Varieties of clay soils
Before determining the type of foundation, it is necessary to clearly understand on what type of soil the construction will be carried out.
 Loams are widespread in central Russia
Loams are widespread in central Russia
Depending on the amount of clay content, soils are of the following types:
- sandy loam - loose rock containing sandy and silty components in combination with 5-10% clay;
- loam - soil, in which the clay component is present in the amount of 10-25%, and the rest is occupied by sand;
- clay is a fine-grained sedimentary rock with a high percentage of clay matter from 30%.
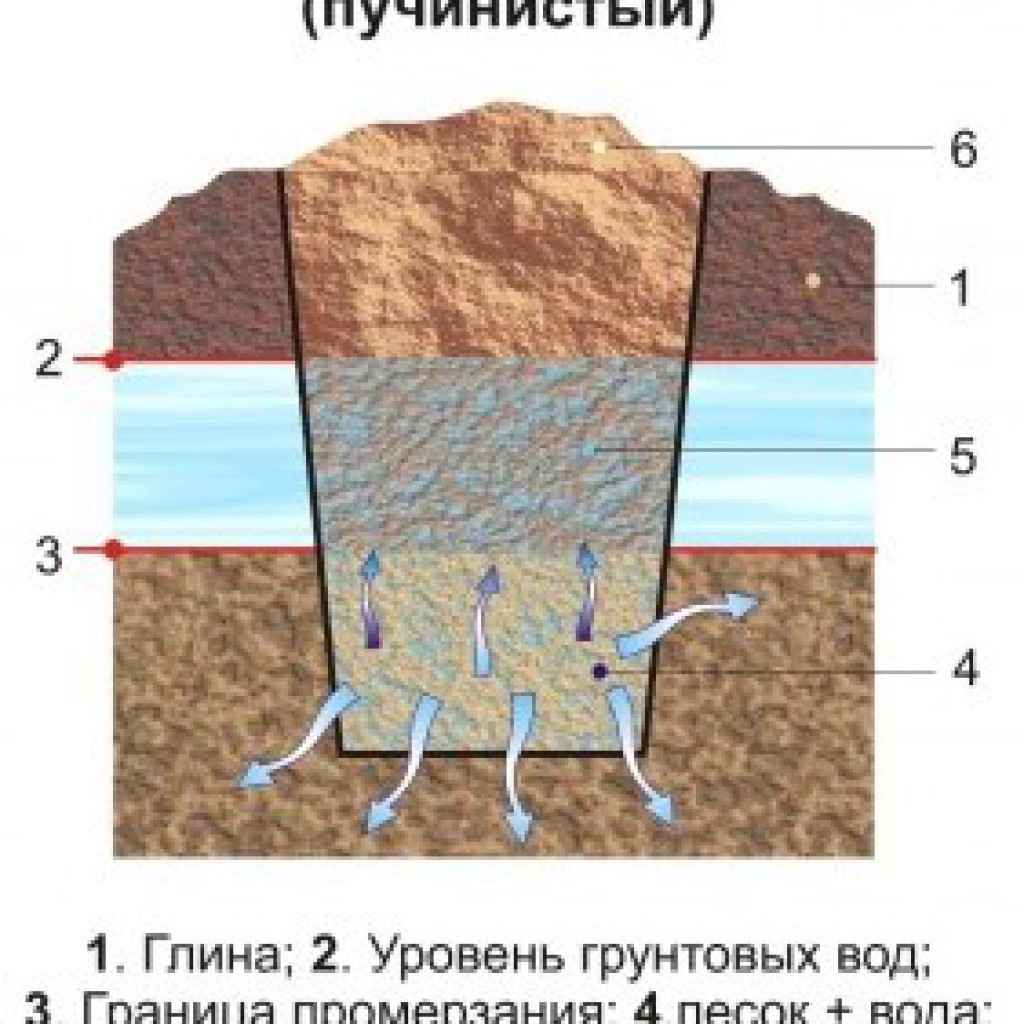
The main distinguishing characteristic of clay is its weakness in front of moisture, due to which it quickly turns into a pasty mass and prevents further seepage of liquid into the soil. The layers of the studied rock can be located at a significant depth, which increases the risk of soil swelling in winter due to freezing of stagnant water.
Characteristics of clay soil and its types
In order for the structure to be reliable and durable, it is necessary to decide in three directions:
- What can be built on clay soil.
- What materials to use for construction.
- What is the best foundation to choose.
To answer these questions, you should familiarize yourself with the types of clay soils and their features.

Types of clay soil
Pure soil rocks are very rare, in most cases they contain various impurities. In the case of clay soil, sand is mainly used as an impurity. Depending on its amount, clay soil is divided into the following types:
- Clay. In such soil, the net clay mass is more than 30 percent. The soil belongs to the category of heaving soils due to the ability of clay to retain water. When it freezes, the soil expands, which always becomes the cause of the destruction of the foundation. In addition, under the influence of groundwater, clay is quickly washed away, this leads to the formation of voids and subsidence of the foundation.
- Loams contain 10 to 30 percent pure clay. Such soil can also be called unreliable, since its behavior changes under the influence of certain factors. Construction on such a site is possible only if the soil is strengthened.
- Sandy loam - soil with a content of no more than 5 percent clay. It is also one of the problematic soils, as it changes its characteristics under the influence of groundwater. If it becomes necessary to build a house on such a site, then it is best to use a pile foundation.
When studying clayey soils, you should pay attention that clay can be red and blue. The first form contains a large amount of sand, which promotes the conduction of moisture
Because of this, the soil can change its properties and collapse. Blue clay is more durable and less susceptible to destruction, since it practically does not allow moisture to pass through. However, a large accumulation of water can be observed on its surface.

Clay characteristics
Also distinguish between glacial and alluvial clays. If the glacial layers are deep enough, then a concrete foundation can be erected on them without fear. Alluvial or river clay is found in lowlands and near water bodies, and is characterized by high plasticity. In such areas of the house, it is better not to build a foundation; in extreme cases, you can make a pile foundation.
Is it possible to build a reliable foundation for a house if there is clay soil on the site?
Clay soil consists of scaly elements that tend to accumulate moisture.
 A variety of heaving soils are clay, loam, and clay combined with sand
A variety of heaving soils are clay, loam, and clay combined with sand
Clay, loam, as well as clay in combination with sand represent a variety of heaving soils, characterized by an unpredictable nature:
- dry clay soil is characterized by friability, which complicates the construction of a foundation on clay soil;
- waterlogged soil is subject to frost heaving, gradually destroying the foundation on clay soil.
These factors negatively affect the strength characteristics of the foundation.
You should take seriously the choice of the optimal foundation option and pay special attention to the following factors:
- characteristics of clay soil. Sampling for laboratory research is carried out by making pits to the design depth. It is advisable to analyze samples in the spring months, when moisture in the soil rises close to its surface;
- the level of soil freezing. Literary sources and professional sites provide information on the maximum possible depth of freezing of soil in various regions, which makes it possible to determine the type and level of deepening of the foundation base;
 The choice of the optimal foundation option should be taken seriously
The choice of the optimal foundation option should be taken seriously
the proximity of aquifers and the ability of clayey soil to absorb moisture. The depth of water formations is determined during drilling, and the tendency of clay to absorb moisture is determined in laboratory conditions. The samples are moistened with subsequent control of the drying time.
