Troubleshooting options
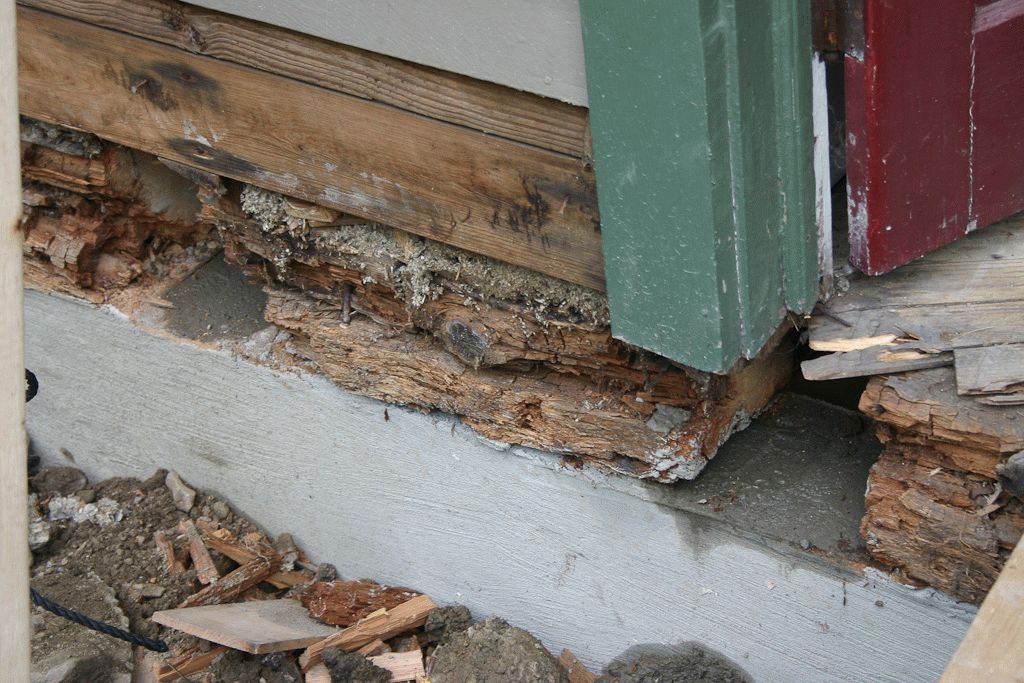
If the surface of the foundation is covered with cracks that do not increase, it is recommended to proceed with their elimination. Damage must be repaired quickly. Exposure to the external environment will only exacerbate the problem. The concrete base will suffer from moisture, precipitation, sudden changes in temperature.
Ice is considered dangerous for the foundation. Physical laws dictate the expansion of water in volume after freezing. The water in the foundation cavity is clogged. Destructively affects the structure from the inside. The critical scale of the development of the foundation crack must not be allowed.
There are several techniques for repairing foundation damage. The choice depends on the cause of the occurrence. When the basement cracked immediately after pouring the concrete solution (after 1-1.5 hours), you don't need to worry. Most likely, the concrete solution is not compacted enough.
A construction vibrator is enough. You need to walk on the concrete solution, compact. Masters are advised to repeat the manipulation regularly when pouring concrete.
Small damage can be covered with ordinary cement mortar. It should be finely dispersed. After applying the substance to the surface, grouting is performed with a trowel, float.
Elimination of the gap from concrete shrinkage
Repair work is simple to perform. The active period of shrinkage of the concrete foundation ends after 2 months. The elimination of the problem is carried out by joining the cracks. The solidity of the base is provided by Dehydrol.
Detailed description:
- A groove is cut on the crack, with a typical section of 20 * 20 mm.
- The resulting groove is filled with Dehydrol injection. The mixture is a highly fluid composition of a waterproofing cementitious agent designed to effectively remove damage. Surface decoration is possible. Beforehand, the time for complete drying of the coating is expected. You cannot proceed to the next stage of construction work until the surface of the base is dry.
 Dehydrol
Dehydrol
Consumption of building materials
The main consumable is the tool Dehydrol luxury brand 5, 3. You will need 800 grams for a groove with a diameter of 20 * 20 mm per 1 running meter.
Methods for eliminating foundation cracks
If, after pouring the foundation, cracks appeared on the surface, and as a result of long and careful observations it was possible to establish that their growth is absent or insignificant, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the depressions. This must be done due to the negative effect on concrete of moisture in all its forms - dew and fog, rain, snow and ice.
Ice has a particularly harmful effect on the base of the house. From the school physics course, everyone knows about the significant expansion of water when it freezes. Moisture trapped in the crack will act on its walls, which will certainly lead to the expansion of the deepening and the destruction of concrete up to a critical scale.
Currently, there are several common and affordable ways to remove acceptable cracks in the foundation. The first of them refers to small depressions that appear in an hour and a half after pouring the mixture. This is usually due to insufficient concrete compaction. In the inquiries of the grief builders, the problem most often sounds like "flooded the foundation - cracks appeared."
If cracking of the fresh concrete is observed, it must be re-compacted thoroughly with a construction vibrator. The same operation, in order to avoid the occurrence of cracks, is recommended to be performed directly when pouring the tape or slab concrete base of the house.
If cracks are found after pouring and hardening of the concrete mixture on the surface of the foundation, they can be dealt with using a finely dispersed sand-cement mortar. It is prepared before starting work, applied to the surface of the cracked base of the house and rubbed with a trowel or float. A more reliable option are special repair compounds for foundations, realized in the form of ready-made dry mixes of a complex composition.
