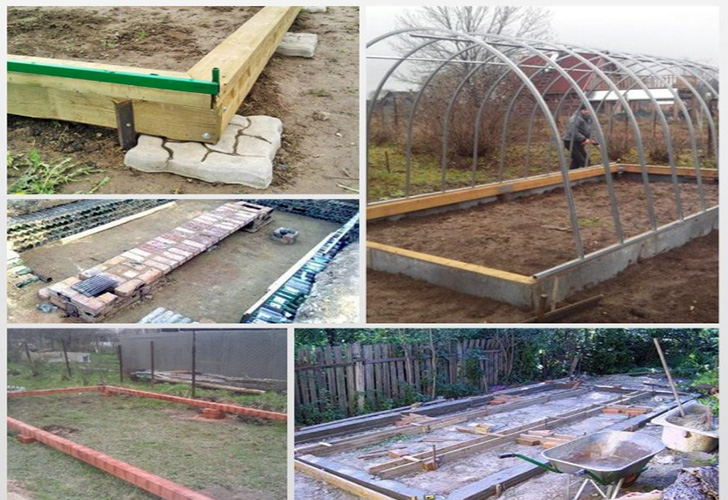
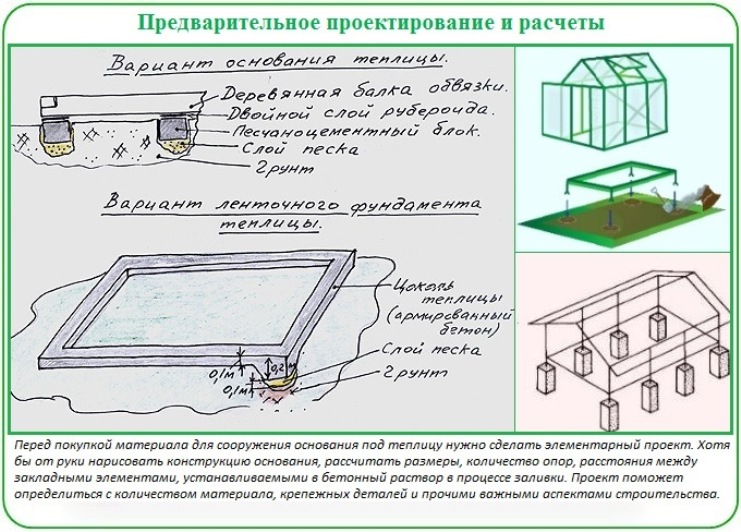
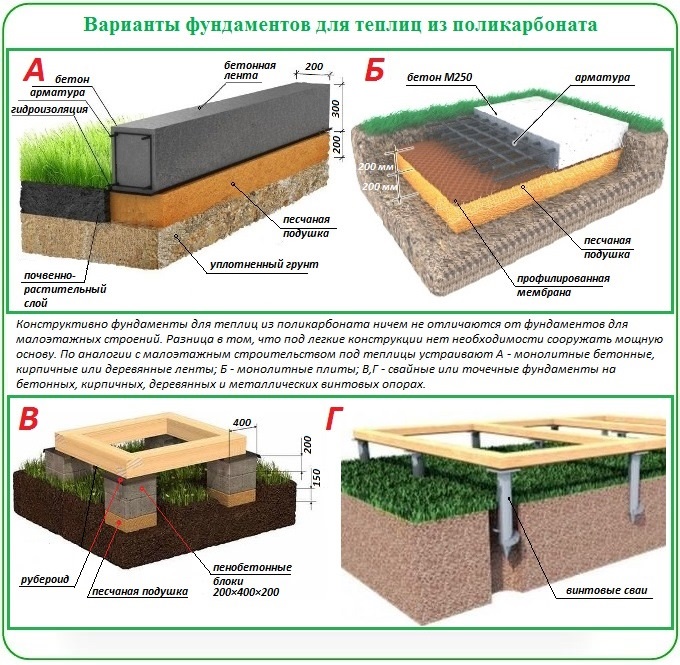
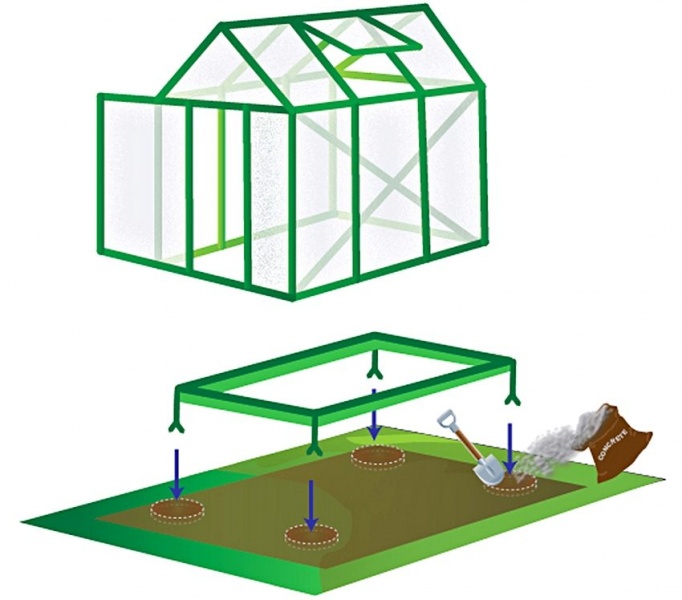
Choosing the type of base for the greenhouse

distinctive features
For polycarbonate greenhouses, it is customary to build two types of bases:
- tape;
- superficial.
The principle of their construction is almost identical, with the only difference that in order to place the strip foundation, it is necessary to dig a deeper trench.
If we talk directly about materials for creating foundations for polycarbonate greenhouses, then in this case there is also some classification. Foundations, depending on the selected building material, are of the following types:
- lumber;
- block;
- concrete and brick;
- slab.
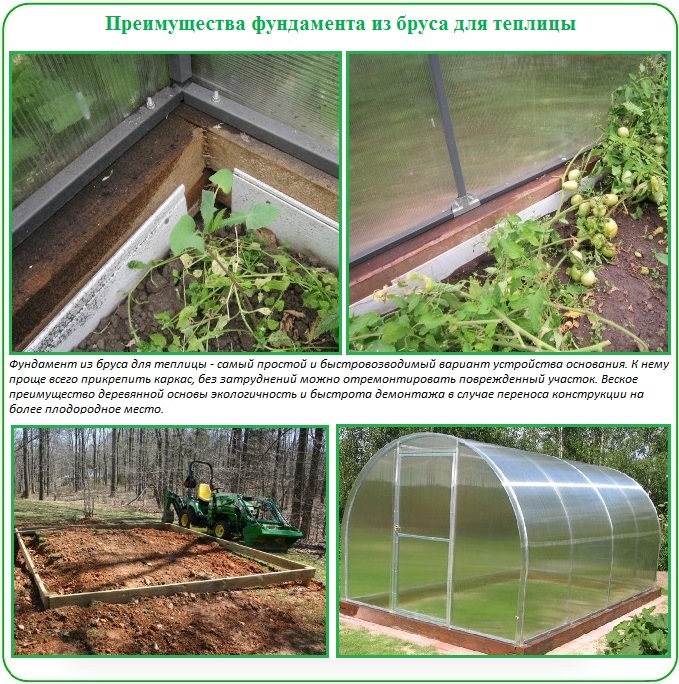
Timber bases are most often used by summer residents, since they are relatively inexpensive. In addition, they are very easy to install, which saves the developer from the problems of studying sophisticated installation technology. In general, a timber foundation is an excellent option for beginners in the construction business, as well as for those who want to save money. True, it also has a significant disadvantage - the material begins to rot after a couple of years.
