Foundation depth
It is advisable to lay a strip foundation to a depth of no more than 2.5 m. If a greater depth is required, then it is better to consider a pile foundation. It can be significantly reinforced with welded beams.
In most situations, the bearing capacity of the foundation is provided by a normal indicator of the resistance of the soil layers. We are talking about a depth of 40 to 70 cm. In such cases, problems are solved with the help of assistive technologies.

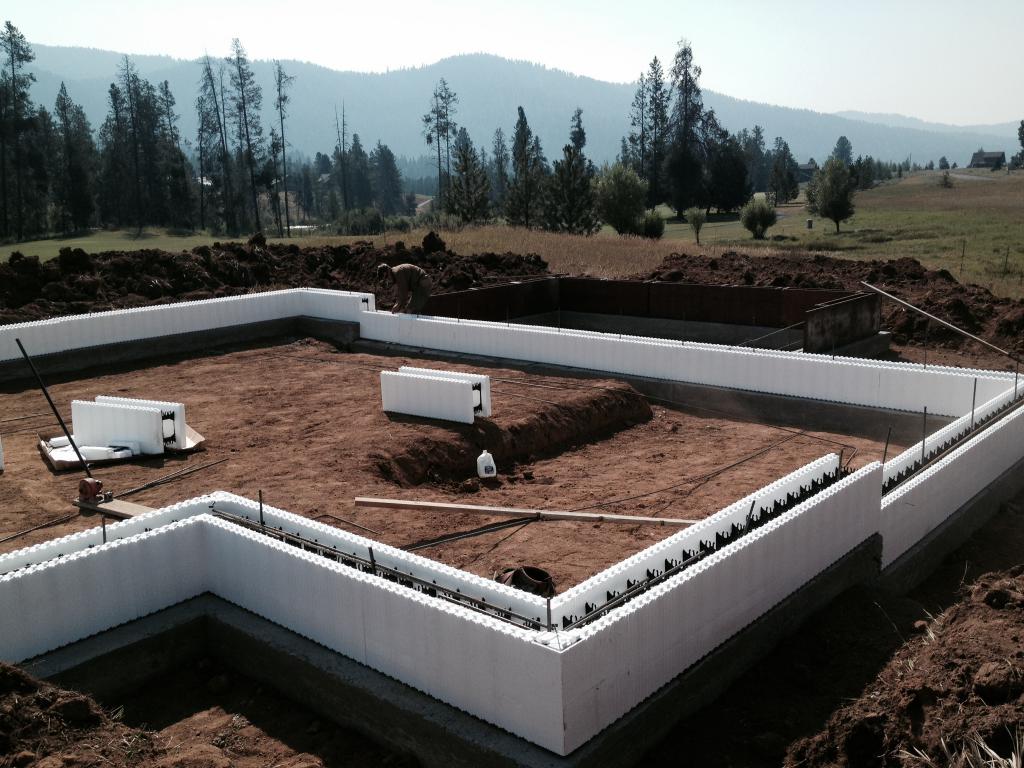
A monolithic belt and a non-recessed base have one very important advantage. The device of these types of foundations does not imply a lot of time spent on earthworks.
However, here the budget is much higher than for the construction of a shallow foundation.
Both the belt and the unburied foundation require the purchase and installation of insulation materials. Also, for such a base, you will need to install a drainage system and a sand layer. These elements have a long service life and are not afraid of the effects of heaving.
Types and methods of installing a columnar base
It is customary to distinguish between supports for the columnar foundation of a frame house:
- by size;
- type of section;
- materials of manufacture;
- production method;
- digging depth.
Views by material and installation method
The section can be of two types - round and rectangular.
The materials used are:
- concrete mix (reinforced concrete);
- rubble concrete;
- rubble stone;
- brick;
- blocks;
- wood.
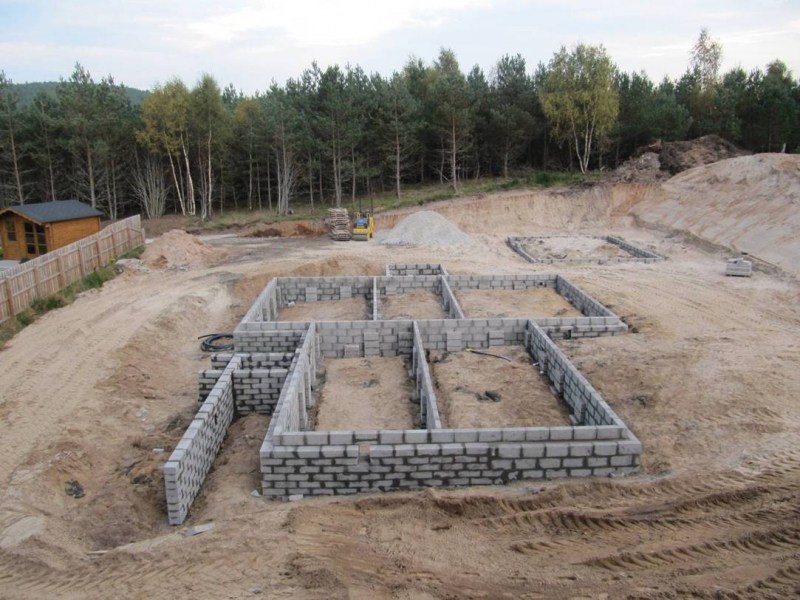
A columnar foundation can be done in two ways:
- Monolith. The mixture is poured into the formwork.
- Prefabricated structure. Builders assemble the foundation from composite components (blocks, bricks, stones).
