Other types of foundations for heaving soil
In any case, for heaving soil, you need to use only an unburied or shallow foundation, not necessarily a strip foundation. It can be a pile, columnar or slab base. If the pillars can be installed below the freezing point, a columnar base is used.
A shallow or shallow pile foundation is not a very popular foundation, but it is also used for construction on heaving soil. Installation of this design is complicated by the fact that careful calculation is required. In addition, it is only suitable for freezing depths over 1.5 meters and with a good drainage system.
The pile foundation increases the mass and increases the shrinkage of the building, does not allow equipping the basement or basement. Installation is notable for its laboriousness and a large number of small physical work. But the construction is quite easy to build. In addition, the installation takes only 1-3 days, and the construction of the house can begin on the day the foundation is poured.
The columnar foundation is suitable for loam and soil with close groundwater occurrence, for swampy and damp areas. However, columnar bases can only be used for structures with a slight load without a basement and foundation. This is the best option for building a bathhouse or a compact country house.

Support pillars are installed around the perimeter of the future structure and screwed into the ground below the freezing level. Such a foundation is distinguished by affordable cost, ease and efficiency of installation, reliability and durability. It does not require serious waterproofing and is characterized by a simple installation of communications.
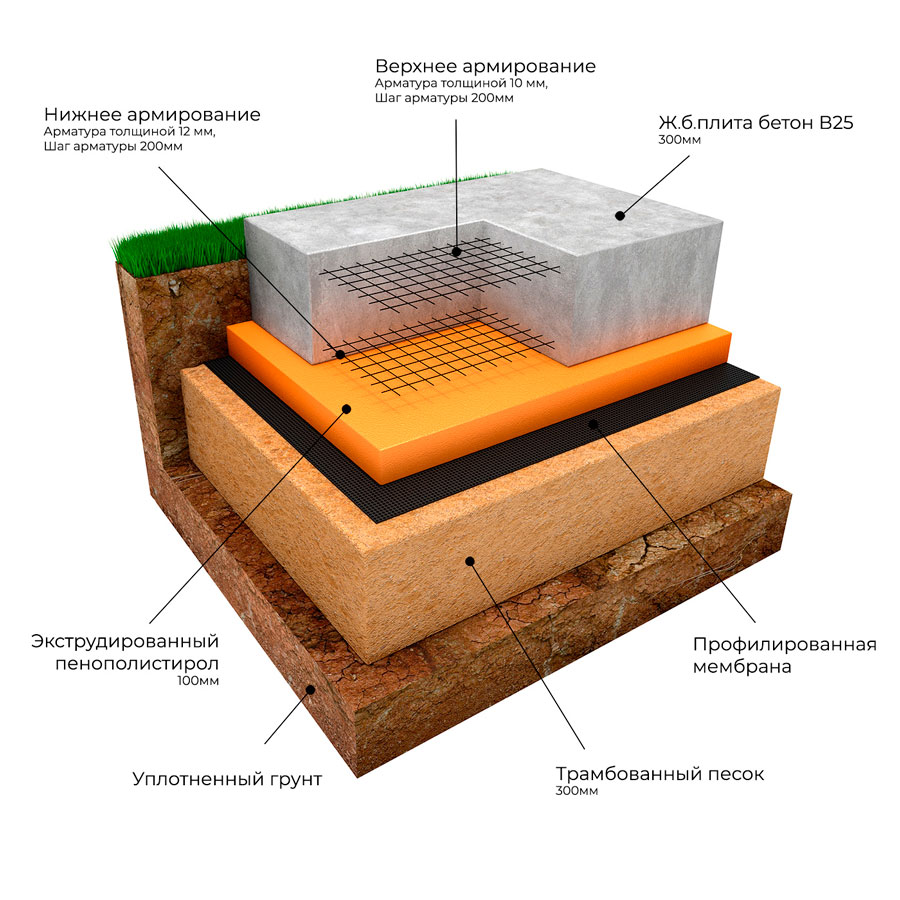
Slab foundation is the strongest, most reliable and durable foundation, which is a monolithic slab of a large area around the perimeter of the house. It is suitable for every type of soil or soil and for every type of building. Reduces building pressure and moves smoothly with the ground. At the same time, changes in the soil are evenly distributed over the surface of the slab, which prevents deformation of the walls of the structure. In addition, a monolithic slab, if necessary, will serve as a floor for the basement floor.
But the slab foundation requires the use of special equipment, which complicates installation and increases financial costs
In order for the base to serve for a long time, not to deform or collapse, it is important to choose the right type of structure, choose high-quality materials and follow the installation technology. To avoid mistakes and problems, contact the professionals!
