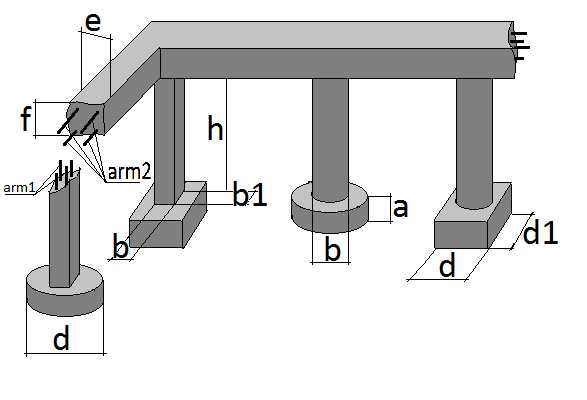
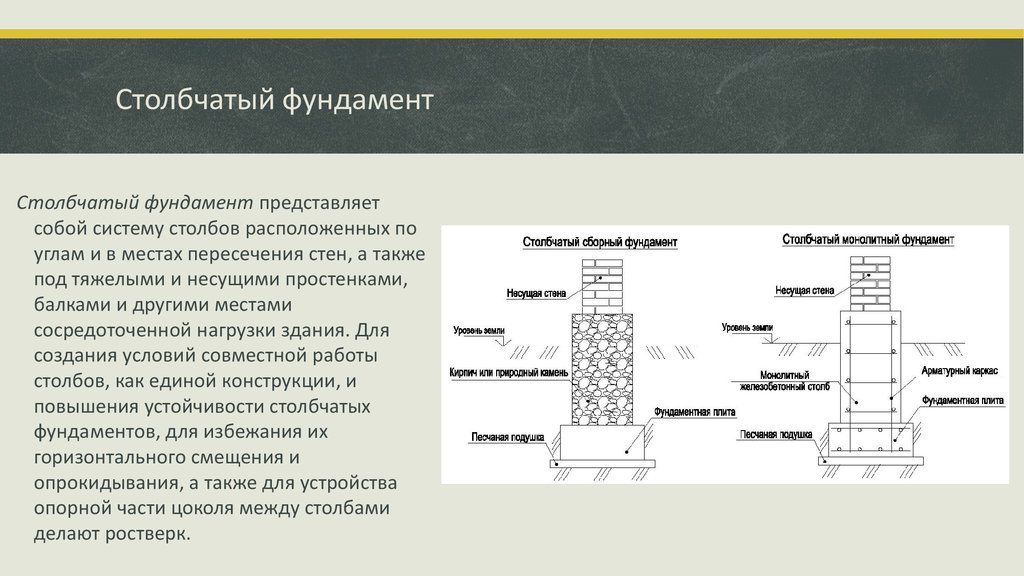
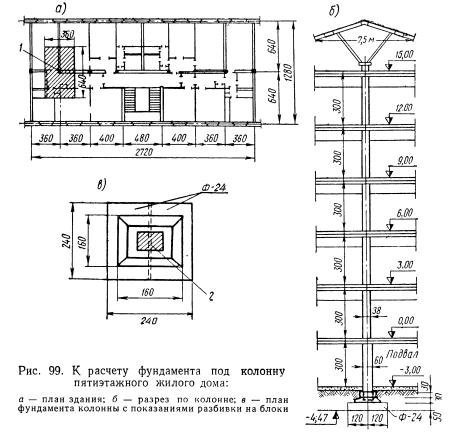
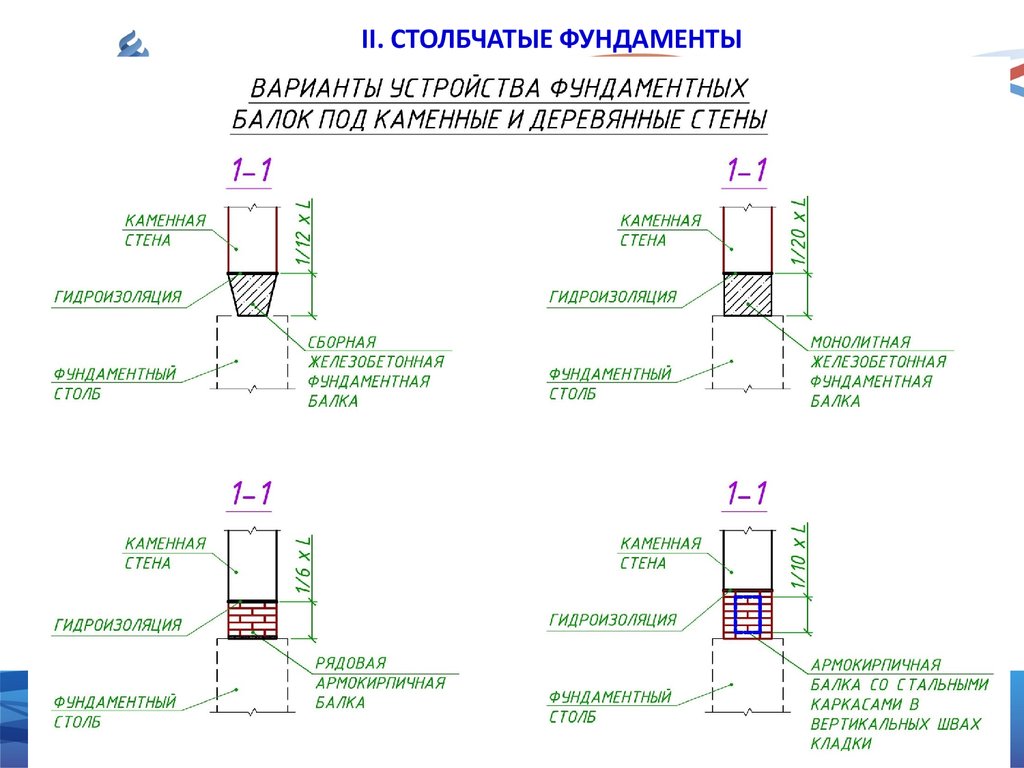
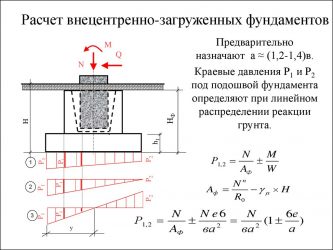
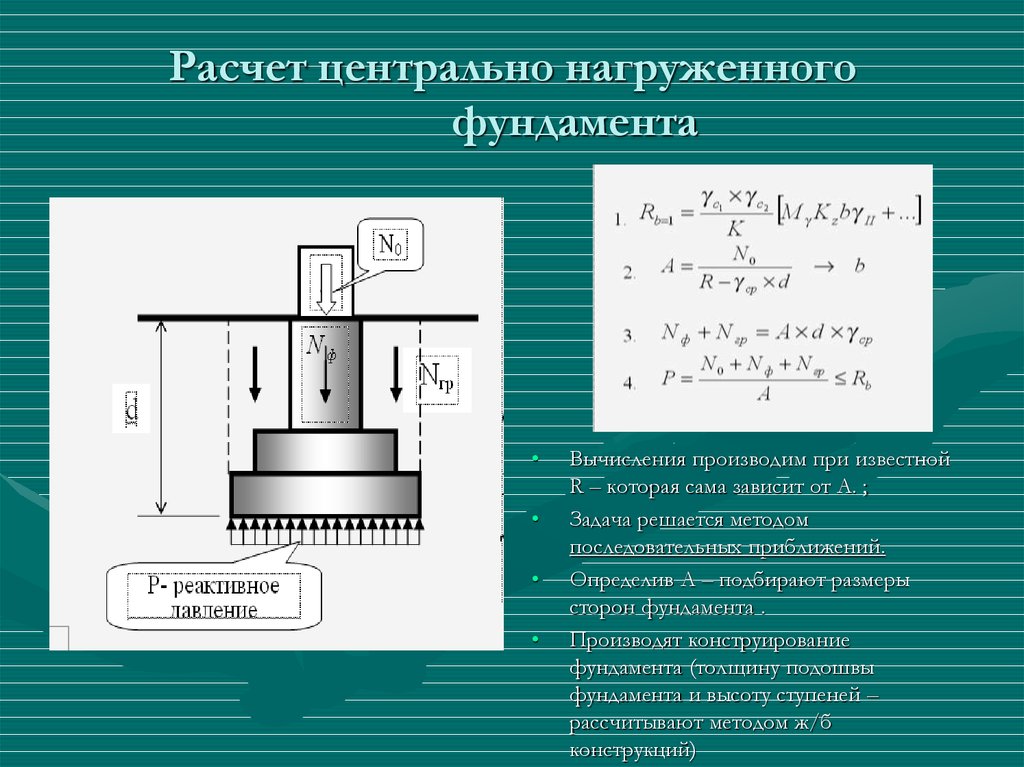
Advantages and disadvantages of a columnar foundation
Self-calculated and self-equipped columnar foundations for frame houses and buildings without basements, which do not exert strong pressure on the ground, are simple to perform and relatively cheap.
