixed with a binder - synthetic resin. Particleboard was manufactured back in the 1930s by the German inventor Max Himmelheber, and in 1951 he received a patent for his invention. "Ideal tree" - so then called chipboard for the homogeneity of the structure and the absence of defects inherent in wood (knots and cracks).
The most common material for the production of cabinet furniture - laminated particle board - or LDSP , in common parlance chipboard. This is chipboard, on which decor is glued on both sides, imitating the texture of wood of various species.
+ products made of laminated chipboard are resistant to moisture due to the laminating coating, in contrast to the analogue of solid wood described above. Furniture products made of laminated chipboard are as convenient as possible during operation: they can be easily cleaned and washed with usual detergents. Although, of course, it is better to refuse abrasive preparations, they can ruin the surface;
+ low price with a large number of colors;
— the material is not suitable for creating bent furniture elements;
— the main negative characteristic of chipboard is the presence of formaldehyde resins in the composition, which, at high concentrations, have a negative effect on human health. That is why it is necessary to ensure that there are as few uncoated chipboard sections as possible in the finished product.
Since 1986, an international scale has been in effect, which determines the emission class of wood-based board materials.It regulates the content of free formaldehyde in the products of manufacturing firms. The following international classification has been adopted: formaldehyde-free board of emission class E0.5 is used in the production of special furniture, for example, medical and children's furniture. Furniture made from chipboard with emission class Е1, approved by all Western countries, Ukraine and Russia for use in residential premises ... Particleboard with E2 emission class is prohibited from use in residential premises by the ministries of health of all European countries. EZ - wood-based panels, suitable only for use in construction.
Fibreboard and DVPO
Fiberboard or Fiberboard, in common parlance - hardboard. In composition, it is similar to MDF, but less in density and thickness, and does not have a decorative finish. The use of such a plate in the manufacture of furniture allows you to make products more affordable.
Refined fibreboard or DVPO. Slab, one side of which is painted with a solid color or imitates wood. The scope of application of such a plate in the manufacture of furniture is limited: rear walls of cabinets, drawer bottoms and other parts that do not require a large load.