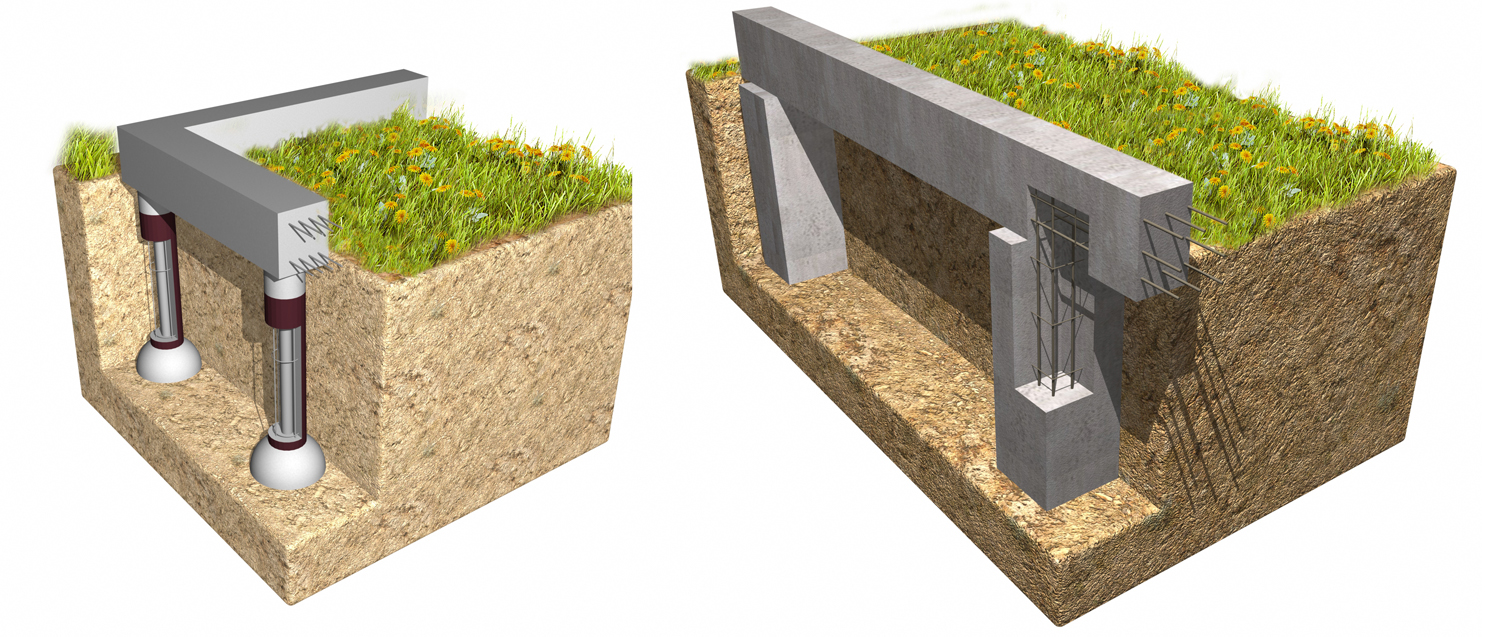
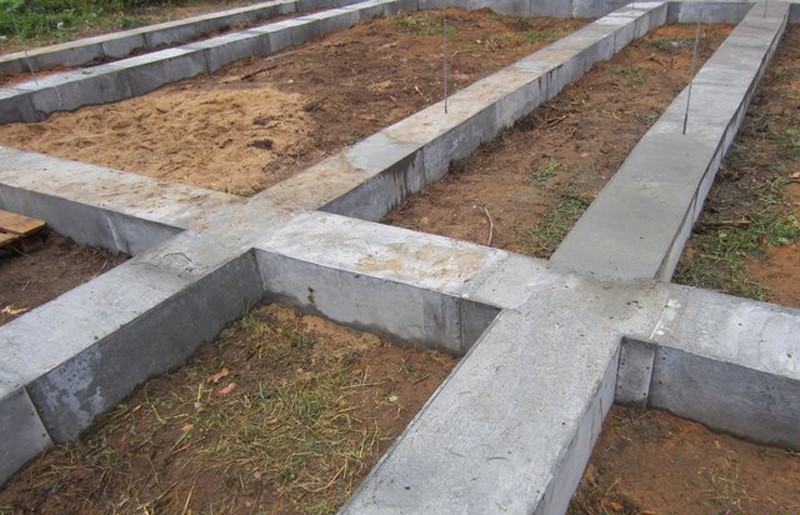
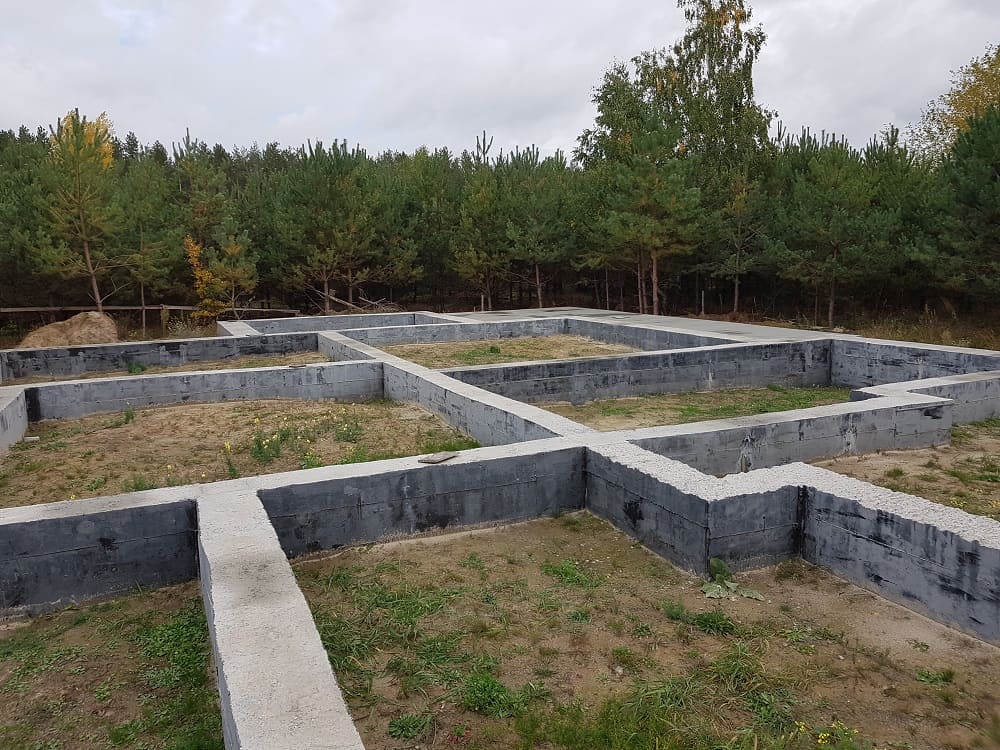
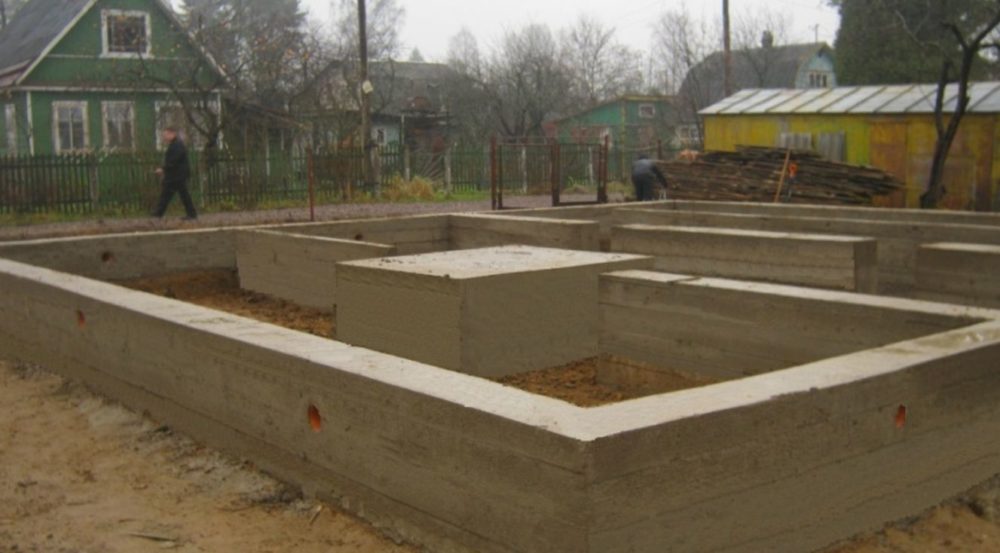
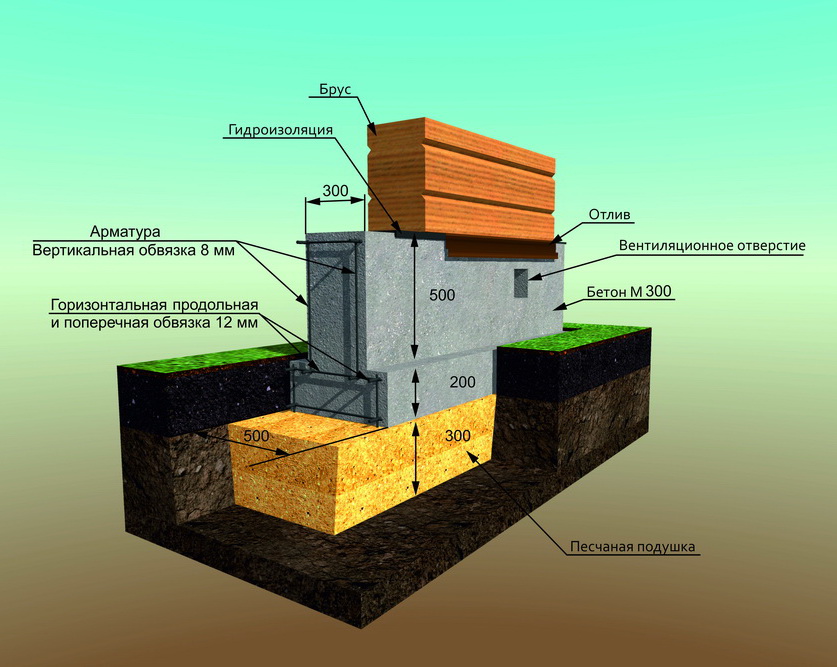
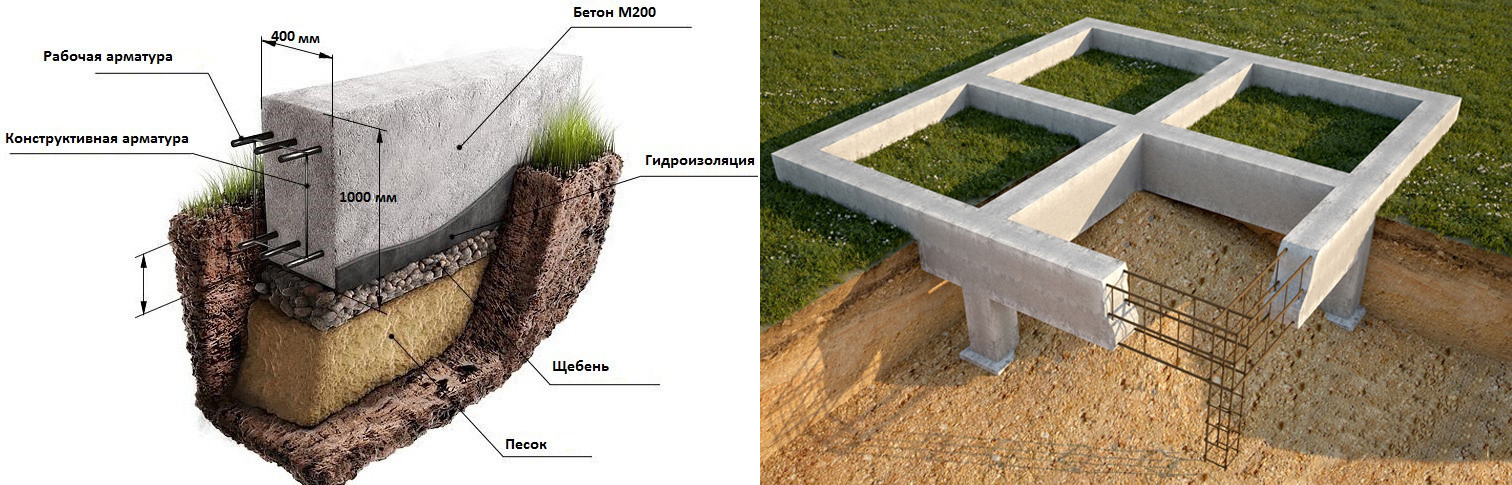
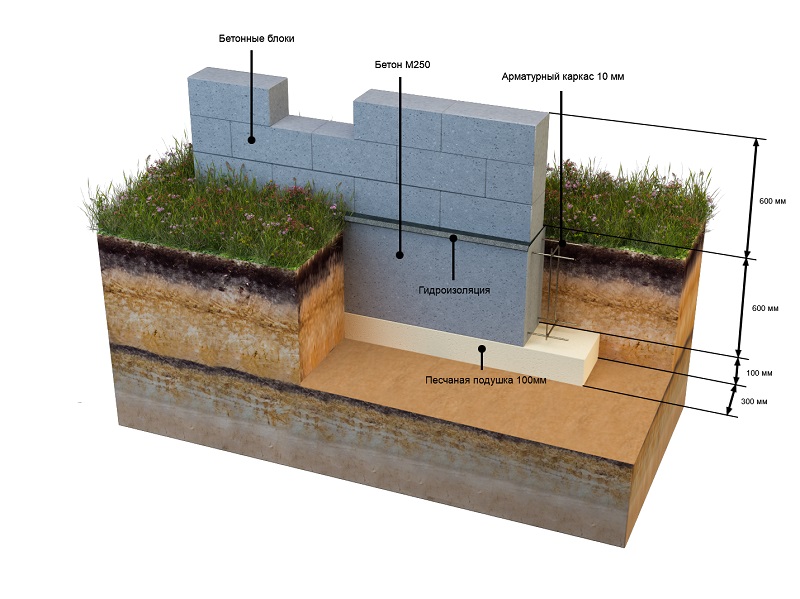
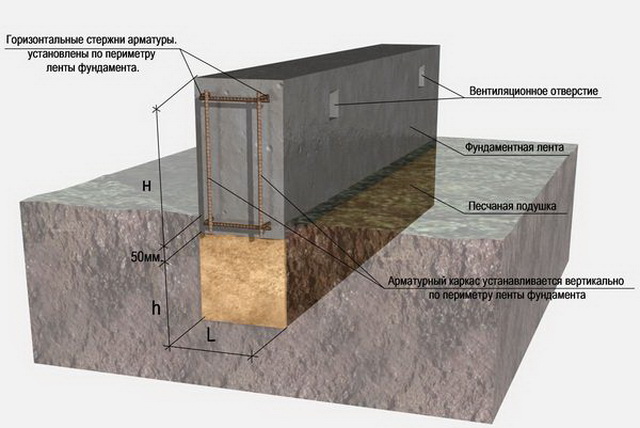
Columnar foundations
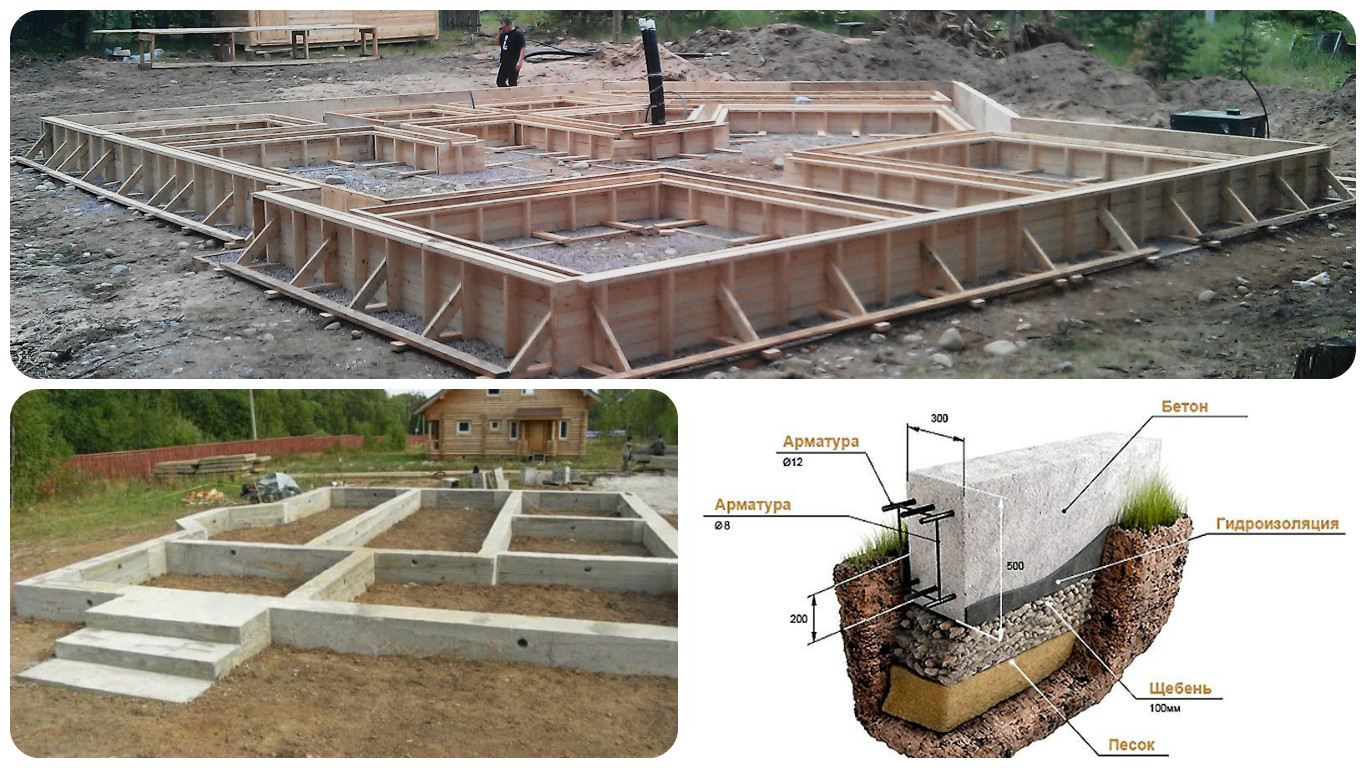
Strip foundation diagram.
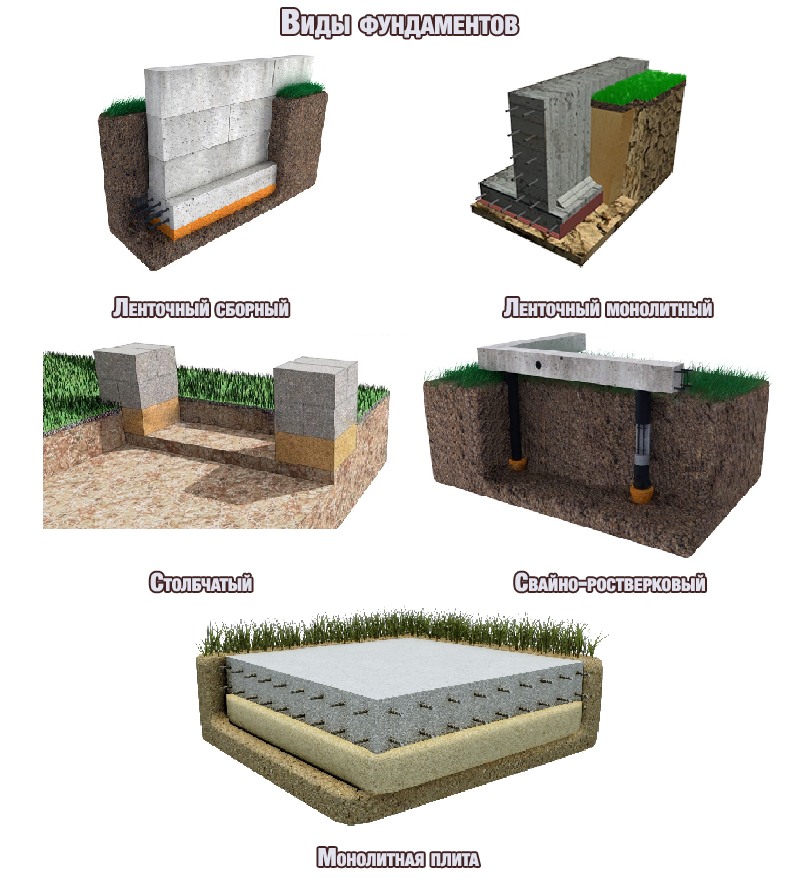
The main structural elements are the pillars. Their construction requires almost 2 times less material and labor costs than the construction of tape bases. This type of base is ideal for the construction of cottages without a basement with light frame, cobbled, panel or chopped walls.
As a material of manufacture, you can choose rubble stone, rubble concrete, concrete blocks, solid ceramic iron ore brick.
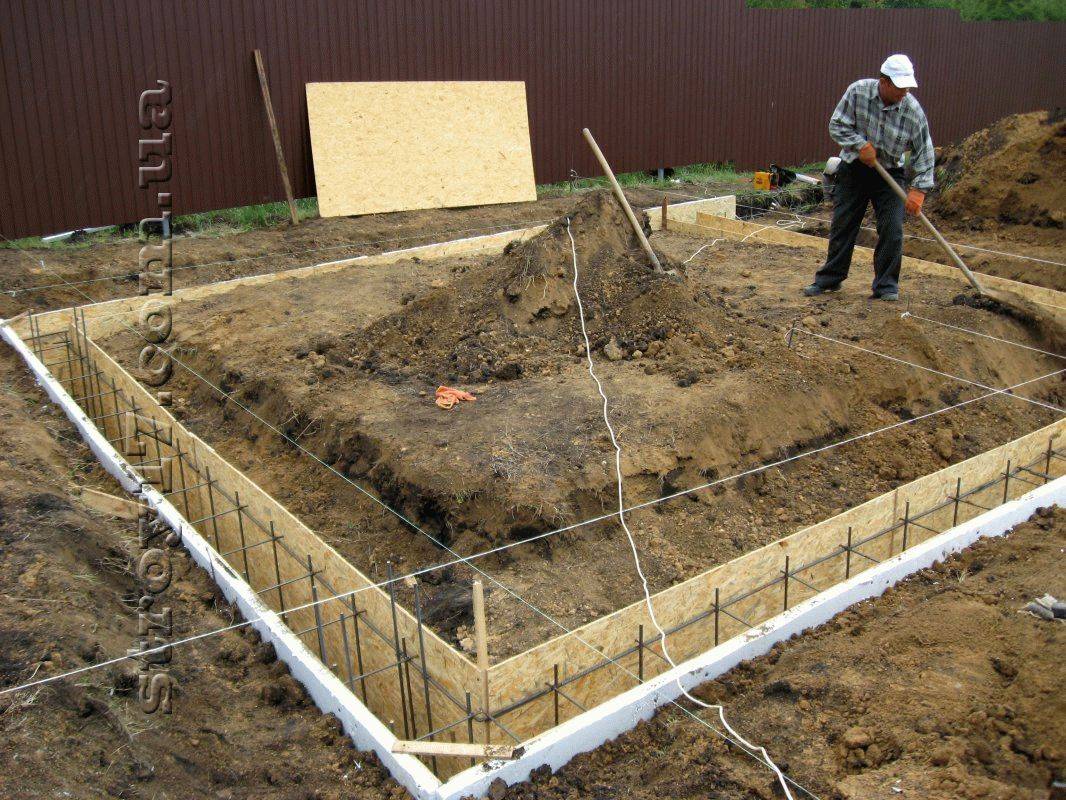
The posts are installed at the corners and intersections of the outer walls. The pillars are placed with a step size of 1.5-2.5 m along the entire perimeter of the building. Strapping beams are placed on top. If the distance between the separately standing columnar bases is more than 2.5-3 m, it is necessary to lay massive reinforced concrete or metal randbeams.
The minimum cross-section of the pillars depends on the material of manufacture. For example, pillars made of concrete, buta-slab or rubble concrete should have a cross-section of 40 cm.Masonry from natural stone - 60 cm, pillars of brick - up to 38 cm.
Formwork design for a strip foundation.
Columnar bases are divided into prefabricated and monolithic. Which type to choose depends on the specific conditions.
