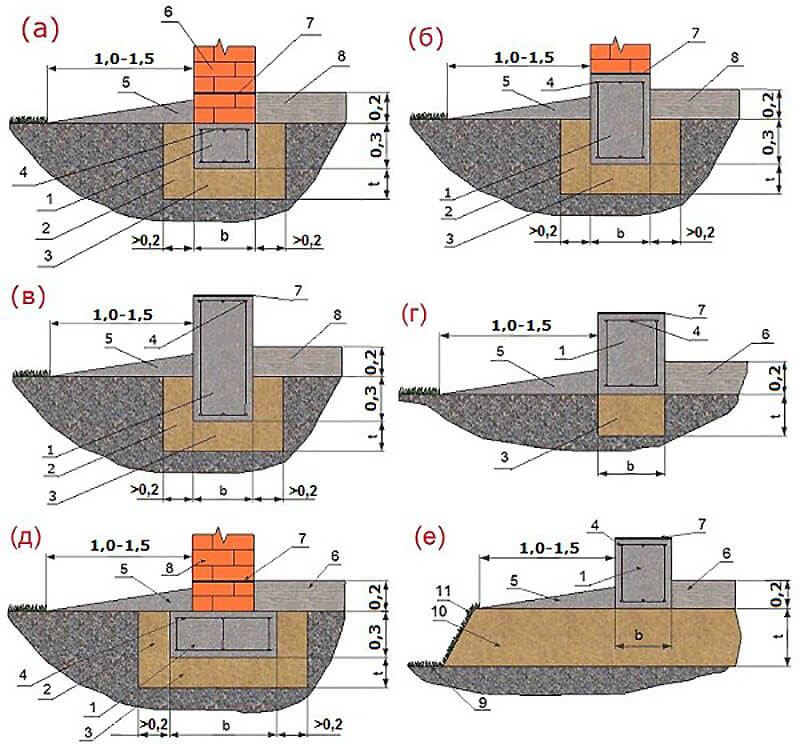
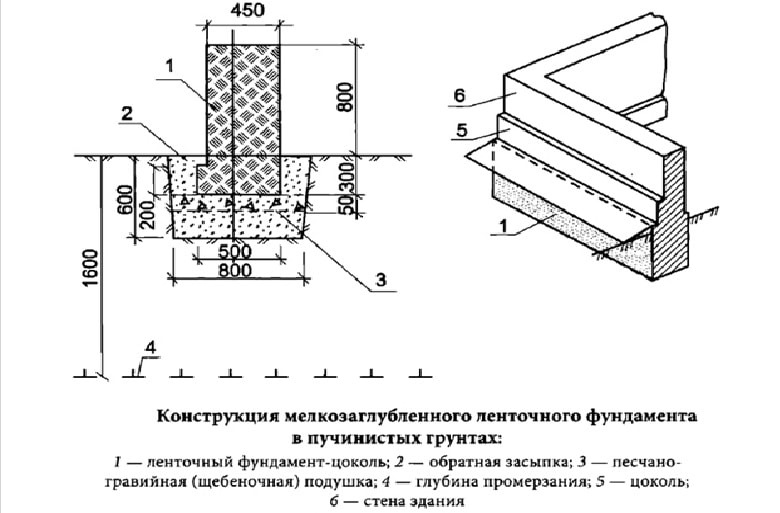
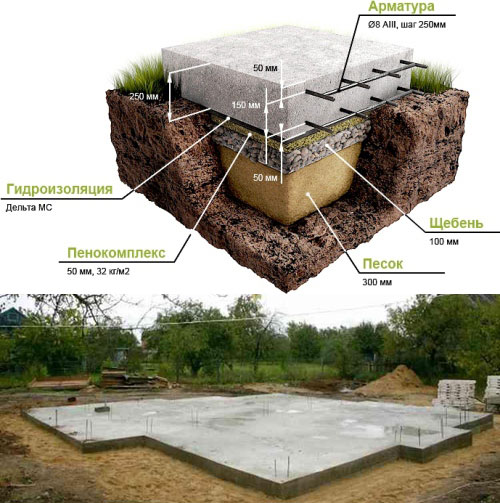
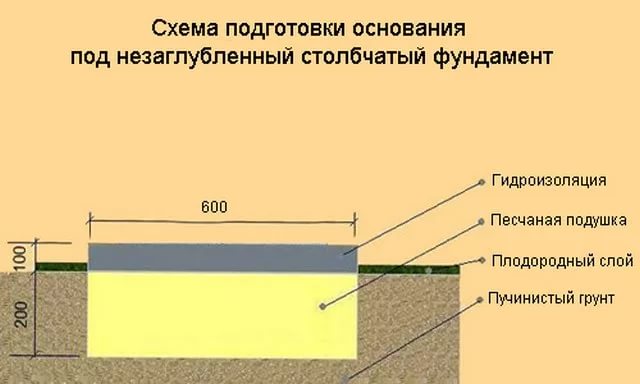
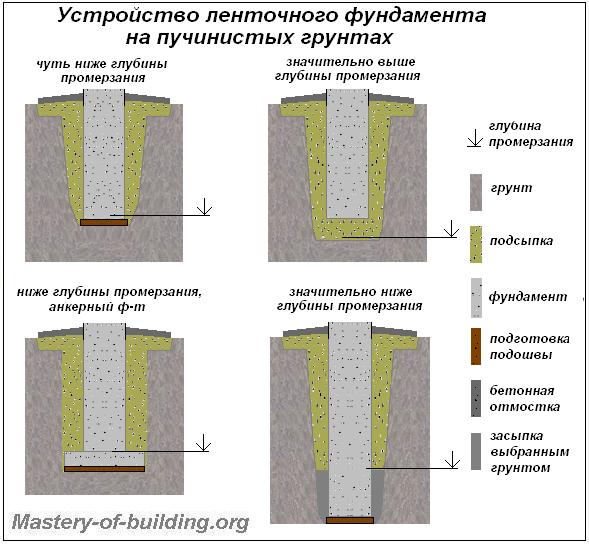
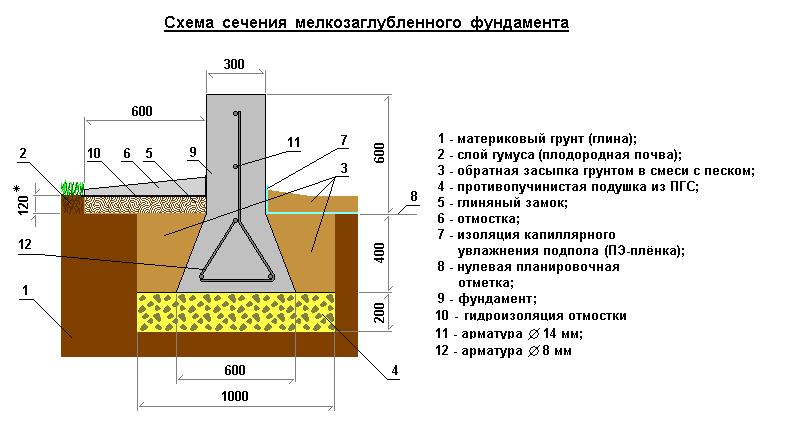
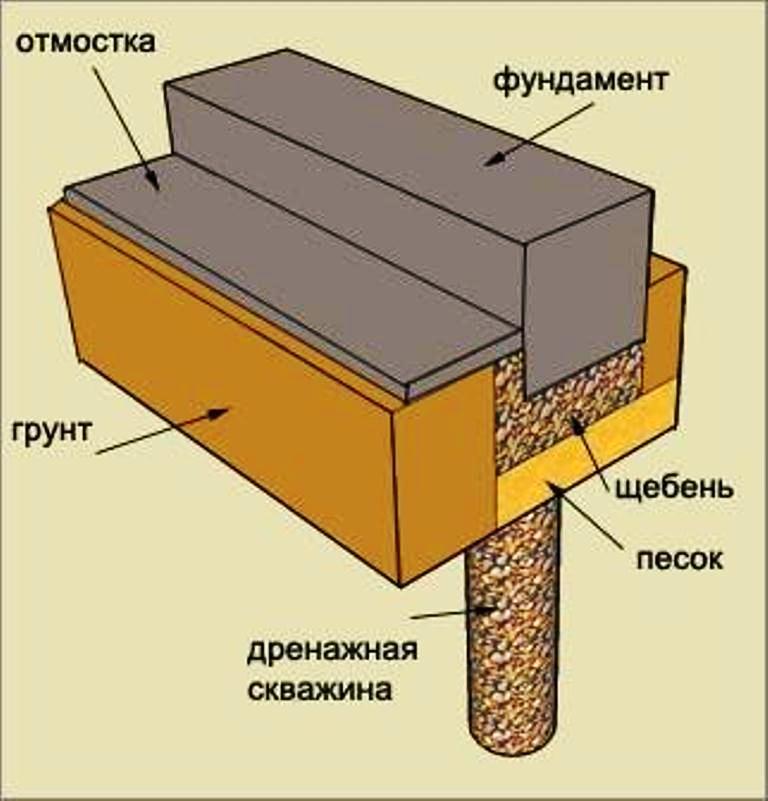