The experts of the MariSrub company will analyze the soil and the land plot in order to choose the right type of foundation, correctly calculate and design the foundation. We carry out the installation, insulation and waterproofing of the structure in a high-quality and efficient manner.

We carry out a full list of works, including the installation of the foundation and roof, design of a house or bath and the manufacture of lumber, carrying out and connecting engineering networks. We make the finishing of the building, install windows and doors. If necessary, we will install a reliable drainage system and blind areas. We guarantee the quality and timeliness of work!
Calculation of the heaving intensity in the area
To calculate the degree of soil heaving on a construction site with your own hands, you must use the formula: E = (H— h) / h, in which:
- E - corresponds to the degree of heaving of the soil;
- h is the height of the soil mass before freezing;
- H - the height of the soil mass after freezing.
To calculate the degree, it is necessary to make the appropriate measurements in summer and winter. The soil can be considered a heap, whose height has changed by 1 cm at freezing by 1 m. In this case, "E" will be equal to the coefficient 0.01.
Soils with a high moisture content are more susceptible to heaving processes. When frozen, it expands to the state of ice and thereby raises the ground level. Loamy soils are considered: clay soils, loam and sandy loam. Clay, due to the presence of a large number of pores, retains water well.
How to remove the effect of heaving on the ground?
There are simple ways to remove the swell around the foundation with your own hands:
- Replacing the soil layer under and around the base with a non-porous layer.
- Laying the foundation on the soil mass below the freezing layer.
- Thermal insulation of the structure to prevent soil freezing.
- Drainage system.
The first method is the most time consuming. To do this, it is necessary to dig a pit under the foundation, at a depth below the freezing level of the earth, take out the heaving soil, and fill in heavily compacted sand in its place.
