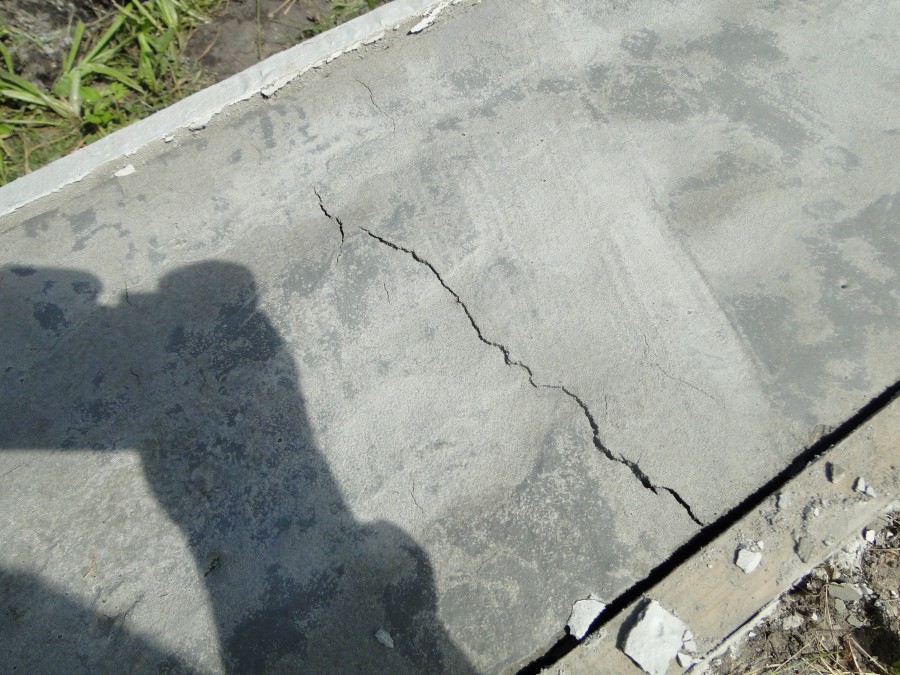
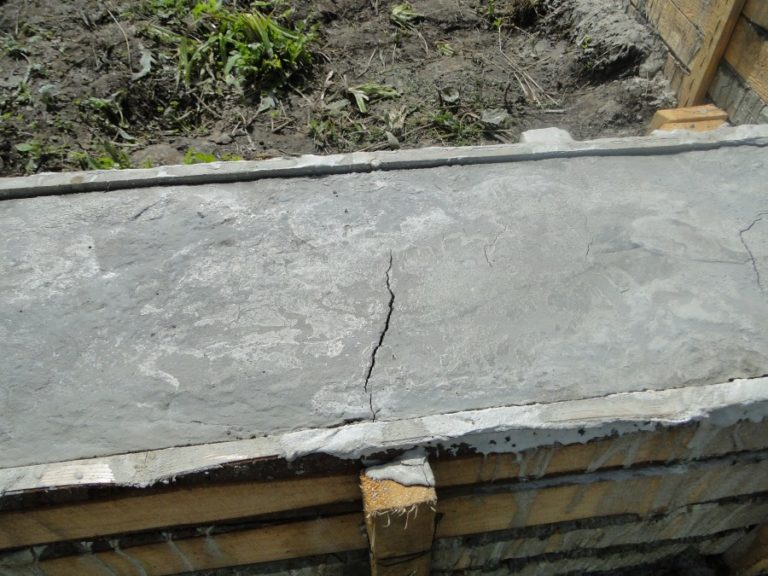
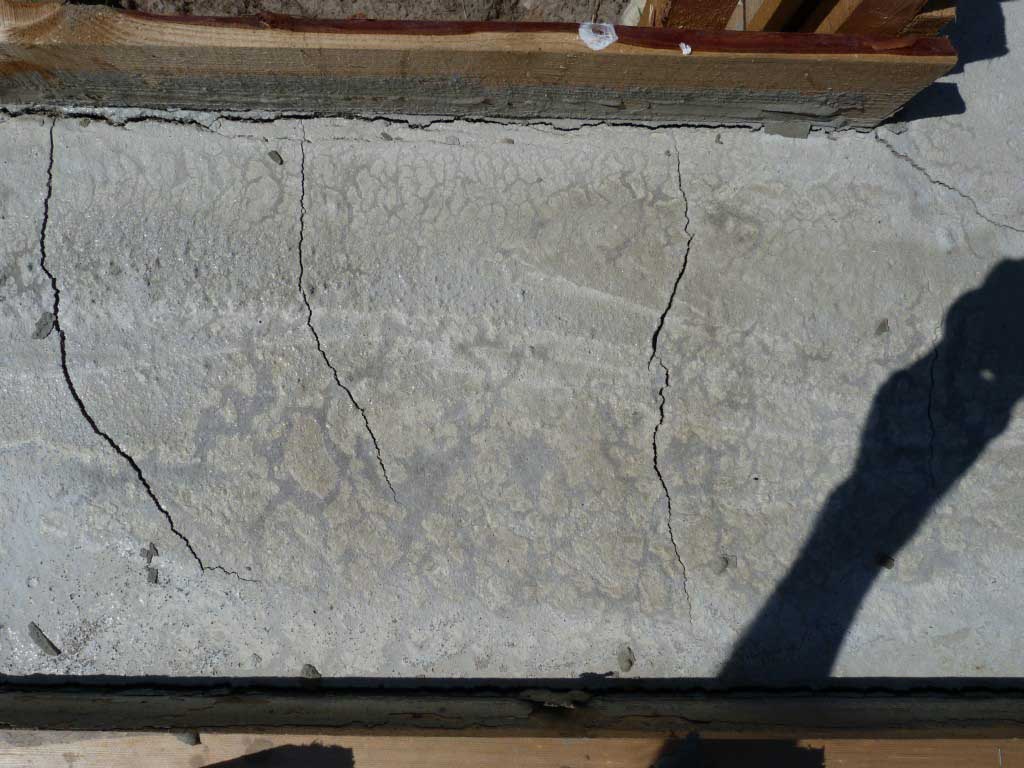
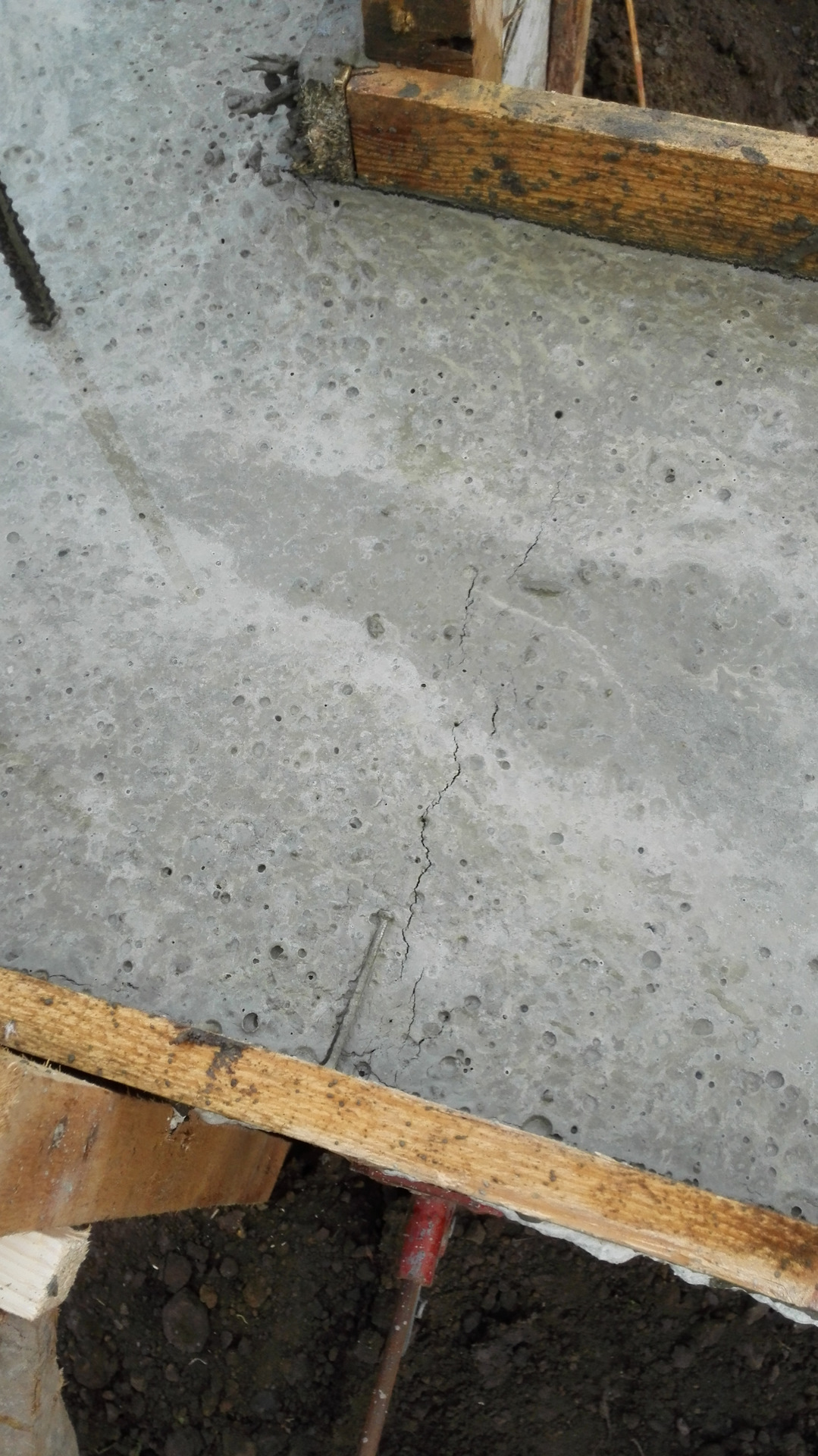
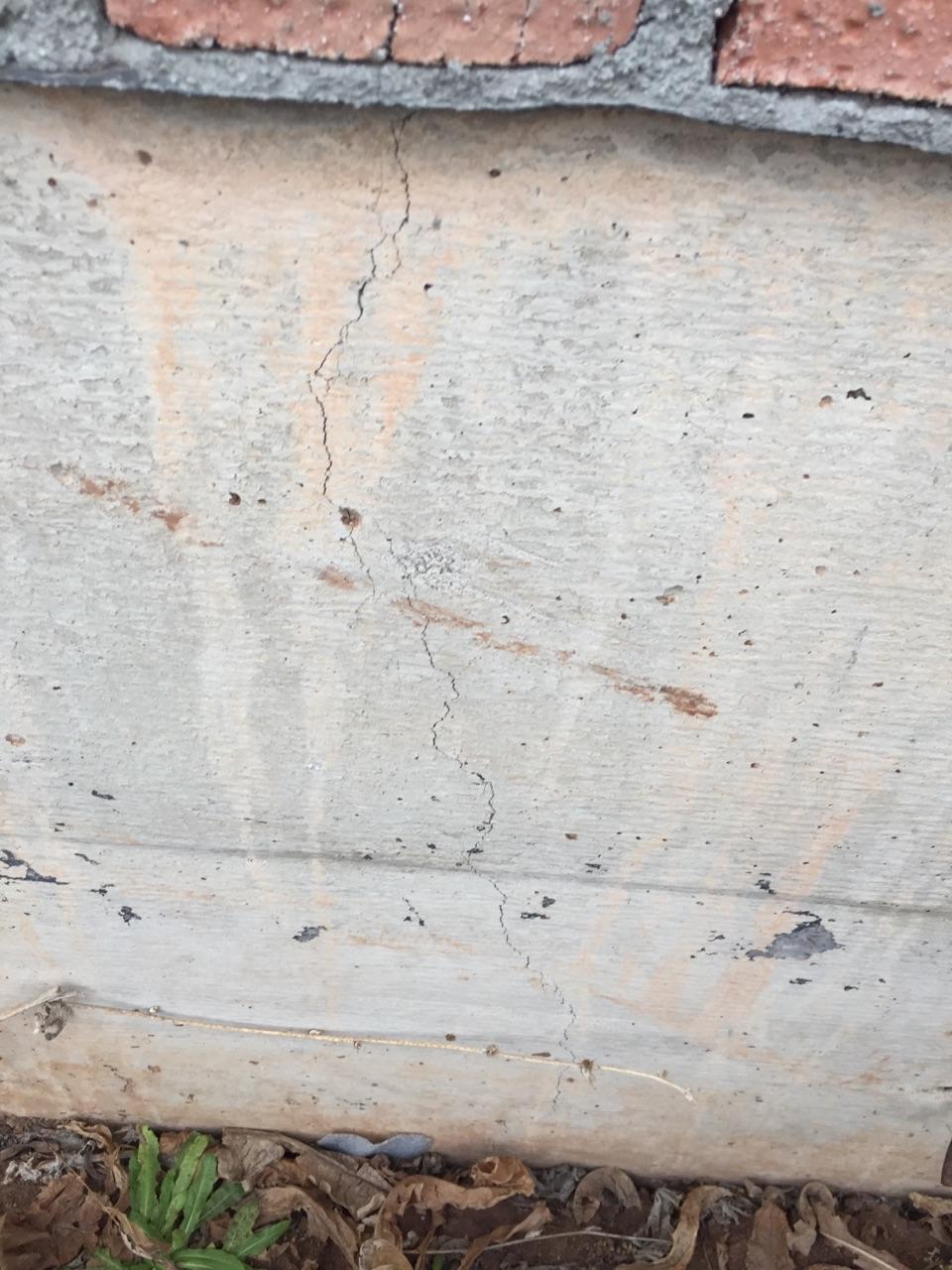
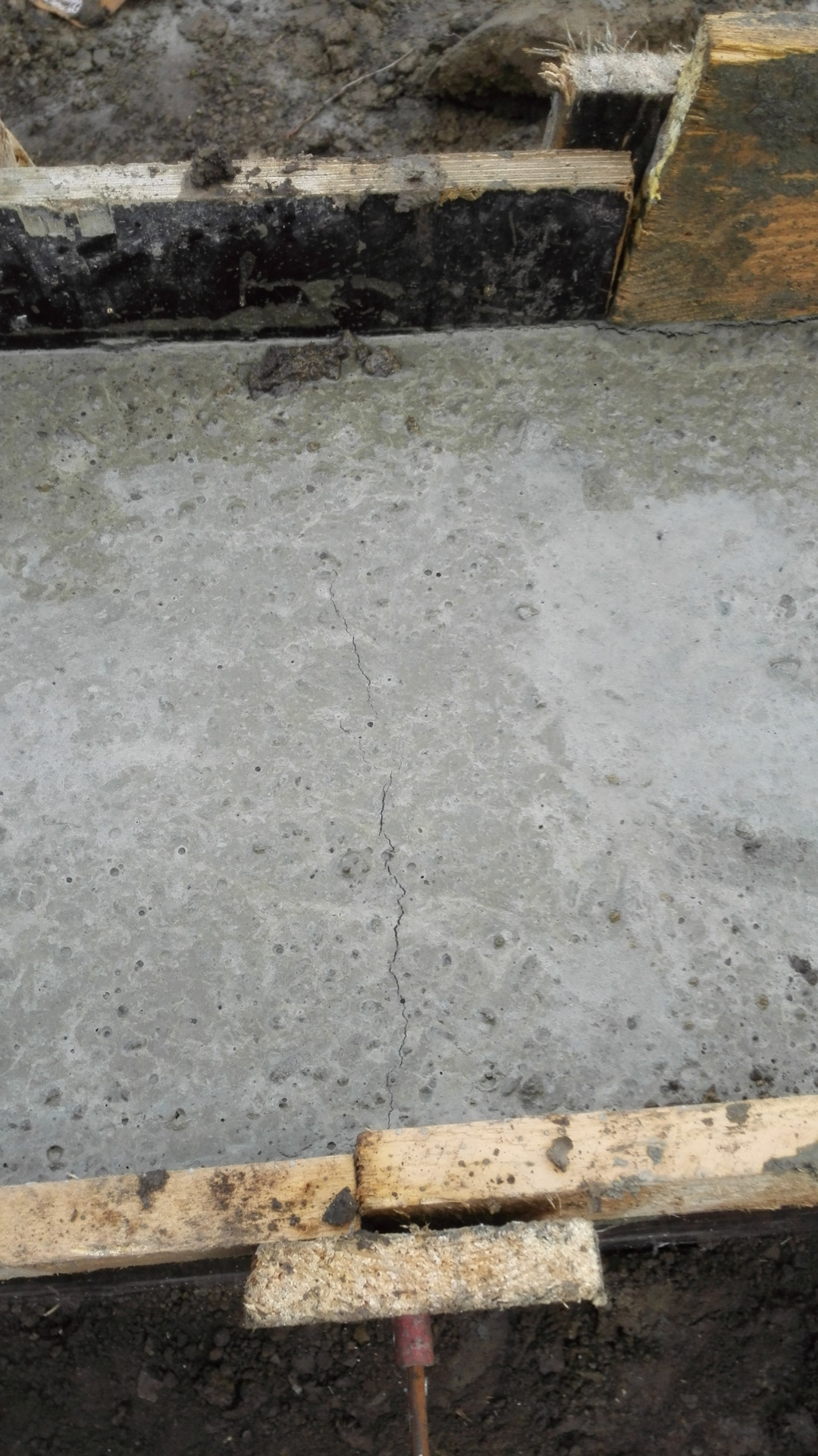
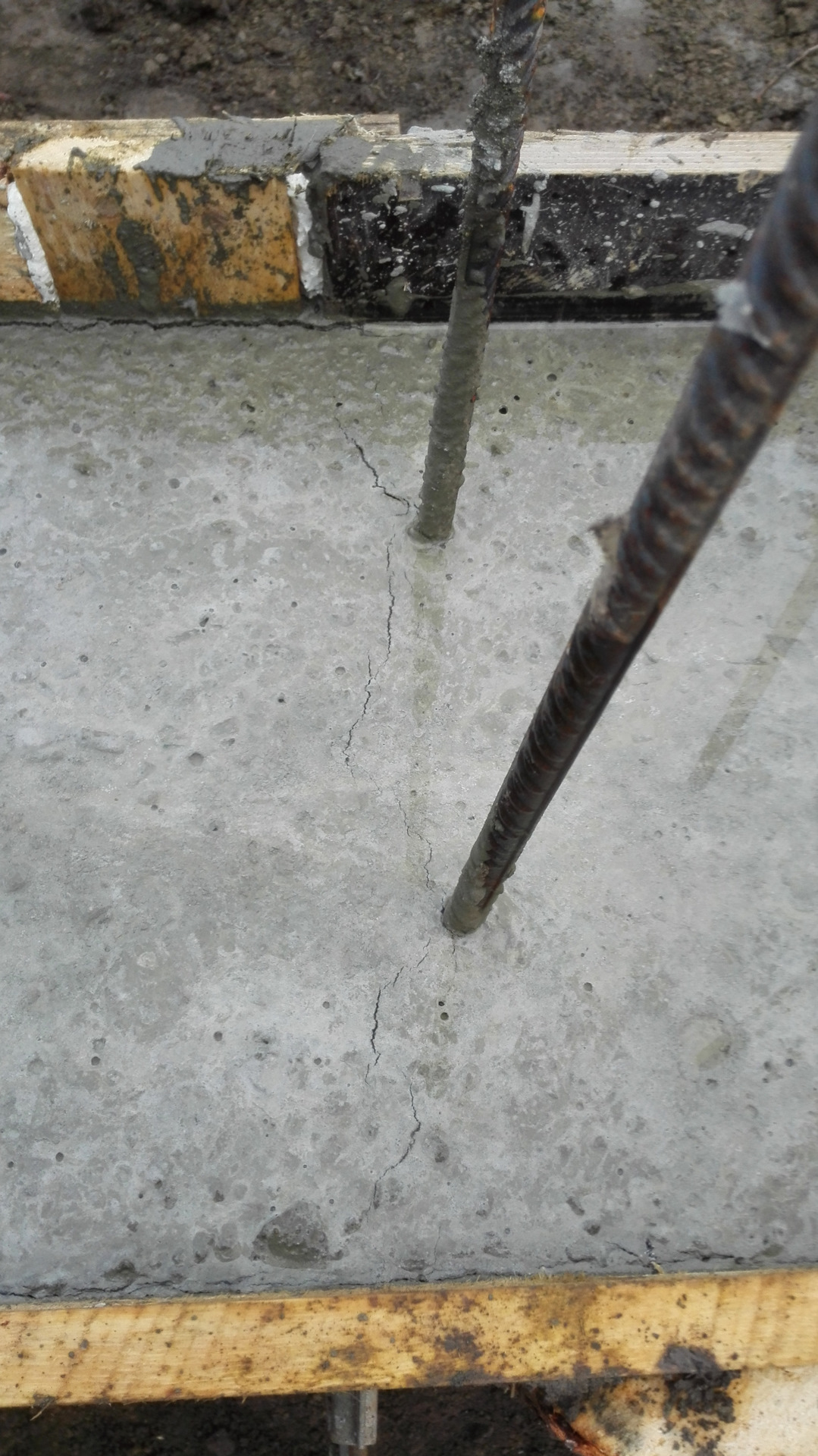
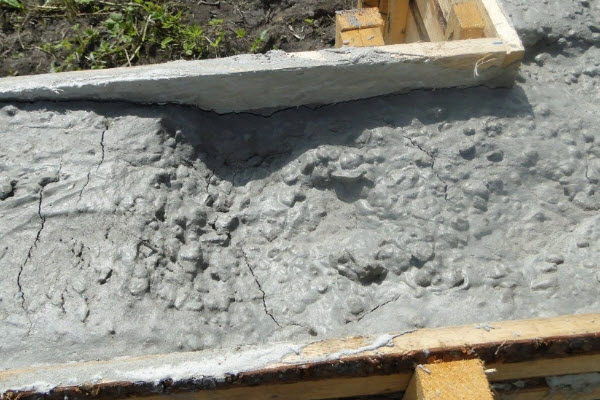
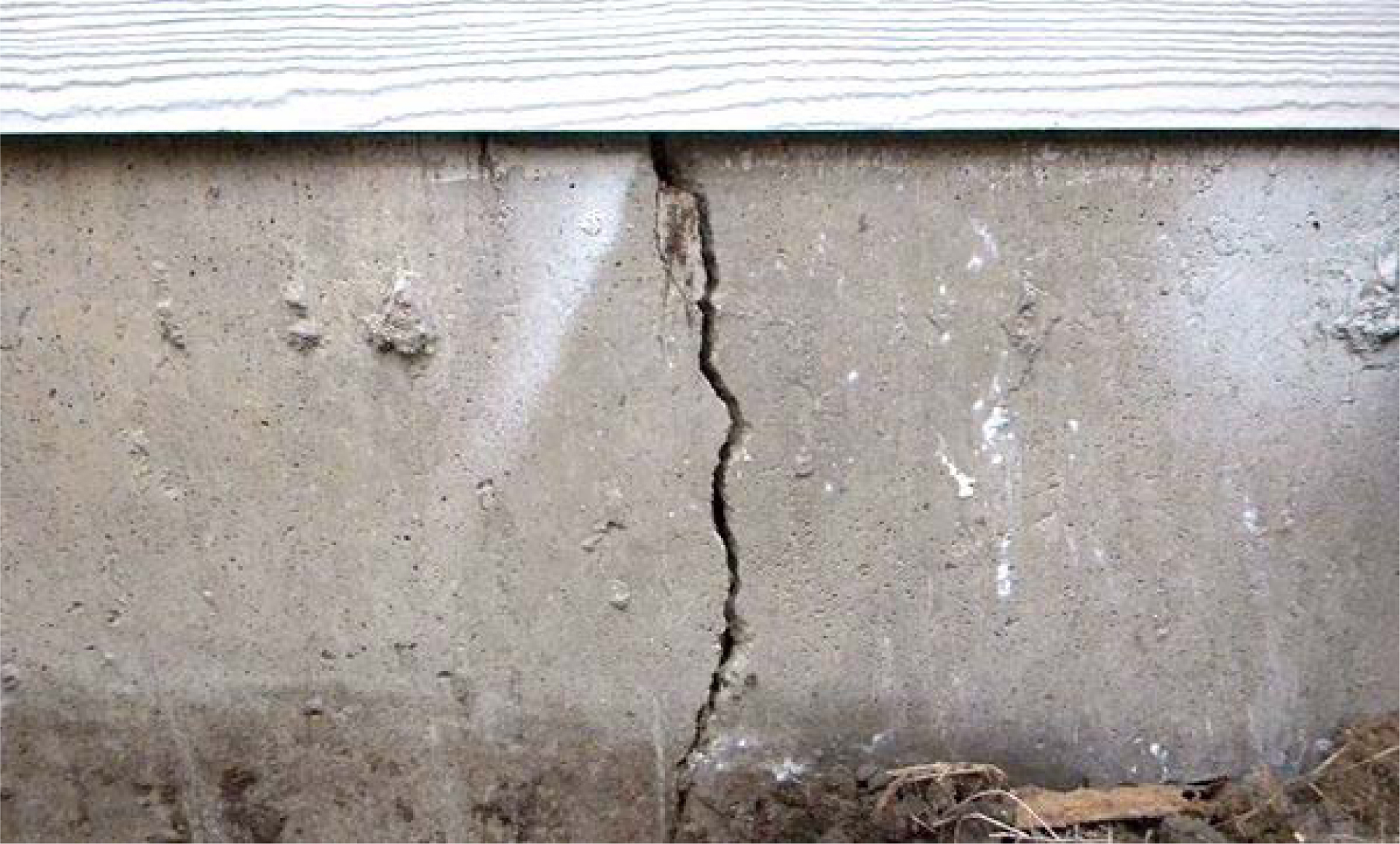
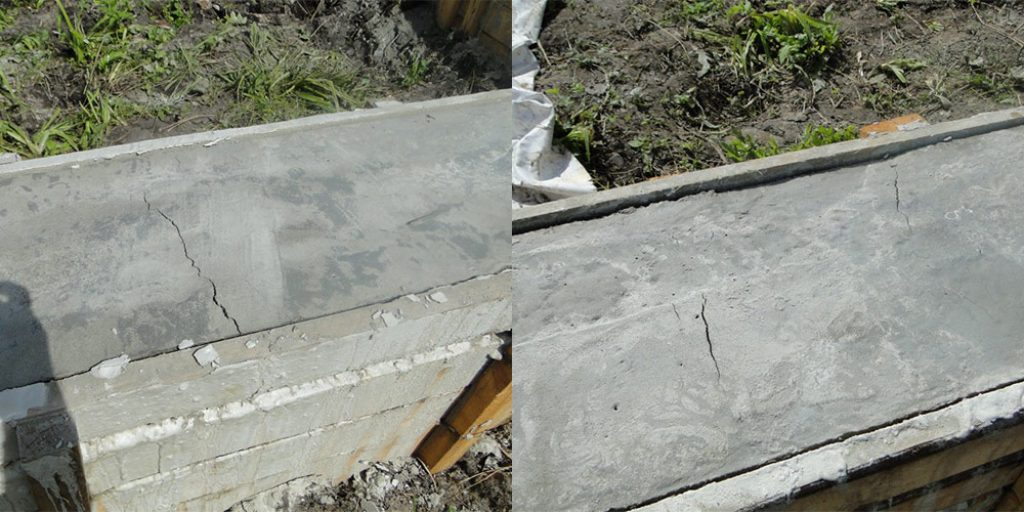
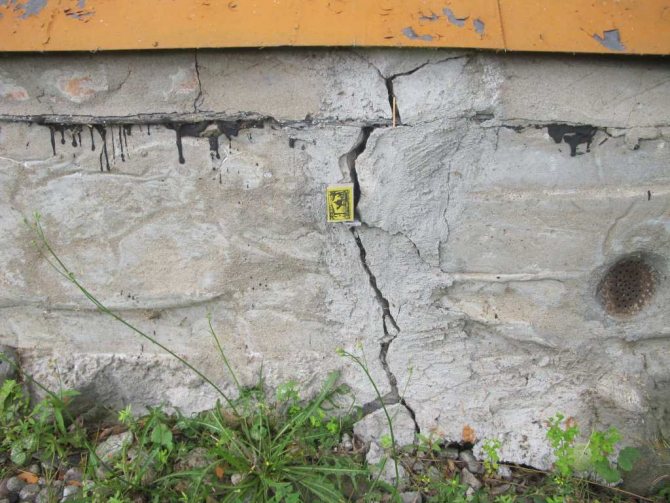
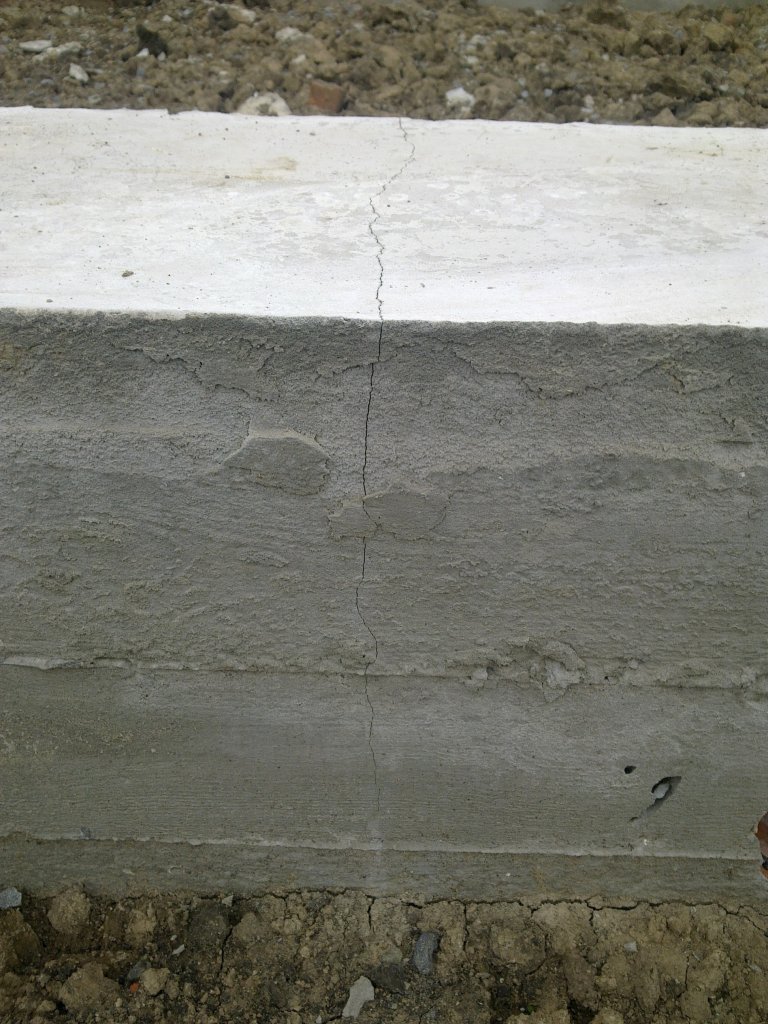
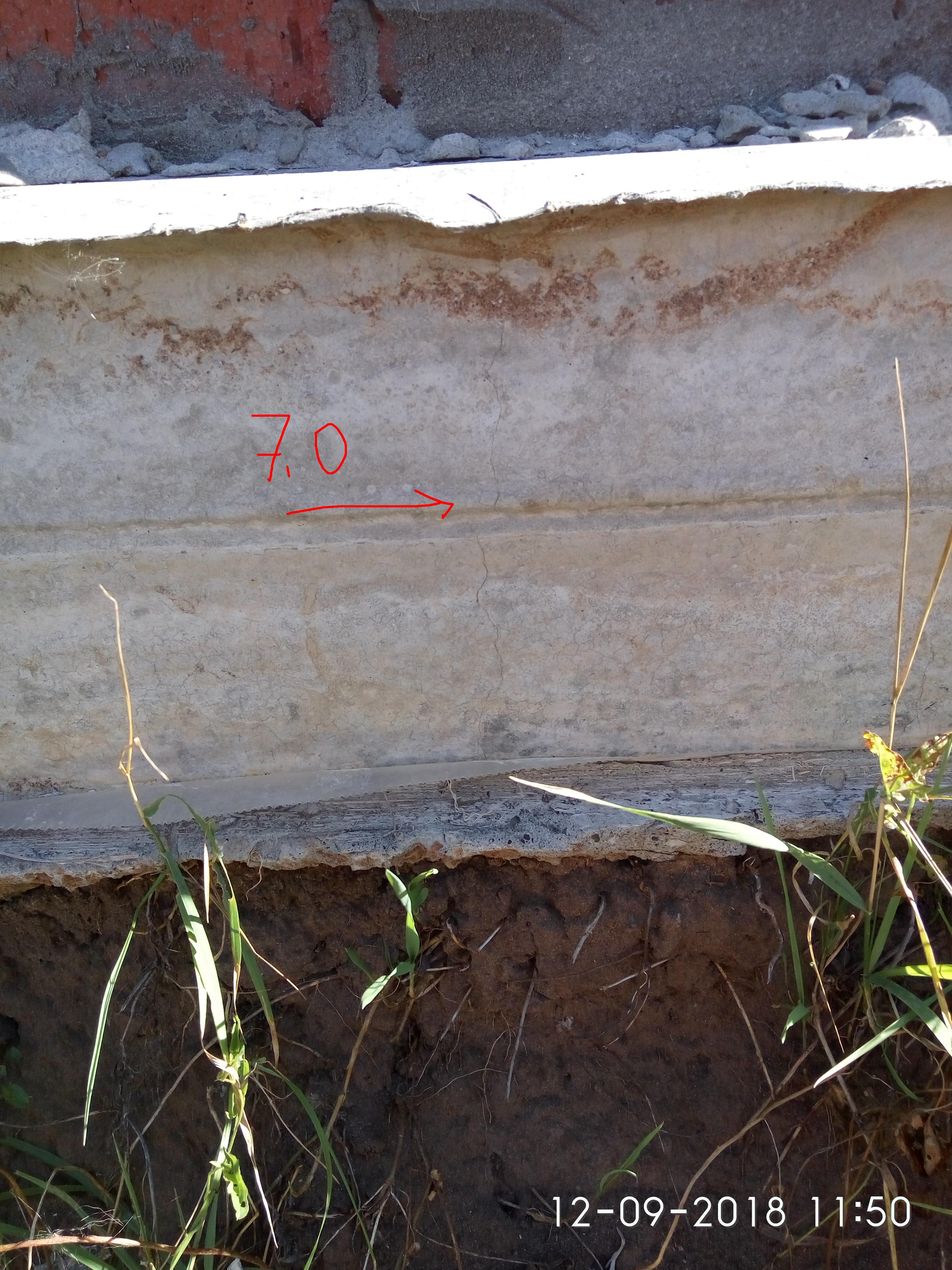
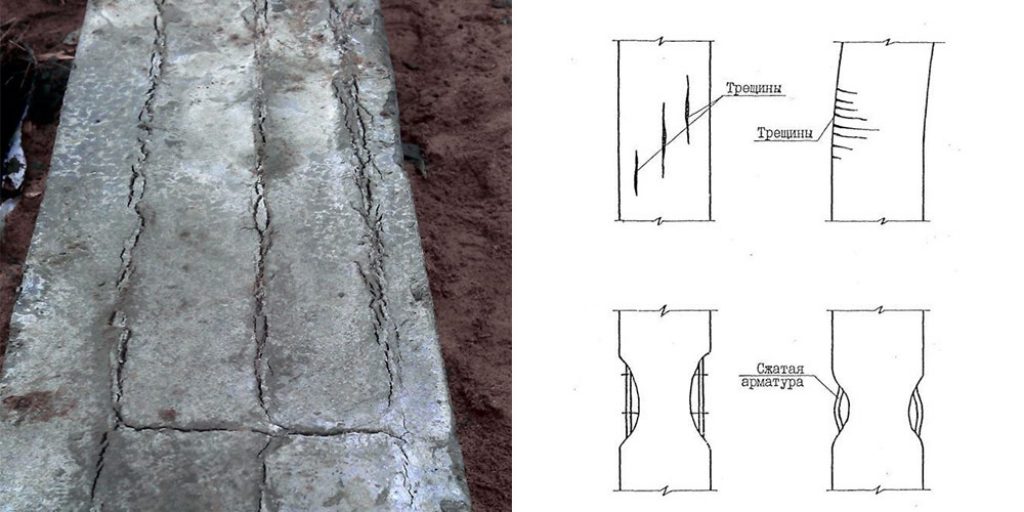
Reasons for cracking
If the technology of pouring concrete is violated or due to poor-quality care for it until sufficient strength is achieved, various types of cracks may form:
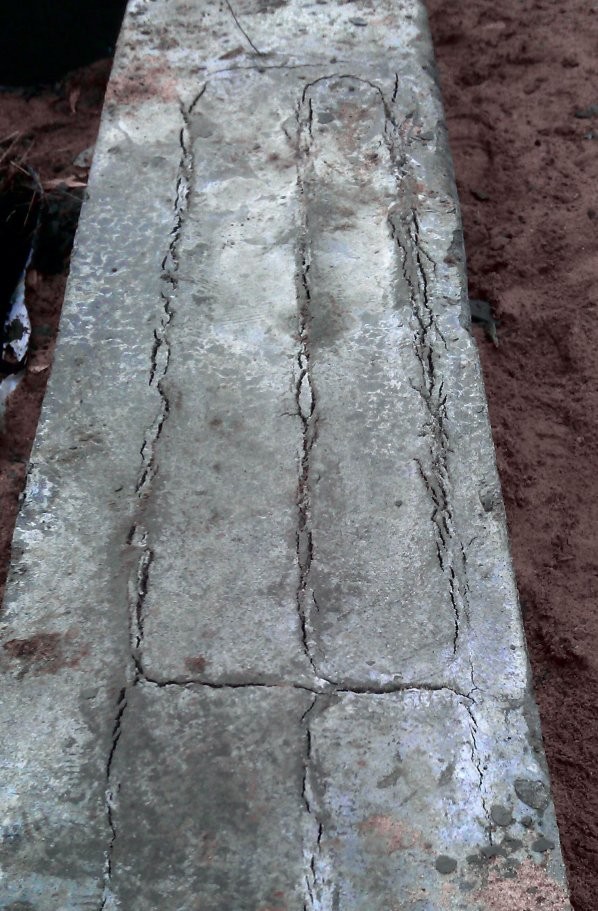
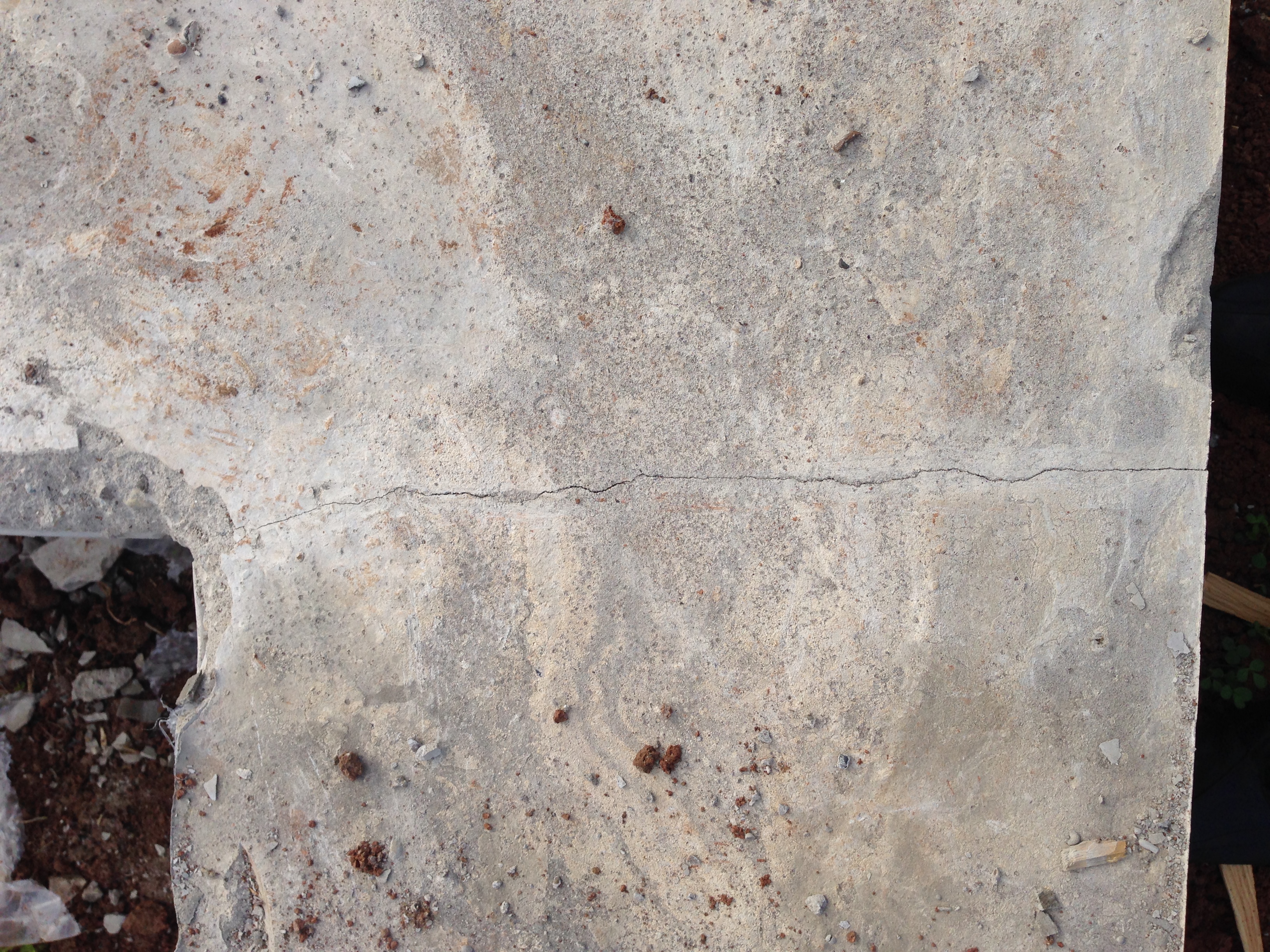
- In the first 1.5-2 hours, while the concrete remains plastic, it may shrink. Shrinkage is caused by a rapid decrease in the volume of the surface layer as a result of dehydration, which occurs under the influence of wind, sun or low temperatures. Longitudinal cracks originate above the upper reinforcement; such a defect can be avoided with careful preparation of the mixture and repeated vibration, performed before the mortar sets.
- Premature plastic shrinkage occurs in the first 1-2 hours after the concrete is poured. The reason for its manifestation is the drying out of the concrete and the compression of the outer surface layer. Surface cracks do not have a specific direction. To prevent premature plastic shrinkage, you can reduce the rate of drying of concrete, you can resort to repeated vibration before setting the mixture.
- The release of the heat of hydration is observed in the first days after concreting due to the heating of the concrete core during the cooling shell due to contact with the atmosphere and soil. Due to the temperature difference, compressive stresses are formed, which lead to the appearance of surface or through cracks. It is possible to prevent the appearance of cracks due to the release of the heat of hydration by arranging expansion joints.
- Shrinkage due to drying can be observed several weeks after the concrete is poured in the form of surface and through cracks. Such shrinkage can be avoided by the correct selection of the mixture, strong reinforcement and the device of expansion joints.
- Thermal deformations can occur at any time during the operation of concrete due to sudden temperature changes. Deformation manifests itself in the form of bending cracks or surface cracks. Reinforcement, expansion joints, and prestressing of reinforcement allow to avoid thermal deformations.
- Mechanical deformations can occur at any time; they manifest themselves as through cracks and bending cracks. This disadvantage can be avoided by reinforcement, prestressing of reinforcement, device of expansion joints.
- Its own stress state can cause the appearance of various cracks at any time of operation. This negative impact can be avoided with proper reinforcement.