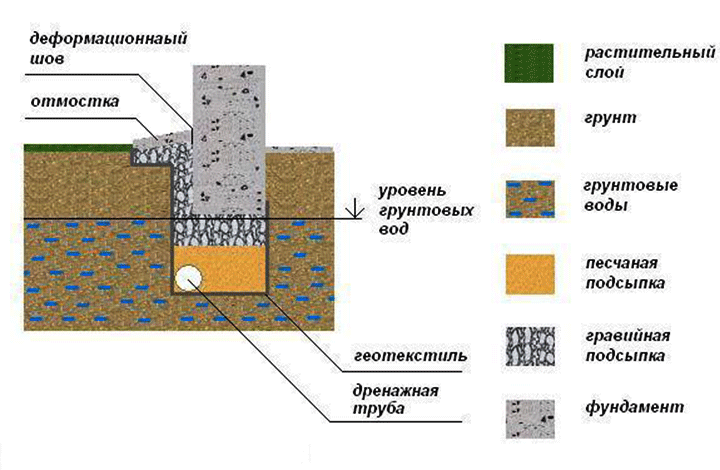
Types of foundations for heaving soil
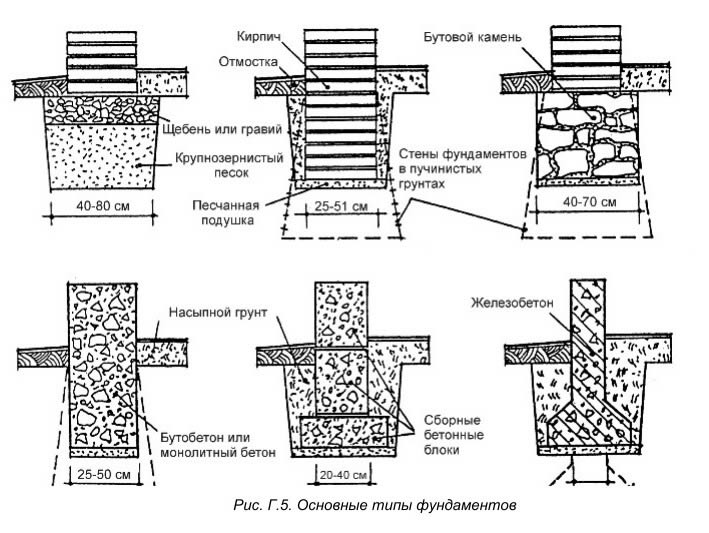
Types of foundations.
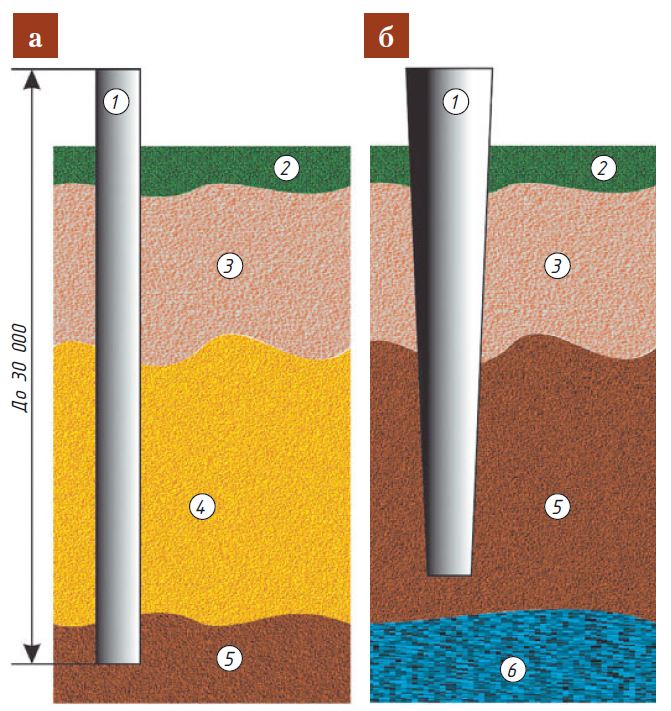
Before starting construction work, as well as creating a project, you need to determine the type of soil and the level of its freezing.
