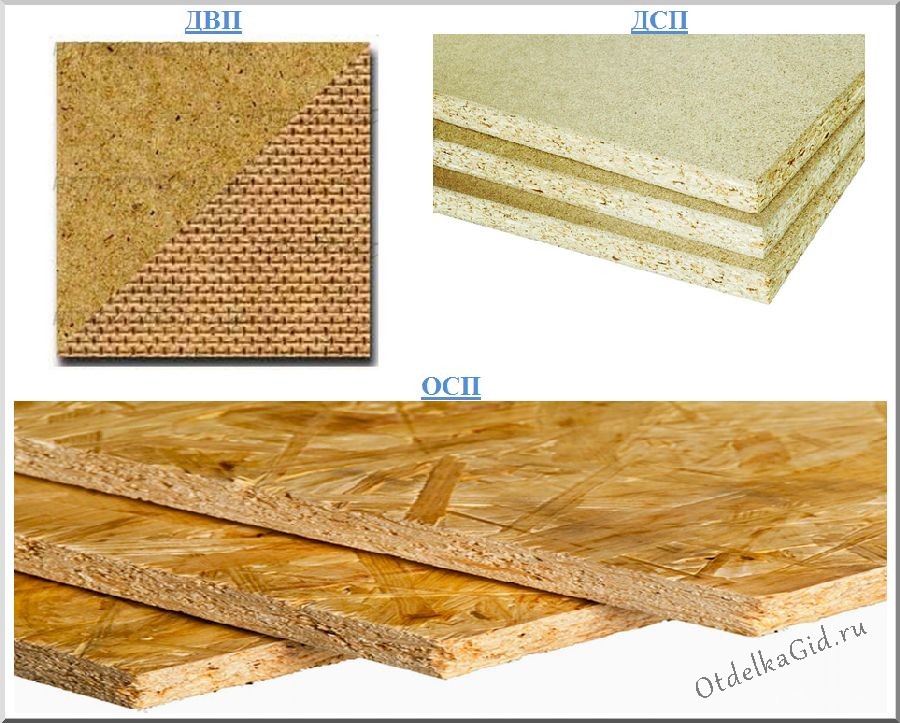
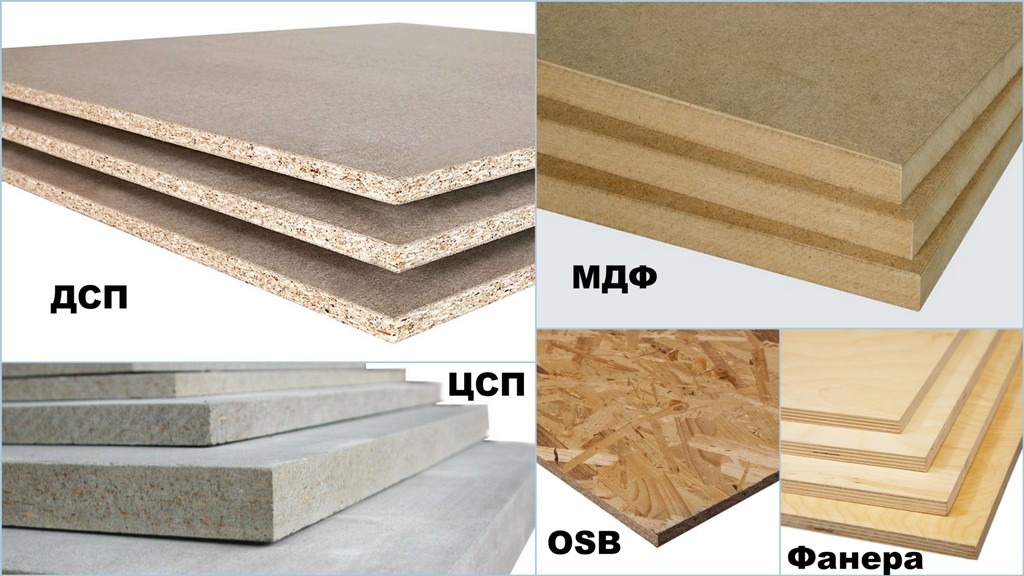
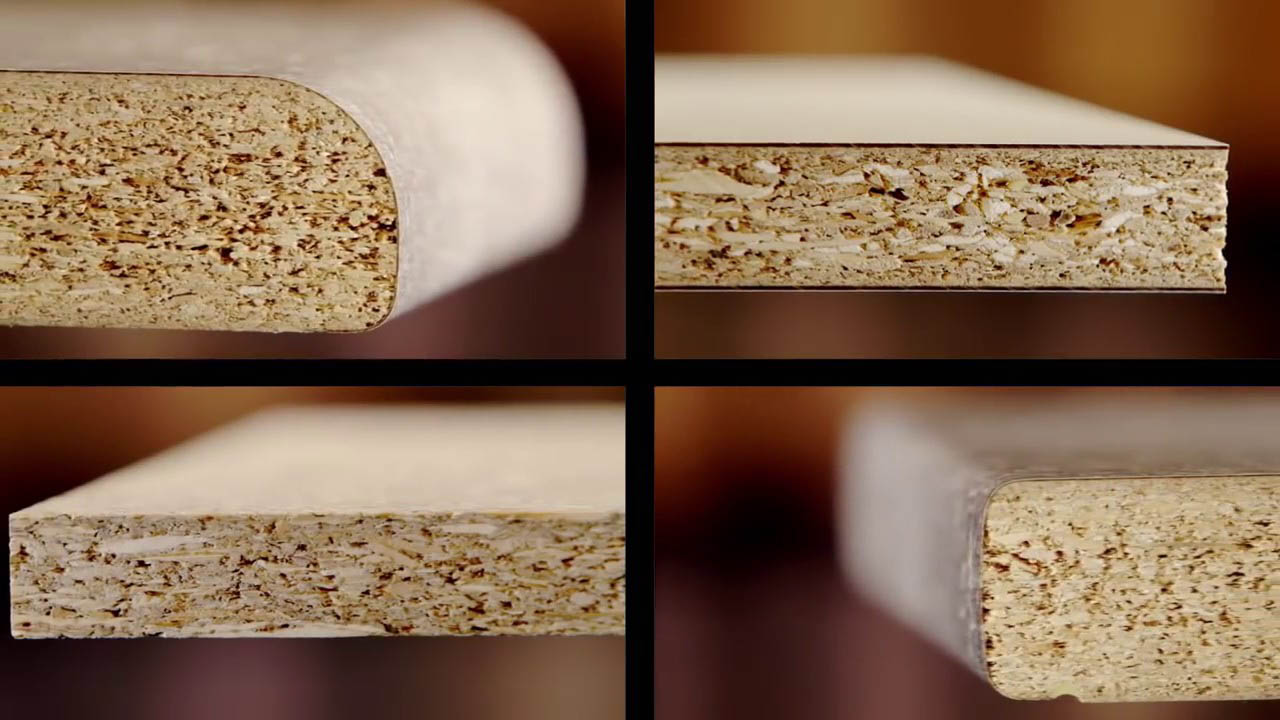
Chipboard
The abbreviation stands for "chipboard". This material is the result of pressing a raw mass consisting of shavings, sawdust mixed with resin (usually formaldehyde). Moreover, in the process of squeezing the mixture, it is exposed to significant thermal effects.
