Peculiarities
It is not for nothing that the TISE foundation is called universal, it is designed for various soils, the only exceptions are rocks. The building may have several floors and a reinforced concrete floor, but this will not affect the strength and reliability of the structure. But this does not mean that he has absolutely no flaws.
This structure has proven itself excellently on highly loosened soils, on which other types of foundations crack after a few years. The TISE foundation is appropriate for use in areas located close to railway tracks or the main highway of trucks. An ordinary columnar foundation collapses during vibrations, and for the TISE foundation they are completely invisible.


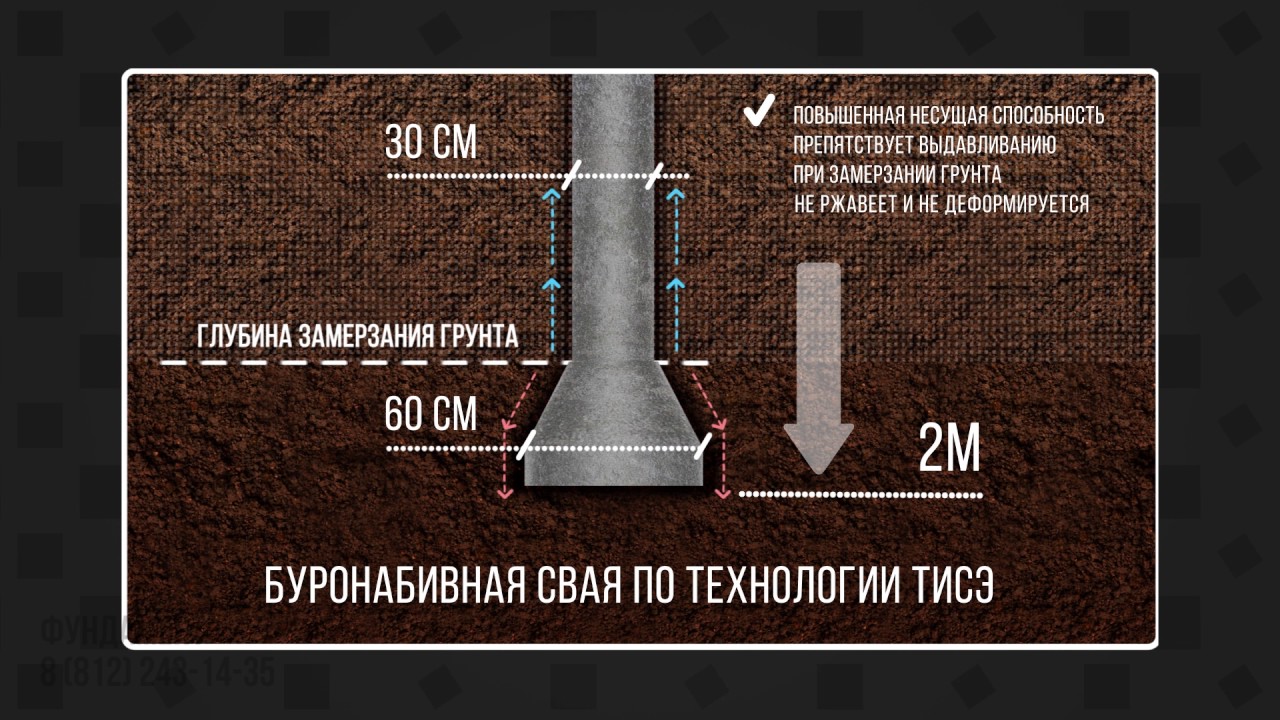
The calculation of the foundation must begin with a thorough study and analysis of the site. After that, the territory is marked and drilled. For this, a manual foundation drill TISE F300, F250, F200 is used - the diameter corresponds to the indicator in the name. The piles can be deepened to a maximum depth of 2.20 meters. There are practically no reviews against the founding of TISE, all the owners were satisfied with their choice.


Description and features of the TISE foundation
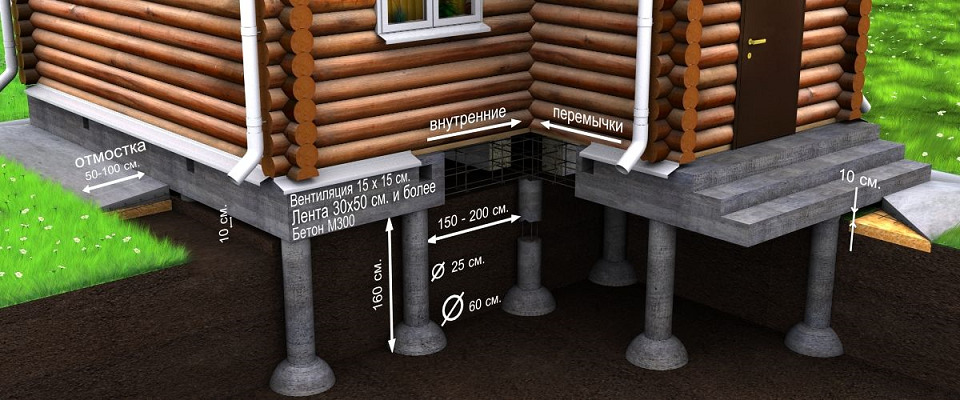
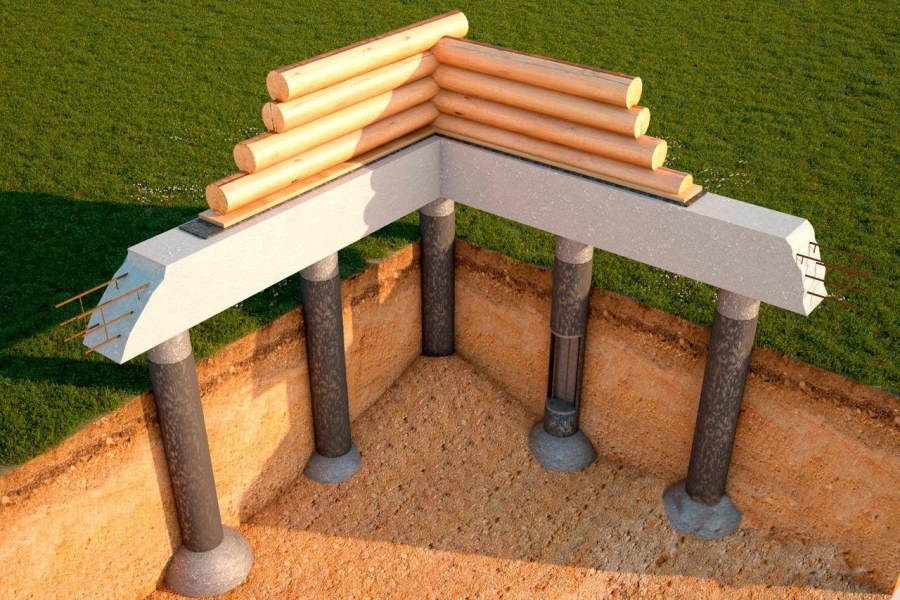
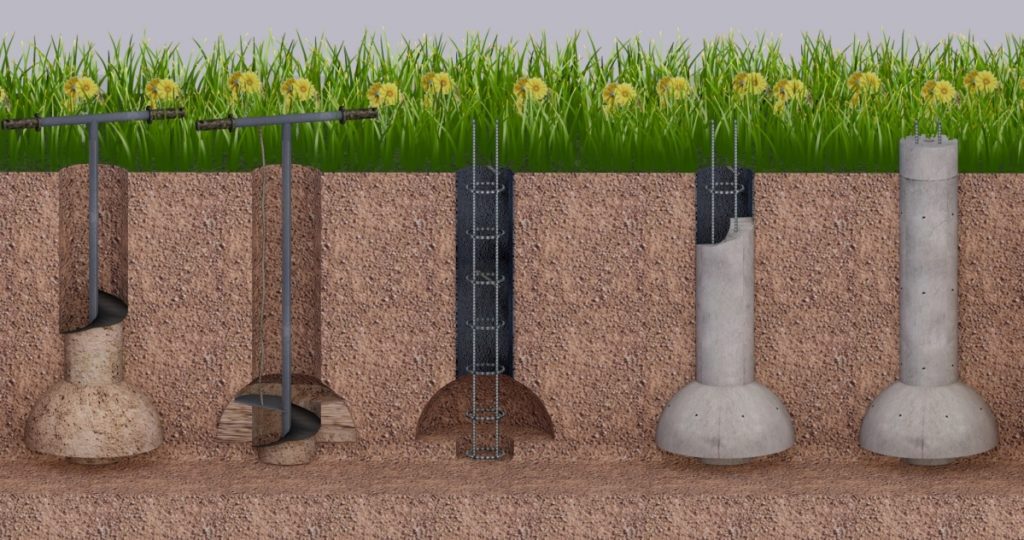
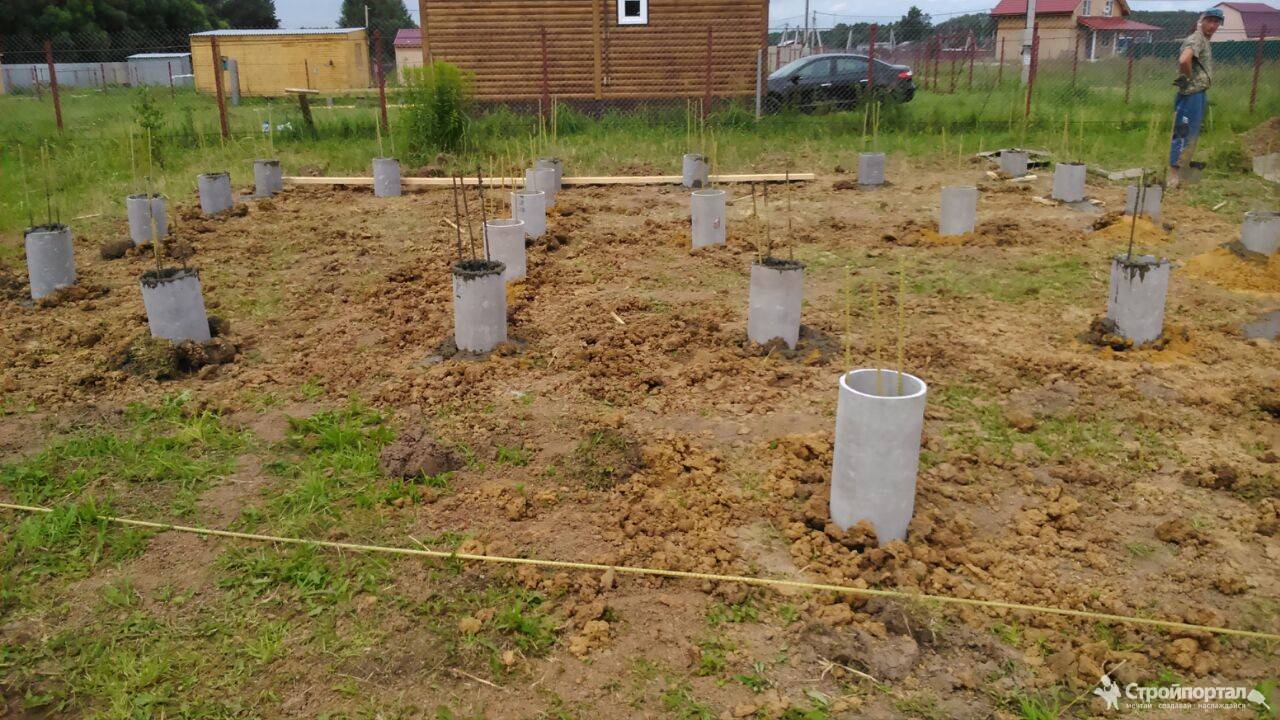
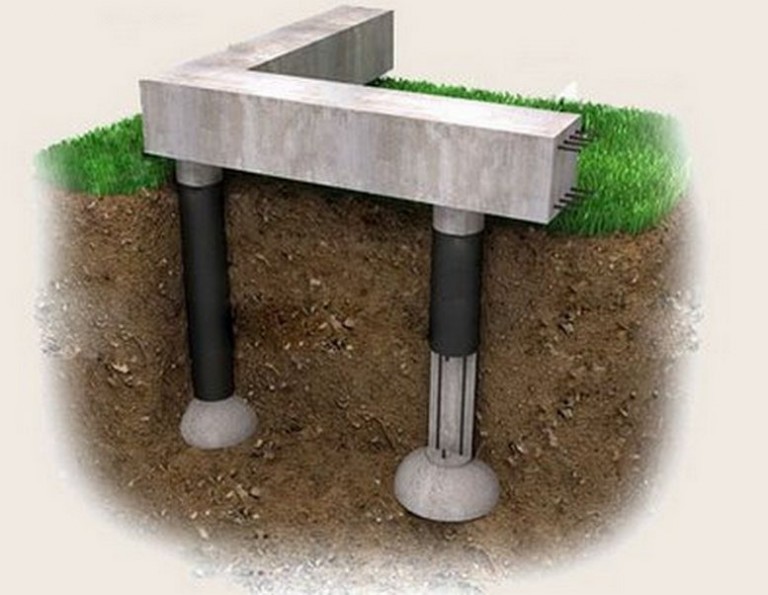
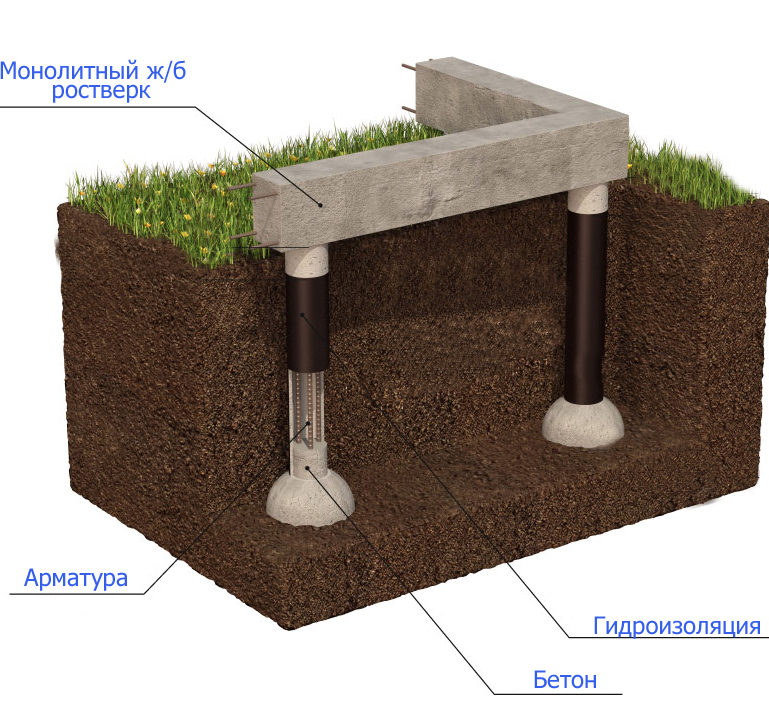
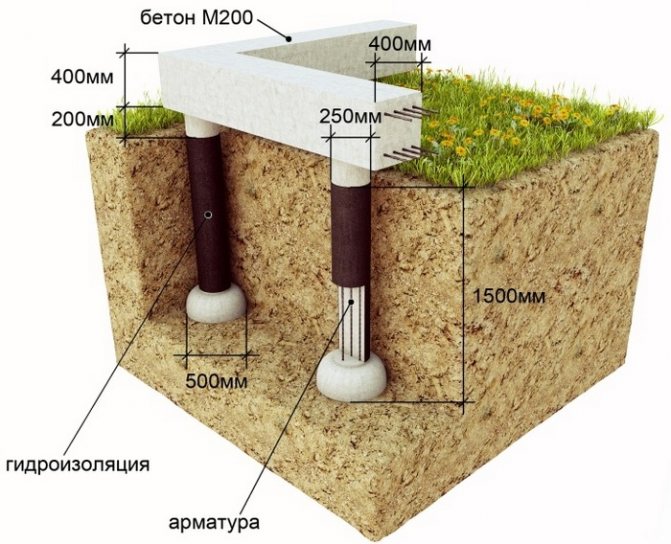
The TISE foundation is columnar. Instead of continuous or tape pouring of concrete, columns from it are dug into the ground. These columns, like ordinary ones, have bases. In other words, the piles are widened from below. This gives stability by interfering with the buoyancy forces of the soil.
The TISE technology of the foundation, if it implies tape filling, is in a truncated form. A strip of concrete is poured over the piles protruding above the ground. You can reduce the width of the tape from the standard 40-50 centimeters to 35-30.
If the foundation tape is in the ground, there is a risk of groundwater rising to the surface. This will make the soil heaving. In addition to its movements, moisture that penetrates into the capillaries of the base of the house affects the foundation.