Column foundation - easy to install and affordable materials
According to reviews, columnar foundations have a fairly impressive list of advantages:
- They can be designed, calculated and built independently, without the involvement of special equipment and specialists.
- They can be installed on almost any soil (excluding those where heaving processes are possible or there are high ground waters).
- They can be located in areas with noticeable differences in height (and even on the slopes of hills).
- They do not require preparatory work to level the landscape.
- They can be erected in the shortest possible time (the maximum time for building a columnar foundation from scratch is 2 weeks).
- They do not need complicated and expensive waterproofing.
- The strength and durability of the structure (a columnar foundation erected with careful observance of the technology of work can last more than half a century).
- Relatively low total cost.
Reinforcement of the columnar foundation is carried out using steel bars
At the same time, there are only two disadvantages of columnar foundations:
- Not suitable for heavy brick and multi-storey buildings.
- Eliminated the creation of basements.
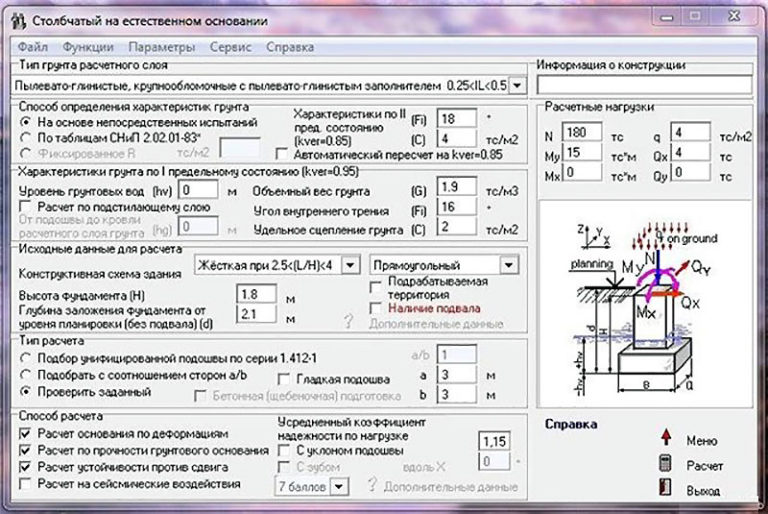
Initial data for the calculation
In order to correctly calculate the number of supports of a columnar foundation, you must have information. These initial data for the calculation include:
- a report on engineering and geological surveys, including the structure of cross-sections of the soil and data on the occurrence of groundwater;
- bearing capacity of the soil;
- the depth of freezing and the amount of snow cover in a given area, taken from SP 131.13330.2012 "Construction climatology";
- data on the specific gravity of building structures from which the building will be constructed, taken from SP 20.13330.2016 "Loads and Impacts".
If you decide not to attract specialists to carry out exploration work, and you do not have information about the geology of the site, then you will need to study the soil yourself.
To do this, on the building site, it is necessary to dig 2-3 pits to a depth of at least 0.5 meters below the support cushion of the foundation. If at the same time a moisture-containing layer is found, then it is impossible to use a columnar foundation for construction. You will have to choose a more expensive base.
 Determining the type of soil with your own hands.
Determining the type of soil with your own hands.
Assessment of the bearing capacity of the soil
The natural composition of the soil determines its bearing capacity and therefore, after studying the geological data, it is necessary to choose from table. 1-5 on page 6 SNiP 2.02.01-83 "Foundations of buildings and structures" data on the design soil resistance corresponding to the real situation. It should be borne in mind that the given numerical values refer to a depth of over 1.5 meters. Lifting up for every 500 mm increases this value by 1.4 times.
 Soil resistance table (R).
Soil resistance table (R).
Determination of weight loads on a foundation foundation
The weight of building structures, snow cover in winter, engineering equipment and household appliances is the most important determining factor for calculating the foundation. You can try to calculate each individual structure according to the specific gravity of its constituent elements, but this is a very large and complex task. In the reference literature, the average summarized data are already given, which can be taken as a basis. Here is some of them:
- timber wall with a thickness of 150 mm - 120 kg / m 2;
- log walls 240 mm - 135 kg / m 2;
- frame walls with insulation 150 mm thick - 50 kg / m 2;
- foam concrete blocks D600 300 mm - 180 kg / m 2;
- interfloor overlap on wooden beams with insulation - 100 kg / m 2;
- the same attic floor, taking into account the insulation - 150 kg / m 2;
- hollow concrete slabs - 350 kg / m 2;
- operating load of floors - 200 kg / m 2;
- metal roofing - 30 kg / m 2;
- roof with slate - 50 kg / m 2;
- roof with ceramic tiles - 80 kg / m 2;
- snow load for central Russia - 100 kg / m 2;
- for the southern regions - kg / m 2.
When carrying out calculations, you should also take into account the mass of the foundation itself. To do this, determine its volume and multiply by the average specific weight of reinforced concrete - 2500 kg / m2. The angle of the pitched roof can decrease or increase the value specified here as it changes.
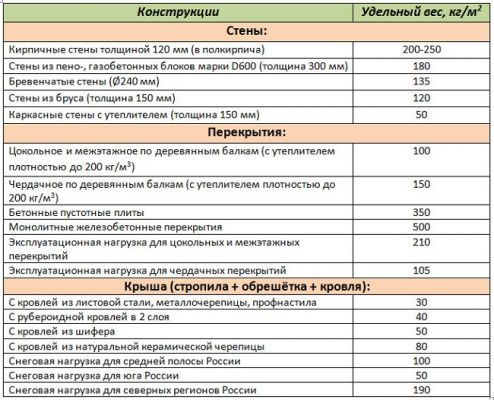 Weight of building structures.
Weight of building structures.
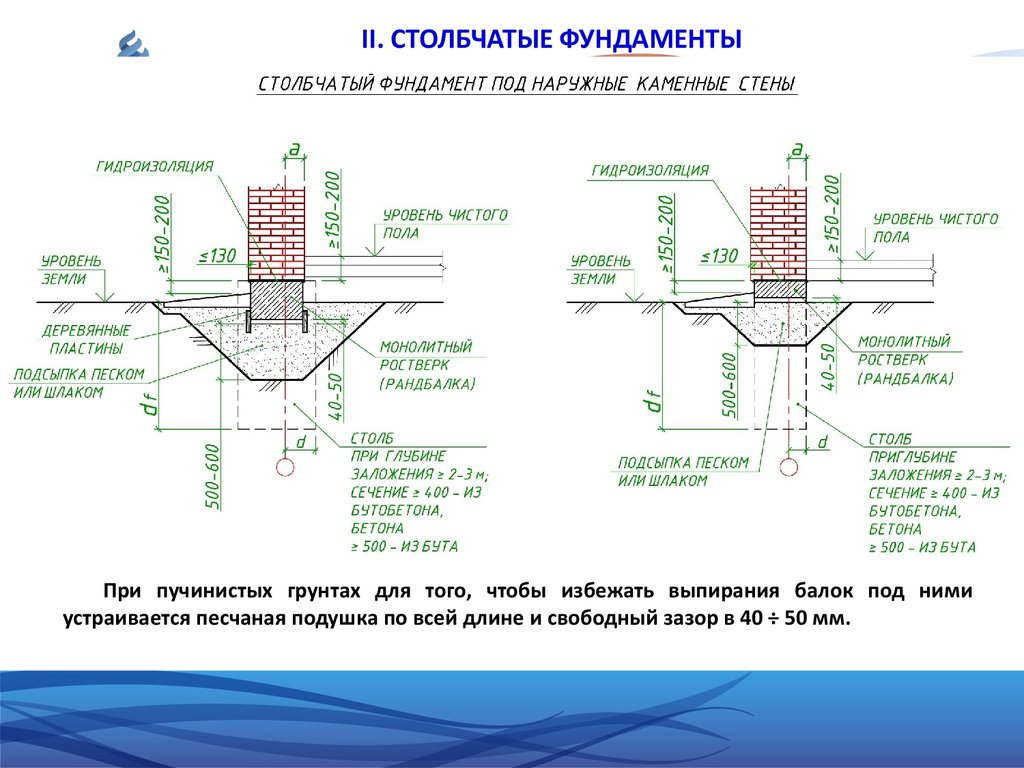
Requirements for the use of columnar bases
The low cost of the structure supported by vertical posts makes it very attractive for private developers. However, this type of foundations has a number of application restrictions.
