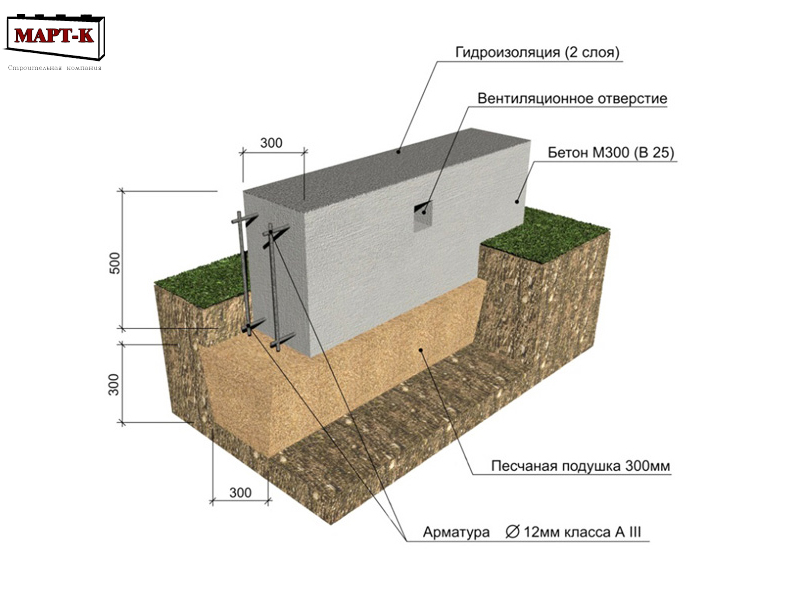
Optimal distance for various buildings
It is impossible to proceed only from the size or purpose of the buildings, since in addition to the weight of the house, the type of soil plays an important role.
The denser the underlying layers, the smaller the width of the tape can be made during construction.
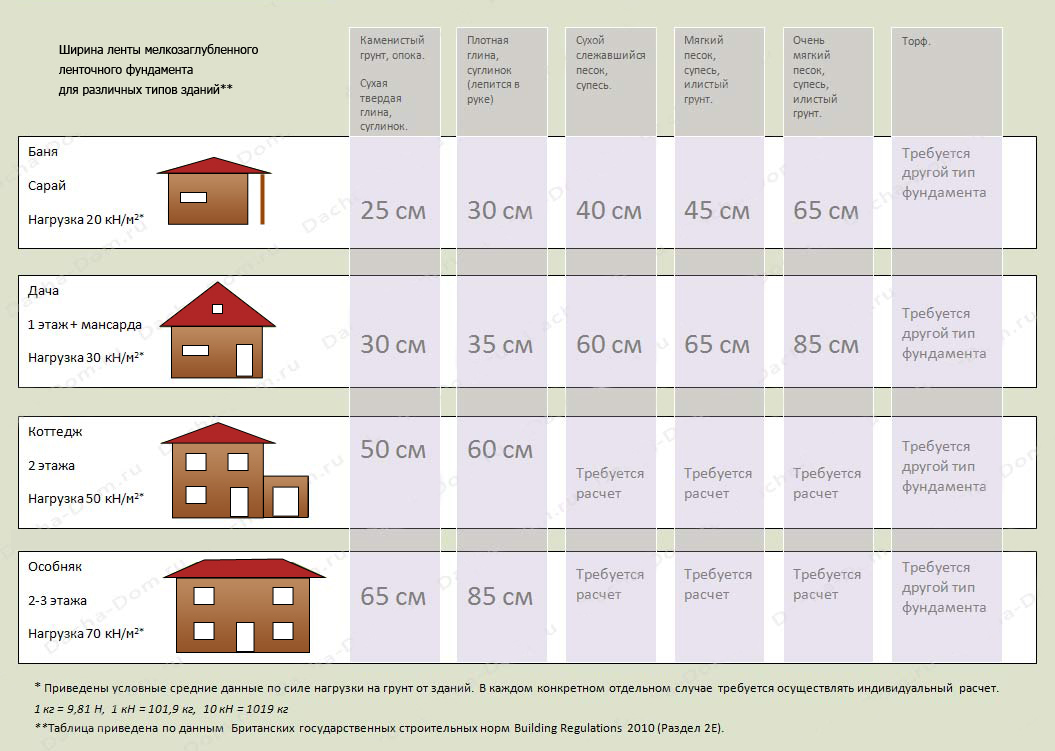
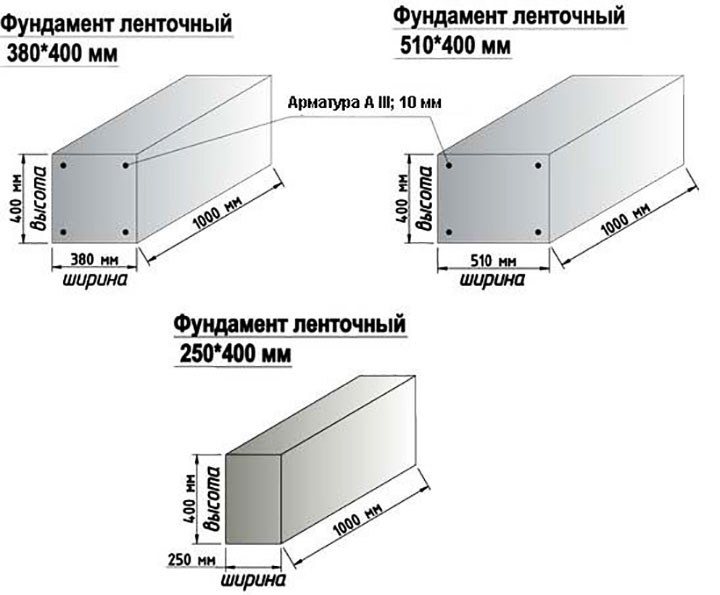
For auxiliary and utility buildings, the width of the tape is allowed:
- Dense (rocky) soil, clay - 25 cm.
- Loam - 30 cm.
- Sand, sandy loam - 35 cm.
- Soft caked sand - 40 cm.
- Very soft sand - 45 cm.
For one-story light houses (summer cottage, frame house):
- Dense (rocky) soil, clay - 30 cm.
- Loam - 35 cm
- Sand, sandy loam - 40 cm.
- Soft caked sand - 45 cm.
- Very soft sand - 50 cm.
For two-storey cottages:
- Dense soil - 50 cm.
- Loam - 60 cm.
- The rest of the soil types do not have averaged indicators and require a separate specialized calculation.
It should be borne in mind that average values are rarely suitable for specific situations, since there are always many additional factors that are not taken into account in the tables.
The impact of these factors can radically change the operating conditions and require a separate calculation, sometimes made according to a completely different method.