Material features
 Such plates are thicker than fiberboard (up to 50 mm), which allows them to withstand high mechanical loads. In everyday life, they are most often used for the installation of "dry" screeds, reinforcement of vertically oriented surfaces (with an obligatory "backing"), as a basis in various designs. Cheap furniture is made of them, partitions, shelves, awnings, fences and the like are equipped.
Such plates are thicker than fiberboard (up to 50 mm), which allows them to withstand high mechanical loads. In everyday life, they are most often used for the installation of "dry" screeds, reinforcement of vertically oriented surfaces (with an obligatory "backing"), as a basis in various designs. Cheap furniture is made of them, partitions, shelves, awnings, fences and the like are equipped.
The main disadvantage is a somewhat "loose" structure. This makes it difficult to bond the slabs to each other or to other structural elements. The self-tapping screw in the material "sits" not firmly. That is why it is not recommended to use chipboard in the manufacture of temporary prefabricated / collapsible structures. Frequent dismantling / assembly leads to damage to the areas where the fasteners are placed, since the base begins to crumble in these places.
In addition, such boards need a systematic surface treatment (for example, varnish), as they absorb moisture well. They are not recommended for use outside buildings, in the open air or in rooms characterized by dampness.
The "rigidity" of the samples does not allow, if necessary, to achieve even an insignificant bending of them. Any attempt will lead to the formation of a crack, which somewhat limits the use of chipboard.
Advantages and disadvantages of laminated chipboard
Like any material, chipboard has its own advantages and disadvantages. Only taking into account all the factors will make it possible to make a choice in favor of this material, or refuse it.
Advantages:
- Variety of colors. You can easily order furniture from any color with a large number of shades. There is also a wide variety of wood-like colors.
- Low price. Compared to other materials, such as solid wood or MDF, it has a low price. This is due to the low cost of the components used to manufacture the board. The production process is also low cost.
- Reliable structure. The material tolerates the mechanical effects of external factors, temperature changes quite well.
- Good performance in thermal insulation and noise absorption.
Disadvantages:
- Exposure to moisture. It is widely known that laminated chipboard does not tolerate exposure to a humid environment. With constant interaction with moisture, the volume of wood chips can increase up to 30%, which leads to swelling of the board and a violation of its strength. The use of a moisture-resistant version of chipboard partly reduces the likelihood of damage to the plate, however, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the effects of moisture.
- Evaporation. The use of formaldehyde resins for the manufacture of chipboard leads over time to the formation of formaldehyde, which evaporates from the board. This substance is harmful to the environment as well as human health. In fairness, it should be noted that the use of laminated film reduces the amount of evaporation to a minimum.
- Repeated screwing of self-tapping screws and screws into the same place entails a decrease in the possibility of their attachment to the chipboard, the plate begins to crumble. Because of this, laminated chipboard is not possible to mill and create curved contours.
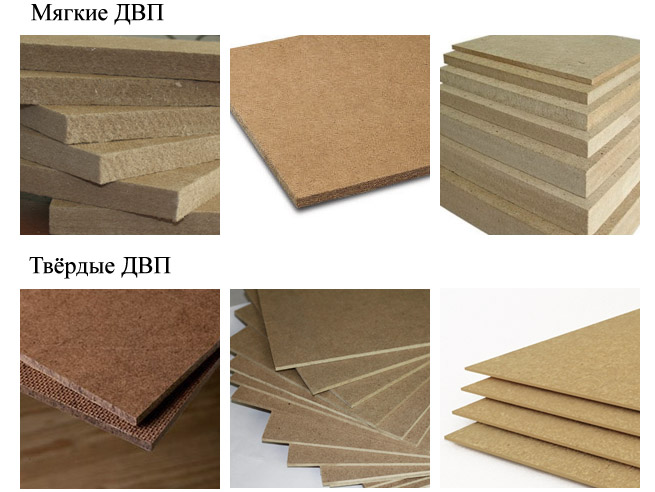
Fiberboard
The peculiarity of the production is explained by the full name - "fibreboard
".Instead of shavings, synthetic fiber + wood dust is used in the preparation of the initial mixture. In addition, various polymers (additives) are introduced, which determine the properties of the finished product. For example, (mainly paraffin, rosin) increase the resistance of products to dampness.
The use of components of the smallest fractions makes it possible to obtain thinner sheets (from 2 to 10 mm) as a result of pressing (also "hot"). Their cost (per 1 m²) is lower than chipboard.

Material features
It is characterized by higher density and increased moisture-repellent properties, and besides, it bends well (within certain limits). Fiberboard sheets are often used in the furniture industry (for the back walls of various cabinets, as the bottoms of pull-out sections), in the manufacture of various containers and the like.
