Barberry and apple compote
Sort the berries and rinse.
Peel the apples and cut into pieces of any shape.
Layer the ingredients in 1 liter jars.
For pouring, boil the syrup from the calculation:
- water - 1 l;
- sugar - 500 g.
The main component of the compote will be fruits and some berries - for color:
- apples - 1 kg:
- barberry - 200 g.
- water - 1 l,
- sugar - 500 g.
In autumn, not only barberry ripens, but also apples. Use these healthy and delicious foods to make a vitamin compote. You will need the following ingredients:
- 1 kg of apples;
- 250 grams of barberry;
- 1 liter of water;
- 350 grams of sugar.
Wash the apples and cut them into small slices, put them in prepared sterilized jars. Top with barberry and pour boiling syrup (sugar mixed with water). Cover the jar with a lid and sterilize for 10-15 minutes.
Barberry compote is not only tasty, but also a very healthy drink. It helps to normalize digestion, has an antipyretic effect. In its pure form, barberry is too sour, and in sweet syrup it is an unsurpassed delicacy.
Recently, it has become fashionable to plant a hedge of perennial shrubs, including barberry, on the site. However, this is not his only merit. Thanks to the abundant harvest of edible red berries, with which the bushes are literally strewn in the fall, you can harvest compotes and jams from barberry for the winter, make tinctures, or simply dry the fruits.

The beneficial properties of barberry compote have been noted for a long time and are beyond doubt. Adherents of traditional medicine recommend drinking it for disorders of the digestive system and with high blood pressure. In addition, it has a mild laxative effect and is used for stool retention. Barberry compote helps to lower body temperature and active perspiration. It is used for diabetes mellitus, excluding granulated sugar from the composition.
For the preparation of barberry compote, ripe berries are harvested for the winter. They have a rather soft structure, so you need to wash them carefully so that the barberry does not burst and does not let the juice out. If you need to remove the seeds from the fruit, it is better to pick a slightly unripe barberry.
Subtleties of the installation process

Installation of the foundation for a two-story house
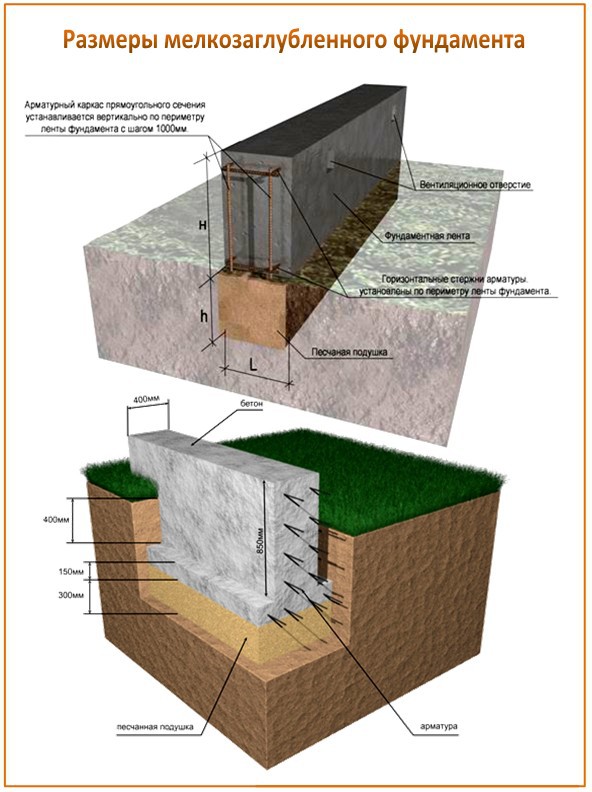
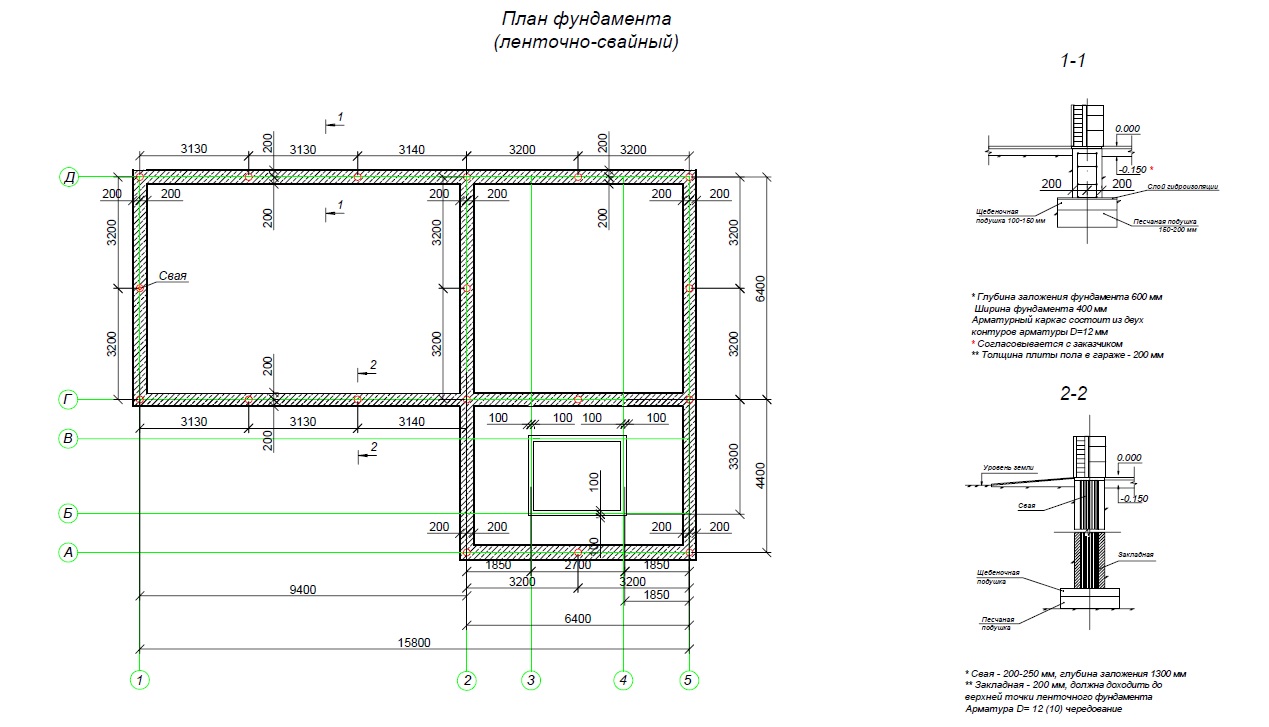
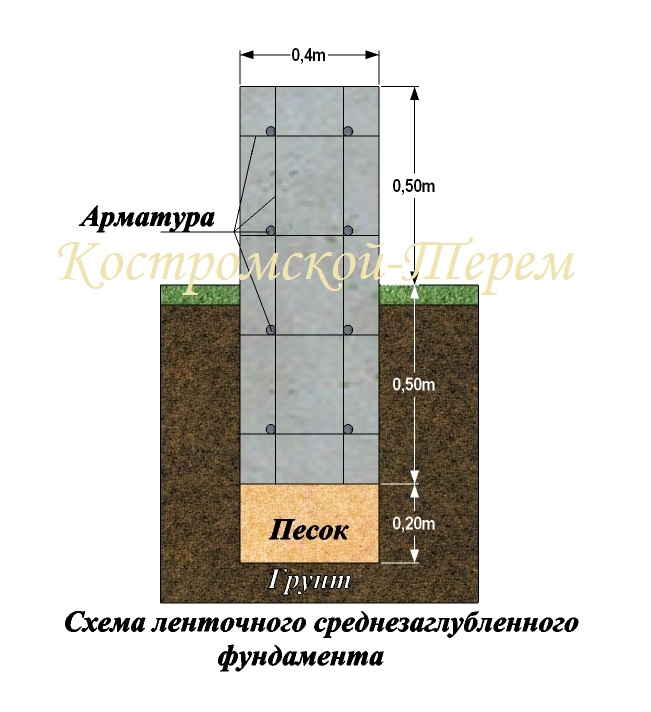
The depth of the foundation for a house among all the listed variations is the most widespread, the first one, therefore, let us consider in more detail the features of construction work. First of all, we note the parameters: dimensions, depth of the strip foundation for a two-story house:
- width - 10 cm more than the thickness of the bearing walls. This is enough for the subsequent execution of external finishing;
- height - 30 cm - optimal;
- depth - from 50 cm or more, if necessary due to the characteristics of the soil.