It exhibits high load-carrying capacity and does not retain moisture. The large amount of land work makes it the least popular, although it is an effective way to fight heaps. This technique is effective for the establishment of low-rise buildings, shallow burial, such as a barn.
A feature of the second method is the removal of the effect of heaving on the base of the foundation, but its preservation when exposed to the walls of the base. The average lateral pressure on the walls is 5 t / 1 m2. It can be used to build brick houses.
The third method allows you to make an unburied foundation for a private house with your own hands in heaving conditions. The essence of the method is to lay the insulation around the perimeter of the foundation to its entire depth. The calculation of the material is done as follows: if its height is 1 m, then the width of the insulation should also be 1 m.
To drain water around a house or shed, you need to build drainage. It is a ditch at a distance of 50 cm from the building, the depth of which is the same as the level of the structure. A perforated pipe is laid in a drainage trench at a technical slope and wrapped in geotextiles, and then filled with coarse gravel and sand.
Below - we will consider the types of bases that can be used on soil prone to heaving.
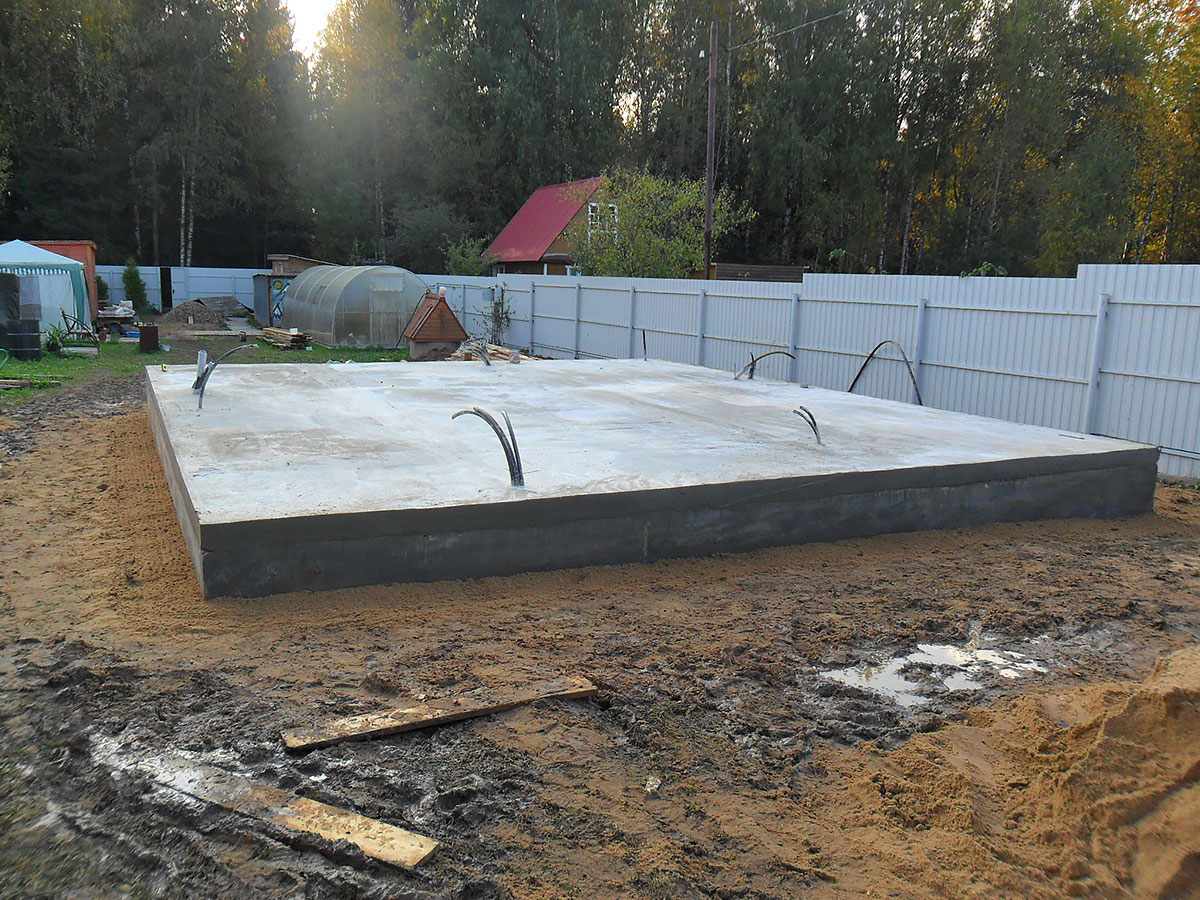
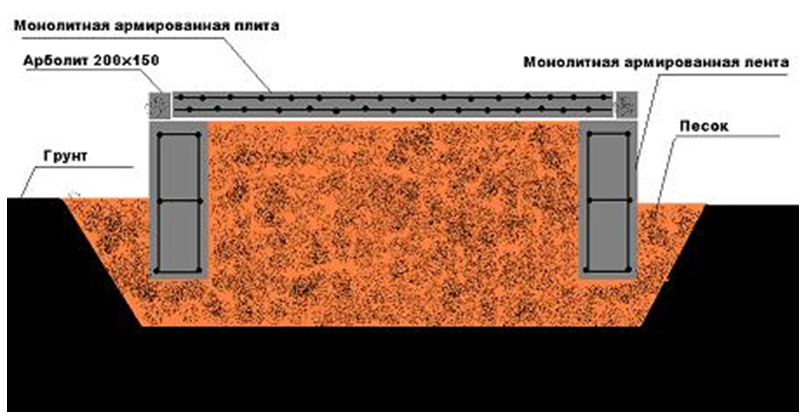
How to build a strip monolithic foundation for a barn
 An example of a finished trench filled with sand as a pillow
An example of a finished trench filled with sand as a pillow
Considering that the overall dimensions of such structures are small, then earthwork is minimal here. As a rule, the construction of a monolithic foundation consists of several stages:
- Development of a sketch drawing of the future building;
- Layout of the construction site, taking into account the dimensions of the foundation slab, its thickness and dimensions;
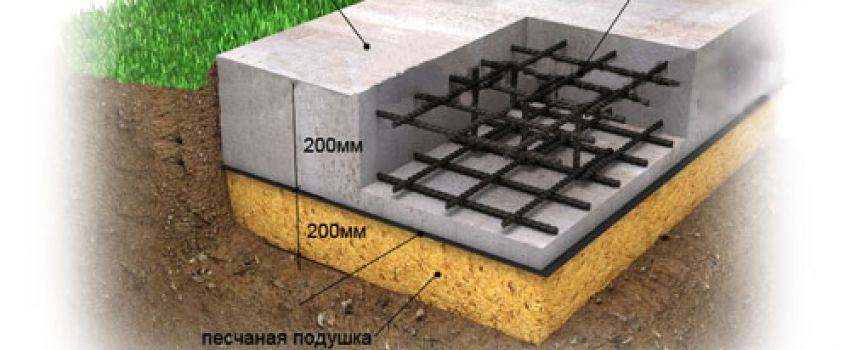
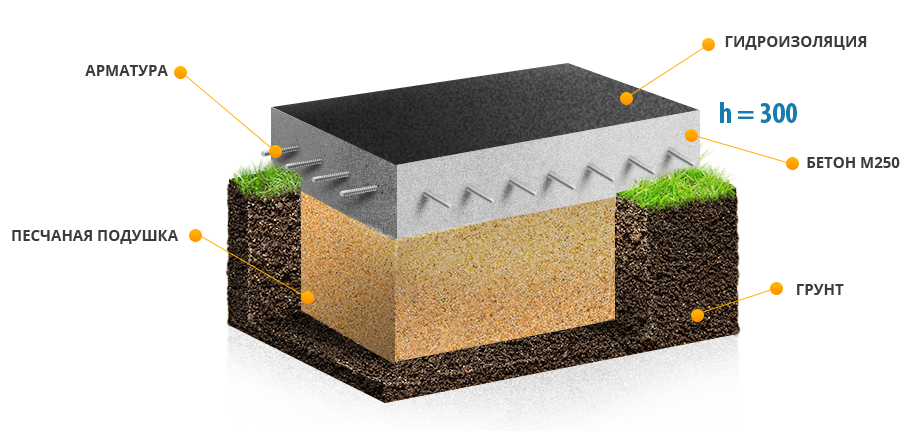
- Digging a pit to a depth of 60 cm, there is no point in doing any more through the high strength of the slab and the uniformity of the distribution of the mass of the structure;
- The bottom of the trench must be carefully leveled, tamped and covered with a sand and gravel pad. It also needs to be tamped so that the thickness of the pillow is no more than 15-20 cm. To facilitate tamping, the pillow can be pre-moistened with water.