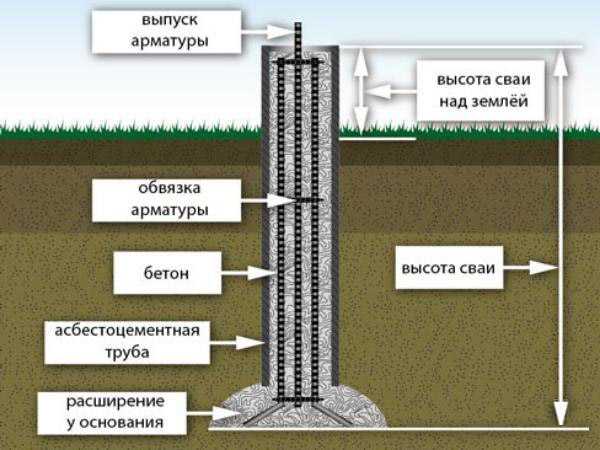
TISE foundation pile
With the onset of cold weather, the water trapped in the concrete freezes, and at the same time expands. Pressing on the walls of the capillaries, ice tears them. The consequences of the changed hydrogeological conditions are especially sad if the foundation was not isolated from moisture by a bituminous composition. The house begins to warp, cracks appear in the walls.
Raising the foundation tape above the ground excludes the action of heaving soils on it. You can, of course, lower the fill below the level of freezing of the earth, but you will have to spend a lot of cubes of the building mixture, suffer with the formwork.
Therefore, piles are placed in place of the lower "floors" of the fill. They rest on the foundations below the freezing line soil, excluding the impact on the foundation of heaving and frozen phenomena. Precisely lowering the posts into the ground saves time and concrete. It is no longer necessary to pour it all over.
Formwork for holes for piles can also be abandoned. On stable soils, it is enough to make a hole with a drill, lay the reinforcement in the recess and pour concrete. Bored piles are obtained. If the soil is heaving, the formwork is done. It can be circular or square, depending on the chosen shape of the foundation pillars.
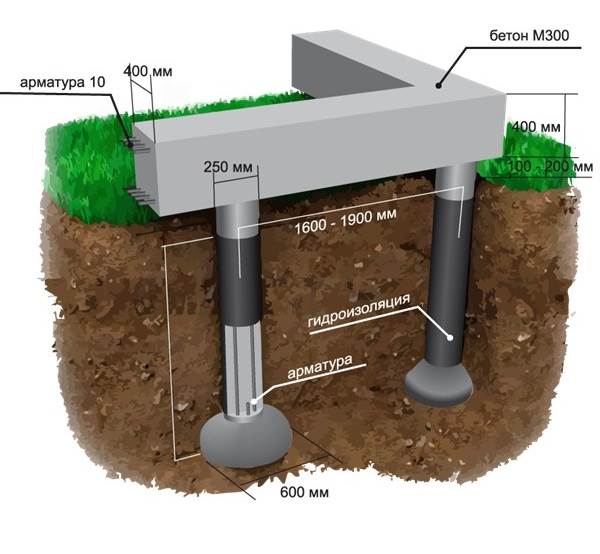
Let us summarize with the thesis that the TISE foundation is universal. It is suitable for all soils, withstands houses up to 3 floors. The material of the walls is not important. It can be a heavy masonry of natural stone or light blocks of aerated concrete.
It is important to correctly calculate the number of foundation pillars and a reasonable location of the piles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a TISE type foundation include:
- low cost;
- no need to use heavy construction equipment;
- autonomy of work during construction: to perform technological operations, no connection to the power grid is required;
- high speed of construction and minimal labor costs;
- the possibility of self-construction by individual developers who do not have experience and special skills;
- ease of supplying engineering communications, even on a fully built facility.