Laboratory analysis of soil raised from various depths will allow you to get a complete picture of the characteristics and structure of clay soil, which is divided into the following varieties:
- clay soil. The concentration of pure clay reaches 1/3 of the total volume of the soil. Such soil is characterized by increased flowability and high plasticity;
- loams. Along with 10% clay, such soils contain a sandy fraction. Depending on the content of sand and clay, they are divided into light, medium and heavy;
- sandy loam. Clay concentration does not exceed 1/5 of the total volume. Due to the increased concentration of sand, sandy loam is of little use for construction.
 Will allow you to get a complete picture of the characteristics and structure of clay soil laboratory analysis of soil raised from different depths
Will allow you to get a complete picture of the characteristics and structure of clay soil laboratory analysis of soil raised from different depths
Clay is divided into the following types:
- glacial. It has an increased load capacity and is suitable for the construction of foundations;
- alluvial. It is characterized by increased plasticity, which makes it difficult to build foundations.
Professional builders give an affirmative answer to the question about the possibility of building a reliable foundation on a site with clay soil
It is important to choose the right type of foundation for the specific conditions of the construction site. With a close location of water layers that are above the freezing level, a drainage system should be made before the construction of the foundation
It will provide effective moisture removal from the base of the building.
 Professional builders answer affirmatively to the question about the possibility of building a reliable foundation on a site with clay soil
Professional builders answer affirmatively to the question about the possibility of building a reliable foundation on a site with clay soil
What is the foundation to make on clay?
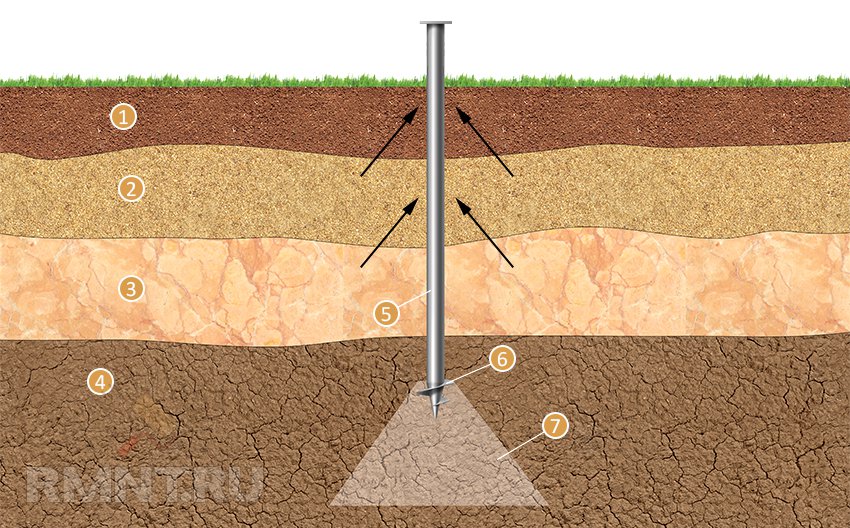
Clay is afraid of exposure to water. It is strongly recommended to carry out geological exploration before starting the foundation. Its purpose should be to determine the uniformity of the soil at the construction site. Often the soil on the site is extremely heterogeneous. Clay comes in layers, alternating with layers of sand. Therefore, the decision on what kind of foundation to build on clay should be made depending on the depth and composition of the clay layers. This is done by drilling pits to the depth of the proposed foundation.
If the composition of the soil is heterogeneous, then the best solution is to replace it with non-porous soil.For example, rubble or sand. If the soil has a homogeneous composition, then its moisture content is examined. In the case of close occurrence of groundwater, it is preferable to use a foundation on piles.
“There is clay soil on my site - which foundation will be the most reliable”? This question is asked by many land owners who are going to build a house or some kind of building. So, the foundation can be different. It all depends on the specific composition of the soil, the location of the site and your capabilities.
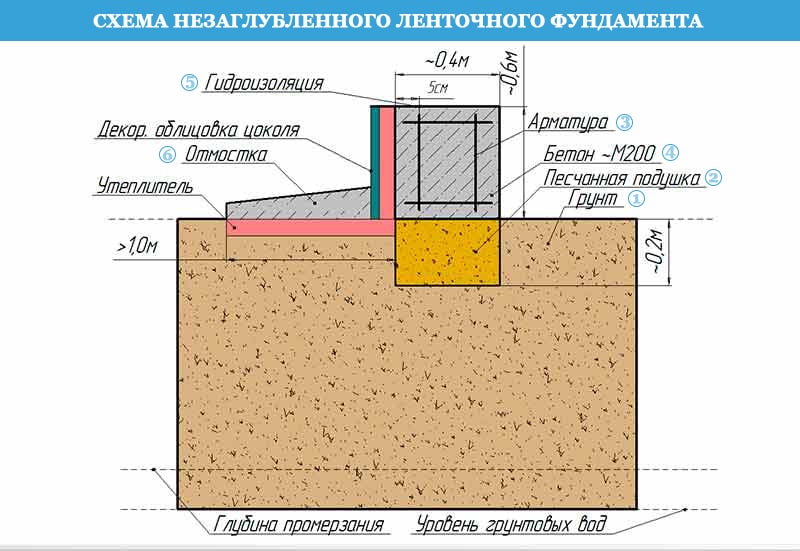
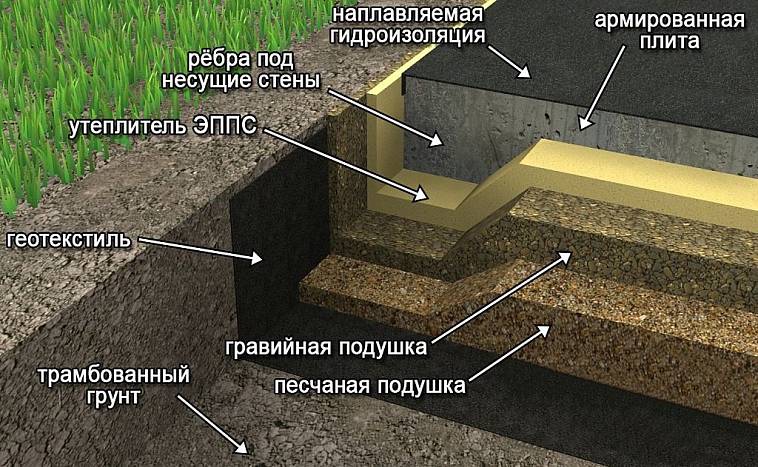
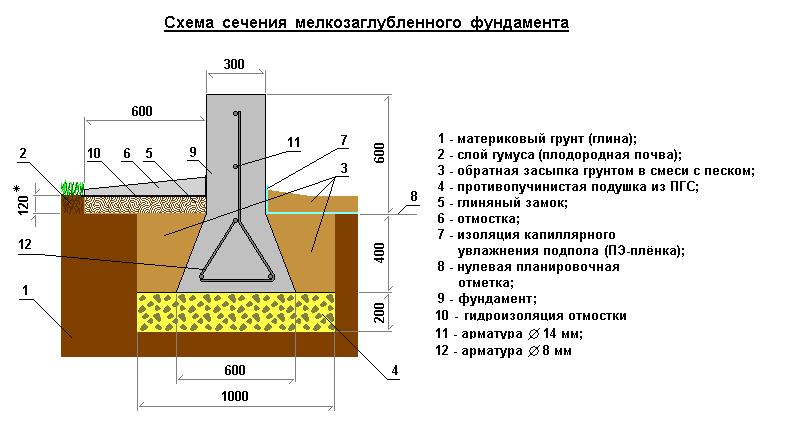
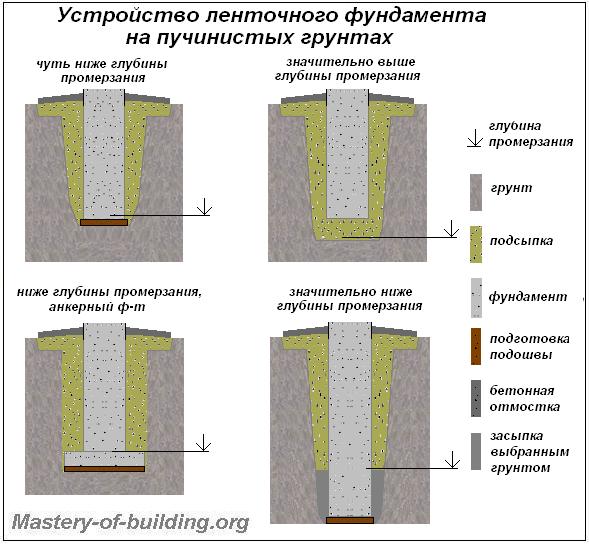
Shallow foundation on clay soil
But a reinforced concrete slab is just suitable for clay soil. The so-called floating foundation will take place.  Movement of clay as a result of heaving or erosion will not affect the walls of the building in any way. The slab can be self-poured from high quality concrete.