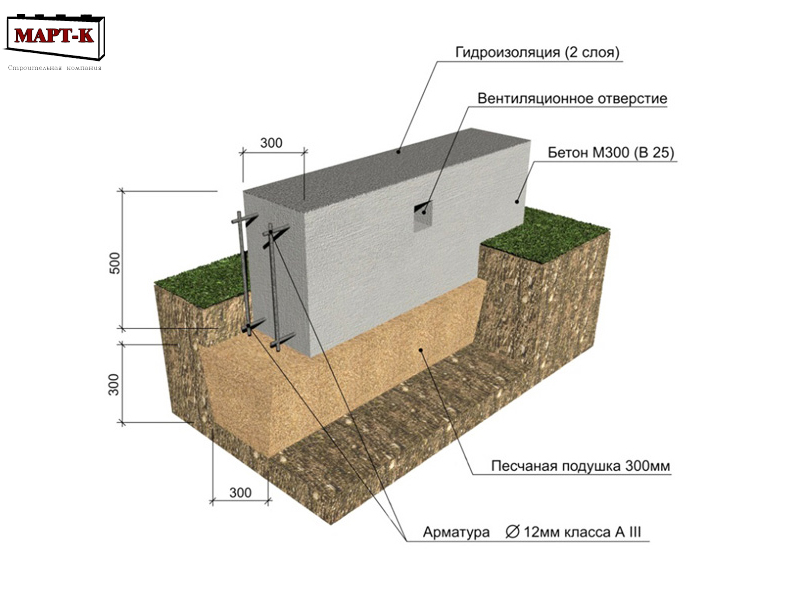
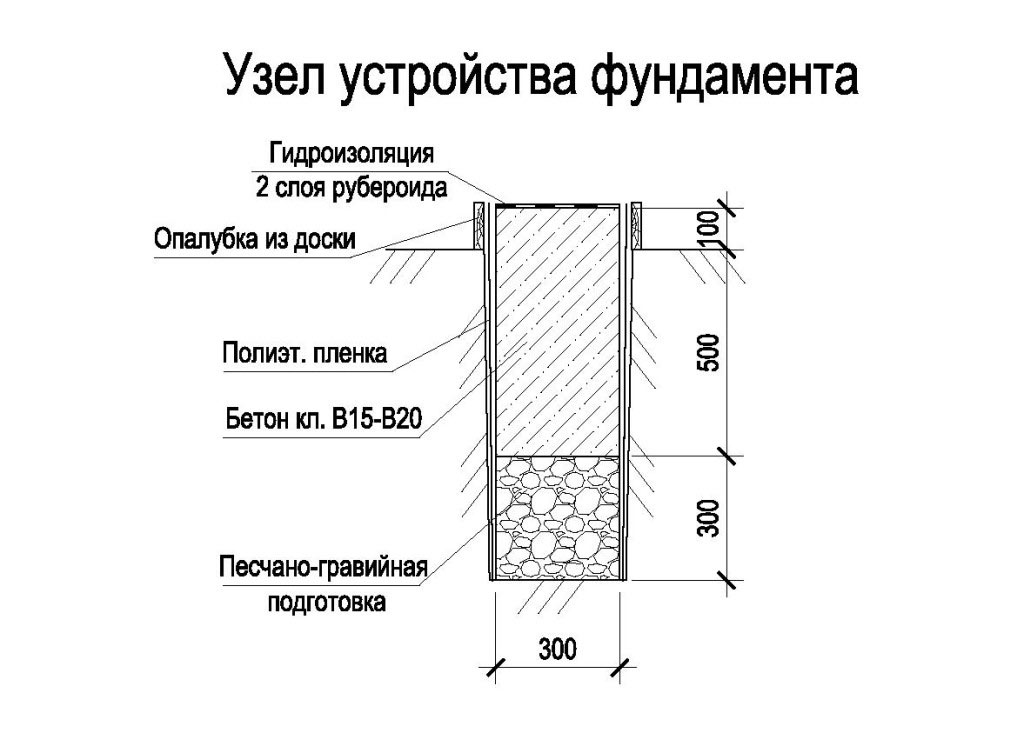
After the completion of the excavation, its bottom is carefully compacted, the pit is filled 1/3 with mixed rubble and fine sand. Loose material must be periodically moistened, so the pillow is more efficiently compacted. Approximate height 15-20 cm. Next, a waterproofing material is laid with an overlap on the pit walls, you can use ordinary polyethylene. A small ball of grout can be poured over the top to give the foundation maximum protection from moisture.
The next stage is formwork
It is assembled from boards 4-5 cm wide, should rise 30 cm above ground level. This space will later become a plinth.