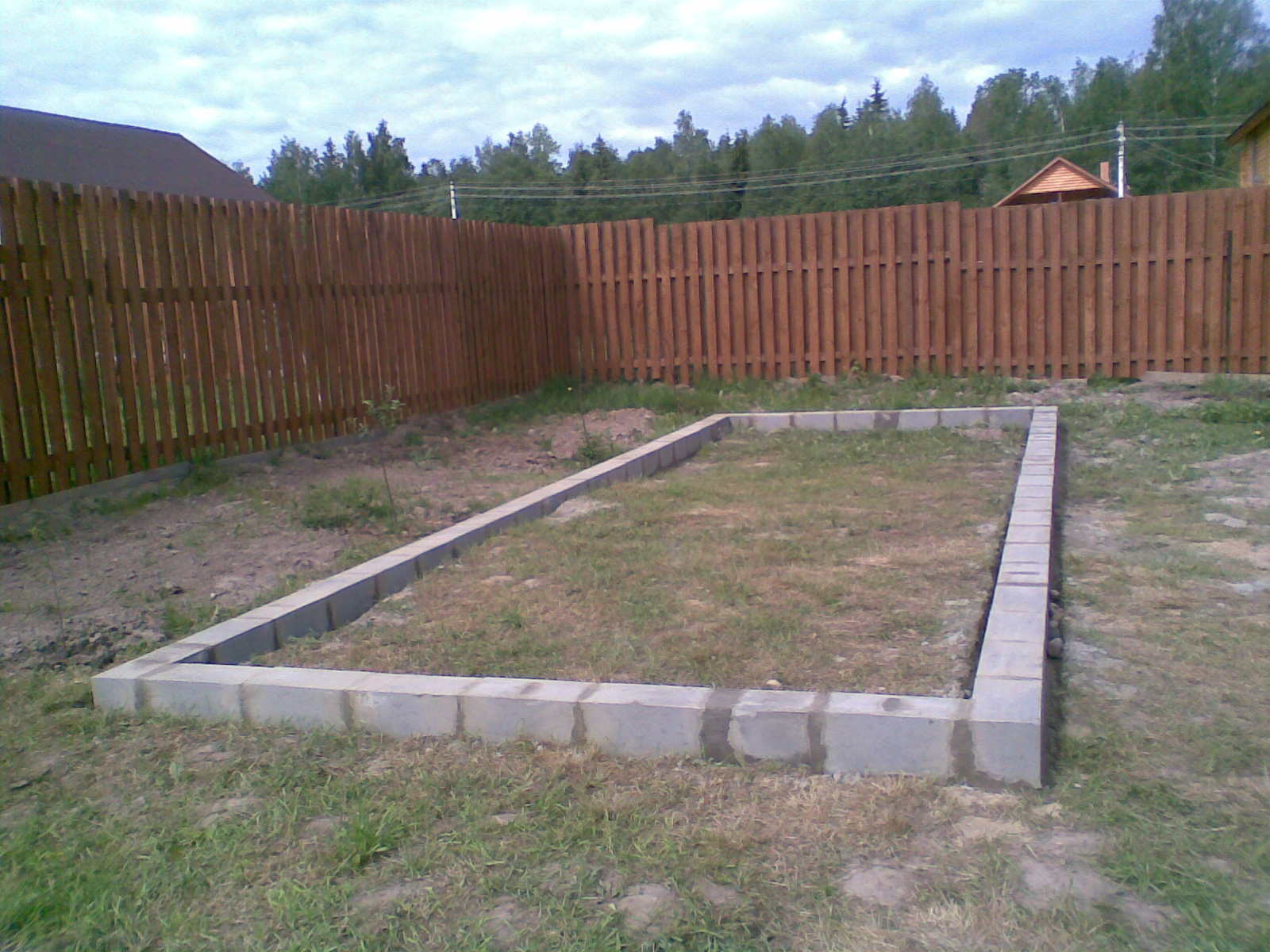
For areas dominated by a humid climate, experts recommend giving preference to block foundations. Such bases are not subject to decay processes, and they are more resistant to stress. Naturally, block foundations belong to a higher price category than timber ones.
Concrete-brick foundations, on the one hand, are very reliable and durable, but on the other, they have many disadvantages. First, the price of materials is far from modest. Secondly, laying bricks on a concrete surface requires a lot of time and effort.
And, importantly, such a foundation is completely unsuitable for year-round greenhouse houses, since in winter it will not at all save plants from severe frosts.
The slab with drainage is the most chic type of base for a polycarbonate greenhouse, and, of course, the most expensive. It is better if the installation of this type of foundation will be carried out by specialists, since in this case you cannot do without skills.
Tips for choosing materials
The materials for the foundation will depend on the functionality, labor intensity, and cost of the foundation. Consider all types of foundations that are suitable for a polycarbonate greenhouse:
-
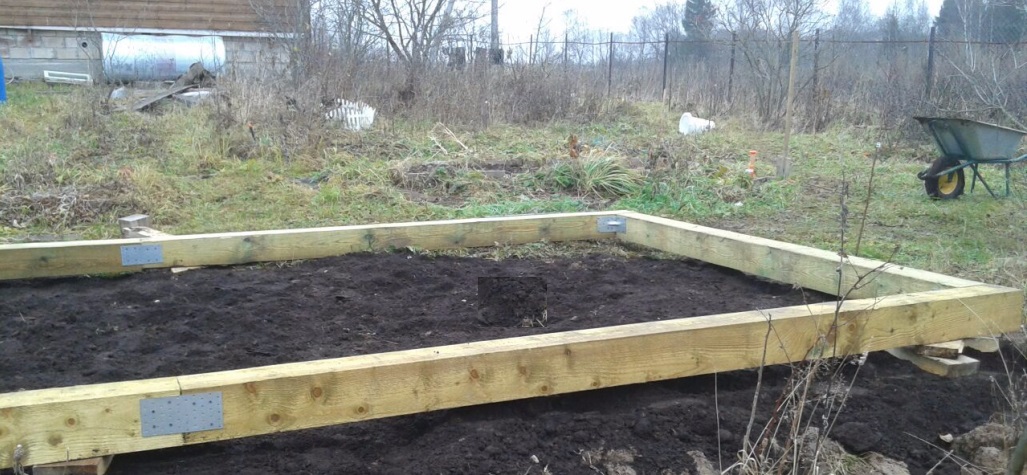
The foundation-frame is made of a bar, which is connected at the corners end-to-end or "in a paw" and placed on a sand-crushed stone pillow (filled into a depression from the removed fertile layer) and waterproofing. Pros: It's quick and easy. Cons: even with a good antiseptic and hydrophobic impregnation, it is short-lived.
-
Monolithic "tape" - is poured into the formwork on the sand-crushed stone drainage mixture either on the ground with the fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow), waterproofing is attached on top. Ready-made concrete or self-mixed cement mortar is used. The most versatile and quickest base in construction: it can be used on almost any soil. But it hardens for a long time.
-
A prefabricated "tape" of blocks connected with a solution is laid on a sand-crushed stone drainage mixture either on the ground with a fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow), waterproofing is attached on top. It is quickly constructed and relatively inexpensive: the price depends on the type of blocks - expanded clay and cinder blocks are cheaper, foam and aerated concrete blocks are more expensive. It is used for all soils.
-
The prefabricated "tape" made of bricks is more difficult to lay. Such a foundation will cost more than a block foundation. He needs a screed (concrete base), which complicates the process and lengthens the construction time. But it is beautiful and does not need plastering. Waterproofing is placed on top.It is laid in any soil.
-
A shallow columnar foundation of blocks connected with mortar is erected quickly. It will be inexpensive. But under it you need to dig a large number of identical neat marked pits. The blocks are placed in pits on the drainage mixture and connected with a grillage (for a greenhouse, a wooden grillage from a bar will be enough). Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used in almost all soils, but it is preferable for marshy and quicksands.
-
A shallow columnar foundation made of bricks on mortar is similar to the same block, but more expensive, and its installation is technically more difficult.
-
An unsubmerged columnar foundation made of concrete blocks is the easiest to manufacture from the above: blocks one by one or two / four (connected with mortar) are laid on a sand-crushed stone mixture on the ground with a fertile layer removed, or simply on the ground, connected with a grillage or strapping. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used for hard soils.
-
A pile foundation made of pipes (metal and asbestos-cement) needs to be connected with a strong grillage, which complicates its construction. The number of supports and pits is much greater here. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to use on marshy soils and quicksands.
-
A prefabricated strip foundation made of heavy concrete slabs connected with mortar can be installed quickly, but only with the help of heavy machinery. If it is shallow, then the walls of the greenhouse will have to be additionally insulated. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is used for all soils.
-
Metal screw piles are reliable but expensive. When screwing them in, skills and special devices are needed. Such a foundation needs a serious, strong grillage. If it is made of metal, it will cost even more, and welding will be required for installation. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to apply on marshy soils and quicksands.
-
A monolithic slab is the most labor-intensive and material-intensive foundation. For a shallow slab, a large pit is dug, and for an unburied slab, a fertile layer is removed. A sand-crushed stone pillow is made, reinforcement is laid. Waterproofing is laid on top. It is applied on any soil. Cons: completely covers the layer of the earth. The fashion for a monolith came from the West - there in greenhouses they always arrange a floor and capital shelves.
For a small polycarbonate greenhouse, it is better to choose a shallow monolithic strip foundation. It is easier to dig a shallow trench on the markings than deep separate pits for concrete "pillars". If you plan to use the greenhouse in winter, then it is advisable to insulate the foundation.
The following materials will be required:
II. Monolithic base for a capital greenhouse
A monolithic flood foundation is used on unstable soils and in regions of harsh climates, for the construction of heated polycarbonate greenhouses. The slab for the greenhouse is poured as follows:
- Using a tape measure, wooden blocks and twine, the area is marked for pouring the base under the greenhouse. On all sides, the markings should have a margin of 10-15 cm, that is, be more than the planned perimeter of the future greenhouse;
- With an even layer, it is necessary to remove the soil surface by 30-40 cm. Fertile soil from this area will come in handy for arranging the beds in the greenhouse. We carefully tamp the earth under the slab, fill it with sand by 20-30 cm and compact it again;
- Around the perimeter, you need to build a formwork from wooden logs or boards and lay reinforcing metal rods on the bottom. The thickness and number of reinforcement layers depend on the loads on the foundation and the perimeter area. For a polycarbonate greenhouse, one layer of metal mesh or a rod is enough;
- Now you need to prepare a solution of sand and cement grade 300-400. The ready-made concrete is poured into the foundation slab along the formwork. It is better to prepare such a foundation in dry weather, it will harden for 7-10 days.