Unfavorable conditions for the use of columnar bases include:
- the probability of horizontal soil mobility and lateral external loads;
- soil prone to subsidence or heaving;
- a high level of groundwater, which should not approach the bottom closer than 500 mm;
- the depth of soil freezing is more than 1.5 m;
- elevation differences on the building site are more than 2 meters;
The reduced bearing capacity allows it to be used only for frame houses, the construction of light residential buildings from panel and wooden materials, as well as small baths, verandas, outbuildings, utility structures and for a frame garage.
For premises such as verandas, outbuildings and outbuildings, it is recommended to make your own foundation. The weight of their structures is much less than the residential building itself. Therefore, a simpler and cheaper design can be used. In addition, such a separation can significantly reduce the total area of the home and will lead to different calculated results.
An example of calculating the number of pillars
The task is to calculate the foundation for a small frame house in the middle climatic zone of Russia measuring 5 x 6 meters with a floor height of 3.0 meters and a metal roof. An example of calculating a columnar foundation includes several points.
- we take the foundation on round reinforced concrete pillars as a support;
- the main soil on the building site is loam (Ro - 3.5 kg / cm 2);
- freezing depth 1.1 meters;
- no groundwater was found when drilling the control hole.
Determination of weight load:
- the total area of external walls and partitions is 76 m 2 and then their total weight will be 76 x 50 = 3800 kg;
- the mass of the basement floor with an area of 30 m 2 is 30 x 100 = 6000 kg, and the weight of the attic floor is 9000 kg;
- the roof area is 52 m 2, which means that such a roof weighs 30 x 52 = 1560 kg;
- the snow load will be 20% of the standard at a slope of 46˚, which will be 100 x 52 x 0.2 = 1040 kg;
- the operating load on one floor is 30 x 210 = 6300 kg;
- to estimate the mass of the foundation, we take the number of pillars from the previously drawn up diagram and take their diameter equal to 400 mm, then the mass of 10 pillars with a height of 1.5 meters will be 540 kg;
- the weight of the grillage is the mass of reinforced concrete beams with a section of 400x400 m, which will be equal to 980 kg.
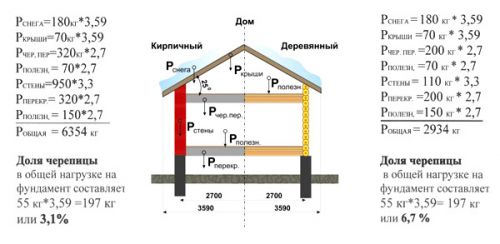 Conditional weight of a wooden and brick house.
Conditional weight of a wooden and brick house.
Summing up the obtained data, we get the total weight of the house equal to 29110 kg. To determine the total cross-sectional area of the pillars, we divide 29110 / 3.5 = 8317 cm 2.
Then the cross-sectional area of each of the 10 pillars will be equal to 832 mm 2, which corresponds to a diameter of 326 mm. We take the diameter equal to 400 mm and determine that the minimum number of pillars required for this building is 9 pieces.
However, taking into account the need for a strength margin of 40%, 13 pillars with a diameter of 400 mm should be accepted for installation.
Do-it-yourself column foundation: step-by-step instructions
Having determined the depth and distance between the posts, proceed to earthworks. Each pit must be 2 times the size of the base plate. The depth is equal to the deepening of the base.

Marking and digging holes for a columnar foundation
Once you have dug a hole, compact the bottom with a hand, electric, or gasoline rammer.

Gasoline rammer
Add sand (layer thickness 7 cm) and compact with a rammer.

Sand pillow
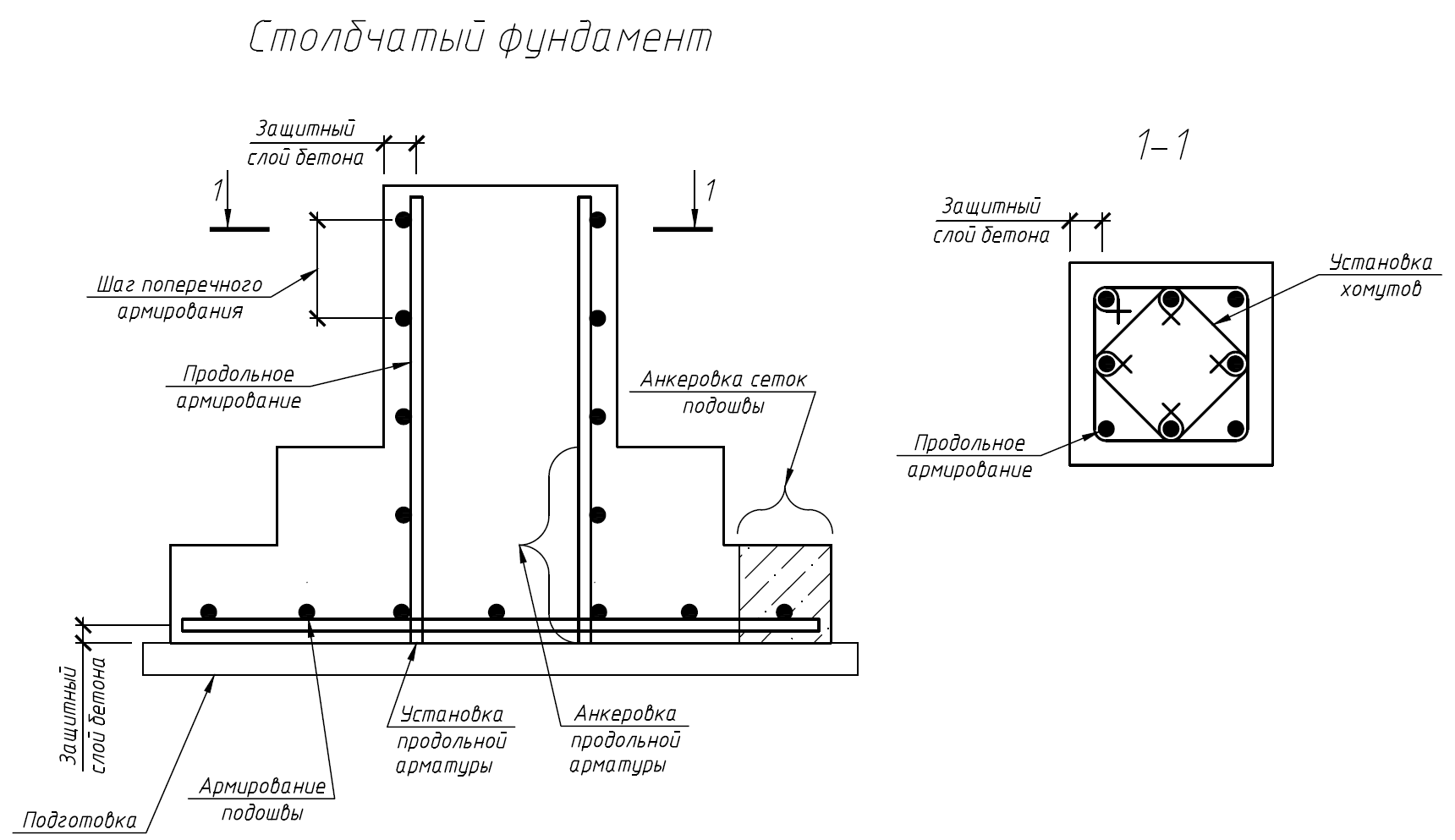
Scatter three layers of crushed stone one by one. Bottom fraction 40-50 mm, then 25-35 mm and the top 5-15 mm. Pack each layer separately. Lay the reinforcement mesh and tie the vertical reinforcement to it, which will be located inside the post. The height of the reinforcement must be sufficient to tie the grillage reinforcement to it.