- this construction method cannot be used on swampy areas, watered and silty soils;
- the use of only manual labor: the construction process because of this becomes very difficult on rocky and hard soils. True, now they have begun to produce TISE drills with a mechanical drive powered by a light gasoline engine;
- there is no way to arrange a basement under the whole house;
- a device for a blind area of increased width is required.
The aforementioned disadvantages of the TISE foundation are overridden by pluses, so this technology can be considered the most economical and progressive for private construction.
Calculation of the TISE foundation
The calculation methodology is no different from the calculation in the general case. The load from the house is calculated and then compared with the total bearing capacity of the planned number and diameter of piles.
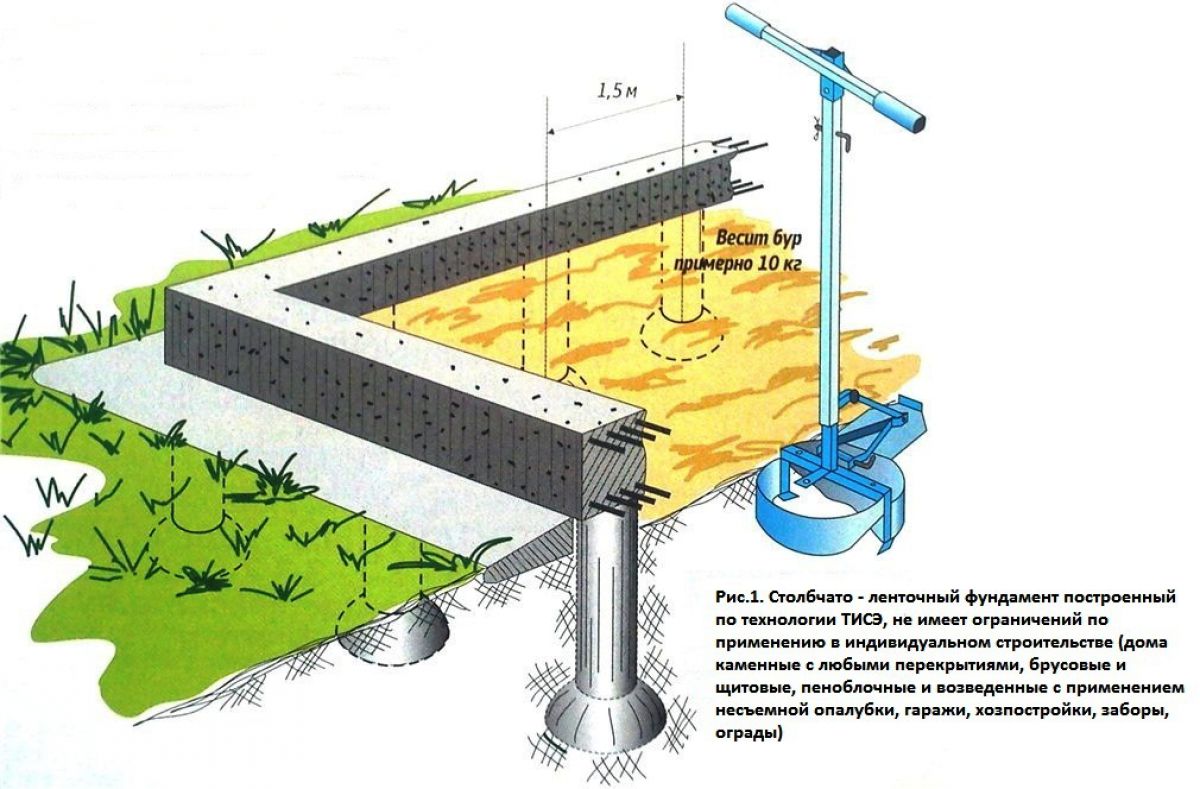
First, place piles on the plan of the house. They must be in the corners and at the junction of the walls. If the distance between the piles is more than 3 meters, intermediate ones are placed between them. So place all the supports on the plan, adhering to the rule:
- the minimum distance is 1.5 meters;
- maximum 3 m.
Then you calculate the load from the house. To do this, you first need to calculate the weight of the house (all building materials + furniture, plumbing, heavy household appliances).
Average loads from different types of house nodes
If we talk averaged, then for buildings made of brick or shell rock for each square of the area, you can take 2400 kg, from light building blocks (foam concrete, aerated concrete, etc.) - 2000 kg, from wood and frame frames - 1800 kg. These averaged rates can be pre-guided. If you decide to take everything seriously, you will need to follow the entire methodology: count the materials of walls, ceilings, roofs, finishes, etc. Since technologies and materials can be used differently, the discrepancies can also be significant.
The resulting value is multiplied by a correction factor - 1.3 or 1.4. This is a margin of safety. The resulting figure is the load that will need to be transferred through the piles.
Now, according to the table, you select what diameter the pile should have so that it can transfer the required weight.
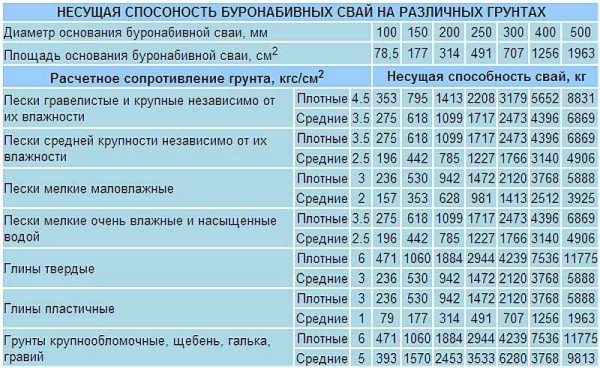
Bearing capacity of piles of different diameters in different soils
If the planned number of columns with the expansion of the selected diameter can transfer the required load, you do not need to redo anything. If the transferred mass is too small, it is necessary either to increase the number of piles or to make a "heel" of a larger diameter.
Advantages and disadvantages of TISE
The TISE foundation allows you to save money and labor costs, since the method involves reducing the volume of soil and concrete work, building material, and also allows you to do without the involvement of labor.
For example, using the dimensions of the foundation of a house 5 × 10 m, you can calculate the consumption of building materials. For a traditional strip foundation 0.70 × 0.40 × 30 m, concrete with a volume of 8.40 m3 will be required, and for TISE with its own hands, only 2.00 m3, based on the calculation that 20 piles of 1.20 × 0.60 m are needed.
In addition to the economic benefits, reviews from developers also help highlight the following advantages of the technology:
- no need to use expensive equipment for turnkey construction, thanks to the TISE 2 and TISE 3 technology (except for the drill);
- autonomy of work; construction is carried out without being connected to the power grid, therefore it can be carried out even in the field;
- reducing the time spent on work;
- the TISE foundation is available even to those who have no experience in building a house;
- the ability to dissolve communications even in an already built house;
- Yakovlev developed a universal method suitable for all types of soils (heaving, with a close location of groundwater, in seismological regions).
Demonstrating obvious advantages, TISE technology also has disadvantages. Reviews of individual developers reveal the following disadvantages:

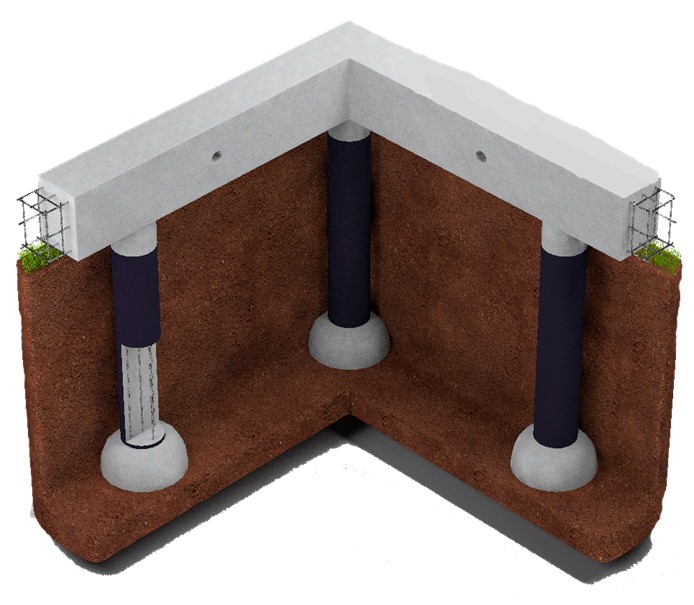
Ground and underground part of the TISE foundation
- the inability to work on swampy soils, where the columnar foundation can simply drown or break;
- the complexity of drilling on stony soils, which increases labor costs at the initial stages of construction;
- some call such disadvantages as a decrease in the basement area due to the inability to equip it under the whole house;
- the foundation based on TISE technology requires a wide blind area.
Despite the disadvantages, the method proposed by the designer Yakovlev remains the most environmentally friendly and convenient for private construction of a turnkey house.
Foundation calculation
The calculation of the foundation gives the developer an idea of how many supports he will need, with what step they will be placed and how deep they will go into the ground. Before starting to determine these indicators, it is necessary to identify what the bearing capacity of the soil is in relation to the dimensions of the future house. To do this, you need to make a calculation:
- building weight;
- its operational load;
- snow loads;
- bearing capacity of the pile.
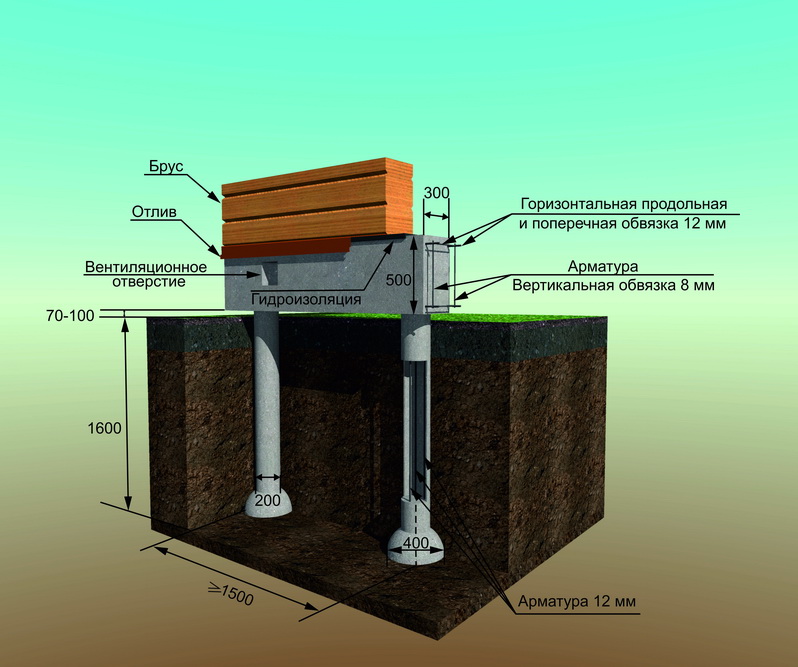
To calculate the weight of the house, you need to add the mass of the foundation, walls, floors and roof. The weight of the foundation is determined by roughly determining the weight of the building materials spent on it, based on the volume of the piles.