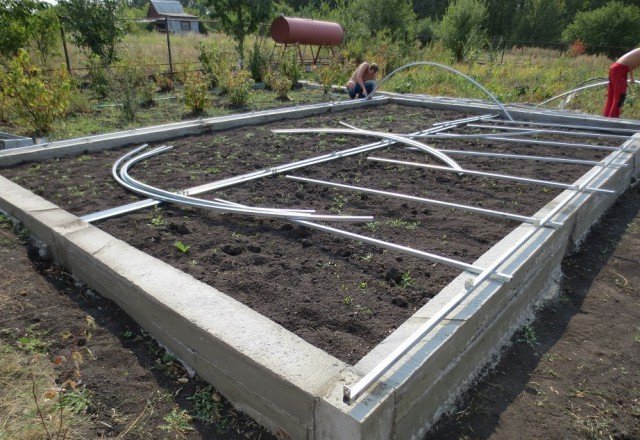
Types of foundations
Strip foundation
A greenhouse needs a solid foundation
The design of the strip foundation is universal, as it is suitable for the construction of the foundation of buildings of any type. Depending on the depth into the ground, it can be:
- Shallow. It is installed directly on the ground, from which the top fertile soil layer has been removed.
- Shallow. The construction provides for a deepening of the order of 700-800 mm. At the bottom of the trench, a sand or gravel cushion is constructed. In the presence of groundwater located on a high horizon, the installation of such a structure is undesirable.
- Recessed. The trench is buried below the freezing level by 200-400 mm, depending on the region.
A strip foundation can be built as follows:
- monolithic made of concrete with a frame made of steel reinforcement;
- using prefabricated blocks that are linked together;
- construction of rubble using stone and clay;
- construction of bricks or foam blocks;
- from scrap materials.
Construction takes place in the following order.
The area that is required for the construction of the foundation is determined.
A pit is dug in accordance with the configuration of the greenhouse, and a pillow is arranged at its bottom. When constructing the formwork, it is necessary to proceed from the calculation that the height of the foundation should provide an elevation above the ground level by 200-300 mm.
The depth of the trench is taken to be of the order of 500-600 mm, and the width is 250-400 mm.
The formwork is mounted on the pillow. A concrete solution is prepared and poured into the formwork. To increase the strength, a light reinforcement belt is constructed.
Monolithic concrete slab foundation
With a high groundwater level or the construction of a greenhouse in unstable soil, it is advisable to erect a slab-type foundation. Such a foundation is arranged in two ways:
- Floating. The concrete platform is located very high, practically on the surface of the ground.
- With stiffening ribs. It is a combined structure. It consists of a monolithic slab that sits on concrete strips. Unlike the strip foundation, the design does not provide for the obligatory closure of the circuit.
For the construction of such a foundation, a pit is required, the depth of which is 300-700 mm. At its bottom, a cushion of sand and gravel is built, which is covered with geotextiles and roofing felt to create reliable waterproofing.
When erecting a light greenhouse, it is sufficient to build a base with a thickness of 100 mm, massive stationary buildings require an increase in this parameter to 200-250 m.
Greenhouse base
Column foundation
The construction of a columnar foundation for a greenhouse saves time and money for its construction. For this, the pillars are deepened by 700-800 mm. When installing lightweight structures, slight deepening is allowed. The distance between the posts should be 1.5-2 m.
Column foundation
The material of the columnar foundations are:
- Brick or rubble stone;
- T-shaped concrete pillars;
- Concrete pillars obtained by casting into a special structure buried in the ground;
- When arranging a non-recessed base, you can use a foam block, a flat-shaped quarry or tree stumps.
The main disadvantage of such foundations is the presence of a gap between the base of the greenhouse and the ground, which allows cold air to freely penetrate into the structure. This is unacceptable, therefore, it is necessary to provide for various measures to insulate the structure.
What type of foundation for a greenhouse is better
The choice of the optimal type of foundation depends on the material for making the greenhouse, the available funds and the time and climate of the region. Glass or polycarbonate greenhouses require a sturdier base. These can be strip or surface types of the base.The installation method is similar, but a deeper trench is required for the tape type.
Among the materials for making the foundation, the popular use of wood, brick, concrete. You can also use concrete blocks or slabs. Each material has its own characteristics of use.
Foundation types:
- Wooden beams;
- Concrete and brick;
- Concrete tape;
- Using blocks;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Monolithic.
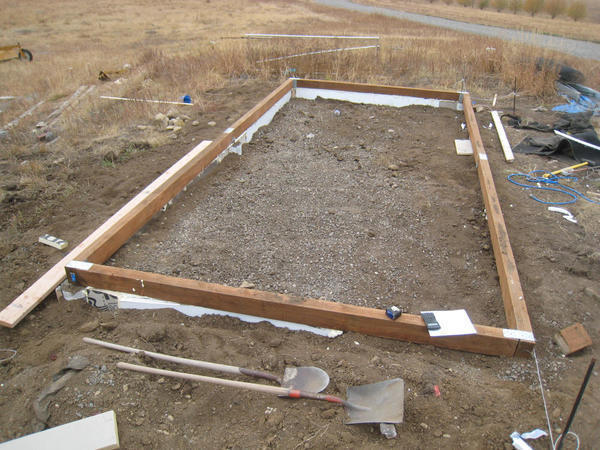

The wooden base is lightweight and affordable. High-quality wood will serve as a material. You can use materials at hand, even the use of old window frames will do. But at the same time there are disadvantages of using wood - a short service life, under the influence of moisture it begins to rot, is exposed to the negative influence of fungus and mold.
The base on a concrete-brick version is lightweight and easy to install. However, it is sturdy and suitable for creating a warm foundation for a winter greenhouse. But this type tends to accumulate moisture and crumble.
The concrete strip foundation is durable and will last a long time. It is resistant to any aggressive environmental factors. But at the same time, it does not retain heat well, it is rather heavy and difficult to install.
Using blocks is a cheap and easy option. It is resistant to the negative influence of external factors. But it has poor thermal insulation properties and low strength.
The columnar foundation has the required strength, durability and low cost. But the installation has its own characteristics and requires rigid fixation and insulation of the base. The same disadvantage applies to the installation of the foundation on piles. The use of a screw-pile structure implies a strictly vertical placement of sleepers. It can be moved if desired. But if the frame is metal, then the piles should also be made of such material.
The monolithic version is quite durable and has a long service life. It protects the soil well from weeds and pests. But at the same time, such a foundation is quite heavy and expensive. In addition, it is necessary to additionally insulate the base. It is also necessary to provide for the construction of a drainage system.
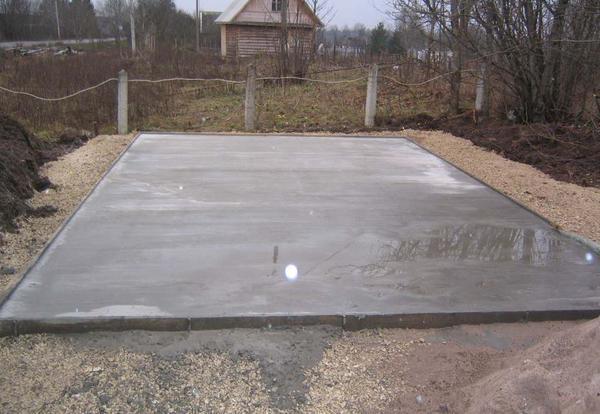

Rules for choosing the right foundation:
- There is no need to build a greenhouse on a buried base. The soil will swell and deform the greenhouse.
- The foundation should not be heavier than the greenhouse structure itself. Otherwise, over time, the greenhouse will warp.
- The insulated foundation is needed only for winter greenhouses.
- In cold areas, a brick-concrete foundation is not necessary. It does not hold heat well, and under the influence of cold weather it will begin to collapse.
- There is no need to build a common foundation for a greenhouse and a residential building. The buildings have different loads.
- Piles and shallow foundations are best used in climates with significant freezing of the ground.
- For polycarbonate greenhouses, it is better to use a strip foundation, monolithic or using cinder blocks.
To build a reliable foundation, you must follow all the rules for building a foundation. Useful advice should not be neglected. Before installing any type of base, it is necessary to prepare the area. To do this, they clear the ground, level it and make markings.
Requirements
Before placing a greenhouse structure on a land plot, it is necessary to lay a solid foundation. It can be made using various technologies using any material.
When choosing a suitable type of base, you should take into account some of the nuances.
The dimensions of the building. The larger its area, the stronger the installation becomes.
This is especially important if the dimensions exceed 40x40 m.
Characteristics of the soil where the installation of the structure is planned. For this, the type of soil, the depth of its freezing and the passage of groundwater are determined in advance.