recommended at a depth of more than 1 m from the ground surface in the absence of groundwater.
For its construction, holes are manually dug in the ground or drilled using special equipment. The posts must have a reinforcing strap. It is needed to prevent the destruction of the column during seasonal ground movements. Formwork is also required, which can be round or square. It is necessary to provide for a gap between the walls of the pit and the formwork of at least 10 cm, which will avoid the deforming effect of soil movements on the post. After removing the formwork, sand or fine gravel is poured into it.
Prefabricated columnar bases are intended for damp and wetlands. They consist of reinforced concrete pillars and base plates. Wire and metal rods are used as reinforcement.
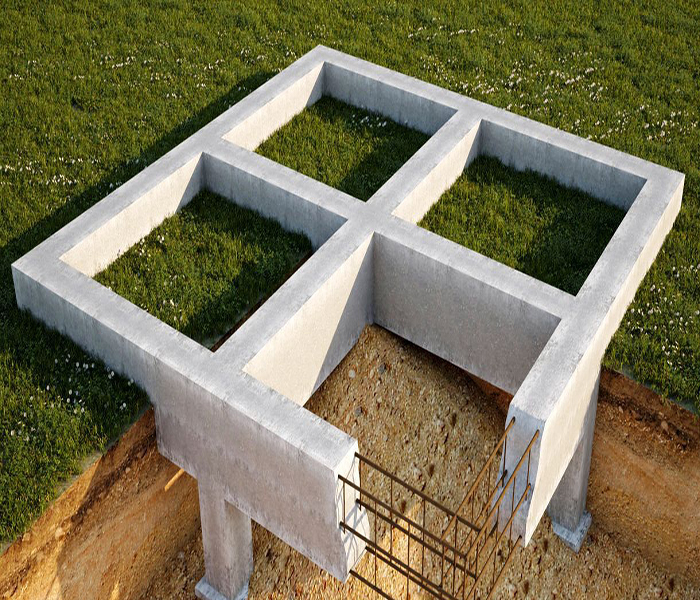
This type of base is usually not used in the construction of houses with a basement and basement. It is not used on uneven terrain due to the possibility of overturning by soil pressure from the side.
However, this type of foundation is the cheapest. It is most effective on heaving soils with deep freezing. On moving soils, such foundations are unstable to tip over.
Types of strip foundations.
When erecting columnar foundations, problems arise with the construction of the basement, since it is necessary to arrange a concrete lintel between the pillars.
The advantages of columnar bases are:
- less laboriousness in construction compared to other foundations;
- profitability.
Disadvantages of Columnar Bases:
- the need for a basement device;
- low stability in moving soils;
- the need to limit their use in the construction of buildings with heavy walls on sandy-clay soils.