The calculation of the weight of the walls is determined by the load of the building material. When using TISE 2 formwork, add 270 kg to the total weight, while using TISE 3 formwork - 400 kg.

Ready foundation TISE
Overlappings give different loads, depending on the type: wood - up to 100-150 kg with insulation; reinforced concrete - 500 kg, concrete slabs with voids - 350 kg. For 1 m2 of roof there is a weight of 50 kg for slate roofing, 89 kg for ceramic tiles and 30 kg for sheet steel.
To calculate the operational load that the TISE foundation receives, it is necessary to determine the approximate weight of all household appliances, the number of people living, communications, etc.
For pitched and gable roofs with a slope of 25˚, the load factor is - 1, with a slope of 26-60˚ - 1.25. Adding all the indicators together, and multiplying the number by a factor of 1.3, we get the calculation of the total weight of the house.
The calculation of the bearing capacity of the pile is determined depending on the type of soil, the value of its resistance per 1 m2, as well as the diameter of the support, which the developer plans to use when equipping the foundation using the TISE technology on a turnkey basis.
For example, on loam, the soil resistance index is 3 kg / m2. For a pile with a diameter of 250, the bearing capacity will be 1.5 t, for 500 mm - 5.88 t, and for 600 mm - 8.40 t. The best performance is demonstrated by piles with an average thickness of 500 mm on all types of soil.
To calculate the drilling depth, it is necessary to determine the level of soil freezing and add another 20 cm to the number. To equip the TISE foundation, at the final stage, the step of installing the pillars is calculated in this way. For example, there is a house 5 × 10 m, the soil of the massif is loam, the weight of the house is 350 tons, the dimensions of the perimeter of the house are 30 m.
The bearing capacity of the clay is 6 kg / cm2. If the expansion of the selected base is 600 mm, then one pillar can support 17 tons. We divide 350 tons by 17 tons and get 20 piles. The perimeter of the house is 30 m, which means that the step of installing the supports is equal to one and a half meters.
Technology features
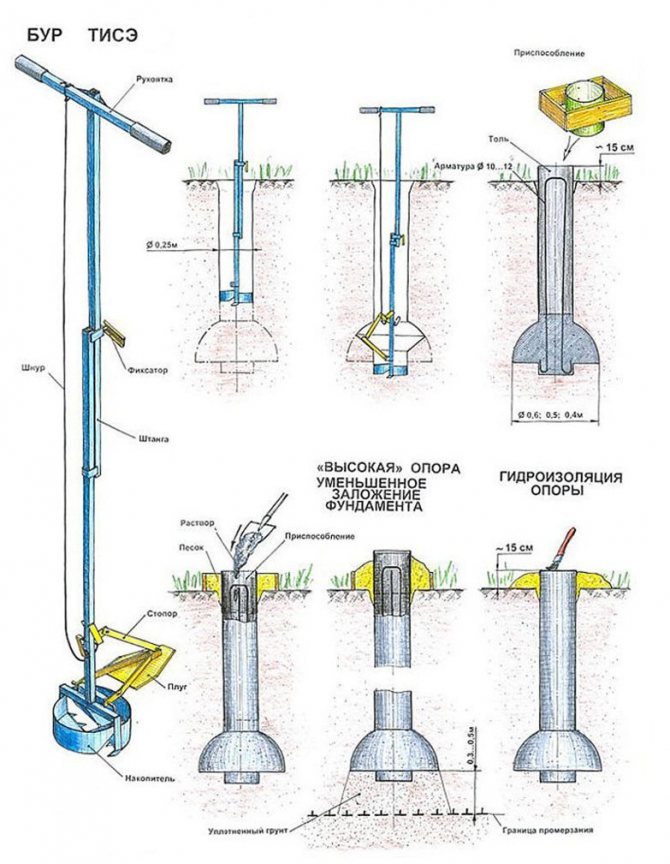
The abbreviation TISE stands for “technology of individual construction and ecology”. This construction technique was developed and patented by the engineer R.N. Yakovlev, who, in addition to the technology itself, also created a special working toolkit - a hand drill with a knife of a special shape.
Piles-pillars
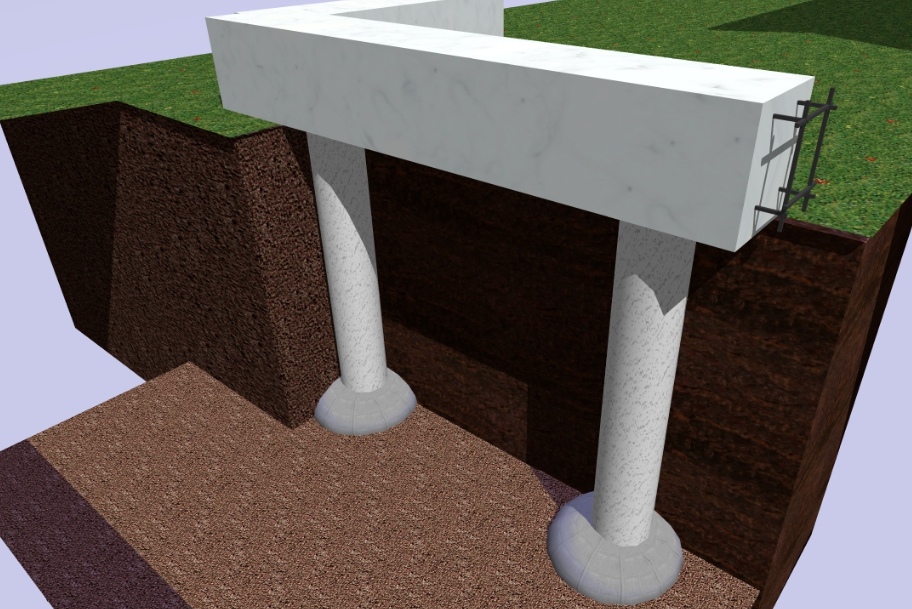
This technique is inherently hybrid, incorporating the advantages of columnar and pile technologies. Technically, it belongs to bored ones, since the construction of the TISE foundation is carried out by pouring concrete into a pre-drilled well.
A distinctive feature of the TISE pile is that it has a peculiar design with an expansion in its lower part. Other piles, designed for driving, twisting, and cast using the bored technique, do not have such an expansion. This expansion-sole plays the role of a support base and brings the Yakovlev pile closer to the support of the columnar foundation. It increases the support area of each pillar, thereby reducing the specific pressure of the building on the ground.
TISE foundation device
Due to the fact that the device of the supports is made exclusively with the help of the muscular strength of a person, they have a limited bearing capacity. It is not recommended to install overly massive buildings on it - brick houses or buildings made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
The TISE foundation is perfect for a frame house; you can also install a garage, a bathhouse or other not too massive structure on it. In addition to distributing the pressure of the building's weight on the ground, the pile base also acts as a kind of anchor.
Application area
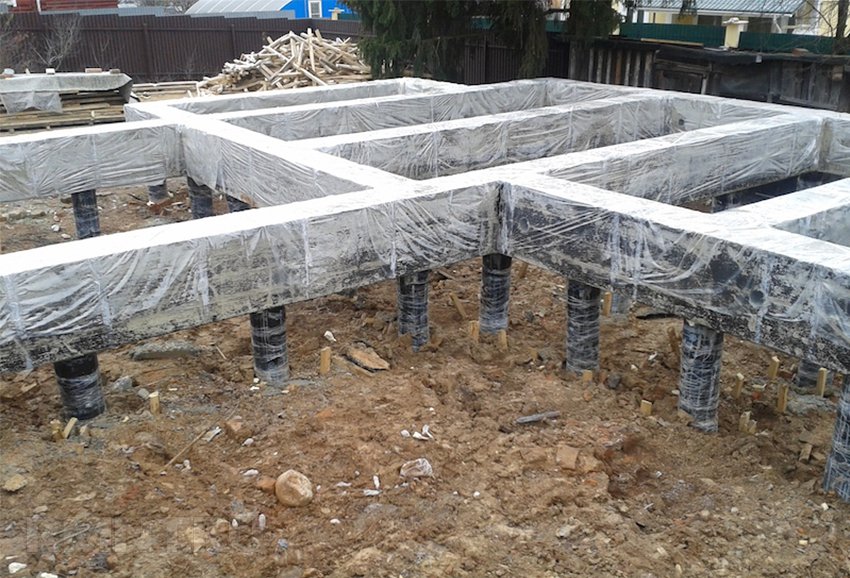
Construction of the TISE foundation
These advantages of the TISE pile foundation determine the area of its use. These are weak swampy soils, as well as clayey, loamy and sandy loamy soils with a high level of moisture saturation. It is these soils that are most susceptible to winter swelling.
Usually, when building houses on water-saturated soils, various expensive technologies are used to combat the effect of swelling.
- The device is an effective drainage system. Drainage is designed to drain groundwater from the base of the building. The work is associated with extensive earthwork, excavation, laying branch pipes, filling trenches with coarse material, etc. The disadvantage of a drainage device is a large expenditure of time and effort, as well as high financial costs.
- Use of a monolithic slab as a bearing support for a house. A shallow foundation slab is poured over a sand and gravel cushion that softens the pressure of frozen soil. The absence of a rigid coupling between the base and the soil gives it the opportunity to "float" - to rise and fall with the ground, avoiding deformation and destruction. Disadvantages of the slab foundation: it is intended for small buildings with low weight. If it is necessary to erect large buildings, for example, a two-story residential building, then the costs of pouring the base plate increase exponentially.