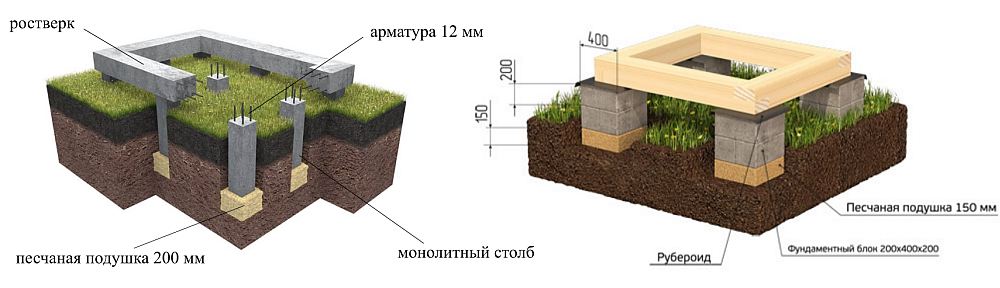
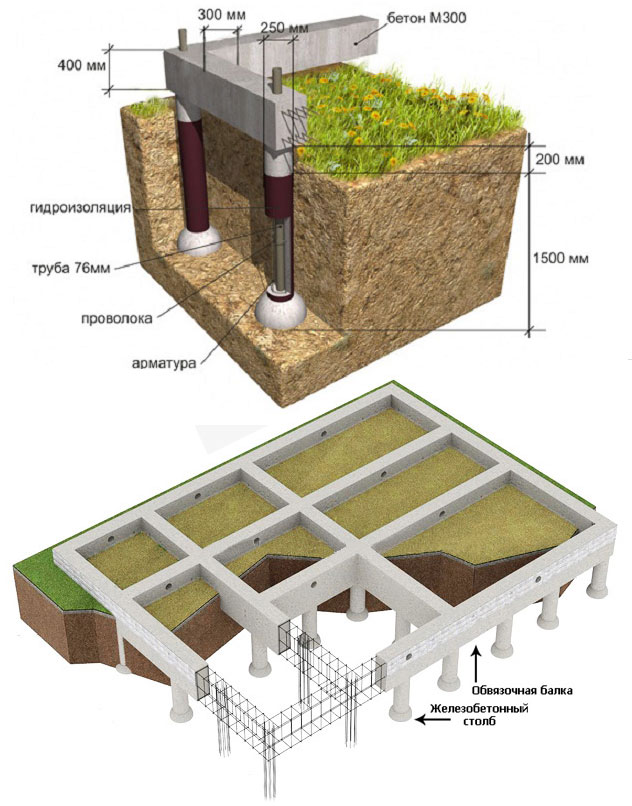
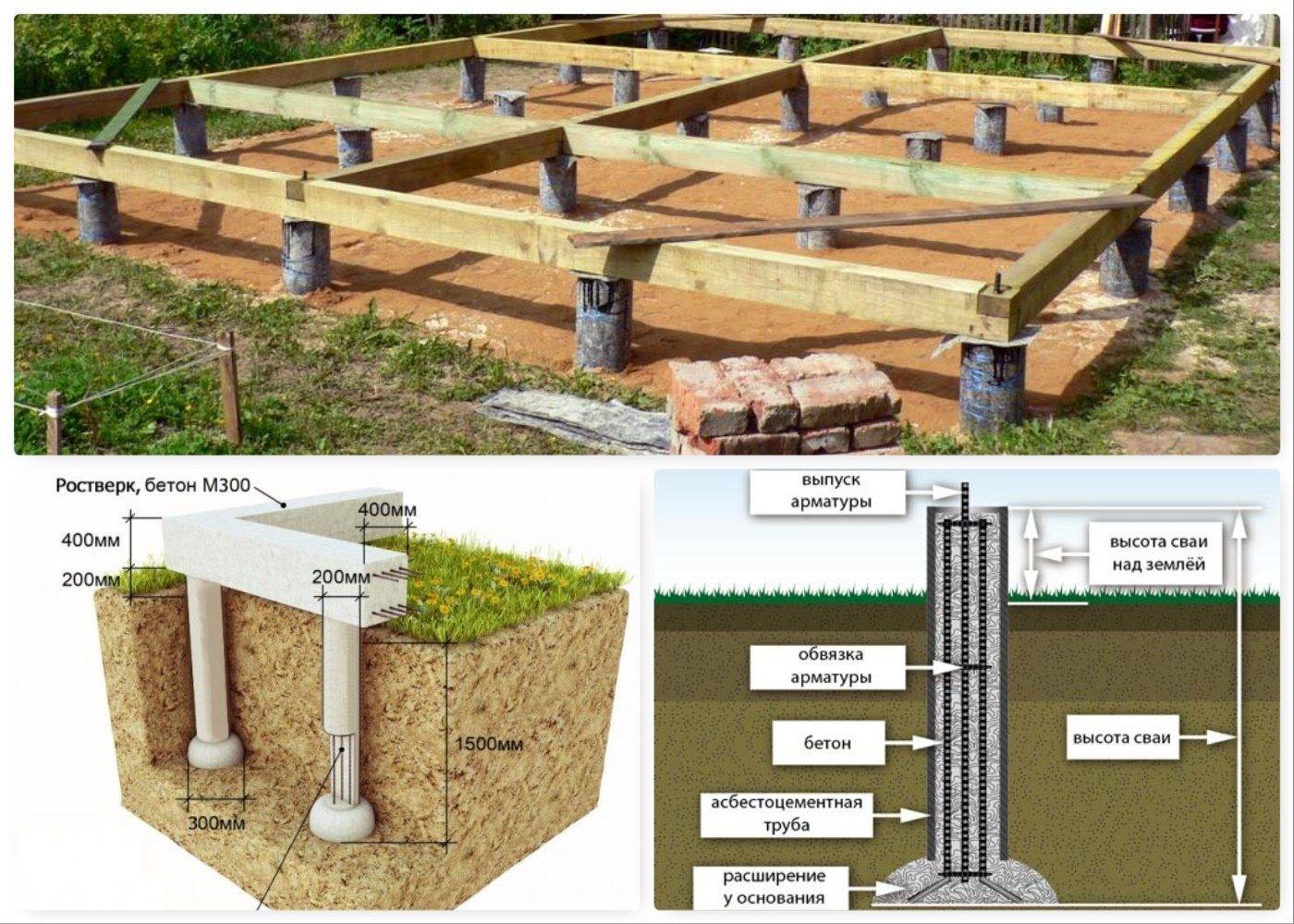
Pole digging depth
Columnar foundations can differ in the depth of the laying. It is customary to highlight:
- The deepened one is laid at a depth not lower than the level of soil freezing. Such a foundation is made when building houses on heaving soils (clay, loam). Recessed foundation is the most expensive and time consuming type of pillar foundation.
- Shallow is laid at 50-70% of the depth of soil freezing. About 50% of the depth will be a cushion made from a mixture of sand and gravel.
- Shallow. The lower part is located on the ground or on a special cushion made of gravel and sand. Shallow foundations do not require large financial costs. They are applicable exclusively on non-porous or low-porous soils. Can be used in the construction of light one-story structures.
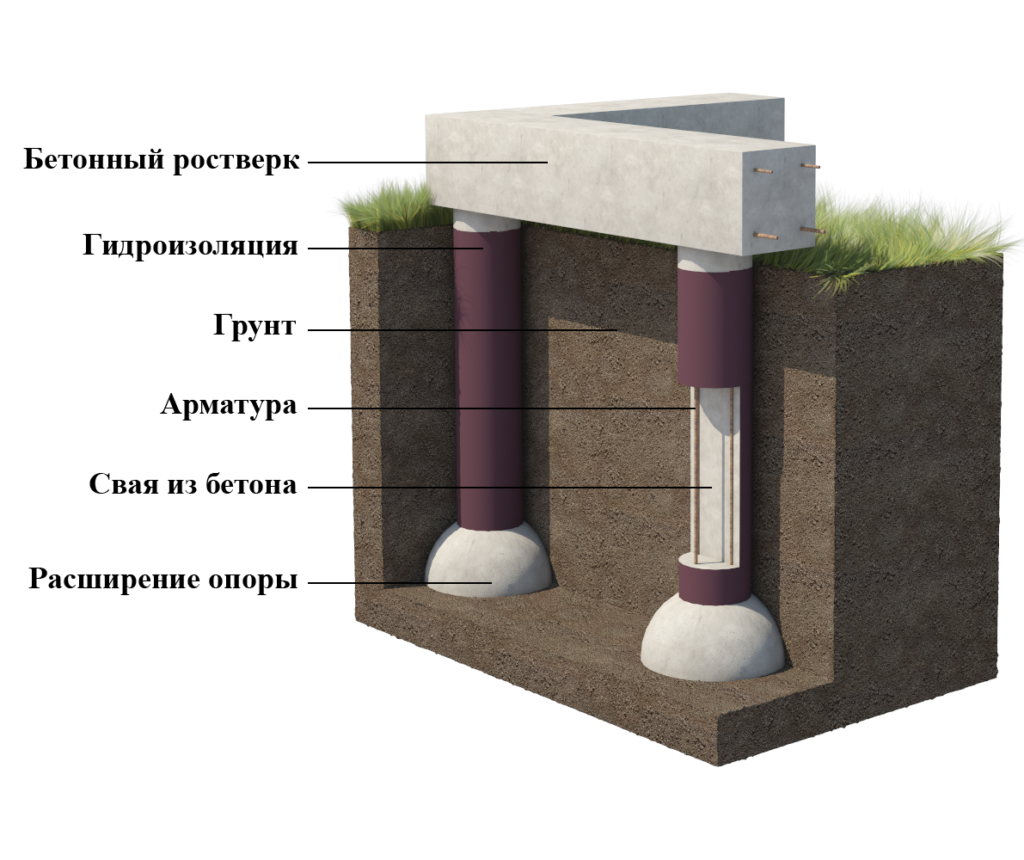
Using a grillage on columnar bases
Columnar foundations for frame-type houses can be laid with a grillage. There are situations when builders refuse to use this design. The grillage allows you to distribute the load of the structure evenly over all the supports and protects the supports from tipping over when the soil moves. The grillage is a beam that is mounted on the top of the pillars.

Installation of a grillage implies additional financial investments and increases the total time for building a house. For this reason, most of the frame houses are built without a grillage. The foundation piping is mounted directly on the supports on top of the waterproofing layer. As mentioned above, such structures are less resistant to ground shifts.