Movement of clay as a result of heaving or erosion will not affect the walls of the building in any way. The slab can be self-poured from high quality concrete.
You can also use a ready-made plate. The depth of the slab depends on the mass of the structure. It is forbidden to lay the slab on clay. Before the start of the laying, a pit is dug, gravel and sand backfilling is performed.
The only drawback of this method is the relatively high cost of the project.
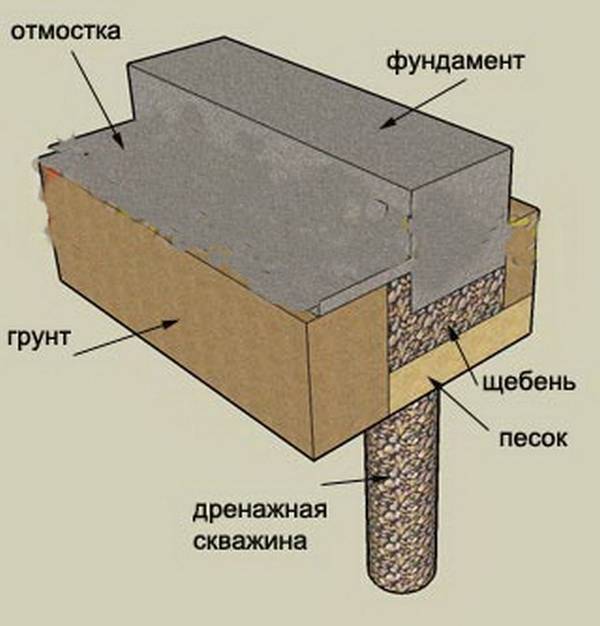
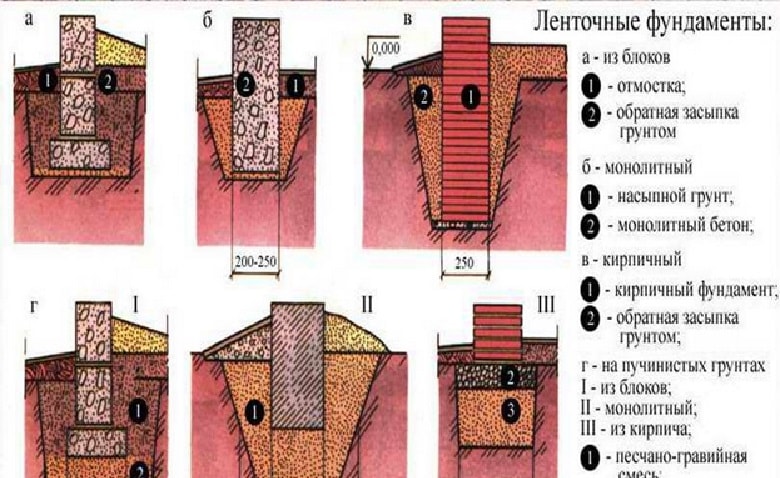
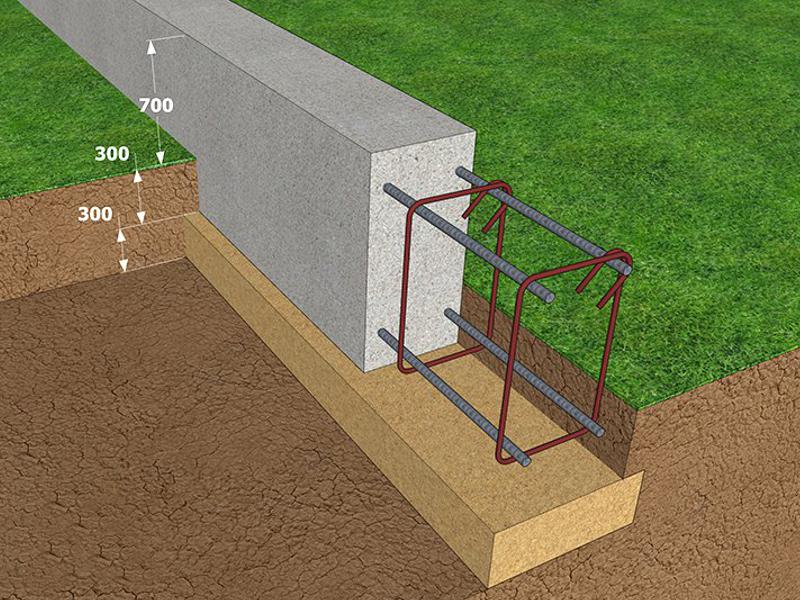
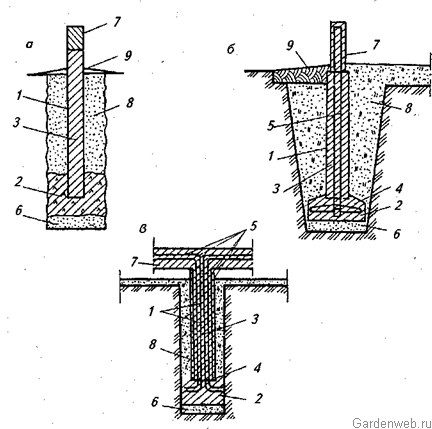
Tape base
A trench is dug under it to a depth that should exceed the level of freezing of the soil. For different climatic zones, this indicator will differ. In the northern regions, it is sometimes necessary to dig a pit up to one and a half meters deep.
 The bottom of the pit is covered first with gravel, and then with a layer of sand. The deeper the pit, the more sand must be filled. The bottom of the trench (on top of the sand layer), as well as its walls, must be laid with polyethylene or roofing material to ensure waterproofing of the foundation and reduce the effect of soil pressure on it.