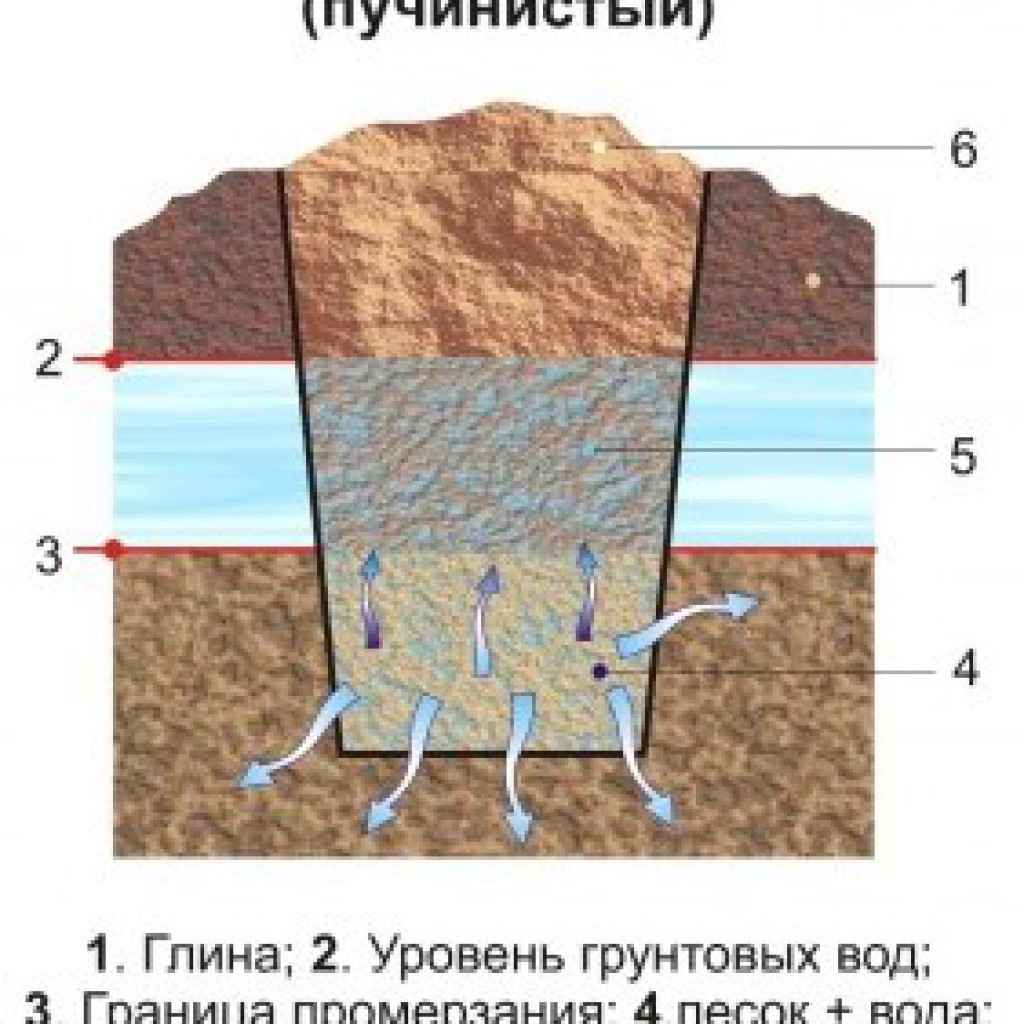
Heaving species include soils that can accumulate water:
- clay soil;
- ;
- silty and fine-grained soils.
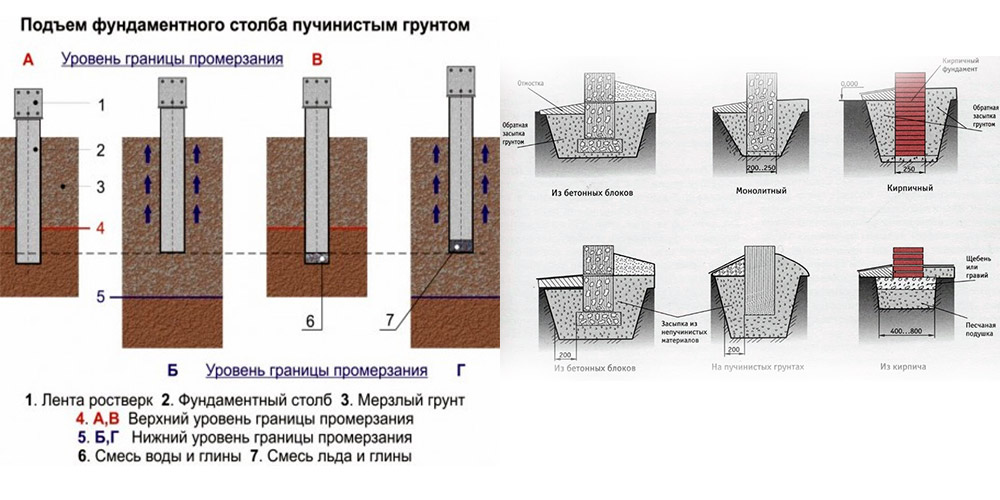
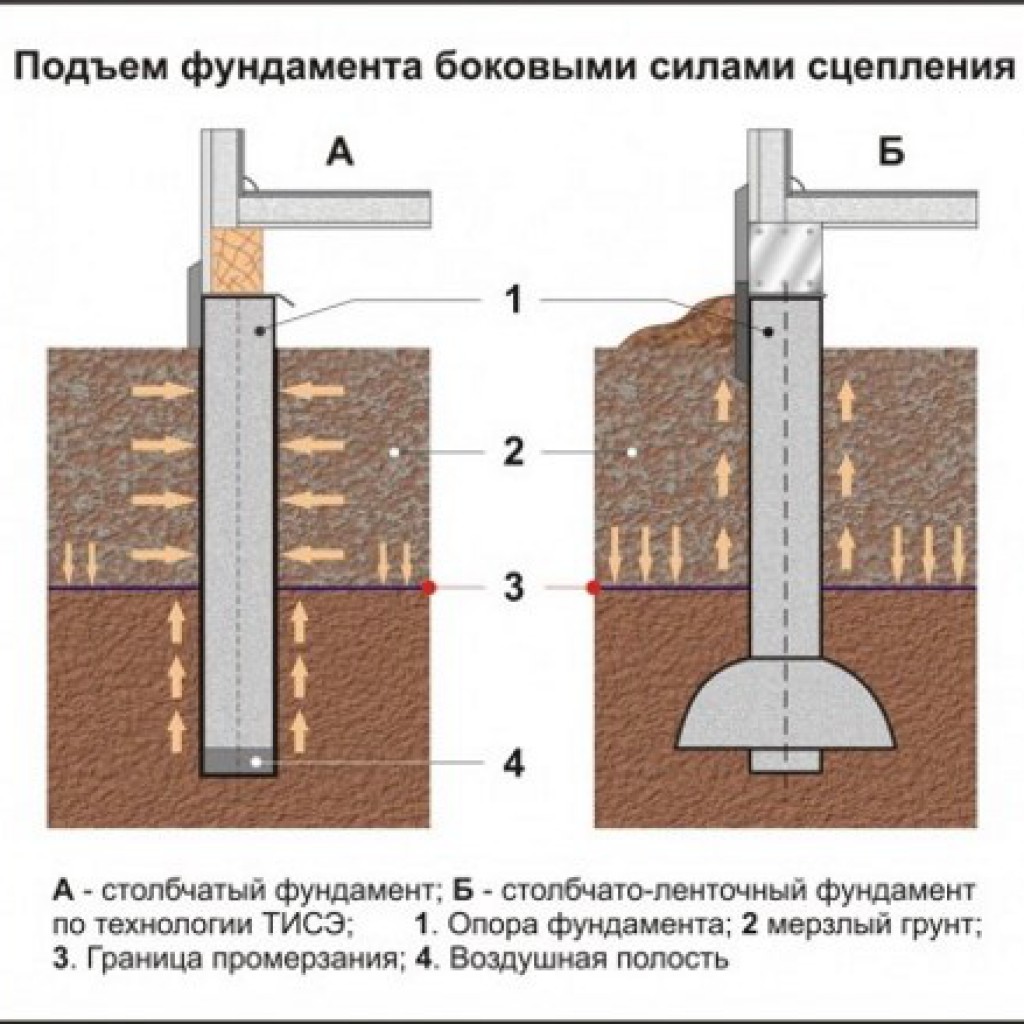
In winter, the water contained in water-saturated soils, when freezing, swells unevenly. This results in uneven settlement of the structure, damage and deformation of the supporting structure.
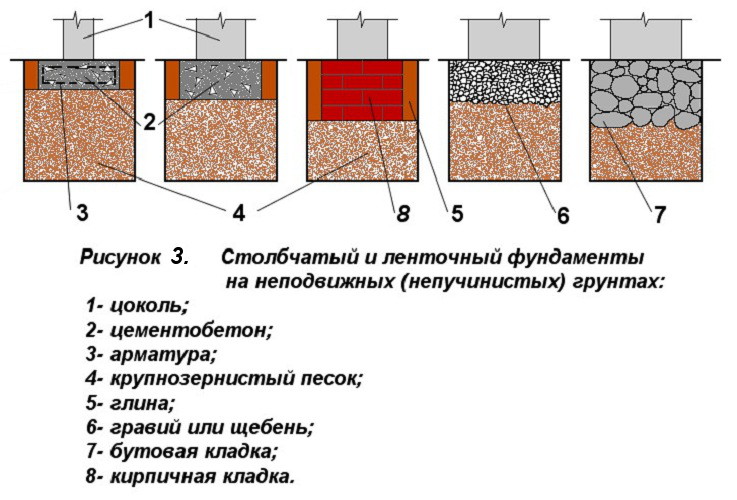
Therefore, it is necessary to immediately determine the type of structure (for example, a columnar foundation or some other), its dimensions and the depth of the bookmark. Today, two types of structures are known and widespread on heaving ground, since they are weakly susceptible to negative influences. They are used regardless of the type of element, since they are less susceptible to destruction during a change in the state of the earth:
- construction of the base of the building, which has a minimum depth;
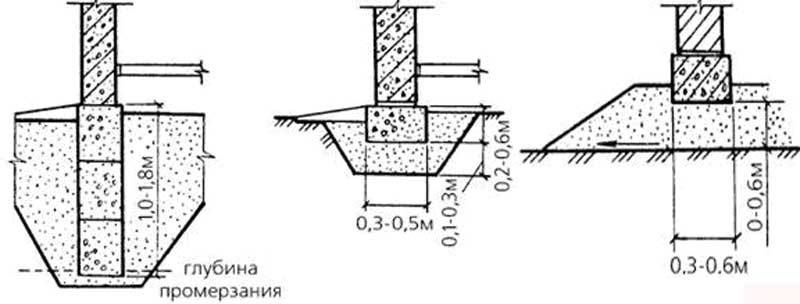
- deepen the foundation so that it is below the level of soil freezing.
In this case, slab, columnar, pile and strip foundations are used.
Calculation of the index of flexibility of building structures
1. Index of flexibility
building structures l is determined by the formula
,(1)
whereEJ - reduced stiffness on
bending of the cross-section of building structures in the foundation-plinth-belt system
reinforcement - wall, tf.m2, determined by the formula (4);
WITH - stiffness coefficient
foundations with heaving of the soil for the bases of strip foundations;