This fact must be taken into account
Types and types of foundations
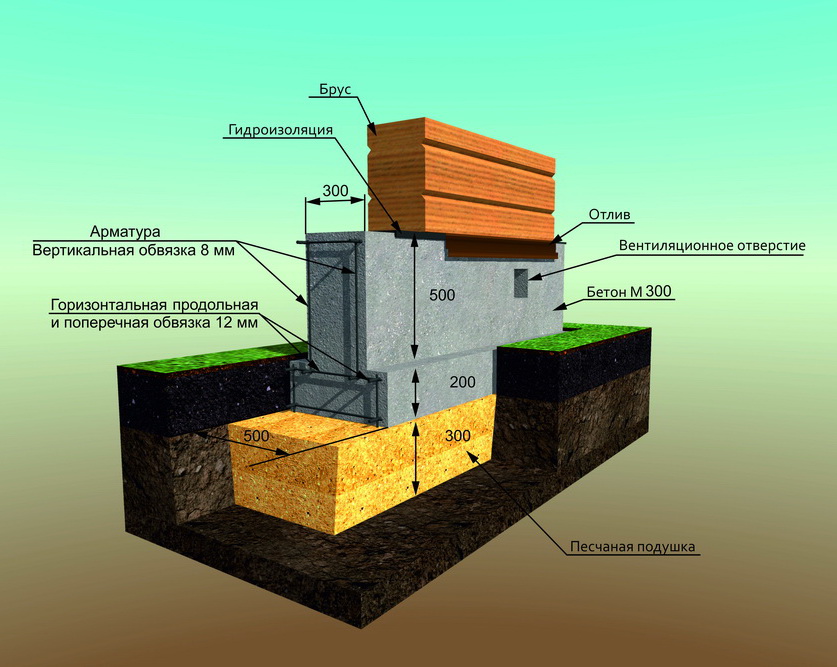
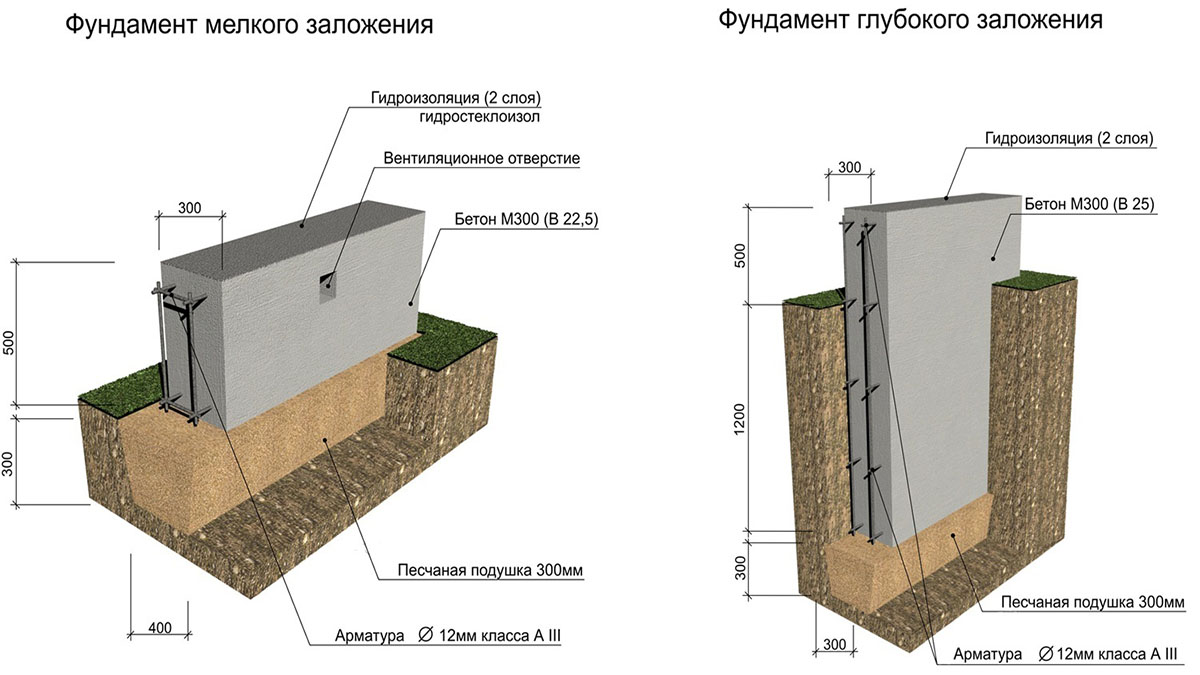
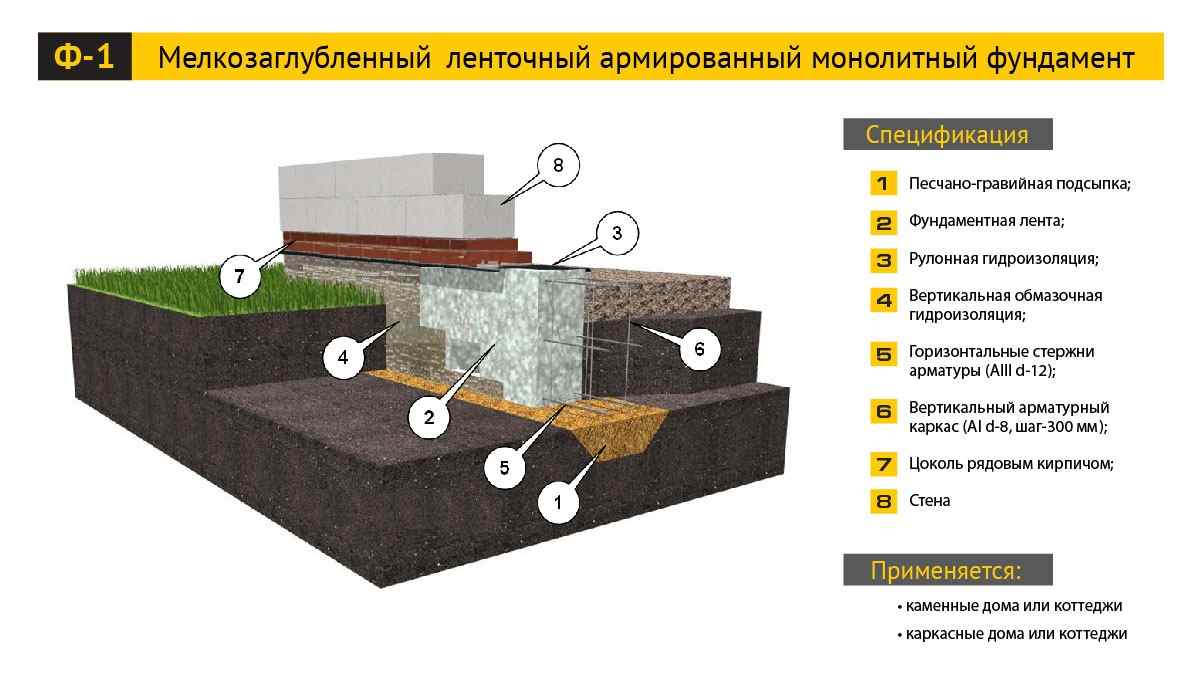
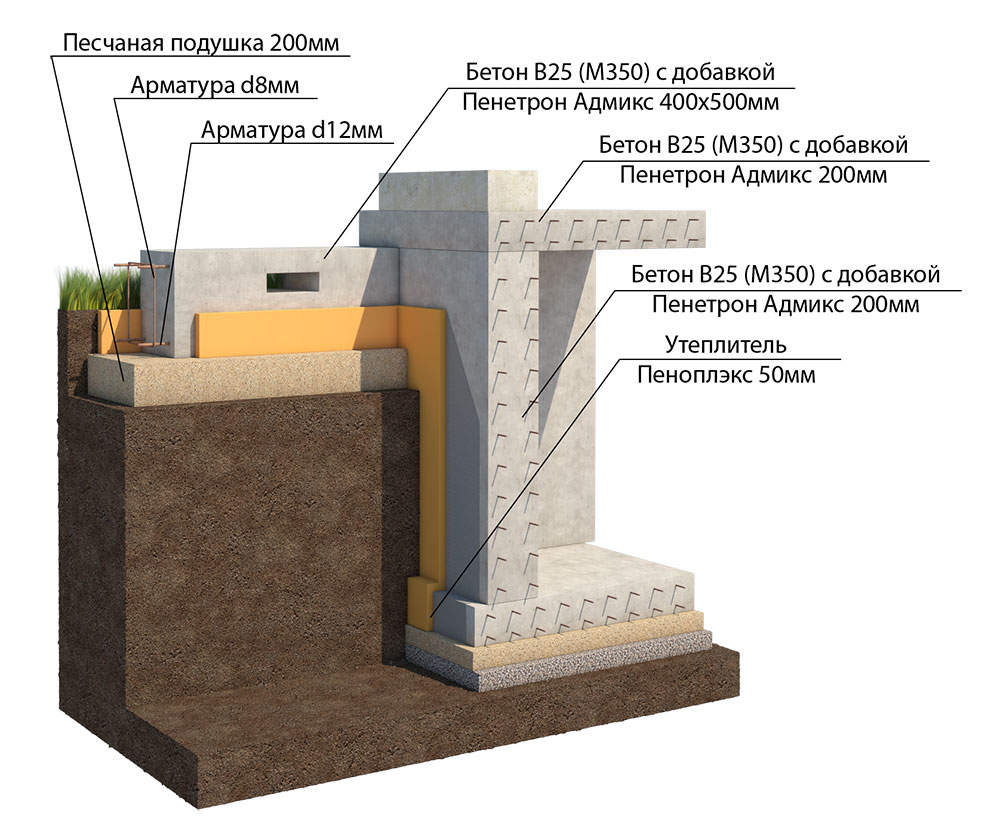
In terms of depth, it is MZLF (shallow) and simply buried. In the first case, a concrete belt under a low-rise house is buried only 200-400 mm into the ground, and in the second, it is buried up to one and a half meters (below the freezing level land).
If the soils at the construction site are rocky, and the groundwater is deep, then it is better to choose a shallow, cheap and small-volume concrete option. On heaving, high groundwater level and sandy areas for the house, you will have to make a more powerful and expensive support. Often, the estimate for such a basis for a dwelling comes out such that you have to choose a different type of foundation altogether.
