Flammability

An important role for the appearance of fire is played by the power of the heating source, the cross-section of the wood, the speed of the air flow and the density of the material. The early appearance of a flame can be caused by light wood with high porosity.
As for wet wood, it ignites more slowly, since it must dry before an open fire appears.
Expert advice: for storing firewood, you should choose dry places, away from moisture. Otherwise, they will dry for a long time in the oven.
Also, burning will depend on the shape of the logs, since the round shapes of the tree will not burn so well than the rectangular logs with a small section, sharp edges and a developed lateral surface. Unplanned birch logs are more likely to ignite than smooth woods.
A very important condition for the combustion of any kind of wood is a normal oxygen supply. In some respects, the combustion of wood even surpasses the combustion of coal.
Primary requirements
The best firewood for heating stoves is dry. Humidity should be within 20%. This is the main requirement. The calorific value of wood depends very much on its moisture content.
Dry wood flares up and burns well, emits more heat, smokes less. The logs should not be rotten, saturated with water. A water log is not suitable for heating stoves.
Good wood leaves little ash. It is advisable to harvest wood in late autumn or winter, when sap flow stops, the wood is denser.
The size of the wood for the stove depends on the size of the firebox, usually 35-40 centimeters long. Thickness - medium, thick logs split. Small logs are easy to light. They also burn out quickly, which must be taken into account when preparing them.

Bird cherry

This tree often accompanies alder with willow, although it is not found so massively. I still don't know anything about the exact calorific characteristics of bird cherry. However, according to all estimates - it should stand on the same level with an oak, because in its density it approaches it - which we have repeatedly seen when harvesting bird cherry wood, which differed from others by a heavier weight. Tests have shown that they flare up quite difficult (approximately like elm trees), the flame gives a quiet and even, and they form little coals. But while they are burning, heat is emitted at the level of alder, or even a little more. It is quite possible to warm up and cook food on bird cherry logs. The only "but" - all bird cherry rusks that we came across - both standing on the vine and lying on the ground - were saturated with moisture. It is possible that in dried form, this tree will show itself many times better.
Moisture factor
The main negative factor is, of course, humidity. Freshly felled forest has a moisture content in the range from 40 to 55%, and in some tree species the moisture content can even reach 65%. You can melt the stove with raw wood, they will even burn, but the bulk of the heat will be used to dry the wood and evaporate moisture. Consequently, the temperature in the oven on damp wood cannot reach its peak level in any way, which means that the heat transfer from such wood will be mediocre.