- On the sides of the finished pit, formwork must be installed, in which the internal dimensions correspond to the specified parameters of the foundation. Align the finished formwork horizontally and vertically.
- Now you need to make high-quality reinforcement of the pit. For this, a metal mesh with dimensions of 8 mm is used, you can use a smaller one, only then you need to reduce the interval between the rods. It is recommended to connect it to the formwork, but this is often not practiced in order to build the foundation in a much shorter time.
- Now you need to fill the pit with liquid concrete, carefully level and tamp. If necessary, the upper edge must be leveled with liquid concrete using a hydro level.
The monolithic strip foundation for the barn is ready. Now it remains to wait about 3-4 weeks until the concrete gains its brand strength and you can begin to erect load-bearing walls from foam blocks or other heavy building materials.
Varieties of foundations
There are several types of foundations:
Columnar. It has become widespread due to its low price.

- Monolithic tape. As a rule, these are shallow foundations. Often, a brick base is erected together with a monolithic tape.
- Pile. The foundation is made of metal pillars. Such structures are built rather quickly and are relatively inexpensive.
- Plate. Such a foundation has the greatest bearing capacity, but its construction is more expensive than other types of foundations.

If we proceed from the use of the usable area of the site, then the basement floor is the best option, since thanks to such buildings, the living area is significantly increased. However, this option of the foundation will cost even more than the slab option.

But, it is not enough just to decide which foundation is more suitable for finance. It is necessary to understand whether he can cope with the exerted loads. This in turn depends on the soil.
Calculation for a shallow foundation
An example of the calculation of shallow foundations on heaving soils should be given. For example, a one-story house is being built with the following dimensions:
- height - 4 meters;
- width - 5 meters;
- length - 10 meters.