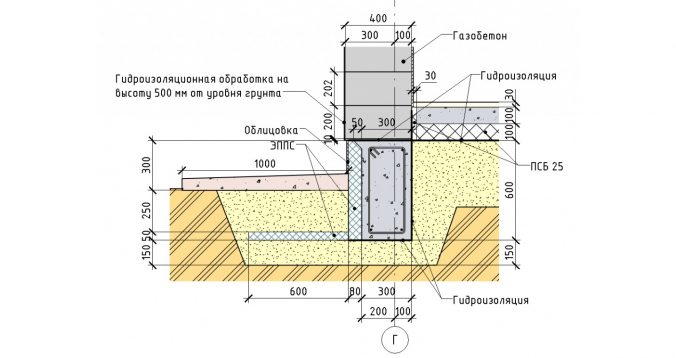
Scheme of walls with MZLF
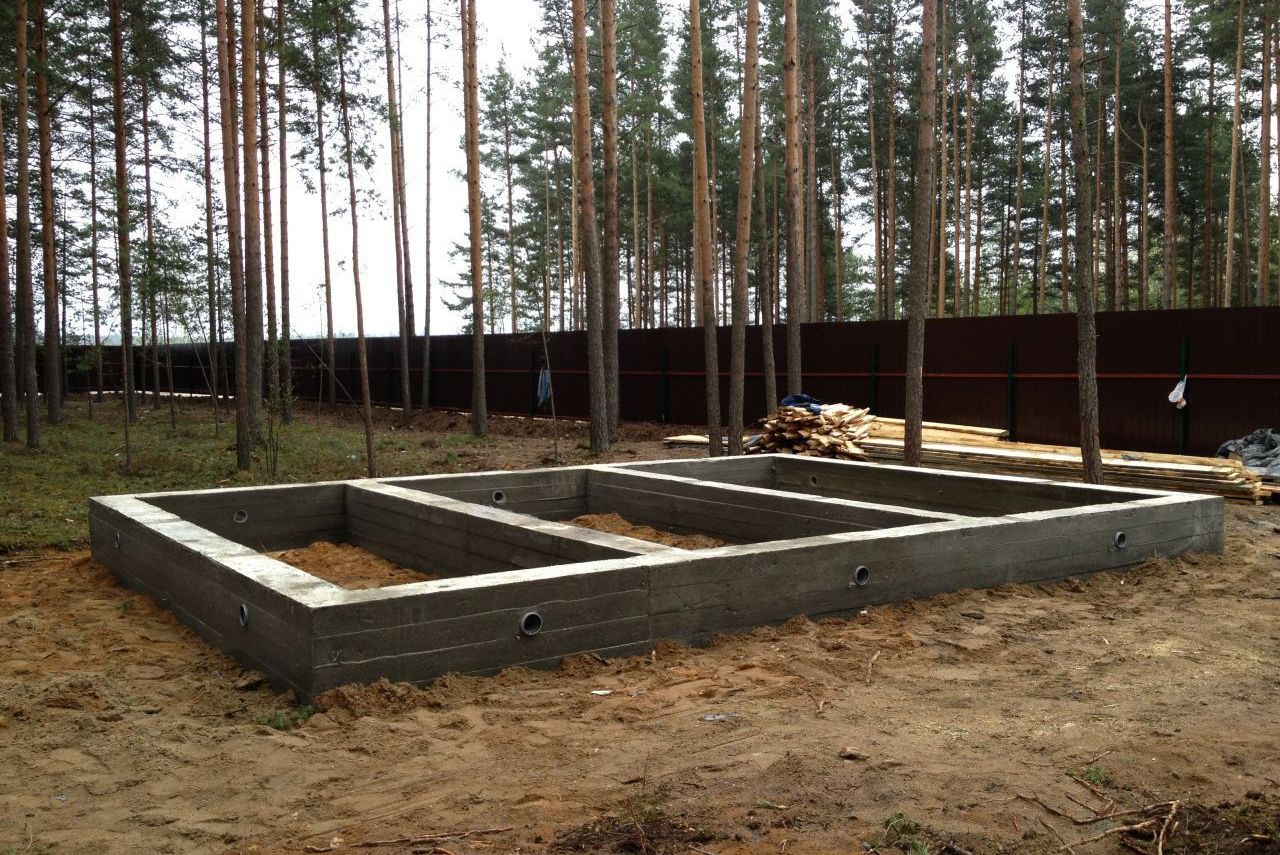
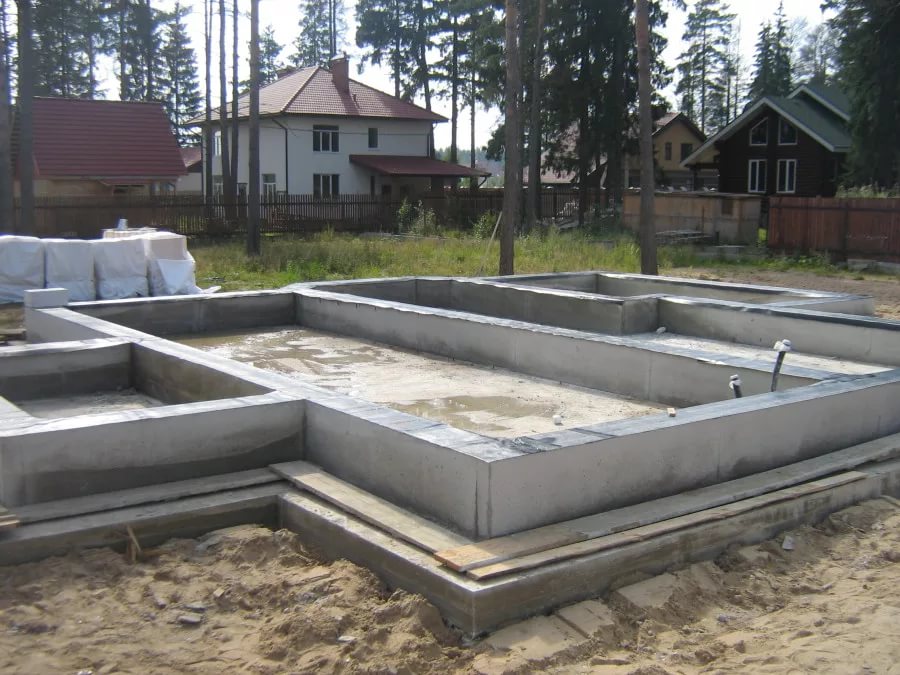
Structurally, a tape reinforced concrete base is:
-
Monolithic;
-
Blocky.
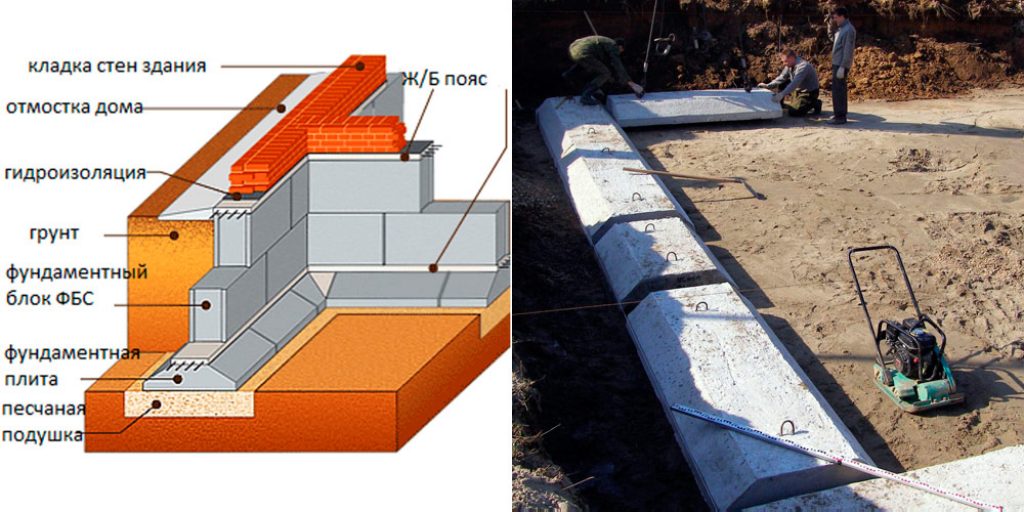
The first type is performed by pouring a reinforced concrete belt. The second option is laid out from special factory-made foundation blocks (FBS) or bricks.
Benefits of strip foundations for building a house
All consumers familiar with this design highlight several advantages in it:
- the foundation is extremely simple in the device, since any builder, even a beginner, can pour concrete mixture and lay out blocks;
- the versatility of the strip foundation under the house - it is allowed to put frame structures, houses made of brick and foam concrete materials, log cabins on this type of foundation;
- the correct strip foundation has the ability to withstand significant loading effects not only from below the soil, but also from above the total mass of the object.