It will take a long time until this forest turns into full-fledged dry firewood.
Of course, the owner of the house can use both raw and dry firewood to heat it:
- You can burn freshly cut wood in the oven, as well as recent stocks, but it should be understood that in this case the firewood consumption will be an order of magnitude higher, since they will give less heat. An additional negative phenomenon will be a large amount of soot in the chimney, which appears during the combustion of raw wood.
- To get dry firewood, you should properly prepare the forest, saw it, chop it into pieces of wood of the required length, store it in a wood-burning box, dry it for six months or even a year, and then use it. It is believed that firewood harvested in the winter and lying in the shed for two summer seasons is optimally dry, their moisture content is usually about 20%. A long way, but it allows you to achieve greater heat transfer from the firewood, and as a result, save on the forest.
Note that there are trees that are not at all intended for kindling freshly cut stoves. These include such species as poplar, willow. During the combustion of these types of wood, practically no heat is generated, and it is hardly possible to call them smoldering. After drying, the poplar already burns with a bright and beautiful flame, but it still does not give much heat.
At the same time, the difference in heat transfer of different types of wood is so great that it allows you to burn some varieties fresh, for example, birch, oak, ash. These undoubted leaders have such a high combustion temperature that they are able to dry themselves and heat the house. Birch firewood additionally has a pleasant aroma, which is considered to be healing. Conifers do not have such impressive characteristics, since they contain a large amount of resin, so raw spruce or pine can only be laid in a melted oven.
In order for the wood to give off the maximum amount of heat, so that the temperature in the fireplace or stove reaches high values when burning wood, it is imperative to dry the wood.
How to measure the burning temperature of wood
It is quite difficult to measure the temperature on your own at home. It is necessary to purchase a special measuring device - a pyrometer. Experts have carried out the necessary research, and deduced data on the maximum combustion of various types of trees. It remains to rely on the measurements taken, and take care of high-quality furnace equipment. Modern furnaces are equipped with a convenient regulation of the timely supply of oxygen, thus it is possible to regulate the maximum heat output during combustion.
You can determine the approximate combustion temperature by the color of the flame of the burning wood in a Russian wood-burning stove. When burning rocks with low heat transfer, the color of the flame will be dark red. If birch or oak is burning, you can admire the light yellow fire.
Based on the measurements of the combustion temperature in the laboratory, it is possible to select the most suitable type of fuel. Ash, hornbeam and beech firewood is distinguished by its high heat output. Oak and birch have a lower index, but are great for high-quality heating of residential premises.
What is the combustion process
An isothermal reaction in which a certain amount of thermal energy is released is called combustion. This reaction goes through several successive stages.
In the first stage, the wood is heated by an external fire source to the point of ignition. As it heats up to 120-150 ℃, the wood turns into charcoal, which is capable of spontaneous combustion. Upon reaching a temperature of 250-350 ℃, flammable gases begin to evolve - this process is called pyrolysis. At the same time, the top layer of wood smolders, which is accompanied by white or brown smoke - these are mixed pyrolysis gases with water vapor.
At the second stage, as a result of heating, the pyrolysis gases ignite with a light yellow flame. It gradually spreads over the entire area of the wood, continuing to heat the wood.
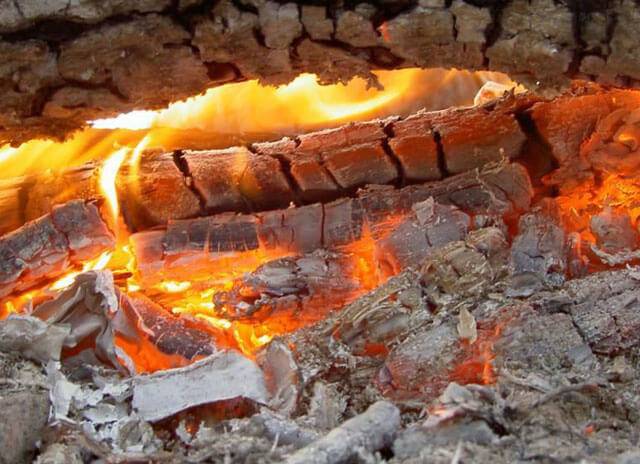

The next stage is characterized by the ignition of the wood. As a rule, for this, it must warm up to 450-620 ℃.In order for the wood to ignite, an external source of heat is needed, which will be intense enough to rapidly heat the wood and accelerate the reaction.
In addition, factors such as:
- traction;
- wood moisture;
- section and shape of firewood, as well as their number in one tab;
- wood structure - loose firewood burns faster than dense wood;
- placement of the tree relative to the air flow - horizontally or vertically.
Let's clarify some points. Since damp wood, when burning, first of all evaporates excess liquid, it ignites and burns much worse than dry wood. Shape also matters - ribbed and serrated logs ignite more easily and faster than smooth and round ones.
The draft in the chimney must be sufficient to ensure the flow of oxygen and dissipate thermal energy inside the firebox to all objects in it, but not blow out the fire.
The fourth stage of the thermochemical reaction is a stable combustion process, which, after the outbreak of pyrolysis gases, covers all the fuel in the furnace. Combustion takes place in two phases - smoldering and burning with a flame.
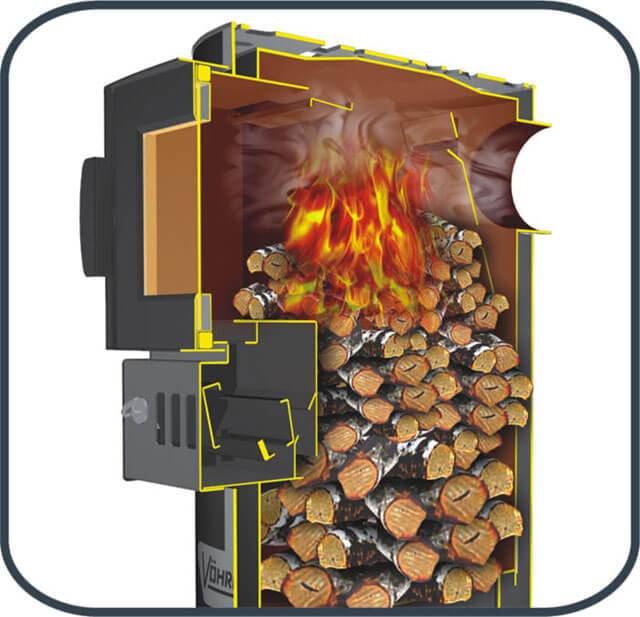
In the process of smoldering, the coal formed as a result of pyrolysis burns, while the gases are released rather slowly and cannot ignite due to their low concentration. Condensing gases produce white smoke as they cool. When the wood smolders, fresh oxygen gradually penetrates inside, which leads to a further spread of the reaction to all other fuels. The flame arises from the combustion of pyrolysis gases, which move vertically towards the exit.
As long as the required temperature is maintained inside the furnace, oxygen is supplied and there is unburned fuel, the combustion process continues.
If these conditions are not maintained, then the thermochemical reaction passes into the final stage - attenuation.
Burian