Reinforcement of the pillar and grillage
Fill with concrete grade not lower than M300.
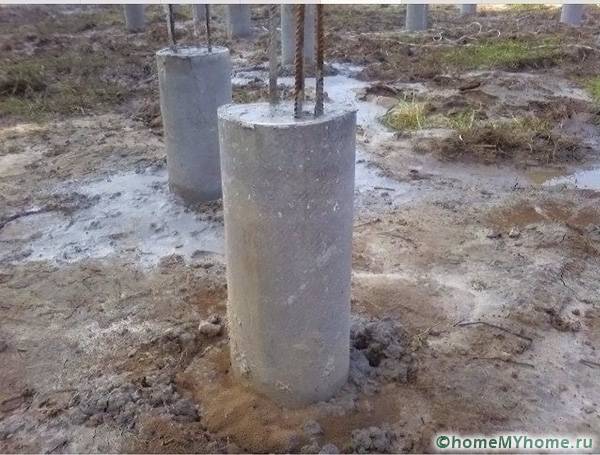

Pouring asbestos pipes with concrete
After 3 days, put an asbestos pipe with an inner diameter of more than 15 cm on the fittings. Be sure to check the pipes using a level. It is necessary not only to set each one vertically, but also to ensure the same height, otherwise it will be very difficult to make a grillage. Fill the pipes with concrete and backfill with earth from the outside. Cover the ends of the pipes with roofing material or coat with bitumen for waterproofing.
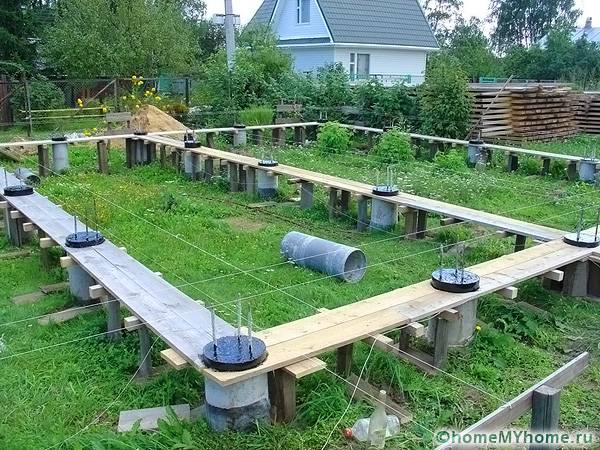

Poles waterproofing
After 10 days, install the formwork and fill the grillage.

Filling the grillage
We calculate the number of supports
The number of supports directly depends on what area of its base will be. Let us give an example of how to calculate the number of pillars in the case of arranging bored piles with a diametrical section of 300 mm, followed by arranging a shoe with dimensions of 50 cm. We use the formula for calculating the area of a circle S = 3.14 * r2. Substituting all the values, we get an area equal to 1960 cm2. For more information on calculating base pillars, see this video:
We take the assumed load equal to 100 t (F), soil resistance - 4 (R). Using the formula R = F / (S * n) and putting all the known values, we get an equation, solving which, we get the value n (the number of piles). In this example, we get 13 supports.
 Add the weight of the support itself to the load at home
Add the weight of the support itself to the load at home
Do not forget that the supports themselves also have a certain weight, therefore we also take them into account in the total load. For this, we make additional calculations. For example, if the length of the post is 2 m, then the volume of the support is calculated by multiplying the area of the base by the length of the post. As a result, we get a value of 0.14 m3. We multiply this number by the volumetric weight of reinforced concrete 2400 kg / m3 and determine the weight of one support, approximately 340 kg. And the weight of 13 such supports is bet equal to about 4.5 tons.
Adding the weight of the supports to the total load and making repeated, more accurate calculations, we find that it is necessary to lay 14 supports.
In principle, the calculations presented are not so difficult, and it is quite possible to perform them yourself. To facilitate the calculation of the pile foundation, you can use the online calculator. In this case, you simply enter the initial data, and then use the results obtained.
Pile or column foundation load calculator
A pile foundation can help out in those circumstances when no other type of foundation for a building under construction is possible or becomes extremely difficult and unprofitable. Piles buried below the freezing level of the soil and reaching its dense layers are capable of withstanding a very serious load. Of course, this requires correct calculations of their bearing capacity and, based on this and the total load, the number and layout.

Calculator for calculating the load on a pile or column foundation
This, by the way, also applies to the columnar foundation - the possibilities of the supports are not unlimited, and it is extremely important to correctly distribute the load on them. This means that it is necessary to somehow assess what kind of weight and operational load the building planned for construction will have on a similar foundation.
A calculator for calculating the load on a pile or column foundation will help to do this quickly and with a sufficient degree of accuracy.
The necessary explanations on the procedure for making calculations will be given below.
Explanations for making calculations
Of course, the proposed algorithm does not pretend to be professional accuracy, but when planning small houses and outbuildings on a suburban area, it may well help to assess the emerging picture.
The load falling on the pile foundation primarily includes the mass of the structure itself, which is planned for construction.
The calculator provides for the entry of the area of the walls and the indication of the material of their manufacture. If desired, in order to obtain a more correct result, you can exclude window and door openings from the area. The calculation of the areas of the walls must be carried out separately, I agree with the existing plan, or at least the outlines for future construction. A special portal publication will help you calculate the area correctly.
Screw pile prices
External walls and internal capital partitions may differ in both thickness and material of manufacture. Therefore, the user is given the opportunity to add two wall options. If there is no such need, then simply leave the value "0" in the area input field.
This is followed by the entry fields for floor parameters, where there are also two possible options, for example, for the floor of the first floor and for the attic floor. The calculation program has already made the necessary corrections for the operational loads on the floors - the weight of furniture and other furnishings, the dynamic effect of people in the house, etc.
The next data entry block is the roof parameters. When choosing the type of roof, the average weight of the rafter system will be taken into account immediately. In addition, in winter, a considerable load is exerted on the roof from the snow that has fallen. To take this factor into account, it is necessary to indicate the zone of your region according to the level of snow load (according to the proposed map-scheme), and the steepness of the roof slopes.

Schematic map for determining your zone by the average level of snow load on the roof
Piles or pillars are connected by a strapping bar or grillage. If a wooden trim is used, then it will not be a big mistake to simply include it in the wall area.
But in the case when a grillage is made of metal or even a reinforced concrete tape, it makes sense to take it into account additionally. When you select this calculation path, additional data entry fields will open - the length of the grillage and the material of its manufacture
The final result will be given in kilograms and tons. Having received this value and knowing the bearing potential of the support, it will not be difficult to determine the number of piles or pillars.
This parameter depends on the characteristics of the soil at the assumed depth of the screw part of the support and on the dimensional parameters of the pile itself. To calculate the bearing capacity of a screw pile, a special calculator will help, to which the indicated link leads.
Soil type
 While studying the soil, drill a hole below the freezing depth
While studying the soil, drill a hole below the freezing depth
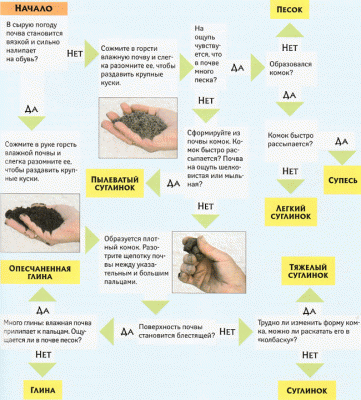
Columnar foundation and its calculation are determined by geological conditions. When performing private construction work, determination of the type of soil in laboratory conditions is not made. Most often this is determined by the means at hand.
To do this, it is necessary to prepare a hole, which will be equipped to a depth below the level of soil freezing. These indicators differ for each region. This value can be found in the reference materials. For example, if the level of soil freezing is about 1 m, then the hole is equipped with a depth of 1.3 m. Then we take soil samples and roll it into a small ball.
 Clay soils easily clump and stain your hand
Clay soils easily clump and stain your hand
Further, according to this sample, we draw conclusions:
- If the ball cannot be formed, then the sandy type of soil prevails on the site. By the fraction of grains, we determine the soil resistance: for small - 2, for medium - 3, for large - 4.5.