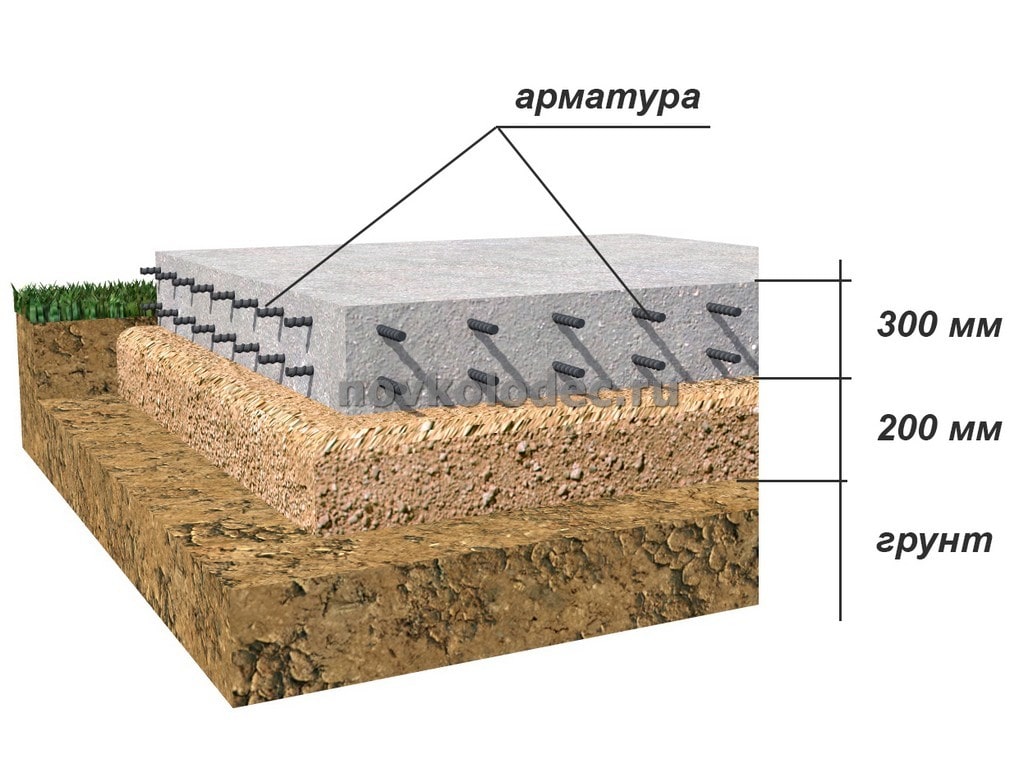
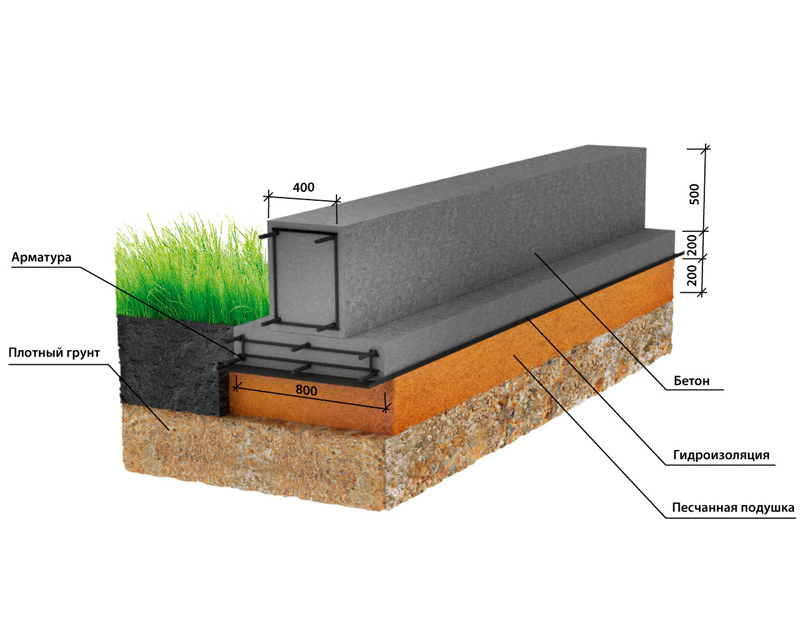
The structure includes two load-bearing internal walls, each 4 m high and 3 m long. The floor does not rest on the foundation, it is poured with concrete. The base will be in the form of a tape with a base width of 40 cm and a depth of 70 cm. The foundation is made of reinforced concrete, for which reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is used. The frame will have two belts, each of which consists of five rods, jumpers with a length of 25 cm.Such jumpers are placed in 50 cm increments.