Since the foundation will serve as the main protection for the building, it must necessarily meet the following requirements:
have a high resistance to the negative influence of the external environment, this is especially important in spring, when groundwater rises in level and snow melting is observed;
be resilient in supporting the structure and frame, strengthen it and withstand the weight of the structure;
provide an indoor climate suitable for growing plants;
be made of high-quality building material in order to maximize all its functions.
Determining the type of building
Greenhouses are built not only from wood, timber, covering them with film. They are also made of polycarbonate. The weight of the polycarbonate top is not large. The method of arrangement and foundation depends on the general configuration of the greenhouse itself.
A wooden foundation from a bar for a greenhouse, can have a horizontal or vertical arrangement. In the case of a small greenhouse, a temporary type, horizontal, is used.
When building large and powerful structures, the second, powerful option is with wooden posts deepening into the ground.
Forest selection
The base is made from a wooden bar of hardwood, it is chosen very carefully. The lower part of the tree trunk (butt) is just what you need for these purposes. There should be no rotten or gray areas affected by the fungus.
The greenhouse is a specific structure. The humidity there is always high, plus chemicals and fertilizers quickly render the structure unusable.
Therefore, the forest must have a moisture content of no more than 20%, otherwise it will begin to deform over time.
Leading to undesirable consequences, subsidence, cracks and distortions of the entire structure are formed, this is unacceptable for a polycarbonate greenhouse.
Treatment
Collecting the wooden frame of the base cannot do without special processing of such a foundation. Biosecurity with special solutions will give excellent protection against insect pests
Antiseptics also need to be used, they provide protection against mold, fungi, which is very important when growing seedlings
Apply it to the prepared timber easily with a roller and a brush. If the polycarbonate greenhouse will stand in a humid place, it is recommended to process the forest by immersion in a special mixture.
Making an impregnation bath is not difficult. The galvanized sheet is bent so that it has two sides and a solid bottom. Then the edges are rolled. It turns out like a trough.
But if there is no suitable material on hand, use a shovel and thick plastic wrap. Dig a ditch and cover it with a film. Having poured the solution directly into the pit, process the timber by immersing it in the solution for 5 minutes. Then dry.
Moisture protection
Creating a wooden foundation for any greenhouse made of metal, wood or polycarbonate, you cannot do without protecting the base from moisture. Moisture is always present here, flowing down the inner surface of the polycarbonate or film.
Usually the beam lies on a concrete base, but sometimes it is laid on a compacted cushion of rubble, laying a layer of waterproofing materials.
Oil is one of the best products. Some impregnations contain different oils, from cottonseed to bitumen-based oils. By impregnating a wooden foundation from a bar, you will significantly extend its service life. Processing is carried out in two layers with a brush or roller with artificial pile.
Greenhouse foundation: functions and features
The foundation for the greenhouse is a reliable foundation for the structure, which prolongs its service life, as well as protects the plantings from negative factors. Many summer residents have a question: is it possible to build a greenhouse without a foundation for the sake of saving money and time?
How to choose a foundation for a greenhouse
Of course, this is possible, but arranging the base for a greenhouse has a number of advantages:
- the foundation firmly anchors the greenhouse to the ground, so that even the strongest winds will not be afraid of it;
- the structure will be located above ground level - this will save about 10% of the heat inside;
- insects, moles and other pests will not be able to reach the plantings;
- plants will be protected from frost, precipitation and other adverse factors.
The greenhouse foundation plays a very important role
Some of the most important characteristics that a greenhouse foundation must have are strength, resistance to the environment and conformity to design features.
- Reliability. The stability of the base plays a special role during the end of winter, since melted snow and water can destroy the entire structure.
- Resistance to negative factors. For the sake of economy, some summer residents build a foundation from improper tools for these purposes (for example, plastic bottles or old tires) or low-quality material, which can be a big mistake - due to the influence of groundwater and temperature changes, such a foundation can quickly collapse.
- Compliance with the size, shape and material of the greenhouse. If the technical features of the structure differ significantly from the features of the foundation, the greenhouse will quickly deform and may even collapse.
Diagram of a wooden greenhouse with a sheathing of cellular polycarbonate
Summing up, we can say that not only the appearance and functionality, but also the "health" of plantings and the future harvest depends on the correct choice of the type and material of the base of the greenhouse.
Greenhouse layout
The optimal bed width for planting tomatoes should be 80 cm, and 40 cm between beds.
And then we proceed to fertilizing.
-
First of all: (taking into account that the soil is mostly acidic) we add dolomite flour, at the rate of 100-150 gr. per square meter. We pour out armfuls from the bucket, rubber gloves should be on our hands in any case. This is an additional feeding not only with calcium, but also with magnesium.
-
Second: The next fertilizer that tomato needs is superphosphate. They bring it 50-80 gr, sometimes up to 100 gr. per square meter. Superphosphate is a difficult-to-dissolve fertilizer, but you should not be afraid that there will be a root burn of the system, because then we will mix everything, level it. And even if the granules are visible, do not be afraid, the plant will not receive a burn.
-
In the 3rd stage: Then we apply Kemira Universal complex fertilizer or Nitrofoska 50 gr. To the soil. per square meter. if you have some fertilizers available, then you can apply them directly to the hole later.
And mix the garden well. The soil must be pre-moistened so that fertilizers dissolve well, and tomatoes like a sufficient amount of moisture, especially when planting. The soil is moist, not only on the bed itself, but even between the beds, the distance, more precisely 40 cm wide, should be wet in the place where you walk. All greenhouse soil must be moistened.
Polycarbonate greenhouse foundation

reliable
- the dimensions of the planned greenhouse house. The larger the area of the greenhouse, the stronger the base should be;
- features of the soil on the site where the canopy is supposed to be placed. This item includes characteristics related to the depth of freezing of the earth, as well as the processes of its thawing.
The foundation is designed to perform protective and supporting functions
In order for it to flawlessly cope with these tasks, it is important to comply with the established requirements when building it. Correctly erected foundation must meet such characteristics as:
- resistance to environmental influences;
- strength to support the greenhouse frame;
- conformity to the size and shape of the polycarbonate structure.
The first requirement is very important for the longevity of the greenhouse house, since in the spring, when the groundwater begins to thaw, a poorly installed base can begin to stagger, leading to damage to the building.As for the strength, but it must be such that the foundation can withstand the weight of the polycarbonate walls, and there is no risk that the frame will simply fall apart
Well, the ratio of the base to the perimeter of the greenhouse is a matter of not only aesthetic, but also a functional plan. In no case should the foundation deform the frame, otherwise the stability of the structure will come to naught.
Types of foundations
The foundation for greenhouses and greenhouses can be created with your own hands using various materials. The result directly depends only on the wishes and capabilities of the customer. The most economical foundation is a point foundation. Its essence is to create an additional frame base under the supporting columns of the building. This coating ensures the stability of the structure, but it does not provide frost resistance. The most practical building foundations are those created with concrete blocks or concrete pours.
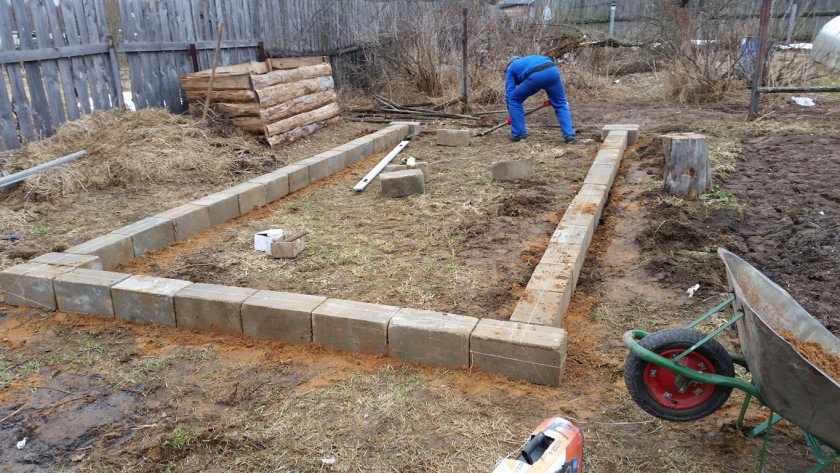
Block foundation
This base is suitable for all types of buildings, from polycarbonate greenhouses to heavy glass buildings. With a high concentration of moisture in the soil, the greenhouse must be erected on a foundation with high waterproofing qualities. Excess moisture is harmful to plants. Waterproof concrete blocks provide the best insulation from moisture.
There are some features of this material:
- blocks are made by casting, which ensures the emptiness of the concrete. It is necessary to initially calculate the dimensions of the material taking into account the seams, since its subsequent splitting is undesirable;
- the process of laying blocks should take place from the corner to the center of the trench with a predetermined doorway;
- the bottom of the trench is covered with gravel (layer - 10 cm). Also, increased moisture makes it necessary to use moisture-insulating clay or sand;
- the first block row is laid out on a 2.5 cm layer of solution. The substrate of each next row is a mortar bed, which is applied to the ends of the blocks. They fit tightly to each other by pressing into the concrete mixture;
- blocks should be located horizontally, especially control over corner blocks is necessary;
- voids must be completely eliminated with concrete mortar;
- the greenhouse frame must be secured with anchor bolts. They are installed by filling the hollow surface with mortar and securing 12mm bolts in the correct locations.