- If the ball has formed, and crumbles at the slightest pressure, then the type of soil is sandy loam. Its resistance is 3.
- If, when pressed, the ball turns into a cake, and no cracks form at the edges, then we have a clay soil. In this case, the degree of resistance varies from 3 to 6.
- When the ball is crushed into a cake, cracks form at the edges, then the type of soil is loam. Resistance indicators 2 - 4.
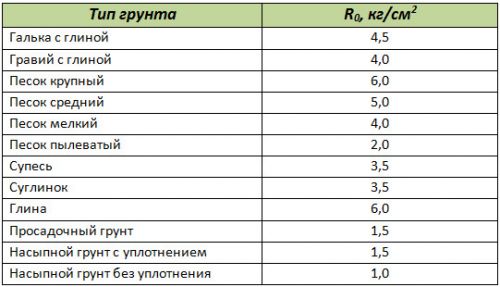
It should be remembered that the value of soil resistance depends on its moisture level and porosity. The data presented in the table will help to correctly determine this value:
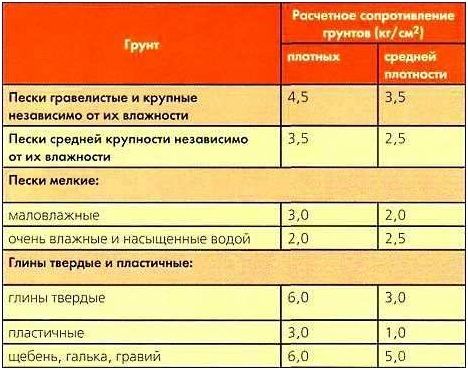
If it is planned to equip a shallow foundation, then the resistance should be calculated according to the following formula: R = 0.005xR0 (100 + h / 3), where R is a tabular value, h is the planned depth of laying the supports in centimeters.
Collection of loads and calculation by the formula
A complete calculation of any foundation is carried out only by specialists. In private construction, it is enough to provide estimated calculations that allow you to determine the required dimensions and number of pillars, as well as the need for materials.
The development of the foundation project should be based on the results of geological surveys to determine the structure of the soil and its condition. Before construction, exploration wells must be drilled to a depth of 60-70 cm, exceeding the expected depth of the pillars. The structure of the soil, the level of groundwater and the presence of quicksands are determined.
The next step is to determine the real and maximum loads on the foundation during the operation of the structure. The total weight of all elements is taken into account - walls, floor and ceiling, roof, etc., as well as full operational load - furniture, equipment, people.
In addition, the snow load must be taken into account. With a roof slope of more than 60 degrees, it tends to zero, but with smaller slopes it can reach significant values. For example, for the European part of the Russian Federation, the load reaches 100 kg / m². Finally, we must not forget about the weight of the grillage and the posts themselves.

After obtaining the necessary data, you can calculate the required total support area (S) by the formula - S = K × P / R, where:
- K - safety factor taken equal to 1.3-1.4;
- P is the total load from the weight of the structure, kg;
- R - soil resistance, kg / sq. Cm.
The R value depends on the type of soil:
- for sandstone it is 4-6 kg / cm² (for dusty sand - 2 kg / cm²);
- for loam and sandy loam - an average of 3.5 kg / cm 2;
- for clay soil - 6 kg / cm².
Filled soil with compaction has an R of about 1.5 kg / cm 2. These indicators correspond to the depth of the layers of 1.2-1.5 m. At the surface soil, the resistance decreases by an average of 1.4-1.5 times.
An example is the following calculation option:
- Initial data: frame house with dimensions 5x6 m, wall height 2.7 m; soil - loam with a resistance of 3.5 kg / cm 2, freezing depth - 1.3 m.
- Weight calculation. The panel walls have a total area of 72 m², i.e. weight 3600 kg. Ceilings (floor and ceiling) - area 60 sq. M, weight 6000 kg. The roof is planned from slate and has an area of about 46 m², which corresponds to a mass of 2300 kg. We do not take into account the snow load, because the slope of the slopes exceeds 60 degrees. The operational load is assumed to be 12600 kg. To calculate the weight of the foundation, it takes an approximate number of pillars installed with a step of 2 m - 11 pieces. Deepening and elevation above the ground gives the total height of the pillar 2 m. The weight of one pillar will be 600 kg, and the total foundation is 6600 kg. Finally, the total load will be 31,100 kg.
- Determination of the total area of the support by the formula. As a result, S will be 11550 cm².
- Clarification of the area of one pillar. If we proceed from the planned number of supports, then it will be 11550: 11, i.e. 1050 cm².
Calculations give the minimum acceptable values. Naturally, to increase the strength, you can increase the number of pillars and their area. If you want to make an extension to the house, the supports for it are calculated separately.

Calculation of the area of the base of the foundation
An important place in the design of the base for future construction is occupied by the calculation of the area of the base of the foundation. This stage of work is carried out according to the formula shown in the figure below.
The value obtained as a result of the calculations is the approximate total area of the base of the foundation, necessary in order not to literally push the soil under load. If we are talking about the construction of the most expensive - slab monolithic foundation (in the article, the calculation of reinforcement for the foundation, you will appreciate how "economical" this solution is), then you can completely avoid these calculations, because it is enough to fill the slab under the entire area of the house, and such a sole with an excess is enough to prevent all the surprises that the soil presents.
Each type of soil, depending on the depth, density and porosity, has its own load resistance. It goes without saying that soil layers at great depths as a result of natural compaction are characterized by high values of resistance. So, if you plan to build a foundation to a depth of less than 1.5 m, then the calculated soil resistance will take on a slightly different value. In this case, it will be calculated according to the formula: R = 0.005R0 (100 + h / 3), where R0 is the tabular value of the design resistance, h is the depth of the foundation relative to the zero mark, see. In turn, a lot depends on groundwater, because increased soil moisture reduces its resistance to load.
Naturally, when calculating the foundation for a house on your own, you will have to tinker with calculating the load from the structure being erected, which will be on the soil layers under the base of the foundation. This includes:
- the total load from the structure, including the approximate one - from the foundation (data from the table presented in the figure below are used);
- load from objects that will be placed in the building (fireplaces, furniture, people);
- weight of seasonal snow loads. For the middle lane, it is taken equal to 100 kg per sq. m of roof, for the south - 50 kg, for the north - 190 kg.
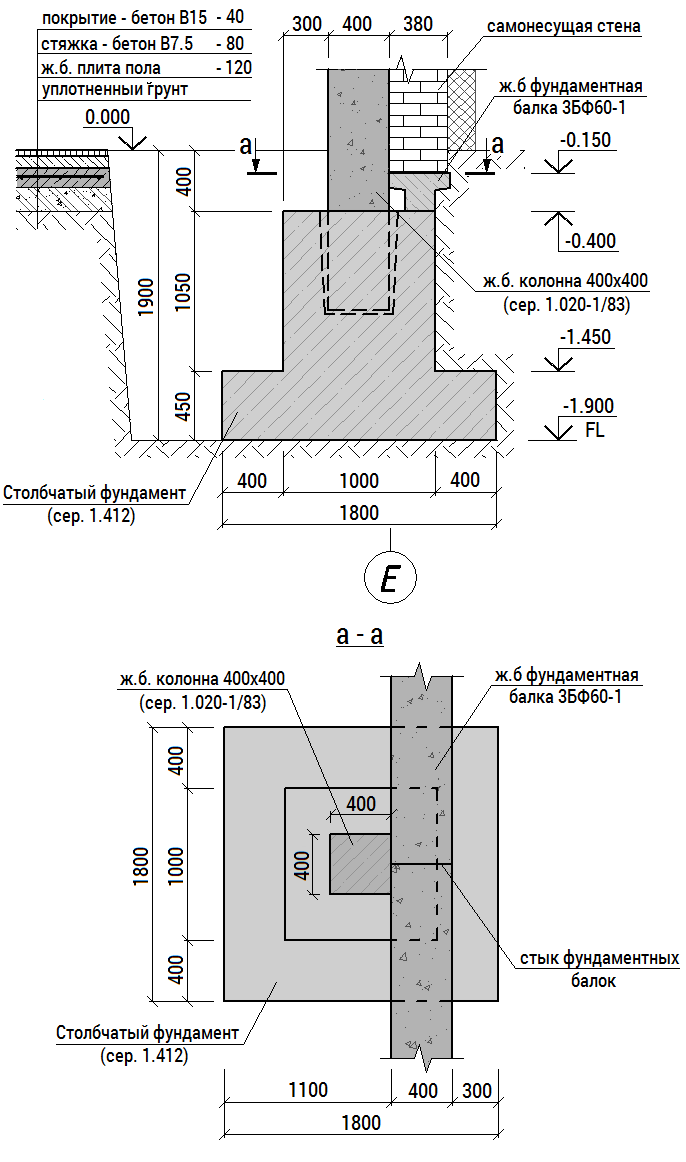
The value of the basement foot area obtained as a result of calculations is used when drawing up the foundation project: choosing the width of the tape (for a strip monolithic base) or the support area (for columnar, pile types of foundations). Consider a specific example of calculating the foundation for a stone house 6? 8 m. How the reinforcement for the foundation is selected will be discussed in a separate article.