 In everyday life, this material is often laid on plank floors, when large gaps have formed between the boards, and there is no way to repair them ("shifting" the coating). As an option - arrangement of a multi-level ceiling. When self-manufacturing doors, fiberboard is used for sheathing the frame.
In everyday life, this material is often laid on plank floors, when large gaps have formed between the boards, and there is no way to repair them ("shifting" the coating). As an option - arrangement of a multi-level ceiling. When self-manufacturing doors, fiberboard is used for sheathing the frame.
In garages, walls, gates, even ceilings are often finished with such sheets, which allows you to "cover" the cracks and additionally insulate the box (especially metal). These products are distinguished by high sound and heat insulation characteristics, which cannot be said about chipboards.
The range of fiberboard sheets is much wider than particleboard. On sale there are samples with a laminated or painted front side, and in different color shades.
Comparing these materials, it makes no sense to determine which is better. Each is distinguished by its inherent specific properties and is good in its own way. It is only necessary to take into account when buying what these plates will be intended for.
The raw material for the manufacture of this material is wood and processing waste (wood chips, shavings). All this is mixed with glue and pressed under pressure at a high temperature. Some other ingredients are also added: paraffin, synthetic resins, antiseptics, ceresin. Depending on the environment where the material is formed, there are two production methods: "wet" and "dry".
The first method differs in that all available raw materials are soaked in water. Components are added there, depending on what properties the material should have. It can be gypsum, wax emulsions, synthetic resins, rosin, bitumen, asbestos and others. Further, the composition is molded, compacted, dehydrated. Then they are divided into appropriate plates and again dried and pressed. In this case, one side of the board is laminated or cached, and the other is sanded.
The second method does not use water. All components, including binders, are mixed. Then they move to a special form. The pressing process is carried out at a lower pressure and high temperature. As a result, tiles with a smooth surface (on both sides) are formed. However, the structure inside the material is more porous and loose. For a presentable look, fiberboard is treated with wood stain, tinted or varnished (it is possible for parquet).
Array or chipboard? Pros and cons of materials
Solid wood, chipboard, MDF, Fiberboard - what do these terms, and how not to get confused in them by an uneducated buyer? What is the furniture around us made of - wardrobes, dressers, cabinets, furniture for the kitchen, bathroom and bedroom?
Solid wood
Furniture made of solid wood gives a solid and noble look to the room. Often these are exclusive custom-made furniture.
+ naturalness and environmental friendliness of the material;
— natural wood is prone to darkening, sensitive to dampness and temperature extremes;
— expensive and not always affordable option.
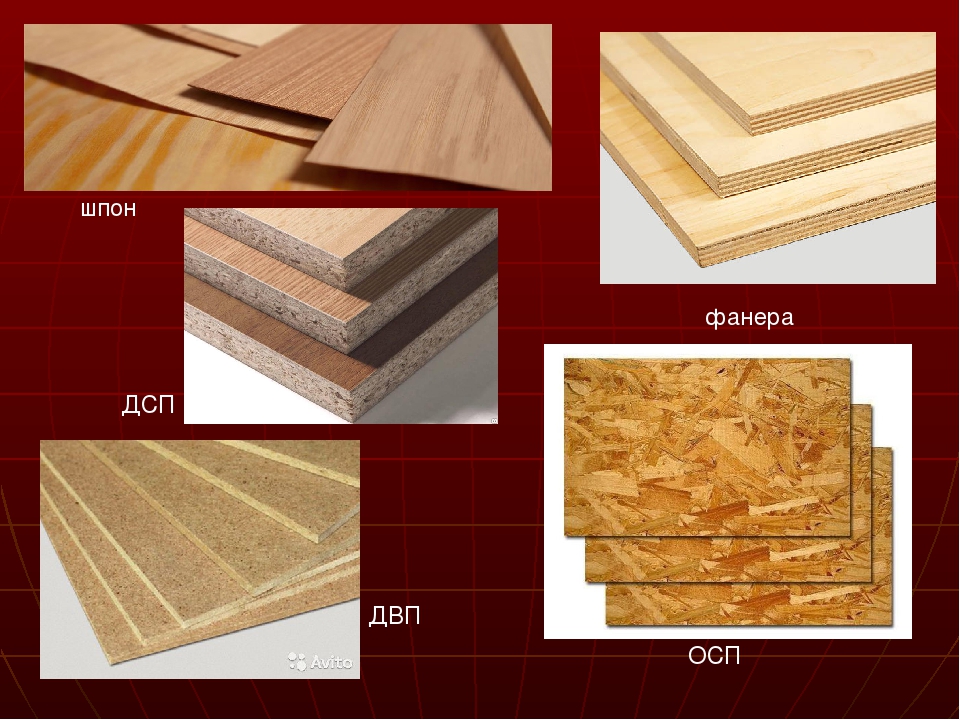
A cheaper analogue is furniture made of wood-based panels.MDF, chipboard, laminated chipboard, fiberboard are materials based on wood, but in the form of shavings, fibers and sawdust. Most often it is woodworking waste, as well as raw materials obtained in the process of sanitary felling of trees.
A classic option in the production of furniture is considered: the front part is made of MDF, the body is made of laminated chipboard, the back wall is made of fiberboard.
Medium Density Fiberboard (from English Medium Density Fibreboard - MDF - MDF ). In the production of MDF, the raw materials are crushed into practically dust and mixed with organic or non-toxic resins. It is a material that is easy to process, which is very much appreciated in the manufacture of furniture that requires elegance and subtlety of lines.
+ the density of the board, which almost corresponds to the density of natural wood, holds screws and other fasteners well;
+ the ability to produce bent furniture elements
+ the plate is immune to microorganisms, mold and mildew.
— reacts painfully to temperatures above 70 degrees Celsius: it swells, warps, and the decorative coating bubbles and peels off, which is why it is not recommended to place furniture made of MDF near heating devices;
— furniture made entirely of MDF is quite expensive, therefore such plates are most often used only in the production of facades.