L —
length of the wall of the building (compartment), m;
,(2)
for reasons
columnar foundations
,(3)
Here pr, hfi, b1 - the same designations as in paragraphs. -;
Af - the area of the foot of the columnar foundation, m2;
ni - the number of columnar foundations within the length of the building wall (compartment).
2. Reduced stiffness at
bending of the cross-section of building structures in the foundation-plinth-belt system
reinforcement-wall, tf / m2, is determined by the formula
[EJ] = [EJ]f + [EJ] z + [EJ] p + [EJ]s,(4)
where EJf,
EJz, EJp,
EJs - accordingly, rigidity
on the bending of the foundation, basement, reinforcement belt, building walls.
3. Flexural stiffness, tf / m2,
foundation, base and reinforcement belt is determined by the formulas
f= gfEf(Jf+ Ayc2);(5)
z = gzEz(Jz+ Azyz2);(6)
p = gpEp(Jp + Apyp2);(7)
where Ef, Ez, Ep - respectively, deformation moduli tf / m2,
foundation material, base and belt;
Jf, Jz, Jp- respectively moments
inertia, m4, cross-section of the foundation, base and reinforcement belt
relative to its own main central axis;
A, Az, Ap- the area of the transverse
section, m2, foundation, base and reinforcement belt;
y, yz, yp - respectively, the distance, m, from the main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation, plinth and reinforcement belt up to
conditional central axis of the section of the entire system;
gf, gz, gp
- respectively, the coefficients of the operating conditions of the foundation, basement and belt
gain, taken equal to 0.25.