Now is the time to consider alternative types of fossil fuels with which you can fuel your campfire on a hike.
Sometimes it happens that there are no dead wood near the camp, and the conscience does not allow to saw green trees (foresters do not allow), or there is a decent distance to them. Then you have to get out with the help of herbaceous plants. As a rule, if the area is more or less wild and open, such large types of grasses as:
- Sagebrush;
- Burdock;
- Sow thistles, thugs and others like them;
- Blooming Sally;
- Large umbrella: hemlock, kupyr, angelica, hogweed (including the notorious giant);
If the terrain is swampy or borders on water, then the above list is supplemented by the following plants:
- Cane;
- Cattail;
In rural areas, the following options are possible:
- Straw;
- Sunflower stems;
Best of all, of course - thick, not hollow stems (wormwood, burdock, sunflower). All this nonsense usually dries up in the fall, stands all winter, spring and the first third of summer, then - as the green herbs grow, most of last year's dry stems rot and fall. Nevertheless, you can collect a certain number of such "firewood" for a fire at any time of the year.
Dry weeds burn quickly and hotly, they practically do not form coal, because its density is very low. For a full-fledged night fire, you will need a dozen cubic meters and a specially trained farm laborer who will constantly throw this business into the fire. It is also possible to use ingenuity: twist the grass in dense sheaves with twine. It will burn longer.
But in order to light a mini-fire, for example, for boiling water, weeds will do quite well. The only thing you need is a few stones.In order to lay out a little bit of a hearth and not emit heat in vain into space, thereby increasing the efficiency of the fire.
Next are the parameters of weeds as a fire fuel (in the calculation, straw indicators were used as the initial parameters).
- Fire power: 0.1de.
- Calorific value: 378 kWh / m³.
- Combustion temperature: 800-900 ° C.
- Burning time: very short.
- Flame: even, with a characteristic crackle. Smokes, the less dry the material, the stronger.
- Coals: Does not actually form.
- Lighting difficulty: extremely low, dry weeds - excellent kindling.
CORRECT BOILER FURNACE
There are several simple rules that must be followed in order to achieve maximum efficiency and proper operation of the heater:
- Whatever fuel is used, the firewood should be at least half of the bookmark.
- The gas-fired boiler must not be heated with insufficiently dry wood. The maximum humidity level is 20-30%. If they are damp, this will lead to a decrease in the combustion temperature, as well as a drop in the level of efficiency by 2-3 times.
- The efficiency that the boiler is able to achieve decreases if the filling is incomplete. It is not recommended to lay the heater in less than half way, as as a result the wood does not burn out completely and there is an increased formation of soot and soot. As a result, the chimney and heater will have to be cleaned much more often.
- The correct length of logs is 25-35 centimeters. Firewood can be bought in bulk or by weight.
How to choose the right one