Foundation installation rules for a country house
Do-it-yourself foundation installation is a laborious, complex and responsible process
Incorrect installation and calculation, poor-quality materials will lead to mold formation, subsidence, flooding and destruction of the house, distortion and cracking of the walls! During installation, it is important to follow the sequence of actions:
- Before making a foundation for a house, an analysis of soils and soil is carried out, consumables are selected and calculated;
- The construction site must be cleared of debris and the ground must be leveled. The foundation can only be erected on level ground! You can add sand or gravel into the pits or level out the bumps with a shovel;
- The foundation is marked with pegs and a rope. More accurate results can be achieved when using laser levels;
- A pit of the required depth is dug according to the markings. A sand cushion with gravel about 30 centimeters high is laid on the bottom, the layers are rammed;
- Already at the stage of building the foundation, waterproofing and insulation of the structure is done, communications are carried out for a private house;

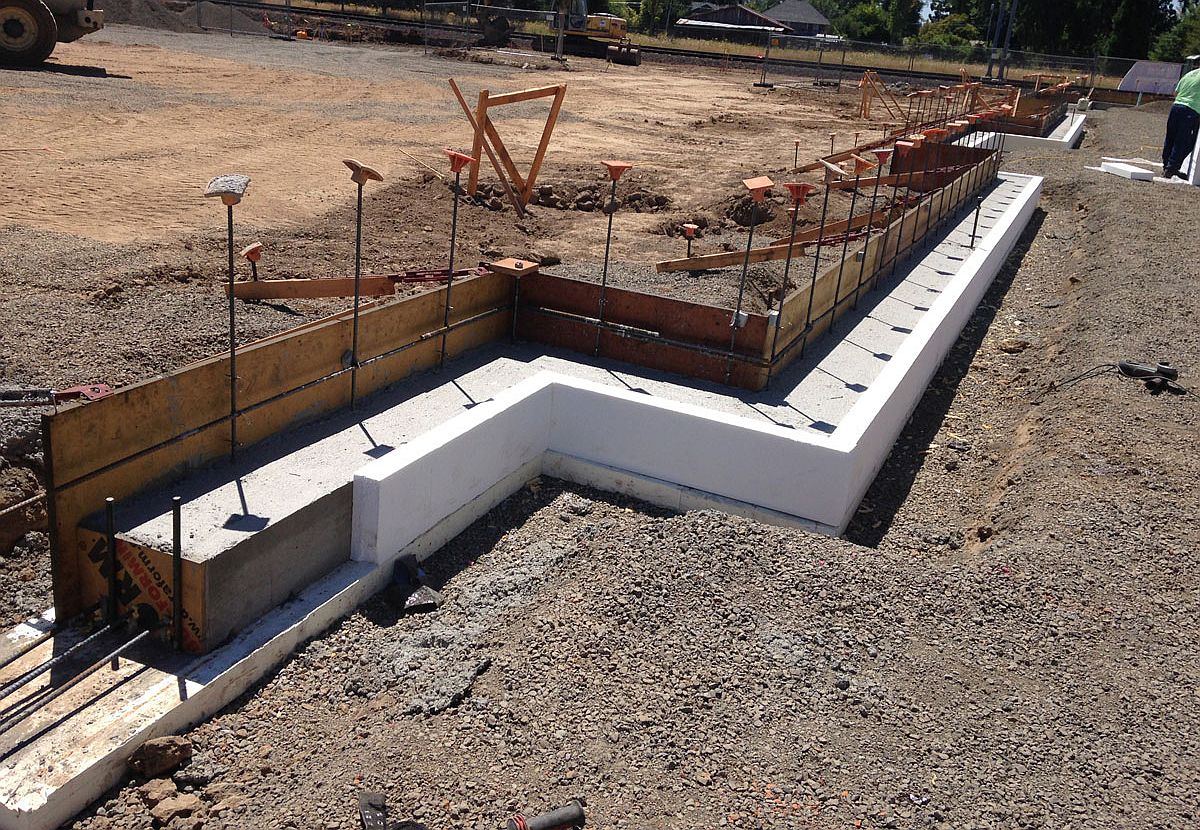
- Further actions depend on the type of foundation. If necessary, do wooden formwork and reinforcement, wells and other work;
- When pouring concrete, remember that the mixture must dry! After all, the concrete foundation is gaining basic strength in the first 20 days;
- After installing the foundation, experts recommend carrying out the final waterproofing and insulation work. Waterproofing will protect the structure from the negative effects of moisture, precipitation, temperature extremes and frost. Special heaters will prevent freezing and cracking of the base. You can also create blind areas around the house that will drain water away from the walls and foundations.
To avoid serious problems and extend the life of your home, contact the experts in wood construction! Masters of the company "MariSrub" will conduct a study of the land plot and select the appropriate type of foundation, calculate and select the necessary building materials, reliably perform the installation and arrangement from A to Z. Next, we will consider in more detail the design and construction features of each type of foundation.

Choosing the right design and size
When building a frame house, different types of strip foundations are possible:
- Shallow. This option assumes the presence of a double reinforced layer. The depth of the base does not exceed 1 m.
- Monolithic belt. Such a foundation is laid on the ground.At the same time, the fertile soil layer is removed, replacing it with a sand embankment.
- Shallow. A pillow is made of non-metallic materials. This type of foundation is slightly higher than the monolithic belt.
Details about the types and their features are described in the video.
Each of the options listed above needs to be protected from heaving. It is created by a drainage system, insulated blind areas, side edges. Protection is also provided by replacing the heaving soil with a layer of sand or crushed stone.
It is not recommended to lay shallow strip foundations in mountainous areas. In such regions, there is a possibility of a shift in the basement. When working on dusty soils, the lower part of the foundation is expanded with a slab.

Interaction of slotted bases with soil
When the air cools during the cold period of the winter season, the process of soil freezing begins. In heaving soils, the following process is characteristic: as the freezing front deepens from the earth's surface into the soil mass, tangential heaving forces appear, applied to the lateral surfaces of the foundations. With a decrease in soil temperature, the values of the specific tangents and, accordingly, the total heaving forces Qf increase almost to 30 tf / m. The freezing of the soil as a whole supports the ice, however, during the spring warming, the ice loses its binding properties. With a decrease in the temperature of the frozen soil, the values of the total forces Qf reach their maximum and then begin to decrease. In the process of changing the tangential loads of heaving, two variants of events are possible:
- If the impact loads from the side of the built house are exceeded over the values of the Qf indicators, the stability of the support will be observed, the heaving deformation will be zero;
- When the Qf values are exceeded over the loads from the side of the building, the foundation loses its stability and begins to move upward along with the frozen soil. In this case, the base of the foundation is detached from the soil base with the formation of a volumetric mini-cavity under it. In the process of spring subsidence of the building, associated with a decrease in heaving forces, soil from the walls of the trench gets into the formed cavity. The foundation support CANNOT return to its original position. The tilt of the entire structure begins, which is growing over the years.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any other construction technology, slotted foundations have their pros and cons. Therefore, the use of this technique can be both justified in one case, and unacceptable in another.
disadvantages
 This technology is not used in industrial construction, because it is not adopted by SNiP
This technology is not used in industrial construction, because it is not adopted by SNiP
Let's start with the cons. It should be noted right away that this method of pouring foundations contradicts building codes - in particular, paragraph 22.13330 SNiP.
As a result, a description of such a technique cannot be found in the official construction literature. The slit foundation was invented long ago, but did not receive official recognition from construction technologists.
The fact is that such a technique cannot guarantee the strength of the base for the house required by building standards. As a result, this method of constructing foundations is the lot of private developers - it is not officially allowed even for the construction of light one-story structures.
Among other disadvantages are the restrictions already listed above for use on clay and non-porous soils. These special conditions for the use of slot technology are the main limitations in its widespread use. The fact is that clayey soils themselves are very water-saturated. Therefore, in the cold season, they are extremely prone to heaving, which leads to deformations and even destruction of the foundation.
Advantages
 In some cases, it is worth abandoning the slotted base in favor of a more reliable tape
In some cases, it is worth abandoning the slotted base in favor of a more reliable tape
But the foundations, erected without the use of formwork, have their own indisputable advantages. First of all, this is a reduction in the cost of construction by eliminating the construction of formwork, which leads to less labor costs and reduces the total construction time.
If the use of slot technology is possible at a given construction site, then this can be an excellent way to optimize financial costs. As practice shows, the rejection of internal formwork also allows you to reduce the labor and time spent on pouring the foundation by almost half.
However, there are several options to avoid the restrictions imposed on the use of this method when building foundation foundations for a house. To minimize its "walking" when the surrounding soil freezes, it is enough to deepen the base of the foundation below the freezing point.
For different regions, the depth of winter freezing of the soil is different - for example, for central Russia it is about 0.8-1.2 m. For the same purpose, an effective drainage system is being built around the foundation of the future house, which allows excess subsurface moisture to be removed.