Types and their general characteristics
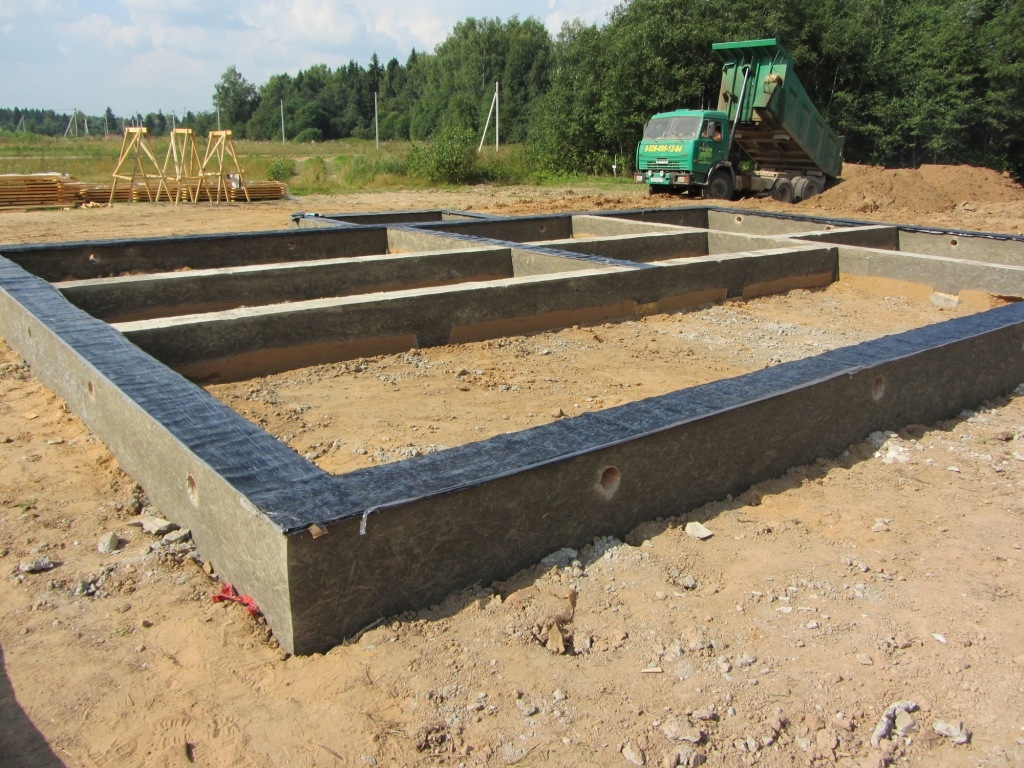
In practice, there are two types of tape bases. The first one is monolithic, and the second one is created from special blocks. In addition, most specialists divide such structures into several more types, that is, shallow and deep. In order to figure out which type is better, it is necessary to analyze in detail all types, and make a choice in favor of the option that is best suited for the future structure.
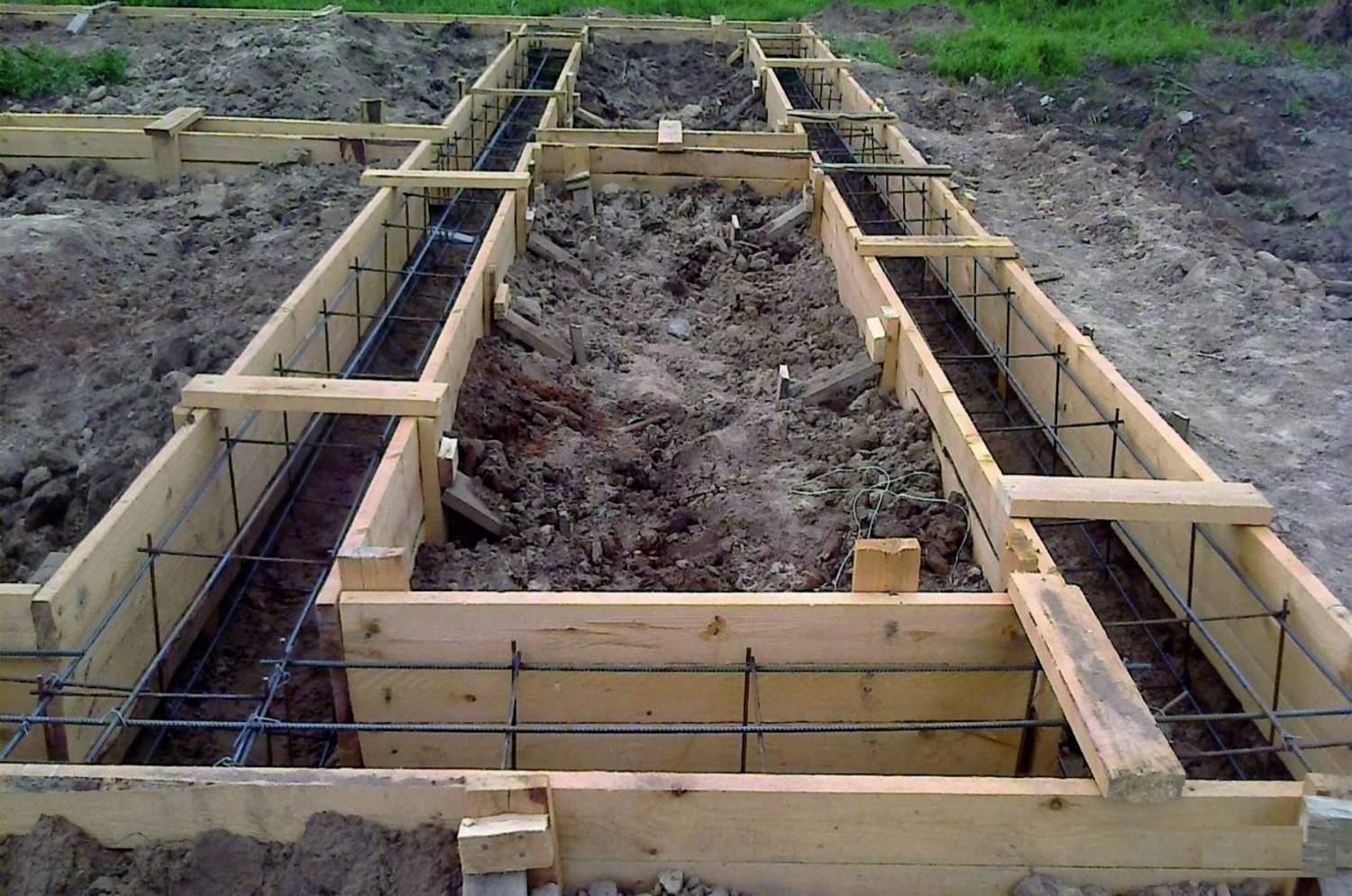
 An example of a plan of a monolithic strip foundation with a basement
An example of a plan of a monolithic strip foundation with a basement
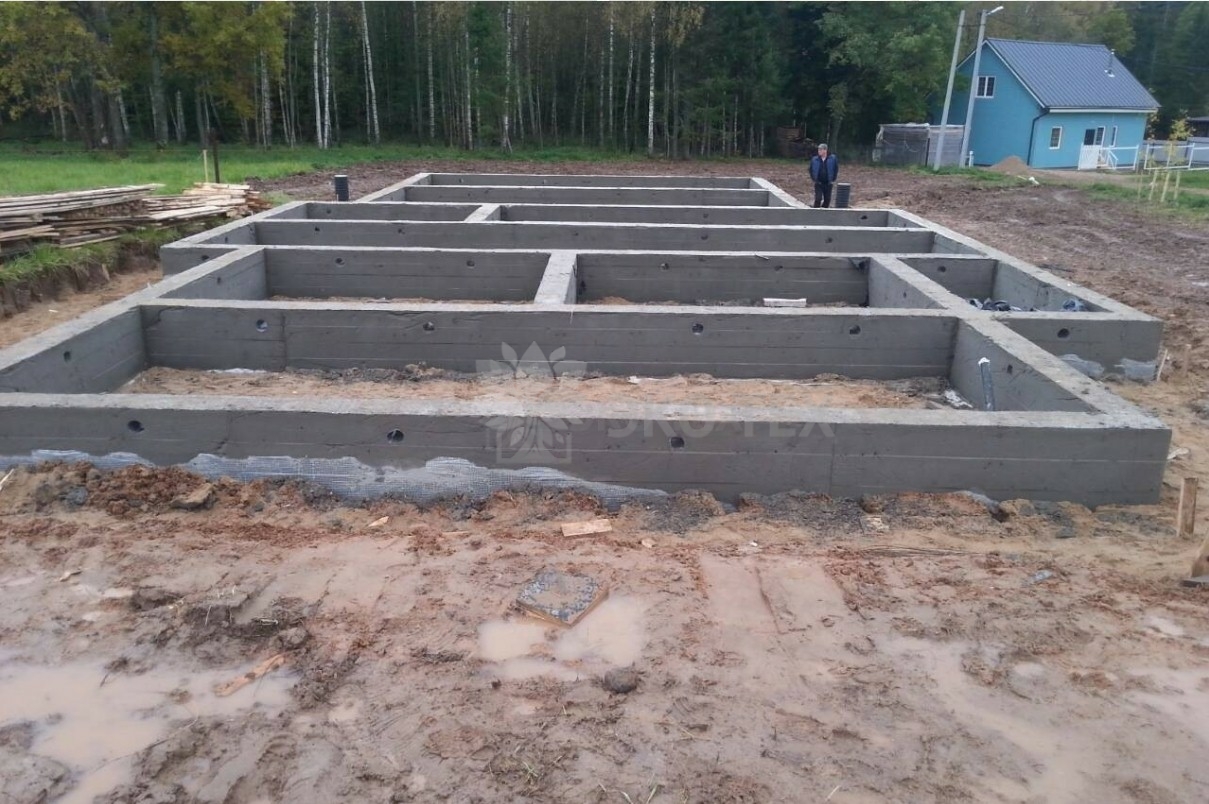
The first type is a strip foundation, consisting of a monolithic strip.Its positive aspects are that it can be not only shallow but also deeply buried. Due to its robustness and reliability of construction, it is ideal for heavy houses, and heaving soils. Such a strip foundation has high performance characteristics, and its service life ranges from 35 to 150 years. But one question may arise, why such a difference in service life. To answer it, you need to tell that a monolith is made of three types of materials.
- Butovy. It is based on a cement-sand mixture, to which large stones (quarry) are added. Such a base has high strength and reliability, therefore it is used for heavy structures. The service life of such a foundation is 75-150 years.
- Reinforced concrete. Such a strip foundation is made of concrete, which includes a cement-sand mortar, crushed stone of large fractions and a reinforced skeleton, which works as an additional element of concrete strength. The service life of such a foundation is also from 70 to 150 years. Its strength is achieved through a combination of metal and concrete, so it can be both shallow and deep, and is used for the construction of heavy houses and structures.
- Brick. It is made of bricks, in the form of brickwork. The service life of such a foundation does not exceed 50 years, and depends on many factors. The peculiarities of such a foundation are that it is not designed for heavy structures, although it can easily withstand light houses (made of wood, or built on the basis of frame structures), as well as buildings built of foamed concrete.
Understanding what the features of the three indicated types of monolithic strip base are, you can determine which type of foundation is better to choose for the construction of a particular house.