Bending stiffness
a foundation consisting of blocks that are not interconnected is taken equal to
zero. If the basement is a continuation of the foundation or their joint is provided
work, plinth and foundation should be considered as a single constructive
element. With no reinforcement belts EJp
= 0. In the presence of several belts of reinforcement, the bending stiffness of each of them
is determined by formula (7).
4. Flexural stiffness, tf / m2,
walls made of bricks, blocks, monolithic concrete (reinforced concrete) is determined by
formula
s = gsEs(Js
+ Asys2),(8)
where Es - deformation modulus
wall material, tf / m2;
gs
- coefficient of working conditions of the wall, taken equal to: 0.15 - for walls made of
bricks, 0.2 - for block walls, 0.25 - for monolithic concrete walls;
Js- the moment of inertia of the transverse
section of the wall, m4, is determined by the formula (9);
As
- cross-sectional area of the wall, m2;
ats—
distance, m, from the main central axis of the cross-section of the wall to the conditional
the neutral axis of the section of the entire system.
Moment of inertia of the cross-section of the wall
is determined by the formula
,(9)
where J1 and J2 - respectively, the moment of inertia of the wall section
along openings and walls, m4.
Cross-sectional area
walls are determined by the formula
,(10)
where bs - wall thickness, m.
Distance from center of gravity
the reduced cross-section of the wall to its lower edge is determined by
formula
,(11)
5. State from main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation to the conditional neutral axis
systems foundation-plinth-reinforcement belt - the wall is determined by the formula
,(12)
where Ei, Ai- deformation modulus and area, respectively
cross section i-th structural element
(base, wall, belt);
ji - coefficient of working conditions ith constructive
element;
yi - distance from the main central axis of the cross section ith
structural element to the main central axis of the cross-section
foundation.
6. Flexural rigidity, ts.m2,
walls made of panels is determined by the formula
,(13)
where Ej, Aj- respectively, the modulus of deformation, tf / m2, and the area of the transverse
section, m2, j-to communication;
m —
the number of links between panels;
di- distance from j-that connection to the main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation, m;
y - distance from the main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation to the conditional neutral axis
foundation-wall systems of the building, determined by the formula
,(14)
wherein n —
the number of structural elements in the foundation-wall system.
Belt structures - features of construction on heaving soils
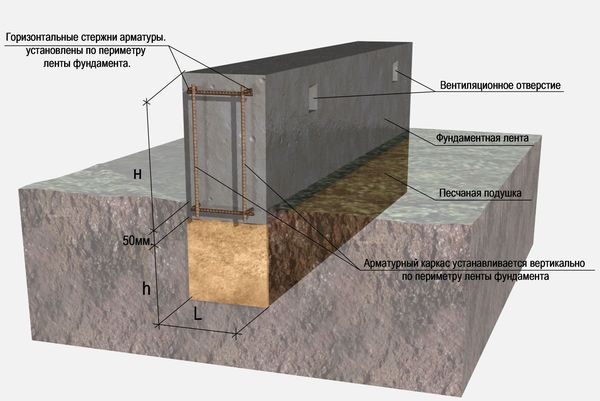
The underground part of the building is able to take the mass of the house and transfer it to dense layers of soil
When planning what foundation will be relevant in areas with plastic intumescent soils, pay attention to the reliability and durability of the tape. To complete a reinforced concrete strip, you will need a maximum of materials, but the costs will be justified
Conditions for the construction of a strip foundation
Shallow tape type of base on swollen soils provides for engineering and geological surveys
Loose soils can lead to cracked soles, so it's important to consider:
- a kind of soil massif;
- the level of freezing of the ground and the amount of water;
- bearing load of the building;
- the presence of an underground and underground highways;
- the period of operation of the building.
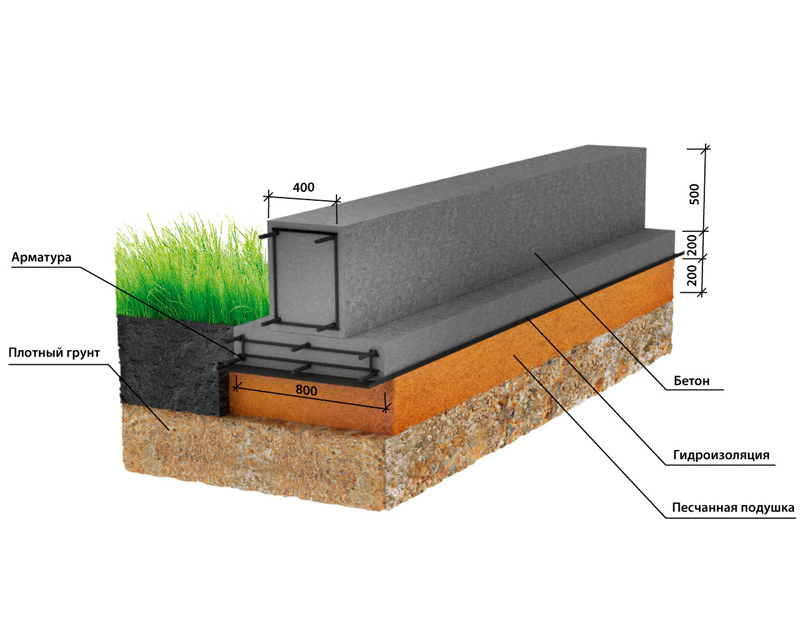
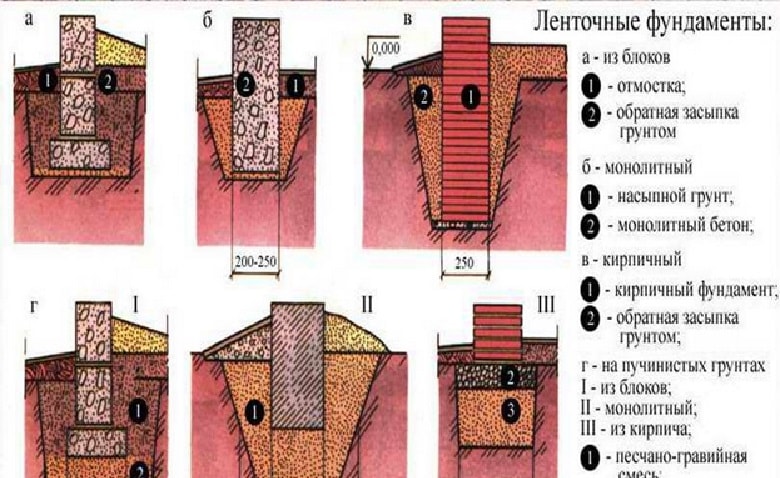
The construction-tape is relevant for brick, concrete houses with dense walls, structures with reinforced concrete ceilings. The walls of the tape can form the walls of a basement or cellar.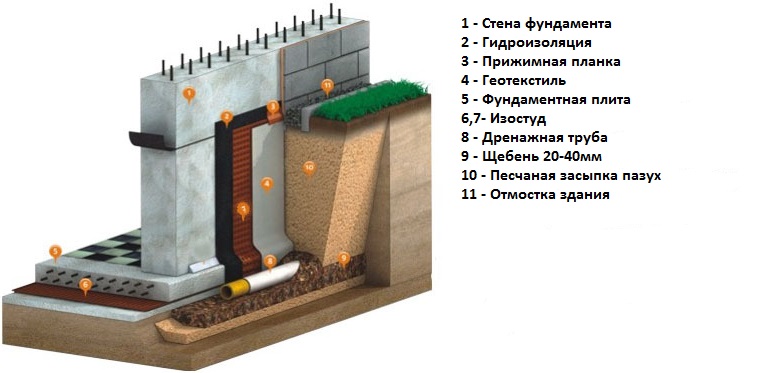
Bookmarking tools and materials
The construction of a buried fundamental structure is carried out using the following inventory and consumable raw materials:
- level and knitting wire;
- shovels - bayonet and shovel;
- cord for marking the territory;
- reinforcement with ribbed section with a diameter of 10-14 mm;
- wooden planks, an ax, a hammer, nails and a hacksaw;
- cement, crushed stone and sand;
- concrete mixers.