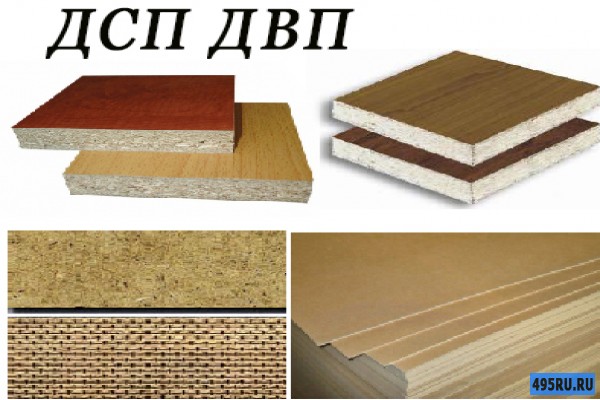
Chipboard and chipboard
Chipboard (official abbreviation is Particleboard , in common parlance chipboard) is made by hot pressing of large shavings mixed with a binder - synthetic resin. Particleboard was manufactured back in the 1930s by the German inventor Max Himmelheber, and in 1951 he received a patent for his invention. "Ideal tree" - so then called chipboard for the homogeneity of the structure and the absence of defects inherent in wood (knots and cracks).
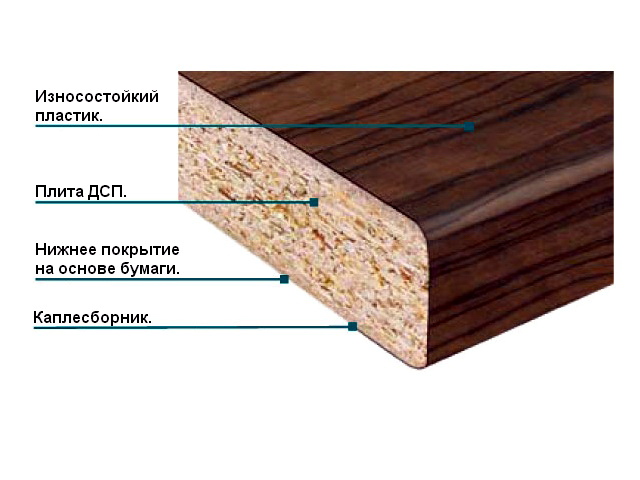
The most common material for the production of cabinet furniture - laminated particle board - or LDSP , in common parlance chipboard. This is chipboard, on which decor is glued on both sides, imitating the texture of wood of various species.
+ products made of laminated chipboard are resistant to moisture due to the laminating coating, in contrast to the analogue of solid wood described above. Furniture products made of laminated chipboard are as convenient as possible during operation: they can be easily cleaned and washed with usual detergents. Although, of course, it is better to refuse abrasive preparations, they can ruin the surface;
+ low price with a large number of colors;
— the material is not suitable for creating bent furniture elements;
— the main negative characteristic of chipboard is the presence of formaldehyde resins in the composition, which, at high concentrations, have a negative effect on human health. That is why it is necessary to ensure that there are as few uncoated chipboard sections as possible in the finished product.
Since 1986, an international scale has been in effect, which determines the emission class of wood-based board materials. It regulates the content of free formaldehyde in the products of manufacturing firms. The following international classification has been adopted: formaldehyde-free board of emission class E0.5 is used in the production of special furniture, for example, medical and children's furniture. Furniture made from chipboard with emission class Е1, approved by all Western countries, Ukraine and Russia for use in residential premises ... Particleboard with E2 emission class is prohibited from use in residential premises by the ministries of health of all European countries. EZ - wood-based panels, suitable only for use in construction.
Fibreboard and DVPO
Fiberboard or Fiberboard, in common parlance - hardboard. In composition, it is similar to MDF, but less in density and thickness, and does not have a decorative finish. The use of such a plate in the manufacture of furniture allows you to make products more affordable.
Refined fibreboard or DVPO. Slab, one side of which is painted with a solid color or imitates wood. The scope of application of such a plate in the manufacture of furniture is limited: the back walls of cabinets, the bottoms of drawers and other parts that do not imply a large load.
Hardboard
The structure of hardboard can be compared to the structure of paper or cardboard. The finest fibers (most often waste from the sawmill industry) are mixed with binders (if necessary with water) to form a mushy mass. The fibrous material is spread over large pallets, covered with sieve cloth and fed to the press. There, under high pressure and at a temperature of more than 200 degrees Celsius, plates are formed, one surface of which is smooth, and the other is rough with a pattern of sieve fabric.
This is the process of making hardboard. In addition, the industry produces medium-hard and porous hardboards, which are pressed without adding water or with pressure, and then dried. For furniture and interior work, both simple hardboard and hardboard with a structured or milled surface and perforated are used. Simple hardboard (it can be covered on one side with paper impregnated with malamine resin) is most often used to cover the backs of drawers and tables.
"Tile
Hardboard with a decorative coating for tiles is often used for home improvement. In appearance, such a coating is almost indistinguishable from a real tiled one. But the time and money for such a cladding is spent quite a bit.
"Tiled" hardboard tiles are not the only way to decorate the surface. So, there are hardboard slabs, the coating of which imitates wood, natural stone or brickwork.
Particularly noteworthy is the perforated hardboard, which was originally supposed to be used as a sound-absorbing material. However, it is increasingly preferred as a very practical material for wall cladding.
Hardboard is produced with a thickness of 1.2 to 6 mm. Regular rough or paper-coated boards are 3.2mm thick. The length of the slab reaches 5.5 m, width - up to 2.1 m. Common to all hardboards is that under the influence of water, water-soluble paints or liquids containing alcohol, the material swells. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully seal the joint edges of the slabs in the bathroom or in the kitchen.
The main brands of hardboard:
- T - hard;
- ST - superhard (increased strength);
- STS - increased strength, with the front side (coating layer);
- NT - semi-hard (reduced hardness).