- Bending cracks as well as external microcracks as a result of external loading can occur at any time during operation. Correct reinforcement helps prevent concrete deformation due to external loading.
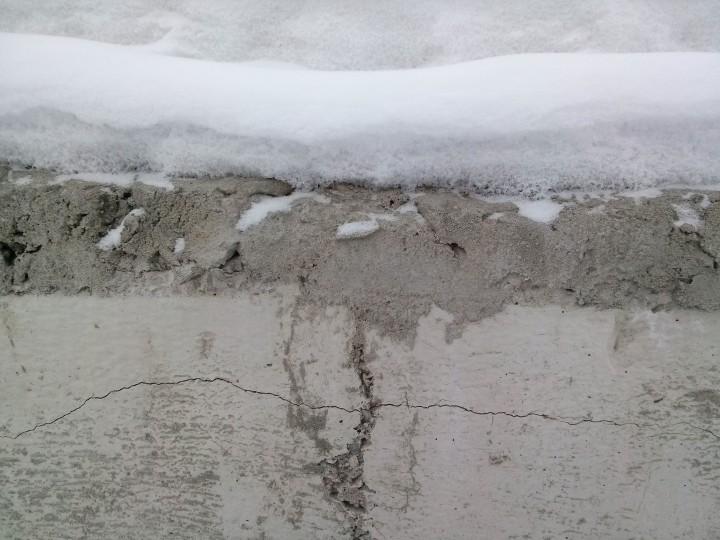
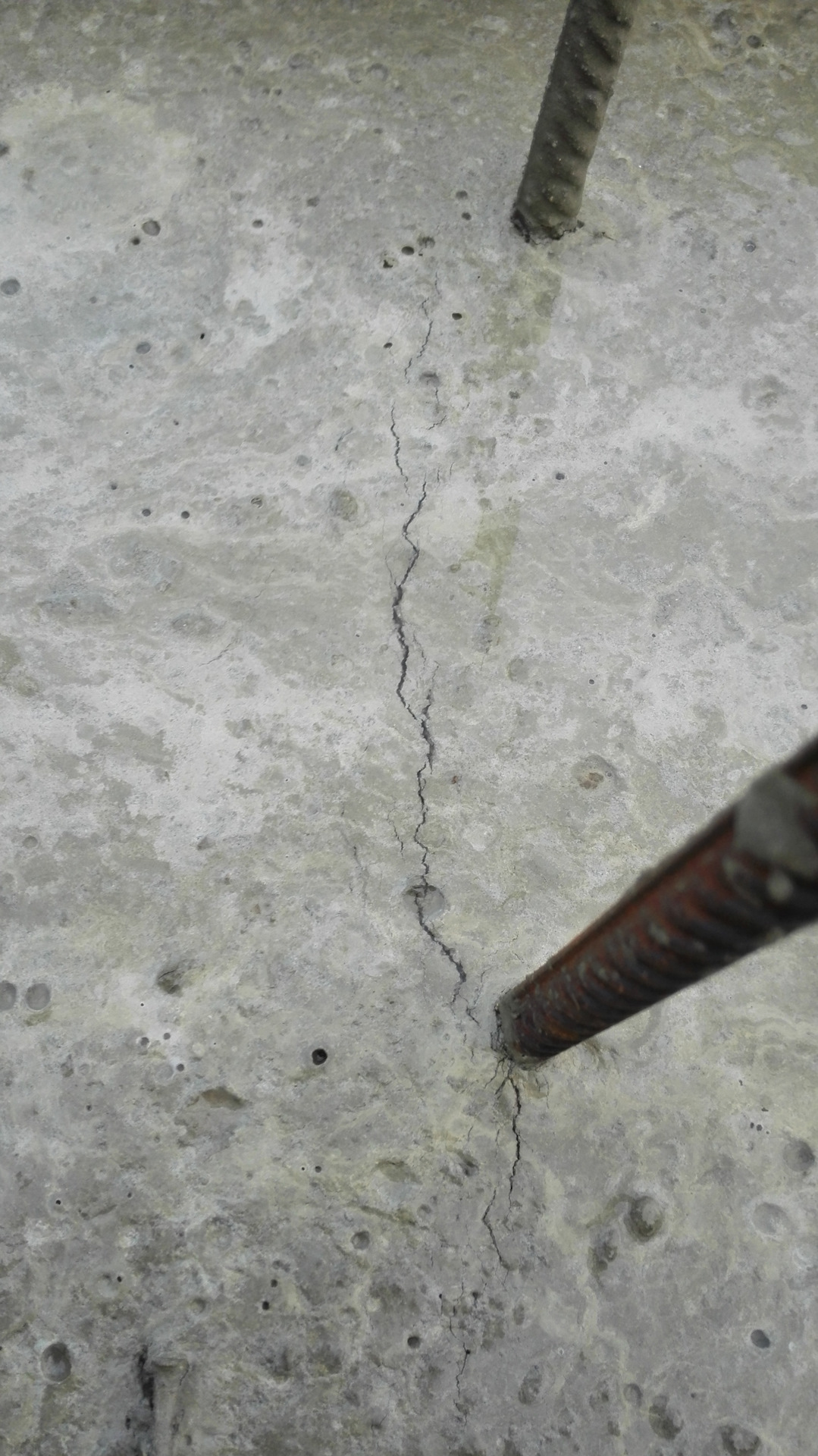
- Cracks along the reinforcement or in the area of water-filled voids due to frost can occur when exposed to the lowest possible temperatures. It is possible to neutralize the effect of frost with high-quality vibration compaction of the mixture.
- Cracks in the corners of building elements and along the reinforcement can appear several years after concreting due to corrosion of the reinforcement. Such defects can be avoided by observing the technological standards for the construction of the protective layer, as well as by excluding the contact of the reinforcement with the ground.

What to do to prevent the concrete from cracking
It is impossible to avoid the occurrence of cracks when they have already appeared. It is necessary to understand the physical meaning of the appearance of breaks. A feature of the phenomenon is the latent mode of cracking.
Their appearance can be prevented only in advance, by using the correct technological methods, using the appropriate materials, and performing work in favorable climatic and temperature conditions.
Grouting technology requires the use of appropriate amounts of sand, cement and filler. Excess of the concentration of the binder contributes to the appearance of microcracks, dangerous in their quantity and invisibility.
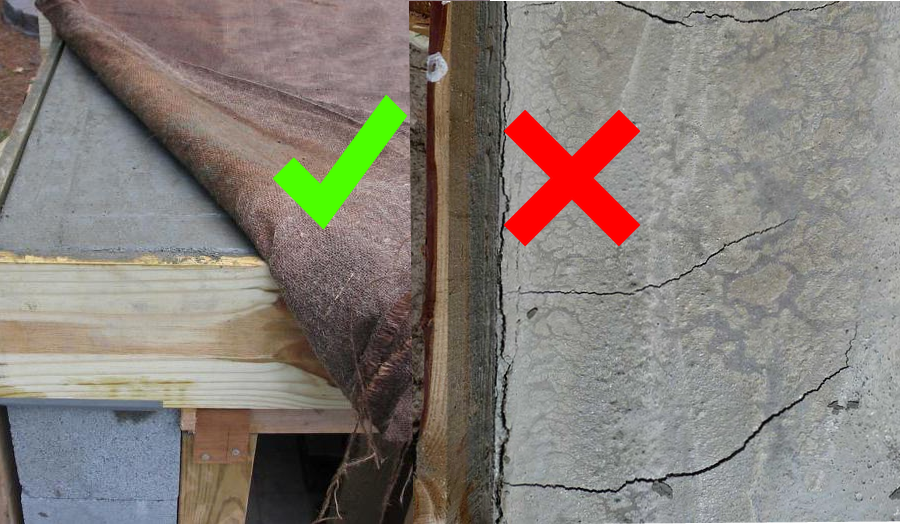
Crystallizing concrete must be wetted with water. The surface receives moisture, the volume of the outer layers is leveled out relative to the inner ones, which did not have time to give up water. The drying process is accompanied by the release of heat; on hot summer days, wetting should be done 2-3 hours after pouring.
Pouring of concrete must be accompanied by periodic bayonetting and ramming of the array. Elimination of cavities, bubbles inside the solution will avoid the appearance of deformation stresses that cause rupture of the surface layers.
The main causes of damage to foundations
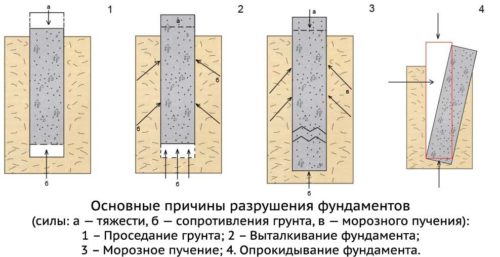
Conventionally, all factors that lead to cracks in the foundation can be divided into the following groups:
- Natural. This is the action of soil swelling, the effect of surface and ground waters, as well as seasonal freezing.
- Anthropogenic. Through exposure to groundwater contaminated with pesticides, acids and alkalis. There is also the possibility of exposure to acid rain through an improperly executed drainage system.
- Technological. These include incorrect calculation of the permissible base load, selection of the wrong type of cement and poor connection of the reinforcement. Also, the human factor cannot be excluded, especially when calculating the load on individual supports.
Therefore, in order to make it easier to choose the optimal technology for repairing the base and supports, all possible reasons are listed in the main groups:
- Unauthorized increase in loads on the base;
- Incorrect foundation calculation;
- Deformation of the masonry through the violation of the waterproofing layer;
- Displacement of supports through seasonal ground movements;
- Damage to the base and ingress of water;
- Moving structures in case of improper fixation of supports on quicksand;
- Engineering communications accidents;
- Incorrect proportions for concrete or poor building materials were used.
If there is a violation of the waterproofing layer, then it will not be difficult to eliminate the cause. To do this, you just need to punch a hole in the base a couple of bricks deep, level the surface and lay out a couple of balls of waterproofing. The rest of the reasons are not so easy to eliminate; you will have to spend a lot of time and financial resources.
Where do the cracks come from?
There may be several reasons for the appearance of cracks in the foundation, but even one is enough to start the destruction of a seemingly solid building. Although several reasons can be combined at once.
- Incorrect engineering calculations during design, incorrect assessment of the foundation's ability to withstand a specific structure, unaccounted for factors of the geological structure of the soil (for example, the depth of groundwater flow).
- Unscrupulous builders working on the principle "and so it will do." But it didn't go away - the foundation was covered with cracks!
- Influence from the outside: sharp fluctuations in temperature, strong soil moisture up to unexpected flooding and, as a result, soil shrinkage, soil erosion, etc.
It is necessary to make a reservation that usually most of these factors in serious construction are calculated at the stage of building design. And if something went wrong, the design engineers are to blame, who had to take into account the terrain and climate conditions.
When self-building in the country, it is, of course, difficult to calculate everything. Therefore, the discovery of a crack in the foundation of a private house or bath, provided that the workers worked responsibly, we will classify it as "everyday business, we will fix it."