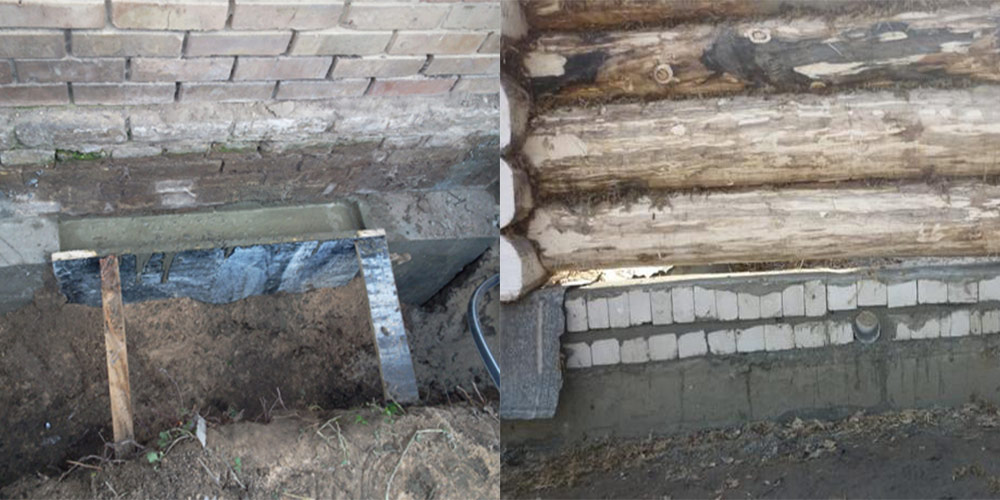
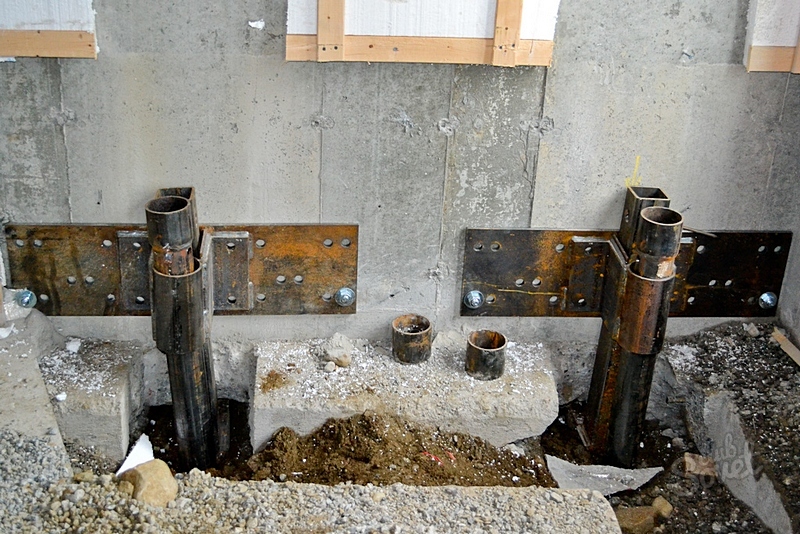
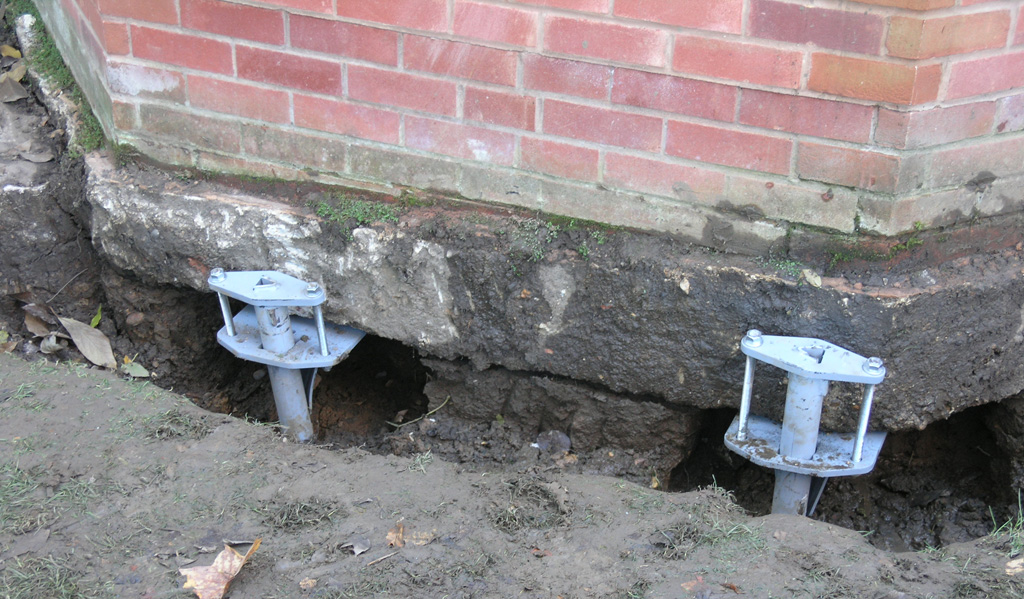
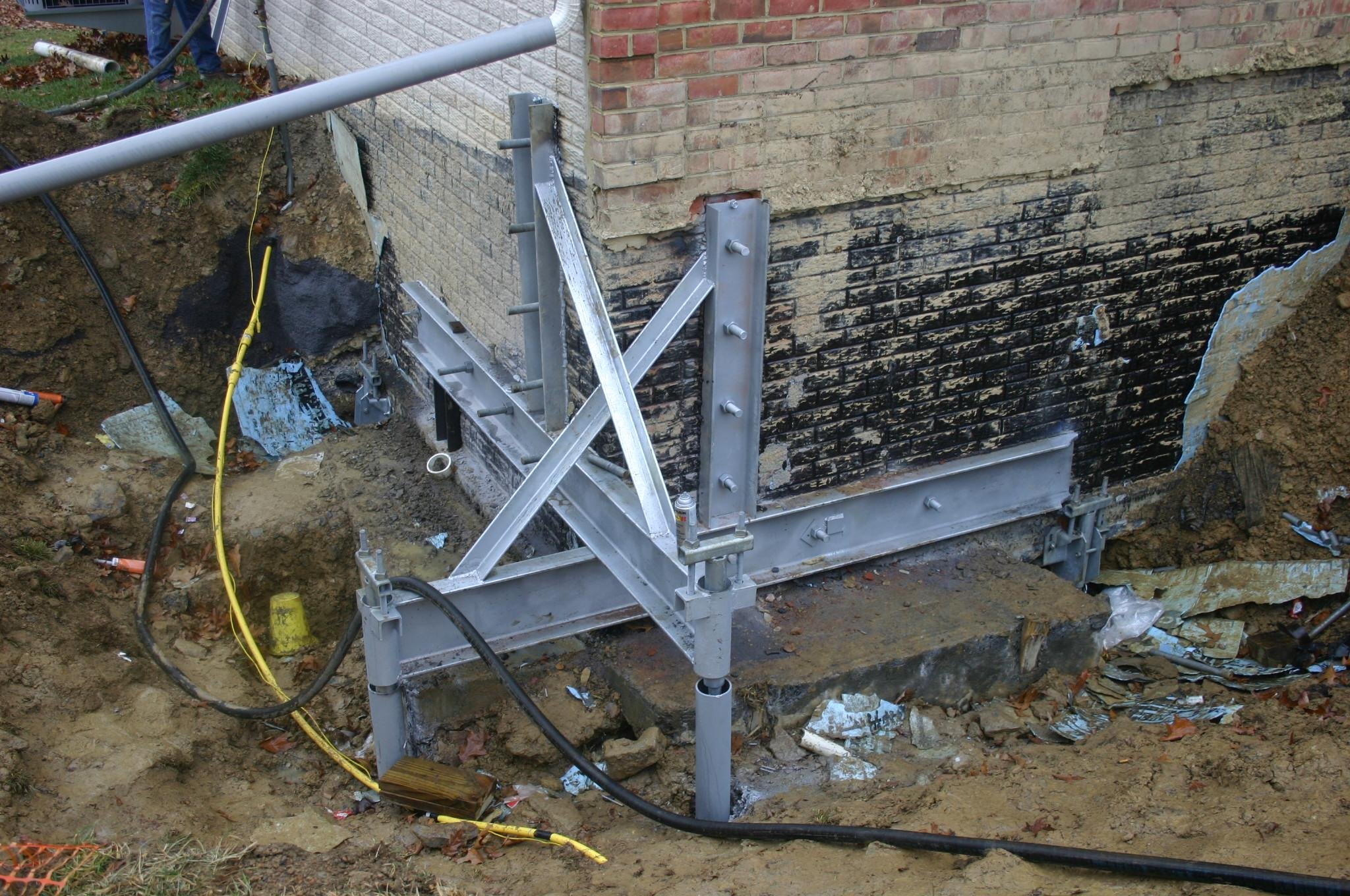
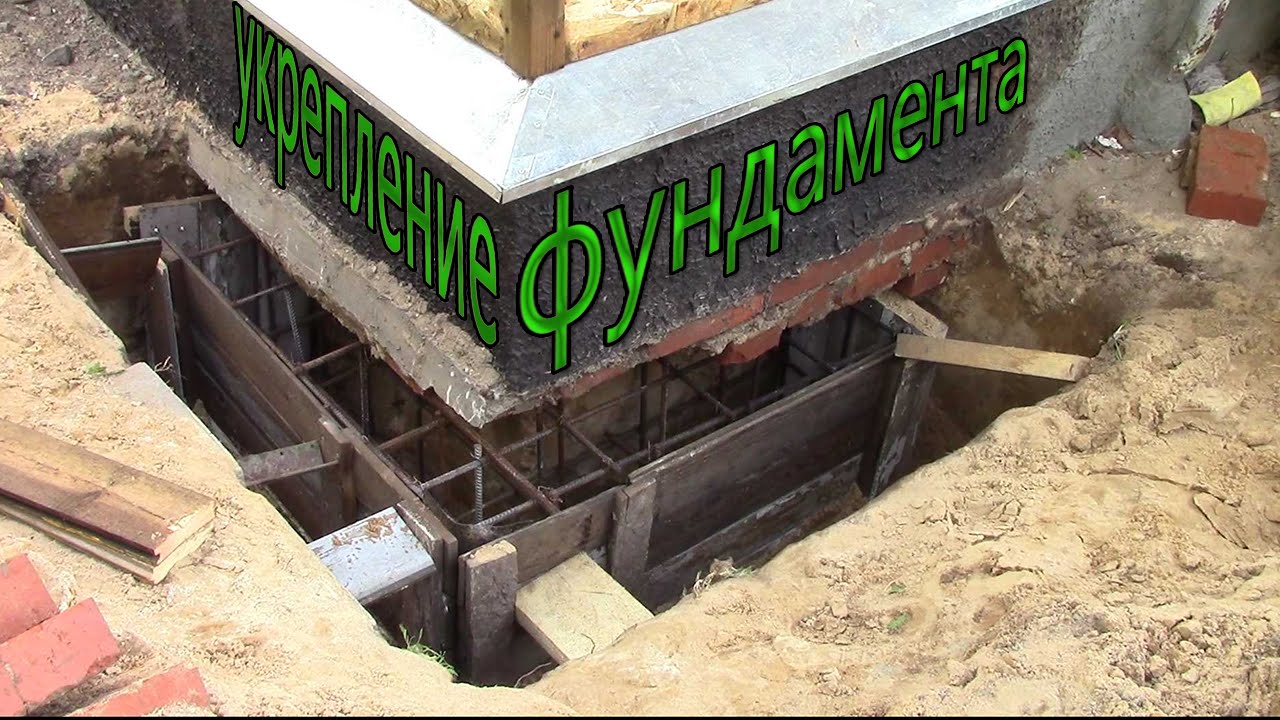
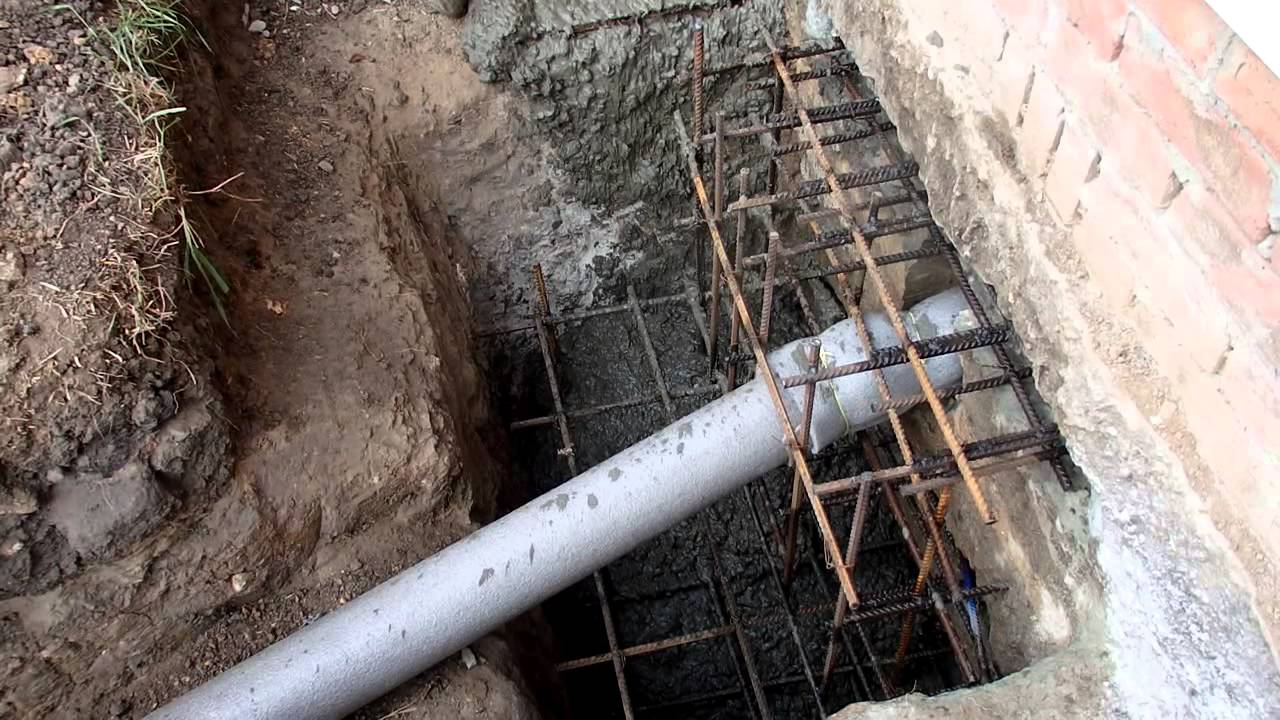
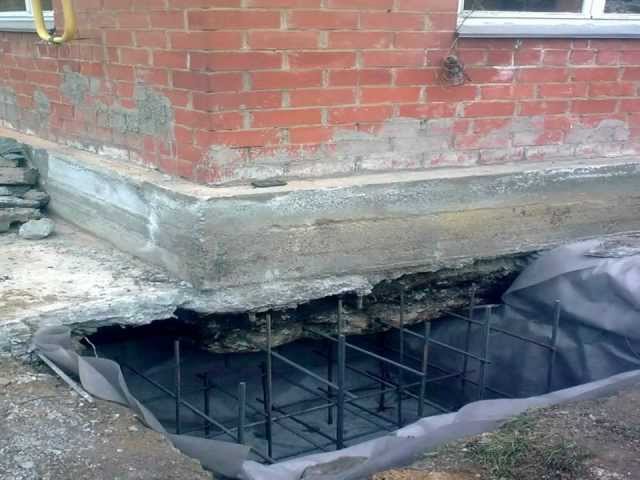
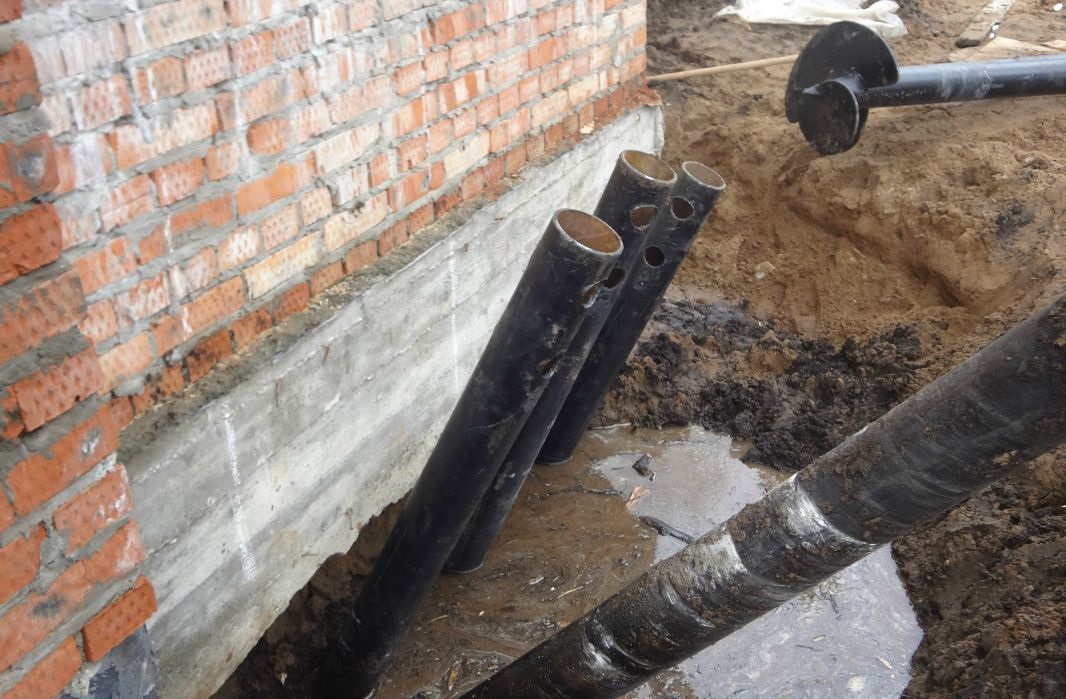
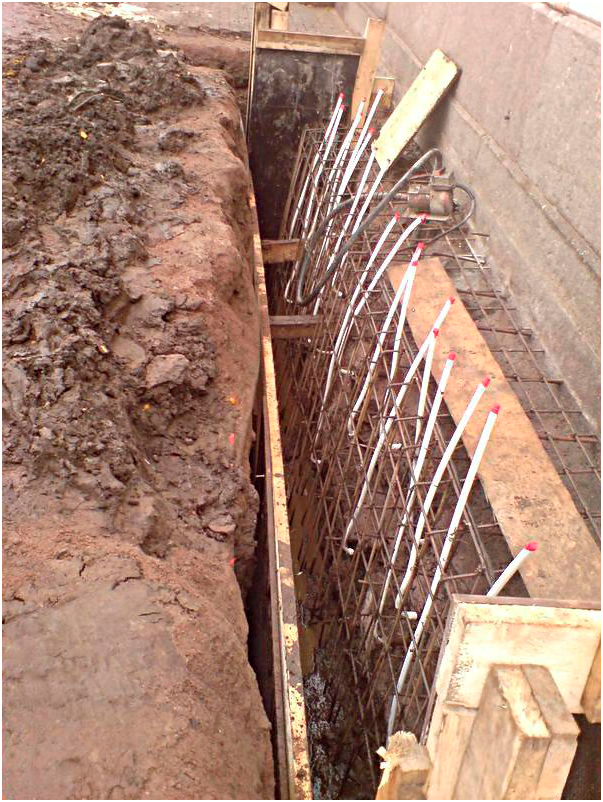