Slab foundation - what is it
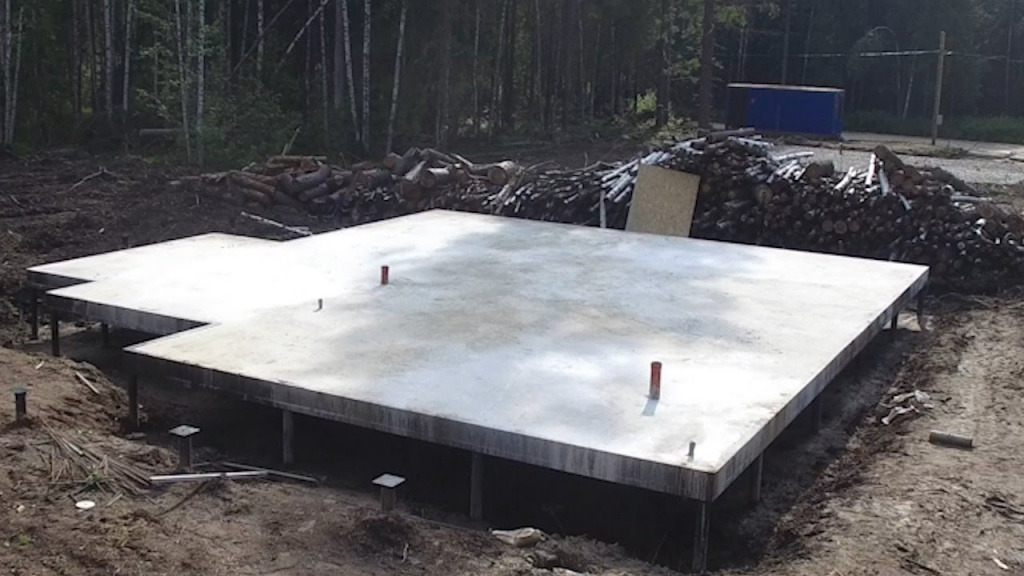
A monolithic slab for a house belongs to floating unburied foundations, there are also shallow foundations. It got its name due to the fact that the reinforced concrete base is poured under the entire area of the house, forming a large slab.
A prerequisite is the presence of a sand and gravel cushion, which redistributes the load from the house to the ground, and serves as a damper in case of frost heaving. Often, such a foundation is the only possible solution. For example, on unstable, loose soils or on clays with a large freezing depth.
The construction of a monolithic slab foundation is simple and reliable, but its production requires a large amount of reinforcement and large volumes of high grade concrete (not lower than B30), because the entire area occupied by the building is reinforced and concreted, and even with a margin - for greater stability. Therefore, such a foundation is considered expensive. In principle, this is so, but it must be considered. In some cases, its cost is lower than that of a deep belt - due to less land work and less concrete.
The depth of the monolithic slab is determined depending on the mass of the house and the type of soil. With shallow depth on heaving soils in winter, the house, together with the base, can rise and fall. With the correct calculation of the reinforcement and the thickness of the slab, this does not affect the integrity of the building. The slab compensates for all changes due to the elastic force. In the spring, after the soil has melted, the house "sits down" in place.
There are four types of slab foundations:
- Classical. A reinforced concrete slab is placed on a sand and gravel cushion with or without insulation. The thickness of the concrete layer is 20-50 cm, depending on the soil and the mass of the building. The thickness of the pillow layers depends on the depth of the fertile layer - it must be completely removed. The resulting excavation can be filled with sand and gravel by 2/3.
- Insulated Swedish plate (USHP) with built-in underfloor heating. Firstly, it differs in that the slab formwork is non-removable - made of L-shaped polystyrene foam blocks. This significantly reduces heating costs - heat loss is minimal. Also, underfloor heating pipes are laid on top of the insulation, reinforcement is laid on them (sometimes under them) and everything is poured with concrete, the thickness of the concrete layer is 10 cm.All communications, including water supply and sewerage, are laid even at the stage of base preparation - in a sand cushion. That is, after the foundation is made, the heating system is ready and the engineering systems are installed. This approach allows you to speed up construction, but the foundation itself is expensive.This type of foundation requires a competent engineering calculation and the same execution: when calculating and laying communications, one cannot be mistaken, since alterations are impossible. Also, questions arise about the repair of systems embedded in the foundation. It is impossible, therefore expensive materials are laid with a long warranty.
- Russian - plate with stiffeners. To strengthen the structure for heavy houses and in difficult operating conditions (strong frost heaving), Russian scientists came up with the idea of making more massive stiffeners. They are usually arranged under load-bearing walls. At the same time, the complexity of the work increases - stiffening ribs are separately arranged, separately - a slab. But the bearing capacity of such a foundation is much higher, which makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the slab - up to 10-15 cm.
Execution options for load-bearing floating structures
If you do not go too deeply into the technical nuances, this is a reinforced concrete slab of various thicknesses, which is installed (poured) on a dense cushion of bulk materials. This type of base is used when:
- Construction of massive large buildings, the supporting structures of which are made of concrete, brick or stone;
- When creating fill foundations of all types, where fillers are not used. It is enough for this to use gravel or crushed stone of a small fraction;
- When erecting buildings on sandy, clayey soils of all types, as well as on soils prone to seasonal movements (swelling) through freezing.
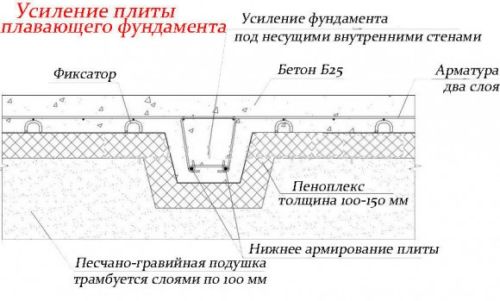 The figure shows a schematic drawing of a slab foundation.
The figure shows a schematic drawing of a slab foundation.
For the construction of such supporting structures, it is necessary to use wooden formwork. A classic vibrator is well suited for compacting the pillow material, which improves the quality of the concrete. The thickness of a concrete slab rarely exceeds 40 cm and this is the key advantage of this type of base, since no need to use a large amount of ready-mixed concrete. It is also worth remembering that the dimensions of the slab must meet the strictly specified design parameters of the building, while they can be slightly larger, but not less.
Pros and cons of a slotted foundation, interaction with soil
The advantages and disadvantages of a slotted foundation are almost the same as those of a strip foundation. This is due to the identity of the designs.
The most common pros and cons of slotted support structures are shown in the table below.
| № | Dignity | disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | reducing the volume of work on digging trenches and installing shields | can only be erected on clay, dense soils |
| 2 | improved adhesion of concrete to soil mass | cannot be used on an area with heaving soil, due to the adhesion of the walls of the base to it |
| 3 | simple construction technology | the weight of the erected buildings is limited |
| 4 | the construction of the structure does not have a destructive effect on nearby buildings and utilities | the strength of the concrete can be reduced if it is poured into dry soil |
Due to the better adhesion of the monolithic reinforced concrete tape to the ground, when it heaves, the following consequences are possible:
- if the load from the structure is equal (or greater than it) to the force of frost expulsion, the structure does not deform;
- if the heaving forces are greater, then the base is pushed out of the ground and destroyed along with the erected building.
When building a rigid slit foundation on soils subject to strong heaving, the structure may not crack, only over time will it tilt to one side.