The bottom of the pit is covered first with gravel, and then with a layer of sand. The deeper the pit, the more sand must be filled. The bottom of the trench (on top of the sand layer), as well as its walls, must be laid with polyethylene or roofing material to ensure waterproofing of the foundation and reduce the effect of soil pressure on it.
The base of the concrete foundation should be made 30% wider than its main part. This is necessary to increase the stability of the foundation and resist heaving of the soil. Before pouring the concrete solution into the pit, reinforcement is laid, tying it together.
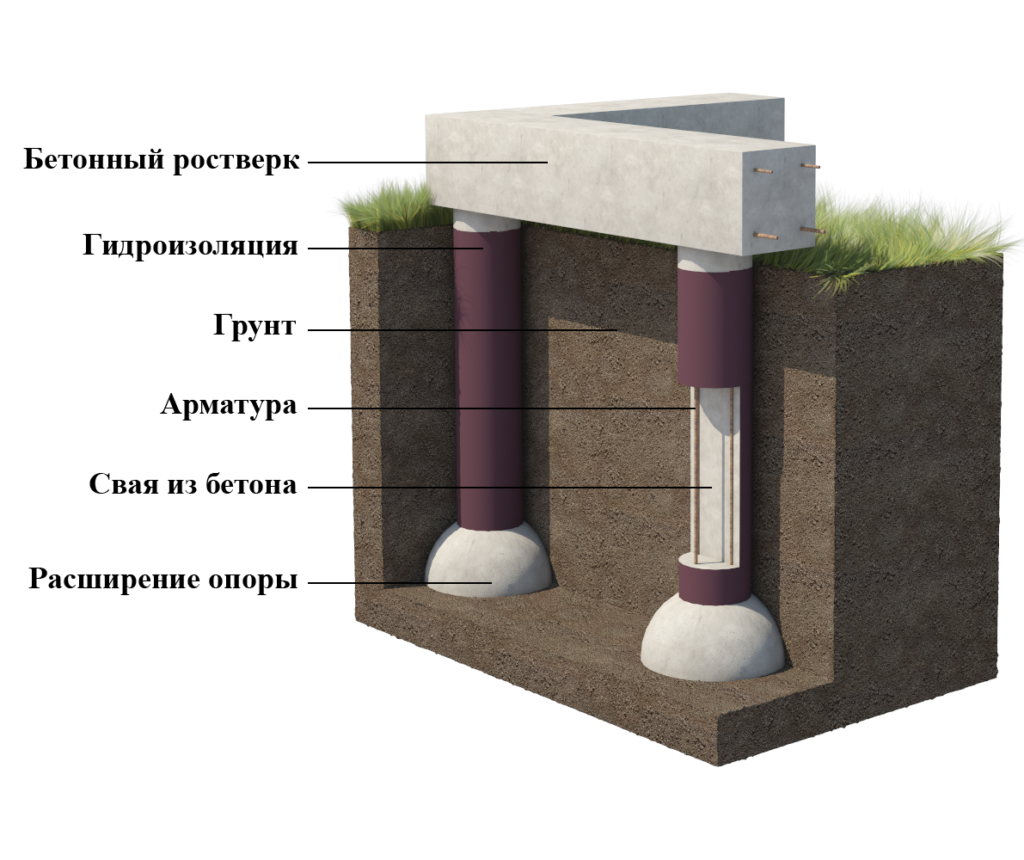
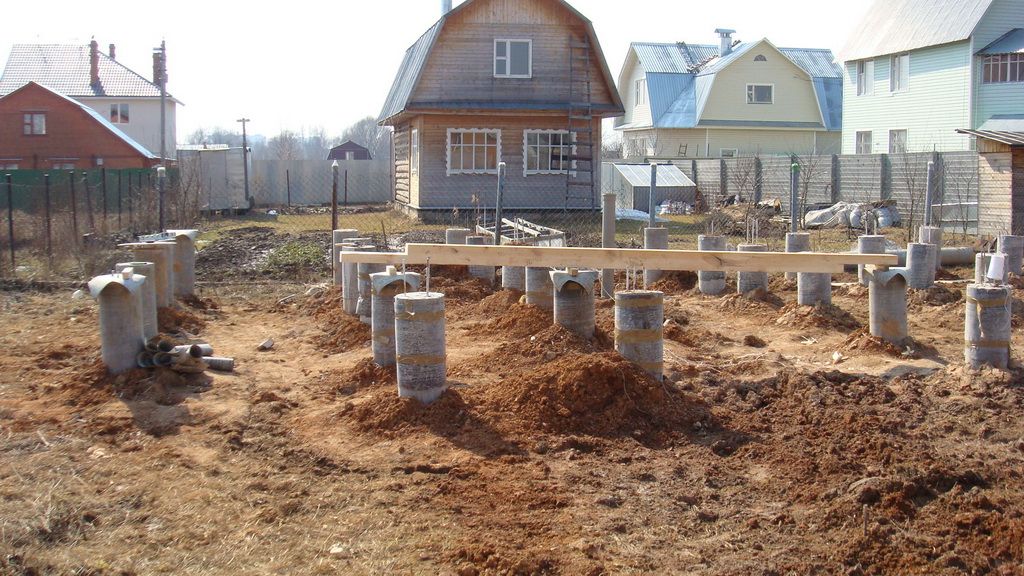
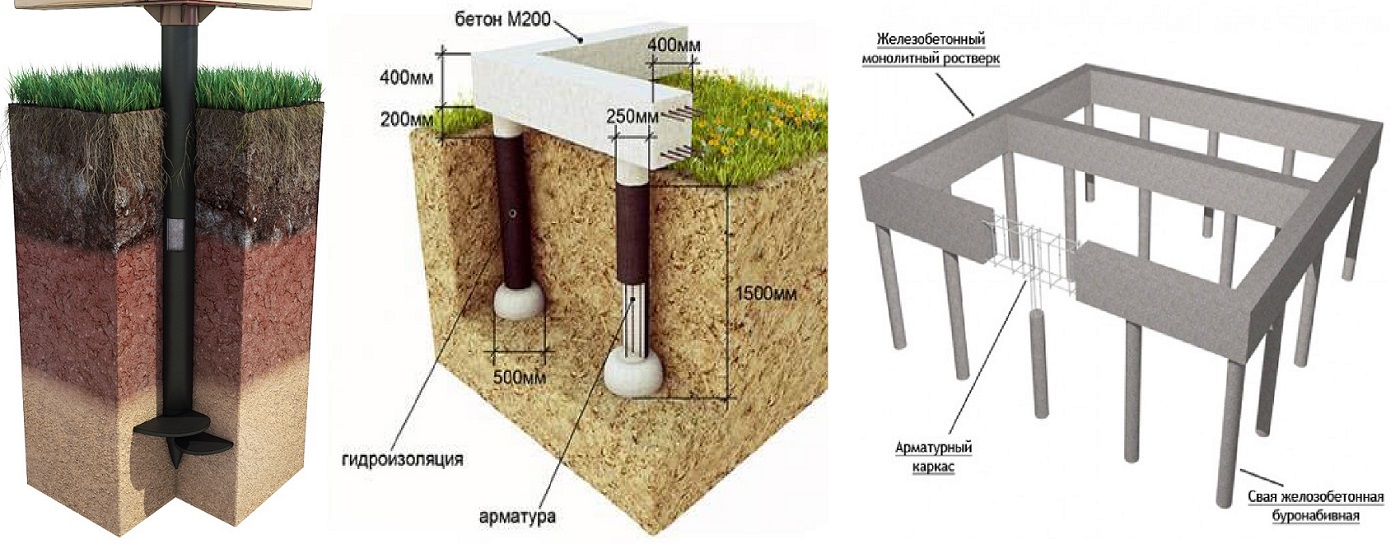
Pile foundation
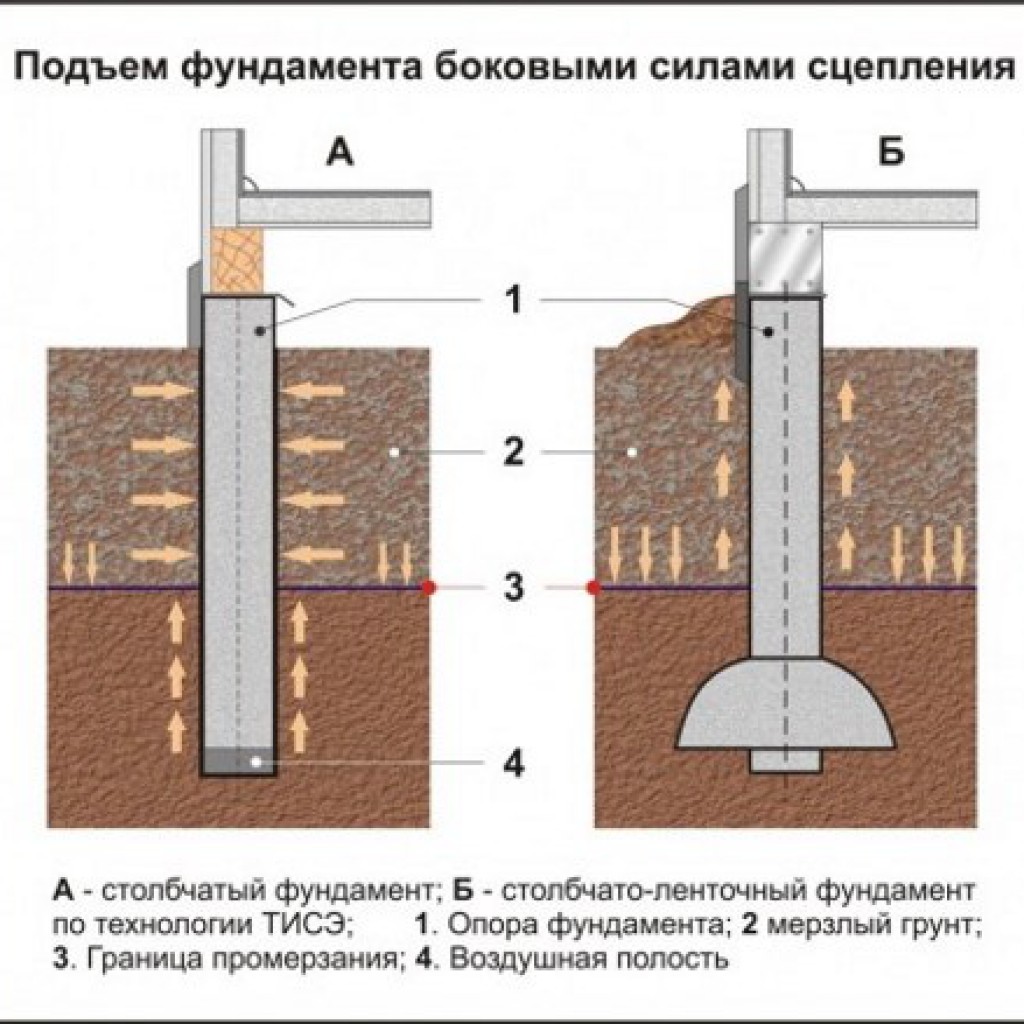
A pile foundation on clay is the best due to the fact that piles make it possible to equip a foundation on almost any type of soil, even on swampy soil. By hammering or screwing piles into the ground, it is possible to get to solid soil layers that do not depend on groundwater or freezing. The lower soil layers are immobile, therefore the foundation will not depend on extraneous factors.