Concrete pouring
The most important stage in the construction of this foundation is the construction of the formwork. You can use self-knocked down boards or purchase a ready-made structure
The formwork serves as a kind of form for erecting a foundation of the required dimensions. The bottom of the trench is covered with sand and only after that the formwork is installed. Its height should reach 40 centimeters, 20 of which are in the trench, and the other 20 - above the ground.
The finished solution is poured in layers into the formwork container. After that, concrete should be carefully tamped in order to get rid of air. Only then can work on the foundation be continued. To increase the strength of the foundation, as well as to avoid cracking or destruction, it is advisable to reinforce the concrete using separate rods or a reinforcing belt along the entire perimeter of the structure. For laying the ground base, brickwork is used.
After leveling the surface, it is necessary to make sure that it is horizontal, and also to install fasteners (for example, anchor bolts) to connect to the greenhouse. The formwork is removed after the base has completely hardened. If all these recommendations are followed, your design will be reliable and durable.
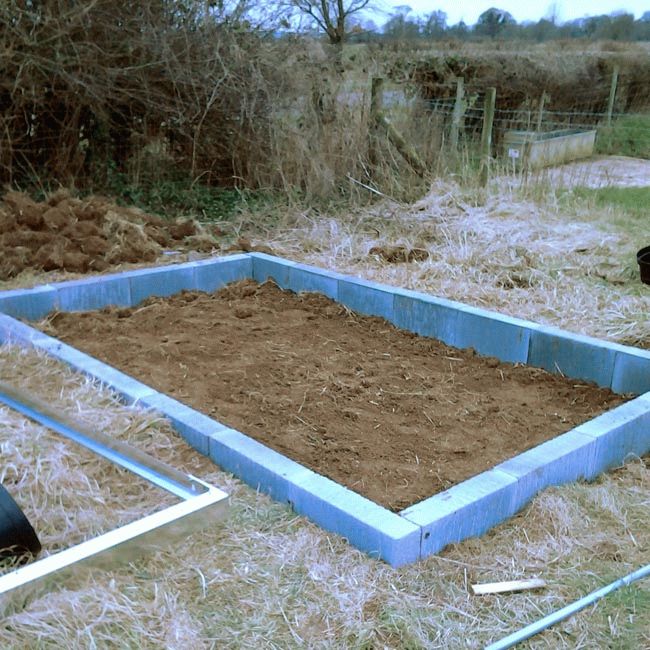
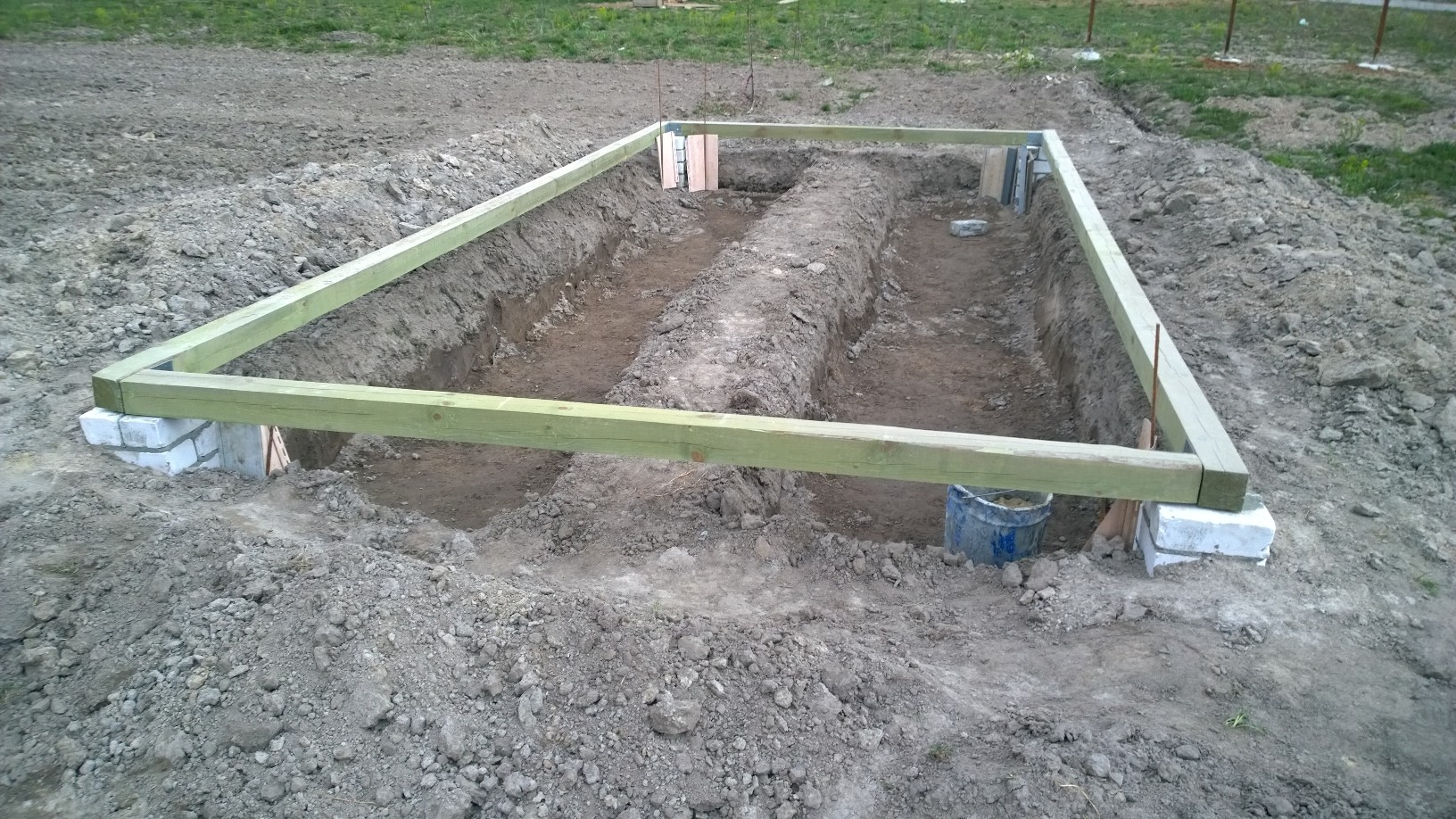
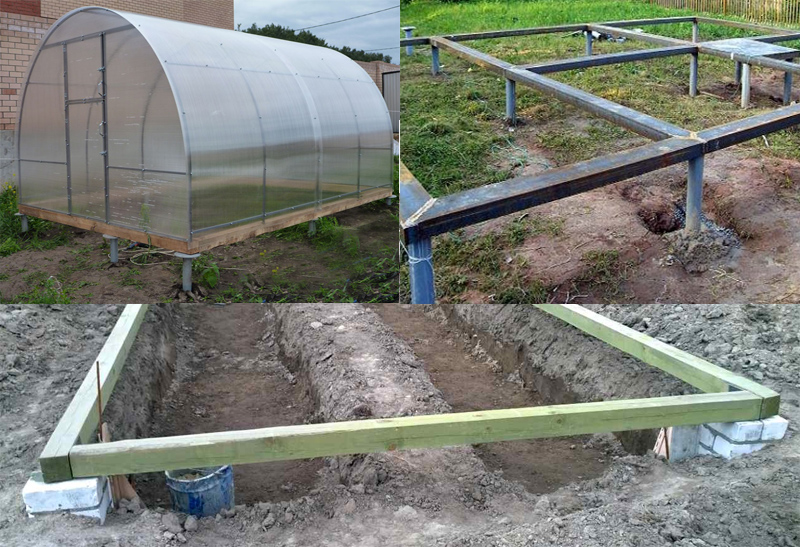
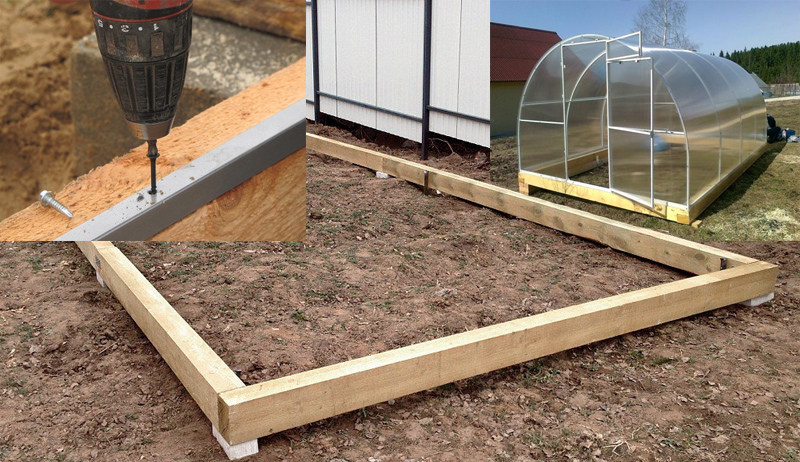
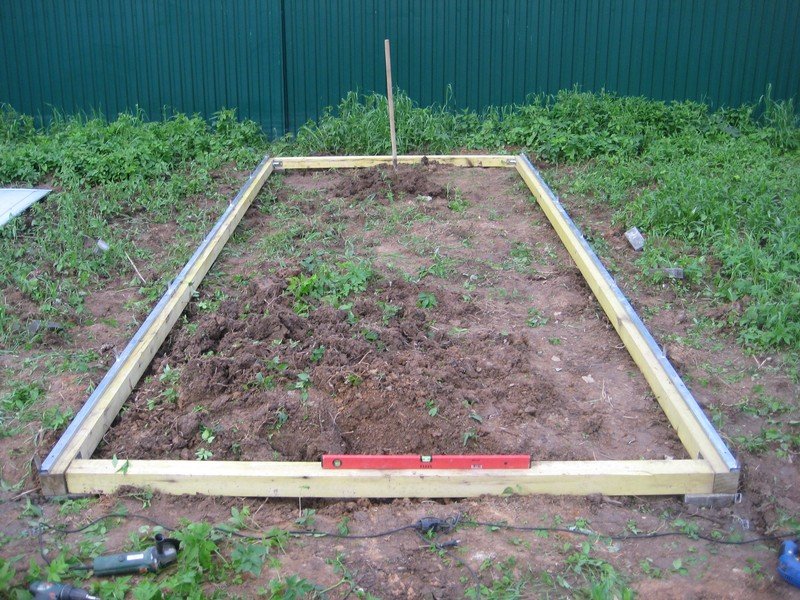
Base on a wooden beam for a greenhouse
You can make a foundation for a timber by purchasing two options for wood. The first is deciduous or coniferous trees. Before work, they will need to be treated with an antiseptic.The second option involves the use of ready-made bars that have already been treated with the necessary substances.