Using hardboard
Hardboard is a common material in our time for the construction of residential buildings, fences, decoration, sometimes it is even used in art to create a basis when working with oil. It is a building material from which bottoms and back walls are often made for cabinets, drawers, the bottom of sofas (boxes inside sofas) and pedestals. Sami slabs usually consist of wood chips processed into fiber, to which substances are added that make the wood more moisture resistant. Such substances are paraffin and rosin, which have increased water resistance properties. In the production of dense boards, special resins are added to the mixture, the amount of which depends on the composition of the board. Binder need not be added to soft boards. Special additives such as antiseptics and flame retardants are also added. In the production of superhard plates (grade ST), pectol is also used - a by-product of the processing of melted butter, from which the strength of the plate can increase up to 30%.
Hardboard is sometimes called fibreboard. One side is always smoother than the other, often varnished or painted, as it is the front.The inner part is processed minimally, it is not covered with either varnish or a special film, in order not to spend extra money on processing both sides and to make it possible to distinguish them. Hardboard is also used for covering and cladding, in particular, doors.
Fiber boards are very convenient and profitable for purchase, since they are a fairly cheap material, have a number of useful mechanical properties, with careful use they serve for a long time, do not change their texture when processed by various means. Plates are easy to cut and do not deform due to humidity or temperature changes
You can use the material for any purpose you need, including even for the construction of something, any kind of cladding (when using the outer, smooth side), even as a basis for pasting wallpaper, so as a material will not deform from the use of glue and make the base smooth if, for example, you have rough walls. Or, if you wish, you can cover the walls with them, thereby making a convenient basis for creating any interior, especially if you have concrete walls and find it difficult to work with concrete.
determined that the difference between chipboard and fiberboard is as follows:
Chipboard is made from shavings and other waste of low-value wood species with the addition of synthetic resins, and fiberboard is made from wood dust and cellulose fibers with the addition of synthetic polymers, rosin and paraffin.
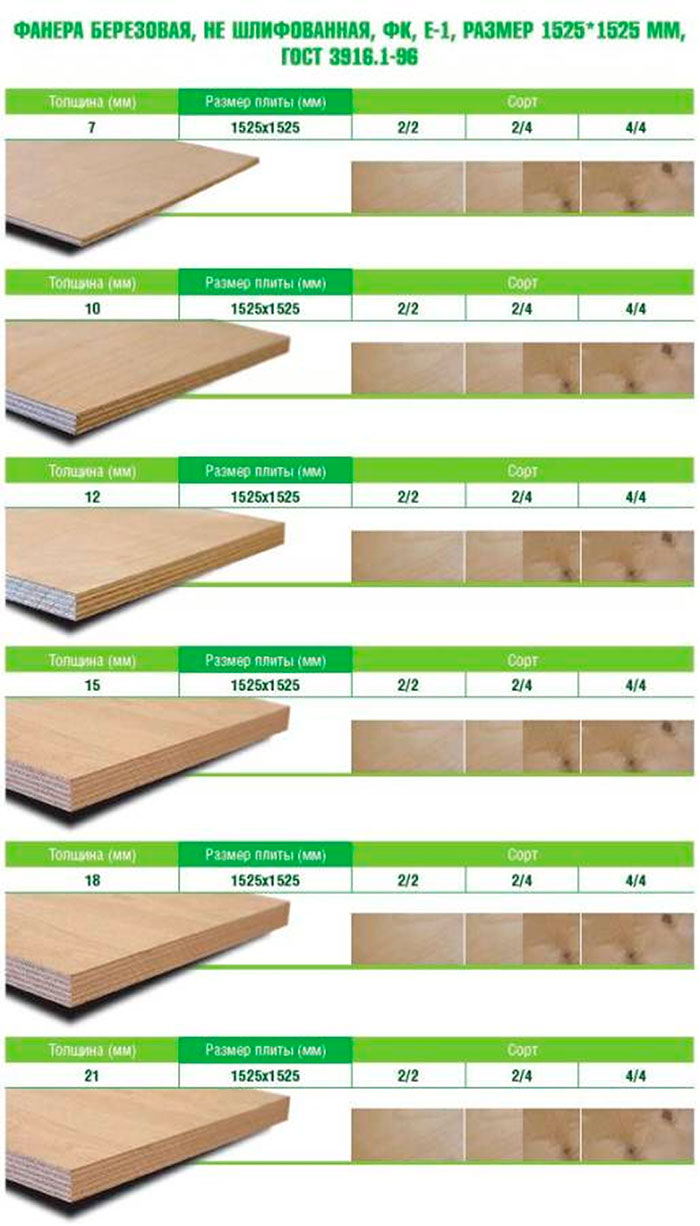
The thickness of the fibreboard is from 2.5 to 12 mm, and the thickness of the chipboard can be up to 25 mm.
Fiberboard has higher moisture resistance, and chipboard can withstand heavy loads.
The cost of fiberboard is much lower than particleboard.
Chipboard is used for the manufacture of furniture structures, when laying floors, and fiberboard - in the production of drawers, rear walls of furniture, shelves, racks, erection of partitions.
The service life of fiberboard is longer than particleboard.
These sheet lumber is in great demand among buyers due to its low cost and availability in processing with the simplest, household tool, that is, the fact that the owner is always at hand. In the process of construction, restoration or repair, if everything is done on their own, they are really irreplaceable.
But the erroneous opinion of people who are not particularly versed in the varieties of the same type of products that fiberboard and particleboard are practically the same, often leads to the fact that over time it becomes clear that the choice of material was made incorrectly. So is there a difference between fiberboard and particle board, and if so, what exactly and how important is it?
The apparent identity of chipboard and fiberboard is that fractions of wood (or components based on it) are used as raw materials in the production of these boards. And the difference, and a very significant one - in particular in the manufacture of plates, more precisely, in their structural composition. It is he who determines the basic performance characteristics of the samples.
Components
- Wood shavings, as the name suggests.
- Sawdust.
- Resin (mainly formaldehyde), which acts as a binder to hold the individual fractions together.