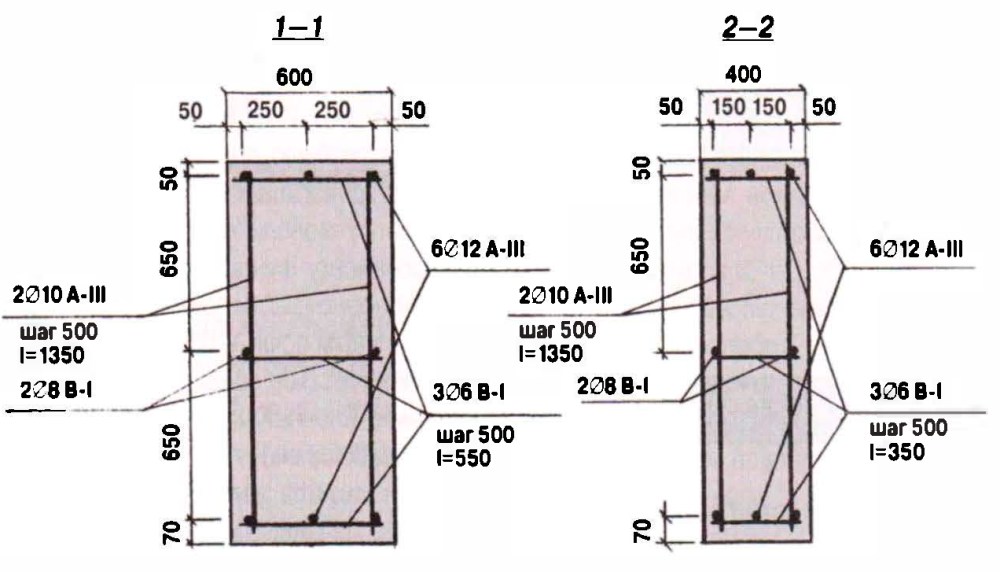
Now you can start installing the fittings.It is better to use ribbed rods, because they more firmly hold the concrete mortar, which will subsequently be poured. Long rods are located along the pit at a distance of 30 cm (5 cm indent from each edge), and short rods are placed perpendicularly in the upper and lower parts with a step of 25-30 cm. The frame elements can be connected by welding and knitting using special wire and hooks. The latter method is considered preferable. Experts say that welded joints have lower strength due to the violation of the integrity of the metal.
To prepare a concrete solution, which is subsequently used to fill the reinforcing cage, high grade cement is used. This ensures the proper strength of the solidified foundation, respectively, the stability of the dwelling. The filling is carried out in layers of 15 cm thick. Each of them must be well leveled and given time to completely solidify, covered with a film.
The formwork is removed 7-10 days after the completion of the casting work, the complete arrangement of the foundation. After the same period of time, you can continue construction, being completely confident in the proper strength of the foundation.
The final stage is waterproofing the foundation
On the hardened concrete, liquid glass or bitumen mastic is applied, after which roofing material is glued on top or using modern materials Gidroizol or Technoelast
It is important to ensure a tight seal over the entire surface of the waterproofing, while maintaining its maximum effectiveness. The remaining free spaces (sinuses) are filled with fine sand
It is periodically moistened and compacted thoroughly.
Having figured out what depth of the strip foundation for a two-story house is considered optimal, having studied the sequence and subtleties of the installation work, it remains to calculate the amount of material required. The project of the building will help here, indicating the number and types of walls, their length and width.
The scheme is compiled without fail with a mark of all significant parameters and sizes. It is necessary to purchase materials with a small margin so as not to stop the installation process due to their shortage
Pay attention to the diameter of the reinforcement - it is determined by the value of the load on the foundation, it can fluctuate within 0.8-15 mm
How to calculate the cubic capacity of the foundation
It is better to take into account the mass of the foundation when calculating its volume: this figure will come in handy when pouring the foundation: you will know how much concrete to order or how many materials will need to be purchased.

All the initial data are already known: the height, width and length of the tape. Multiply them, you get the cubic capacity of the foundation.
For example, let's calculate the volume of the foundation for the previously calculated tape: 44 m long, 30 cm wide (0.3 m), 1.75 m high.Multiply: 44 m * 0.3 m * 1.75 m = 23.1 m3. In fact, the consumption is likely to be slightly higher: about 25 cubic meters. You should be guided by this figure when ordering concrete.

The cubic capacity of the foundation is calculated based on the found (estimated) dimensions of the tape: length, height and width by multiplying them
Factors affecting the depth of the foundation
Regardless of what type of base you will use, the bottom of the sole of the structure is determined by a set of rules, taking into account the following factors.
Regardless of what type of base you will use (shallow or not buried, tape or slab, from FBS or monolithic), the lower elevation of the sole of the structure is determined by the joint venture, taking into account the following factors:
Soil type, their features and characteristics. Full information on the composition of the soil at the construction site can be obtained after conducting geological surveys. It will not be possible to carry out these activities with your own hands, you will have to contact the specialists.
Also, the calculation of the depth of the base is influenced by the elevation at which the groundwater passes.You will also receive this data after conducting hydrogeological studies of the area.
According to the joint venture, the average temperatures in the region should also be taken into account.
This is especially important if a shallow or shallow foundation will be used, because heaving forces can affect the structures in winter.
The presence of a heated basement.
Average depth of rock freezing in the region.
Soil type, ground level and heaving force
If you are making a shallow or buried foundation for a house with your own hands, then you should adhere to some recommendations
If you are making a shallow or recessed foundation for a house made of aerated concrete, brick, wall blocks and other materials with your own hands, then you should adhere to the following recommendations from the joint venture:
- When building on rocky and coarse rocks, as well as on gravelly, coarse and medium-sized sands, the distance from the top of the earth to groundwater in the winter season does not matter. In this case, you can apply any type of foundation, regardless of what depth of soil freezing the calculation will show. According to the joint venture, on such soils, shallow foundations and non-buried foundations can be used.
- When erecting foundations from FBS and reinforced concrete on a rock of fine and dusty sands, as well as hard sandy loam, the choice of the type of foundation:
- does not depend on the freezing depth according to the calculation, if the groundwater is at least 2 m below the calculated freezing mark;
- the foundation should not be higher than the freezing point according to the calculation, if the groundwater level is not more than 2 m above the freezing point. Under these conditions, sandy loam can have any consistency.
- On sandy loams of plastic and fluid consistency, at any ground level, the shallow foundation and the non-buried foundation should not be higher than the freezing point of the rock according to the calculation.
- On hard loams and clays, a shallow slab or strip foundation can be used, provided that the groundwater level is at least 2 m below the freezing point.
- On soft-plastic loams and clays, provided that the groundwater level approaches the freezing mark no closer than 2 m, any type of shallow foundation can be used (the classification of shallow foundations is given above) for houses made of aerated concrete, logs and timber. However, in this case, according to the joint venture, for houses made of aerated concrete and other light materials and blocks, measures should be taken to protect the base from saturation with surface water.