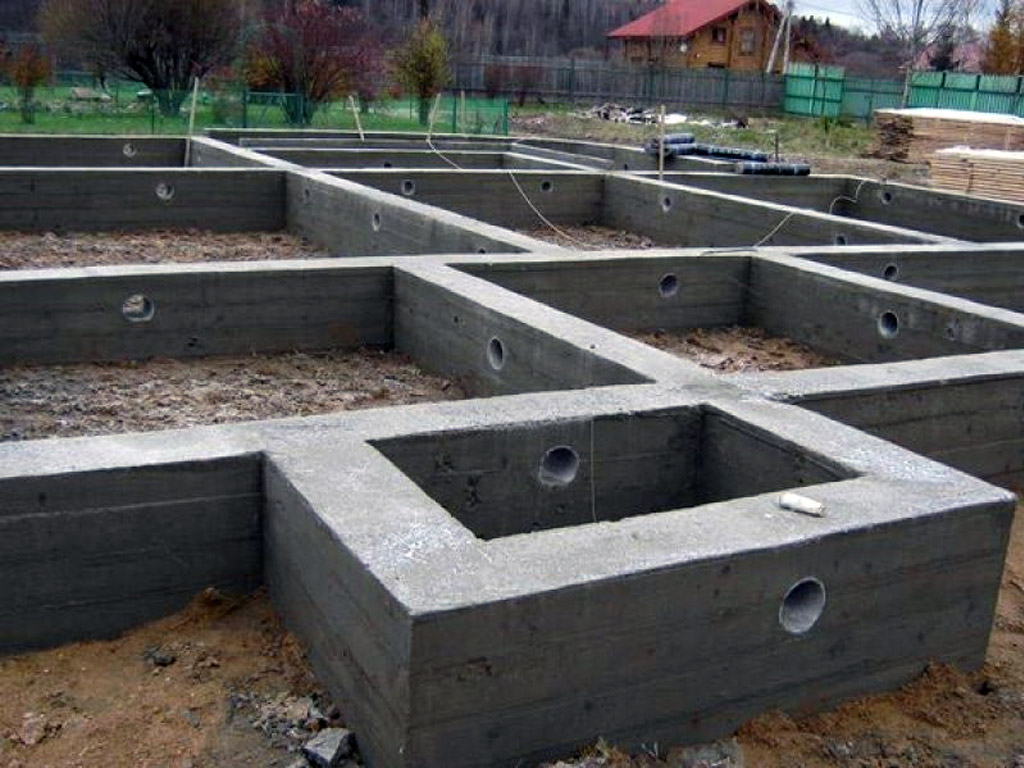
 Strip block foundation design
Strip block foundation design
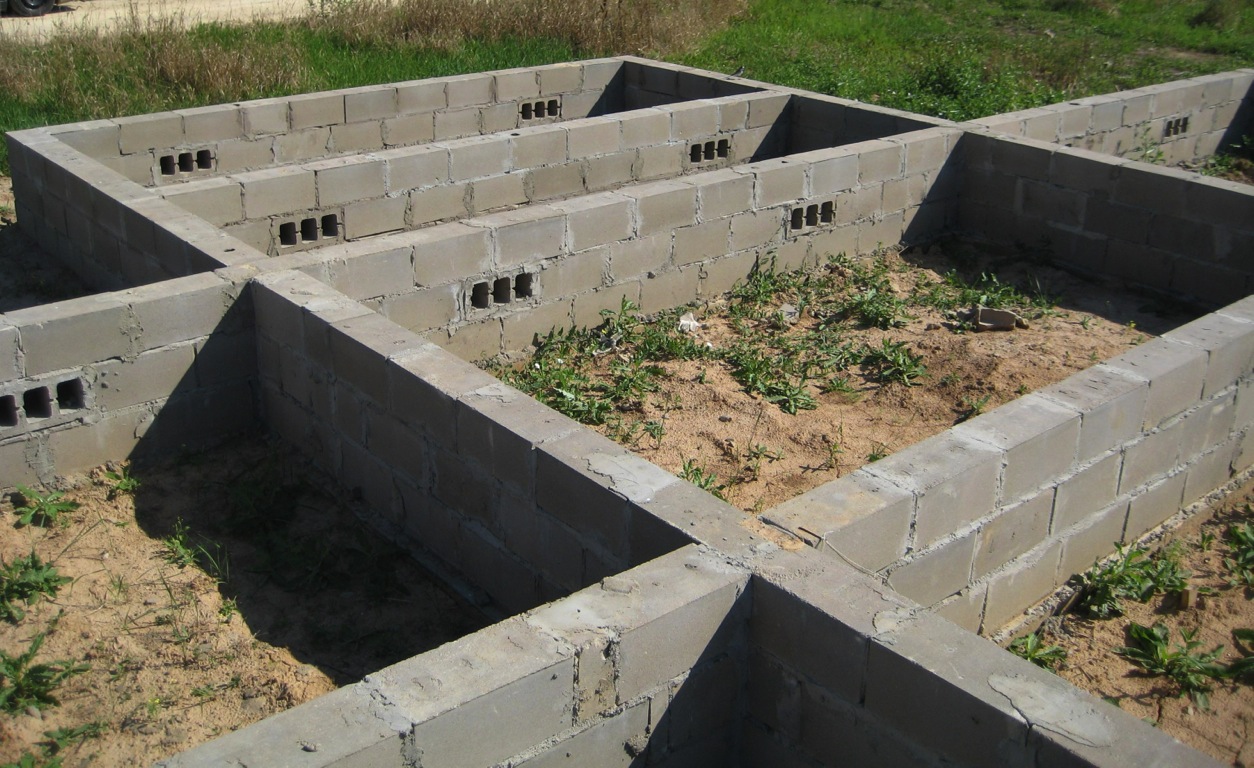
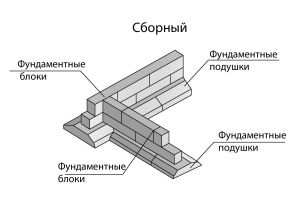
The second type of strip base is a structure made of special blocks or reinforced concrete slabs. There are also two types of such a foundation.
- Blocky. It is made of special concrete blocks that are manufactured industrially. Its peculiarities are that such a base is shallow and cannot be deep. It follows from this that the use of such a foundation can only be for soils that have little heaving, and only for houses with light weight. With a high level of groundwater, or a high level of heaving of soils, such a foundation, under the influence of the gravity of the house, will begin to sag and crack at the junctions of the blocks. This is due to the fact that industrial blocks are connected to each other with a simple cement-sand mortar, and in the case of uneven soil movement, the connection of the blocks is simply destroyed. The service life of such a foundation is up to 100 years, provided that there is a low level of groundwater and a low heaving of the soil.
- A strip base created from reinforced concrete slabs. Such a base is made of the block type, and has the same performance characteristics. This means that this type of strip base for the house has all the positive and negative qualities of its predecessor.
In order to determine which one is better, made of blocks or reinforced concrete slabs, it is necessary to understand that they are suitable only for high-quality soils and not very heavy houses or structures.
Summing up, we can say that in order to determine which type of foundation is better, you need to carefully study the characteristics of all types of these foundations and choose the best option.
Parameters for determining the cost of the foundation
 The cost of building a frame is 30% of the total cost of building a house as a whole
The cost of building a frame is 30% of the total cost of building a house as a whole
In order to understand how much money will be spent on installing the base of the house, they take into account such important criteria as:
- Remuneration of labor for the designer of the house. It is this person who is able to make for you the optimal profitable structure on the specified site.
- Geological analysis of the soil.
- The sum of the costs of all building materials for the foundation.
- Excavation costs including backfilling of the base.
- The cost of installing a reinforcing belt and installing formwork.
- Wages to workers, if any, will be involved in construction work.
In addition to these two important components of the subsequent savings in construction, it is necessary to take care of high-quality insulation, waterproofing of the base of the house, as well as a reliable drainage system.
Pile foundations
The most popular foundations in industrial and multi-storey residential construction. They are often used in the construction of small private houses and cottages using modern technologies. If during construction in an industrial way on pile foundations houses are built from any materials, then in the private sector on piles there are mainly light structures made of SIP panels, beams, logs.
Various types of pile foundations allow you to choose the one suitable for any type of structure, on almost any soil. Piles are very convenient for construction in areas with difficult terrain, including on unstable soils. The fact is that the length of the piles is practically not limited - they can reach a depth of 50 meters or more, which makes it possible to guarantee stable soil layers on which a building of any size and mass can lean.
Modern construction technologies use three main types of piles: screw, bored and bored.
Foundation on screw piles
The most popular screw piles in low-rise construction are ordinary metal thick-walled pipes with a screw in the lower part. They are screwed into the ground like ordinary screws, this is done by hand or using special machines. The length of the piles can reach 10 -12 m with a diameter of 50 - 150 mm.
After screwing in such supports, they are cut at a given height and connected by horizontal beams - a grillage that acts as the base of the house, on which the harness is laid, the floor is laid and then the walls are erected.
+ Pros of foundations on screw piles
- Simplicity and speed of installation,
- The ability to use on any soil,
- Low cost of the finished foundation.
- Cons of foundations on screw piles
- Fragility (metal in the ground corrodes).
- The need for screwing to a great depth.
- Lack of ability to equip basements.
Foundation on bored piles
Bored piles are mounted using a different technology - first a well is drilled, in which a reinforcing cage is mounted. Then the entire structure is poured with concrete. Heads protruding above the ground are cut off at a given height and connected by a grillage. The depth of such piles can be up to 50 meters.
+ Pluses of foundations on bored piles
- The possibility of building multi-storey buildings on any type of soil - the piles are immersed to the required depth, to dense layers that can support the weight of the building.
- Uniform distribution of the load on the base.
- Adjustment of the weight acting on one pile by changing the number of supports.
- Reducing the amount of earthwork.
- Cons of foundations on bored piles
- The complexity of calculations and installation.
- The need for expensive geological surveys.
- The need to use heavy lifting and drilling equipment.
Driven pile foundation
Driven piles - concrete products in the form of square or circular beams of great length - 12 meters or more. They are driven into the ground by impact devices or by vibration immersion.They are used mainly in industrial construction - for hammering, complex and expensive equipment is required.
Having considered all the main types of foundations for a private house, the choice of the best option is simplified. For brick, block and stone buildings, the optimal strip foundation. For frame construction, houses made of timber and logs, slab or pile (screw) ones are more suitable, on solid soils - columnar. But in each case, a different option is chosen, the main thing is that the foundation fulfills its main function - it serves as a reliable support for the house.
Bored foundation
The bored foundation belongs to the pile type. It is also considered to be one of the economical and reliable ones.
Bored piles are made directly in the ground.
- Wells are drilled at pre-marked places, into which metal reinforcing cages are installed, and then a solution is poured into them.
- If the soil is loose, then in order to keep the walls of the well from destruction, a roofing material lining is used.
- Next, a grillage is installed, thanks to which the underground part of the foundation is tied together and an even distribution of weight is ensured.
A big plus of a bored foundation is its ability to withstand not only light wooden or frame houses, but also the load of heavy stone houses, without settling.

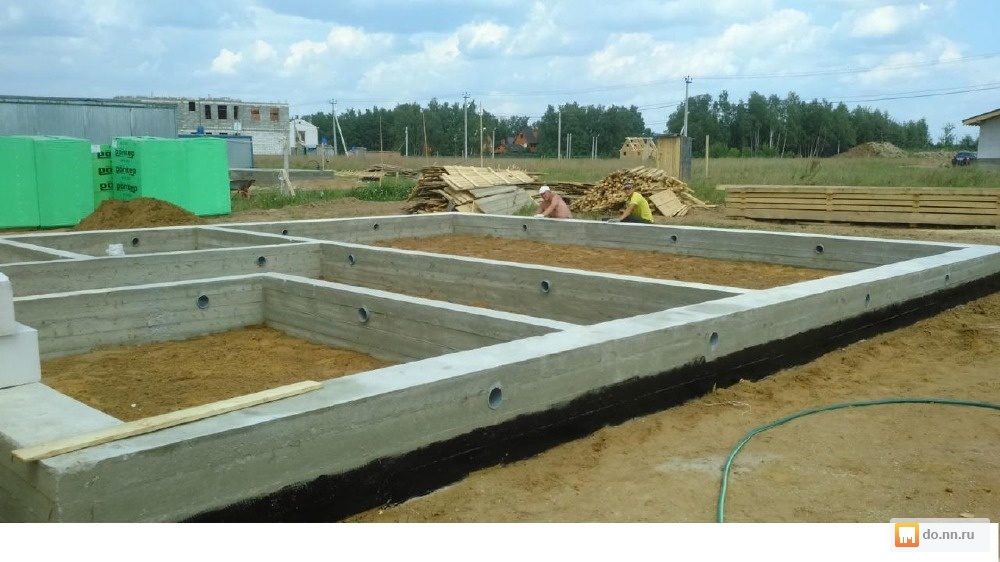
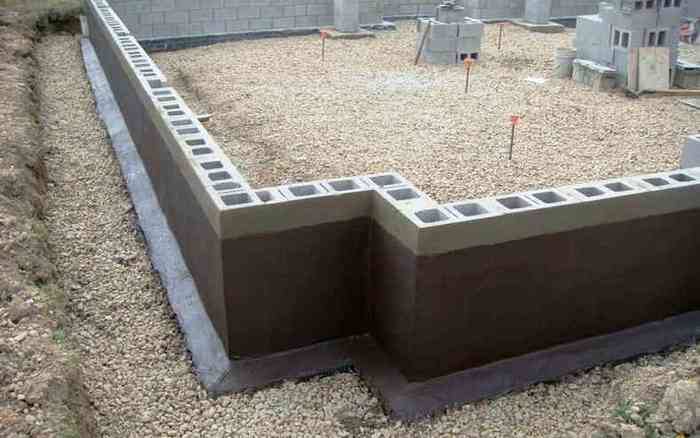
Monolithic base and FBS foundation, cost comparison
 From the beginning of the construction of the formwork to the complete maturation of the concrete, it takes 1-1.5 months, which is much longer than the FBS masonry
From the beginning of the construction of the formwork to the complete maturation of the concrete, it takes 1-1.5 months, which is much longer than the FBS masonry
If we consider both technologies from the point of view of the installation of a buried foundation, the initial work and the associated costs will be approximately the same (preparation of a construction site, digging a foundation pit). Further, the process of erecting the underground part of the building is fundamentally different in terms of labor intensity, costs and time required to carry out a set of works.
This is how the construction of a foundation structure in blocks looks like:
- layout and bedding of the base;
- FBS masonry.
It will take 2-3 days to erect the foundation for an average house with the involvement of 2-3 workers and a crane. In addition to the foundation blocks, 3-4 tons of sand and a ton of cement are needed for masonry.
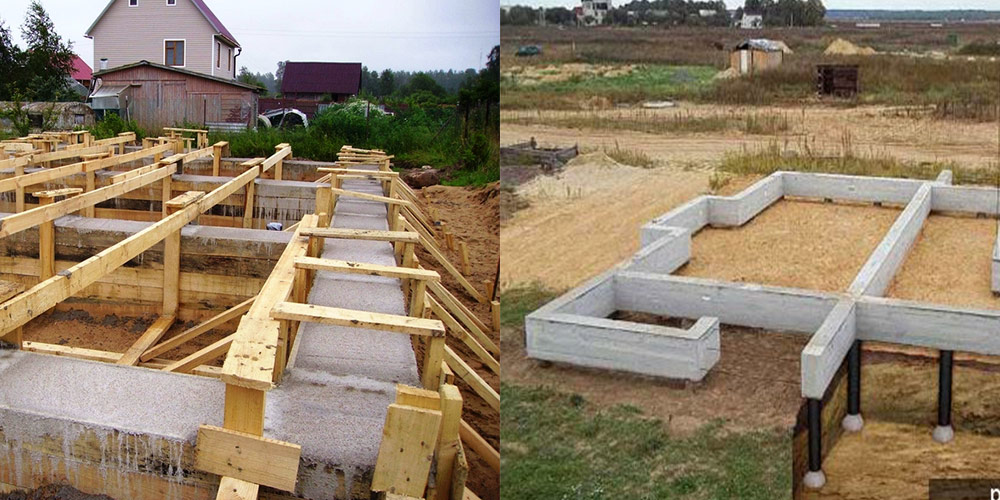
Filling is much more difficult. The following technological processes consist of the formation of a concrete monolith:
- exposing the formwork;
- waterproofing device;
- knitting of a reinforcing structure;
- stage-by-stage filling of the formwork cavity;
- removal of the formwork.