Particleboard features
In terms of strength, these plates are superior to products under the abbreviation of fiberboard. This is also due to the fact that they are produced with a greater thickness (up to 5 cm), therefore, they are able to withstand such a load at which wood fiber samples deform or break.

- Insufficient density. Simply put, chipboard is a somewhat loose material.
- Increased hygroscopicity.
- Rigidity. Dense fastening of chipboard on an uneven base leads to the formation of cracks in the slab.
Examples of using
- Arrangement of a "dry" screed.
- Installation of decking.
- As a continuous sheathing.
- For strengthening the vertically oriented base.
- Construction of awnings, partitions, fences, flooring, chests, furniture items (and in a number of other cases.

Limitations in the use of chipboard
- In conditions of constant dampness or systematic fluctuations in humidity, the service life of the chipboard is sharply reduced.
- Do not use for the erection of collapsible / prefabricated structures. The constant reinstallation of fasteners leads to the fact that the material on this segment begins to literally crumble, and self-tapping screws or screws (if we are not talking about through drilling with fixation on a harder base) at this point no longer hold.
The most reliable, durable and versatile chipboard is with a three-layer structure.
Where is it used?
Chipboard is widely used in the furniture industry. This material is practically irreplaceable in the manufacture of cabinet furniture. Budget options for kitchen furniture can consist entirely of chipboard. This material is often combined with more expensive MDF. Cabinets of various models are also made of chipboard.
Many interior elements of an apartment or house are also made using laminated chipboard. Beds, sofas, hangers and many other furniture contain details from laminated chipboard in their construction. It is also used by:
- for the construction of decorative partitions;
- wall cladding and door leaf;
- as load-bearing structural elements;
- for the device of the rough field;
- as a work surface for bar counters and kitchen countertops.
You can see how to look chipboard on furniture in the interior of the apartment in combination with the color of the walls and floor in this designer.
Differences in use in furniture production
For those who are going to use these materials for assembling cabinets, beds or decorative elements of the interior, it will be useful to know
what is the difference between MDF and particleboard in furniture.
The finely dispersed fraction is easy to cut and process. The screws can be screwed in without much difficulty. Ideal in cases where curly cutting is required - the cut is perfectly even and neat. At the same time, the material is heavy and has a different color on both sides (one side is white).
More capricious in processing. The cuts often turn out to be sloppy, “ragged”. When screwing in the screws, chips and cracks may appear. The advantage is that the weight of the material is light and the sides are the same color.
Furniture makers are familiar with one more material - laminated chipboard. This board is essentially the same as chipboard, only slightly improved. The surface of the slabs is covered with a special cladding film. This coating is made of paper and melamine resin.
The film is literally pressed into the surface of the slab and gives the finished products increased strength and protection from moisture. The only drawback of this material is the high cost.

How to choose material depending on the room
In order to correctly determine the material for the manufacture of interior items for different rooms, it is necessary to take into account some recommendations.
Each variety is created for its own purposes, so it is fundamentally wrong to declare unequivocally that some material is better or worse.
Hallway furniture
This is a room with high traffic and fluctuations in temperature and humidity. Water carried from the street can create problems. Therefore, the following rules exist for furniture in this room:
The standard economy option assumes the use of products made entirely of chipboard. But all the outer edges are processed with a PVC edge of 2 mm, and the inner ones - 0.4 mm. Printed piping can be an alternative for some areas.
Particular attention is paid to the racks located directly on the floor: they are additionally raised above the surface with the help of special "boots"
Melamine and thin (up to 1 mm) PVC or ABC tape is considered an unreliable option, it is used only for processing internal surfaces, the outer edge is processed with an edge from 2 mm, while the highest protection is given by PVC and aluminum moldings for a milled groove
A better solution involves a combination of materials.For facades, MDF is used, where HDF is suitable for insertion with a frame version. The body is made of laminated chipboard with maximum edging.
On a note! If the lower ends are not protected, then they can be additionally covered with silicone sealant.
The box, assembled from laminated chipboard and decorated with an MDF facade, significantly reduces the price of the headset, and without losing quality in operation and appearance
Kitchen set
While Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is the optimal solution for high humidity, it is not used for all kitchen items. Therefore, when they say that products are made of MDF, only facades or a dining table cover are meant.
For the kitchen, the same rules are true as for the hallway, but there are additional nuances:
- The table top of the headset must be moisture resistant. Such a protective impregnation is clearly visible on the cut: most often it gives the structure a greenish tint.
An ordinary chipboard sheet is not suitable for a countertop, such a plate should be thicker and denser than the facade material and have a higher class of moisture protection
It is better to refuse laminated chipboard facades with melamine edges. It is easy to distinguish it: to the touch, the surface resembles very thick paper. The best solution is with a 0.4 or 2 mm PVC tape. The latter has slightly rounded corners.
The ends of objects located next to the stove must be covered with a special aluminum plate. The attachments are positioned to minimize steam ingress.
In kitchen sets, it is not so important whether the facade is made of MDF or chipboard, the main thing is to choose a good countertop and provide protection from moisture in the floor area
Children's room and bedroom
Furniture for a child's room (as well as for any other premises) must have mandatory certification. But unlike previous objects, beds for a nursery can be made entirely of MDF.
Particular attention is paid to the internal stiffening ribs, on which the mattress flooring is located: such parts are made of wooden beams, which provide the necessary strength and reliability
Both MDF and laminated chipboard are widely used for the production of children's furniture, in this case, it is not so much the material that is important as the level of trust in the brand.
The rest of the furniture should be as functional as possible. The following requirements are imposed on them:
- For children under 6-7 years old, it is better to choose products with rounded edges, which is inherent in milled parts with a wood-fiber structure, or to equip them with special overlays.
- The fittings should be matched with a smooth closing of the facades, which will exclude injuries.
Furniture for the bedroom and walls in the living room are selected based on personal preferences, but the best solution would be a combination of MDF and chipboard.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each of the listed materials has its own purpose. Let's take a look at the pros and cons of each.