Screw and driven metal piles are used. Driven piles are driven into the ground using driving machines, and screw piles are screwed into the ground.
Bored piles are also common. For them, holes are drilled in the ground beforehand, from which water is pumped out. The holes are reinforced and concreted. With a relatively low concrete consumption, it is possible to achieve high strength of such a bored foundation.
A foundation on clay soil, built in accordance with all the rules, will provide a reliable foundation for any structure.
About the site
zalman
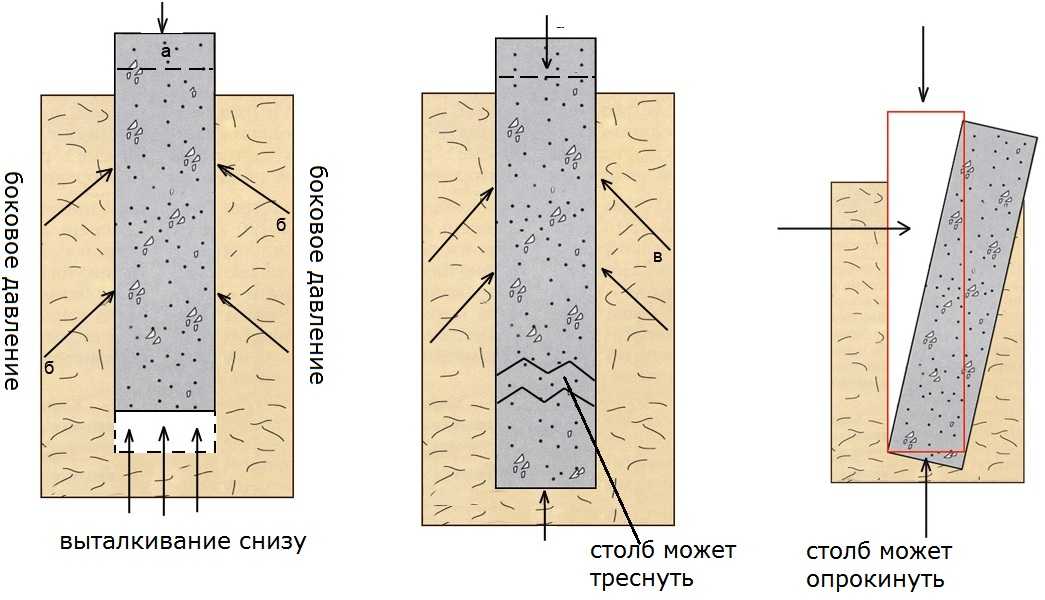
Ways to counter heaving
Scheme of interaction of properly arranged foundations with heaving soils.
If the foundation is being built on problem soil, measures are taken, among which the following should be highlighted. In some cases, it makes sense to replace the soil that is on the base with a non-porous one. Crushed stone and sand are poured under the foundation. Backfilling is also done with non-porous materials. This technique is used when it is necessary to reduce lateral heaving. The next method is with smooth wall structures. Soil swelling is not neutralized by a waterproofing layer on the side walls.
