Slab foundation construction technology
Features of the installation of a monolithic slab foundation (diagram).
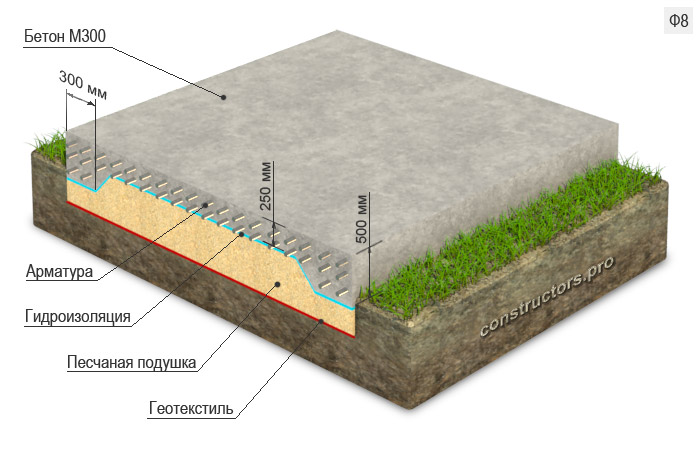
The construction of any foundation begins with digging a foundation pit over the entire area of the building. The depth of the pit for the slab foundation is 40-50 cm.After that, the foundation is made of M50 concrete 10 cm thick.If the soil contains moisture or the groundwater is too high, the bottom of the pit should be covered with fine gravel or sand with a layer of 20 cm.
The sand must be carefully tamped. After that, you can start building the base. Work should only be continued after the base has completely hardened.
The sand cushion and base must be covered with roll-up waterproofing to protect the foundation from moisture ingress. After that, the reinforcement cage is mounted: rods with a thickness of 10-12 mm must be welded. It is unacceptable to tie the rods with wire. For greater strength, metal pipes or scrap iron can be added to the frame. The frame is placed on a waterproofing layer.
Now you can start pouring concrete. For this, concrete of a grade not lower than M300 must be used. For frost-resistant foundations, special additives are added to concrete. The concrete must be poured into the pit evenly, the reinforcement cage must be completely immersed in the concrete, otherwise it may corrode. The minimum thickness of the protective concrete layer must be at least 30 mm. The concrete mix is leveled and left to harden completely. Care should be taken that the mixture does not dry out too quickly, otherwise the concrete will not acquire the required strength. After the concrete has set, waterproofing is done.