An example of a foundation calculation
Suppose we are building a two-story stone house 6? 8 m, the project of which includes one internal load-bearing wall. The mass of the house, taking into account all the loads, turned out to be equal to 160,000 kg. The soil is wet clay (design resistance - 6 kg / cm2). Condition factor - 1. Reliability factor - 1.2. We substitute all the values into the formula for calculating the area of the base of the foundation:
S = 1.2? 160,000 / (1? 6) = 32,000 cm2 = 3.2 m2
For strip foundations: with a total strip length of approximately (6 + 8)? 2 + 6 (inner wall) = 34 m the minimum tape width is 3.2 / 34 = 0.1 m. This is the minimum value!
If we consider the foundation for a light wooden house, provided that the minimum foot area is equal to 1 m2, then for the construction of a pile foundation (the base area of each pile is taken equal to 0.07 m2, provided that the lower part of the pile is 0.3 m in diameter ) would need:
1 / 0.07 = 15 piles
Bored foundation
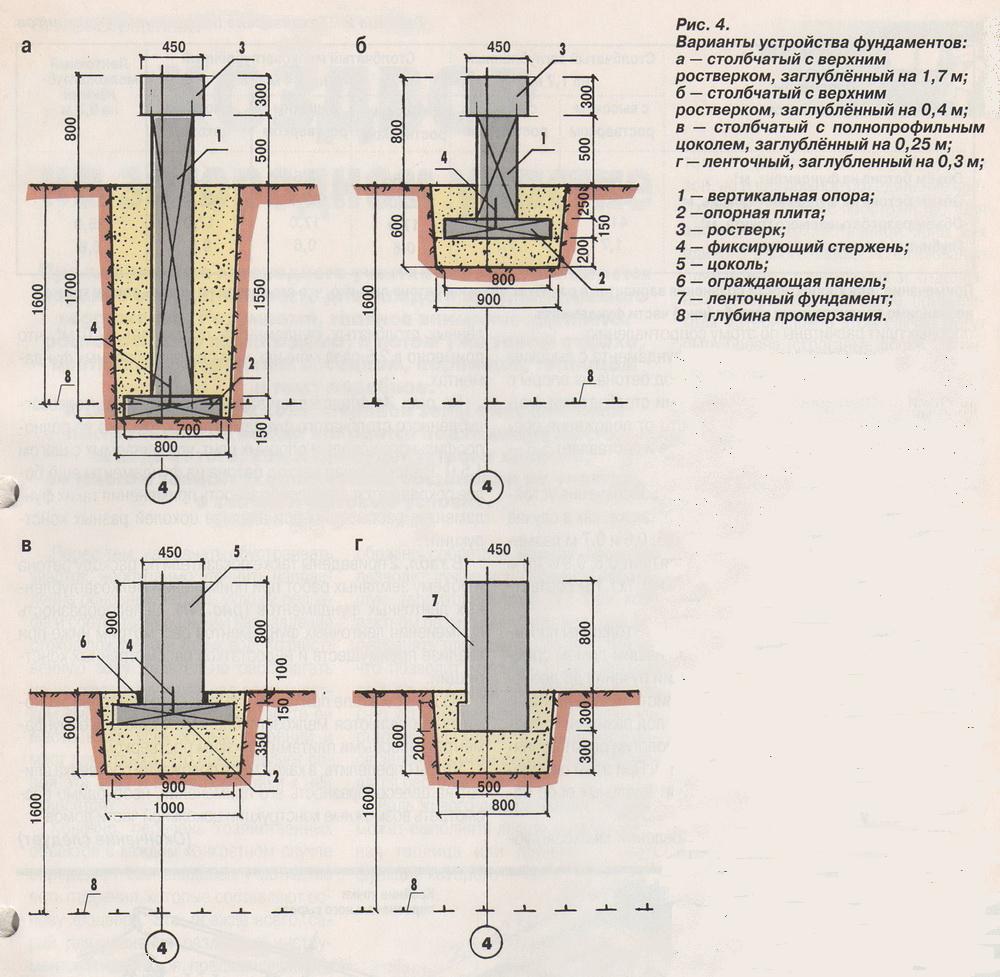
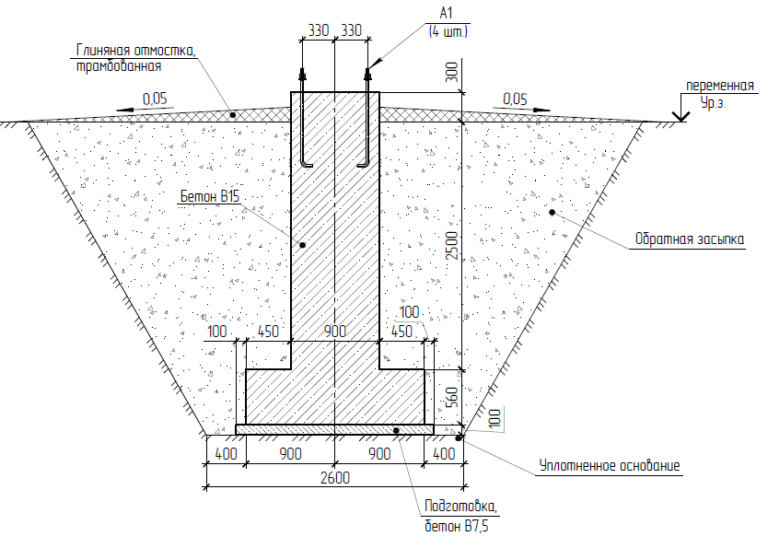
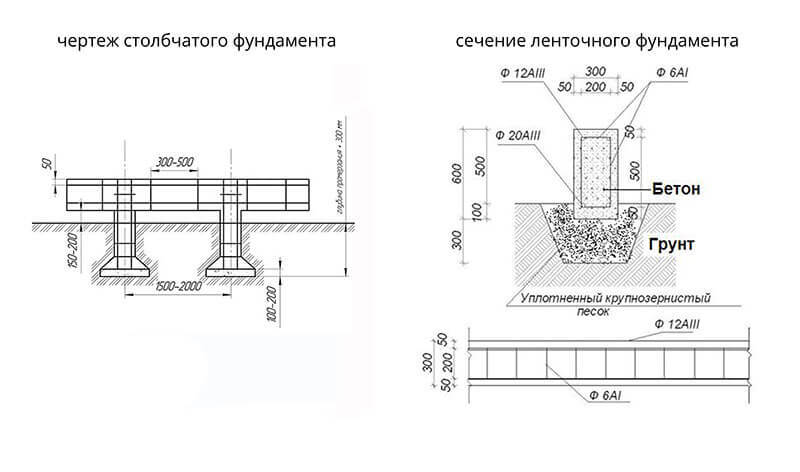
 The pillars are created by pouring concrete into pre-drilled holes. Work on the device of the bored foundation is carried out in the following sequence:
The pillars are created by pouring concrete into pre-drilled holes. Work on the device of the bored foundation is carried out in the following sequence:
1) Based on the calculation, the foundation is marked on the site.
2) With the help of a manual (mechanized) drill or a special drilling machine, wells are made 20-30 cm below the freezing depth.
3) From ordinary roofing material, cylinders are rolled up (along the diameter of the wells) and wrapped with tape. They perform two roles: firstly, it is a permanent formwork for the pillars, and secondly, their waterproofing.