- The use of piles as bearing supports. In this case, pile technology is the most preferable. The piles are buried below the level of freezing of the soil, which reduces the heaving forces acting on the base of the building. Recessed piles allow you to optimize the construction process on difficult soils, speeding up and reducing the cost of work due to the absence of expensive excavation work. But this technology also has its drawbacks: in some cases, piles can be pushed out by frozen soil. This is due to the fact that, freezing, the expanded soil grasps the upper part of the pile and carries it upward.
TISE technology allows avoiding the possible extrusion of the pile. The extension located at the bottom rests against the layers of soil lying above, and the frozen soil, rising up, simply slides along the surface of the pile. The main condition: TISE foundation must be buried below the level of soil freezing, otherwise the support will simply be squeezed out from below.
TISE foundation under the house
This indicator may have different meanings for each region. You can find out the level of freezing for a certain city from the summary tables of SNiP.
Equipment for TISE technology
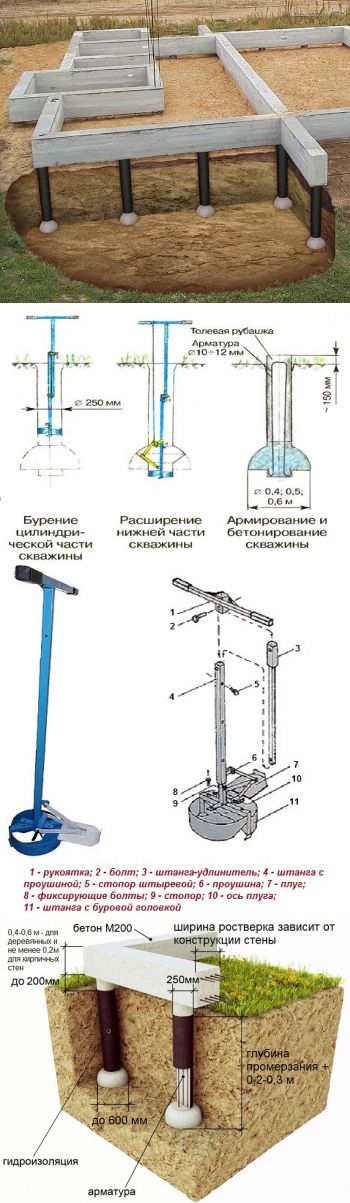
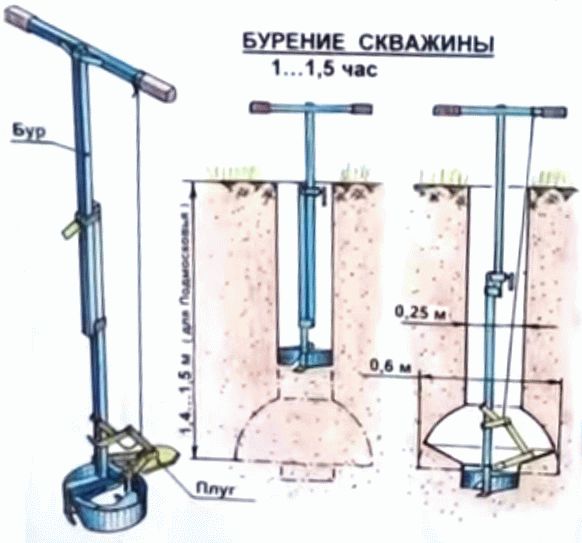
You can find a tool for performing work using this technique in construction markets, in specialized stores and on network sites. Two types of drills are offered - TISE - F and TISE - FM, each of which has three working diameters - 200, 250, 300 mm. The first type has one drilling blade. The second, more productive, is two. It does not cost much more. Both types are successfully used both for the construction of the foundation and for some agricultural work on the site.
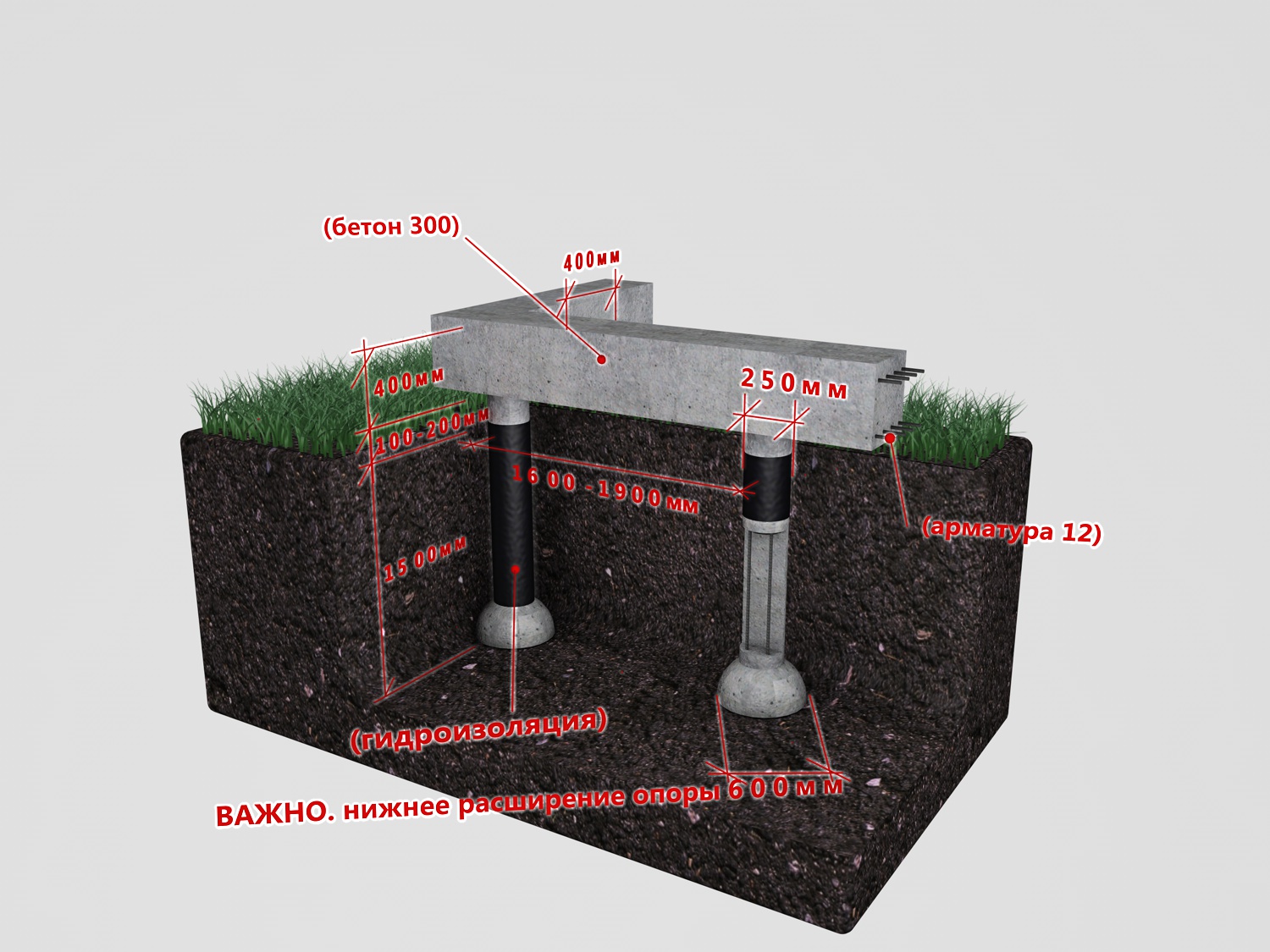
The larger the diameter, the more weight the structure can support. A pile of 200 mm has a base of 500 mm. Support 300mm - 600mm. It is easy to calculate how economical the application of this method turns out to be. The area of a circle of 300 mm equals approximately 70700 mm². If the base is 600 mm, this figure increases to 282800 mm². When the diameter is doubled, the area quadruples.

Standard complete set
The manufacturer offers a ready-to-use tool. The main product consists of the following elements:
- Handle for rotation.
- Bar set. The main and additional section, which allows you to adjust the drilling depth.
- Ground elevator. With its help, the collected soil rises upward.
- Swing drill for expanding production.
The basic kit can be supplemented with a cover, spare parts and formwork elements. With the help of TISE equipment, all issues of foundation construction are solved. Possible well depth is 2.3 m when expanding at the base. Without the last operation, you can create a hole up to 3 m. The drill is made using a special technology and is washed out in a telescopic rod after the plow has passed. When the set depth is reached, the cutting part extends and expands.
The collection mechanism allows the waste soil to be efficiently delivered to the surface. Recently, the demand for an additional drive has increased. Many sellers offer to equip the device with a gasoline engine, which significantly reduces labor intensity. The costs are paid off by the speed of the operation, less fatigue of the performer and do not significantly reduce the economic benefit when using the TISE technology.