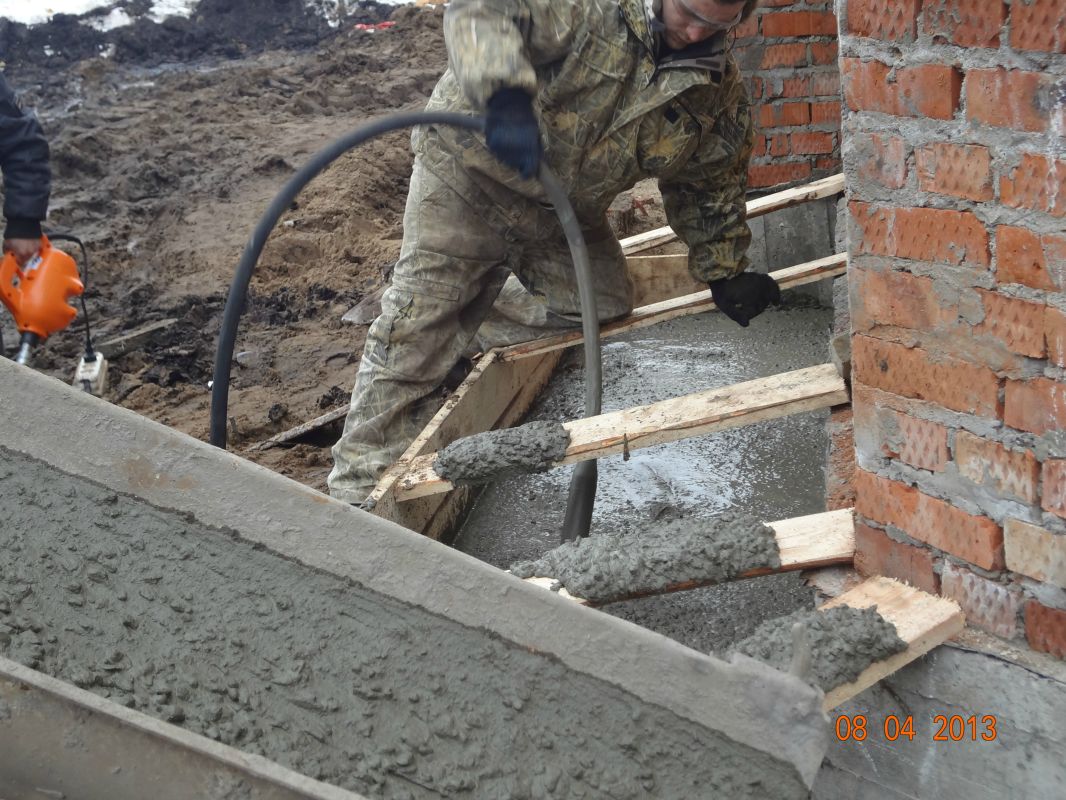
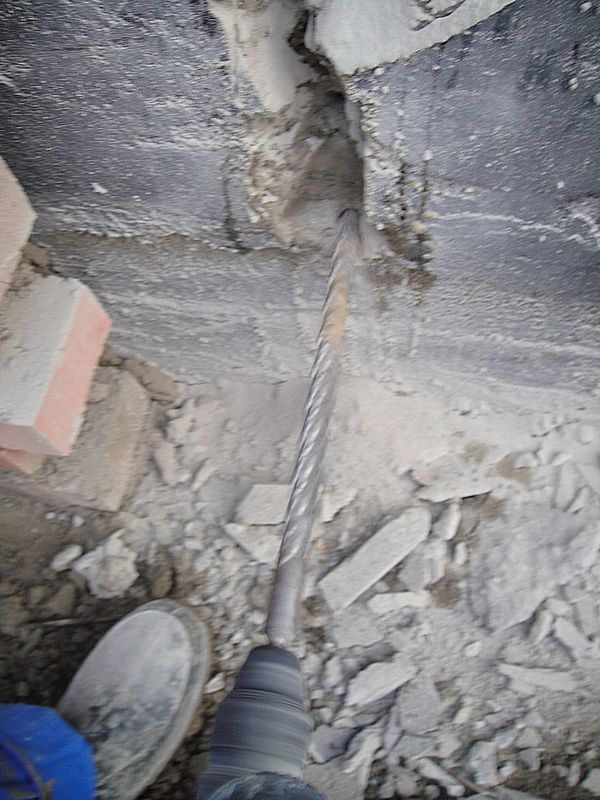
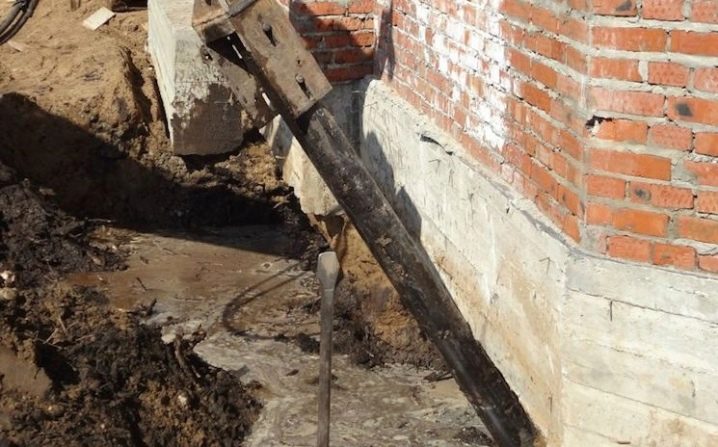
More complex and expensive methods are used to not only get rid of cracks in the foundation, but also to significantly increase its bearing capacity. We are talking about the so-called injection method and the manufacture of an additional concrete base under the existing one. The first option involves drilling inclined holes in the base and walls of the house and pumping special bonding solutions into them. With the second, typical for incorrectly calculated strip foundations, an additional base is mounted under it with a large depth and support area.