- If a slab or strip foundation made of FBS or a monolith is erected by hand on flowing and fluid-plastic loams and clays, at any GWL, according to the calculation, the depth of laying should not be higher than the freezing point.
- In conditions when a slab or strip foundation made of reinforced concrete or FBS is built on loams and clays with a groundwater level no more than 2 m above the freezing point, the level of the foundation of the foundation structures, according to the calculation, is not higher than the freezing mark.
Calculation method
The strip foundation can be calculated in two ways: by the bearing capacity of the soils under the sole and by their deformation. The first way is simpler. We will consider it.
We know for sure that the foundation is built first. But it is designed last. Its task is to transfer the load from home. And we will know it only after we decide on the type of all building materials and their volumes. So before starting the calculation of the foundation, you must:
- draw a plan of the entire building with all the walls;
- decide whether or not a basement is needed, and what depth it should be, if needed;
- know the height of the base and the material from which it will be made;
- determine the type and thickness of materials used for insulation, wind protection, waterproofing, decoration both inside and outside.
For all materials used during construction, you need to find their specific gravity. It is advisable to draw up a table: it will be easier to work.Only then can you start calculating.

To calculate the strip foundation, you will need a project with a detailed indication of the materials used and their thickness
The strip foundation is most often made monolithic or precast concrete. Much less often today brick or rubble concrete tapes are made: they are less reliable, but at the same time, more material is required for their construction, although its cost may be less.
Conventionally, the calculation of the strip foundation can be divided into several stages:
- Determination of the load on the foundation.
- Choosing ribbon options.
- Adjustment depending on conditions.
Now about all the stages in more detail.
Description
Deciduous, highly branched thorny shrub, up to 3 m in height, with a powerful superficial root system. The bark of old branches is gray, cracking; on young stems, it is furrowed, yellow-brown or yellowish-gray. The branches are yellowish-gray, thin, directed upwards, with large simple and tripartite spines (modified leaves), in the axils of which there are buds.