Fiberboard
Fiberboard is a very resistant material to various changes in moisture. The back walls of most cabinets, the bottoms of drawers, these sheets, rough to the touch, are fiberboard. (In the most expensive furniture, plywood is used instead of fiberboard, but it is not much better in terms of performance).
Plus: low price with high durability.
Cons: a small range of uses.
Chipboard
Pros: water resistance, strength, ease of processing. Chipboard “holds” nails and screws that hold the structure together well. Chipboard lends itself well to mechanical processing (sawing, planing, drilling, milling), easily glued and painted. Another advantage of chipboard is that it has a low price. That is why chipboard is the most widely used material for economy class furniture; most of the office furniture is made from chipboard.
In some physical and mechanical properties, chipboard is superior to natural wood.In particular, they swell less from moisture; less flammable; with an uneven change in humidity, they do not warp; have good heat and sound insulation properties; more biostable.
Cons: the presence of the very formaldehyde resins that hold the wood particles together. The fact is that chipboard releases a certain amount of formaldehyde into the air - not the most useful product, it should be noted. But not so scary. There are two types of chipboard: E1 and E2. E1 is more environmentally friendly, its formaldehyde emission rate is noticeably lower. But E2 is forbidden to be used in the production of children's furniture: draw conclusions. Particleboards of Austrian and German production are considered the most environmentally friendly.
MDF
Pros: This type of semi-finished product is highly environmentally friendly, and also has excellent compactness, fiber cohesion, and dimensional stability over a long period of time.
The strongest point is the extremely favorable ratio between hardness and thickness: MDF sheets can be from 4 to 22 mm. Recently, door blocks with frames and platbands made of MDF, covered with veneer of valuable wood species, have begun to appear. The MDF surface is flat, smooth, homogeneous, dense, all this makes the external processing of the boards extremely easy.
The use of this material in the manufacture of interior doors allows the latter to acquire the properties of excellent planarity of the leaf surfaces, surface hardness and impact resistance.
This material is widely used for the manufacture of veneered and laminated platbands, extensions, frame racks, paintings for painting and various overlays for entrance doors.
Minus: the only one is not established production of MDF in Russia.
The choice is yours.
What is the best material for the floor?
To select the most suitable option, the specifics of the room and the final coating are taken into account:
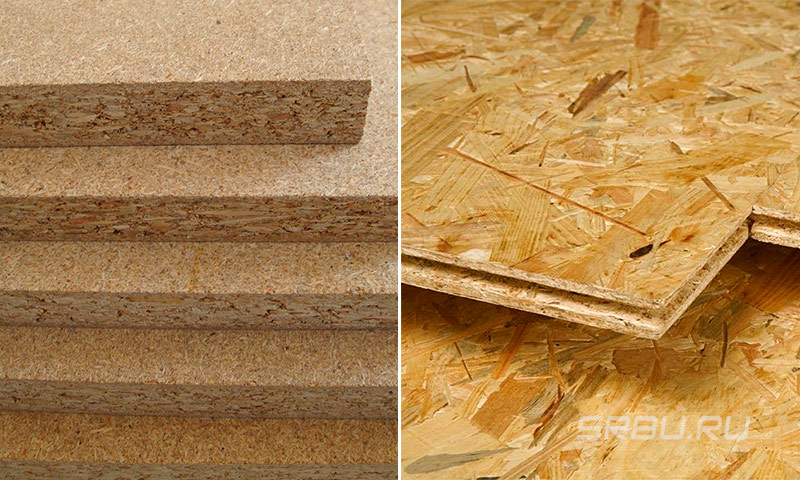
- Particleboard and OSB can be used under the tiles in the bathroom, but only varieties with moisture-resistant impregnation. If you put the products without processing, then there is a high probability of the appearance of mold and mildew. This also applies to the decoration of the kitchen, hallway and balcony.
- Old wooden bases, prepared in advance and without serious defects, can be leveled with hardboard by laying it directly on the boards.
- When installing "dry" screeds, preference is given to plywood and chipboards.
- If the house does not have a solid foundation, then OSB is hemmed along the logs on both sides. Another option is the simultaneous use of plywood and OSB.
- Fiberboard can be used to level the floor under the laminate. But if it is necessary to create a rigid base, it is better to lay plywood and OSB.
Thus, it is impossible to single out any one material. It is preferable to combine products in order to obtain the best result and increase the service life of the coating.