Strengthening the base
In the event of the destruction of the basement, it is urgently necessary to prevent the settlement of the structure. Such restoration of the foundation involves the installation of beacons in the cracks. They are gypsum building adhesives. Each label is marked with a date. If the patch breaks, a 35-degree hole is pulled out in the immediate vicinity of the base. Metal and asbestos pipes are installed in it, after which everything is poured with concrete. This process does not stop until the solution stops decreasing. The next filling is done every other day and with the same frequency 3-4 more times.
Eliminate perimeter destruction problems
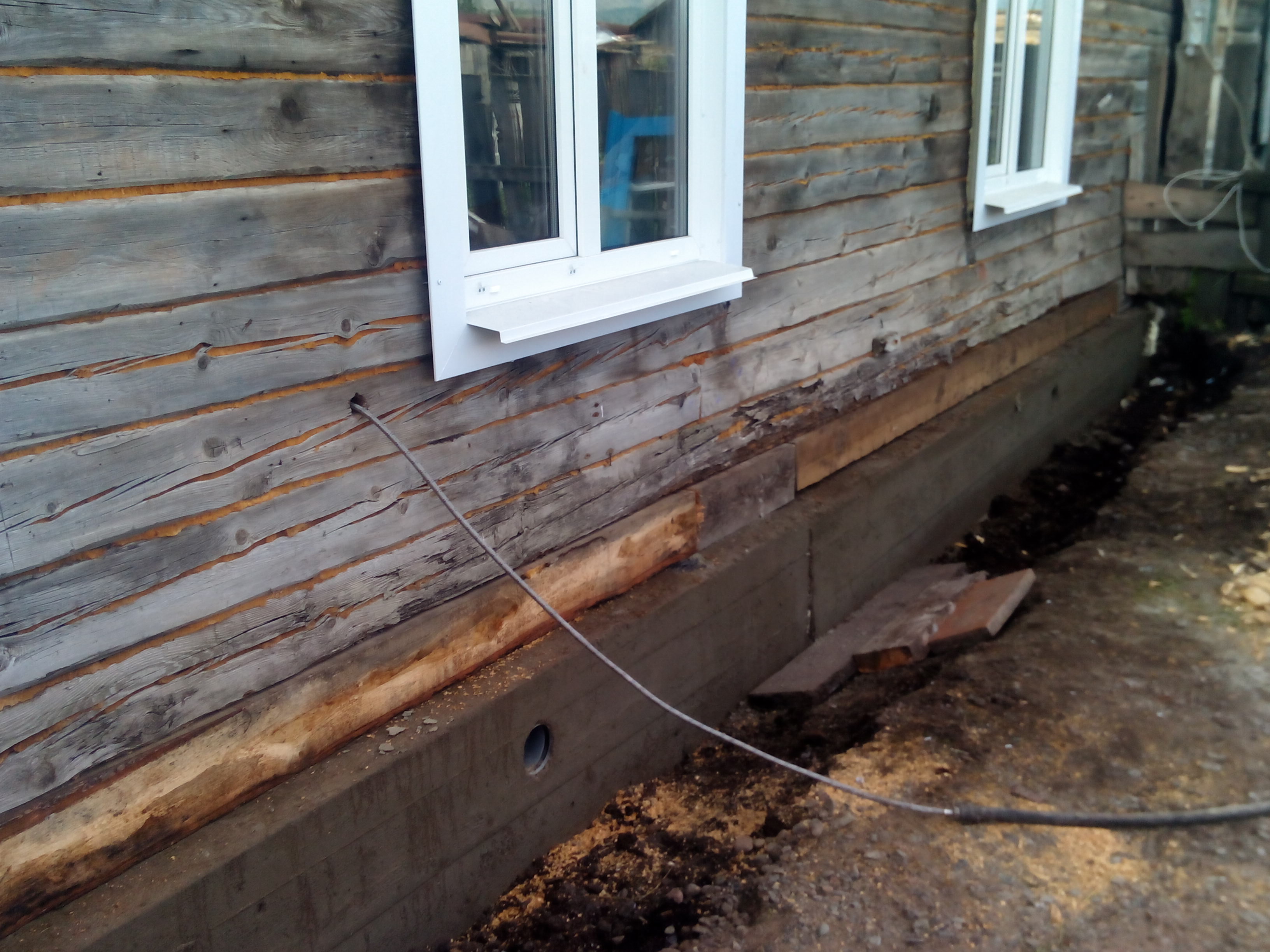
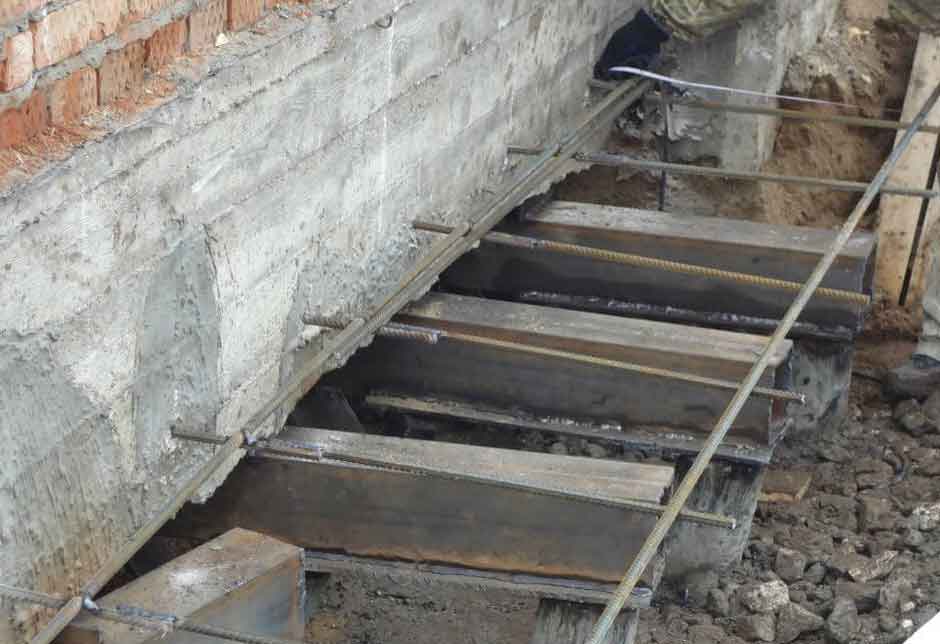
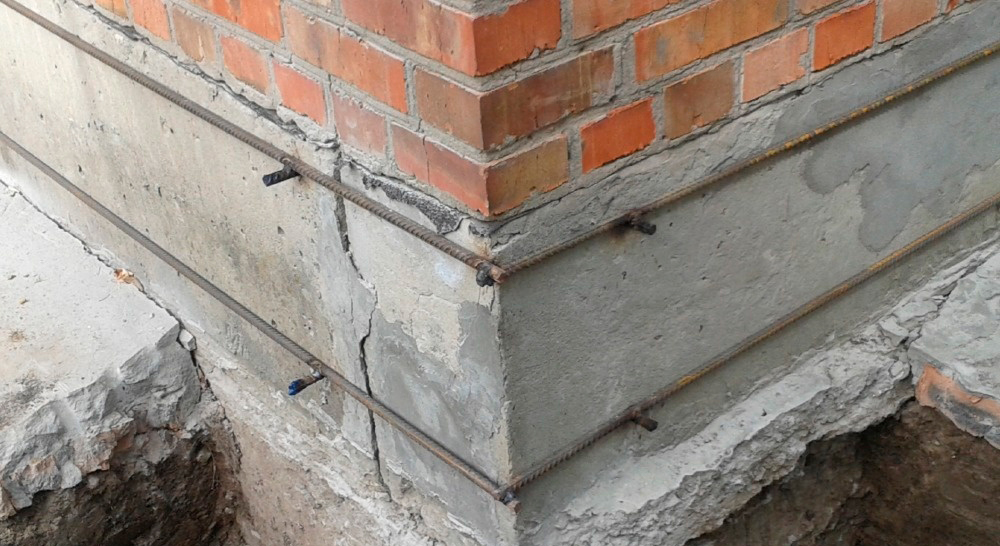
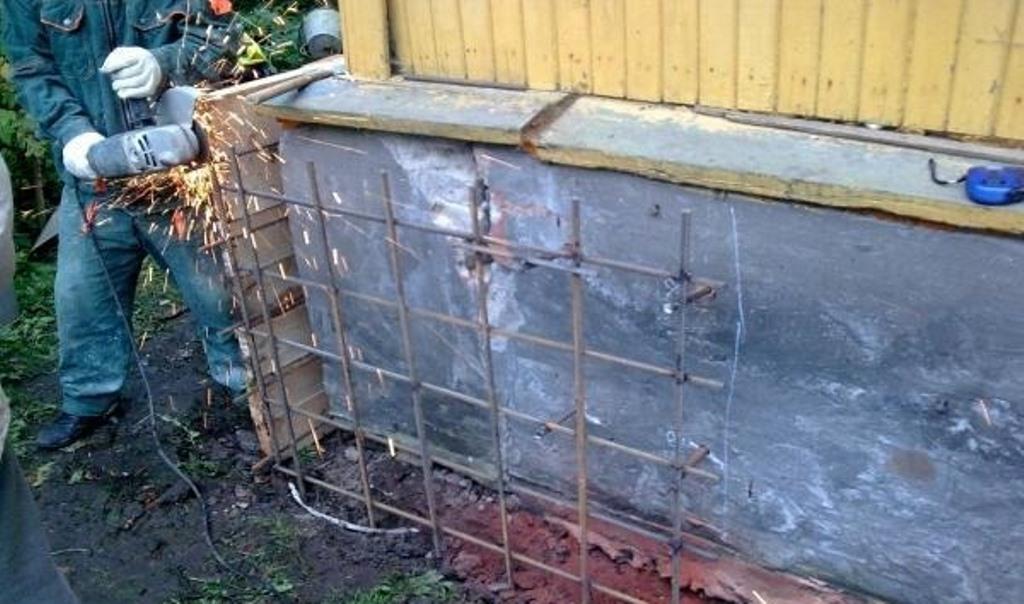
Cracks appearing across the entire base of the building suggest a multi-stage foundation reconstruction. To begin with, remove the plaster and remove dirt deposits, after which a metal mesh is mounted. It is retracted to a certain distance and fixed with anchors on the plinth. At the second stage, the formwork is created, everything is poured with concrete, carefully rammed, and the trenches dug earlier are filled up. Different repair mortars are used depending on the type of foundation. So, it is impossible to strengthen the strip and pile foundations using the same technology.
Improved bearing capacity
This procedure will stop subsidence. For these purposes, a new part is laid out along the weak point. The load is relieved by concrete blocks with iron inserts inside, which will pass through the plinth. Fresh plots are anchored using through-type fasteners.
Note! Reconstruction of the foundations of a brick house takes quite a lot of time, since after each stage solidification and "building up the fortress" follow.
Recovery in case of major destruction
It belongs to the most difficult to implement event. With severe deformation, when the base can no longer be repaired, the load must be redistributed. This suggests that it must be removed from the support in whole or in part.
At the same time, it is extremely important to maintain the stability of the structure itself and the partitions. Such work has many nuances, so only experienced specialists can do it.
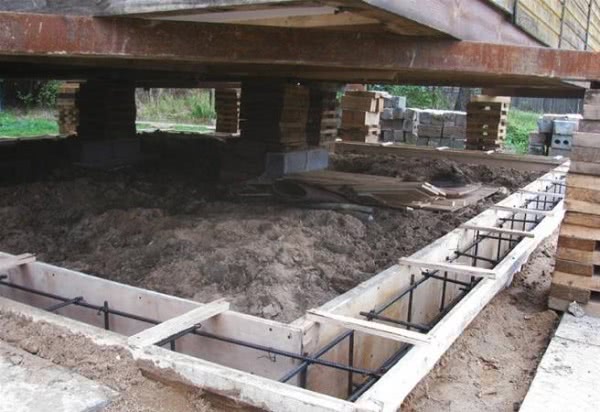

How to observe a crack that appears
After the appearance of a gap in the base of the structure, observation is required. Damage is located along:
- horizontals;
- vertical;
- diagonals.
The dimensions of the slit are small, large, and through.
The horizontal direction of the fault indicates that errors were made during the work. It does not affect the overall stability of the capital structure. The design is safe. The problem is eliminated by plastering the facade, hiding the crack.
Dangerous are large diagonal faults, common cracks in the base. Microcracks in the foundation, barely exceeding a thickness of 1 mm, can form for various reasons. But you need to eliminate them quickly.Moisture, water, penetrating into the cavity of the foundation, exacerbate the problems. The faults will widen.
Step-by-step instructions for determining the nature of the crack:
- The slit is cleaned from cement mortar, dirt.
- Installation of plaster beacons no more than 5 mm is in progress. Control their location.
- Observed for several weeks. If there are no changes, the beacons did not crack - damage from shrinkage. There is no danger.
If the damage to the foundation has intensified, the damage has become through, you need to quickly organize the elimination of cracks. Proceed with the restoration of the foundation of the capital structure.
Foundation survey
If during the examination you find a crack, you need to determine if it is progressing. For this, it is convenient to use ordinary paper tape. Stick it on the damaged area so that it connects both parts of the crack. Check it once a day for 2 weeks.

If the paper is deformed or torn, then it is necessary to urgently repair or change, if the breakage cannot be repaired. If the crack does not grow, then the damaged foundation can be easily repaired, if the problem does not threaten the integrity of the house, then it can simply be filled with cement mortar.
A more informative way to determine the severity of damage is by digging holes. A pit is a depression in the ground adjacent to the foundation. It must be the same depth as the foundation, at least one meter long and they must be made at least 2. To avoid a collapse, it is necessary to install wooden supports on the walls of the recess.


Causes of deformations
Most often, problems with the foundation are due to the following reasons:
1. The foundation has lost its strength
 This event can occur due to the fact that:
This event can occur due to the fact that:
A) Foundation materials were exposed to a chemically aggressive environment.