All work steps are laborious and time consuming. From the beginning of the construction of the formwork to the complete maturation of the concrete, it takes 1-1.5 months, which is much longer than the FBS masonry. Of the materials, you will need several self-propelled concrete mixers, 6-10 cubic meters of wood, 2-4 tones of reinforcement, and this is not counting the "little things" (nails, knitting wire, plastic film). Building blocks and hiring a crane are also far from free, but with careful calculations, the end result is block laying. Another important factor is the saved time, which is much less for laying blocks.
What is a monolithic slab
A monolithic foundation is a solid reinforced concrete slab, which becomes the basis for the future building. The slab does not create a large load, because due to the significant area, the specific pressure is low. In the event of soil movements, the house easily moves along the ground, but the rigid and durable slab guarantees the reliability and evenness of the building.
For the construction of this type of foundation, a pit is dug, removing the top layer of soil. Then a sand cushion is poured, equalized, the layer is compacted, geotextiles and insulation are placed on top. Next, the formwork is mounted and a reinforcing cage is formed in it, poured with concrete.
After 28 days, concrete is gaining strength and a reliable, durable, well-insulated and protected base is obtained, capable of taking loads from the building and resistant to various soil movements.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before deciding which foundation is better (strip or slab), you need to study the soils and conditions at the facility, consider each suitable option in terms of implementing the tasks and improving the quality of construction, reducing the cost of the project.
The main advantages of a monolithic foundation:
- Good indicators of strength and reliability on heaving, weak bearing, watered soils
- High load-bearing capacity of the base - even heavy large buildings are robust
- Provided proper reinforcement, the foundation successfully resists any influences
- Easy perception of ground movements - due to the fact that the slab on the surface seems to "float"
- Ease of design creation - serious mistakes in construction are extremely rare
- Pouring the slab makes it possible to immediately get half of the floor, further work is simplified
Of the shortcomings, it is imperative to mention: the lack of the possibility of creating a cellar or basement, the exclusion of the chance of repairing the slab, a large amount of earthwork and a significant consumption of building materials. Due to these disadvantages, the base slab is usually an excellent choice where there are no alternatives.
Varieties
Reinforced concrete slabs can be made in several ways, according to one technology or another.
Types of slab foundations:
- Monolithic slab - cast on site
- Prefabricated - assembled from ready-made reinforced concrete blocks that are stacked on a pre-prepared site
Types of slab construction:
- Solid - well suited for small, lightweight buildings
- Ribbed - with special stiffening ribs that fix the structure in the soil and do not allow it to move in space. The ribs also contribute to a more even distribution of the entire load.
- Box - in such a slab, the floor of the first floor is made in the form of a separate overlap, while the surface of the slab creates a basement room
Suitable conditions
When thinking about which foundation is better (tape or monolithic), first of all, they take into account the conditions at the facility and the type of soil. The slab foundation is relevant for the construction of buildings in a region with heaving, unstable, watered soils.
This is a good alternative to piles when there is no possibility of using special equipment on site. Also, the slab base can be poured where dense layers of soil lie very deep (and the length of the piles is simply not enough).
Which type of base design is best?
The answer to the question of which foundation is better lies in the economic feasibility of using one or another type of foundation. The strip foundation occupies one of the leading positions in the construction of country houses. All the intricacies of choosing a foundation for a future home, see this video:
In suitable soils, the belt can be shallow, which will significantly reduce construction costs. The narrow range of soils reduces the use of this type of foundation. But this once again emphasizes that the desire to build exactly the strip base prevails when choosing the type of construction.
For the construction of something more than a country house. For example, when building a heated two-story country house with an attic, which uses brickwork and reinforced concrete floors. It will be necessary to calculate the cost of the strip base and the concrete sub-floor in comparison with the device of the slab foundation.
You will also need to estimate the cost of waterproofing and insulation of both types of bases. After such a comparison, it will be possible to talk about which foundation is more profitable to use.
Before starting construction, you need to go a long way. Sometimes it is longer than the building period itself. The final result will largely depend on the quality of the work done at the preparatory stage.
It is important to correctly determine all the necessary requirements for the building, embodying them first in the design at the design stage, and then in construction.
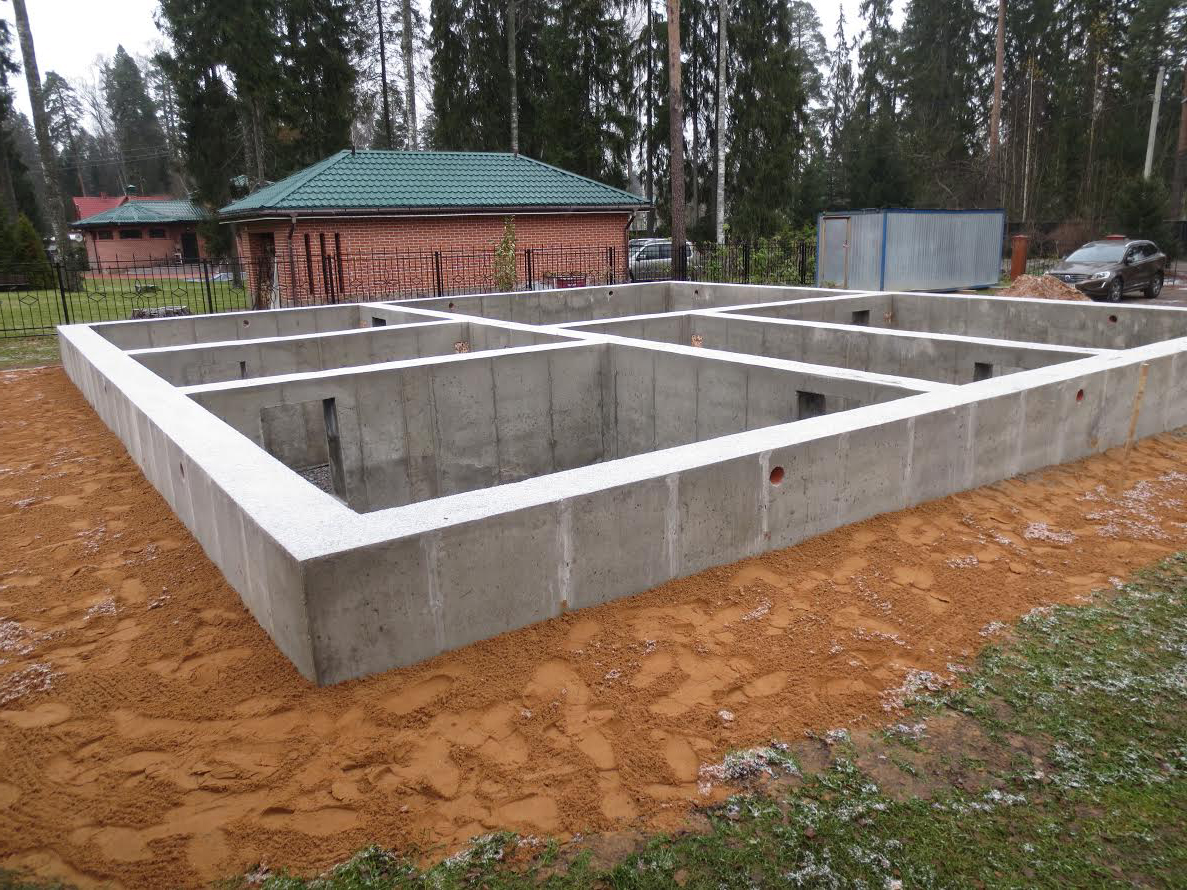
Recessed and shallow strip foundation, features
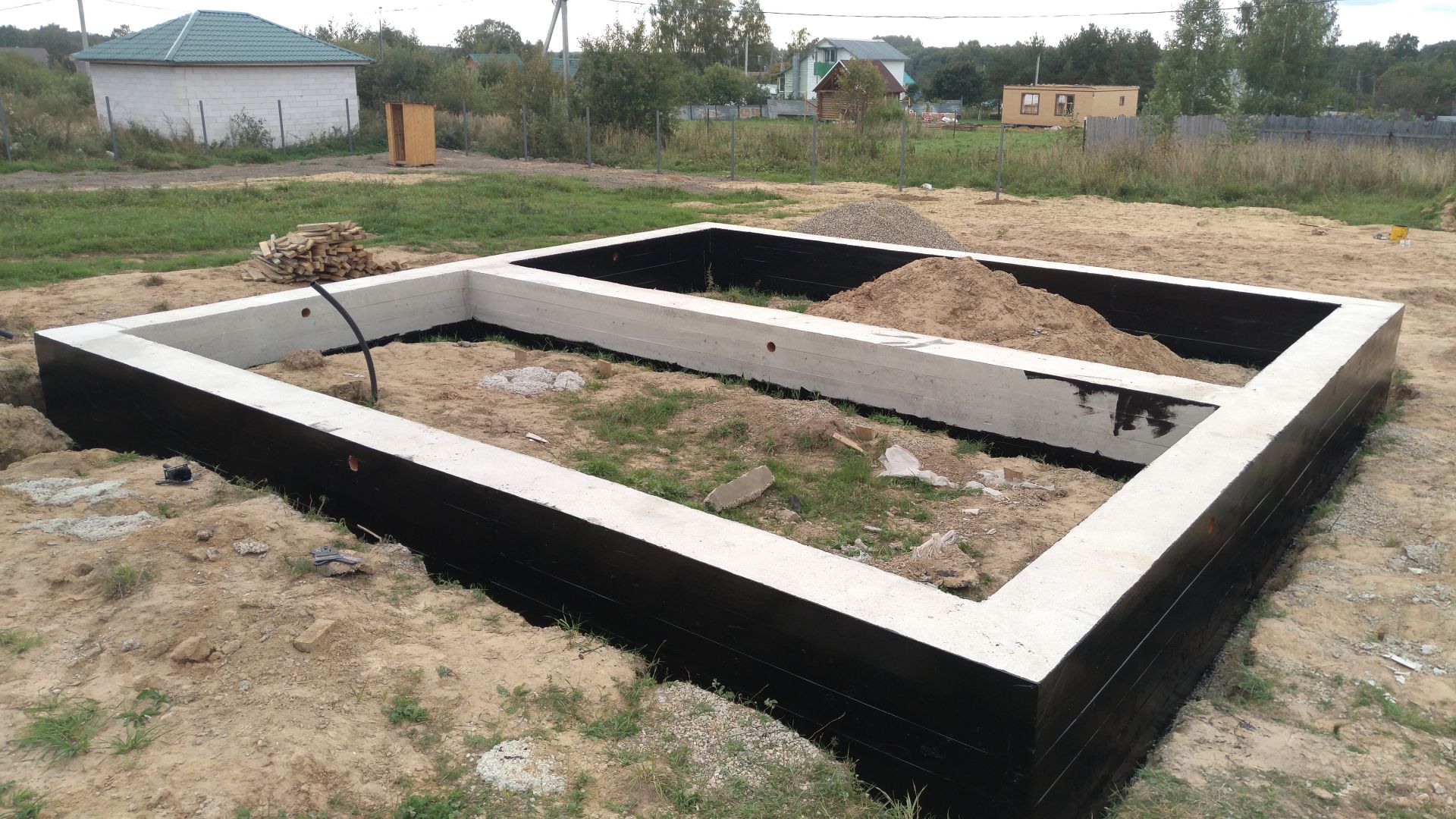
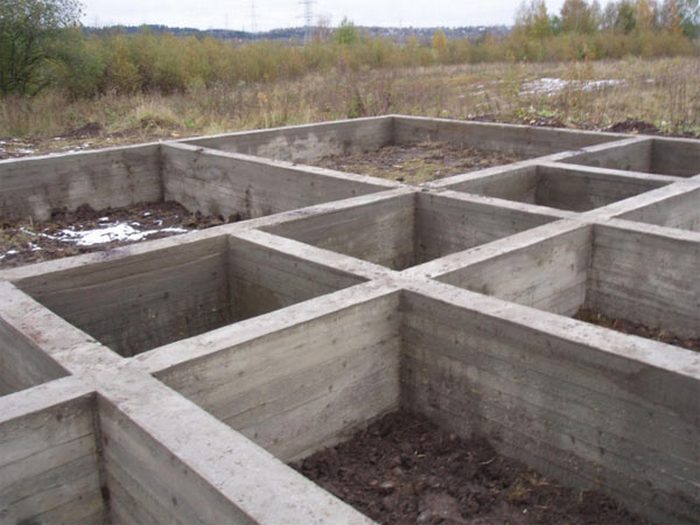 A tape deepened by 3-4 meters is poured or laid out with FBS, when it is planned to arrange a basement floor or a technical basement room
A tape deepened by 3-4 meters is poured or laid out with FBS, when it is planned to arrange a basement floor or a technical basement room
A tape deepened by 3-4 meters is poured or laid out with FBS, when it is planned to arrange a basement floor or a technical basement. This is the most voluminous type of foundation in terms of labor costs and material resources.
In addition to the possibility of constructing a basement, a buried foundation has another advantage - such a foundation is much more stable when compared with a shallow tape. Considering this factor and significant material investments in the construction of an underground structure, it is logical to use technology that will be cheaper.