Before starting work, it is important to draw up a project that will indicate the necessary parameters of the product
Ribbon bookmark sequence
The construction of the strip base is carried out in several stages:
- A plan of a building or utility block is created, the depth of the structure is determined.
- The foundation diagram is transferred from the finished drawing to the ground.
- The cast-off is mounted at a distance of 1-2 m from the side of the house.
- A trench 1 m deep is dug, a sand and gravel cushion 12-15 cm high is covered.
- A layer of waterproofing is laid on the pillow - polyethylene or roofing material. As an alternative to roll materials, bitumen filling is used.
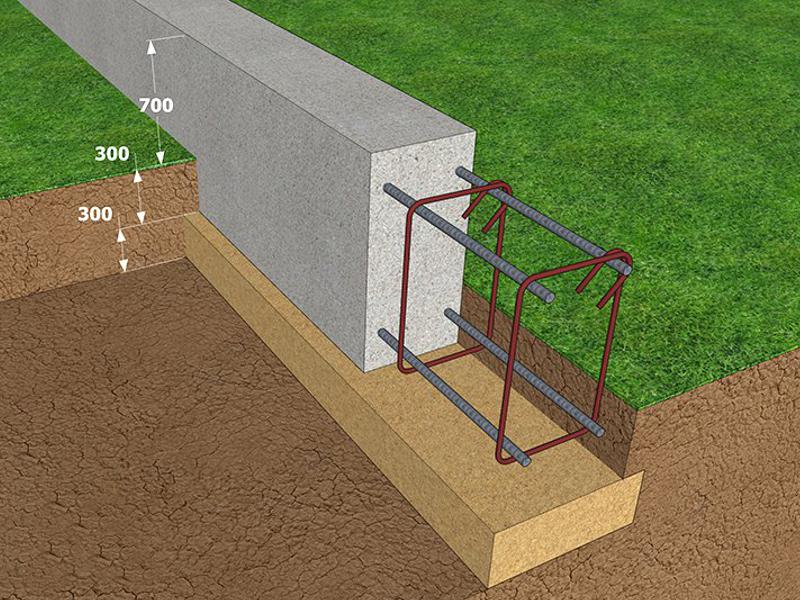
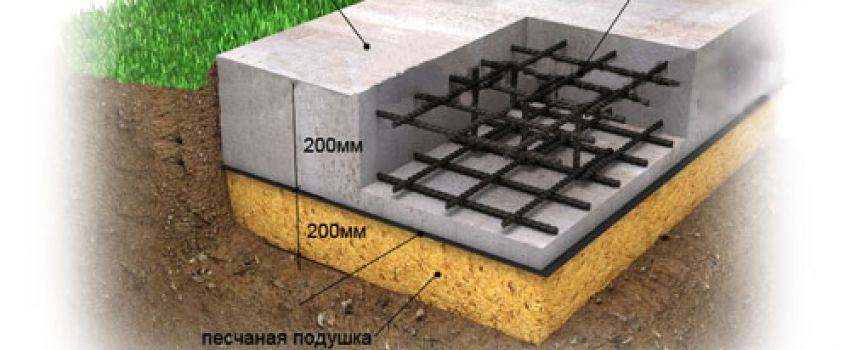
- A formwork frame and a reinforcing mesh made of rods with a diameter of 8-14 mm are being equipped.
- Concrete paste made of M200 cement, sand and crushed stone is poured into the formwork.
Construction experts recommend deepening the base below the freezing of the ground and withstand up to 28 days, and then remove the formwork.
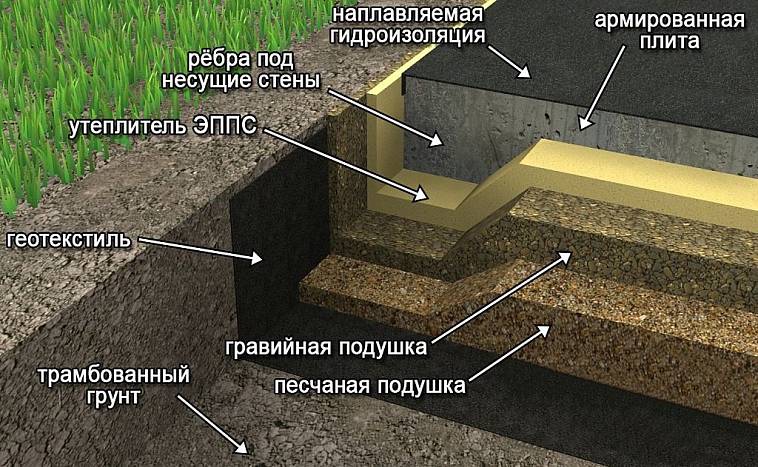
Reducing heaving of soils
As you already know, the heaving of soils is the result of wetting the soil and an increase in its volume due to freezing of the moisture contained in it. In order to somewhat reduce the moisture content of the loam, you can provide for some measures. These activities include:
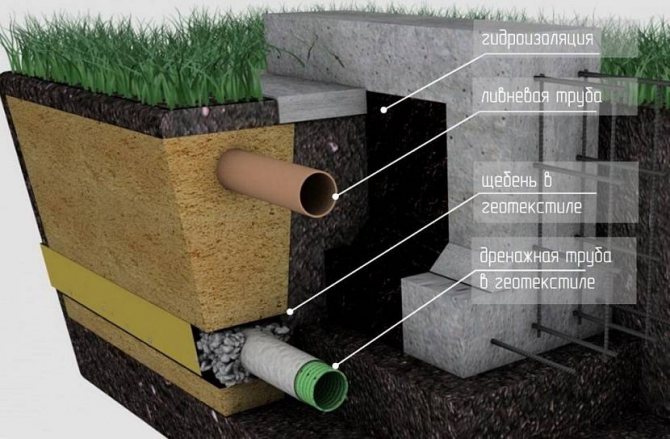
- Wall drainage device to reduce water content in soils.