If you have sprinkled roofing material, roll the smooth side out. The worse the soil sticks to the surface of the pillars during freezing, the less tangential forces that tend to pull the pillars out of the soil in winter will act on them.
4) Roofing material cylinders are inserted into the wells. In the picture above, you can see that the roofing material does not reach the very base, about 20 cm remains.This is done for a reason. Through the uncovered part of the pile, when pouring concrete, cement milk seeps into the ground and additionally binds it. At the same time, depending on the type of soil, the bearing capacity of the column can increase up to 2 times. This increase is not included in the calculation. It additionally increases the safety margin of the foundation. In addition, the pillars will anchor better in the ground.
5) A little concrete (20-30 cm) is poured into the well, after a short pause, a reinforcing cage is inserted so that it does not sink under its own weight until it touches the ground. Then the entire pillar is poured to the top. The contact of the reinforcement with the ground is not desirable, because this leads to its faster corrosion.
Usually, the frame is made of three or four bars of working reinforcement A-III ∅10-12 mm, tied together with auxiliary reinforcement Bp-I ∅4-5 mm. It is desirable that the reinforcement is not closer than 5 cm from the outer surface of the post.
If, after pouring the pillars, a monolithic grillage will be built on them, the working reinforcement is released from the pillars to the height of this grillage. If a strapping is made of wooden beams on the posts, then a threaded rod (for example, M16) is inserted into the upper part to fasten it when pouring concrete.

At an air temperature of 15-20 ° C, the columnar foundation can be loaded in 4-5 days. This is due to the fact that after this period, the bearing capacity of the foundation is no longer determined by the strength of the pillars, but by the strength of the soil under them. In addition, you will not be able to quickly give the full design load on the foundation (walls, floors, roof, operational loads). While the construction is in progress, the concrete will "mature".
IMPORTANT: Do not leave the columnar foundation unloaded for the winter. The tangential forces of frost heaving can raise and warp the pillars, all in different ways
Foundation creation cost
When calculating the cost, it is necessary to take into account not only the price of the material and its delivery, but also the wages of the builders who will perform some work. If you decide to do all the work yourself, then you only need to consider the cost of materials, including delivery. To build a columnar foundation with your own hands, the step-by-step instructions of which are set out in this article (a house of 10x10 meters, asbestos pipes with a diameter of 200, a freezing depth of 1.5 meters), you will have to spend 20-25 thousand rubles without paying for delivery.
Number of blocks: 23 | Total number of characters: 26983
Number of donors used: 7
Information for each donor:
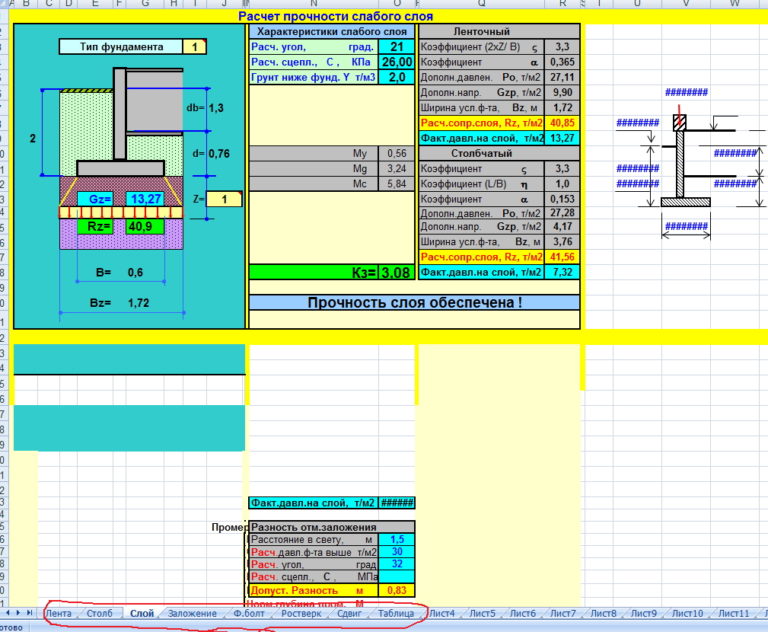
Calculation of a columnar foundation
Let's calculate the bearing capacity of a columnar foundation made of monolithic reinforced concrete (the perimeter of the walls and the structure of the whole house remain the same). Consider an example of a calculation for such a columnar foundation:
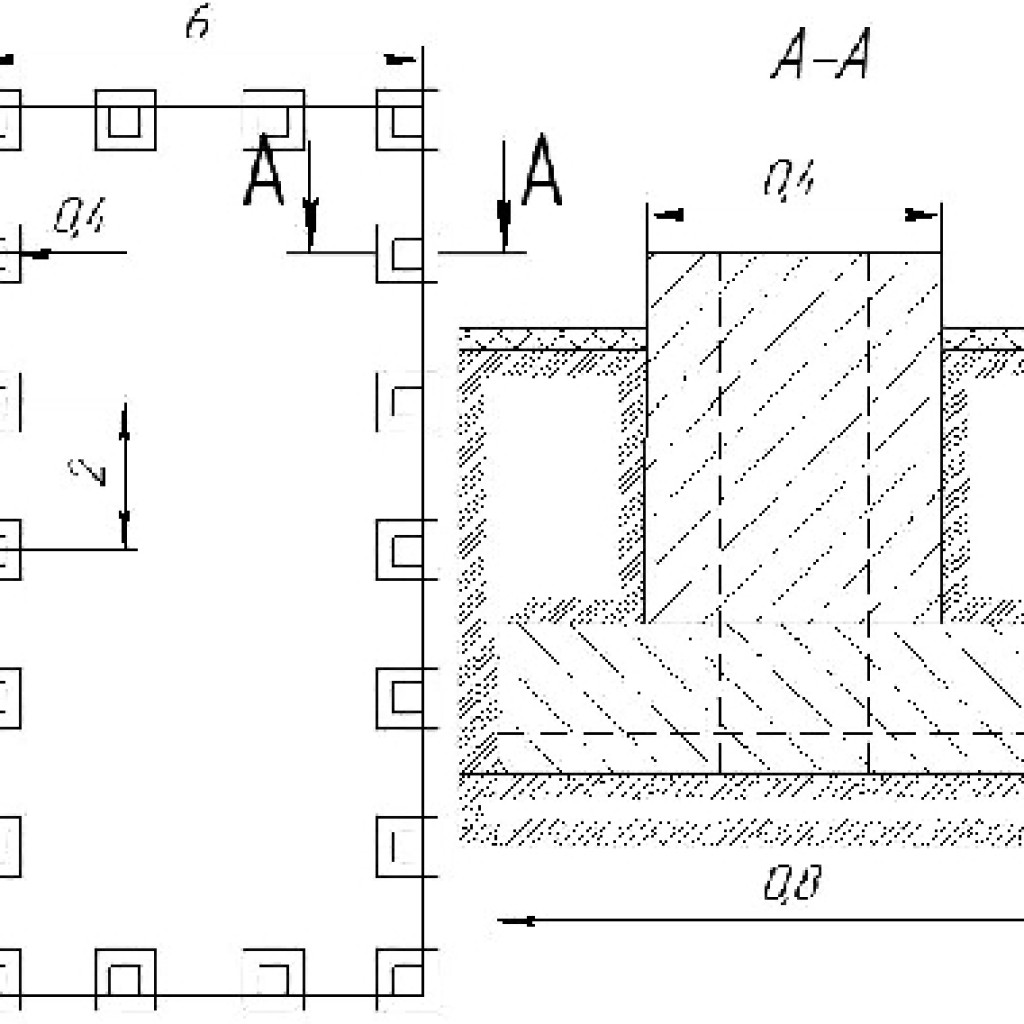
- the section of the column in the upper part is 40x40 cm; - the section of the foot of the column is 80x80 cm; - the distance between the posts is 2 m (that is, 1 post per 2 m long wall).
The plan of the columnar foundation is shown in Fig. 3.