To find out the mass that the strip foundation will have, it is necessary to determine the following values:
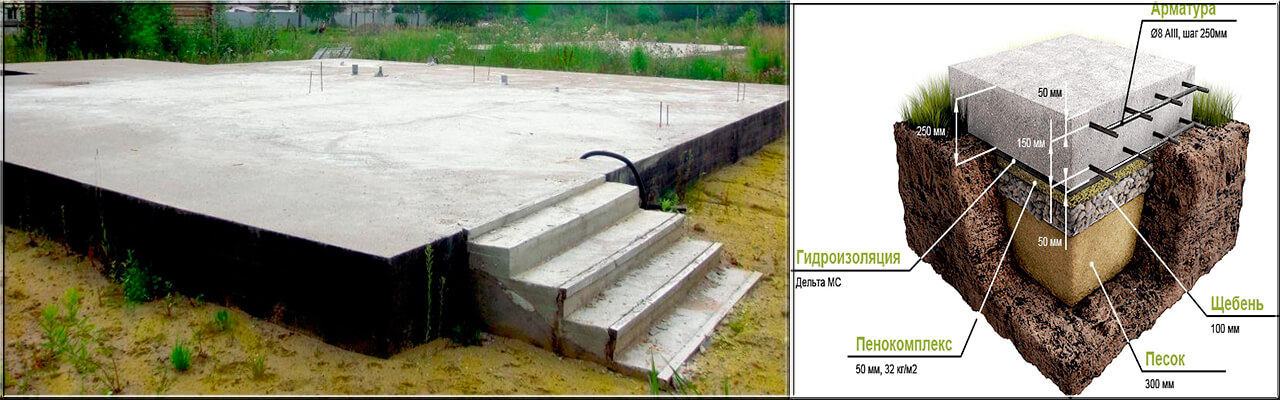
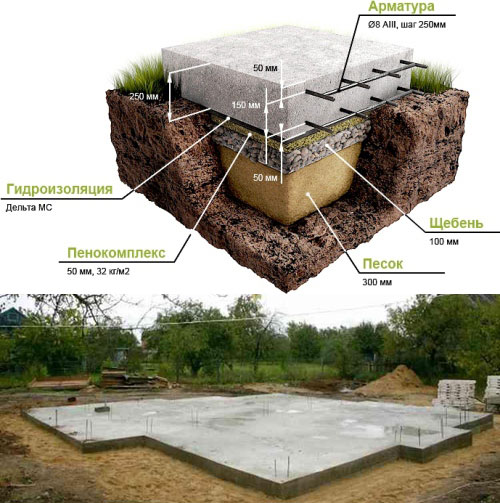
Scheme of a shallow foundation with waterproofing on a baked pillow.
- geometric dimensions of the structure;
- the density of the building material used.
It is quite easy to find out the geometric dimensions. So, the length of the foundation is equal to the perimeter of the future building, that is, you just need to calculate the sum of its sides:
10 + 10 + 5 + 5 + 3 + 3 = 36 meters.
The strip foundation will be poured not only under the external facade walls, but also under the internal load-bearing ones, therefore, they are also taken into account.
Now you can find the volume based on the fact that the height of the tape is 70 cm and the width is 40:
V = 36 × 0.4-0.7 = 10.08 cubic meters.
But this is the total volume from which the reinforcement must be subtracted in order to find out the amount of concrete. Knowing that the strip foundation has two belts of five rods with a dressing, they calculate the length for each:
10-0.5-0.5 = 9 meters.
The length of all belts will be equal to:
2 × (9 × 2 + 4 × 2 + 2.5 × 2) = 62 m.
Each belt has five rods, which means that their total length is: 62 × 5 = 310 m.
Now determine the length of the required lintels for the reinforcement:
Reinforcement scheme for a shallow foundation.
9 / 0.5 + 1 = 19 pcs.,
4 / 0.5 + 1 = 9 pcs.,
2.5 / 0.5 + 1 = 6 pcs.
For one upper belt, the number of jumpers is:
19 × 2 + 9 × 2 + 6 × 2 = 68 pieces,
Since the length of one jumper is 0.25 meters, the total length is:
68 × 0.25 = 17 meters.
For all horizontal frame lintels, the length is:
17 × 2 = 34 meters.
For vertical jumpers, take into account that there are 68 of them on the one side and the same number on the other. That is, it turns out 136 pieces with a length of one of 40 cm.Their total length is:
136 × 0.4 = 54.4 m.
Now calculate the total length of the reinforcement required by the shallow foundation:
310 + 34 + 54.4 = 388.4 m.
To find out the cross-sectional area for reinforcement, use the formula for the area of a circle:
Scheme for the preparation of concrete solution for the foundation.
3.14 × 0.000036 = 0.00011 sq. meters.
To obtain the volume, use the formula:
0.00011 × 388.4 = 0.04 cbm meters.
Now the volume is obtained for reinforcement only:
10.08-0.04-0.04 = 10 cubic meters meters.
A value of 0.04 is taken on the basis that a shallow foundation will be reinforced at the corners as well.
With the help of such a not too complicated calculation, it is determined what requires:
- 10 cubic meters meters of cement (with a density of 2500 kg per cubic meter);
- 0.08 cc meters of metal reinforcement (with a density of 7800 kg per cubic meter).
That is, the total mass of the entire base, which is being erected on heaving soils in the form of a strip foundation, will be:
10 × 2500 = 25000 kg,
0.08 × 7800 = 624 kg,
25000 + 624 = 25624 kg.
That is, the strip foundation has a mass of 25624 kg.
Building a house on heaving soils is not the best option. But if there is no other way out, then it is necessary to carefully calculate the future foundation so that after its construction the structure is not pushed out of the soil during the winter heaving. This is not so difficult to do, but care must be taken so that during operation there are no deformations of the foundation, and therefore the house itself.