- Installation of a blind area around the perimeter of the building and gutters from the roof with a drain into the storm sewer.
- Replacement of heaving soils of the base with sandy soil before starting construction.
- Insulation of the blind area to reduce freezing of loams.
We also recommend that you watch an interesting video on how to reduce frost heave:
- What to do if the foundation has sagged? >
How to properly build a foundation on heaving soils
Components of the foundation structure
Reinforcement scheme for the corners of the strip foundation.
When carrying out engineering and geological work on the site, one should not save on research. This will help not to waste extra effort and money in the construction of deeper foundations.
The choice of the type of foundation should be given special attention. Only then will the support of a building or structure be as strong and stable as possible.
The foundation is not considered an underground part of the building, as it is not only underground, but partially above the ground. The structure of the building support must transfer the entire load of the structure to the ground
First of all, attention is paid to the arrangement of the underground part of the structure.
When it should be remembered that its quality is determined some time after the construction of the support. The most important thing is to accurately carry out all calculations when designing a building support. Deformations caused by an incorrect foundation arrangement can be as follows:
- Temperature related to temperature changes.
- Sedimentary, associated with the displacement of the ground as a result of movement at a certain depth of groundwater.
- Shrinkage, occurring due to loss of moisture disappearing from those materials that are part of the support.
When constructing a foundation, the main elements that make up the support of a building or structure are taken into account:
- The sole, which is a horizontal plane that is the bottom surface of the foundation.
- Side surfaces, which are internal and external vertical planes.
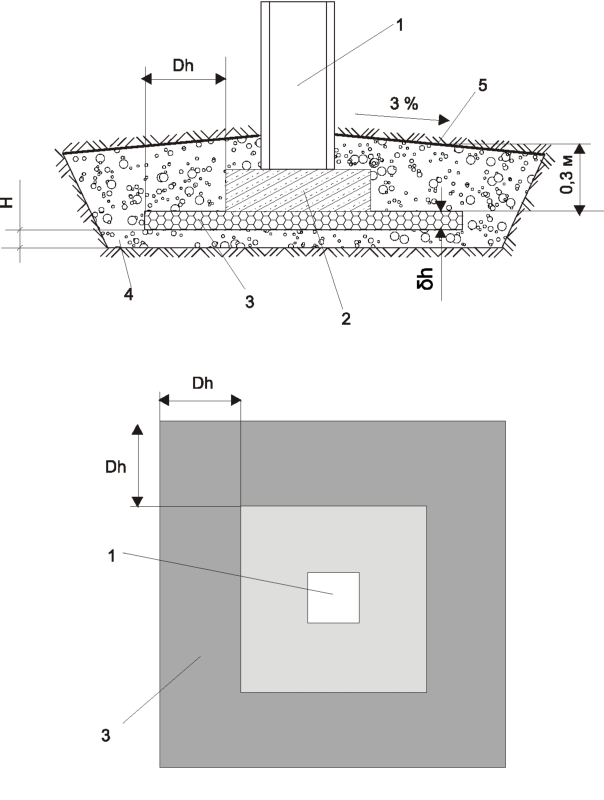
- A plinth located above the ground, the height of which can be from 30 cm.
- Waterproofing layer, which is a structural layer, laid horizontally or vertically.
The top layer is the load-bearing layer, and the other layers of soil under the foundation are called sub-layers. The distance between the surface of the ground and the base is called the depth of the foundation. The boundary between the building support and the ground part is called the edge. When building a foundation, the length and width of the sole and the edge are taken into account.
Criteria for choosing the type of foundation
- High level of reliability
- Increased strength
- Ability to work with any type of building
- The ability to complete construction in a short time
The main cons:
- Long period of time for earthworks
- Large mass of materials
- High cost of materials
- Difficulty of work
When installing a foundation on piles, it is necessary to take into account its main positive and negative features.
Pros:
- The minimum amount of building materials used
- Affordable cost
- Low material shrinkage
- Ease of execution
- Can be installed in the most difficult areas
Minuses:
Of the main drawbacks, only one can be distinguished - when carrying out work, it is required to use specialized equipment.
As a material for installing piles, you can take wood, concrete, as well as reinforced concrete canvas.
Types of piles. They are divided depending on the methods of installation in the ground:
- Driven type of piles. They are pre-made and then lowered into the soil.
- Printed look. Installation is carried out directly in the ground in a special channel.
Also, piles are classified according to the way they are in the soil:
- Rack. Installed in solid ground. Provides additional ground pressure
- Hanging view. Installed in cases of low soil density.
To achieve high efficiency, it is recommended to use wooden piles. However, when installing them, the characteristics of the soil should be taken into account. With constant humidity, equipment will quickly deteriorate, and its service life will decrease.
To increase the service life and achieve the greatest strength, it is recommended to use reinforced concrete piles. They are not subject to damage due to moisture, but they are in a high price category.