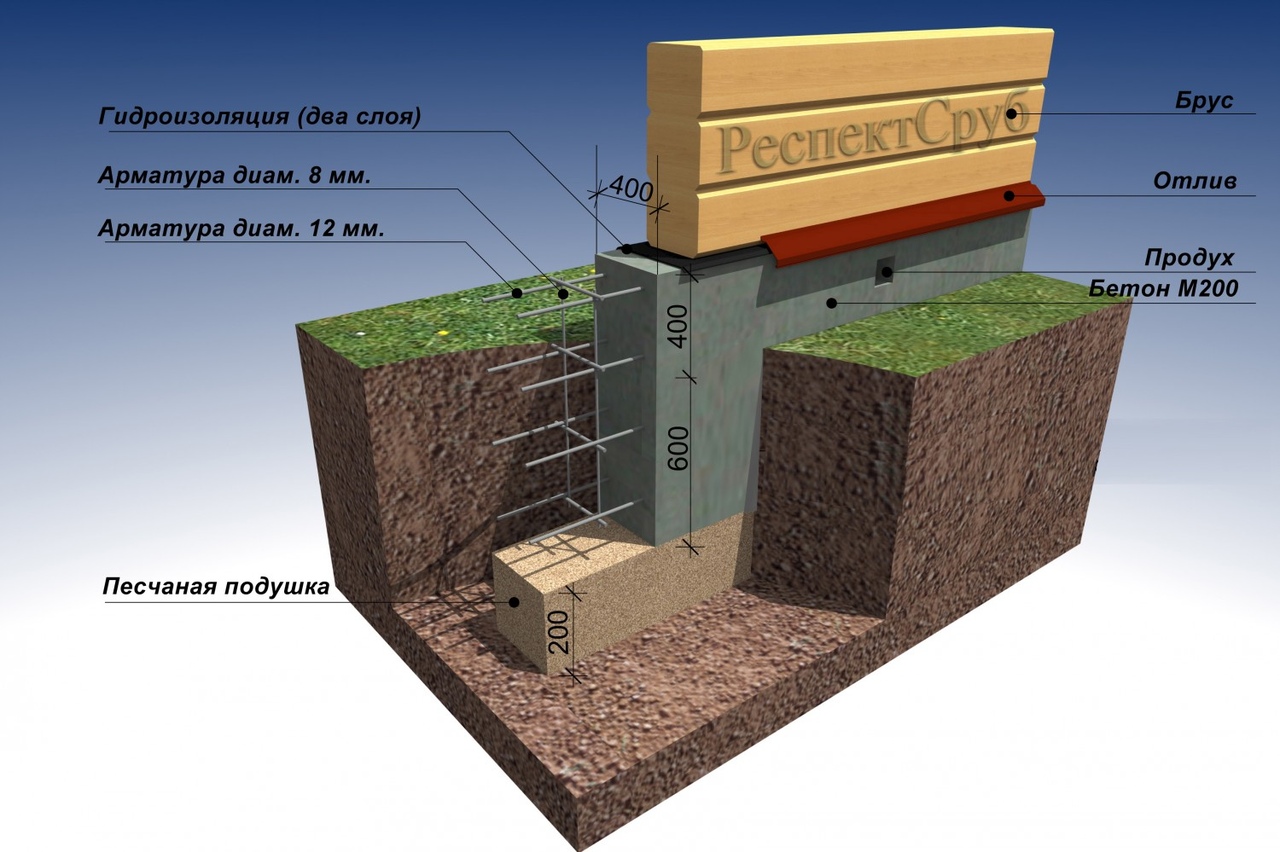
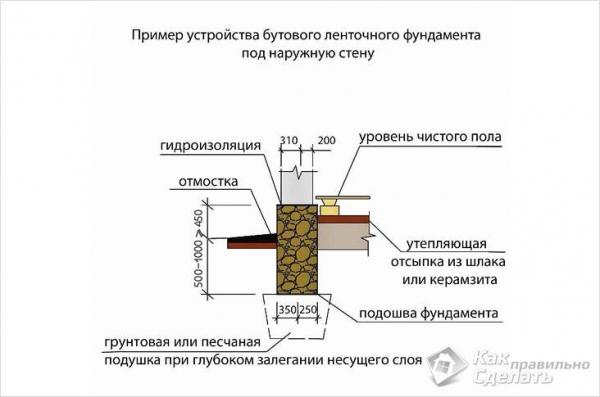
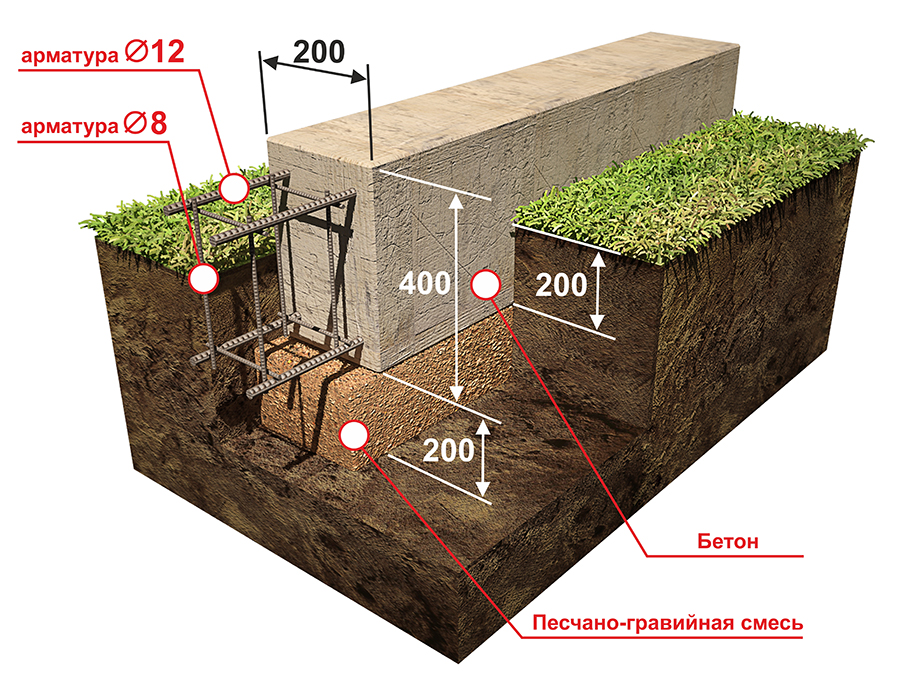
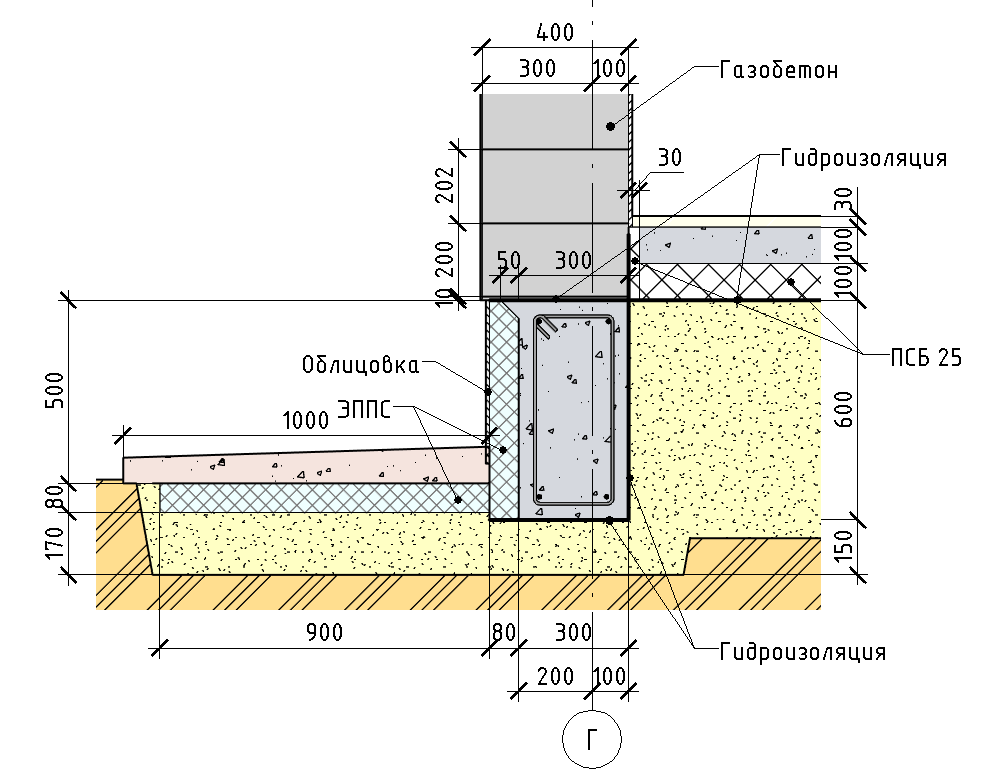
What should be the height of the foundation above the ground
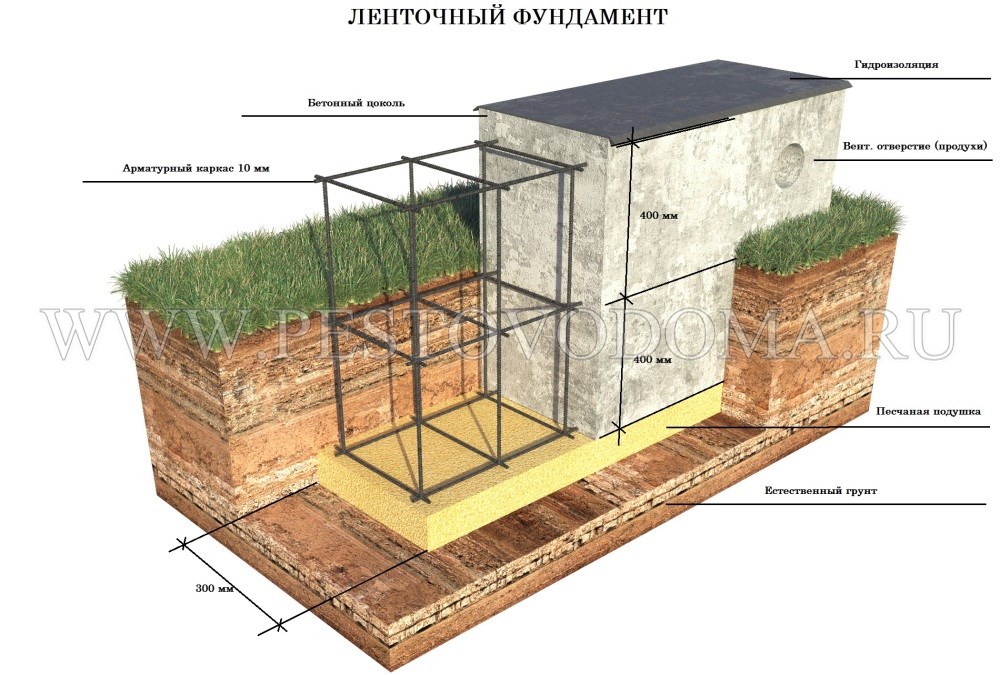
The device of most types of foundations for a frame or brick house requires an aboveground part. Its main purpose is to provide protection from atmospheric precipitation and temperature fluctuations of the supporting part of the structure, which is located underground. How high should it be? On the one hand, it is logical to increase the above-ground part in order to protect the house itself, but on the other, it will be costly to do it from a financial point of view.
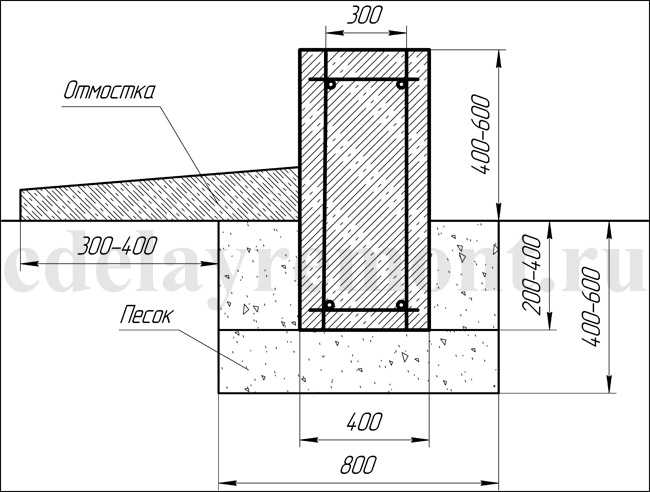
The device of a strip base made of blocks or bricks or slab for a frame or stone house is recommended to be done with an elevation from the ground surface of more than 30 cm.This device will visually clearly separate the building from the foundation and improve the integrity of the object during operation under the negative influence of the external environment.
This fact must be taken into account and the appropriate dimensions must be applied to the drawing of the house using reliable data for a specific building region. To simplify the task, you can see the finished projects of houses that are erected nearby. But it is still recommended to double-check the accuracy of the calculations.
We recommend watching a video on how deep to dig the tape base.
When building a frame house, they usually try to save on the foundation and make it from a bar. However, to provide additional protection against freezing and heaving of the soil, the height is made much higher than when laying a base from blocks. The maximum permissible length is 30-40% of the total length of the piles, depending on the presence of compressive and tensile stresses in the soil, so that the foundation is not flooded with water.
If you plan to build a house from a bar or brick on a foundation of blocks or a monolith, then the calculation must be carried out taking into account the factor of subsidence of the soil under a heavy load. In such cases, it is required to provide a margin of about 20-30% of the value taken taking into account the amount of precipitation. This will effectively deal with heaving and loose soils, as well as seasonal soil shifts.