Features of clay soils
The main problem when designing a building on clay soil is frosty uneven swelling. However, in clause 5.9 of the set of rules of SP 22.13330 of 2016, measures are indicated to reduce the effect of deformations in soils on reinforced concrete structures intended for operation inside the soil.

The principle of frost heaving is as follows:
- soils contain particles of clay, which is saturated with moisture (rain, ground, melt, waste water);
- freezes in winter to a certain depth (not the same in different regions);
- water in the lenses of clay scales increases in volume by 9%;
- soils tend to push out the reinforced concrete structures in them;
- or overturn them when applying forces to the lateral faces of pillars, belts or piles.
The following technologies are classic methods of protection against frost heaving:
- drainage - the device of a contour of perforated corrugated pipes along the perimeter of the foundation allows you to collect moisture, drain it by gravity into an underground reservoir;
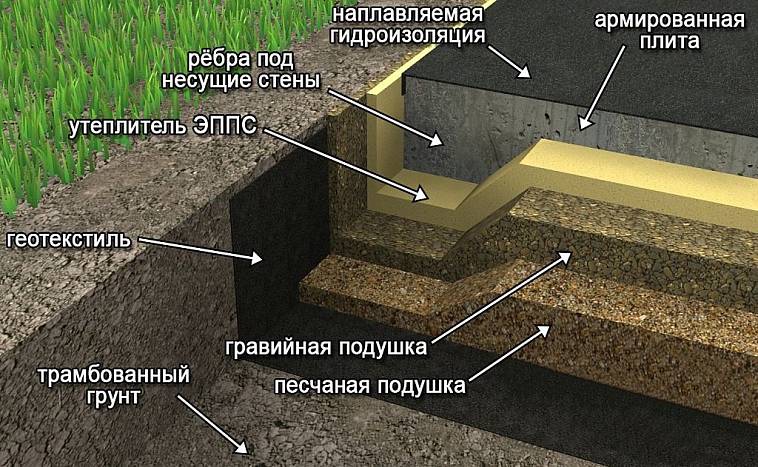
- replacement of clay soils with non-metallic material - natural soil is removed under the sole of the tape, slab or pillar, an underlying layer of crushed stone, sand 40 - 80 cm thick is created (it will not work without drainage with water saturation);
- insulation of the blind area and basement - it is used only for slab and strip foundations, allows you to exclude freezing due to the preservation of geothermal heat of the subsoil;
- backfilling - with the same inert materials that were used for the underlying layer (sand, crushed stone), eliminates pulling forces from tangential loads on the lateral surfaces of posts and belts.
Clays and loams by default have a high design resistance to prefabricated building loads. Therefore, the problem of shrinkage is completely absent. The question of choosing a foundation is decided from the standpoint of the available budget and the need for a basement floor.
How to identify clay soil
After choosing the type of foundation (deep tape for the basement floor, MZLF for a brick cottage, pillars for a log house, piles for a dwelling on a slope), you need to order geological surveys of the site or do it yourself.
It is possible to determine the clay content in a building spot without laboratory analysis:
- clay rolls into a thin rope, the ball from it practically does not crack when squeezed with fingers;
- loam can be rolled into a thick rope (from 1 cm), when the ball is compressed, small cracks form on it.

None of these activities can be done with sandy loam, especially with sand.

After that, it is necessary to plan a set of works to prevent swelling, depending on the chosen foundation:
- pillars - only below the freezing mark, drainage around the perimeter at the level of the sole, a pit for each pillar, the thickness of the backfill layer is from 40 cm on all sides, the blind area is insulated only for a low grillage;
- tape - a full range of similar works;
- plate - insulation of the blind area over the drainage.
Columnar base on heaving soils with a large freezing depth
To reduce the effect of frost heaving forces on the base, it must be laid lower than the freezing level. But some climatic zones are so cold that the level of soil freezing can reach 2 m in depth.
Types of strip foundations.
In this situation, ready-made metal or asbestos-cement pipes are used for the construction of foundation pillars. In the case of using these pipes, the foundation can turn out to be of 2 types:
- with fittings;
- with a metal rod.
The structure of the base with reinforcement is as follows:
- sand pillow, the thickness of which is 10-15 cm;
- foundation block, for example, FL 6-12-3, measuring 118x60x30 cm;
- asbestos-cement pipe with a diameter of at least 20 cm.