A shallow strip base is constructed only where the characteristics of the soil allow. This type of foundation structure will not be an effective support for construction on heaving, sandy soils, with significant swampiness of the site
Even if there is a possibility of pouring a shallow tape, special attention is paid not to the cheapness of the material, but to the strength characteristics of the structure being created.
Cost: strip foundation or slab
Everyone says (and writes) that a monolithic base is much more expensive, that it will cost like two tapes. Yes, you will have to purchase more concrete and reinforcement than for the construction of a strip base. However, there are a few big "BUTs" here:

- A shallow pit is enough for the slab, which in itself promises savings in concrete.
- The material for the formwork for the slab takes much less than for the tape: almost twice.
- For the construction of a monolith, you can use not metal, but composite reinforcement, which is not only lighter, but also cheaper.
- The base plate is a ready-made subfloor, for the arrangement of which the “competitor” takes a rather significant amount, which will almost entirely “eat up” what is saved on the tape.
- A slab foundation can be built in a short time by a couple of unskilled workers. Creating a reliable tape with your own hands is a daunting task, and attracting specialists will cost a lot of money.
For these reasons, those who opted for a tape base now say they made the wrong decision.
Prevention of calves after birth
Disease prevention in calves not only reduces the risk of disease, but also improves the quality of life of individuals, which in turn increases productivity. So, calf prevention - what is it?
- Balanced diet of a cow bearing calves.
- Professional obstetric care is very important!
- After giving birth, you need to properly handle the umbilical cord, check all reflexes in the calf.
- Correct feeding of individuals - the amount of milk and other food should be strictly regulated.
- Timely vaccination of the born calf against paratyphoid fever, salmonellosis, rhinotracheitis, colibacillosis and many other ailments.
- Keeping animals in clean rooms, which are regularly cleaned and disinfected 1-2 times a year.
If you follow preventive measures and monitor the animals, then the diseases of the calves can be easily prevented or cured in the early stages.
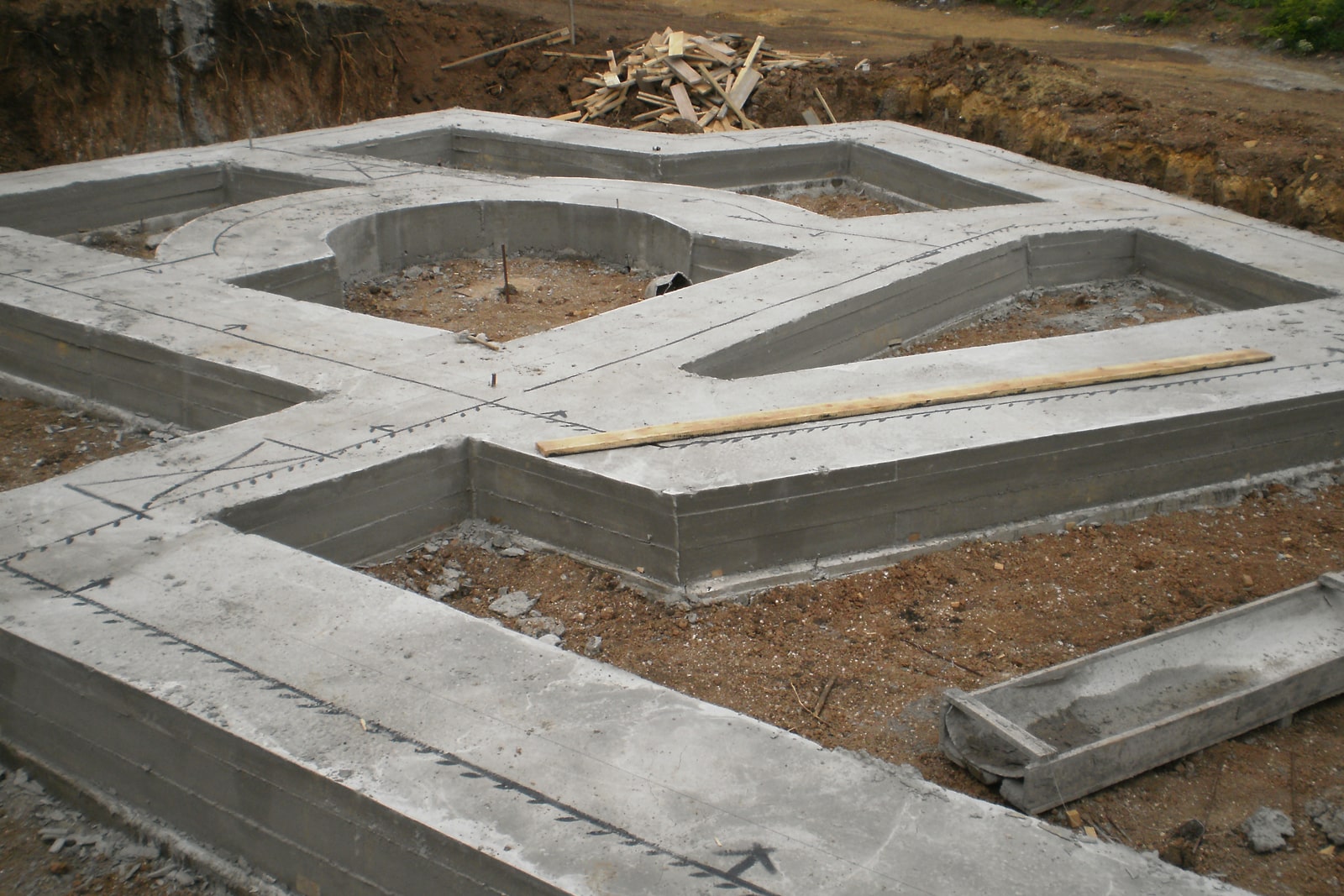
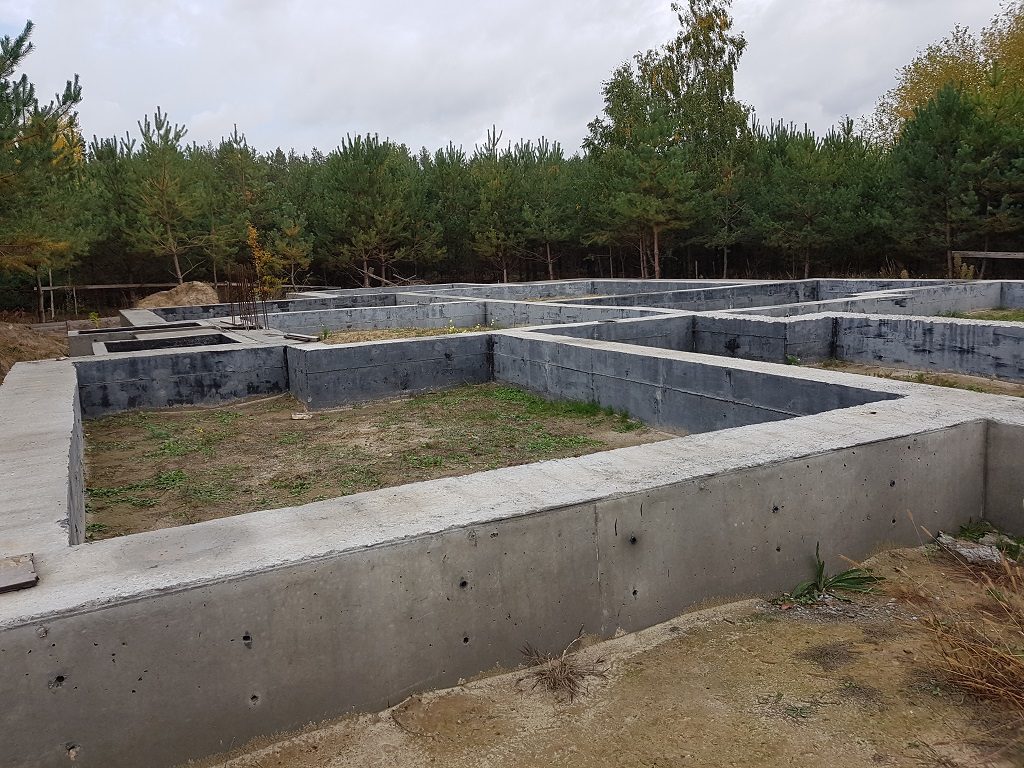
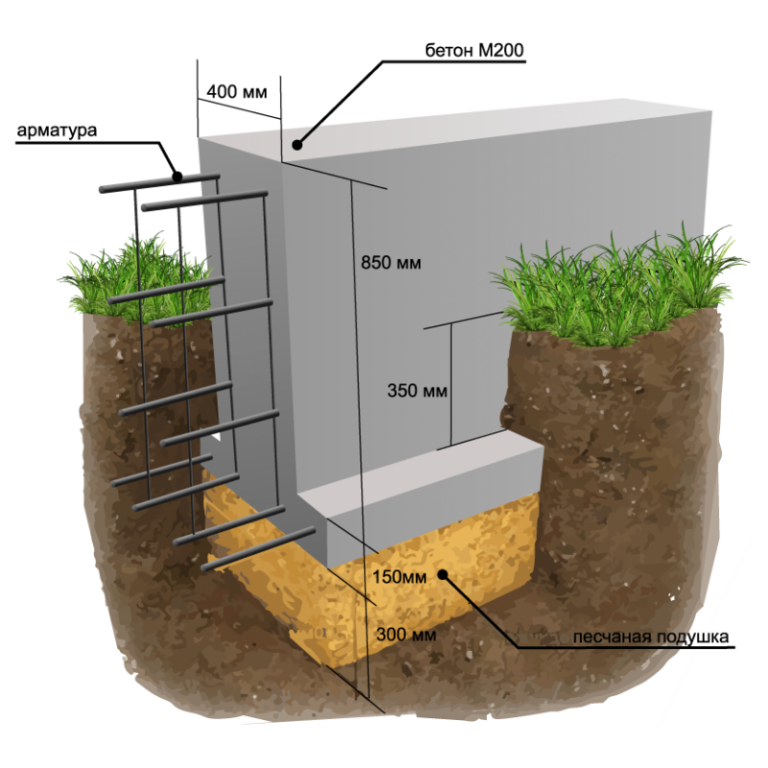
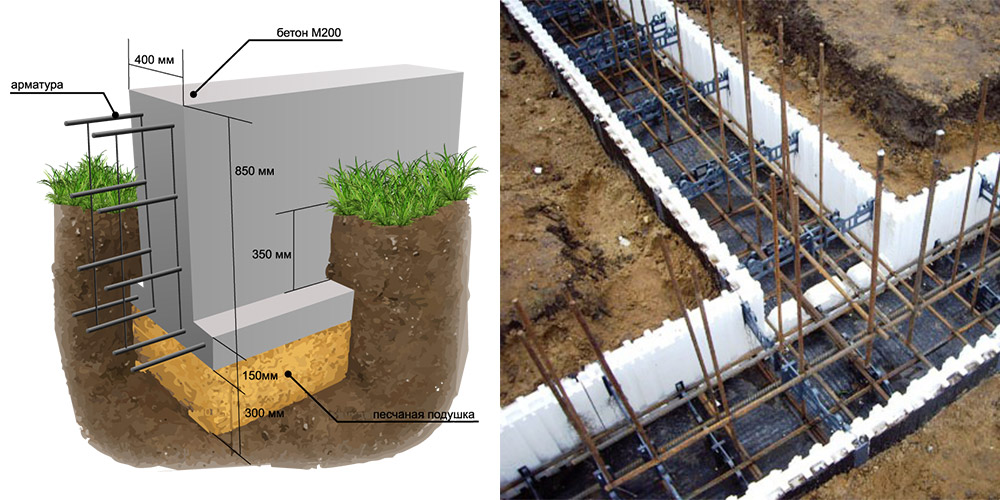
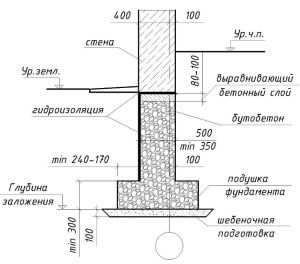
Strip foundation
In contrast to the grillage along the pile field, the strip foundation has several modifications of the same design, different levels of deepening:
- Recessed strip foundation (ZLF) - the bottom of the strip is below the freezing mark without taking into account the bearing capacity of the soil;
- Shallow strip foundation MZLF - is used exclusively when the groundwater level is more than 1 m, the base of the strip is 0.4 - 0.7 m below ground level;
- T-shaped - widening of the sole, buried in the ground similarly to the MZLF;
- not recessed - the tape is placed on the edge;
- tape belt - the tape lies on the side to increase the supporting surface.
If a brick cottage can be supported on piles on any soil, then of all the modifications of tape bases for brickwork, only ZLF is suitable. The solution, bandaging of rows in a half-brick does not provide the spatial rigidity of the structure, comparable to a monolith or the crowns of a log house, which are self-supporting. Therefore, brickwork on a non-buried tape (MZLF) will inevitably crack over time. Thus, when choosing a technology, it is necessary to consider which house will be based on the foundation.