We live in a difficult ecological situation and it is not surprising that soil moisture can suddenly change from a neutral reaction to an acidic or alkaline one. Over time, such a solvent will leave only one reinforcement from the foundation.
B) Technological errors were made or unsuitable / low-quality materials were used.
The waterproofing or reinforcement may have been improperly done. In addition, private traders often build a base not from the "correct" materials, but from what they have or managed to buy at a cheap price.
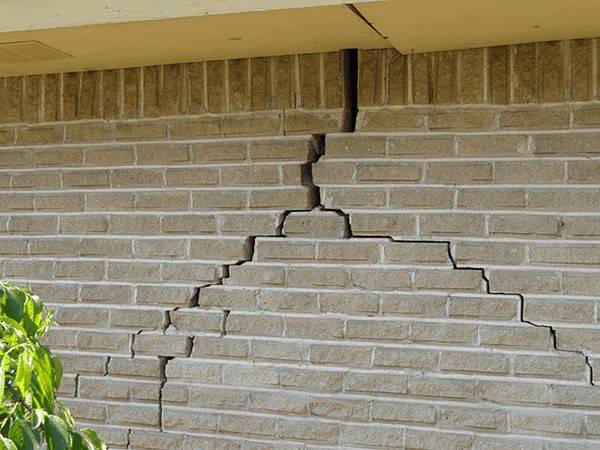

For example, from sand-lime brick or cinder concrete. Most often, such mistakes are made when building small objects that are not used as permanent housing: garages, outbuildings, various buildings on a garden plot.
In order not to spend money in the future on repairing the strip foundation of a country house, use only appropriate materials of proper quality during construction.
2. The underlying soil has partially lost its bearing capacity
 In the overwhelming majority of cases, soil moisture becomes the culprit for this undesirable phenomenon. Flooding provoked by the rise of groundwater or abundant precipitation softens the soil, because of which it begins to sink.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, soil moisture becomes the culprit for this undesirable phenomenon. Flooding provoked by the rise of groundwater or abundant precipitation softens the soil, because of which it begins to sink.
If the base has a heterogeneous structure, some of its components can be washed out. Here, too, the insidiousness of the chemically enriched water can manifest itself. For example, acidic solutions very actively destroy the inclusions of marls and limestones, turning the soil into a fragile porous mass.
Unexpected ground movements may be the result of an unjustified laying of the base of the foundation above the freezing depth.
Moisture-saturated soil also becomes unstable after several cycles of freezing and thawing.
3. The heaving of the soil has exceeded the expected
 Here, too, it was not without water, since its heaving depends on its amount in the soil. The main danger is not so much the heaving forces themselves, but the uneven nature of their distribution.
Here, too, it was not without water, since its heaving depends on its amount in the soil. The main danger is not so much the heaving forces themselves, but the uneven nature of their distribution.
One corner of the house can be raised with swollen soil by 50 mm, and the other by 150 mm. The result of such a skew will be the appearance of cracks in the basement or on the wall.
So, if the soil swelled strongly, the following could happen:
- the groundwater level has risen or the area has been flooded with precipitation, melt water or leaks from the water pipe;
- in an abnormally cold winter, the soil was frozen deeper than usual, while the depth of the foundation was chosen "end-to-end" without taking into account the margin for such a case;
- the depth of the foundation was calculated taking into account the presence of a heating system, but for some reason the building was not heated in winter or was heated poorly.
Causes of destruction
What usually causes deformation of the foundation structure? It is necessary to highlight two main factors.
- The bearing capacity of the soil has become less.
- The material from which the base was assembled has lost its strength.
In the first case, there are several positions, which are often ignored by the developer when constructing a wooden building.
- The type of soil and its bearing capacity were not taken into account. For example, the soil on the site is weak and soft, but the building turned out to be large and heavy. It presses on the foundation, and that, in turn, on the soil, which is pressed under the total mass of the structure.
- Storm and drainage sewerage was not organized. Precipitation undermines the base, it begins to sink. Groundwater has risen, and the soil and the foundation structure are also weakening.
- If another heavy structure is being erected next to the house, which, in its own way, presses on the soil layer. He, in turn, begins to move, rising under lighter structures.
With the loss of strength of the material for the foundation, in general, the situation is not easy. Therefore, when the conversation comes about its construction, you need to contact a specialist. And the reasons for the appearance of defects in this regard are as follows:
- Incorrect foundation type selected.
- This was not how the concrete solution was mixed in violation of technological rules.
- The wrong concrete grade was chosen.
- The level of soil freezing was determined incorrectly.
- Violations were made in the process of pouring concrete into the formwork of the foundation structure.
Therefore, the reconstruction of the foundation of a wooden house begins with identifying the exact reasons for the appearance of destruction.
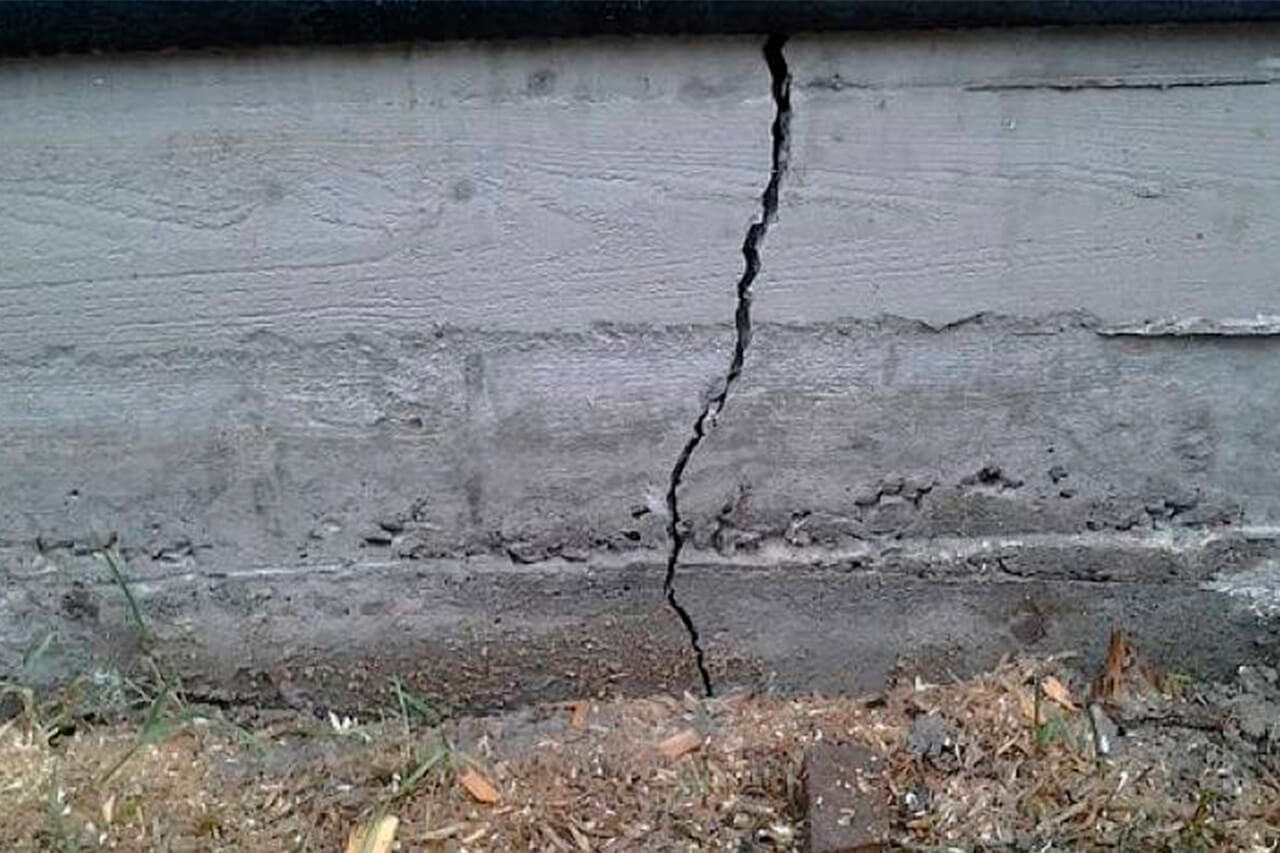
Vertical cracks

This type of crack is more dangerous. If the situation is not emergency, install a beacon on the crack. The simplest is a plaster beacon. Looks like a strip or figure eight. The lighthouse must be fastened to the structure. Remove plaster and loose items from the area.