For many types of foundations, the option of arranging a foundation that looks like an expanded monolith is suitable.Laying soil insulation relative to the perimeter of the building is effective only if there is a heating system and a normally insulated basement floor. The fact is that with good heating, structures in combination with thermal insulation help to reduce the heaving forces.
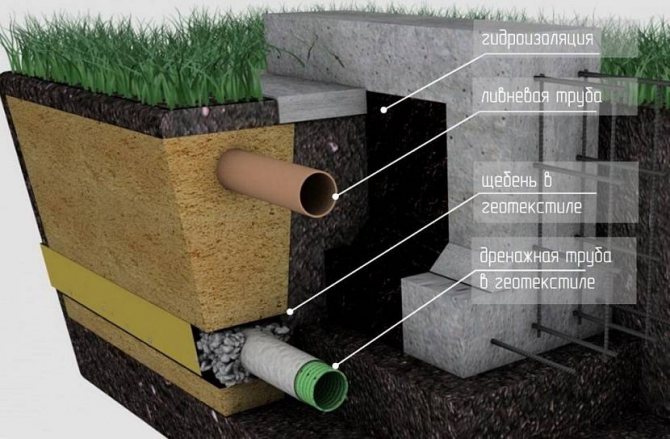
The only exceptions are non-porous soils. The high water content in the soil leads to its erosion. Sometimes groundwater contains corrosive substances that can destroy reinforcement products and concrete structures. These problems can be solved with waterproofing. The device of the drainage system also helps to reduce heaving in the area of the foundation.
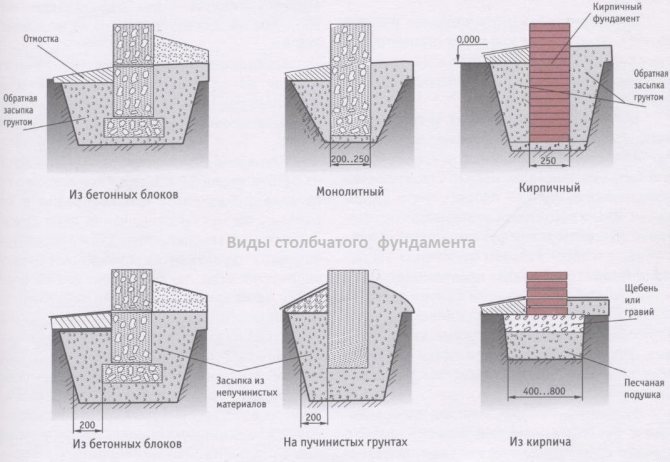
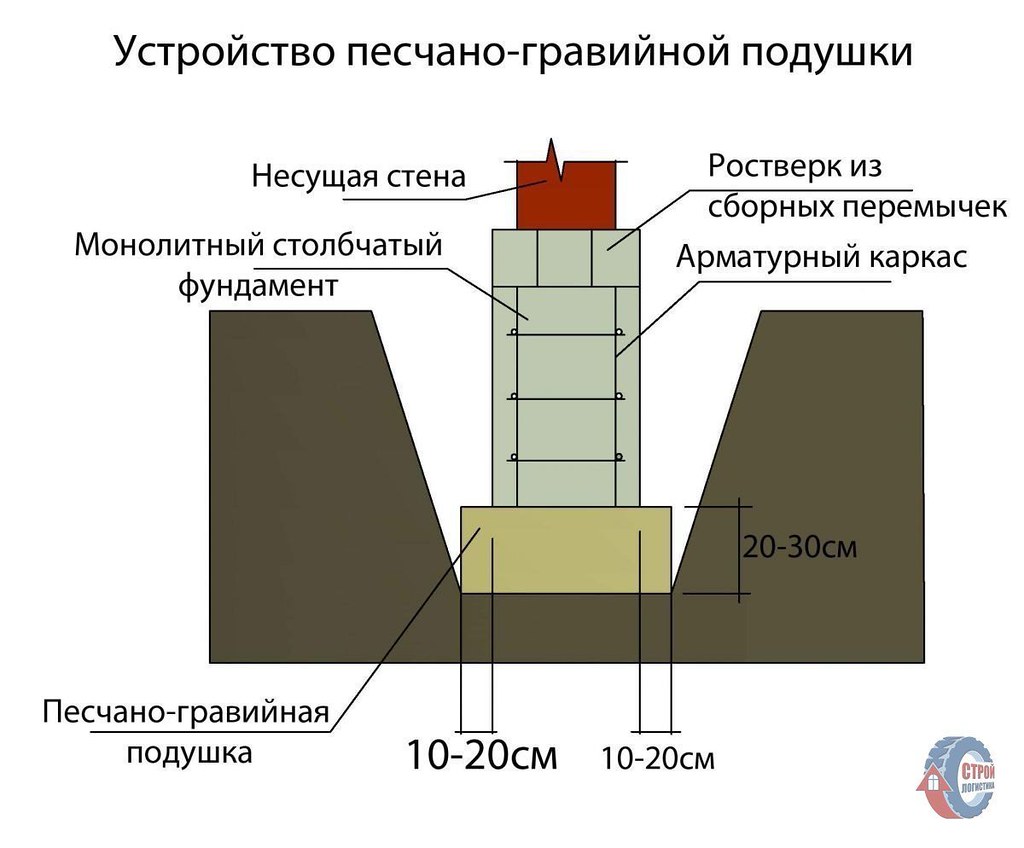
Columnar foundation diagram.
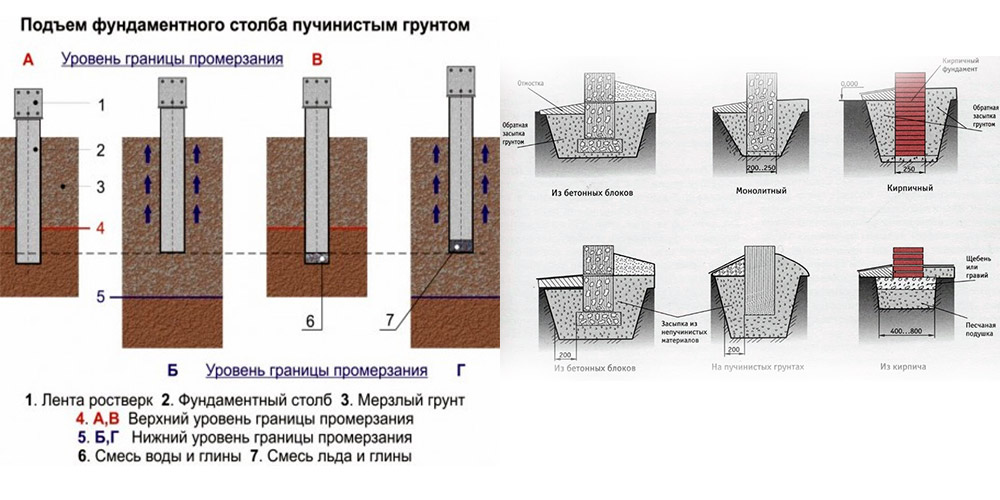
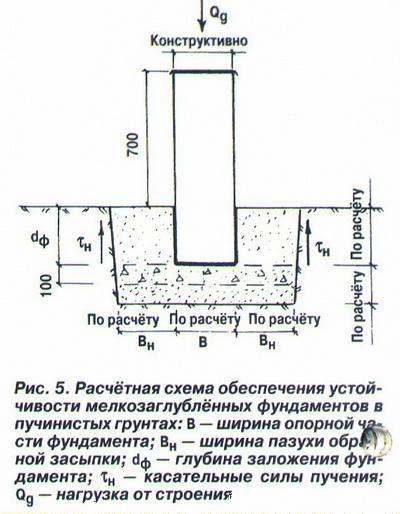
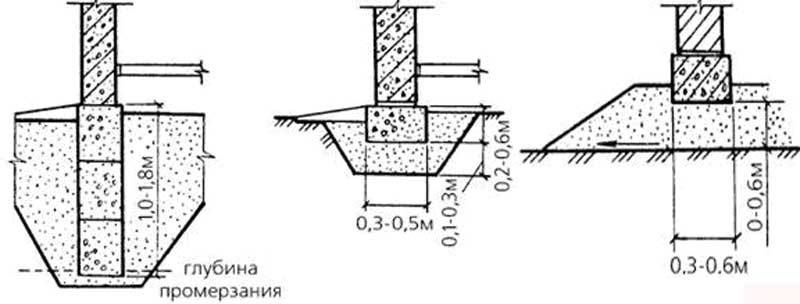
The main solution to the problem of building a reliable one is sufficient deepening of the base, which will be below the freezing level of the soil. If the strength of the base is insufficient, the material may be displaced or deformed. When laying the foundation at a great depth, construction will require high material costs. As a rule, a good foundation on heaving soils reliably resists the effects of heaving and evenly distributes the deformation phenomena of all foundation elements.