The asbestos-cement pipe is attached to the foundation block with concrete mortar, with the same mortar it is filled inside, where a bush of reinforcement is also present. It can be welded in advance and then simply placed inside the pipe and filled with concrete. The reinforcement should protrude 10-15 cm beyond the pipe edges, so that then it can be welded to the grillage reinforcement.
A foundation with a metal bar may have the following construction:
- sand pillow, the thickness of which is 10-15 cm;
- supporting reinforced concrete monolithic slab, the width of which is 60 cm and the height is 40 cm;
- asbestos-cement pipe.
Just as in the previous case, the pipe inside must be filled with concrete, but instead of reinforcement, a metal rod is used, the diameter of which is 8-10 cm.The asbestos-cement pipe itself has a diameter of approximately 20-30 cm.
Foundation and sand bearing capacity
The main characteristic for construction is the bearing capacity, which mainly depends on the moisture content and compaction of the layers. So, the denser it is, the more it can carry the load without much shrinkage.
But with an increase in moisture in it, it negatively affects the bearing capacity (this does not apply to gravelly soil and sand of a coarse fraction). Sand containing larger particles is better suited than fine or dusty sand.
As for any soil, with an increase in the depth of the rock, the resistance to compression increases accordingly, that is, the deeper the sole, the less shrinkage will be.
Measures will be required to protect the substrate from moisture. Although sand does not hold water, waterproofing on the sand is indispensable.
Foundation options
Sandy soil is considered not heaving, it does not retain moisture, therefore, when freezing, it does not increase in volume. So, on such soils, you can build any kind of foundation. Even if the groundwater is close, a drainage device and insulation of the base around the perimeter will make it easy to solve the problem.
Shallow tape is the cheapest type. Suitable for a home without a basement. Taking into account shrinkage, it is better to erect such a base for wooden buildings. Can be assembled from prefabricated elements such as foundation blocks. On sandy ground, a foundation of blocks is quite good.
For buildings with a basement, a recessed tape is suitable. In this case, it is advisable to additionally create a full-fledged drainage system and be sure to waterproof the walls and floor in the basement.
Do not exclude construction on a slab base - the most expensive type of foundations.

Before construction, it is advisable to make pits 2 m deep in order to assess the nature of the soil on the site. In the presence of sandy soil on the site, you can decently save on the foundation. Usually, the groundwater level is low, and you do not need to think about changing the bearing capacity.
Freezing of the soil also does not pose a threat, sand does not belong to heaving soils. So, do not worry about the fact that you have sand on the site, this is a great option for the foundation.
Watch the video: Foundations in the sand
Columnar foundations: advantages and types
On heaving lands, columnar bases are also relevant.Their construction will provide some advantages for the owners of summer cottages and country plots:
- inexpensive cost of materials and fast work;
- use of ready-made slabs that exclude manual activities;
- reduction of the cross-section of the posts, which will allow the construction of economical monolithic structures.
In the domestic space, 2 types of columnar substrates are popular - shallow and grillage.
The bases of the small bookmark
Shallow fundamental structures are made of monolithic concrete products or prefabricated products. Shallow pillars provide:
- Digging a pit to a depth of freezing.
- Sand cushion spillage with a height of 50 cm.
- Immersion of the concrete block to a depth of 10 cm.
- Placement of waterproofing - pasting with roofing material or coating with mastic.
- Laying the second concrete block.
- Making a cement screed with a thickness of 5 cm.
On the sides of the supporting element, a blind area of concrete dough is arranged, tightly adjacent to it. The measure excludes the slope of the pillars.
Precast foundations
The construction of a prefabricated slab base consists in the use of the following techniques:
- Marking the territory, digging a pit.
- Formation of a sandy substrate 15 cm high.
- Lining blocks on top of each other, cementing them together.
- Waterproofing of elements by pasting.
- Covering the material with a concrete block and grouting with cement.
The structure rises 45 cm above the ground.
Arrangement of a foundation with a grillage
The grillage is necessary to maintain the stability of the supports on heaving soils and create a support for the walls of the building. The grillages are formed after adjusting the posts horizontally from concrete blocks with dimensions of 118x80x30 cm and 88x50x58 cm.The grillage product itself has parameters of 246x25x20 cm.
The lintels of the structure are tied with a reinforcing bar. Subsequently, the element is placed on a monolithic belt with reinforcing pins.
The device of all types of columnar foundations provides for digging trenches below the level of freezing of the earth, layer-by-layer backfilling and compaction of each layer.
Foundations built on swelling soils are a costly process. During construction, it is recommended to take into account the heaving forces, to erect one-story buildings without basements. The algorithm of independent work, indicated above, will help to reduce costs a little.
vote
Article Rating