Therefore, it is customary to use birch firewood, which burns at 800 -820 degrees. Also, oak and larch, burning at 840-900 degrees, are suitable for these purposes.
Coniferous species of trees - pine, most suitable for a fire. However, no one prohibits its use as heating for a stove. At a combustion temperature of 610-630 degrees, half the amount of firewood will be consumed than oak or birch.
Features of conifers:
- low combustion temperature;
- smoke and soot formation.
Because they contain a large amount of resins. The latter settle on the walls of the chimney, clog it over time and require cleaning. Therefore, the use of softwood for these purposes is not very desirable and is recommended only in extreme cases.
In addition, you should pay attention to the moisture content of the wood, since its percentage has a direct effect on the combustion process. Accordingly, wet material will not burn well and create a large amount of smoke.
Combustion temperature and heat transfer
These two parameters are interrelated, the higher the burning temperature of wood in a stove or solid fuel boiler, the more heat is released. But everyone who has once had a chance to heat the stove with different types of wood, noticed that some firewood burns brightly, giving off an intolerable heat, while others burn sluggishly and give very little heat.
The reason is that different types of wood have different combustion temperatures and specific heating values.
To understand how large this difference is, a table of the combustion temperatures of various types of wood under ideal conditions is proposed below. You ask - what are the ideal conditions? Actually, there are three of them:
- wood contains a minimum of moisture;
- the process takes place in an enclosed space;
- exactly as much oxygen is supplied to the combustion zone as is required for full combustion.
As mentioned above, the data will be incomplete if the specific heat of combustion of each of the rocks is not presented. The table below shows the heat transfer values of firewood, expressed in various units and in relation to the weight and volume of fuel:
All tabular data are for reference only and are useful for an approximate calculation of the amount of fuel, which is done with a large margin. It is also possible to understand from them that oak and birch burn much hotter than poplar and alder, and therefore will give off more heat energy. But the tables cannot be of practical value for the average homeowner, because the burning conditions in real life are far from ideal.
In reality, the burning temperature of wood in various stoves and fireplaces never reaches the values indicated in the table. To do this, it is necessary that the firewood be absolutely dry, which does not happen in life, people burn in the firebox as much fuel as they have available. The temperature also decreases from a lack of oxygen. We will consider these issues in more detail below.
What kind of wood is better to heat the stove
The choice of the best way to warm the room, cook or light a fire is based on the properties of each type of wood. To achieve the best result, you can combine several types at the same time, while observing the sequence of actions and adding other types of wood.
For home heating
If the calculation is for a small room that requires constant heating, then the use of fruit wood would be the best choice. In the absence of such, you can use needles. However, only for closed type boilers.
You can burn alder or aspen to clear the chimney from combustion products. It is convenient to use them by throwing them into the oven at the end. In this case, it can be combined with birch or acacia logs, or dust.
 Larch
Larch
For a bath
For bathing in baths and saunas, you need to choose firewood with a stable heat, aroma and not smoking. Conifers are not suitable for this. The best choice is linden or alder. Both varieties have pleasant, and most importantly, healing odors, give a sufficient amount of heat and burn out for a long time. To further increase the burning time, you can add birch or aspen.
Alder has a pleasant aroma and burns well. It will not take a long time to set fire to it, so you can quickly go to the bathhouse.
It is convenient to use aspen. However, without combining with other types, it will not work out normally to warm up the room. In combination with birch, which gives a stable temperature, does not smoke, emits an aroma when burning, you can get air with antiseptic properties and a clean chimney.
For barbecue
To get a good kebab, you can use fruit breeds. In addition, chips of birch or linden are used. When cooking fish or beef, you can use birch logs. The use of varieties of fruit crops gives a good result.
Air dependence
The paradox is that we reduce the combustion temperature and heat transfer of the fuel ourselves by limiting the supply of oxygen. The shutters of the furnace or boiler are covered in order to increase the duration of the process and thus, in our opinion, save fuel. An exception is the temperature of the fire burning in an open fireplace, where air from the room flows freely.
But even a fireplace fire obeys the chemical formula for the ideal combustion of wood, presented in a simplified form:
C + 2H2 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O + Q (heat).
On the left side of the equation are carbon and hydrogen burned in the presence of oxygen. On the right - the products of combustion, this is carbon dioxide, water and the released heat, which we use for heating. In practice, it is necessary to supply air to the furnace in the amount of 130% of the volume required for combustion. Then dry wood, when burning, develops a temperature close to the maximum.
When we cover the air supply with dampers, the equation is violated, a third element appears in it - carbon monoxide (CO). This is the result of the fact that not all carbon atoms have met two oxygen atoms, they simply did not have enough air for this. Unburned carbon monoxide flies into the chimney, the temperature in the firebox decreases, and after it the heat transfer.
The correct approach is to install a buffer tank and constantly bring the solid fuel boiler to maximum operation with sufficient air supply and full combustion. But with stoves, such a trick will not work, they heat the air in the room, and not the water in the system, so it will not be possible to accumulate heat.That is why carbon monoxide is always present in the furnaces when burning resinous wood, and indeed any wood in the oven.
What is the temperature in the stove when burning with wood
Burning wood is an isothermal reaction in which heat energy is released. Heat transfer directly depends on the height of the fuel combustion temperature. Well-dried wood burns much better than oversaturated wood. Before harvesting environmentally friendly fuel for the winter, you should study the characteristics of each wood species.