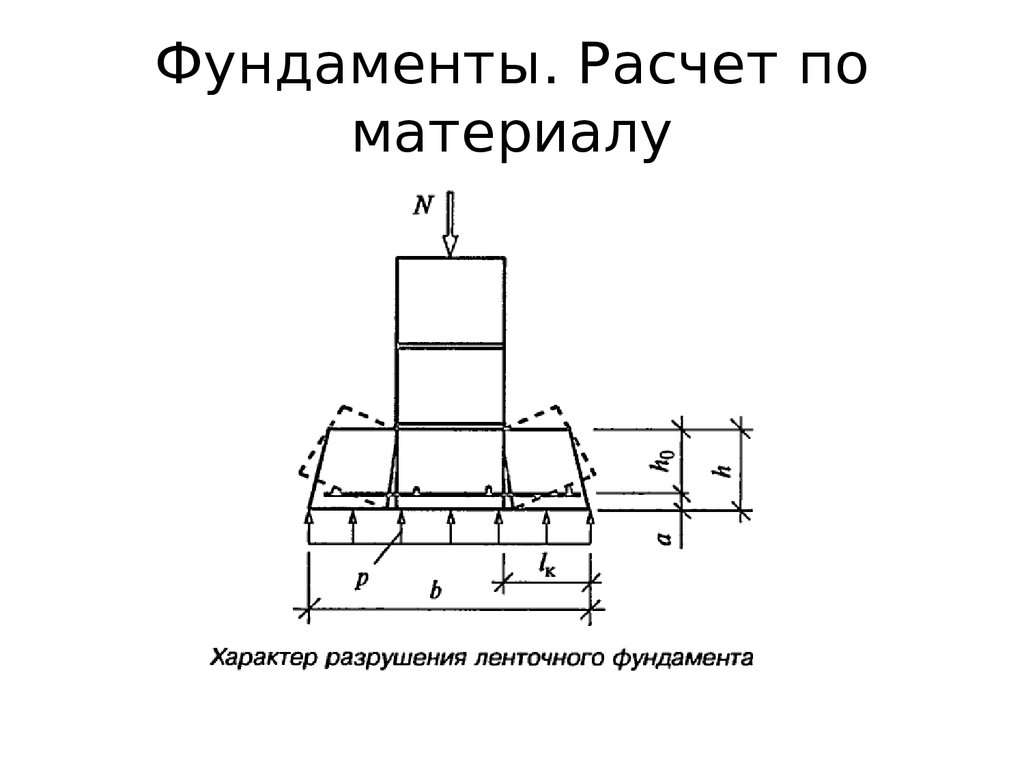
Let's calculate the total load that acts on the soil from the foot of the columnar foundation in section A-A (Fig. 3). It will be equal to the already calculated load acting on 1m of the length of the strip foundations (excluding the weight of the foundation): 5415-1035 = 4380 kgf.
Next, you need to multiply the load by the distance between the posts: 4380 * 2 = 8760 and add the weight of one post. The volume of the columnar foundation of the given structure is approximately 0.25 m3. Thus, the weight of the foundation in accordance with the density for reinforced concrete according to table. 4 is equal to: 0.25 * 2500 = 625 kgf. The result of calculating the load of the foundation on the ground: 8760 + 625 = 9385 kgf per one pillar. In this case, the supporting surface of one column is 80x80 = 6400 cm2.If we take into account the bearing capacity of the soil 1.5 gs / cm2, then the ultimate load of the foundation on the soil will be: 6400 * 1.5 = 9600 kgf, which is more than the design loads (9385 kgf).
Such a columnar foundation will be reliable for the house shown in the example. It should be noted that in the general case for a columnar foundation:
- concrete consumption will be approximately 3-4 times less; - the volume of earthworks is approximately two times less.
That's all for the simplest calculation of the bearing capacity of the foundation. We hope that the above example of calculating the foundation will help you find the optimal foundation design, in which it will be not only reliable, but also economical.
Igor Solarov, specially for.
Calculation example
The example provides the following input data:
- one-storey house with an attic measuring 8 m by 10 m in plan;
- the walls are made of silicate bricks with a thickness of 380 mm, the total area of the walls (4 outer walls with a height of 4.5 m) is 162 m²;
- the area of internal plasterboard partitions is 100 m²;
- metal roof (four-pitched, slope 30ᵒ), the area is 8 m * 10 m / cosα (roof slope) = 8 m * 10 m / 0.87 = 91 m² (also needed when calculating the snow load);
- type of soil - loam, bearing capacity = 0.32 kg / cm² (obtained during geological surveys);
- snow load - 180 kg / m²;
- wooden floors, with a total area of 160 m2 (also needed when calculating the payload).
The collection of loads on the foundation is performed in tabular form:
| Standard load | Reliability factor | Design load |
| Walls: 162 m2 * 690 kg / m2 = 111780 kg | 1,1 | 122958 kg |
| Partitions: 100 m2 * 30 kg / m2 = 3000 kg | 1,2 | 3600 kg |
| Overlaps: 160 m2 * 150 kg / m2 = 24000 kg | 1,1 | 26400 kg |
| Roof: 91 m2 * 60 kg / m2 = 5460 kg | 1,1 | 6006 kg |
| Payload: 160 m2 * 150 kg / m2 = 24000 kg | 1,2 | 28800 kg |
| Snow: 91 m2 * 180 kg / m2 = 16380 kg | 1,4 | 22932 kg |
| TOTAL: | 210696 kg |
The area of the slab for the building is taken taking into account that the width of the slab is 10 cm larger than the width of the house. S = 810 cm * 1010 cm = 818100 cm² = 81.81 m2.
Specific ground load from the house = 210696 kg / 818100 cm2 = 0.26 kg / cm2.
Δ = 0.32 - 0.26 = 0.06 kg / cm2.
M = Δ * S = 0.06 kg / cm2 * 818100 cm2 = 49086 kg.
t = (49086 kg / 2500 m3) / 81.81 m2 = 0.24 m = 24 cm.
The thickness of the slab can be taken as 20 cm or 25 cm.
We carry out a check for 20 cm:
- 0.2 m * 81.81 m2 = 16.36 m3 - slab volume;
- 16.36 m3 * 2500 kg / m3 = 40905 kg - slab weight;
- 40905 + 210696 = 251601 kg - load from a house with a foundation;
- 251601 kg / 818100 cm2 = 0.31 kg / cm² - the actual ground pressure is less than the optimal one by no more than 25%;
- (0,32-0,31)*100%/0,32 = 3%
It makes no sense to check a foundation of greater thickness, since the size requiring less concrete and reinforcement consumption met the requirements. This completes the thickness calculation example. We accept a slab with a thickness of 20 cm. The next step will be the calculation of the reinforcement and the amount of reinforcement.
The reinforcement for the slab structure is selected depending on the thickness. If a slab with a concrete thickness of 150 cm or less is laid, one reinforcement mesh is laid. If the concrete thickness is more than 150 mm, it is necessary to lay the reinforcement in two layers (lower and upper). The diameter of the working rods is 12-16 mm (the most common is 14 mm). Reinforcement rods with cross-sectional dimensions of 8-10 mm are installed as vertical clamps.
For a good slab, you must also count on bending loads, but these calculations are complex and are performed by professionals using special software. In order to understand exactly what diameter of the reinforcement and its step is necessary in your case, you need to carry out accurate calculations, or lay the reinforcement with a large margin of safety and a minimum step, respectively, overpaying greatly.
The difference between pillars and piles
Sometimes the inexperienced owner of the site confuses the pile and columnar foundation when choosing the right option (see: types of foundations for a private house). They really have a lot in common, but they also differ fundamentally. Columnar supports, even when using pipes, have a depth of no more than 2 m, and holes are dug for their manufacture.
No excavation is required to install the piles. Special elements are used that are screwed or driven directly into the ground from the surface of the earth. The basic principle of their installation is to achieve a solid, stable soil layer with the lower end.
The depth can be several meters. This design allows you to build a pile foundation on unstable, heaving and waterlogged soils.The main disadvantage is the need for special equipment.
Conclusion
The essence of columnar foundations, which are a variety of supports for most buildings, are racks extending vertically downward, connected to each other by an overhead grillage. The materials for the manufacture of this base are: wood (usually oak), stones (natural and artificial), brickwork and pipe sections (asbestos-cement and metal).
Columnar foundation is cheaper than others. Its price is mainly determined by the material of manufacture, the technology used and the dimensions. It is necessary to calculate and build columnar foundations on the basis of the relevant GOSTs and SNiPs.