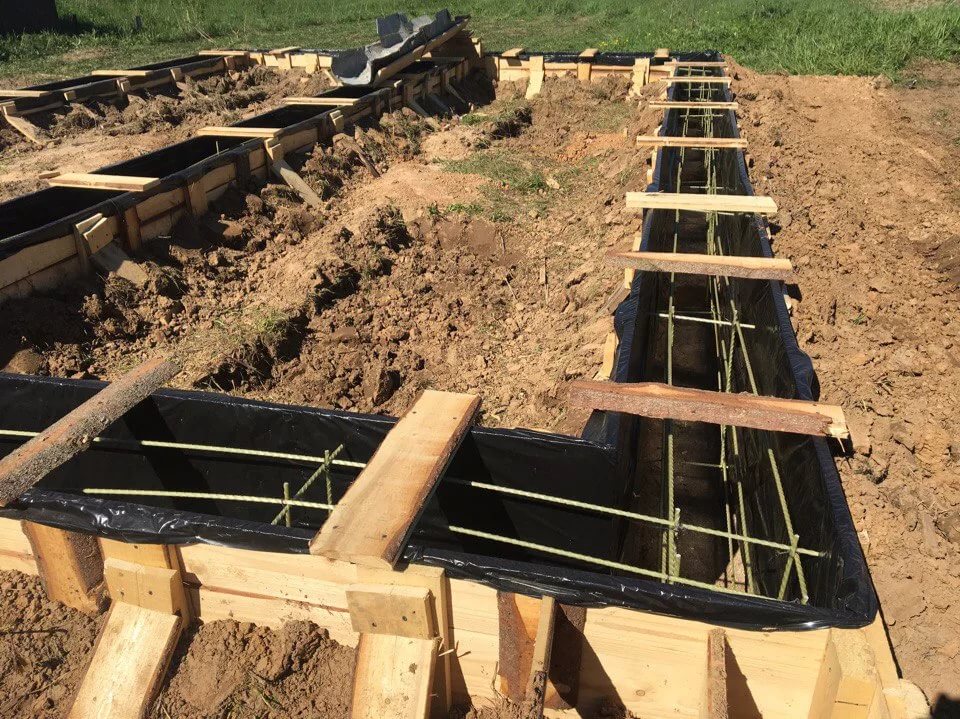
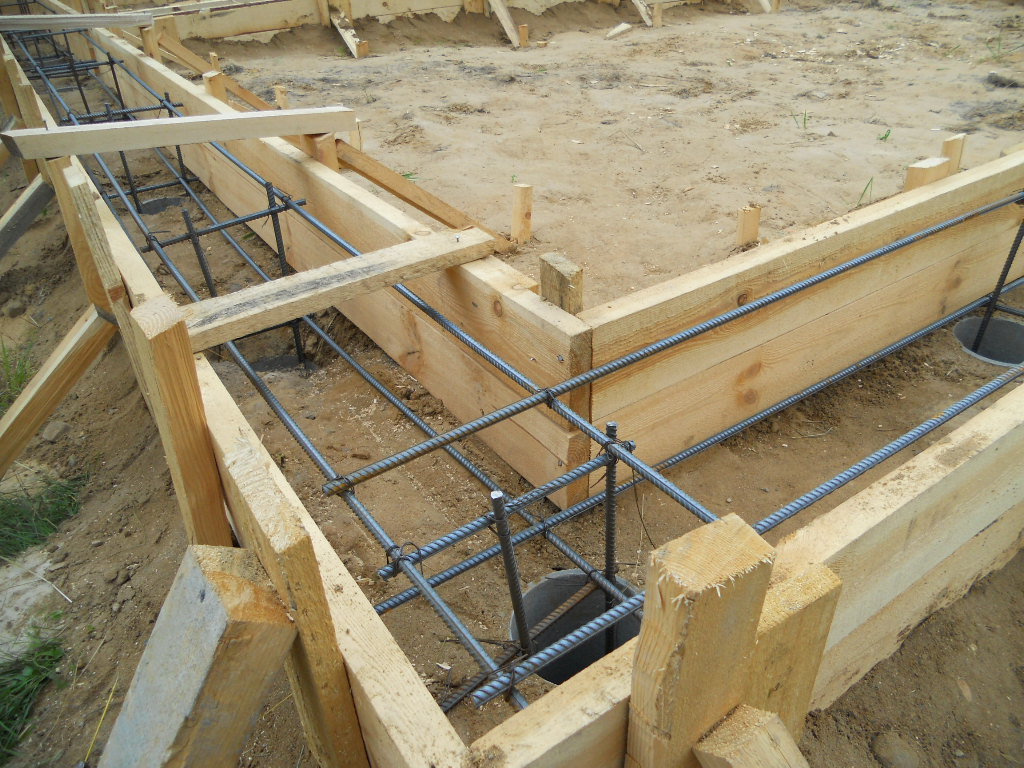
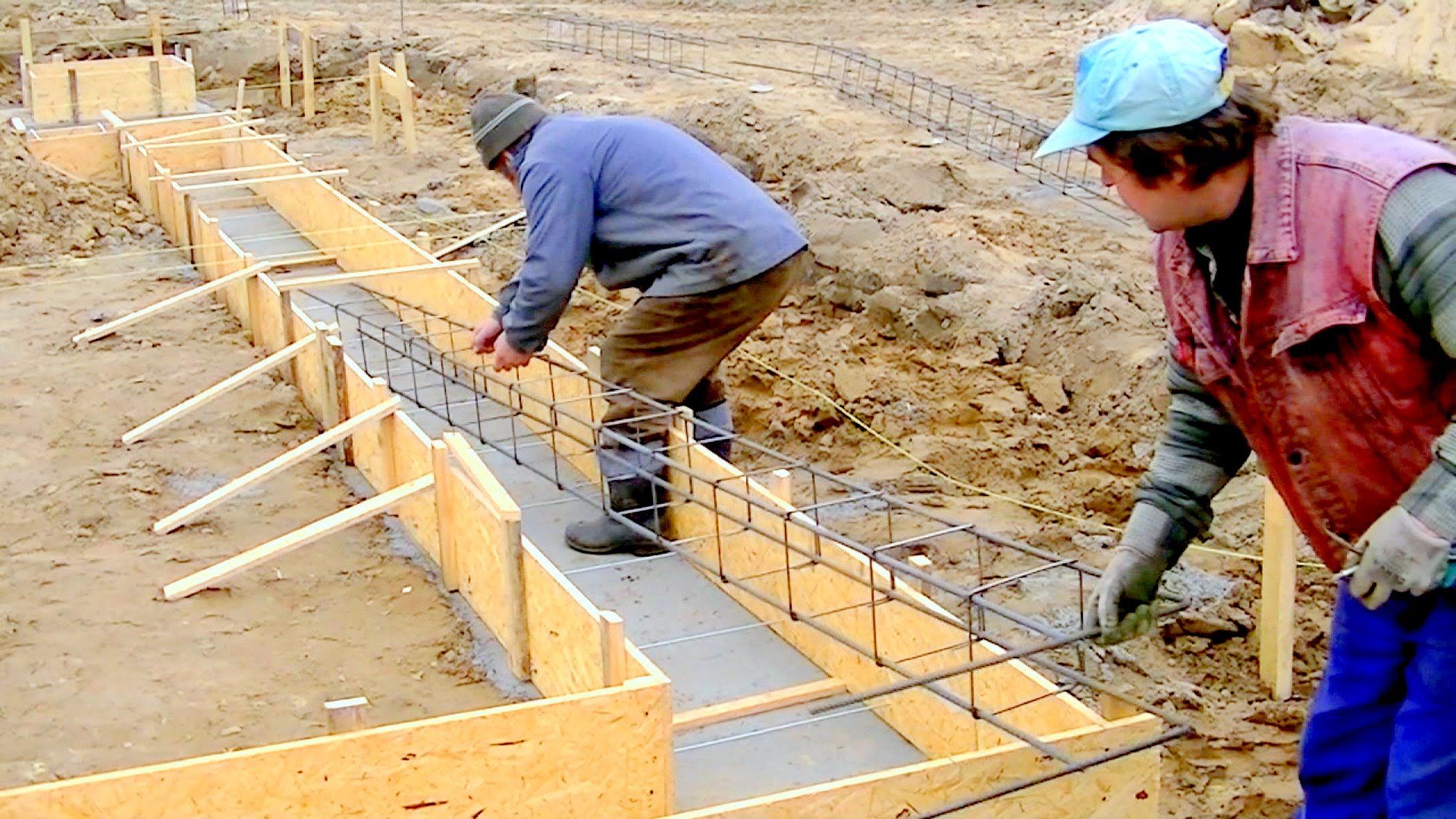
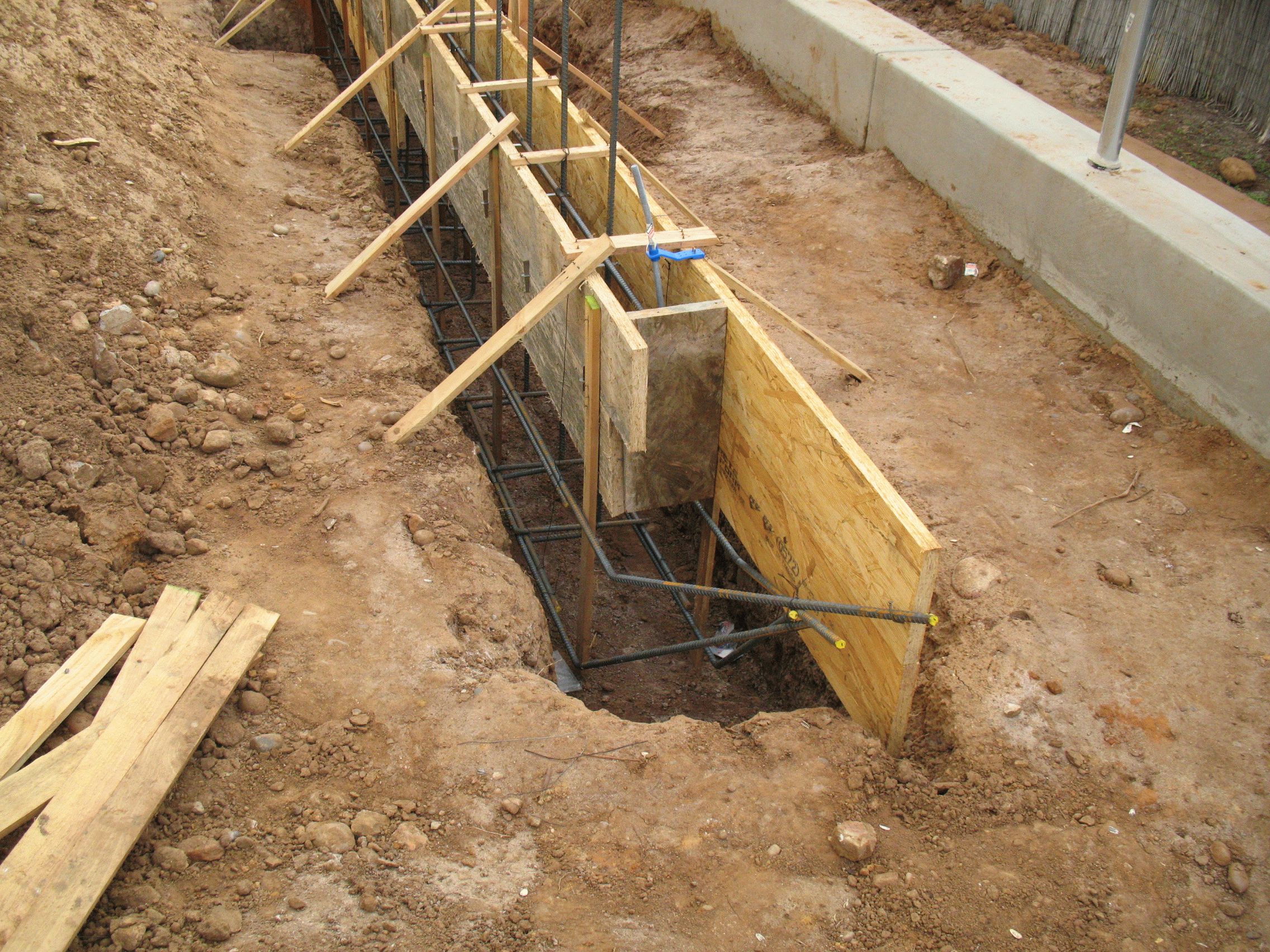
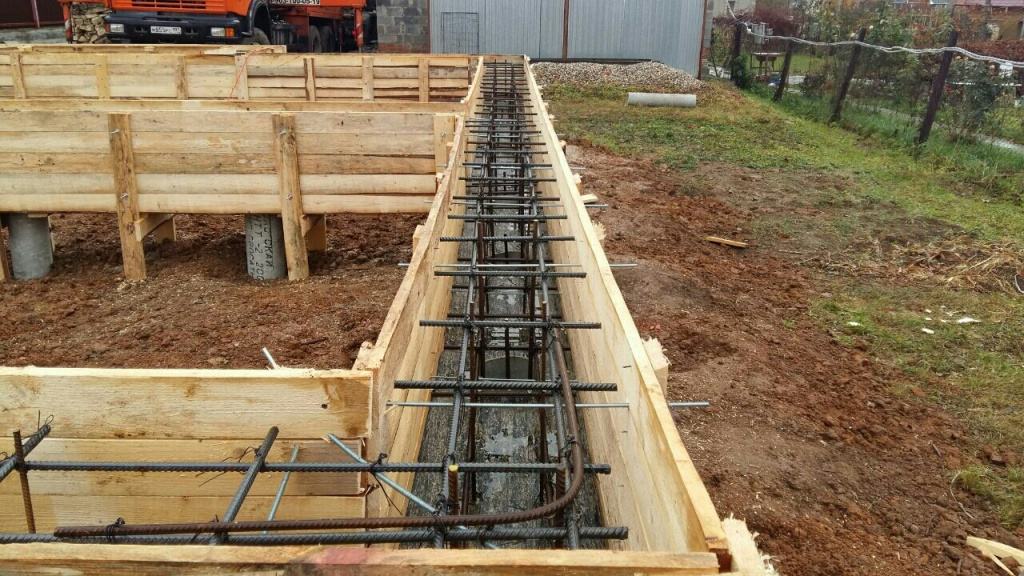
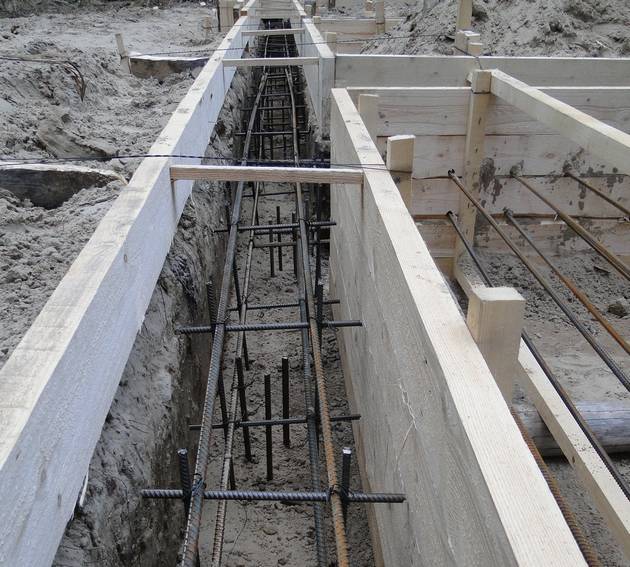
The design of the strip foundation is as follows:
Schematic representation of a shallow strip foundation.