Sepals, six in number, petal-shaped, yellow, with six corolla petals. There are six stamens, a pistil with an upper ovary. The fruit is an oblong, dark red, juicy, very sour edible berry with 2-3 seeds. Seeds are finely wrinkled, oblong, dark brown, somewhat flattened. Propagated by seeds and vegetatively. There are 175 known species of barberry.
Types of foundations for two-story foam block houses
The foundation for a one-story house and a two-story one made of foam concrete does not bear the same load as the foundation for similar buildings made of brick, cinder block, stone, concrete slabs. The foam block is much lighter than the materials considered. But still, if, with an insufficient level of deepening of the base, the building shrinks, then cracks may appear on the walls.
The choice of the type of foundation for a foam block structure should be approached thoroughly. In practice, such varieties are used:
- pile;
- tape;
- in the form of a plate;
- columnar.
 Schematic representation of the base in the form of a slab
Schematic representation of the base in the form of a slab
By depth, support structures are divided into:
- not buried;
- shallow;
- buried.
If the house has a basement, then the foundation should be of the latter type.
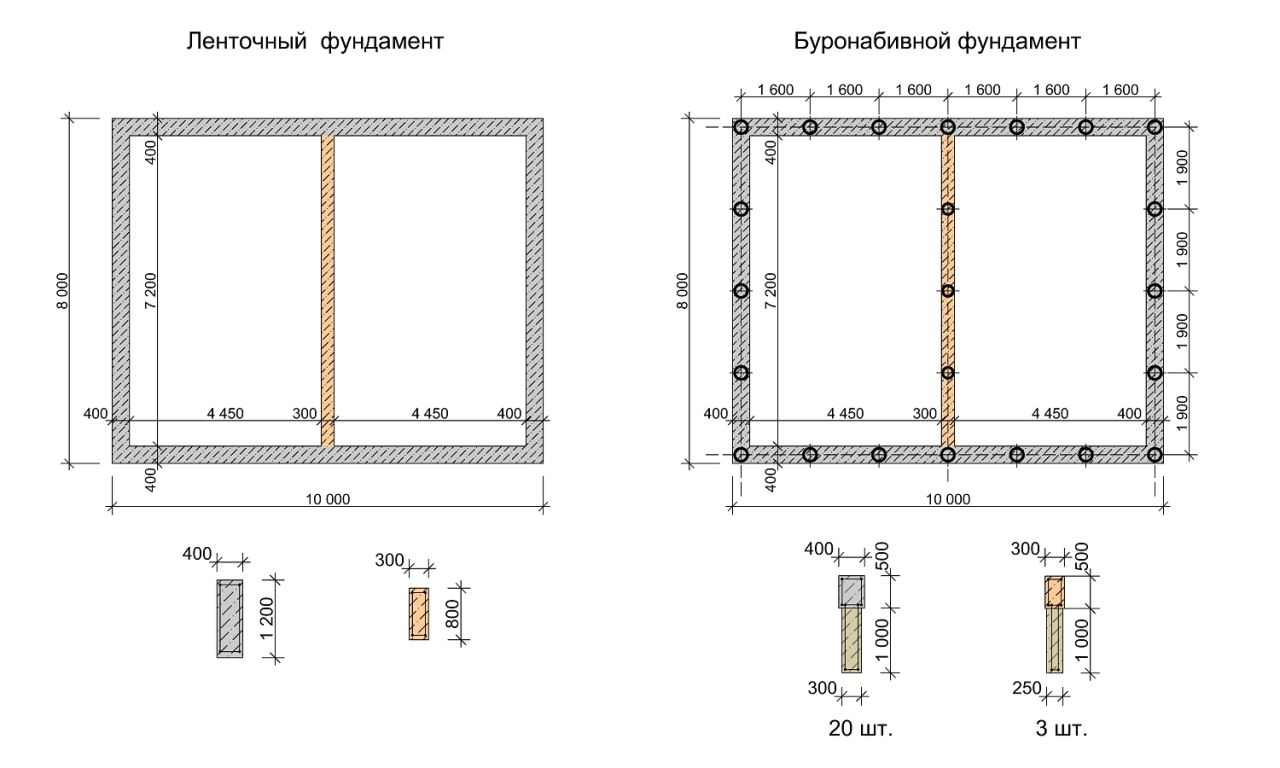
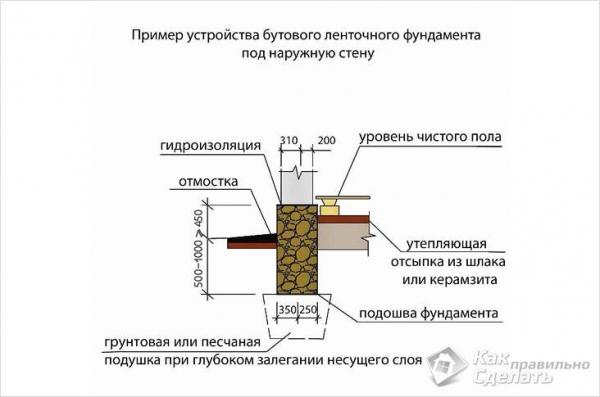
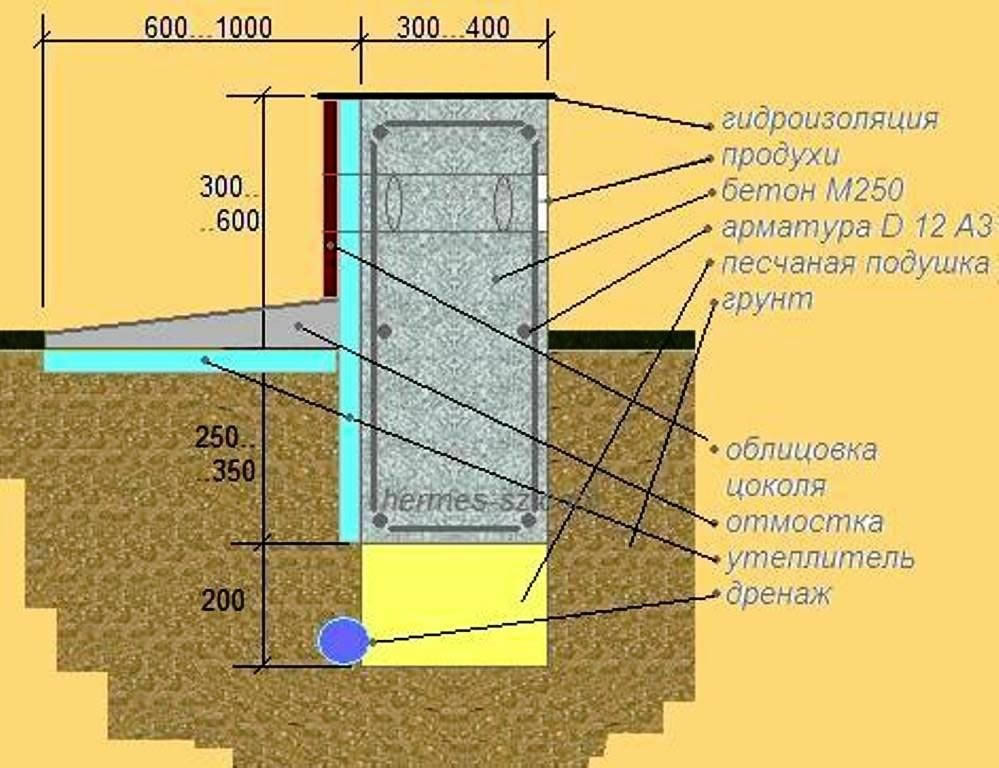
Tape base
The strip foundation is built on dispersed (sandy) or clayey soils. At the same time, the height differences at the construction site are 0.2-0.5 m. The created structure is placed under all load-bearing walls and internal partitions.
The foundation of this type is erected, adhering to the following recommendations:
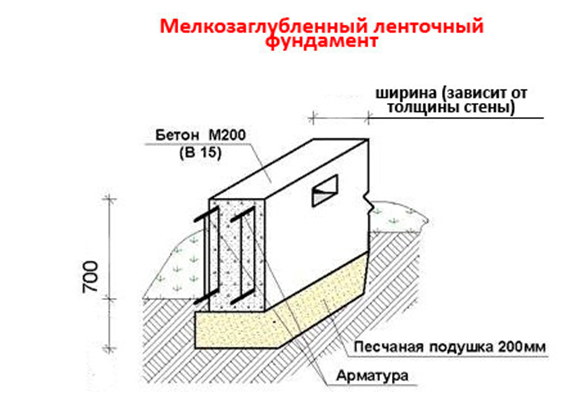
- the width of the supporting structure is made greater than the thickness of the walls of the building by at least 0.1 m;
- it is permissible to make the depth of the strip foundation less than the mark of soil freezing;
- the basement is not built high (usually the height is 40 cm), and reinforcing rods are laid on top, connected by wire or clamps;
- when laying the foundation to a depth of 0.6 m, a pillow is necessarily formed - a layer of sand and medium-sized crushed stone;
- used as a building material: stone, rubble, brick, concrete.
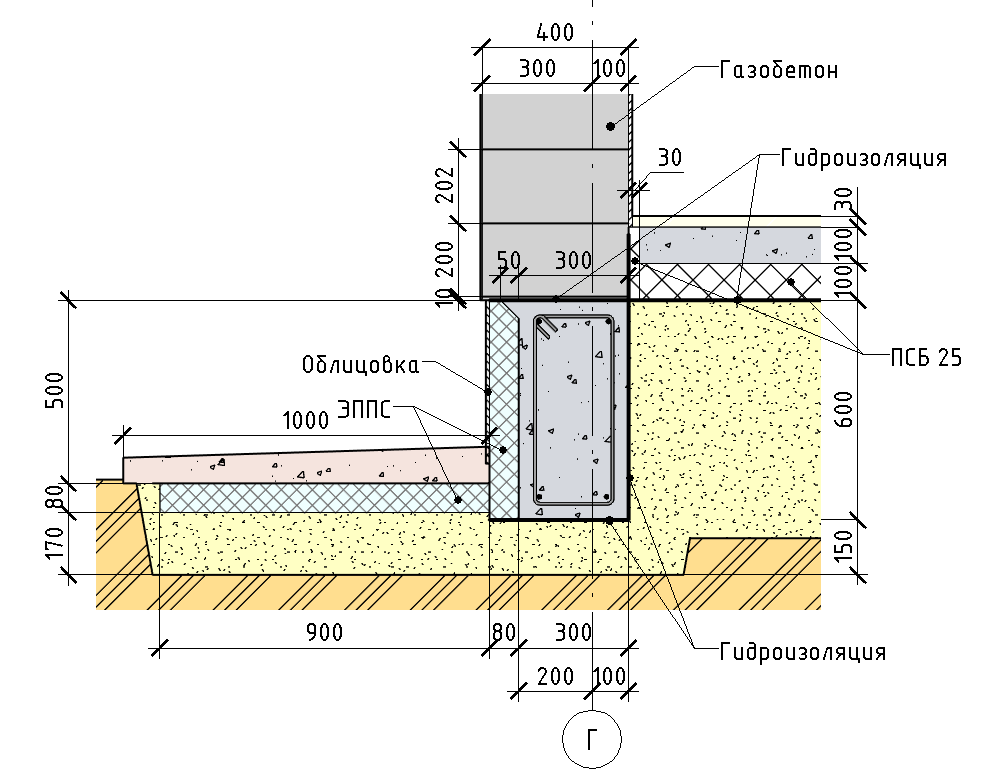
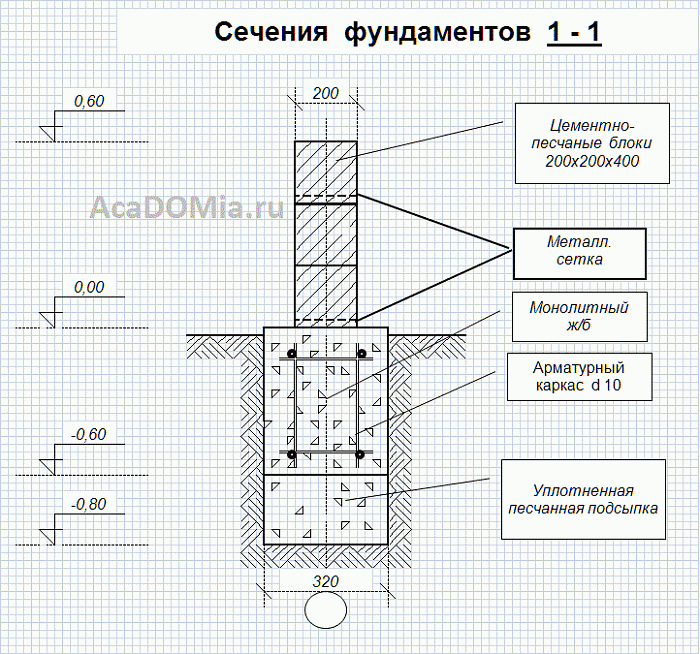
 Belt type base
Belt type base
It is advisable to lay the reinforcement in two layers, reinforcing the joints at the corners of the building, for example, by welding the rods.