Types of base on the timber:
- Tape;
- Columnar.
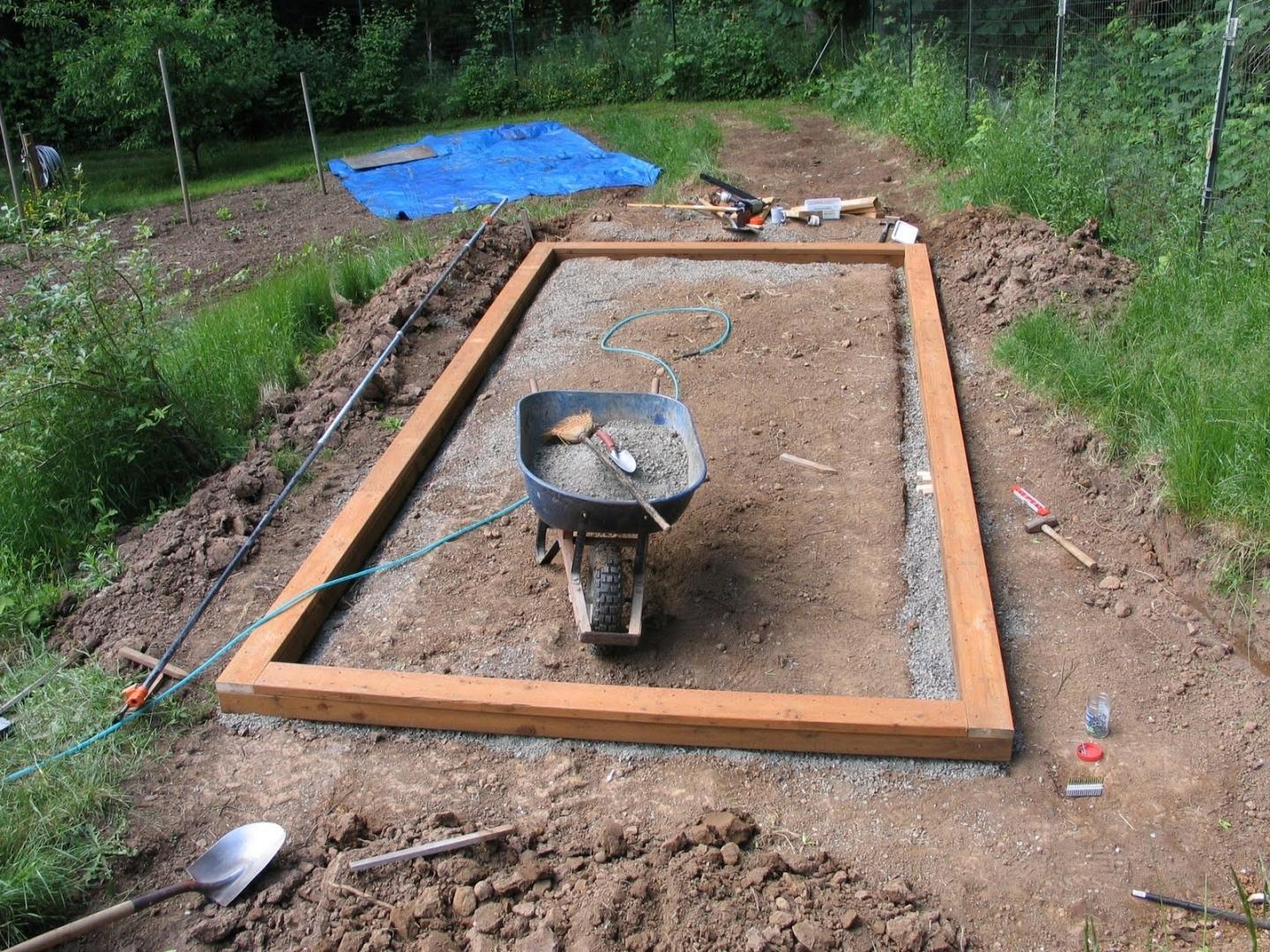
The strip foundation is more popular. Its installation is simple and accessible to everyone. But at the same time, a reliable and solid foundation is obtained.
After preparing the place of work, it is necessary to dig a trench. Its size depends on the load on the foundation. Next, we move on to installing a base from a bar.
Stages of installation of a wooden strip foundation:
- The bottom of the trench must be laid with roofing material to protect the tree from moisture;
- Next, you need to put a bar;
- It is necessary to connect the corner to each other using self-tapping screws, nails, special supports or anchor bolts;
- Next, you need to close the base with roofing material.
The columnar version is cheaper. After preparing the soil, you need to dig holes for the posts. The bottom of the recess must be covered with sand and tamped, having moistened well beforehand. After that, the posts are mounted and covered with roofing material.
Polycarbonate greenhouse foundation - photo and step-by-step instructions
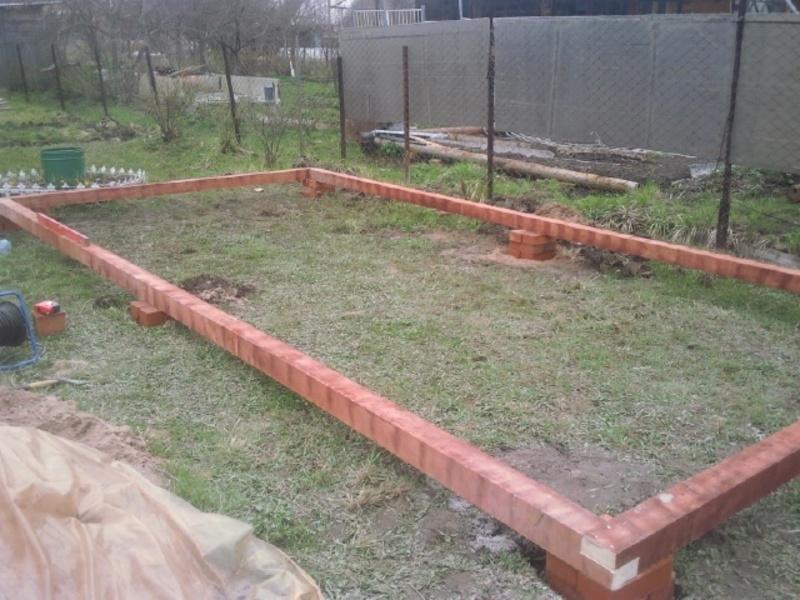
We will arrange a strip foundation for a greenhouse, size 3 * 6 m, with a high brick base and insulation around the perimeter.
Making a drawing
Before building a greenhouse, you should choose a project or make a drawing with your own hands, indicating the dimensions and main structural units. It also determines the materials, their quantity, the main stages of work. It is better to use a typical project and adapt it to your own conditions.
Typical Ergonomic Greenhouse Design
Choosing a place
The choice of location depends on the individual characteristics of the site. It is better to build a greenhouse from the southern and maximum windless side, behind the house. We clear the site from debris, tree roots, weeds. We fence off the perimeter with pegs, pull the rope, check the geometry. The diagonals must be equal. We remove the upper, soft layer of soil.