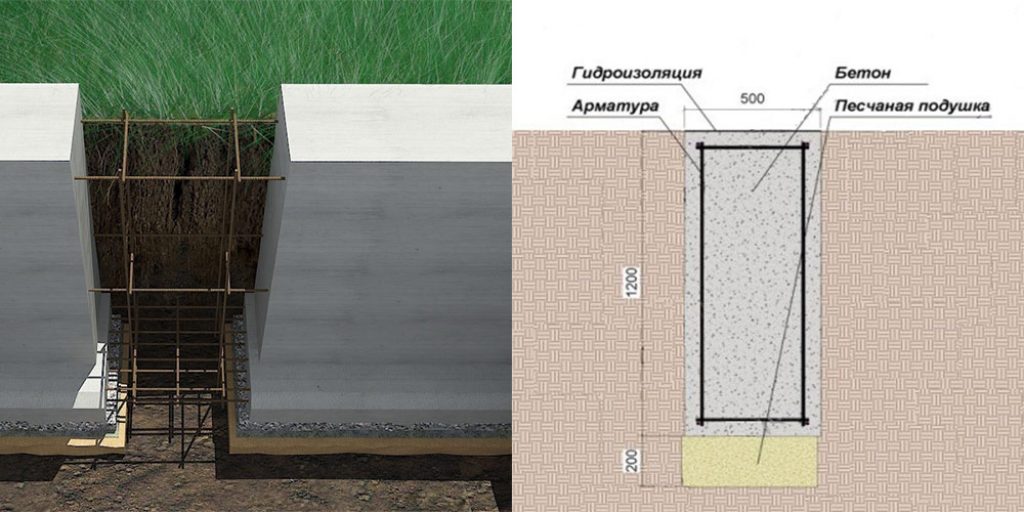
- preparation - a pillow of 20 cm of a layer of sand, 20 cm of backfill with crushed stone (each 10 cm of nonmetallic materials are compacted in layers, they are protected from mixing with the ground with the lower sheet of geotextile;
- footing - 5 cm screed, designed to protect waterproofing from a burst of preparation stones, normal sealing of joints with mastic (it is impossible to perform it on uneven rubble;
- waterproofing - 2 - 3 layers of rolled material (for example, Technonikol) on a polymer, fiberglass base, protects concrete from groundwater;
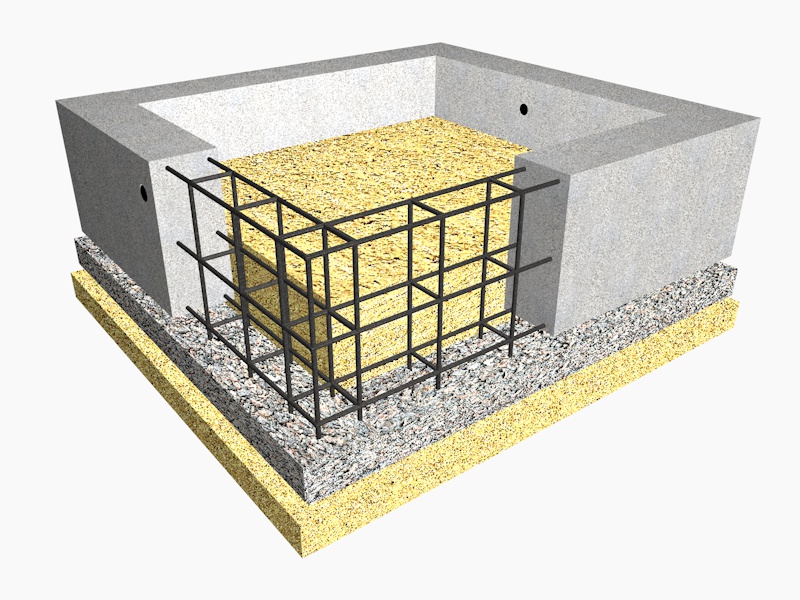
- armopoyas - longitudinal rods connected with clamps or horizontal, vertical bridges near the sole and upper edge of the tape;
- concrete is a monolithic or prefabricated structure to provide strength and rigidity.
For the strip foundation, deep drainage is required at the level of preparation along the perimeter of the building, blind area, storm drain, waterproofing of the walls of the tape. For the operated basement, the waterproofing is glued with insulation. Extruded polystyrene foam is often laid under the tapes and blind area of the MZLF to compensate for the heaving forces. Backfilling of the pit sinuses and trenches should be done exclusively with non-metallic material (usually sand).
Preference situations
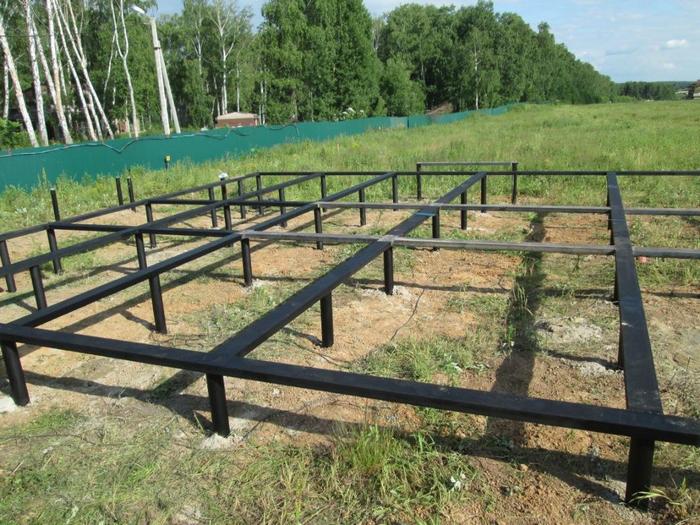
 Shallow foundations in most regions are best poured with the creation of a reinforcing frame
Shallow foundations in most regions are best poured with the creation of a reinforcing frame
Consider the main situations when it is worthwhile to prefer pouring or laying foundation blocks.
- A deepened foundation with an average load on the structure (one-story houses made of brick, stone, cinder block or higher-rise ones made of foam concrete) can be made from FSB. For more massive buildings, it is preferable to fill in a monolithic base.
- Shallow foundations in most regions are best poured with the creation of a reinforcing frame. Only in regions with stable soils can blocks or even rubble natural stone be used.
- Sometimes it makes sense to combine the two technologies. The FSB masonry is meant with the creation of a reinforcing monolithic armored belt on top of it.
As you can see, there are advantages, as well as disadvantages, for each method of setting up a foundation tape.
Considering the importance of creating a solid foundation during the construction process, it is advisable to carefully approach the choice of technology and material, resorting to the help of professionals who would calculate and take into account all the nuances in a particular situation
Description of foundations on piles
According to the constructive solution, the piles are solid pillars, driven, screwed or inserted into the ground and resting on dense soil layers below the freezing point. In the upper part, all the pillar heads are interconnected by a horizontal grillage, which serves to evenly distribute the weight load from the walls between them.
According to the method of installation and execution, three main types of piles are distinguished:
- hammered;
- screw;
- bored.
They can be made from:
- tree trunks;
- rolled metal;
- non-reinforced concrete;
- pre-molded reinforced concrete.
It should be said right away that today pile supports made of wood are used very rarely and only for temporary structures, the operation of which is designed for no more than 2-3 years.
Driven piles. Supports of this type are made in the factory from reinforced concrete and driven into the ground using special construction equipment (you can read more about the topic here). Driven pile technology is used in multi-storey construction and in the erection of massive large buildings in private.
In most cases, a shallow foundation is used as a grillage. Driven reinforced concrete supports are distinguished by a high level of reliability, but they require the greatest costs associated with the high cost of materials and the involvement of special equipment.
Screw piles. They are made of steel pipe metal rolling. They are a steel pipe structure with a pointed end, above which helical blades are welded. Screw supports can be used on any type of soil, except for swampy peatlands and with a high content of stone.
Can be installed manually or mechanically. As a grillage, rolled steel in the form of a channel, I-beam or profiled pipes is used. A grillage made of reinforced concrete or in the form of a shallow tape is allowed.
Bored supports. To install a pile foundation of this type, wells of the calculated diameter are dug to the depth of soil freezing. A sand-crushed stone cushion is poured into them and a hollow formwork made of pipes or rolled sheet material is installed. A reinforcing frame is mounted inside the structure and a concrete mixture is poured. After the concrete has hardened, the upper part of the supports is tied with a concrete grillage.
Due to the increased bearing capacity, bored supports are widely used for the construction of one and two-story stone buildings in private construction. Excellent structural stability allows construction on any type of soil.
Disadvantages and advantages of pile screw foundations
 It should be noted right away that the pros and cons of the basis of this type are very relative and have different meanings in certain individual conditions of use.
It should be noted right away that the pros and cons of the basis of this type are very relative and have different meanings in certain individual conditions of use.
It should be noted right away that the pros and cons of this type of foundation are very relative and have different meanings in certain individual conditions of use. For example, rocky soils are completely unsuitable for arranging a pile-screw foundation, since the difficulties with screwing in the elements significantly exceed all the advantages of the foundation.
So, the advantages of the pile-screw foundation:
- The possibility of arranging the base on various soils, including swampy, prone to frost heaving, with a low bearing capacity, and others.
- When using a foundation on swampy or flooded soils, it is possible to raise the structure to a sufficient height - these are the undoubted advantages of this foundation.
- Affordable cost. Such foundations are much cheaper than any other structure.
The pluses are complemented by a small mass of the base and the efficiency of building the entire system. As a rule, experienced workers cope with the pile-screw foundation in 2-3 days.
Disadvantages:
Not always sufficient bearing capacity. A heavy structure cannot be piled on such a foundation. Or you will have to hammer the elements to such a depth that the strip foundation will be much cheaper.
Mandatory need for preliminary engineering and geological studies
This is important in order to understand what kind of soil the element will rely on, the reasons and possibilities for soil changes, seasonal movements, and so on.
There is a great danger of uneven shrinkage of various parts of the foundation.
Obligatory finishing of the basement part: insulation, waterproofing.
Additional arrangement of ventilation ducts of the subfloor.
Difficulties in using concrete slab structures for arranging the first floor.
And, of course, the disadvantage of such a foundation is that you never know who you will find under the house: free space attracts a lot of animals, since it is cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
In addition, it is worth knowing the disadvantages of excessive metal corrosion. When using metal elements made of non-ferrous metal for the base, this problem does not threaten, but it is too expensive. But iron and alloys suffer from oxides, and this negates all the advantages of the technology. A special paint will help to avoid rusting, but when screwing in, the element is subjected to such strong friction that the coating will simply be removed from the pipe. A small stone or root knot in the ground is enough for a scratch to appear, and because of it the entire pipe will undergo corrosion. However, if the pipe piles are built up to a sufficient thickness, the element will resist corrosion longer.
Also, the elements are affected by "stray currents" that appear in the ground if there are tram or railway tracks nearby. A kind of grounding of a house, without which no building can do, can be destructive for the pile-screw foundation.
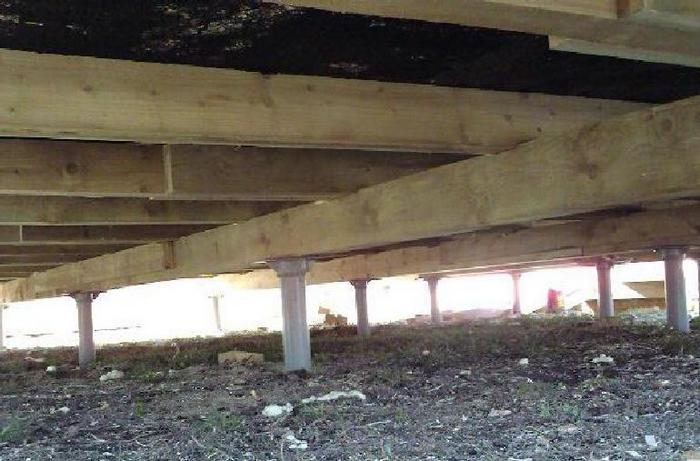 Uneven shrinkage is the main disadvantage of the base
Uneven shrinkage is the main disadvantage of the base
So, the disadvantages of the pile-screw foundation have been disassembled, therefore, before choosing this type of foundation, it is worth carefully calculating all the possibilities. Any nuances in the quality of the pipe will have a bad effect on strength, and raising the structure above the soil level requires additional insulation of the floors, it is impossible to provide for a basement - the foundation simply does not allow such a structure. And, most importantly, when installing piles with preliminary excavation to the depth of freezing, there is a great risk to reduce the strength of the entire structure.