Do not drain water (drainage) as a first priority, as this may worsen the situation.
Based on observations over the year:
- the crack increases to 5 mm per month and no attenuation is observed for several months, urgent strengthening of the foundation and overhead structures is required
- the crack increases in a year up to 20 mm - and there is no attenuation - work is required to strengthen the foundation and aboveground structures
- the crack increases by 5 mm per year - it stabilizes, but if it continues to grow for several years (3 years is enough), work is required to strengthen the foundation and aboveground structures
- the lighthouse cracked by 0.5 mm - thermal deformations - a sign that the crack has stabilized
Shallow strip foundation, slab foundation (monoblock slab)
Causes of deformation and destruction of the foundation:
- Freezing (heaving) due to the small thickness of the sand preparation (pillow)
- Lack or insufficient drainage of sand preparation (cushion)
- Foundation body is insufficiently reinforced
- Different density of soil (preparation, cushion) under the foundation
- Silting up of sand preparation (the soil becomes very heaving)
Solution options (for reasons in order):
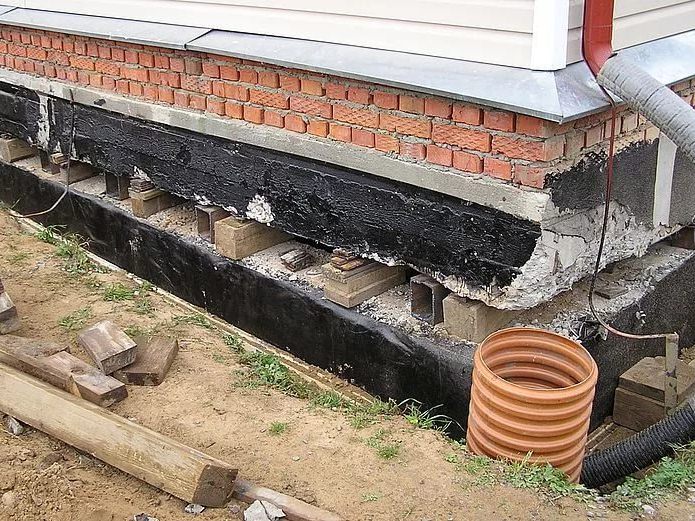
- With a high level of groundwater and sandy loam at the base, drainage should be organized and the blind areas should be insulated
- Drainage device
- For a brick house, reinforce the foundation body with steel ties
- Sign of stabilization of the structure settlement
- Rearrangement of the structure on piles
Pile foundation with grillage.
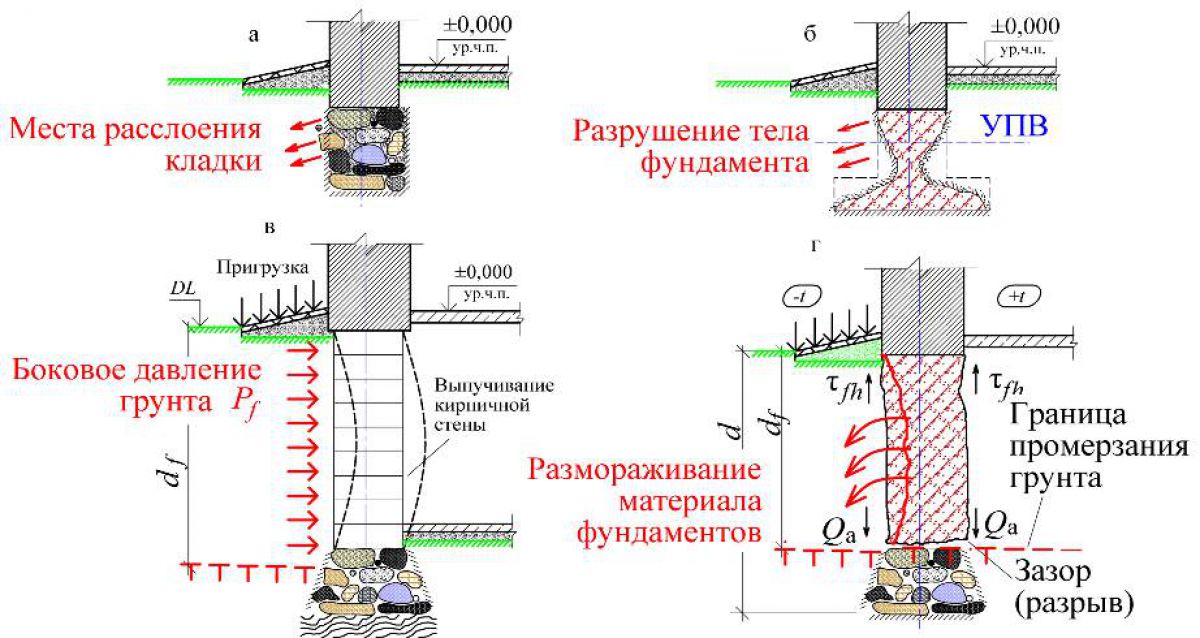
Causes of deformation and destruction of the foundation:
- Tangential forces due to freezing (heaving) along the lateral surface of the pile
- An inhomogeneous base under the tip of the piles
- Insufficient reinforcement or cross-section of the foundation body
- The edge of the pile above the freezing level
- The grillage rests on highly heaving soils
Solution options (for reasons in order):
- Insulate the blind area and foundation or replace the soil around the pile with coarse sand and bring drainage
- Finish off the piles on a sagging section
- Install additional piles between the existing ones
- Insulate the blind area and foundation or rearrange the grillage on new, correctly buried piles
- Insulate the blind area or exclude touching the grillage of the soil (a 10 cm gap will be enough)
Pile foundation (deep piles, no grillage)
Causes of deformation and destruction of the foundation:
- Friction of highly compressible soils
- Poorly compacted base
Solution options (for reasons in order):
- Do not add soil around the house (more than 10 cm), remove the parking lot (if any) from the house on concrete slabs
- Bring additional piles under the settled part of the structure
Strip foundation (the depth is below the freezing depth)
Causes of deformation and destruction of the foundation:
- Insufficient width of the base of the foundation (insufficient bearing capacity of the soil), unevenly loaded foundation
- The depth of freezing is below the depth of the foundation
- Tangential forces due to freezing (heaving) on the lateral surface of the foundation
- Errors in the reinforcement of the foundation body, there are no anti-settling belts in aboveground structures
- The building is not in operation in the winter, freezing of the basement
Solution options (for reasons in order):
- Widening of the sole, driving micropiles, etc. (except for silty soils and peat bogs)
- Insulate the blind area
- Insulate the blind area and foundation, replace the backfill (on non-porous soil)
- Reinforce foundation body and aboveground structures
- Heat the building periodically (the best option is to live in it in winter)