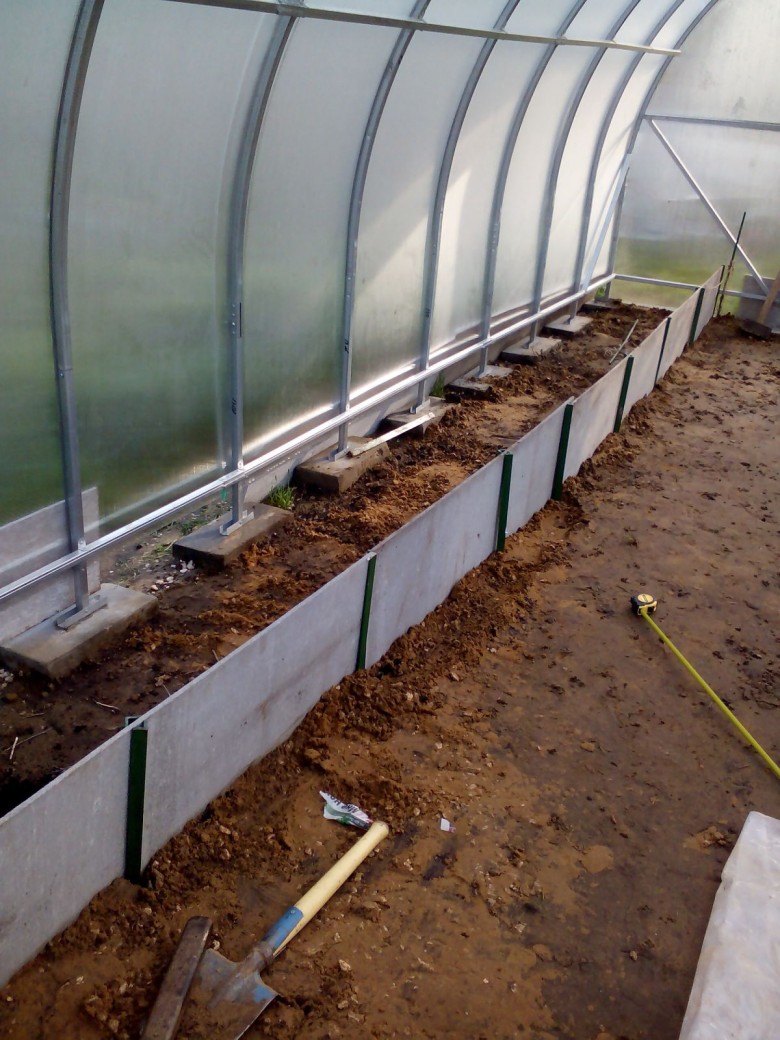
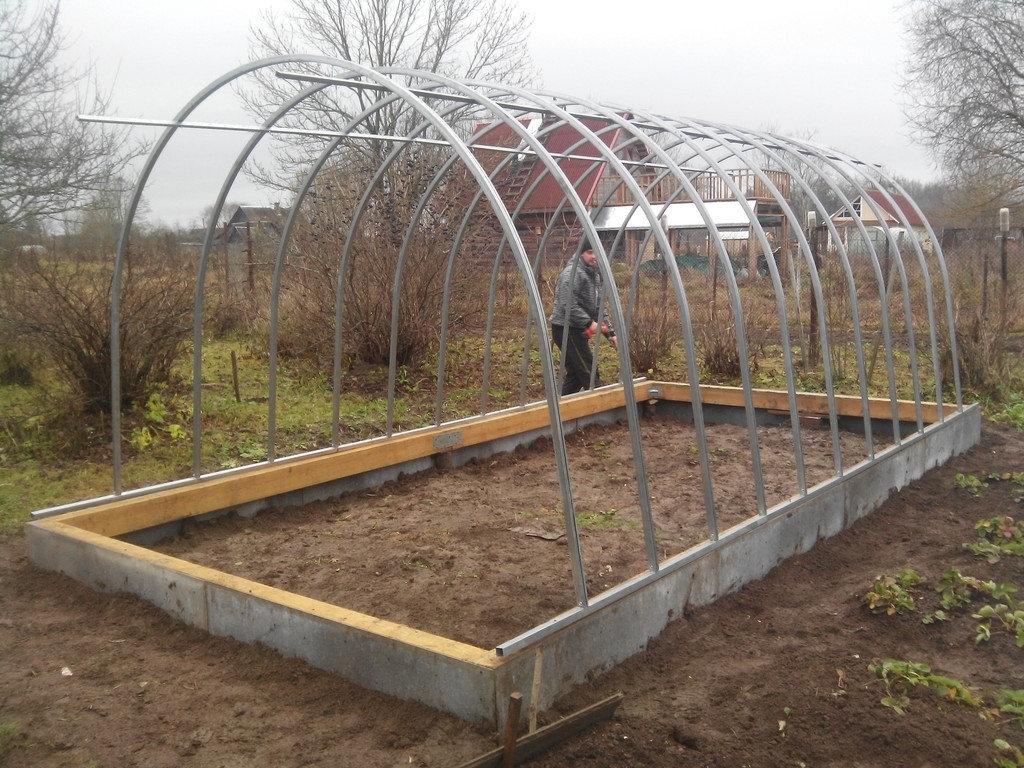
Foundation device
We dig a trench 800 mm deep around the perimeter. Align the bottom. We cover with roofing material for 2 layers, you can lay geotextiles. We fill in crushed stone, sandstone, layers of 100-200 mm, ram the pillow.
We install the reinforcing frame. There will be two horizontal belts, two parallel rods in each, vertical bundles every 300-500 mm. The reinforcement is corrugated, with a cross section of 8-12 mm. We put pebbles, 50 mm high, or stands on the bottom.
We put 2 lower horizontal rods, the distance between them is 200 mm, we lay smooth thin rods perpendicular to better preserve the shape of the frame. At the corners, we bend the reinforcement to the adjacent side, we go in 500 mm or more. Also, on the other hand, a double overlap is obtained to strengthen the structure. We drive in vertical rods, we tie the parts with wire. We mount the upper horizontal belt in the same way.
How to knit reinforcement correctly
The distance between the horizontal belts depends on the height of the greenhouse foundation. If the tape is 400 mm high, then there should be a distance of 300 mm between the upper and lower rods, +50 mm per concrete layer on each side. The width is calculated in the same way, if the overall dimension is 300 mm, then the frame is 200 mm. Remember, the height must be greater than the width of the tape.
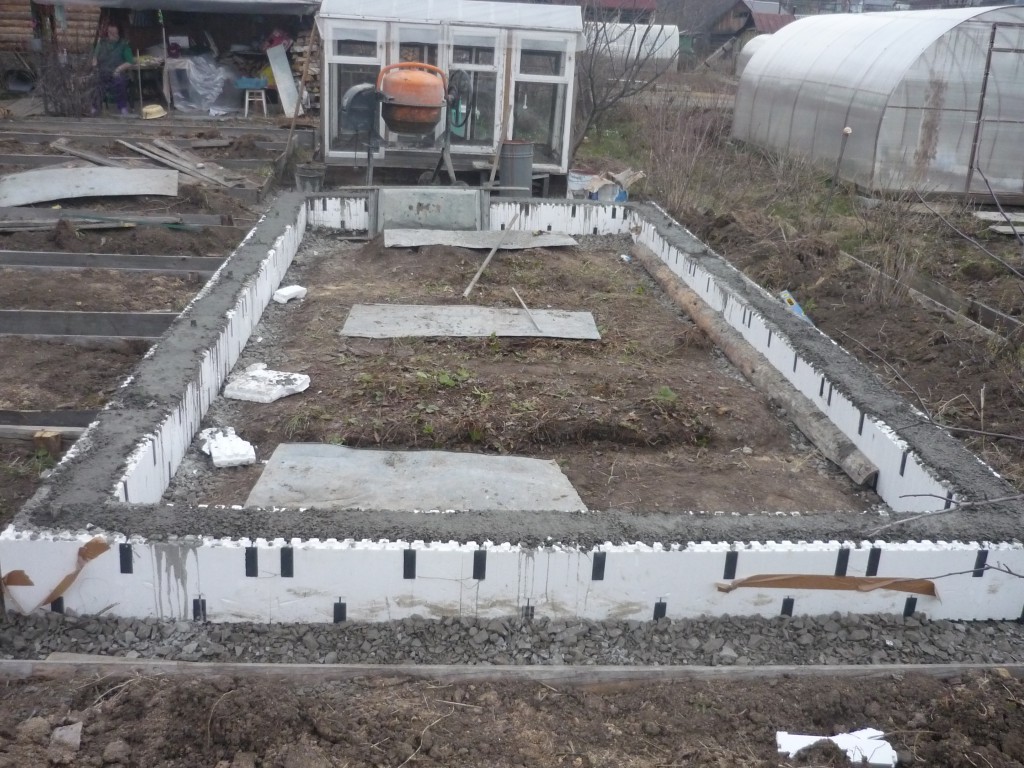
We install formwork in the trench, it can be knocked-down boards from a board, moisture-resistant plywood, plastic durable panels. For the correct geometry, we make a bundle along the top of the sheathing with bars, and on the outside we install spacers, they will hold the structure when poured with concrete.