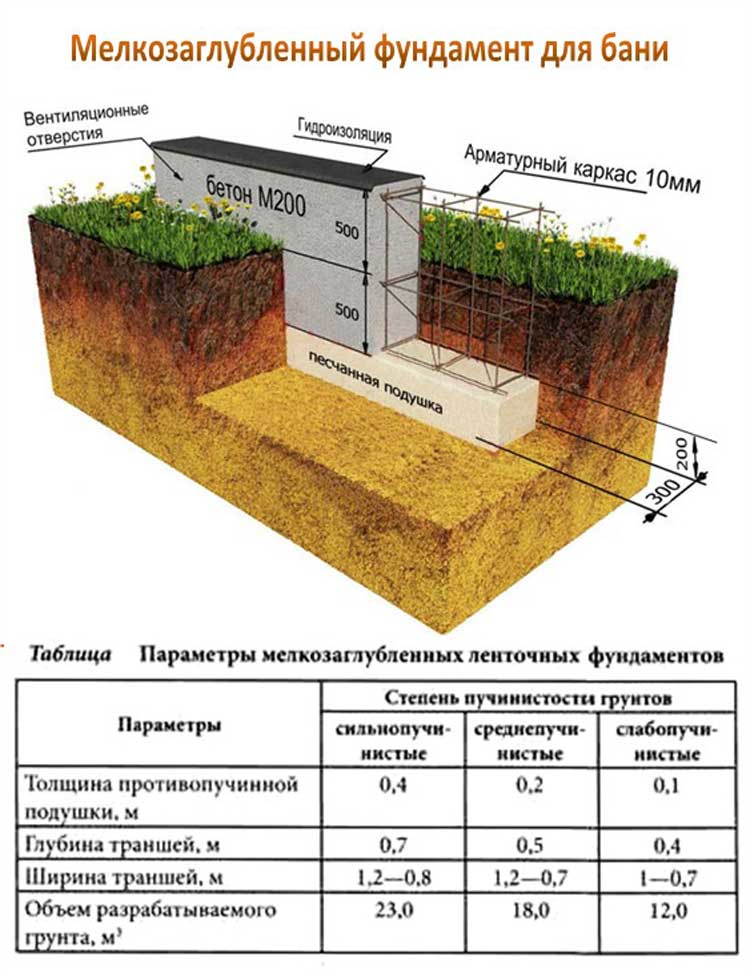
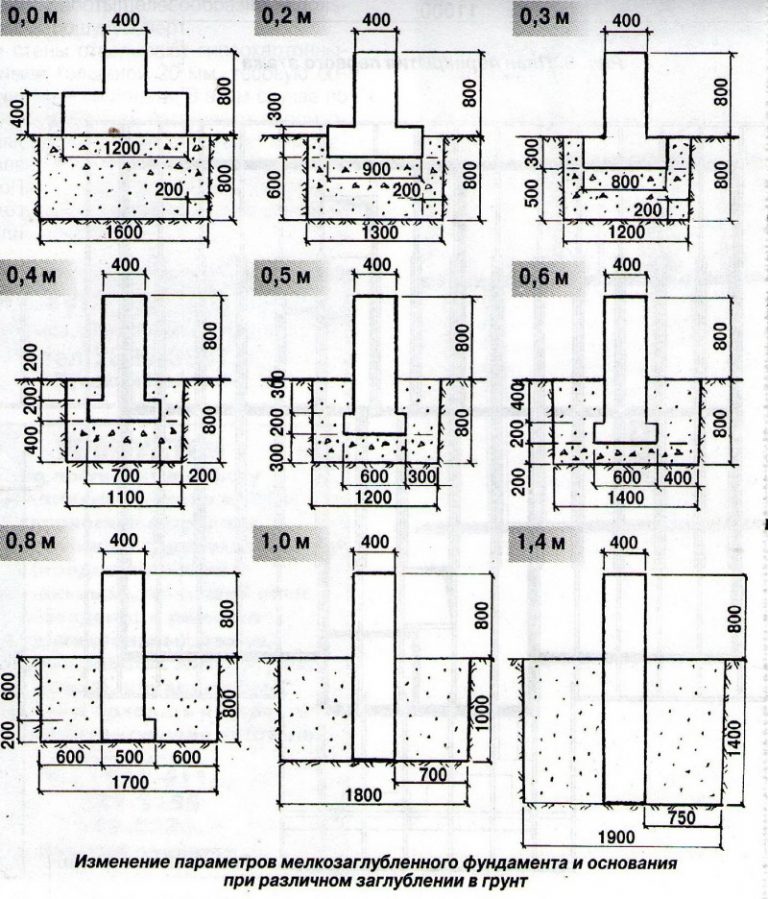
Calculation of the depth of the foundation of a one-story house
 Base trench
Base trench
The foundation for a one-story house must be laid at a depth that is below the freezing level of the soil. The drawing must necessarily take into account this criterion and be executed taking it into account.
The normalized freezing depth is determined on the basis of data obtained over the past 10 years for a specific region.The observation results are compared with GOST 25100, and then the line of transition of plastic frozen soil to solid is determined.
If there is no access to such data or they are lost, then for regions with a freezing depth of up to 2.5 m, it is allowed to perform a calculation using the formula:
where Mt is a dimensionless coefficient, which is determined by the sum of all absolute temperature values below zero, according to SNiP 23-01. If there is no information on temperatures in the regulatory documents, then you must contact the Hydrometeorological Center to obtain them;
d0 is a value depending on the type of soil on the site. You can take it from SP 22.13330.2011.
If the freezing depth exceeds 2.5 m, then it is necessary to carry out heat engineering calculations in accordance with SP 25.13330. The calculation of seasonal soil freezing is carried out according to the formula:
where kh is a dimensionless coefficient that takes into account the thermal regime for the external and internal structures of the base on the basis of information about the heating of the building. Determined according to Table 1 or taken equal to 1.1 for unheated premises (with the exception of the northern regions, where negative temperatures prevail throughout the year).
 Table 1. The value of the coefficient kh depending on the structural features of the building
Table 1. The value of the coefficient kh depending on the structural features of the building
The data in Table 1 are valid for those cases when the distance between the wall and the edge of the foundation is less than half a meter, and if it is exceeded, the coefficients should be increased by 0.1. If the temperature falls within the interval between the table values, then the value with the lower value is taken.
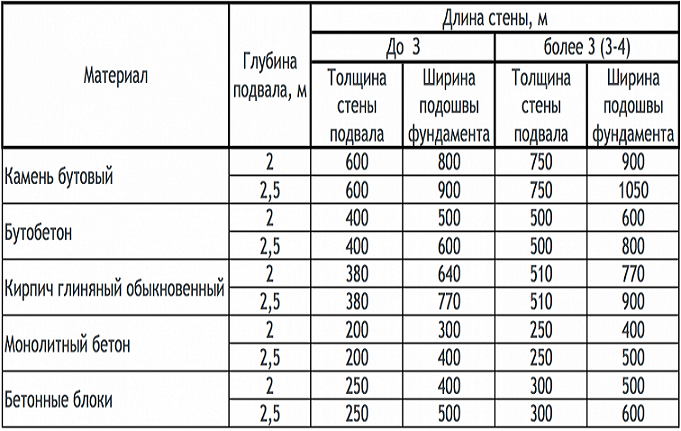
The depth of laying the external or internal foundation for heated rooms with cold basements or technical rooms should be determined on the basis of Table 2.
 Table 2. The depth of the foundation, depending on the type of soil for houses with an unheated basement room
Table 2. The depth of the foundation, depending on the type of soil for houses with an unheated basement room
The calculation of the foundation depth for a house made of blocks or bricks with a basement is carried out according to the following formula:
where hs is the thickness of the soil above the base of the base, as viewed from the basement;
hcf - basement floor thickness;
γcf is the value of the specific gravity of the basement floor structure.
Watch the video on how to scale your own foundation.
An example of self-calculation of the width of the strip foundation
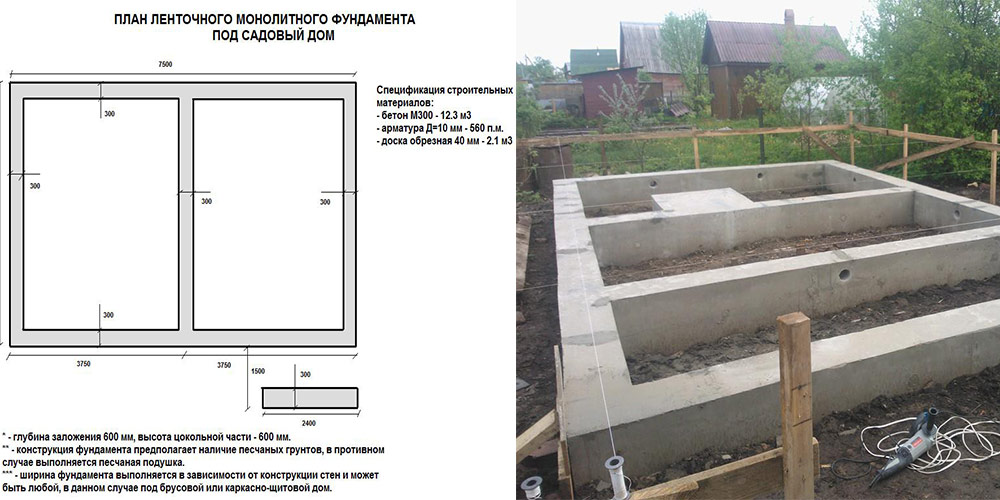
To better understand how to calculate the width of a monolithic tape, you need to consider this with an example. Initially, you need to systematize the initial data necessary for the calculation.