Advantages and disadvantages of the TISE technology foundation
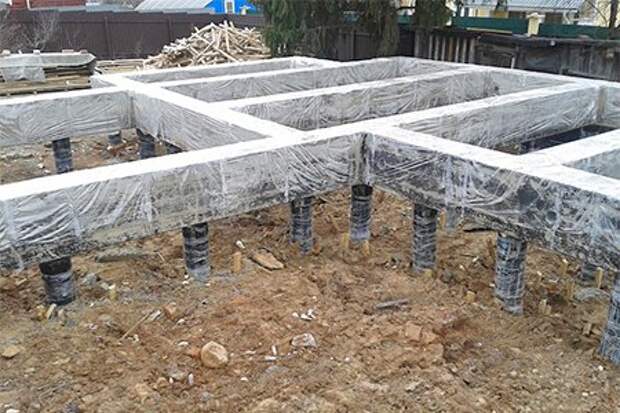
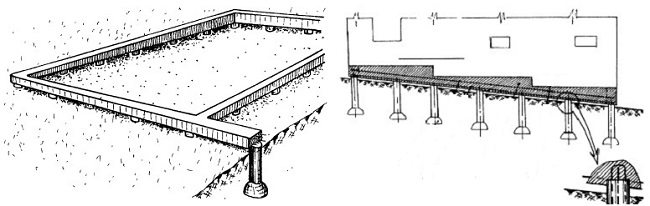
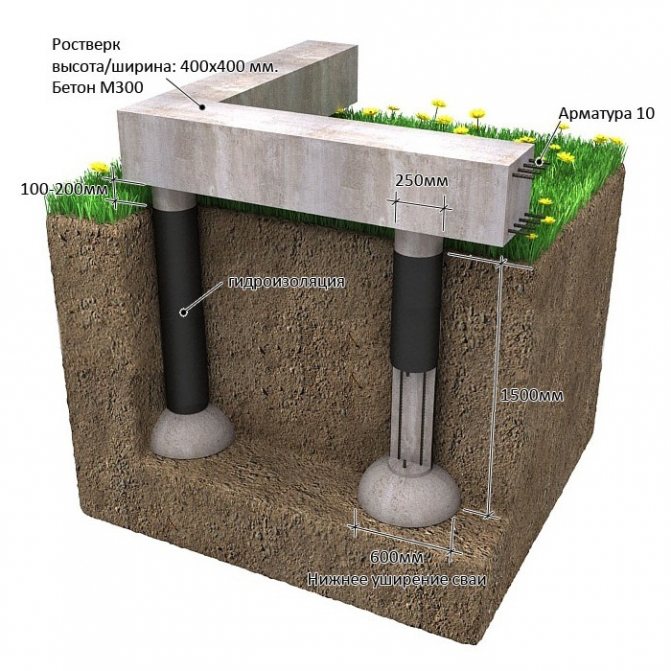
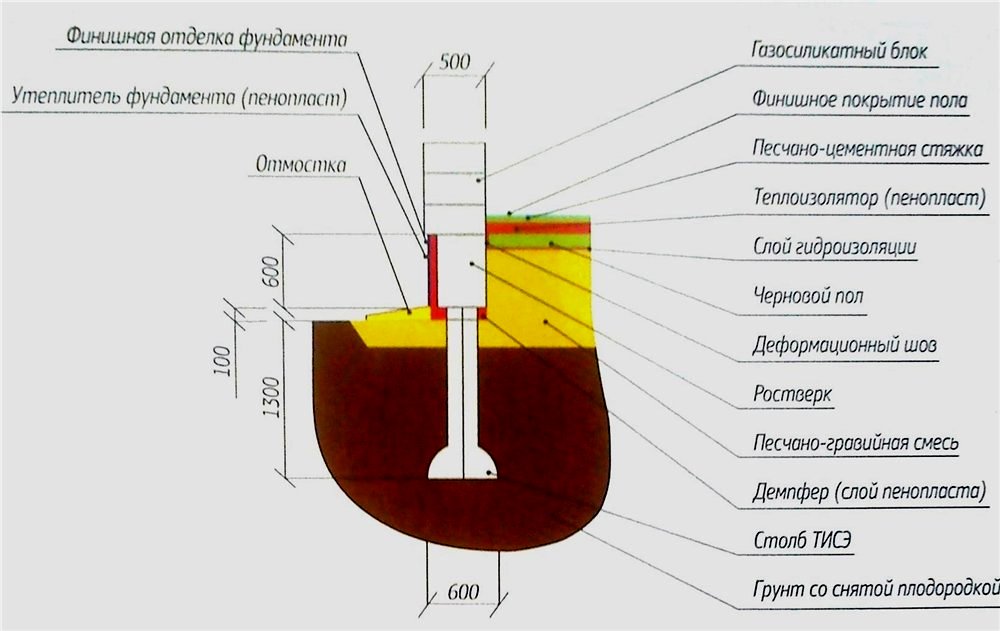
TISE is a pile-strip structure, the erection of the support structure is carried out in the form of a square or rectangle on piles.
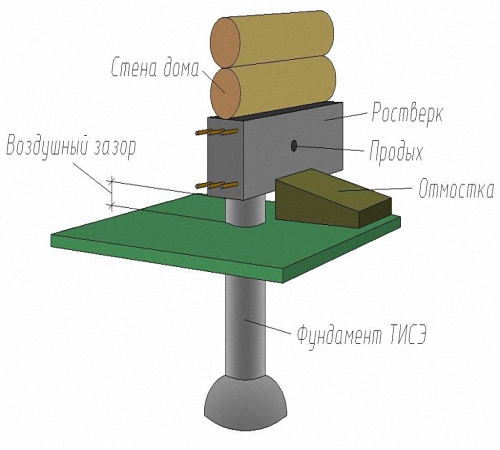
The concrete grillage that connects the piles does not touch the ground. This position of the foundation does not allow the soil to press on itself at any time of the year.
Advantages of the TISE foundation
- An economically advantageous part of the building;
- Reliable construction;
- Fast erection;
- Simple installation;
- Can be built in winter;
- Environmentally friendly design;
- Construction on seismically unstable soil is possible;
- It is possible to build a support at different levels of groundwater.
TISE foundation components:
- Reinforced concrete grillage;
- Reinforced piles.
The lower part of the foundation pile has the shape of a hemisphere - this is a big plus, because this design helps to increase the support area and increase the load-bearing properties. This support structure is used in the construction of houses of different types. Such a foundation does not shrink and is suitable for frame houses, as well as for the construction of stone houses.
The lower part of the pile in the form of a hemisphere has the property of resisting extrusion from the soil, which can be in heaving soils.
The strip part of the TISE foundation is called a grillage - it is made of reinforced concrete. Pouring of this part of the support is carried out at a certain distance above ground level. Due to the gap from the ground to the structure, the heaving does not act on the supporting structure.
TISE foundation: work order
There are some recommendations in the TISE methodology itself:
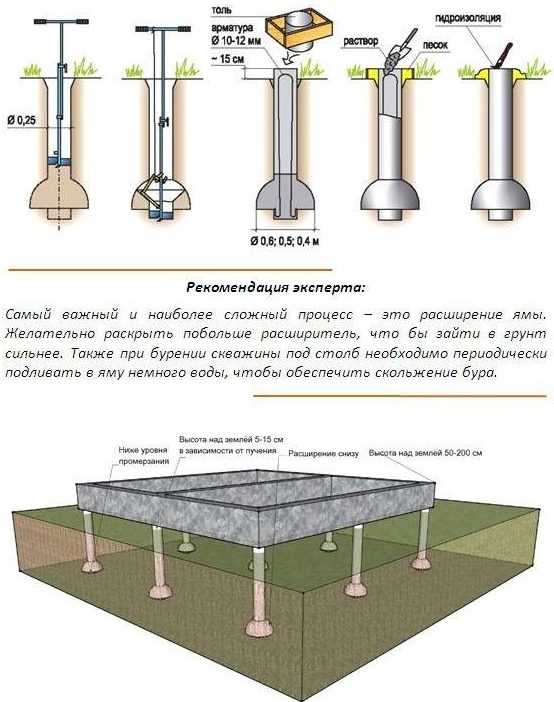
- To deepen the piles approximately 20 cm below the freezing level for the region.
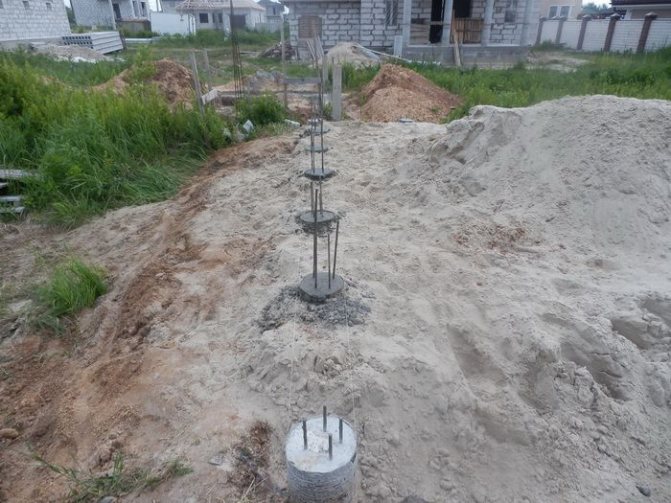
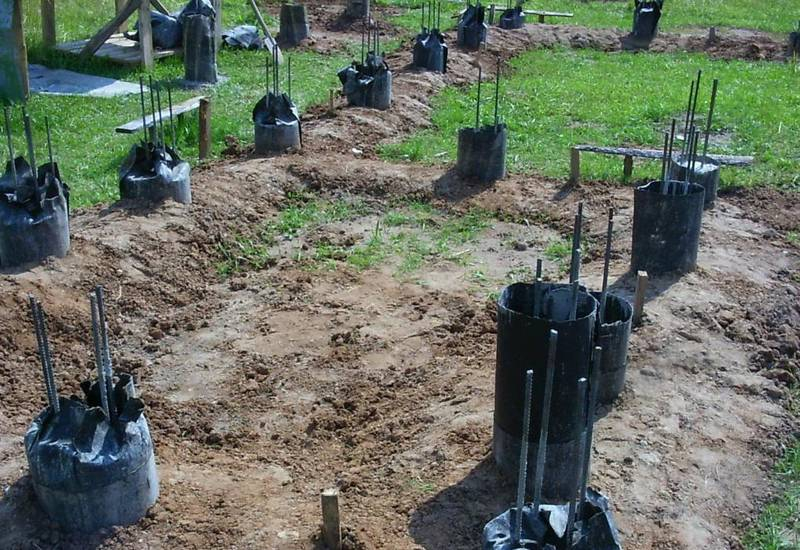
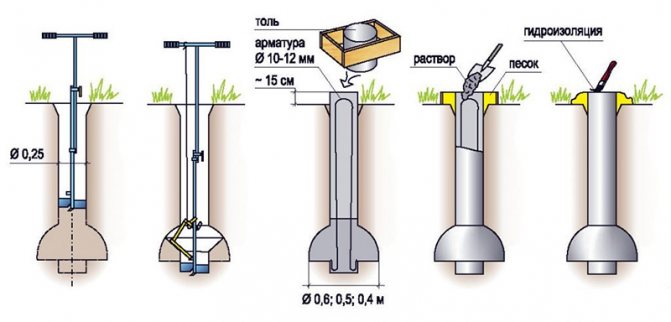
- For the reinforcement of the pile, four rods of ribbed reinforcement with a diameter of 10-12 mm are used.The rods should be placed no closer than 4 cm from the edge.
- If the slope of the site is more than 10%, the release of the reinforcement must be connected with the grillage.
-
Use either a high grillage - raised 150 mm above the ground, or make a pile-strip foundation with a shallow-buried strip. The second option is used for heavy buildings, the weight of which cannot be transferred by means of piles, then a tape is made, which increases the transmission area.