For your information: In order to preserve heat in the greenhouse as much as possible, to protect the structure from harmful influences, the height of the foundation should be calculated in such a way that it rises 1/3 above ground level.
The tape should be poured in at the same time, so that seams and cold bridges do not form.The proportions of the solution for the foundation for the greenhouse: cement (binder) - 1 part, sand - 3 parts, crushed stone, fraction up to 40 mm (preferably 10-20 mm) 4-5 parts, water 4-5 parts, until the consistency of thick sour cream. First, dry components are thoroughly mixed, then water is added.
In the photo, how to properly fill the base for a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands
Pour the mixture into the crate, ram it, remove the air. Bubbles in the hardened concrete will cause destruction. The solution must be hardened, until it is fully formed - 4 weeks, only then the foundation must be loaded.
We remove the formwork, glue the sides with roofing material or coat it with bitumen mastic for 2 layers, attach foam sheets on top, you can order insulation - PPU spraying. From above we close the sheets with 2 layers of roofing material, overlap seams of 100-200 mm, seal with tape, weld with a blowtorch. Backfilling the soil. For horizontal waterproofing, roofing material is laid on top of the foundation under the greenhouse.
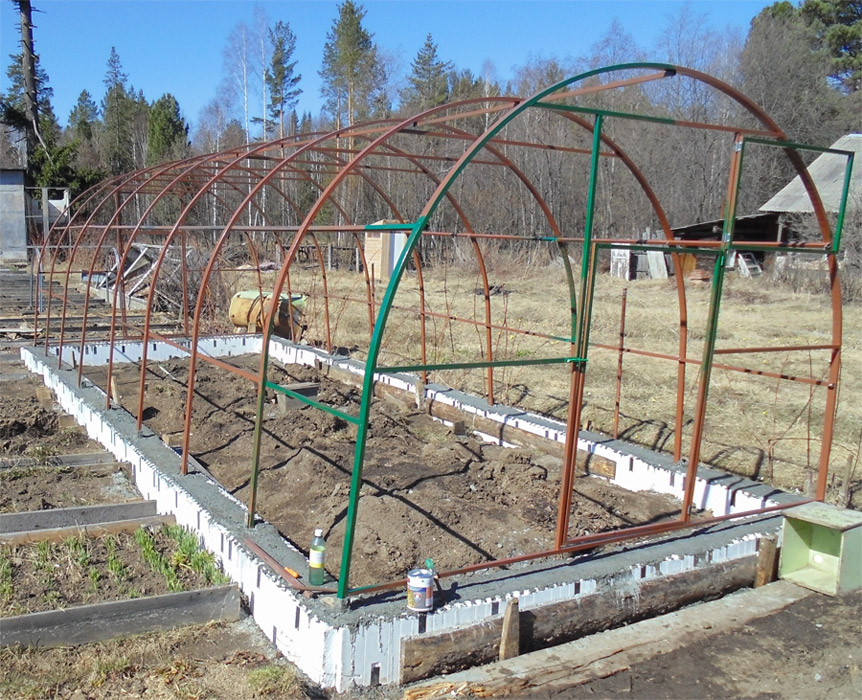
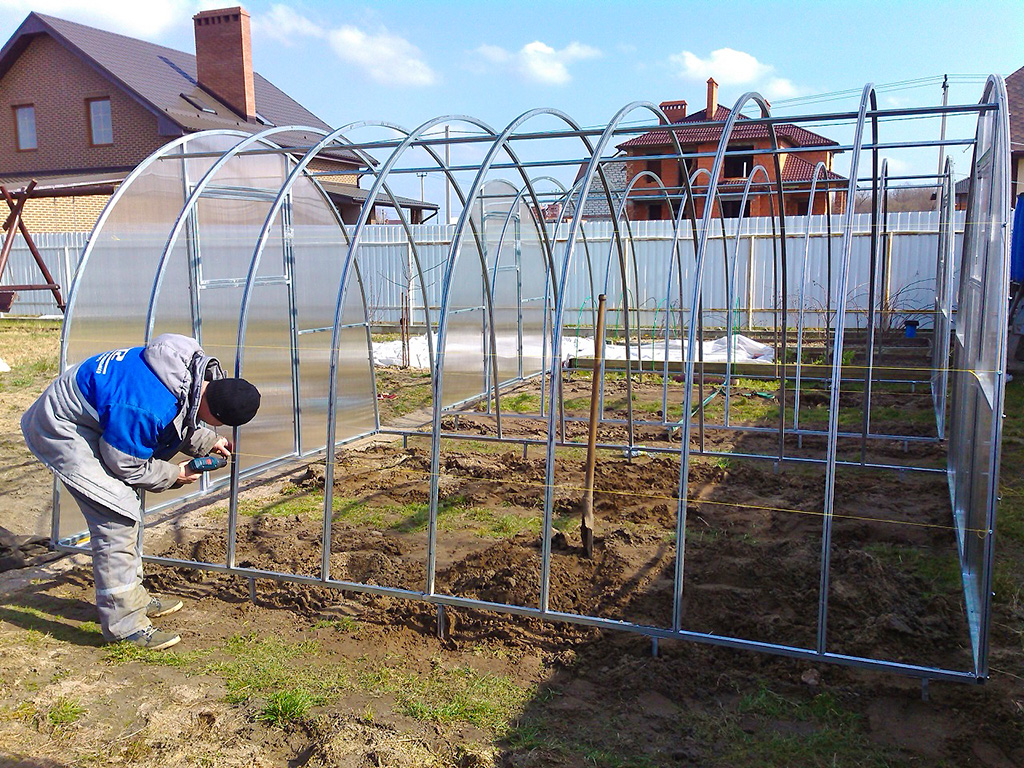
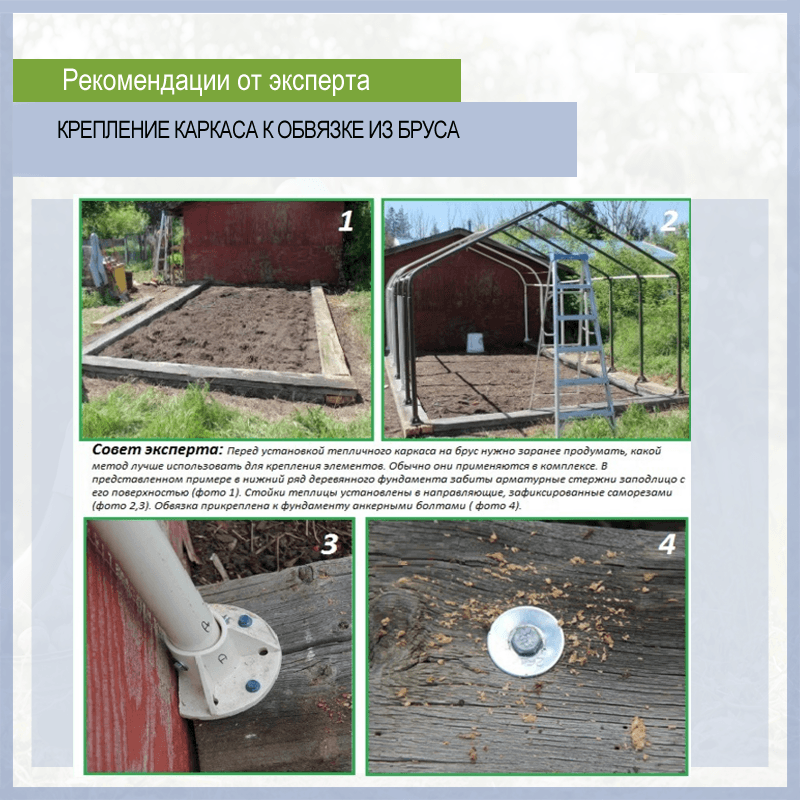
How to install a polycarbonate greenhouse on a foundation
On fresh concrete in the center of the tape, in the corners and every meter, it is recommended to install and release reinforcement for metal structures or special corners with welded anchors to the outside, for fixing the bars, the greenhouse frame will be attached to them. If the mortgages were not provided for in the process of pouring the foundation for the greenhouse, then the frame can be fixed with anchor bolts.
Method of fastening the frame to the foundation
The installation of a polycarbonate greenhouse on the foundation has another important stage: in order to avoid drafts, ice, freezing, the gap formed when the base of the greenhouse adjoins the foundation is sealed with elastic sealants, a gasket with rubber edges is placed in the gap
This is especially important if the structure is insulated and it is planned to grow crops in it all year round. When equipping a winter greenhouse, do not forget about additional lighting and heating
About sowing dates
When do you need to sow seedlings? A lot of literature has been written, how much seedlings need to be kept. Someone thinks that 50, others 60 days from the beginning. But there is no need to rush. Seedlings that are received later, it still catches up with previously planted seedlings, and it turns out to be good and strong.
A good seedling is one grown under the right light and temperature, it is compact, leaves are close together, and has a thick stem.
There can be various containers for growing seedlings, plastic bags or pots, other devices, but a prerequisite is that the volume must be at least 0.5 liters. and not very high capacity.