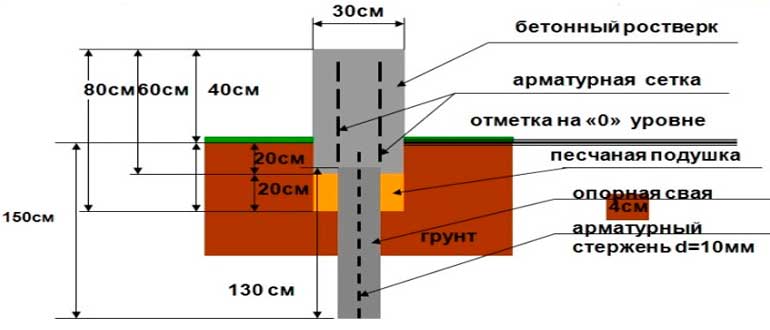
Column and pile foundation
Columnar bases are used when carrying out construction work on clayey soils. The soil on the site should not freeze more than 2m.
The pillars in the pre-dug holes are installed by factory production or they are poured on their own at the construction site. In the latter case, reinforcing rods are inserted into the center of each. The workflow takes place in the following sequence:
- the supports are placed from each other no further than 2 m and no closer than one meter;
- install them around the perimeter of the future walls of the building, always in the corners;
- in areas with presumably high loads - they are placed in greater numbers than usual;
- the required installation depth is 0.15 m higher than the freezing level;
- during work, lay a sand cushion under the supports and between them;
- after the formwork is mounted;
- with the help of steel wire, a reinforcing frame is tied to the reinforcement protruding from the pillars along the perimeter of the structure and at the locations of future interior partitions;
- the structure is poured with concrete;
- waiting for the solution to dry;
- dismantle the formwork.
 Scheme of a columnar type of support structure for a house
Scheme of a columnar type of support structure for a house
If the groundwater is high, then they arrange a drainage system, waterproofing the structure.
A pile foundation is a popular, durable, reliable foundation type on weak, unstable soil types. When using it, deformations, flaws almost never appear.
Piles are used in the following varieties:
- metal with anti-corrosion coating;
- made of concrete and metal fittings.
Manufacturers test products in advance before being sold.
Slab type base
For foam block houses often support in the form of a slab. It is done in two ways:
- the pit is poured with concrete, receiving a monolith;
- floor slabs are placed tightly to each other.
In the latter case, a waterproofing coating is laid on top of the created base. Then a number of concrete blocks are installed and covered with moisture-proof material. Only then do they start building the house.
Below in the video is an overview of foundations suitable for the construction of a foam concrete house.
The process of creating a pile foundation for aerated concrete construction is shown further in the video.
For a two-story house, the depth of the foundation depends on the geological conditions at the site. For buildings made of foam blocks without concrete floor slabs, a monolithic foundation in the form of a slab is suitable. The recessed strip base allows you to equip an underground garage, organize a convenient access to it. The use of piles is the best way to erect a structure on unstable soils. Any supporting structure for a foam concrete building must be reinforced.
Standard height
In an ordinary country house, the basement should rise about 30-40 cm above the ground. If the building is built of wood, then it is better to take a higher height (about 60-80 cm). If the presence of an underground floor is provided in a country house, then the height indicators can reach 1.5-2 meters.
When determining the height of the basement, it is necessary to take into account the weather conditions on the ground: indoor and outdoor temperature in winter, snow level, abundance of precipitation, the likelihood of flooding, the level of groundwater. It is quite difficult for a layman to take into account all these factors.
Therefore, even if you are building a house yourself, it is best to turn to specialists for correct calculations. One-time insignificant costs at this stage will help to avoid serious financial losses in the future for repair and re-equipment of the structure.
It is quite difficult for a layperson to take into account all these factors. Therefore, even if you are building a house yourself, it is best to turn to specialists for correct calculations. One-time insignificant costs at this stage will help to avoid serious financial losses in the future for repair and re-equipment of the structure.

In order to clearly understand what the meaning of a certain basement height is, it is necessary to consider several main functions performed by this part of the building:
- The plinth prevents the internal structures of the house from getting wet.
- The plinth protects the building's finishing materials (for example, plastic panels) from dirt.
- Compensation of soil shrinkage observed due to the effect of the weight of the house structure takes place.
- If a strip or columnar foundation was used to build a house, then the distance from the ground to the floor will affect the duration of the operation of the floor, which is often made of wood. In addition, the thermal insulation characteristics of the subfloor will depend on this indicator.
- The plinth helps to ventilate the subfloor with high quality.
- Among other things, a plinth is an architectural solution that influences the overall visual impression of a building.
Experts recommend paying special attention to the height of the basement in wooden buildings, because when the lower rims rot, it becomes very difficult to carry out any repair work. That is why developers are striving to reduce the likelihood of wood rotting by increasing the height of the plinth.