Foundation tape scheme
Features of slotted tape bases
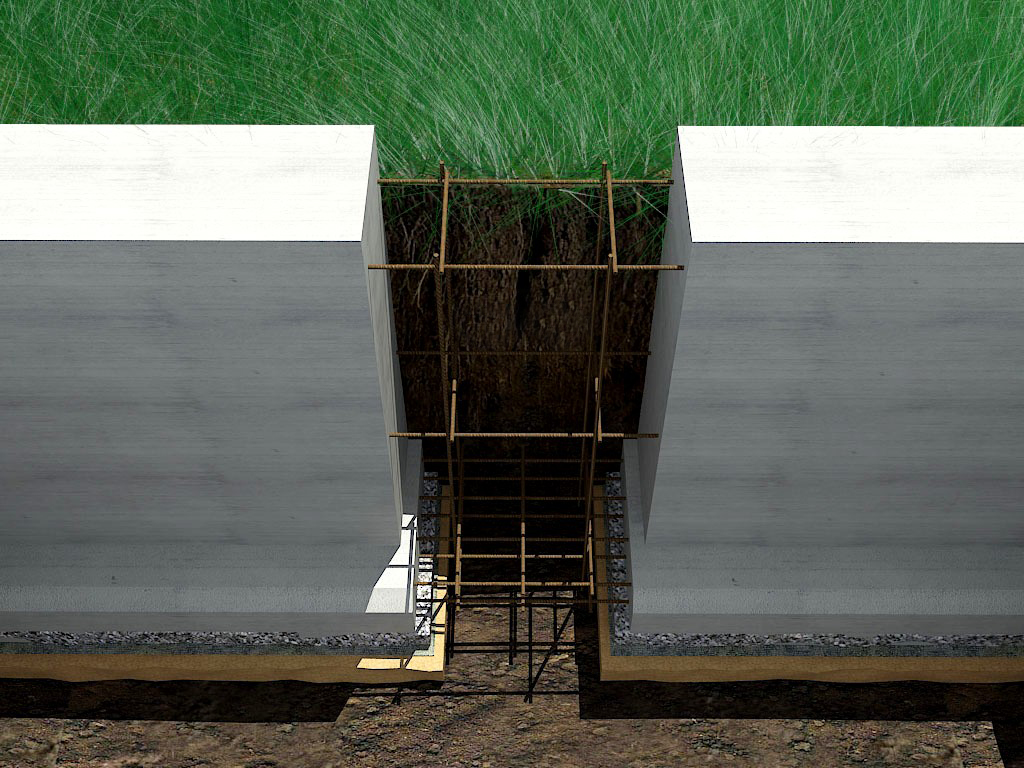
Structurally, slotted foundations are comparable to monolithic strip bases, only a trench is used instead of formwork. Externally, the trench is somewhat similar to a crack in the ground, hence the name "slotted" foundation. The uneven sides of the earthen trench provide strong adhesion of the soil and the poured concrete mixture.
The formation of the lower part of the slotted support occurs by means of soil, which acts as a formwork for the base of the foundation. Thus, the loads on the soil from the side of the structure are transmitted by all surfaces of the foundation - the support plane and side walls, that is, the foundation transmits the full range of loads in the vertical and horizontal directions.
The laying of slotted bases is carried out in clay soils. By pouring a concrete mixture into the trench, a rigid spatial structure is created, which ensures the stability of the structure against weight loads and pushing forces of frost heaving. The manufacture of slotted foundations for houses built on sandy soils is not recommended. The sand does not keep the geometric shape of the walls, as a result, the crumbling soil sharply deteriorates the quality of the concrete mixture to be poured and does not contribute to the creation of a workable foundation monolith.
The advantages of slotted foundations include:
- A significant reduction in the labor intensity of construction work. Statistics claim that the transition to laying a slotted foundation reduces the volume of excavation work carried out by almost half, the volume of work with formwork - up to 60-70%;
- Reducing the cost of concrete - up to 6% and for reinforcement - up to 20%;
- Possibility of using trenching technologies in confined spaces with the prohibition of dynamic impacts on the ground, for example, near communications or near constructed buildings.

The main disadvantage of slit-type bases is the limitation of its applicability:
- It is allowed to pour only in clayey soils to ensure the preservation of the shape of the trench when pouring the concrete mixture and its compaction;
- Use only on non-heaving soils, since frost heaving of high intensity can bulge and warp the erected house, due to the lateral adhesion of the foundation to the ground;
- Massive buildings are not erected on slot supports.
Construction stages
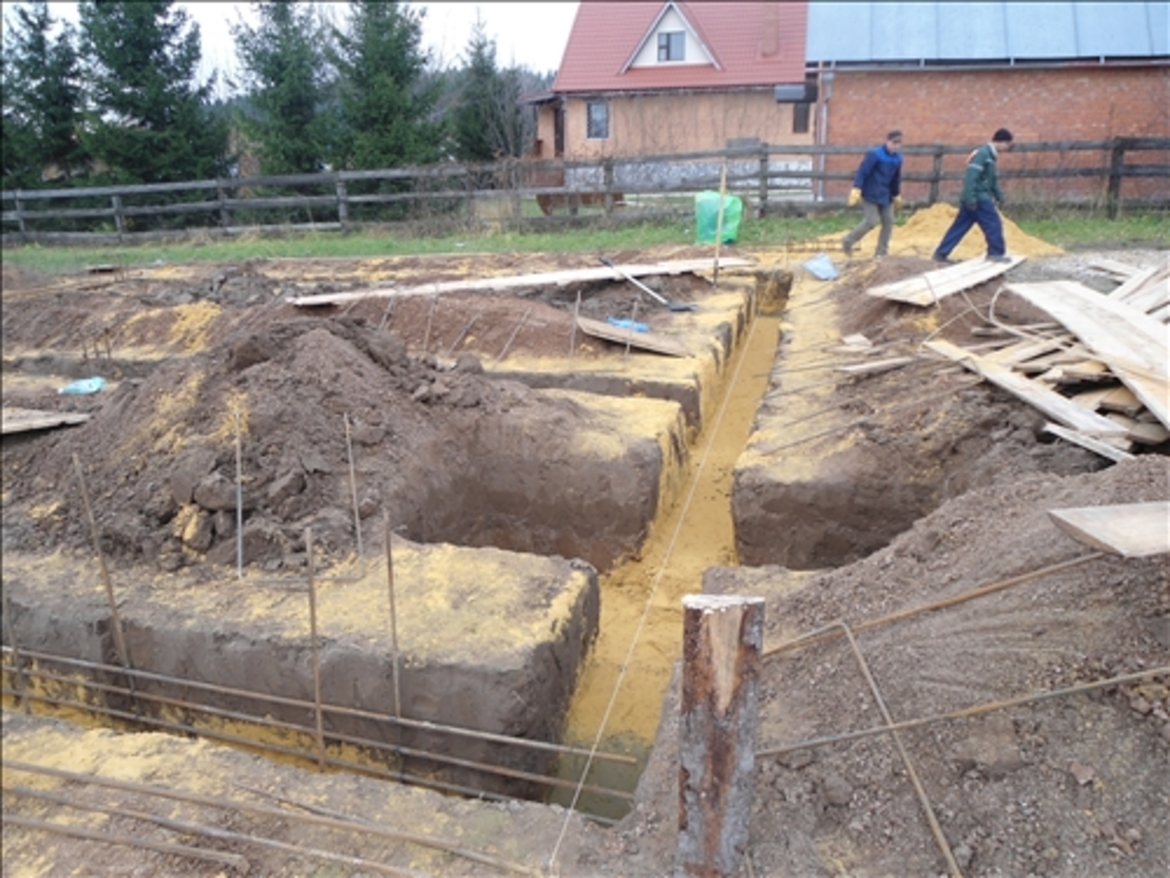
In the manufacture of slotted bases, the following stages of work are performed:
- Excavation works for digging a trench in accordance with the project;
- Installation of the formwork of the aboveground part to the required level - the future basement of the house;
- Reinforcement according to the project;
- Pouring concrete mix;
Excavation
Digging a trench.
Trenching begins with removing the top fertile layer and using it (if necessary) to level the site.
The trench is dug the same width as the width of the foundation. The depth of the trench is defined in the project. The side faces of the trench must be flat and not collapse during all preparatory work. If it rains, then the resulting puddles are sure to be drained. And the "floated" soil is cut to a dry layer.
Expansion of the lower part of the trench for the support sole of the strip monolith is allowed. The device of a sand cushion is not necessary for deep monolithic foundations, and sometimes it can be harmful. If a sand cushion is laid, vibration compaction is necessary.
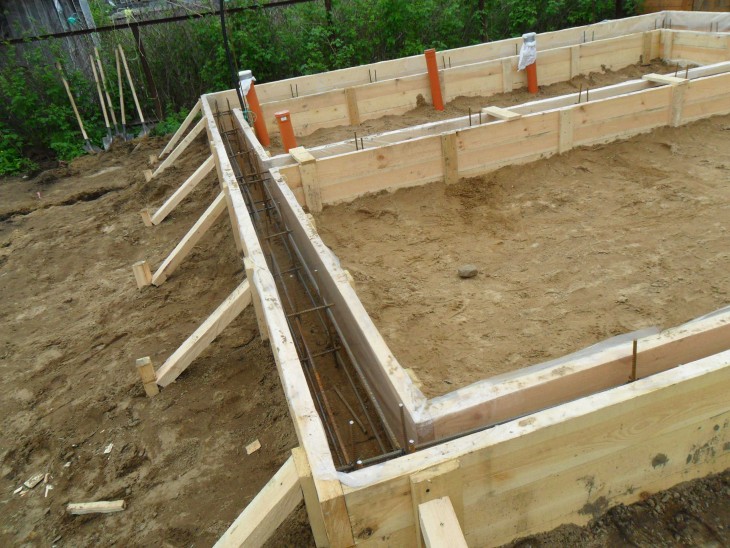
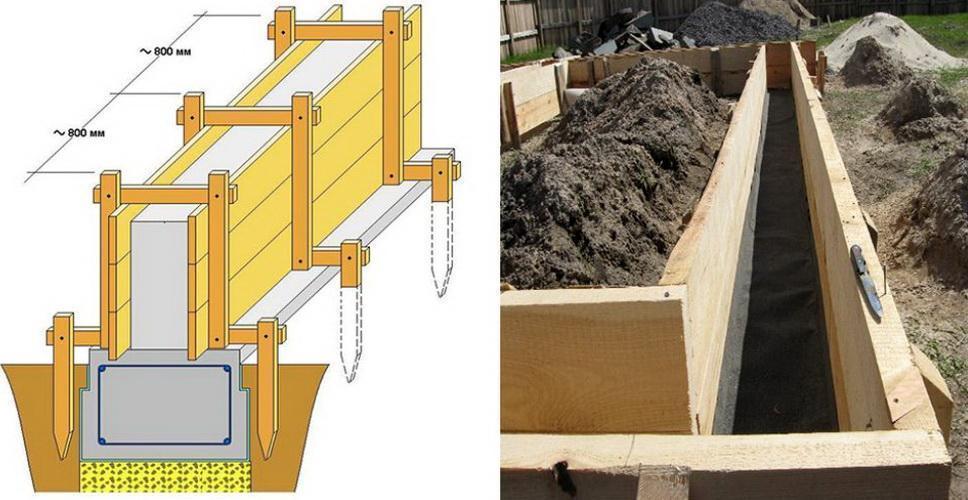
Arrangement of the formwork of the aboveground part
We expose the formwork and strengthen it with lateral supports.