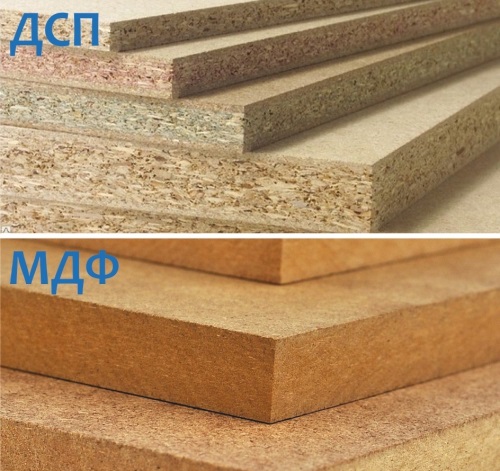
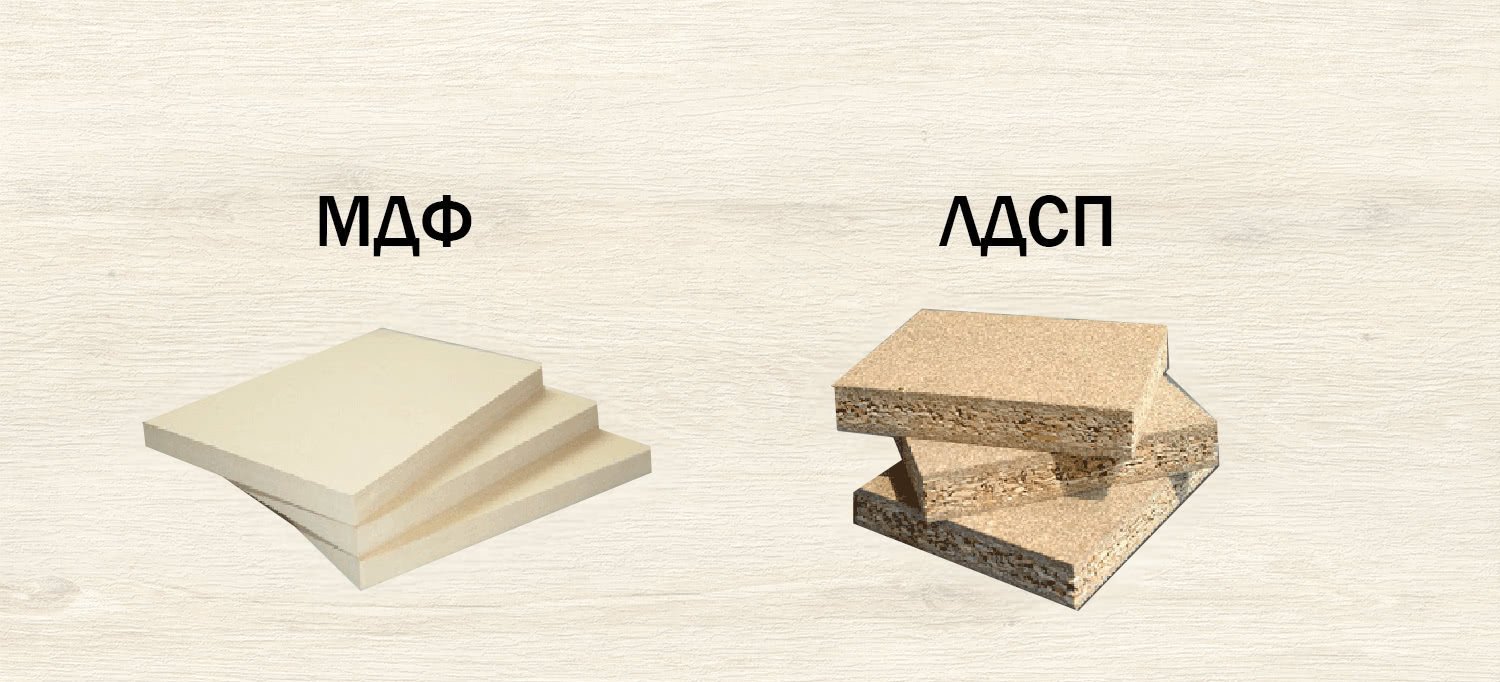
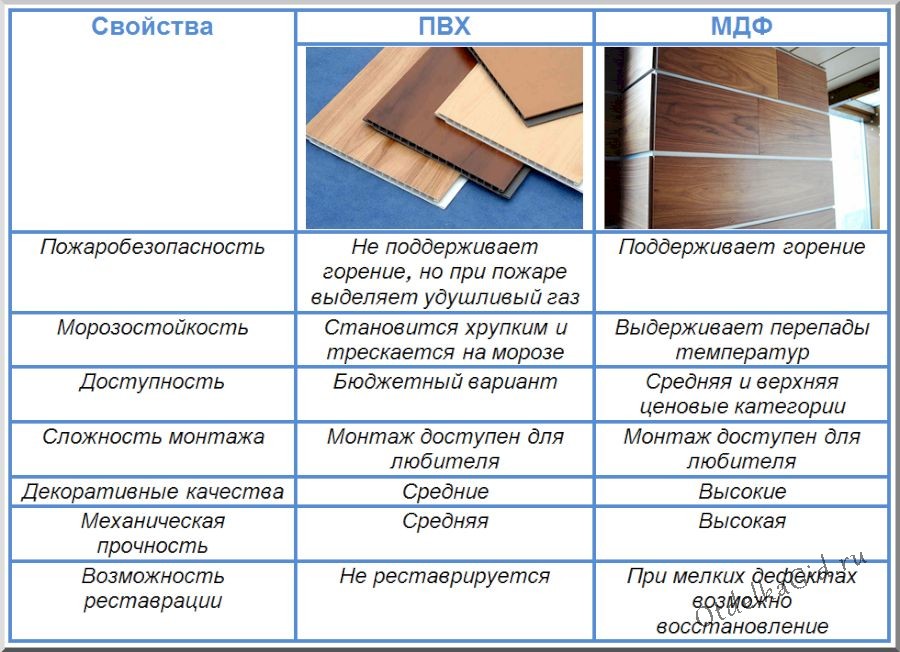
What is chipboard and MDF board
The production of MDF and chipboard is carried out using similar technologies and at first glance, it is quite difficult to find external differences between them. But if we take a closer look at their production in general and the raw materials used for it in particular, then the differences that affect the field of application of materials will be quite significant.
Chipboard - production and application
The raw material for obtaining sheets of chipboard (particle board) is sawdust. The production process consists in mixing raw materials with a binder, which are used as various formaldehyde resins and pressing the resulting mass.
Chipboard plates.
Chipboard plates.
The spheres of application of chipboard are the production of cabinet furniture, packaging of goods and various construction works.
MDF - production and application
Technologically, the production of MDF (fiberboard) boards resembles the manufacture of paper - at least the preparation of raw materials up to a certain point is done in the same way.
To create MDF, not whole shavings and sawdust are used, but crushed to the state of individual wood fibers. This means that any waste from the woodworking industry can be used as raw material.
At the first stage of preparation of raw materials, it is ground to the size of crumbs, after which it undergoes cleaning with hot steam, which is supplied under pressure. After that, the cleaned and moistened mass is fed to the defibrator, which finally grinds its particles to a minimum size.
The last stages of production are drying of raw materials, mixing the whole mass with special resins and hot pressing into finished boards. The result is a material that in many respects not inferior to natural solid wood. He found the main application in the furniture industry, since in other industries it is more profitable to use cheaper analogs.
MDF boards of various thicknesses.
More details about all the characteristics of materials can be found only by comparing them with each other. This will clearly show how chipboard differs from MDF and which is better to choose for specific tasks.