But with independent construction, the owners often, on the contrary, reduce the height of the basement part, trying to make the exterior of the house more aesthetic. Thus, they are making a serious mistake.
The main disadvantage of a high base is that with its increase the cost of construction work will increase.
Regulatory requirements
The construction of a shallow foundation tape under a one-story house is possible even on a cushion of sand and gravel, this helps to save money and speed up work without any risk. But such work can only be done on certain soils:
- not inclined to heaving;
- completely dry;
- characterized by uniform freezing.
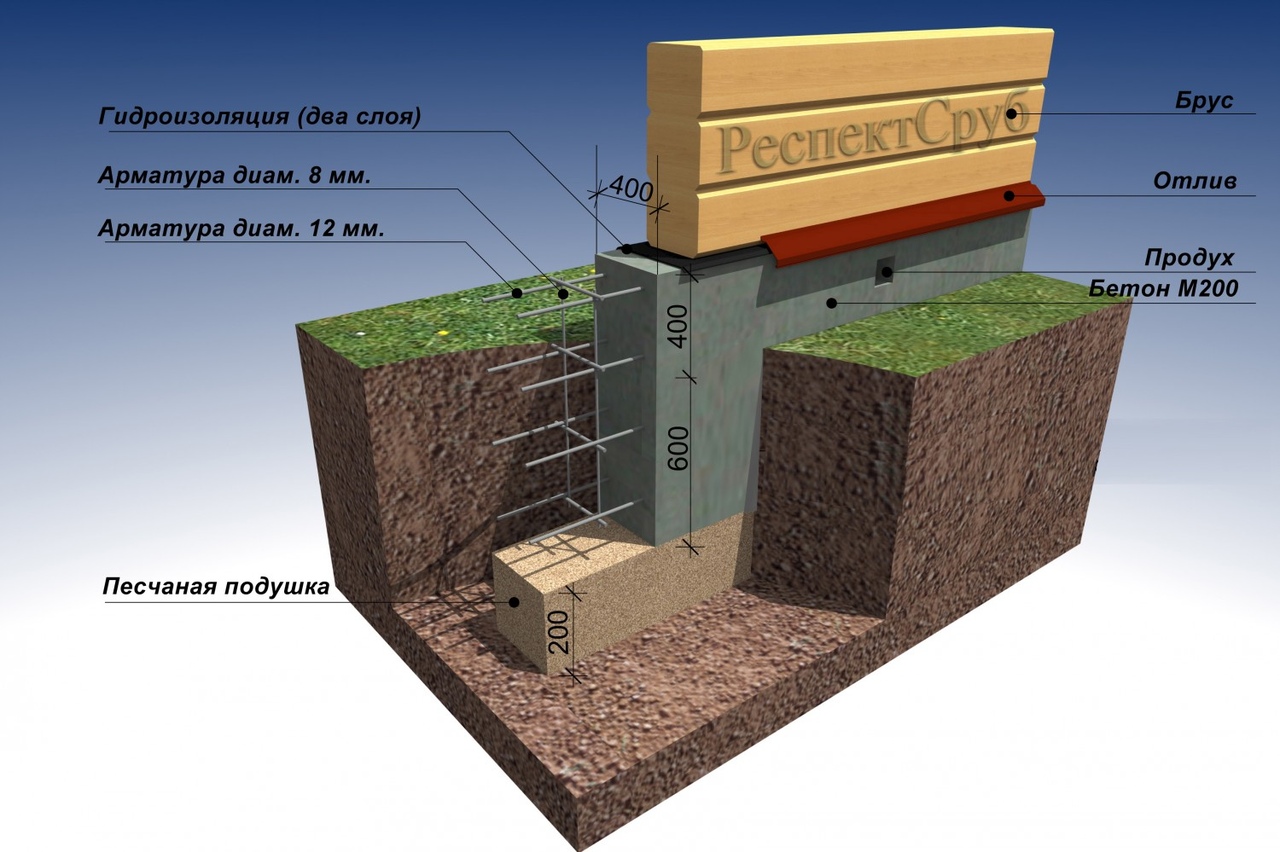
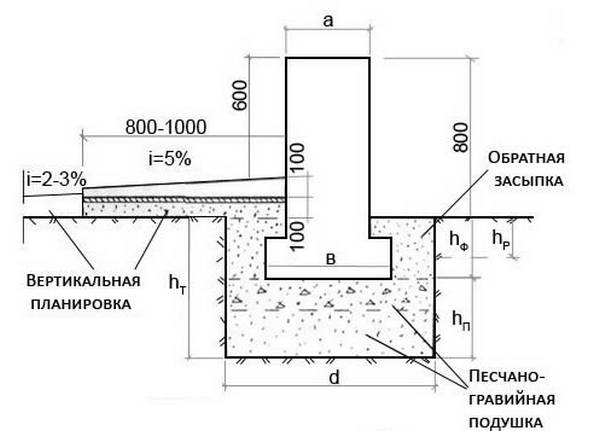
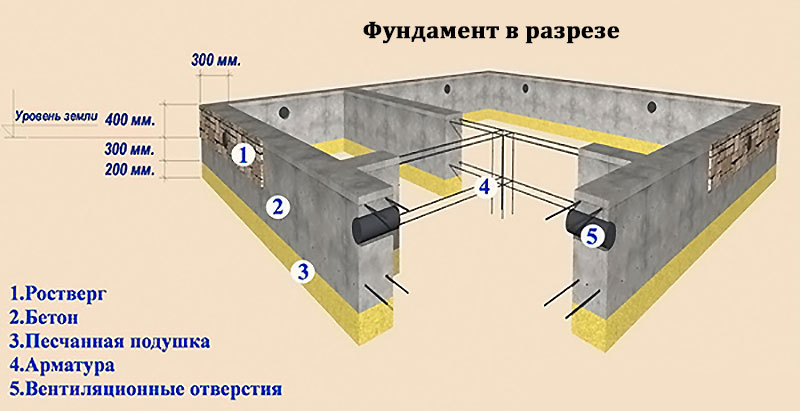
A reinforced concrete tape with a shallow deepening under a small private house is made 0.3-0.5 m wide underground, the height of the basement is at least 0.3 m.For the greatest accuracy, work begins with a marking, then trenches are dug, the walls of which should be vertically even ... The shallow laying makes it possible to do with trenches with a depth of 0.5 and a width of 0.6 to 0.8 m. When the excavations are dug and leveled, a sand cushion of 200-400 mm is made. It is supposed to be rammed, since the denser the base, the less the subsidence of the whole house will be over time.
Sand is filled in layers, 150 mm each, it must be moistened before tamping. For the highest mechanical strength, gravel is poured from above with watering with liquid concrete.