A shallow baseline, characterized by a shallow filling depth, helps to cope with such a problem. Such a laying helps to damp the tangential forces of heaving of the soil, since the foundation is represented by a monolithic structure. In order for such a base to cope with its functions, a special pillow is arranged under it, consisting of materials that are not subject to heaving. It can be medium-sized crushed stone or sand. After pouring concrete, the outer side of the foundation is laid with non-porous materials and sprinkled with earth. The following will describe the main ones being built on heaving soils.
Engineering and reclamation methods of dealing with heaving
Diagram of the stages of pile formation.
- Raising the general level of the construction site using filling from non-porous soils (coarse or medium sand). This will reduce the depth of freezing of heaving soil and reduce the overall degree of its swelling. This method is especially effective on soils, where it is very.
- Deep drainage device. In basement rooms, this method is ineffective, moreover, the device of such a system will be quite expensive. However, for houses with a technical underground or a basement, such drainage will not only reduce the level of heaving, but also prevent flooding of the buried part of the house with groundwater.
- Reducing heaving of the soil by compaction with a heavy rammer, which reduces its porosity. For individual construction, this method is rather laborious and rather expensive, since it requires the use of powerful mechanisms and equipment.
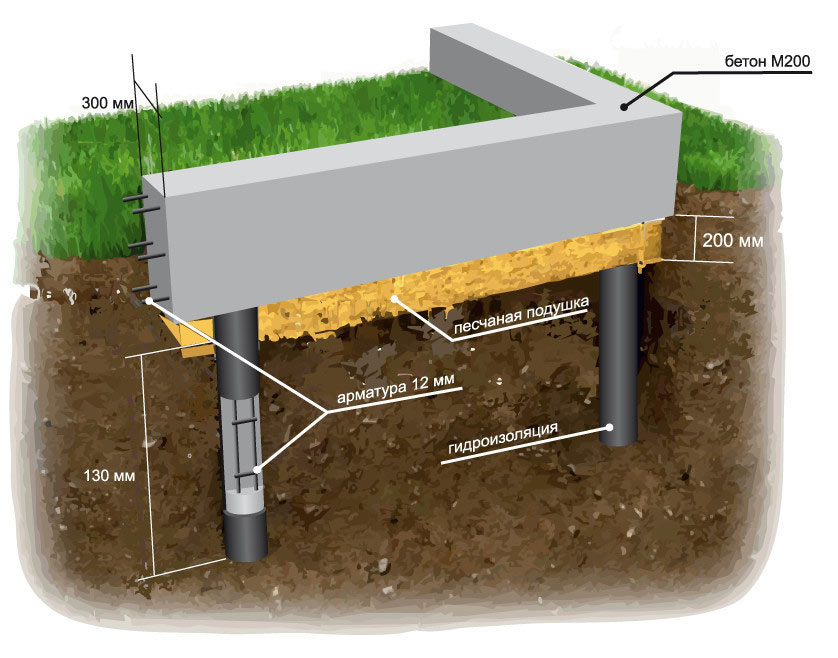
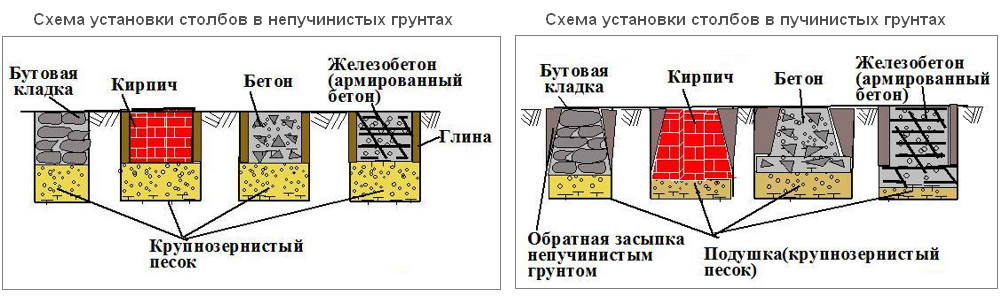
Do-it-yourself columnar foundation on heaving soils
For the construction of such a foundation, the following materials and tools may be required:
- reinforced concrete pillars;
- concrete mix;
- metal pipes;
- shovel;
- waterproofing materials;
- sand, crushed stone;
- drilling rig, etc.
Scheme of a shallow economic strip foundation for heaving soils (clay and loam).
Columnar base can be an excellent solution for the construction of low-rise buildings in heaving soils. The correct columnar foundation should be located below the freezing level. This method saves a large amount of money. In order to avoid stress regarding the acting on the support pillars, reinforced concrete pillars should be chosen. Columnar bases made with reinforced concrete are an excellent solution for laying a foundation in soil characterized by heaving phenomena. This technology is convenient and highly adaptable, so they can be erected in swampy, damp areas and soils with a high level of groundwater.
On these soils, the columnar foundation can have a type of structure in which an anchor platform is firmly tied to the support frame, which serves as a support for the building. The following products can be used as load-bearing pillars of such a foundation: reinforced concrete pillars, asbestos-cement pipes with reinforced inner walls, metal pipes, reinforced from the inside with cement-sand mortar, and from the outside with epoxy resin. The armature can be a wire with a diameter of 6-12 mm, metal rods or parts of water and gas pipes. The concrete mixture should be prepared only on the basis of high grade cement. Crushed stone or sand are suitable as aggregates. The harder the concrete, the stronger the structure will be.
Methods for erecting foundations on heaving soils
The most common solution to this problem is to deeply lay the foundation, the base of which will be below the freezing level of the ground.
Materials and tools for building a foundation on heaving soils:
Diagram of a buried columnar foundation on heaving soil.