To prepare the basement of the house, formwork is placed along the height of the basement part from the level of the ground surface. It is allowed to manufacture a basement as an independent structure of brickwork or block type.
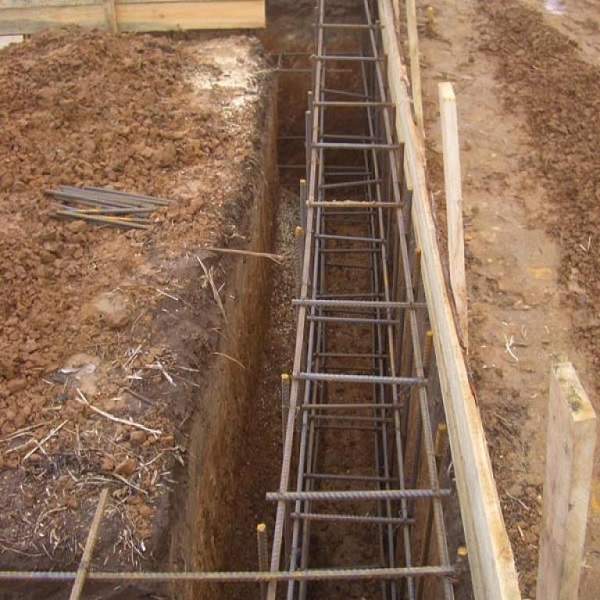
Reinforcement
We lay the reinforcement cage in the trench.
Reinforcement is made by viscous reinforcement
Particular attention is paid to the corners. For more details, see the materials: reinforcement of the corners of the strip foundation, how to choose the diameter of the reinforcement for the strip foundation
We reinforce the formwork with additional transverse bridges from above.
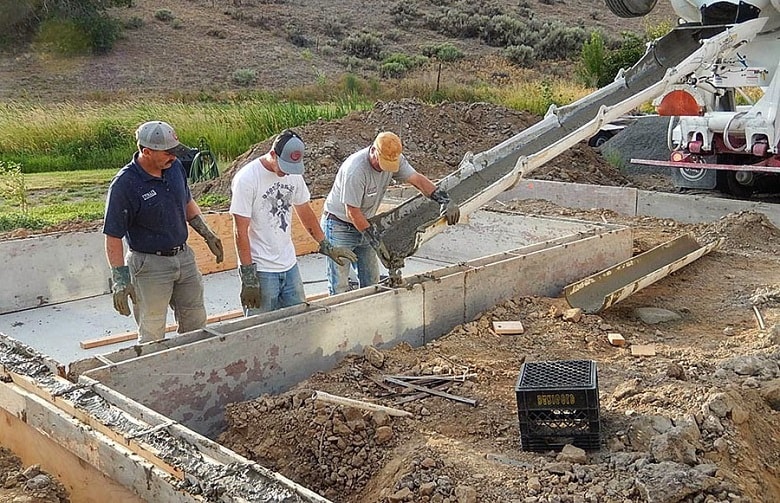
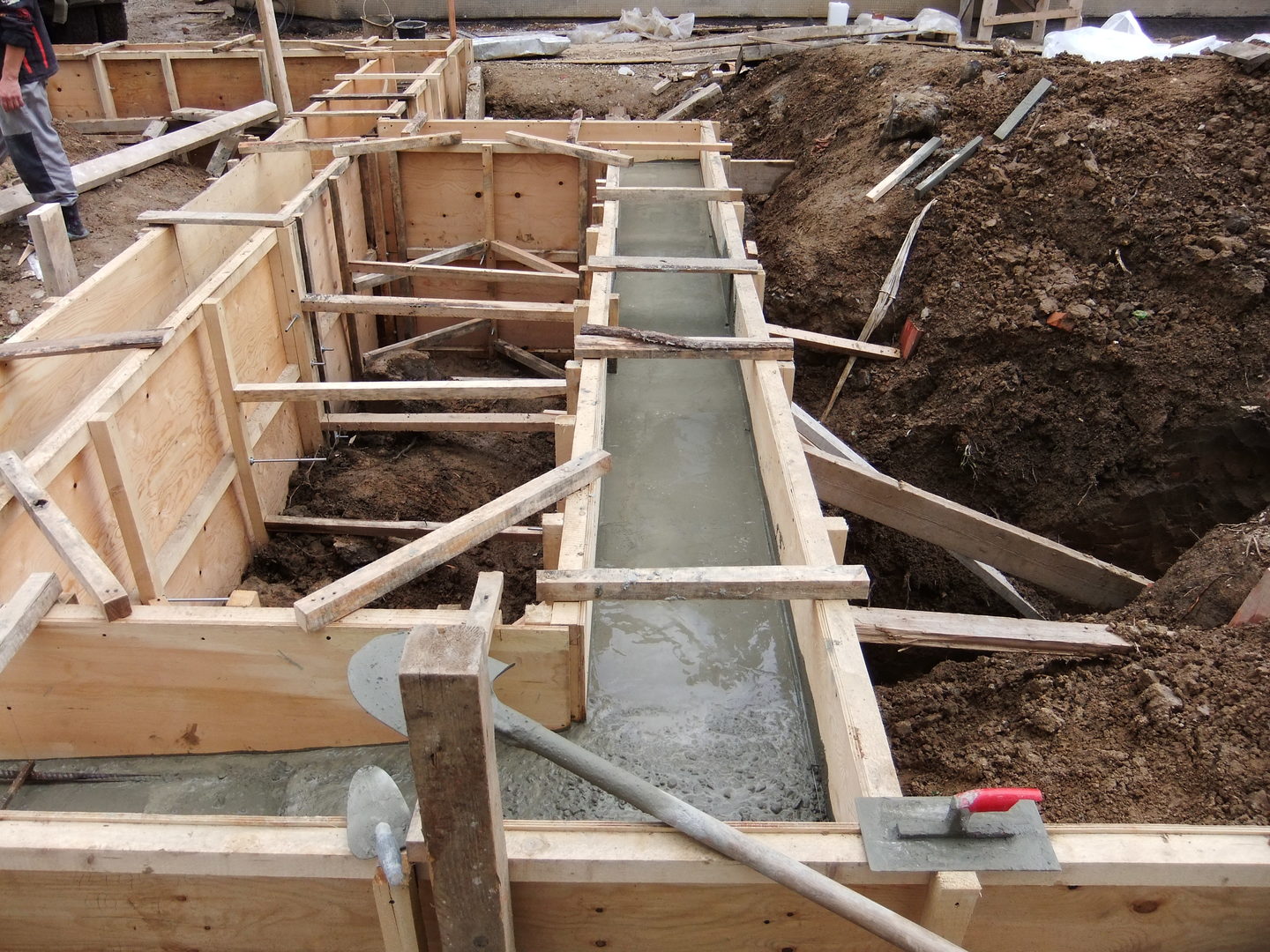
Pouring concrete mix
Pour concrete.
When preparing a concrete mixture, it is customary to prepare it by at least 10% more than the estimated need, complete filling with a solution of all irregularities in the soil.
The prepared concrete mixture is poured into the prepared trench. The best option is considered to be pouring immediately after preparing the trench, until the drying clay edges begin to crumble. To strengthen the concrete base, a compaction process is carried out, as a result, crushed stone / gravel lies as tightly as possible with the removal of excess water and air. Sealing options are bayonet or vibration seal.
We remove the formwork and remove the fertile soil layer inside the foundation.