To form the formwork, boards with a thickness of 2 cm sanded on one side are used.Instead of them, you can take more:
- slate in the form of flat sheets;
- sheet metal;
- plywood.
The reinforcement of the formwork is carried out using spacers and support stakes, it must be verified vertically and horizontally. From the inside, the structure is laid with a dense waterproofing material. In order for the required thickness of this material to be less, the depth of the bookmark should be selected, focusing on the level and movement of groundwater.
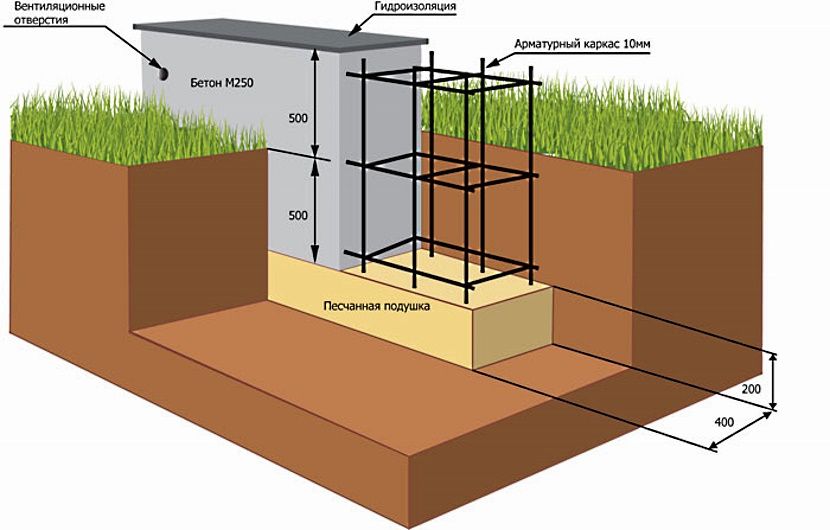
The foundation in the form of a tape for a two-story brick house is laid in a pit filled with 0.3 m of sand. Since the house will have to be equipped with bathrooms, it is recommended to add on top of the plumbing and sewer pipe screed from cement and sand up to 0.1 m thick.
Waterproofing is placed on the hardened screed, but a heat-insulating layer is not always needed. Then comes the frame, created from the reinforcing steel network, then the formwork. Only then can the tape be poured as such. The sole of the base under the house must necessarily go 200-250 mm deeper than the freezing line. Houses made of foam blocks are lighter than brick buildings of similar size.
But this does not automatically mean that you can lay the foundation closer to the surface. We will have to analyze all the parameters that characterize the geological structure of the site
In addition, the severity of the floors, furniture products provided by the project, and the snow load that may be present on the roof even for a short period are taken into account.Among the different options for bookmarks in depth, you should choose the one that you can only afford, for material reasons
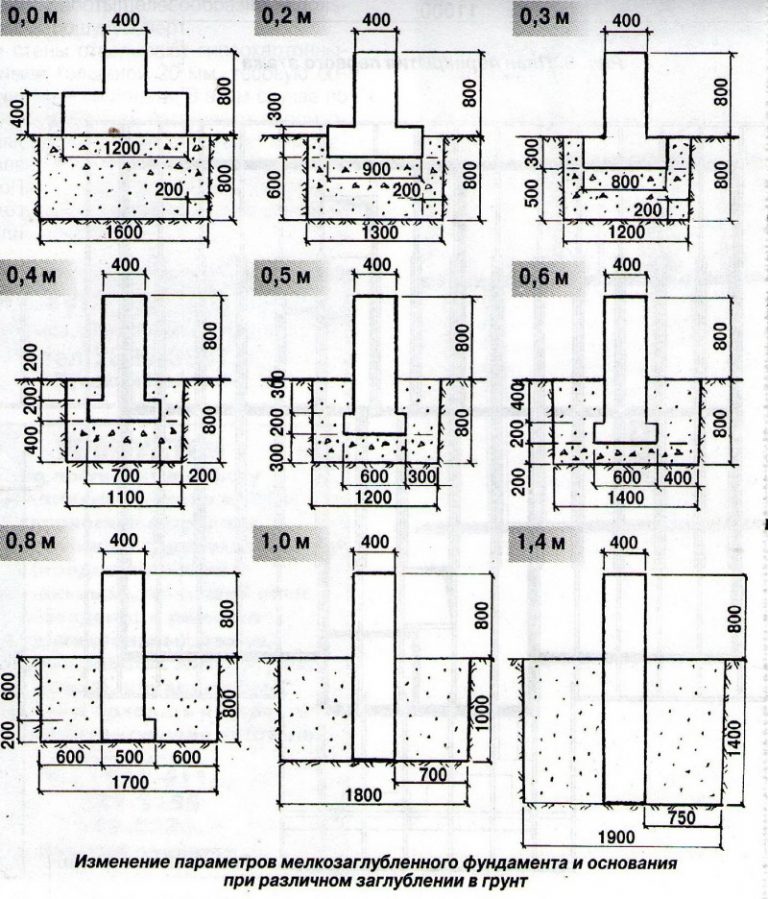
The soil in different areas freezes by 100-180 cm, and in most cases, they choose a laying of up to 150 cm.
It should be borne in mind that even when using geological prospecting information and SNiP norms in calculations, it allows you to find only the minimum required values.
To fully guarantee stability and prevent risks, it is worth bringing the base of the foundation 10 cm further.
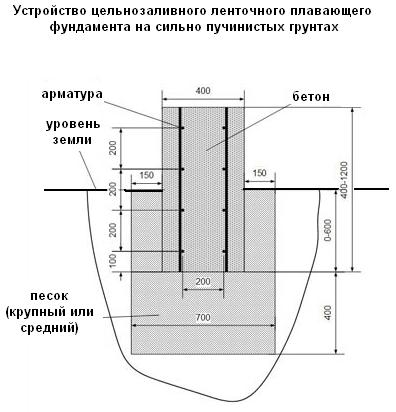
Trenches are thought out and dug out immediately with a reserve for all the necessary layers of bedding, screeds and additional structures. A relatively light house on a ground that is not prone to heaving is allowed to be placed on a base 600 mm deep, made in the format of a floating tape. Such a structure must be carefully calculated, only this allows one to avoid destruction during movements of soil masses.
A tape for aerated concrete should be calculated no less carefully than for a brick or other heavy material. The lightness of aboveground structures is deceiving; without careful calculations of the strength and bearing capacity of the support, they will turn out to be unreliable. The foundation project should be prepared with maximum buoyancy. For heavier wall materials, it is insignificant, but lightweight aerated concrete blocks are easily pushed out of the soil.