"Long haul"
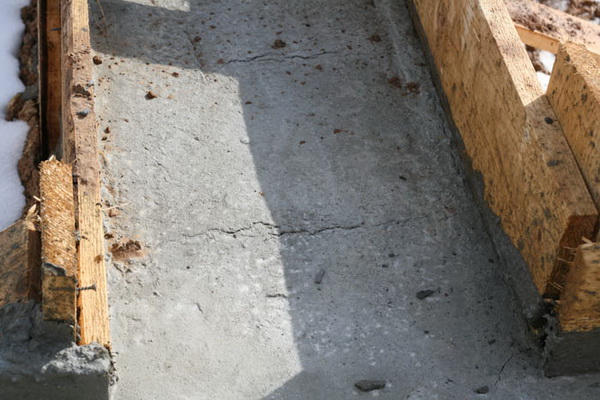
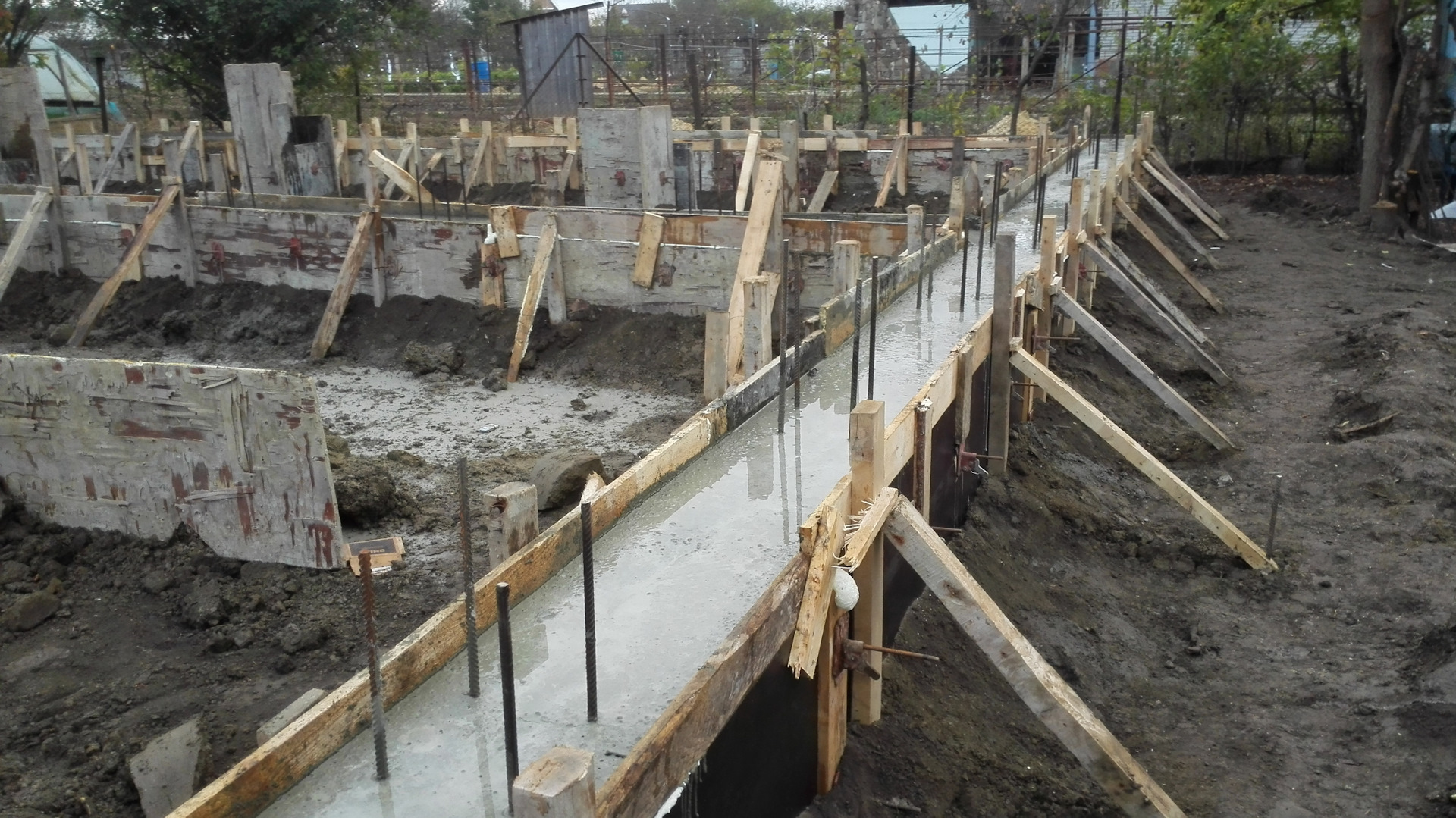
Simple mixers are expensive for the developer, so concrete is often dumped in one place, driven with shovels to distant areas without a tray.This leads to the separation of the mixture into separate fractions - large crushed stone is better captured by the trench tool, the liquid practically remains in place.
Pronounced consequences of concrete delamination.
The result is an uneven concentration of sand / crushed stone in individual areas, which cannot but affect the quality. There