Depending on the type of firewood
Various types of trees are suitable for harvesting firewood, differing in density, wood structure and chemical composition. More efficient space heating is possible when using well-dried raw materials with a dense texture. Such firewood burns completely, does not leave a lot of ash. The combustion temperature in the furnace varies from 800 to 1000 degrees. Deciduous tree species have long-term combustion properties: birch, linden, oak, ash. Firewood with a looser density burns faster, but has a low heat transfer. Therefore, it is unprofitable to use such firewood for heating. Fir rocks provide little heat and generate a lot of soot and smoke. It is good to use them for open areas, for example, when frying kebabs.
Oak wood has a dense texture and burns in the oven up to 900 degrees. Birch firewood provides heat at a temperature of 800 degrees. Poplar has a porous wood, and can only give a low burning rate - 500 degrees. When stoking in a bathhouse or in the open air, it is not cost-effective to use raw materials with a dense structure; it is better to fire with cheaper types of trees with the addition of a small amount of birch or oak logs for the heat. It is better not to use alder raw materials in an open fireplace. When burning, they tend to shoot coals, which can lead to a fire hazard.

Additional influencing factors on the temperature in the oven
The moisture level of the wood plays a huge role in igniting and releasing heat to heat the room. If the wood is damp or poorly dried, during combustion, part of the heat will go to remove excess moisture by evaporation. The temperature in the oven will not reach the maximum heat transfer percentage.
To completely burn the wood and reach a high temperature, it is necessary to supply air to the furnace at regular intervals. Without the required amount of oxygen, the logs begin to smolder and do not emit the full amount of heat into the room. If too much oxygen is supplied through an open blower, an irrational loss of heat transfer will occur through the chimney. Therefore, it is necessary to install stoves with good equipment of important elements. The blower, grates, dampers must be in good condition.
The maximum output of heat and heat during the firebox is influenced by the device of the home stove. What material it is built of, how the dampers and the blower work - everything can affect the generation of heat transfer. Steel furnaces cool down quickly, not having time to heat the room to the desired value. Equipment made of more massive material keeps heat longer, and the logs burn up to the maximum. But, such oven devices require constant monitoring. An explosion may occur due to the high heat output.
The combination of all factors directly affects the combustion process. To generate the maximum amount of heat, it is necessary to use well-dried fuel and provide the combustion process with the required amount of air. The stove should not be heated with rocks with a porous texture. This will be a rather expensive undertaking.