- You should not do a sand bed at the bottom of the well: it will not have a normal density and will not work.
- Use concrete vibrators to keep them secure. Manual vibration with a rebar is ineffective. If the household does not have such a device, rent it for the time of pouring the foundation: the strength increases significantly.
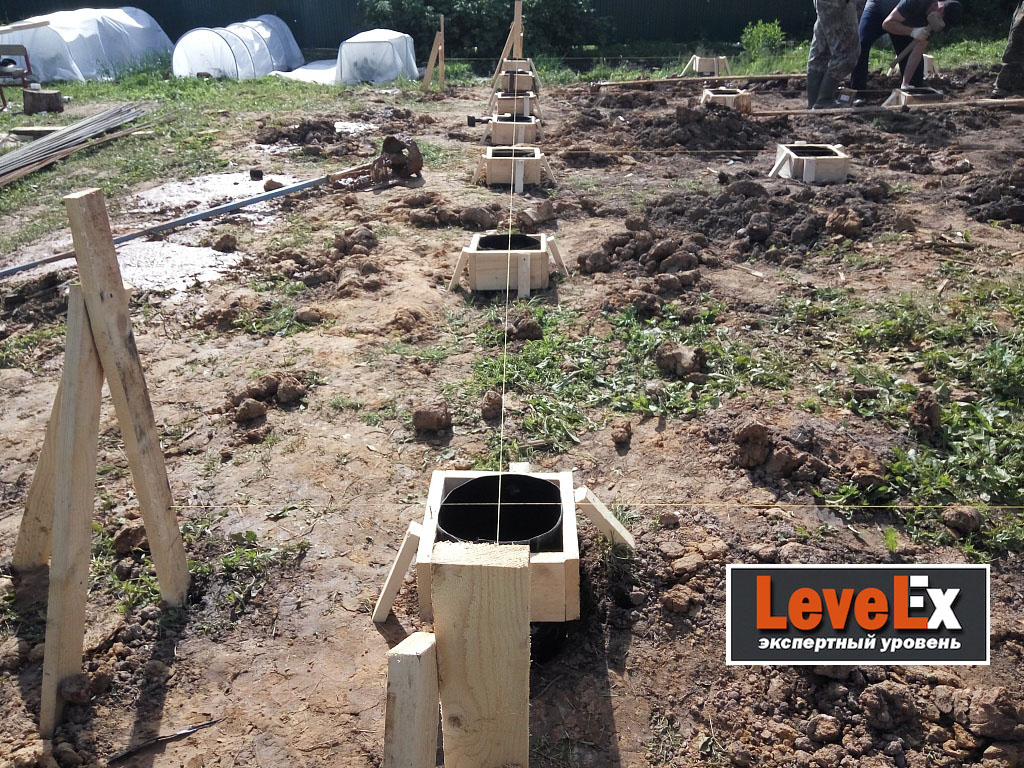
- The pile formwork is made of roofing felt, roofing material or glassine rolled into a tube. It is better that it has several layers (2-3). They do not need to be fastened with anything: they twisted a little less than the diameter, inserted. The height of this formwork is 15 cm above the ground level, regardless of whether there is a slope on the site or not. It is advisable to sprinkle this protruding piece with sand or soil, and compact it around. This will prevent the roofing from collapsing when pouring concrete.
TISE foundation is a subspecies of pile-grillage foundation. And the technology of its manufacture is no different. The whole difference is in the drilling process. No others. The order of work and the technology of manufacturing the pile-dew foundation are described here. And in this article, we'd better give some practical advice.
Difficulty drilling
If the soil is very loose - fine sand - the walls of the well may crumble. To prevent this from happening, pour water. The sand will be compacted and will keep its shape. Water will also help if the soil is very dry and dense. After drilling a few tens of centimeters, pour water into the well. It will soften the soil, it can be chopped up with a shovel or other device, and then removed with a drill.

It is not easy to drill wells under the TISE foundation with your own hands, but it is possible even alone
The powerful roots of trees and bushes create difficulties. They need to be chopped. To do this, the handle is welded (attached) to the handle. By sharply lowering it into the hole, the roots are crushed.
How to form an extension
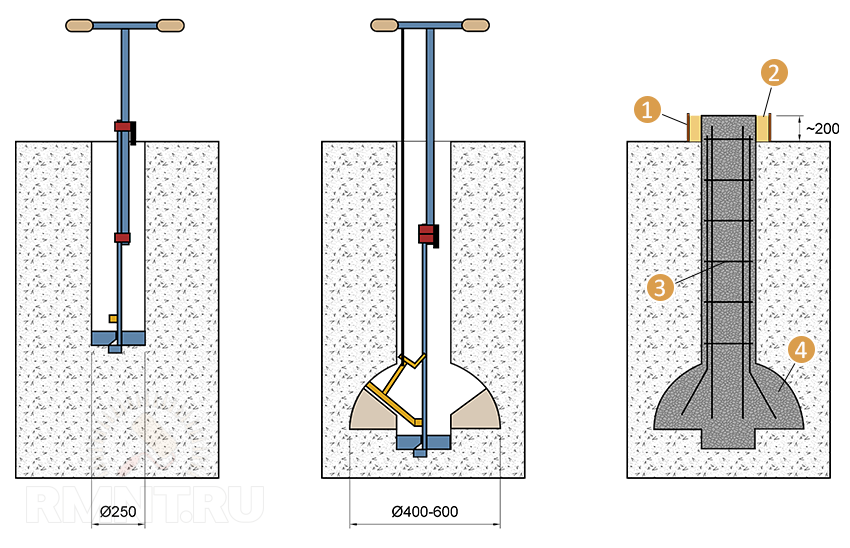
After reaching the design depth of the well, a plow is attached to the drill. It can be fixed in two positions: to form a heel of 50 or 60 cm. The plow is tied to a rope.
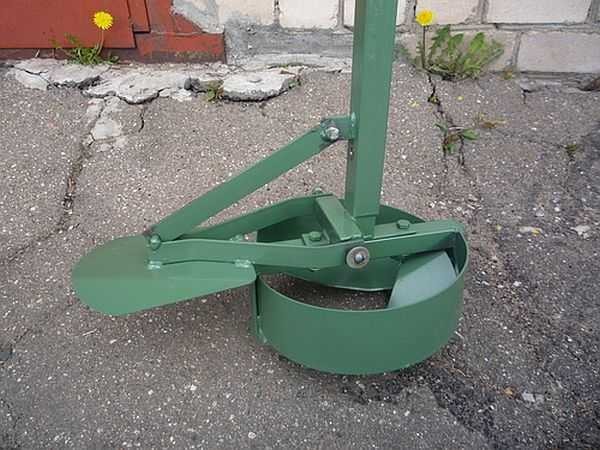

This is the plow, due to which the dome-shaped expansion is formed.
Lower the drill down, the rope is taut, the plow is pressed in. The rope is released, it falls down under its own weight. You start to rotate (it goes hard - the cutting surface is large), the blade cuts the ground, forming a thickening.
You can rotate both clockwise and counterclockwise. If clockwise, then try not to press down: you do not need to go deeper. When rotating counterclockwise, only the soil is cut without deepening, but another problem arises: the soil is poured under the drill, pushing it up.
The optimal order of work is as follows: scrolled counterclockwise several times. As you feel that the blade has rested against the arch, make a few turns clockwise, picking up the cut soil into the body of the drill. You take out the drill, pour out the soil. Repeat several times until the expansion is formed (the soil will stop accumulating).
On hard ground, working with an open plow can be problematic. Then you can form the extension in stages. First, set the plow to the smallest distance, then increase it to the desired size.
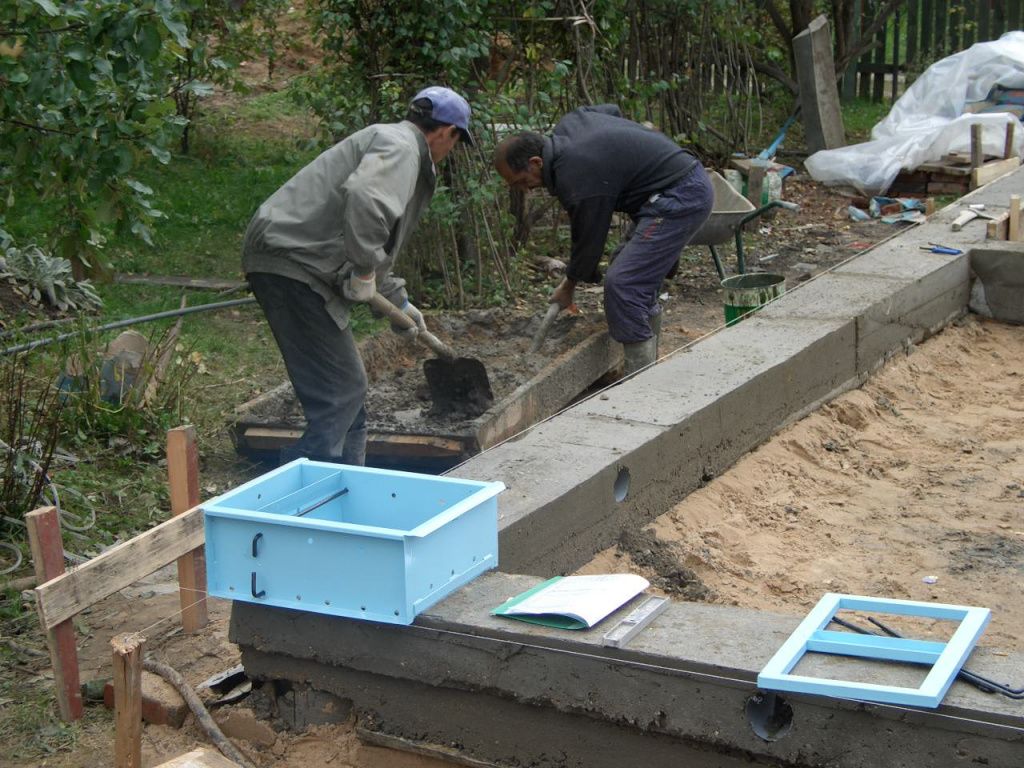
Filling with concrete
If the groundwater level is low, there are no problems: you fill it in, process it with a vibrator. Everything.