will be no design strength in any section of such a foundation, crushed stone is physically unable to envelop the reinforcement, cracks are inevitable.
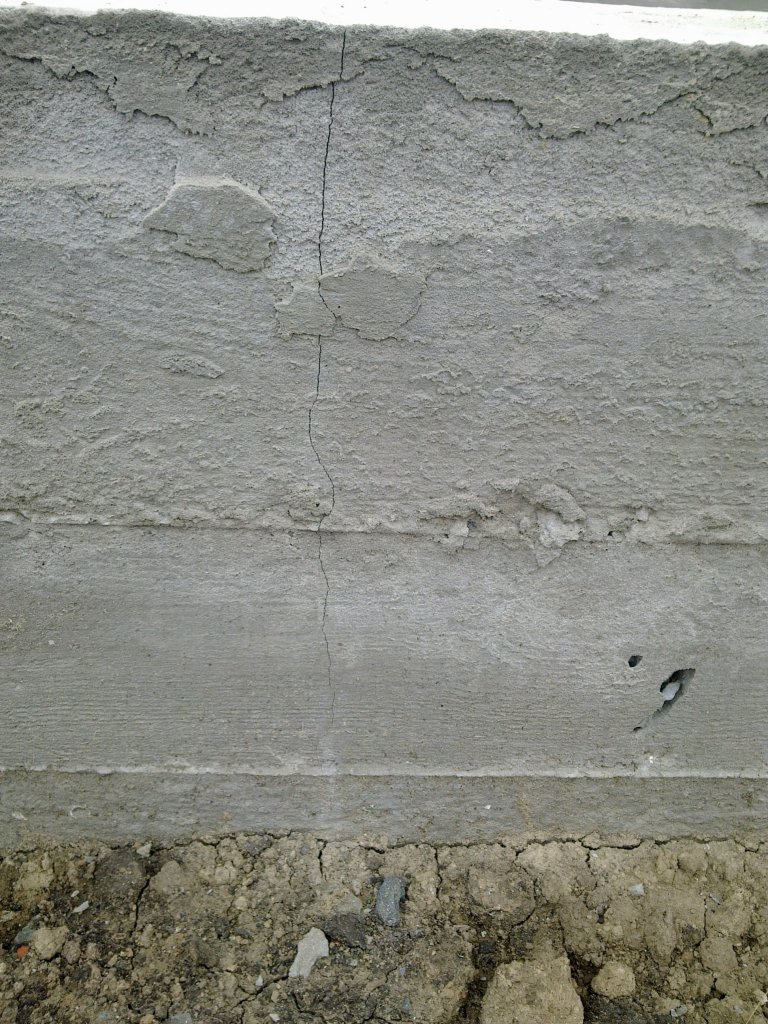
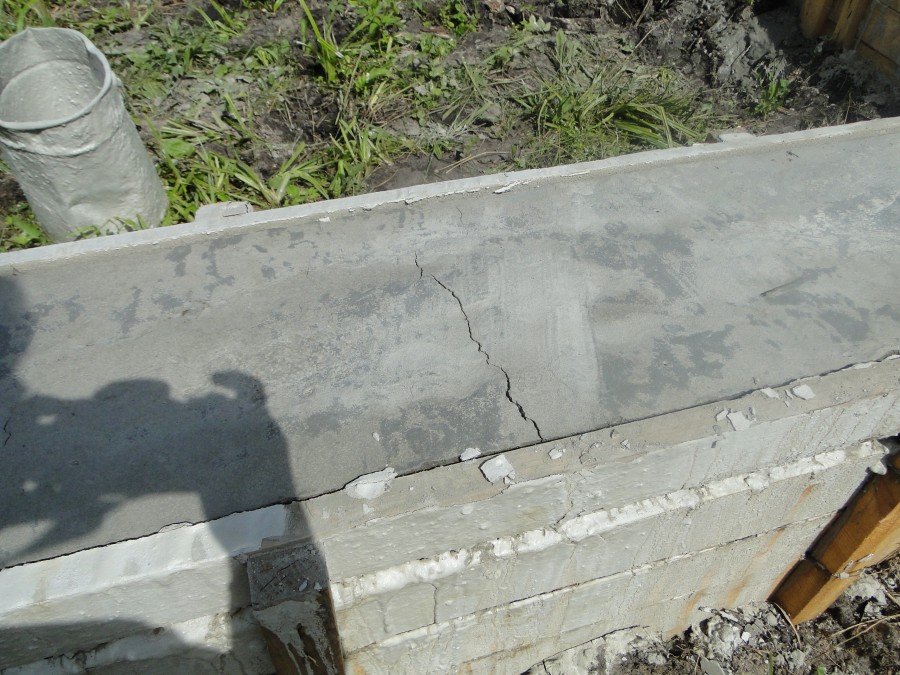
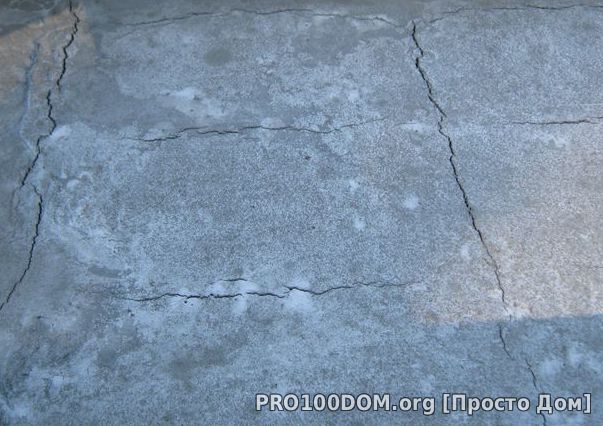
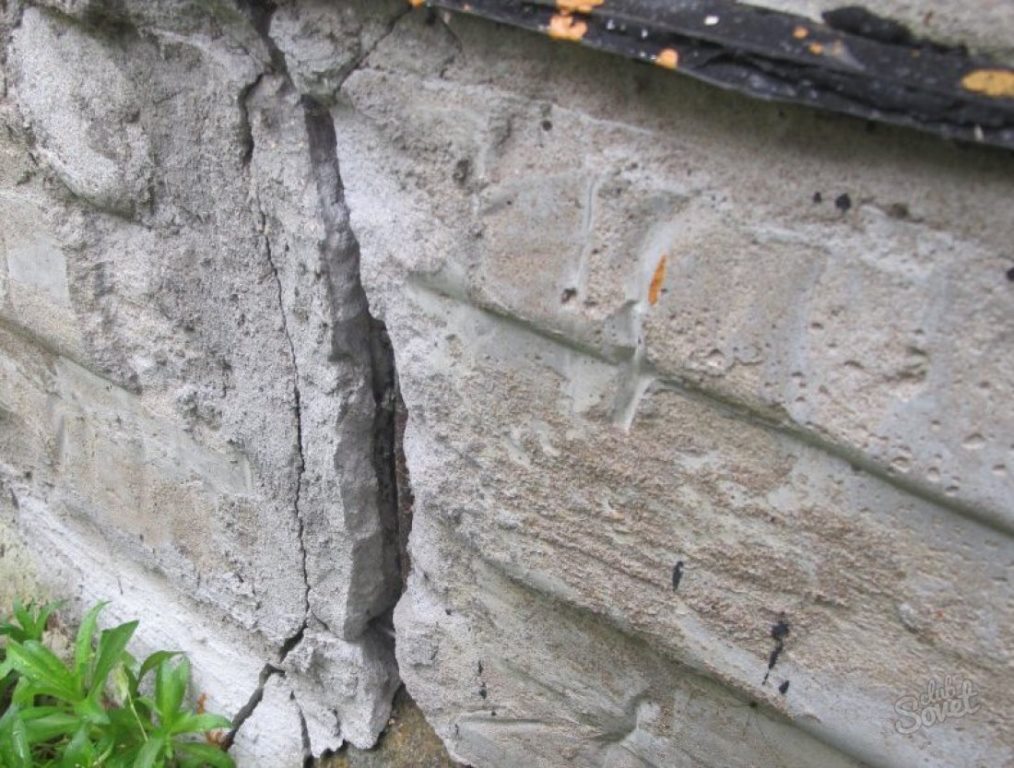
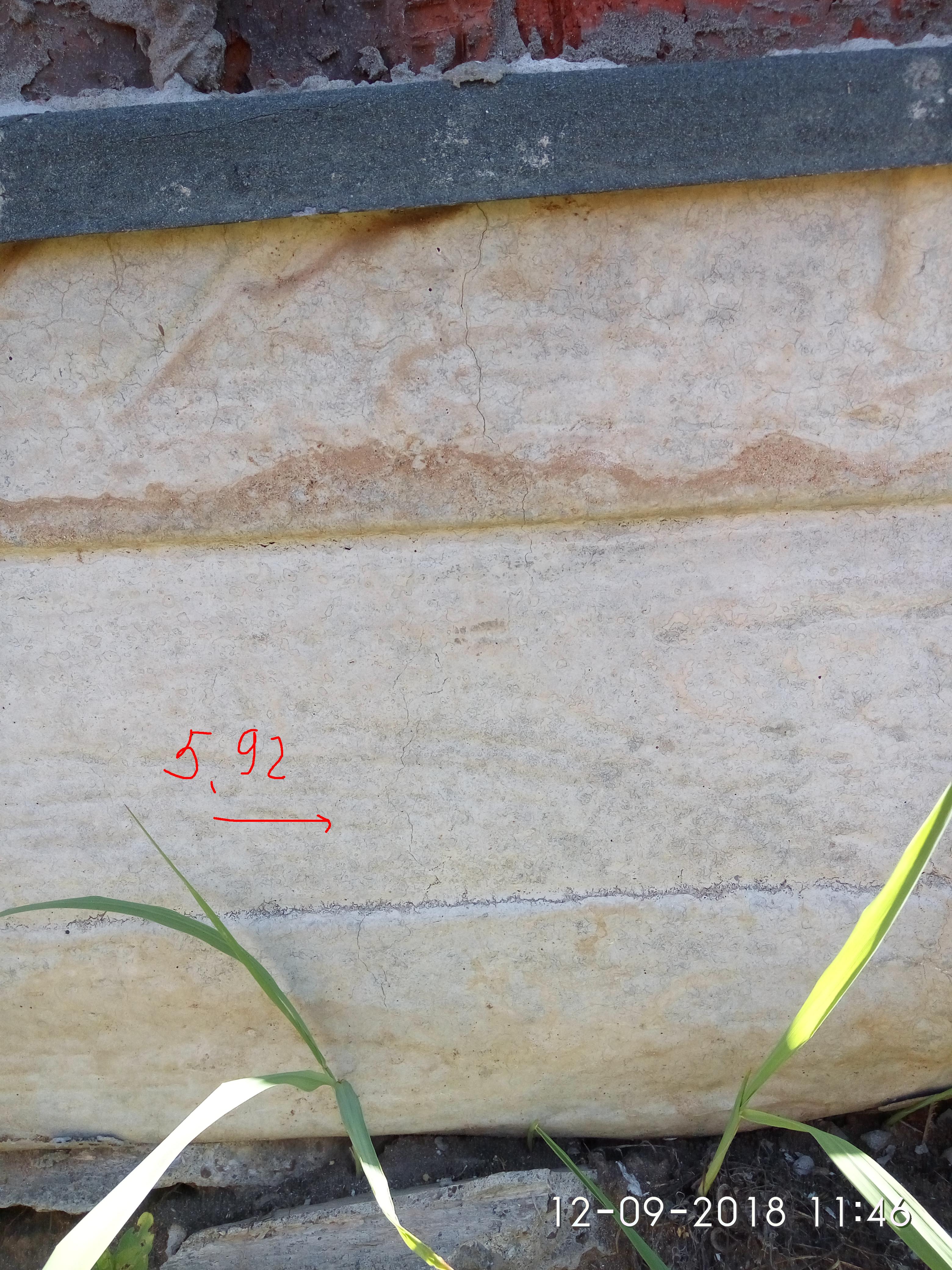
Crack types
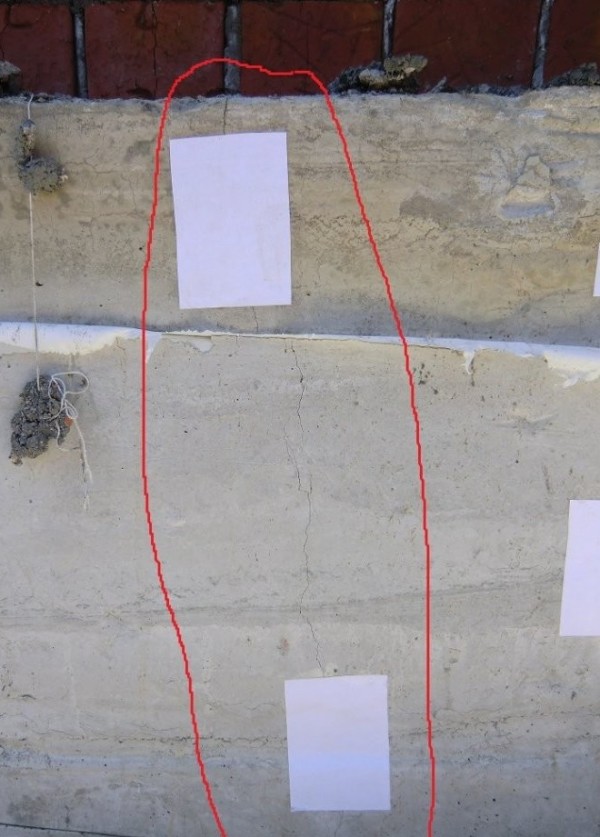
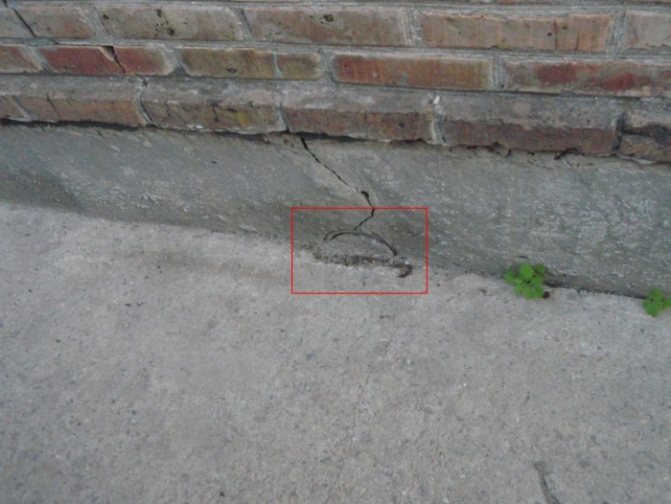
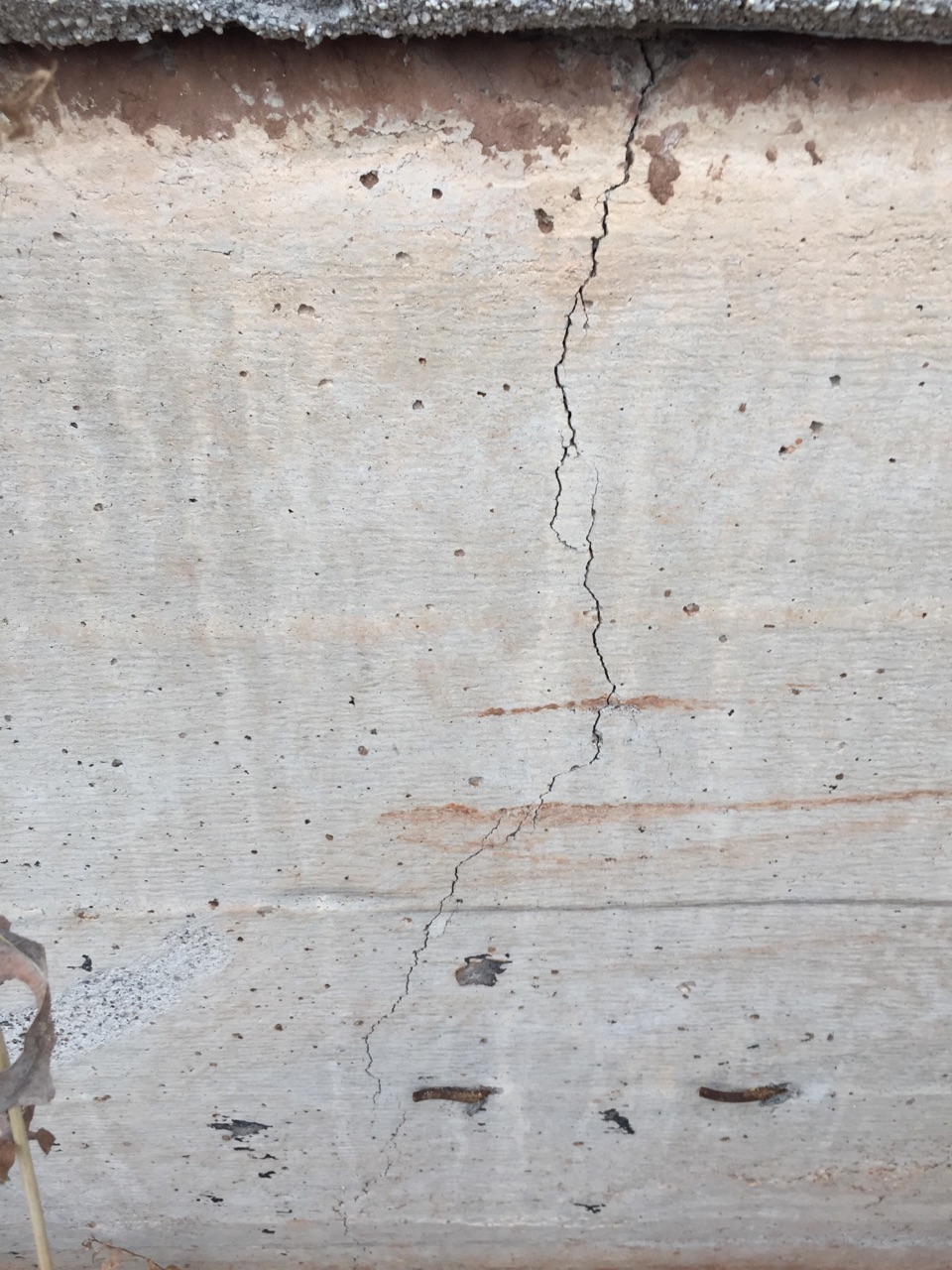
The foundation is cracked. Measurement of the crack size in the strip base of the house.