Combustion

After all, the chemical effect of oxygen should give the soot particles a brighter color, up to white.However, this phenomenon is quite understandable, since the particle size affects its temperature, and the smaller it is, the lower the temperature.
Therefore, burning small particles of wood have exactly the same temperature as the gas surrounding them.
Also, it should be noted that the heat transfer for each wood species is different, and in order to find it out in more detail, there is a special table that shows the thermal conductivity indicators for each wood species.
The best way to heat the stove: with wood or briquettes, see the following video:
Which are best for the oven
Any firewood can be used as fuel. The main thing is that they are. Each region has its own preferences, depending on which trees grow in the area. Many people think that birch or alder are the best. The choice is yours.
To the bath
The choice of logs for heating a sauna depends on the design of the stove. Many people prefer:
- Alder. They give a persistent heat, burn almost smokeless. There is a popular belief about their healing power;
- Birch. It burns evenly, the heat is strong;
- Willow. The heat transfer is low, you will need a lot of them, but the spirit in the bath will be especially light.
It is not recommended to use oak trees - they burn out for a long time, the heat is hard, and they emit a large amount of carbon monoxide. Periodically, aspen is used to clean the chimney. If the furnace is remote, the main selection criterion is heat transfer.
For home heating
Deciduous firewood has the best qualities, and they are used more often. Birch, oak, linden - any, depending on their availability and needs. The main thing is to be dry. In fireplaces, it is better to use those types that smoke less, do not "shoot".
Heating with wood can be caused both by necessity - due to the lack of another type of fuel, and by one's own desire. Logs burning in the oven create an unsurpassed atmosphere of warmth and comfort, emit a lot of heat, and for the most part provide a healing effect.
Thermal properties of wood
For the preparation of firewood, various types of wood are used as fuel, which differ in structure, density and chemical composition. This has a significant effect on the thermal properties of wood - heat capacity, combustion temperature and heat output.

At a heating temperature of up to 150 degrees, wood turns into coal sediment, which is prone to spontaneous combustion. The temperature regime of 350 degrees contributes to the thermal decomposition of the fuel and the formation of smoke of a light blue or brown hue. Further, hot flue gases continue to ignite, turning into open flames. This stage is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 620 degrees and above.
h3> Wood calorific value table
The higher the temperature of the fire when burning wood, the better the calorific value of the fuel.

We present a table of comparative characteristics in terms of density, combustion temperature and heat transfer of different types of wood.
| Wood | Density, kg / cu. m | Calorific value, kW. h / kg | Specific heat of combustion 1 cu. m, kW | Maximum combustion temperature, С ° | Heating capacity,% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hornbeam | 496 | 4,2 | 2150 | 1025 | 86 |
| Ash | 482 | 4,2 | 2050 | 1045 | 88 |
| Beech | 482 | 4,2 | 2050 | 1042 | 88 |
| Oak | 472 | 4,2 | 2050 | 910 | 76 |
| Birch | 452 | 4,2 | 1950 | 820 | 69 |
| Larch | 421 | 4,3 | 1850 | 867 | 73 |
| Pine | 362 | 4,3 | 1650 | 625 | 53 |
| Spruce | 332 | 4,3 | 1450 | 610 | 51 |
When comparing the calorific value by density, it is obvious that hornbeam, beech and ash emit more heat during combustion than birch, pine and spruce with a lower density index. Besides they belong to valuable species, therefore they are less often used for the procurement of fuel material.

Calorific value is an important parameter in choosing the right fuel. Despite the environmental safety, the heat transfer of coal and charcoal is 2 times higher than that of dry firewood.This means that coal will burn longer and generate more heat energy per unit of time.
Options calorific values are indicated for firewoodwhich are incinerated under the following conditions:
- the minimum level of moisture in the fuel material;
- the combustion process takes place in a closed firebox;
- air supply is carried out in a metered manner.
Flame color
The combustion temperature of wood can be determined based on the color of the flame.

- the fire is dark red - low flame temperature with insufficient heat formation;
- white color of the flame - high temperature with increased traction, which can lead to heat losses;
- orange flame color - optimal combustion temperature with maximum heat transfer.
conclusions
From all of the above, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The most popular firewood for a fire are: pine, birch, alder - due to the massive growth of trees of these species and their ubiquitous distribution. Suitable for both cooking and heating.
- Low-quality firewood that can be used when there are no other options are aspen, willow, poplar. Perfect for boiling water or quick cooking.
- In an extreme case, when there are no trees, dried tall forbs or dung will help out.
- The most unsuitable firewood for a fire is spruce and fir.
- Hereinafter - for wood with a moisture content of 12%, which is quite consistent with the not very old dry wood.