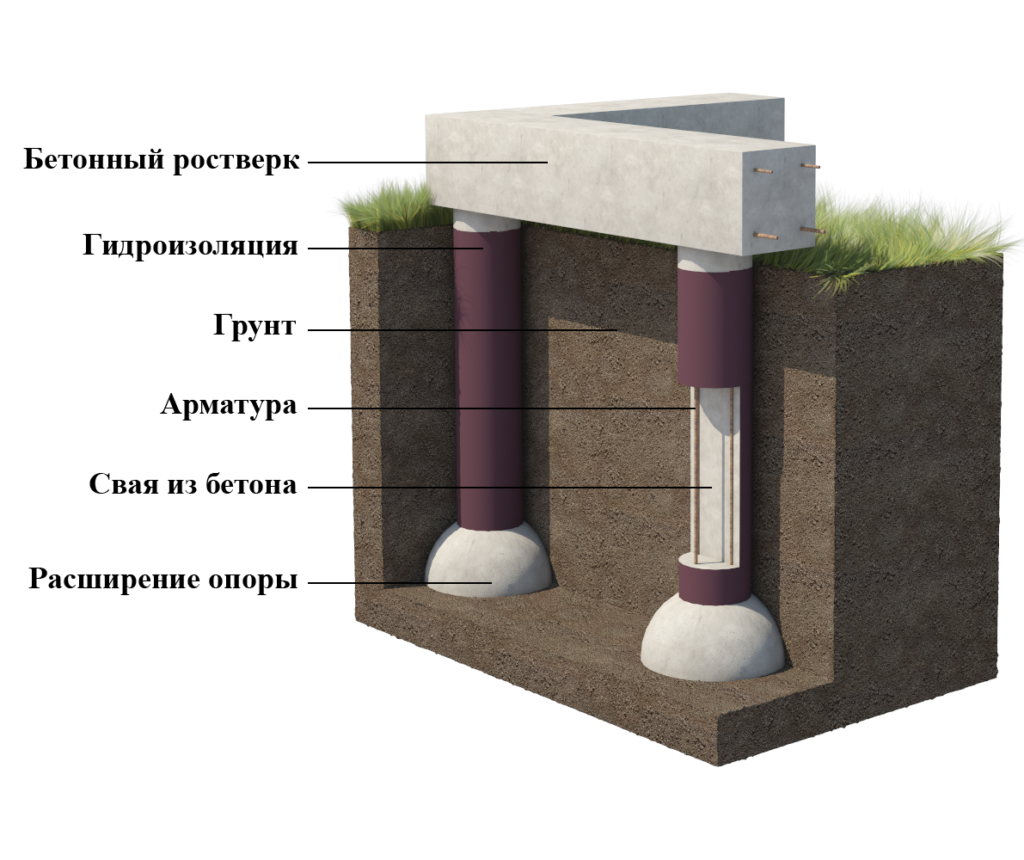
Columnar foundation with grillage
The grillage is arranged for the stability of the pillars in heaving soil and for creating supports for the walls.
It is done only after all the pillars are fitted to one horizontal level.
The design of the posts located above ground level, together with the grillage, can be as follows:
- foundation blocks lying at the base of each pillar. Such a block may have dimensions of 118x80x30 cm;
- concrete blocks for pillars, which can have dimensions of 88x50x58 cm;
- on the top of the blocks, a grillage is placed directly from reinforced concrete slabs or lintels with dimensions of 246x25x20.
Scheme of the formwork device for the strip foundation.
2 adjacent lintels of the grillage are tied with a specially left piece of reinforcement. The grillage itself is laid not on a concrete slab, but on a reinforced monolithic belt laid on it, on which pieces of reinforcement are also left. Such pieces are attached to the lower parts of the reinforcement of the grillage lintels.
If the gap between the posts is more than 2.5 m, then instead of the above jumpers, other ones with dimensions of 298x25x20 cm are used.
It often happens that the mass of the structure turns out to be greater than the estimated possible mass that the lintels are able to withstand. In this case, a reinforced belt is installed on top of them, then the design of the pillar with the grillage is as follows:
- foundation block, for example, FL 8-12-3;
- wall block, for example, FBS 9-5-6;
- concrete lintels;
- monolithic reinforced belt.
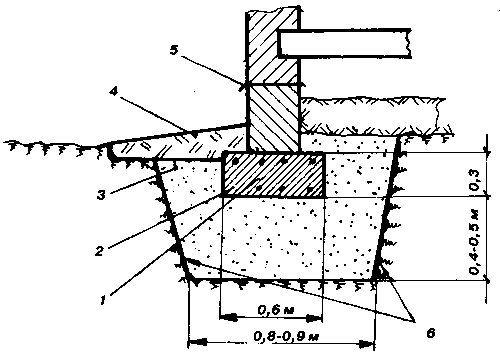
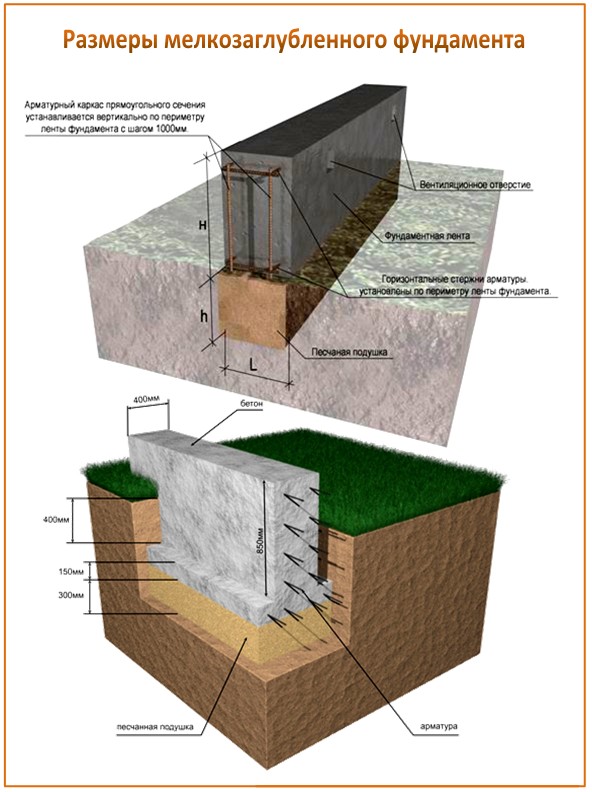
A shallow foundation of a columnar type is either brick or monolithic, in contrast to a normally buried foundation, which excludes 2 such types of columnar foundation.
To carry out the device of a shallow base on heaving soils, first you need to dig a hole with the appropriate dimensions and pour a sand cushion 50-60 cm thick.It is necessary to fill it up in layers, with a thickness of each layer of 10-15 cm, each layer must be compacted and moistened with water.
Diagram of the device of a monolithic strip foundation.
Next, a layer of roofing roofing or roofing material is laid on the sand. They play the role of waterproofing, which does not allow the cement laitance to go into the ground.
When all the pillars are erected, it is required to fit them to one level horizontally. Leveling is done with cement mortar. After that, they start assembling a monolithic or precast-monolithic reinforced concrete belt. During the construction of a wooden house, the first bundle of logs or beams begins to be laid on the aligned pillars.
It should be noted that the device of a monolithic belt made of reinforced concrete is a rather important structural moment, since it is he who will provide rigidity along all the pillars and their stability. Before assembling the belt, it is required to make a bunch of all jumpers with each other. This can be done by welding or tying the loops with wire.
Then formwork is placed on the lintels and concrete mortar is poured.