Cracks are of several types:
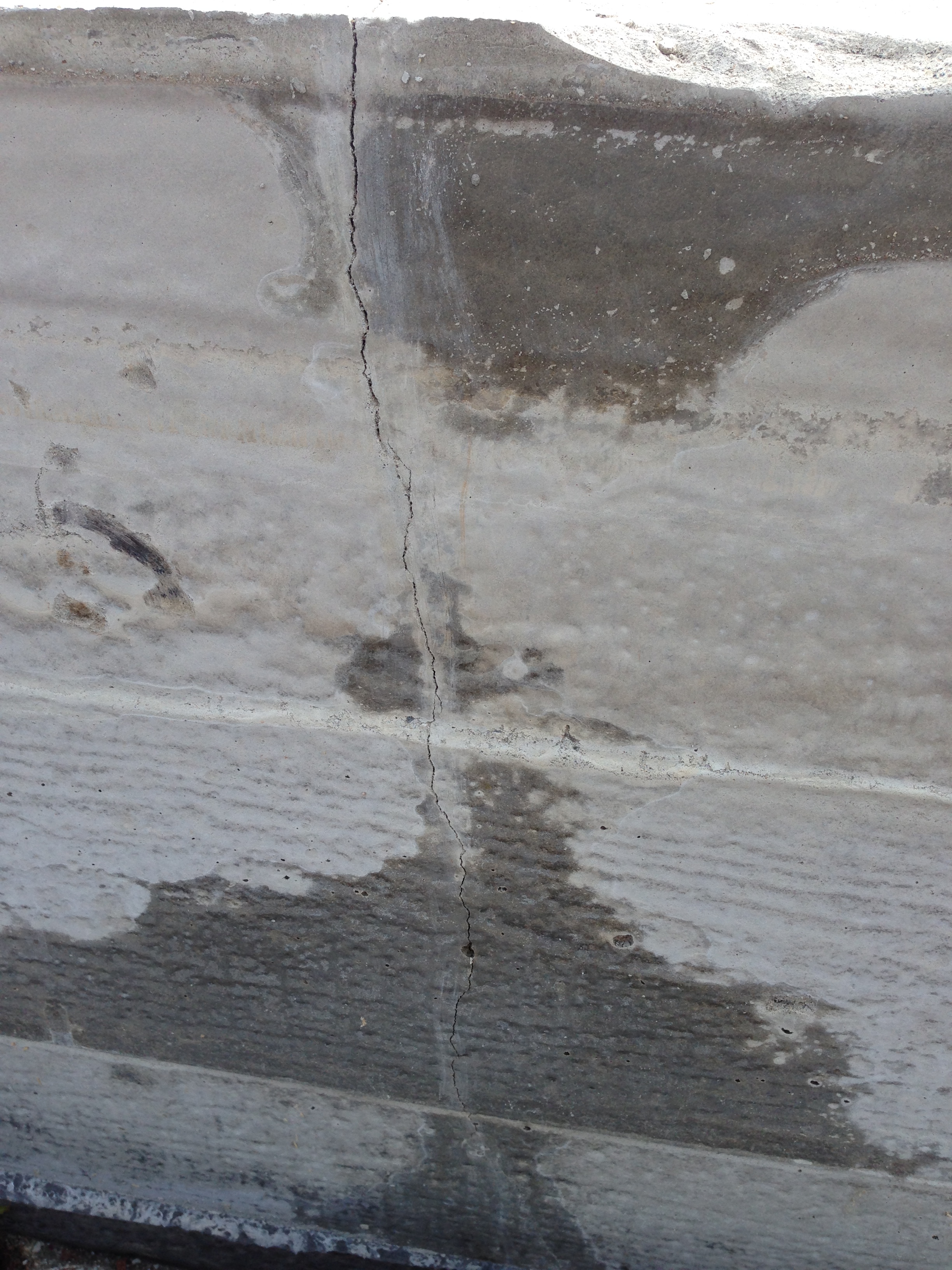
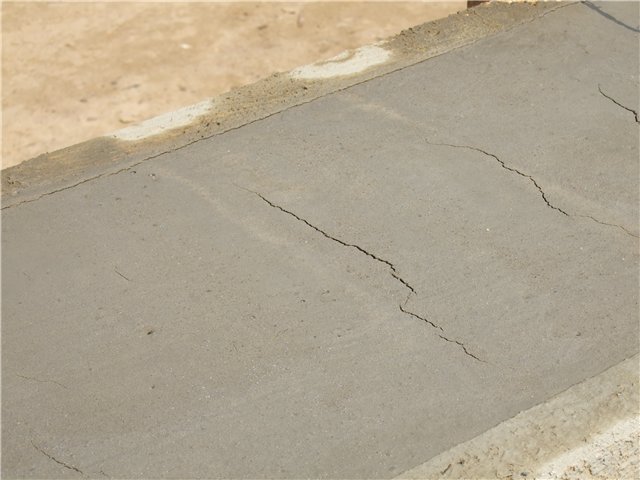
- Hairline cracks. They are small and thick. In most cases, they arise due to deformation of the outer protective layer of the plaster. Such cracks in the foundation of a country house have nothing to do with the deformations of the base; they are eliminated by repeated plastering of the surfaces.
- Horizontal cracks. They arise during the operation of the house, therefore they do not affect the safety of the structure.
- Shrinkage cracks. They arise due to incorrect calculation or errors in the construction of the foundations; the foundation could not have settled. When uneven shrinkage of the foundation sole occurs, then the load on one side of it is higher than on the other. The result will be a slope in the corner of the building, and cracks will grow from the point of shrinkage to the surface relatively evenly.
- If, within a few days after the foundation is poured with concrete, cracks appear on it, this is a violation of the construction technology. In such cases, the damaged area is often dismantled and replaced.
If cracks are found in the strip foundation on an already erected house, then this is already a big problem for the owner. Repairing a strip foundation is an expensive pleasure, because here you need to strengthen the structure, raise individual segments of the base, and only then proceed with the repair. In some cases, only the construction of an additional foundation, its reinforcement remains the only correct decision.
Country houses are often built on strip foundations, as this is cheaper. If the country house is made of wood, then cracks appear extremely rarely due to the low weight of the structure. But if the country house is made of bricks or foam blocks, then cracks will be a frequent occurrence in such structures due to uneven loads.
Features of strengthening stone buildings
To slow down the sediment of the weakened soil under the strip foundation, it is necessary to erect a special pad-belt. For its installation you will need:
- Dig a trench along the perimeter of the strip foundation at an angle of 35 degrees. Its depth should be approximately 40-50 cm, but not less.
- Clean the plinth and the foundation itself from dust and dirt.
- Tap the surface and remove all crumbling and weak concrete fragments.
- Treat the foundation with a primer. It is recommended to give preference to deep penetration formulations.
- Drill 3-4 rows of horizontal holes 60-120 cm apart.
- Hammer anchors into them and weld these elements with reinforcement, the diameter of which will be approximately 10-14 mm.
If the cracks are very deep, it is recommended to prepare local formwork for them and fill the recesses with concrete.
After that, formwork panels are installed around the foundation. You can make them yourself from boards or rent ready-made structures. You also need to make reinforcement, after which you can fill the trench with high quality concrete.
What can be done or methods of correction
There are several ways to repair cracks formed immediately after concreting:
- discrepancy before the start of setting - if defects were noticed on the surface within 2 hours, the concrete can be compacted with a vibrator again to completely correct the situation (the time is calculated from the mixing of concrete at the factory, and not from the time it was placed in the formwork);
- discrepancy after setting - a solution made in a ratio of 3/1 (cement, water, respectively) with the addition of 3-4 drops of plasticizer (detergent is suitable) is rubbed into the cracks, you can use a special repair mixture, which must be bought in advance.
If, within 8 hours from the moment of laying inside the formwork, a network of small cracks is found on the concrete, it can be eliminated by several methods:
- cleaning with a metal brush, foam glass;
- dust removal with a vacuum cleaner;
- putty with a repair compound (for example, CN83 manufactured by Ceresit);
- re-cleaning with foam glass / brush after drying.
Larger cracks in concrete are removed from dust, widened with a spatula, rubbed with compositions with fine-grained sand, rubbed with an abrasive tool. With a high level of groundwater and the possibility of their seasonal rise, injectable compounds, for example Penetron or the like, should be used.
The article discusses the main reasons for the disclosure of cracks in concrete, permissible or making it impossible to operate. Almost any violation of the foundation concreting technology can lead to a sharp decrease in the resource of the structure immediately after removing the formwork. Small cracks in concrete can be repaired in the first days after pouring. To solve other problems, you will need expertise, development of a reinforcement project or dismantling of reinforced concrete structures.
Good publicity
Poor quality raw materials
Cracks may open due to the cement mismatch with the declared quality. Individual developers are looking for cheap prices, often overlooking the packaging. On the bags of a manufacturer that values its reputation, it is mandatory that there are:
- details - you can conduct an examination, file a complaint, at least partially compensate for damage;
- packing period - cement retains its properties if the storage conditions are observed for 3 months, after which it begins to "lose" strength rather sharply;
- the ratio of water and filler - for mortars and concretes;
- composition - the addition of slags, the amount of grinding significantly affects the hydration process, which is important for the thermal regime of massive structures intended for operation in the ground and in aggressive environments.

Concrete cracks on the surface immediately after pouring, including due to plastic shrinkage. The principle of this defect is due to the process of formation of a cement stone:
- the volume of the mixture increases with the release of heat as a result of a chemical reaction;
- the surface cools and dries faster, begins to shrink;
- in the core, the process lasts more slowly, prevents surface compression;
- the result is cracks on all surfaces or individual areas of concrete.
There is no pronounced focus, it all depends on the circumstances. Or there are longitudinal slits with a thickness of 1 - 3 mm of shallow depth. A wet compress in the first three days, made from periodically wetted sawdust, sand, and rags, completely saves from these troubles.