- the size of the house in the plan is 10 mx 10 m. The building area is 100 m 2;
- inside the house there is a load-bearing wall in the middle;
- brick walls, 1 brick thick - 250 mm and 2.7 m high. Specific weight of brickwork - 1600 kg / m 3;
- slate roof - 40 kg / m 2;
- floor from reinforced concrete slabs - 500 kg / m 2;
- depth of soil freezing - 700 mm;
- groundwater level - 2.2 m;
- soil base - dry loam of medium density with a design resistance of 2 kg / cm 2;
- snow load - 50 kg / m 2;
- payload - 20 kg / m 2.
Determination of the total load from the house on the strip monolithic foundation
Based on the available initial data, the total load on the foundation is calculated. The dimensions of the monolithic tape are also determined. It is necessary for developers to make a calculation in the following order:
Roof
Gable slate roof. Taking into account the slope of the roof and its overhangs, a coefficient of 1.1 is applied. The load from the roof will be: 100 m 2 x 1.1 x 40 kg / m 2 = 4000 kg.
Brick walls
To determine the load from the walls, knowing their thickness, you need to calculate their length. The length of the walls along the perimeter will be: (10 x 4) - (0.25 x 4) = 39 m. The deduction of twice the thickness of the brickwork is made because the axes of the house plan are drawn in the middle of the thickness of the walls. The length of the internal load-bearing wall will be 10 - 0.25 = 9.75 m. The total length of the load-bearing walls will be equal to 48.75 running meters.
The volume of brickwork will be: 48.75 x 0.25 x 2.7 = 32.9 m 3. The total load from the brick walls is 32.9 x 1600 = 52 670 kg.
Reinforced concrete slab overlap
The one-storey house has floors on two levels. This is the overlap of the basement and the ceiling in the house. The overlap area is: 100 x 2 = 200 m 2. Accordingly, the load from the floor slabs will be equal to: 200 m 2 x 500 kg / m 2 = 100,000 kg.
Snow load
To calculate the snow load, take the total area of the roof of the house - 100 x 1.1 = 110 m 2. The snow load will be: 110 m 2 x 50 kg / m 2 = 5,500 kg.
Payload
The rate of this load is calculated on the basis of the average values of the weight of technical equipment, internal communications, interior decoration, furniture, and others. The specific weight of the payload ranges from 18 to 22 kg / m 2.
The payload is calculated on the basis of an average of 20 kg / m 2. The weight will be: 100 m 2 x 20 kg / m 2 = 2000 kg.
In total, the total load on the foundation will be equal to: 4,000 + 52670 + 100,000 +2,000 = 159,000 kg.
Calculation of the width of a monolithic tape
According to the above formula, the minimum footprint of the foundation is determined:
(1.2 x 159,000 kg): 2 kg / cm 2 = 95,400 cm 2. That is, the minimum allowable footprint of the base of the house will be 10 m 2.
The total supporting area of brick walls is determined by the product of the length in terms of load-bearing walls by their thickness: 48.75 mx 0.25 m = 12.18 m 2.
As a result, it can be seen that the calculated reference area is less than the minimum reference area of the walls. Therefore, the width of the strip footing should be 250 mm + 100 mm = 350 mm.
The need for materials for the device of a monolithic tape
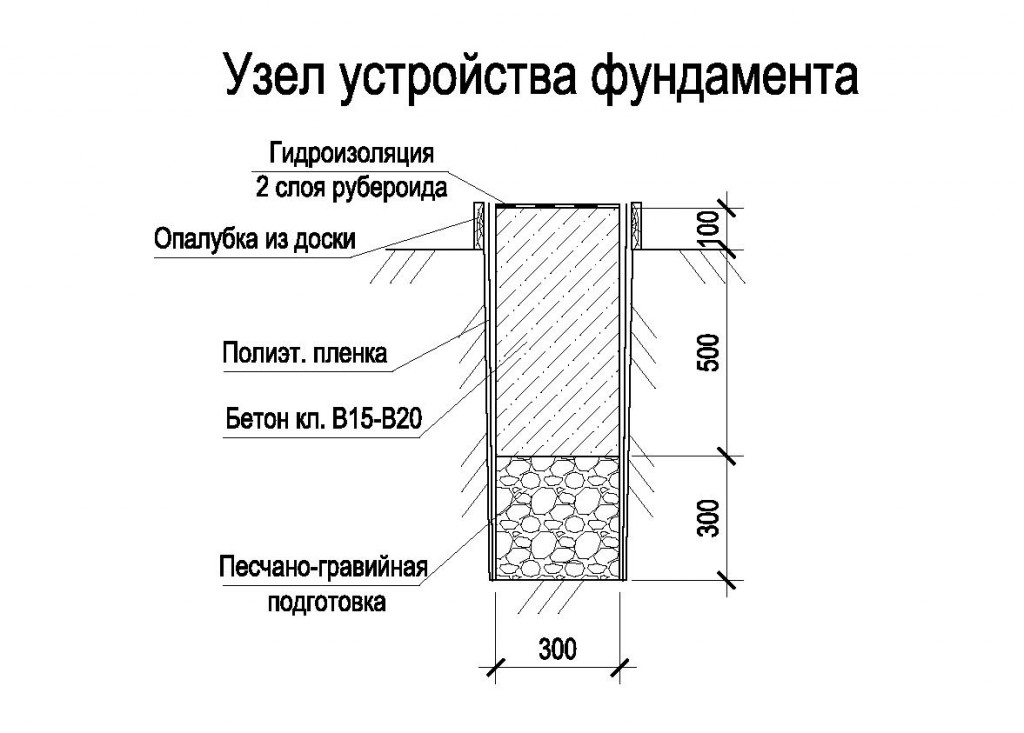
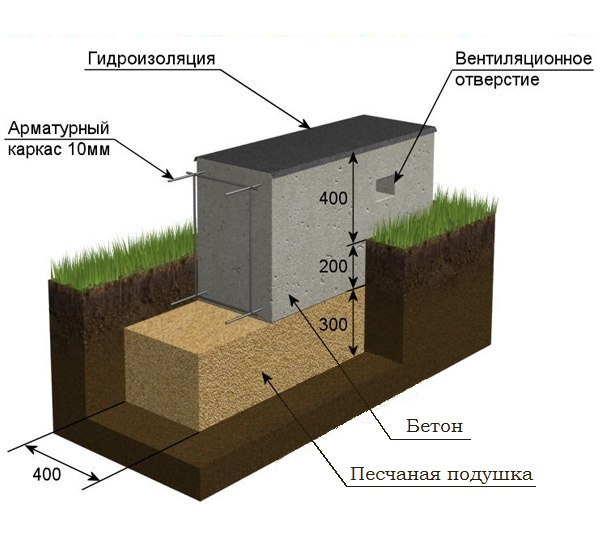
Considering the thickness of the soil freezing (0.7 m) and the depth of the groundwater level (2.2 m), the monolithic tape is made shallowly buried - 1 m.
For pouring the formwork, concrete M 300 is used. The volume of the need for concrete solution is: 0.35 mx 1 mx 48.75 m = 17 m 3.. Taking into account unforeseen losses, the need for concrete will be 17.3 m 3.
The reinforcement cage consists of 4 longitudinal reinforcing bars of a periodic profile with a diameter of 12 mm. Since the transverse rods of the frame are made from the same rods, the total need for reinforcement will be: 50 mx 4 = 200 m.