If the water table is high, the heel can be poured immediately after it has been formed. It will only be necessary to insert the reinforcement. Then knit it before drilling.The filling of the main part of the well can be left for later.

Having exposed the reinforcement and formwork, they begin to pour concrete
If there is a lot of water and it arrives quickly, you will need a large bag of thick film with a hole at the bottom. You insert it into the hole and pour concrete. Since it is denser, it displaces water. After filling the heel, take out the bag. It will come in handy for the following piles.
The video below demonstrates the technology of building a foundation with TISE piles and a high grillage.
Design
The TISE technology is a columnar grillage with widening of the sole of the uprights. All columnar foundations are characterized by disadvantages:
- they are unsuitable for wet soil (high ground level, swamp), fresh embankments and slopes with a height difference of more than 1.5 m between the opposite walls of the building;
- making a full-fledged underground or basement floor on pillars is impossible;
- floors on the ground, considered the most economical option, can only be made in a low grillage, which reduces the service life of wall materials, in contrast to a hanging grillage;
- when using ceilings in the form of PC slabs or along beams, heat loss increases, the consumption of insulation increases;
- underground communications should be additionally insulated;
- for any grillage, a zabirka is required, which increases the construction estimate, since it is forbidden to rest the beams on the ground.
Technical solution for piles TISE on steep slope.
The creator of the technology, Yakovlev, considered the absence of special equipment and the minimum possible construction budget to be the main advantages, without specifying what the TISE foundation was compared to. The main advantage is the broadening of the soles of the posts, which sharply increases their bearing capacity. It is for the design of the TISE drill, which allows to increase the diameter of the well at the bottomhole up to 60 cm without the involvement of special equipment, that the author received a patent.
Bur Tise.
Conventional hand tools and moto-drill accessories allow you to drill holes with a maximum diameter of 50 cm. To make a widening of a standard pillar using the classical technology, you will have to either open a larger hole or use a hole drill to drill a well of the corresponding diameter.
In any of these options, you will have to cast a slab at the bottom, then mount a smaller formwork, fill up the sinuses after the concrete has hardened. The bearing capacity of the pillar will increase due to the wide heel, but will decrease due to the decrease in lateral friction with the layers adjacent to the body of the pillar.
For example, when TISE is supported on clay, each vertical post has a bearing capacity of 10 - 12 tons. This is three times more than that of pillars without broadening or screw / bored piles.
Table: Bearing capacity of TISE piles.
The TISE foundation is inferior to other technologies in the following positions:
- a floating slab allows you to build a cottage on wet ground;
- MZLF tape is suitable for projects with a basement floor;
- bored and screw piles lie, not just "below the freezing mark", but reach the bearing layer, that is, TISE is much more reliable;
- screw piles are the only technology that allows you to erect walls the very next day, since the concrete inside their cavities is not structural, but only serves to protect the inner walls from corrosion;
Cellar inside the TISE foundation.
Due to the high cost of geological surveys, they are replaced by trial screwing of a screw pile in 3 - 5 places inside the building patch. The technique allows you to save money (it will cost 1.5-2 thousand rubles instead of 30 thousand).
Calculation and technology of construction of the TISE foundation
The calculation of the required number of foundation pillars for each specific building is described in detail in the article on columnar foundations. For TISE foundations, it is absolutely similar, so we will not repeat ourselves.
TISE foundation works are carried out in the following sequence:
1) Based on the calculation, the foundation is marked on the building site.
2) Wells are drilled 0.2-0.3 meters below the freezing depth manually or using mechanization.
A few tips:
- It is better to first drill the cylindrical parts of all wells, and then do the expansion (this will save time for installing and removing the plow of the drill);
- During the drilling process, you may come across stones. The small ones will fall by themselves into the drive, the large ones will have to be uprooted and taken out, for example, with a hoe. If you stumbled upon a large boulder, you need to displace the well (displacement up to half a meter is permissible without additional calculations);
- To facilitate drilling out the expansion in dry clayey soils, beforehand (for example, at night), buckets of five water are poured into each well. At the same time, the soil will be moistened and drilling will be easier. Also, water is poured in with dry sandy soils, to prevent spilling of the soil;
- If there is a danger of soil crumbling in the extended base of the borehole, try not to over-tighten with the pouring of concrete. That is, we drilled out one extension, immediately pour concrete, then another, and again concrete, and so on. This is done on sandy soils and at a high level of groundwater, which quickly wash away the walls of the spherical expansion.
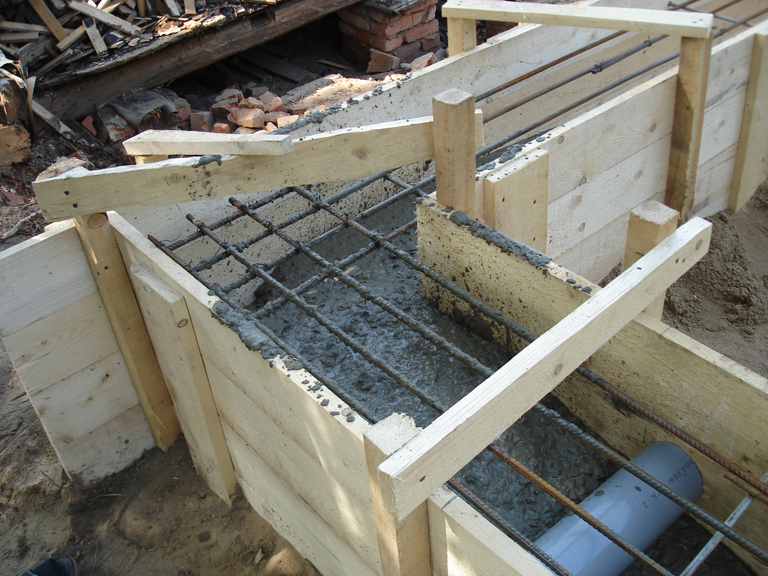
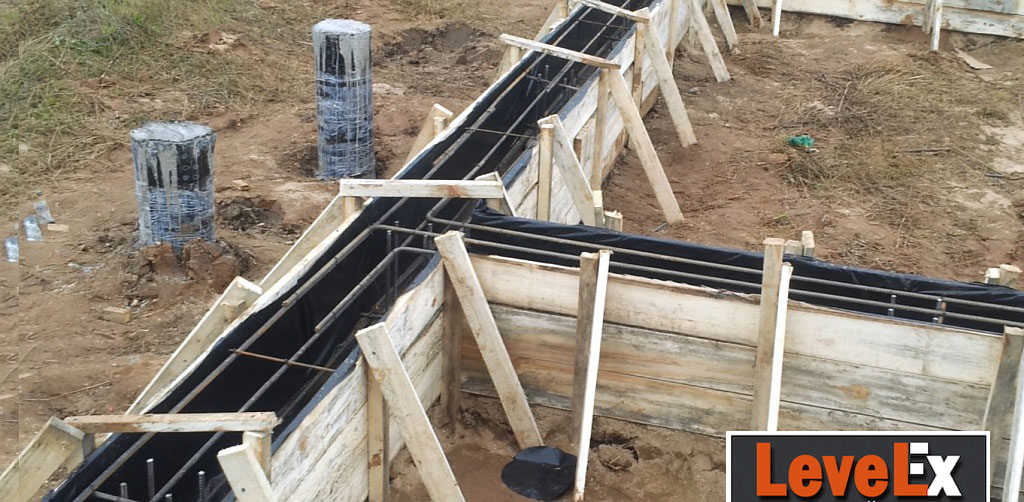
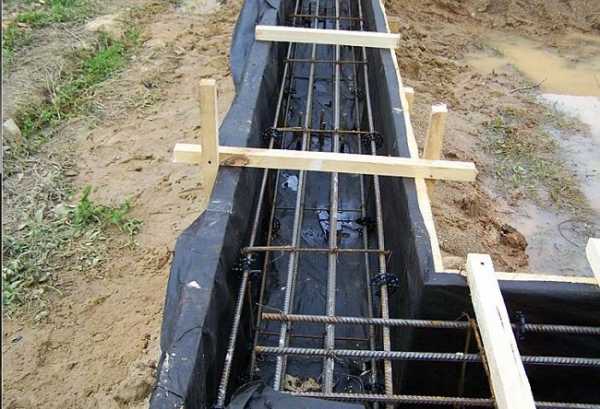
3) A shirt is made of roofing material (the process is shown in the article on columnar foundations, reinforcement is also described there) and inserted into the well before the expansion begins (in the figure below it is shown as waterproofing).
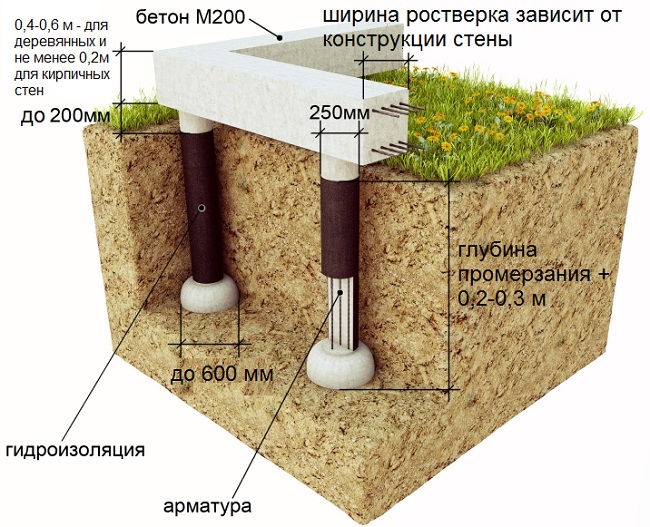
4) The reinforcement cage is knitted, inserted into the well and concrete is poured. The manufacture of reinforcement cages is a rather time-consuming operation, therefore it is better to complete it even before drilling wells.
5) After pouring all the supports, proceed to the construction of the grillage. A separate article "Column foundation with grillage (pile-grillage)" is devoted to this process. To what is written there, it is worth adding only the following: if a high grillage is made, then its level above the ground should not exceed 20 cm. This is due to the small diameter of the cylindrical part of the pile.
If the site is not flat, has a certain relief, the grillage is made either with a variable section height with small slopes (in the figure on the left), or stepped - with large slopes (in the figure on the right).