- cement;
- sand;
- gravel;
- crushed stone;
- water;
- concrete;
- fittings;
- shovel;
- concrete mixer.
Such a solution reliably prevents the effect of swelling in the lower part of the foundation, but the side walls will not receive reliable protection against deformation effects. If the base is not strong enough, its material may be displaced or deformed.
When laying the foundation for heaving soils at great depths, a large amount of material is required, so such a foundation is quite expensive. Optimally, the foundation on heaving soil should resist well the effect of swelling and evenly distribute deformation over the entire surface of the base so that it acts less on the side surfaces.
Shallow foundations cope well with this problem, leveling the influence of problem soil along tangential lines, since the foundation in this case is monolithic. In order for such a foundation for heaving soils to cope better with its work, it is necessary to arrange a special pillow under it from materials that are not subject to swelling. As a rule, medium-sized crushed stone or sand is used for this.
After the base is poured with concrete, it should be laid on the outside up to the pillow itself with non-porous materials, and then sprinkled with earth.
What is the difference between heaving and non-heaving foundations
According to GOST 25100-2011, there are 5 groups of soils that differ in the level of heaving:
- Excessively heaving (the level of expansion of the soil is more than 12%);
- Heavily puffy - 12%;
- Medium porous - about 8%;
- Slightly bulky - about 4%;
- Non-porous - less than 4%.
The last category is considered conditional, since the soil, which does not contain water, is practically absent in nature. Such bases include only granite and coarse-grained rocks, but in our conditions such soils are extremely rare.

Speaking about what heaving soil is and how to determine it, it is worth considering its composition and groundwater level.
Clay as a natural material and its features
On clay soils, you can make the foundations of the house in any way. The use of one or another basis depends on the individual characteristics of the site and the financial capabilities of the owner. Soil analysis will help you accurately determine the type of substrate
When choosing the optimal type of base, the following features must be taken into account:
- the amount of clay in the soil;
- freezing border;
- ground water level.
Determination of all of the above parameters is realized through a qualitative analysis of the soil. In the case of an overlap of the groundwater horizon with a level of soil freezing, it is advisable to equip a primitive drainage system for water drainage before laying the foundation of the house.
Drainage is implemented by digging trenches around the perimeter of the future placement of foundation elements. On clay soils, as a rule, the following types of bases are equipped:
- tape;
- pile;
- shallow slab;
- deep placement (in regions with extremely low temperature conditions).
The main feature of clay is the ability to quickly erode under the action of water, without letting it go deep. Clay layers can lie at a sufficient depth, and water that penetrates them at low temperatures freezes and swells the soil. Therefore, clay soils are called heaving, and before starting construction, it is strongly recommended to conduct research on the composition and homogeneity of soils on the site. Otherwise, the clay can behave unexpectedly, rather quickly turning the buried foundation into a ground one.
In general, river (alluvial) and glacial clays are distinguished. The first occurs near water bodies, in lowlands and has high plasticity. Construction on such sites is contraindicated, and in exceptional cases, houses have a pile foundation. Concrete foundations can be confidently erected on glacial strata, but only if they are deeply buried.
What foundation is suitable for clay soil
Layers of foundation laying for loamy soil with waterproofing.
After accurately determining the type of soil on the site and the depth of the groundwater, it is necessary to decide what kind of foundation can be built. Clay soil limits the choice of the base of the house, so you can use only two options: build a strip or pile foundation. Which one to choose, we will try to find out further.
If the soil is more or less homogeneous, then a strip foundation is suitable for it, a pile foundation is used in cases where stones are found in the soil.
It is not easy to build a foundation on loam, but if you understand all the nuances of this work, you can do it. When erecting a foundation on loam, problems such as breaking off, swelling and subsidence of the structure can arise. Most often this happens due to insufficient depth of laying the foundation or at high pressure that can be exerted on it. Problems can arise at a house whose foundation was built on loam, if small stone was used during its construction, or the walls were built from foam blocks.
Diagram of a strip foundation for clay soil.
To avoid all of the above problems, building a house should be accompanied by choosing the right type of foundation. In this case, the blocks can be sifted out immediately, since a reinforcing frame device will be required in the role of a connecting element. The bottom of the base should be wider than the top. If there are concerns about soil pressure, the base will need to be coated with machine oil or wrapped in PVC film, which will not let water through to the foundation during a thaw. It will be useful to insulate the top layer of the earth, for which you can use expanded clay or crushed stone.
The choice of the type of foundation. which can be erected on loam is also influenced by the material used in the construction of the walls of the house. If it is a brick, then you should stop your choice on a strip foundation that can withstand a heavy load.
If it is planned to build a barn or a summer greenhouse, then it is better to choose a pile foundation that is capable of providing the necessary degree of monumentality of the structure being erected.
On clays and loams, you can also use bases in the form of a monolithic slab, which must be installed on a sand cushion. Its advantage lies in its buoyancy, which means it can easily withstand any ground movements. Another advantage of the monolithic foundation is the absence of the need for global land works.
How to determine the type of soil yourself?
There is a simple home test for this:
- Step 1. Take in the palm of your hand a small portion of the soil from the site where the bath will be built and moisten it abundantly with water. From this cake you need to roll a tourniquet and bend the ring. If it's sand, you can't do it. The sandy loam ring will immediately crumble into small fragments, the loam - into 2-3 parts, but from the clay the ring will remain intact.
- Step 2. Carefully examine the particles of earth in your hands - are there many grains of sand in it that exceed 1.2-1.5 mm in diameter? If so, the foundation will be built on sandy soil.

Step 3. Determine the presence of water in the ground. After all, the foundation on swampy soil is another task. And the most undesirable in this regard are sandy loams and dusty sands - and all because small clay particles in them, which work as a lubricant between large ones, allow the soil to actively absorb water and give it away poorly. Just a little movement - and they easily turn into a quicksand state. In such soil, the foundation can begin to sink and shift to the side ... What to do? First of all, you need to make a pillow of crushed stone or coarse sand, as well as good drainage to drain excess moisture.
Sometimes it is necessary to completely change the weak soil layer with soil with more reliable characteristics. And the most proven method is an embankment of non-porous soil and a foundation that is already being built on it. So two hares are caught at once - the general level of the local area is raised and the soil parameters are improved.
Step 4. Determine the level of proximity of groundwater. This can be done with a simple observation: are there wells nearby and what is the depth of the water in them? Above or below the well is the height of your site and how much? The second point is communication with neighbors, who need to find out how dry it is in their basements and whether there is water there.
The most extreme method is to make a hole with a fishing drill, wait 2 hours and check the water level with a wooden rod. If it turns out that the level of underwater waters (builders call it the abbreviation UPV) is 1.5 meters lower than the depth of soil freezing, then even foundations on heaving soils can be built with such rigidity as on medium-heaving ones. But it is worth remembering about the capillary rise and seasonal saturation of soil moisture, which completely depends on the landscape and the abundance of precipitation in this particular area. That is why it is advisable to check the moisture content of the soil in the area where the bathhouse will be built in the fall - before the natural freezing of the soil begins (see step 5).
Step 5. Determine the moisture content of the soil - preferably in the fall. To do this, roll a ball out of the ground and watch it. If it crumbles right away, it is a slightly moist soil, if it holds, it is wet.