From all of the above, we can conclude that calculating the width, height and length of the strip foundation for your home is quite within the power of people who are in the slightest degree versed in the construction business.
Peculiarities
Advantages:
1. Increased bearing capacity. A monolithic slab creates a slight pressure on the ground due to the uniform distribution of the entire load, regardless of the thickness of the fill. An excellent option for a house made of timber, aerated concrete, even brick.
2. Spatial rigidity. This eliminates the likelihood of subsidence in certain areas (for example, a tape) and the appearance of cracks in concrete, on walls or separated joints.
3. Versatility in application. The slab foundation is suitable for any soils, including those called problematic.
4. Simplified construction technology. The construction of a monolithic slab does not require voluminous earthworks, which significantly saves time.
5. Possibility of high-quality insulation. Options - laying under the base of expanded polystyrene, introducing special / additives into the solution.
6. Reduction of concrete consumption. Although this is true only for cases of arrangement of an unburied monolithic slab.

Disadvantages:
Many of them are relative, but it is worth noting them as well.
1. Complexity of calculations. This applies to the thickness of the future slab. If we are talking about a building with a basement, then it is better to choose another base option. First, the cost of construction will rise sharply. Secondly, calculations for a monolithic slab will become significantly more complicated.
2. High costs. Here a lot depends on the specific scheme, but it is indisputable that with such construction, savings on other materials are achieved. If the slab foundation is shallow, of small thickness, it can be impressive.
3. Labor intensity. The question is how well the construction work is organized. For example, the use of "automatic mixer" greatly simplifies the technology of pouring concrete and saves time. The same applies to the accuracy of calculations of the thickness of the monolithic foundation.
4. Certain difficulties with individual projects. First of all, when implementing a scheme with a basement and during construction on relief ground.
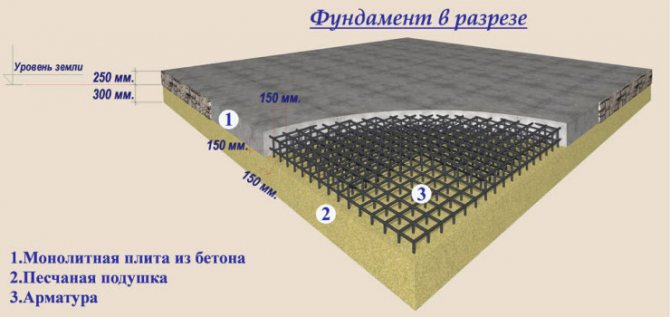
Calculating the thickness of the slab
It is pertinent to give only general instructions and recommendations, since much depends on the characteristics of construction - characteristics of the soil, the number of storeys of the house, the materials from which it is being built, and a number of other nuances.
Initial data for calculating the thickness of the foundation:
- Soil type.
- The configuration of underground aquifers.
- The level of soil freezing.
- The presence of a drainage system on the site and its scheme (if installed).
- The total load on the foundation.
What is determined:
1. Thickness of concrete reinforcement elements (bar, mesh).
2. The size of the cells of the reinforcement and the interval between its layers in the monolith.
3. Distance of the bar from the upper and lower cut of the foundation.
The difference in this parameter of the foundation for buildings of the same type can be significant. For example, the thickness of the slab for a wooden house varies within fairly large limits and depends precisely on the characteristics of the soil, although this is a relatively light structure of 1-2 floors.
* Dimensions - in "mm".
- Bar section - 12.
- 2 reinforcement levels, the interval between which is 70.
- The distance of the reinforcement from the cuts of the concrete monolith is 50 each.
Calculation: 12 x 2 + 70 + 50 x 2 = 194.
Rounded - 20 cm. For example, this is the minimum slab thickness for aerated concrete house. But subject to the construction of a shallow monolithic foundation on good, dense soil. That is why it is advisable to entrust all calculations to a professional.

How to calculate everything correctly
The formula for calculating the base area is as follows S> γn F / γc R0, where
- γn - safety factor equal to 1.2.
- F is the load on the base, i.e. total weight of the house, foundation, snow load, weight of property, people, etc., affecting the underlying soil layers.
- γc - coefficient of working conditions. Depending on the type of soil, it ranges from 1 (clay) to 1.4 (sand).
- R0 - conditional soil resistance. The tabular value is in the SNiP annexes for this type of soil.
As a result of this calculation, the total area of the tape will be obtained. To determine the width of the base (average), the obtained S value must be divided by the total length of the tape, including the inner walls and other sections of the perimeter. The resulting value will show the estimated thickness of the tape base.
This value is minimal. In practice, it is increased, sometimes several times.
It should be noted that the above formula is given only for acquaintance with the calculation methodology. In any case, this work should be done by a competent and experienced specialist. The calculation of the foundation is an important and responsible procedure that has a lot of difficulties and specific points.
An untrained person cannot calculate such a project without making a number of gross mistakes, which may result in the destruction of the house. Alternatively, you can use an online calculator that allows you to obtain the parameters of the tape from known data (type of soil, calculated or tabular resistance values, etc.).
To clarify the data obtained, you should double-check the results obtained on other similar resources.

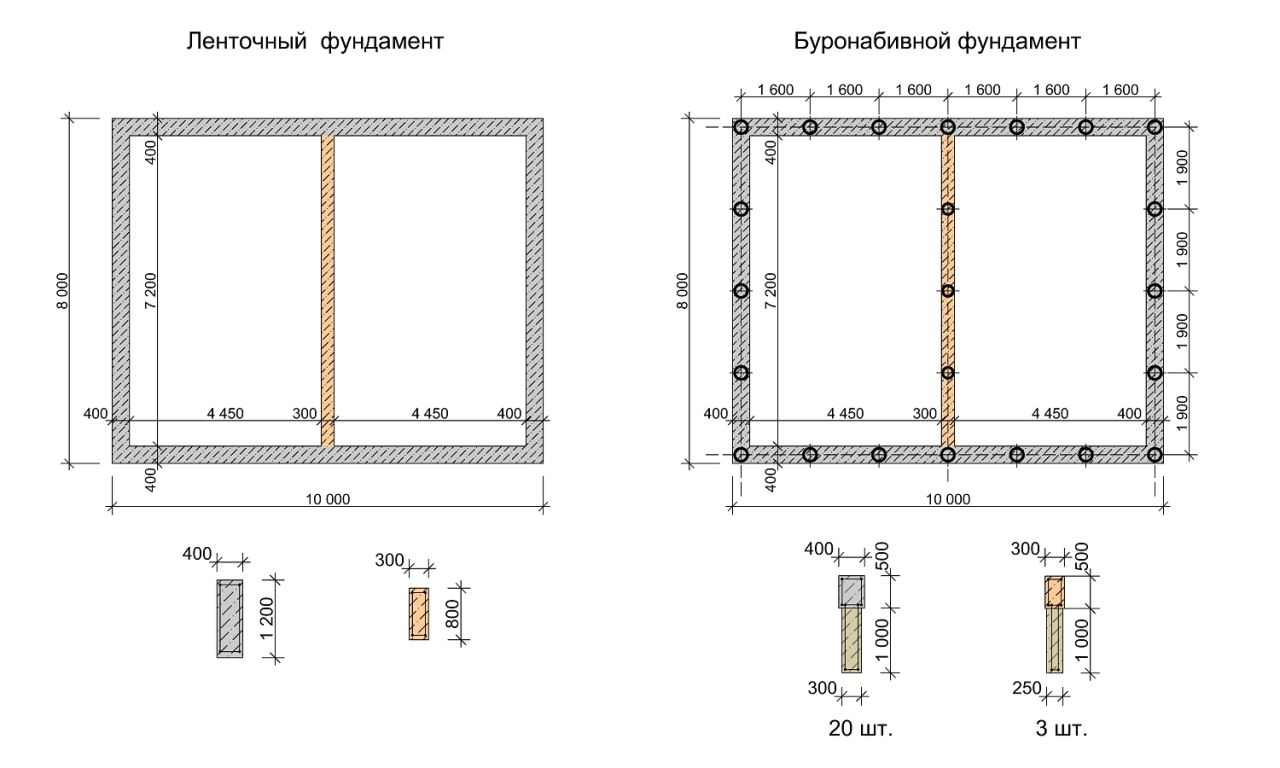
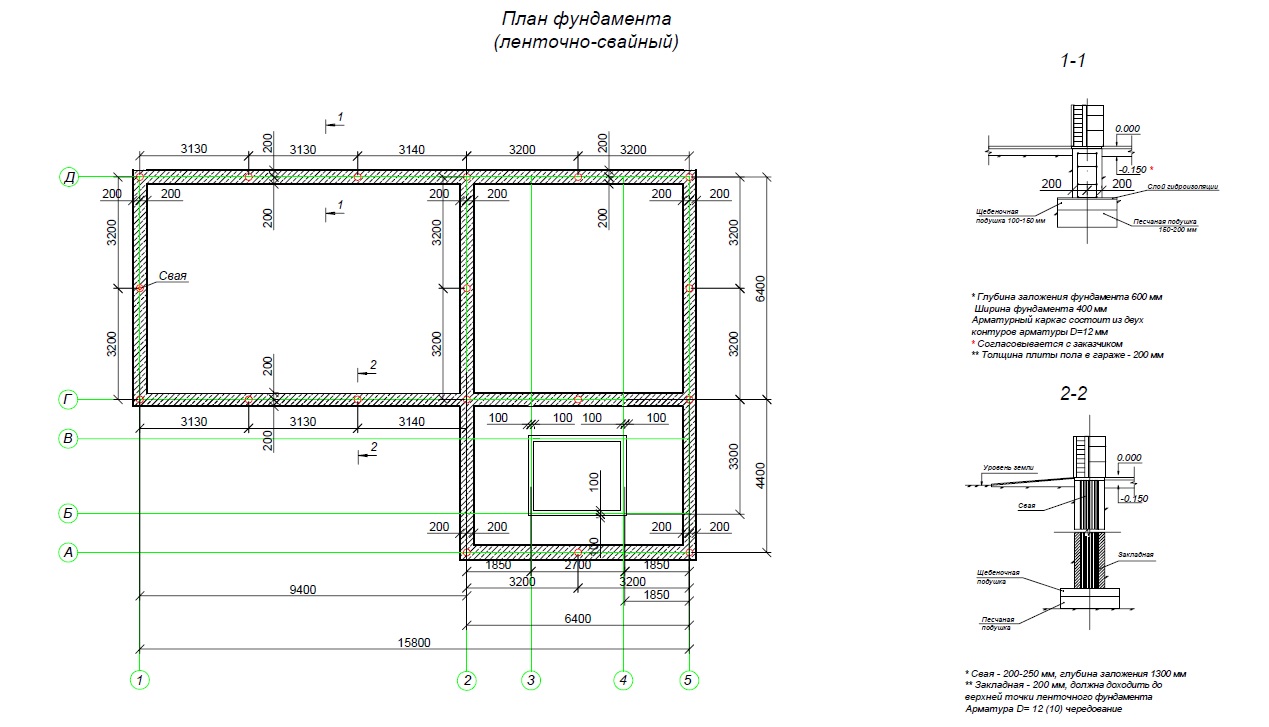
Features of the columnar-strip foundation
Such a foundation is an attempt to combine the advantages of column and strip foundations in one structure and to eliminate their disadvantages as much as possible. I must say that this is a very successful experiment because it brings a number of benefits to this type of foundation:
- Significant reduction in excavation work.
- Possibility of building on medium to highly curved soils, including peat soils.
- There is no need to make sandstone or sand cushions underneath the entire foundation.
- No drainage system required.
- Reduces consumption of concrete, reinforcement and working hours.
- Heat loss is reduced and vibration isolation of the building is improved.
Pillars
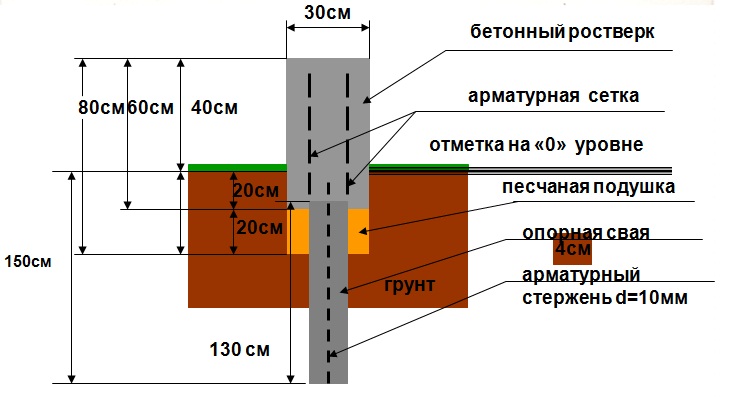
The main problem in our climate is the large difference between summer and winter temperatures, when the freezing of water in the ground in winter leads to high loads on the floor of the building.
One way to protect the foundation is to submerge it deeper than the freezing level of the soil at the construction site. For example, for the Moscow region, depending on the type of soil, this value averages 1.4 meters.
If piles are used, then only they are installed at this depth. Also estimate the difference in the intensity of work and the amount of cubic meters of land that you mined yourself.
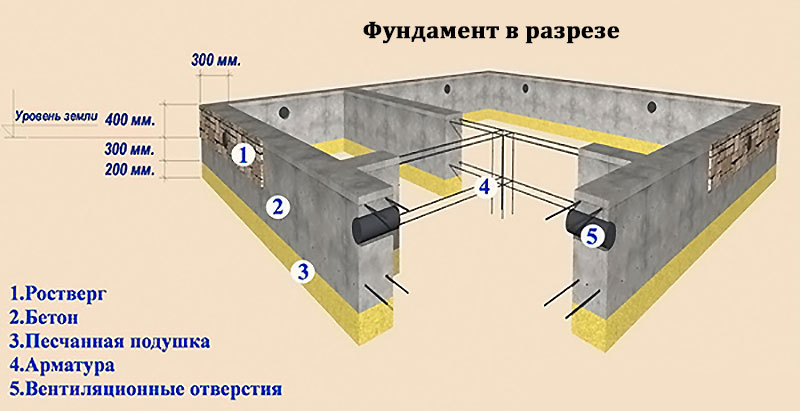
Strip foundation
The strip foundation (crane) in this structure serves as a load-bearing element that absorbs and distributes the load from the walls.
As a rule, it does not touch the ground, as it is located at a distance of 10-20 cm.If the belt is installed in the floor, for example, if a flatter device was chosen, it should be borne in mind that it is also affected by the load from the floor due to temperature fluctuations ...
In order for the belt not to be pulled away from the struts, it is necessary to provide for such a design if it can also move during vertical movements, i.e. when working as a piston. The stems must be smooth without underside expansion.
Materials (edit)
The poles can be made from a variety of materials, from round wood to reinforced concrete. The shape is also round, square, hollow and polygonal.
If this is an independent building with a minimum external attraction of forces and mechanisms, then a round concrete pillar is optimal.
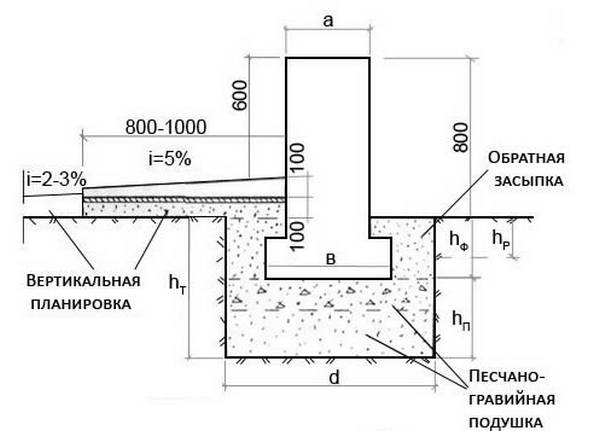
Depth of slab foundation
Due to the fact that it is forbidden to fill in monolithic structures on the arable layer, chernozem is removed from the pit entirely. The depth of the layer is usually 40 cm, which are covered with non-metallic clay-free material. The features of the shallow slab technology are as follows:
The maximum construction budget is observed at the slab deepened below the freezing point. This option is only justified for buildings with a basement floor. The outer perimeter of the underground walls will have to be completely insulated, the sinuses will have to be backfilled with non-metallic material, after having laid the wall or ring drainage.
Attention: Taking into account the removal of the fertile layer, its replacement with nonmetallic material, the foundation 30 - 40 cm thick is buried into the ground by 10 - 20 cm maximum. Therefore, you will need either a brick basement, or monolithic beams under the load-bearing walls, which perform the same function of increasing the distance between the ground and wall materials.
Calculation of the amount of concrete, wire and reinforcement
Having decided on the dimensions of the foundation, you need to calculate how much reinforcement, wire and concrete we need.
With the latter, everything is just simple. The volume of concrete is equal to the volume of the foundation, which we already found when we calculated the load on the ground.
But what kind of metal to use for reinforcement has not yet been decided. It all depends on the type of foundation.
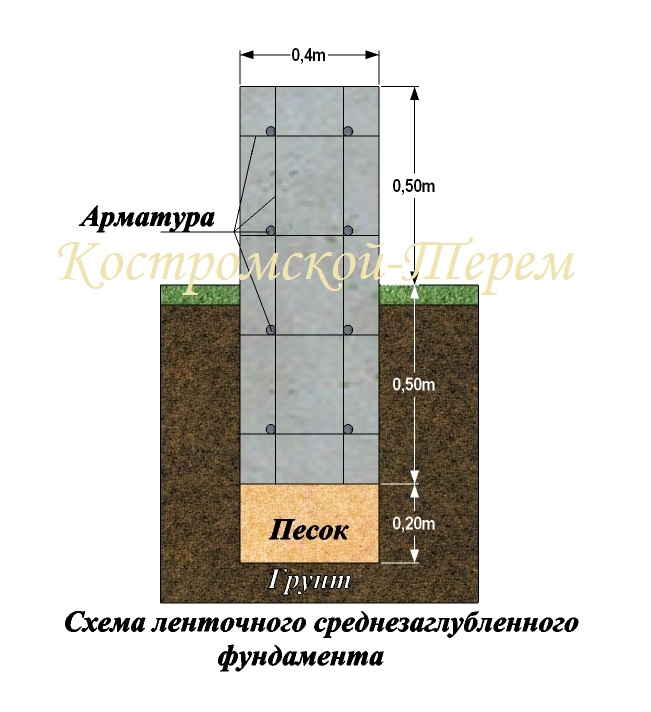
Reinforcement in strip base
 For this type of foundation, only two reinforcement belts and reinforcement with a thickness of up to 12 mm are used. Horizontal longitudinal reinforcement bars are subject to greater stress than vertical or transverse ones.
For this type of foundation, only two reinforcement belts and reinforcement with a thickness of up to 12 mm are used. Horizontal longitudinal reinforcement bars are subject to greater stress than vertical or transverse ones.
Therefore, ribbed reinforcement is placed horizontally, and smooth reinforcement vertically.
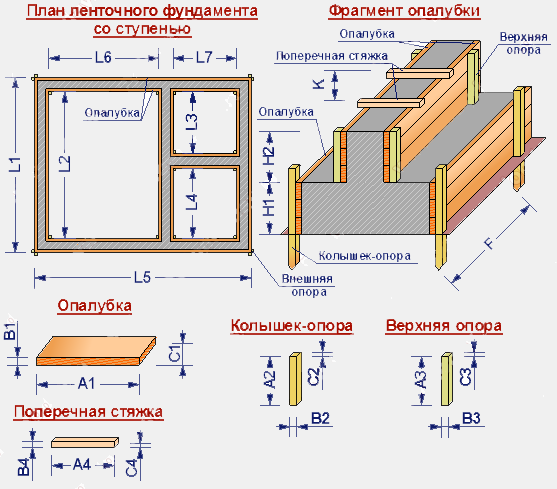
The length of the ribbed reinforcement is easy to calculate if you multiply the total length of the base by the number of rows of bars. If the foundation is narrow (40 cm), two longitudinal bars for each chord are enough. Otherwise, number of reinforcement in the belt will have to increase.
Transverse rods are mounted every 0.5 m, retreating 5-10 cm from the edge of the foundation. Determine the number of connections by dividing the entire length of the foundation by 0.5 (step between intersections) and adding 1.
To find the length of smooth reinforcement required for one intersection, use the formula:
(SHF - 2 * from) * 2 + (VF - 2 * from) * P, where SHF and VF are the width and height of the foundation, from is the indent from the edge of the foundation, P is the number of rows of reinforcement in the belt.
the amount of smooth reinforcement required for the foundation
The cost of knitting wire for the foundation is the product of the wire consumption for one bundle (30 cm), the number of bundles at one intersection (equated to the number of rows of reinforcement multiplied by 4) and the number of joints.
Slab reinforcement
For a slab base, ribbed reinforcement with a thickness of 10 mm or more is used, laying it with a grid, in increments of 20 cm.
That is, two reinforcement belts will need:
2 * (WF * (DF / 0.2 + 1) + DF * (WF / 0.2 + 1)) m reinforcement, where WF is the width, DF is the length of the foundation.
connect the intersection of the upper grid with the corresponding intersection of the lower
Taking into account the thickness of the slab and the distance of the frame from the surface of the slab, we determine the amount of reinforcement required to connect the belts using the formula:
((DF / 0.2 + 1) * (WF / 0.2 + 1)) * (TP-2 * from), where TP is the thickness of the slab, from is the indent from the surface.
how much reinforcement is needed for a slab foundation
The length of the knitting wire is calculated based on the formula:
(DF / 0.2 + 1) * (WF / 0.2 + 1) * 4 * 0.3
Reinforcement in a columnar base
When reinforcing foundation posts, ribbed rods with a thickness of 10-12 mm are used in the vertical plane and smooth six-millimeter ones - in the horizontal plane. The reinforcement is connected every 40-50 cm of the column height.
The length of the ribbed reinforcement is:
KS * DS * KP, where KS is the number of columns, DS is the length of each column, KP is the number of rods in one column.
Number of smooth reinforcement:
Rmp * KP * Kss, where Rmp is the distance between ribbed rods, KP is the number of rods in a column, Kss is the number of connections in one column.
The consumption of knitting wire corresponds to the formula:
0.3 * KP * Kss * KS