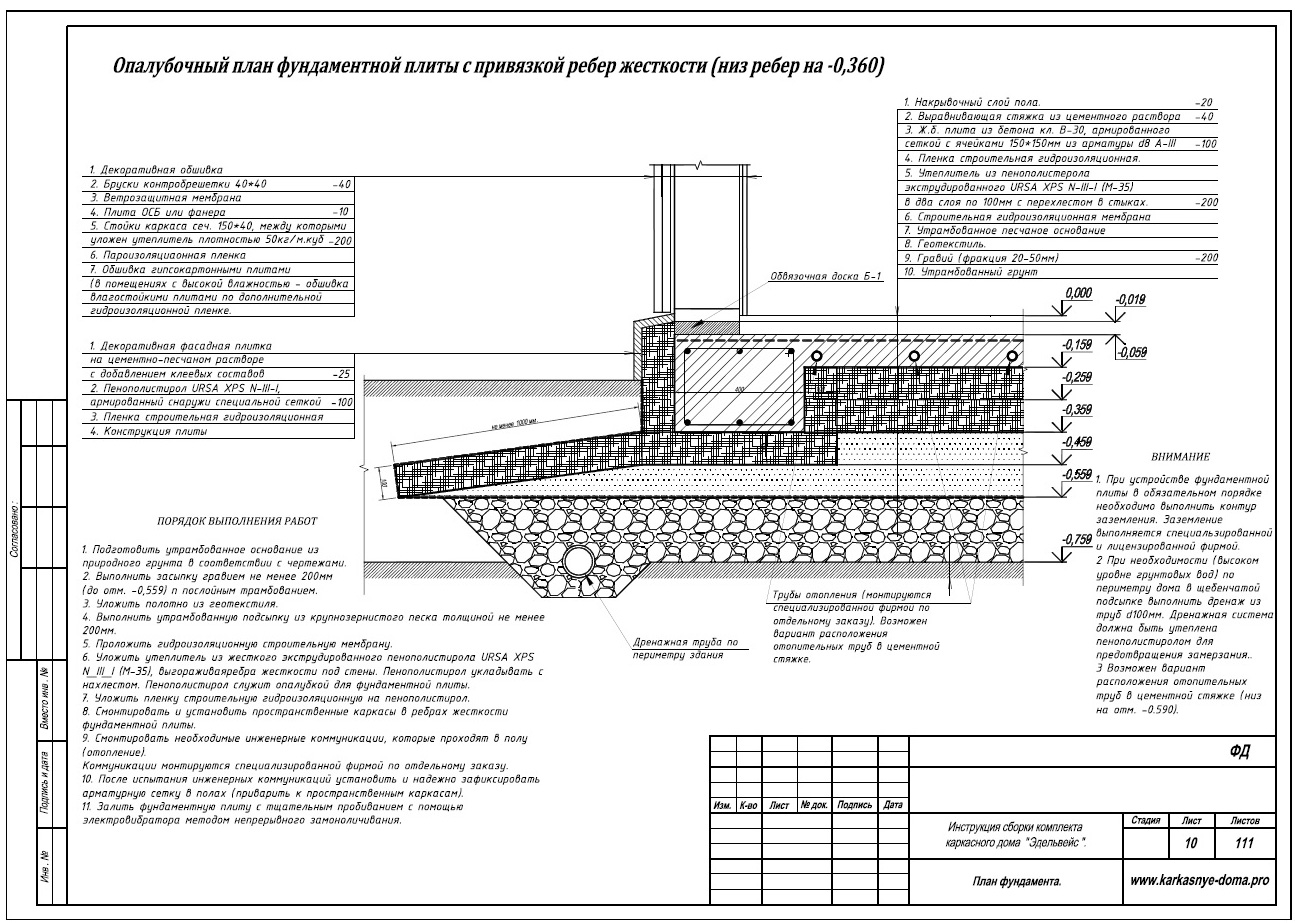
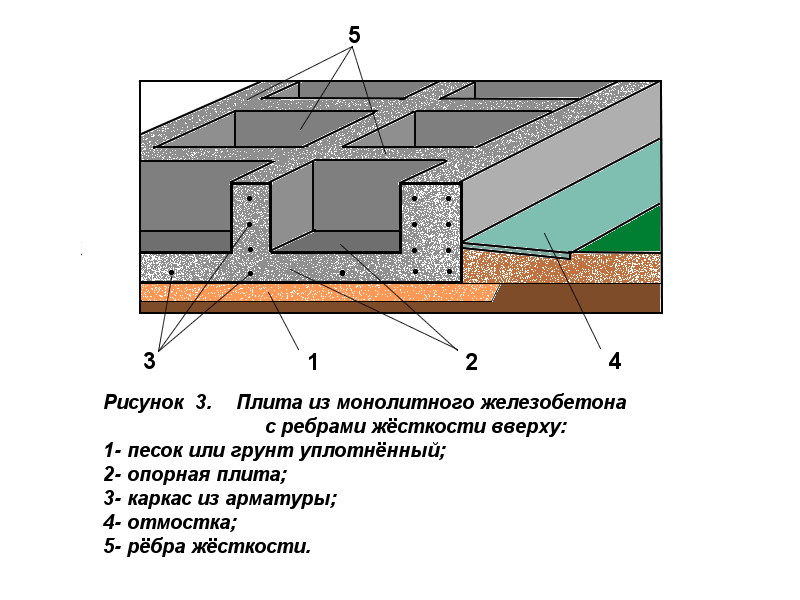
After that, if necessary, base ribs are made: prefabricated or monolithic. For monolithic ribs, formwork is placed. If the foundation is being built in seismically unstable areas, the base ribs are made during the concreting of the slab. Frost-resistant foundations should have thickenings along the edges - contour ribs. Such a foundation must not only be waterproofed, but also insulated. The slab foundation can be built from monolithic reinforced concrete. In this case, it will look like intersecting ribbons.
DIY slab foundation arrangement
Slab foundation
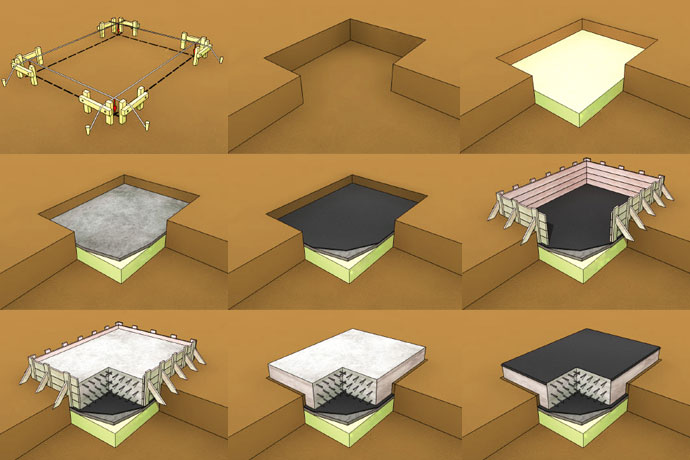
After completing the calculations, proceed directly to the arrangement of the foundation. The work is carried out in several stages.
First stage - site preparation
Most time consuming step. You have to get rid of the soil layer to the calculated depth. You can use special equipment to dig the pit, but it is better to get rid of the last layer of earth by hand to prevent the appearance of irregularities. Even the smallest indentations will distort the load distribution, which will cause deformations.
On each side, the size of the pit should be 1-2 m larger than the future foundation.
Second stage - sand and gravel backfill
This layer will compensate for the loads arising from the natural deformation of the soil. Also, backfill is needed to drain underground waters and exclude the possibility of their rise to the bottom of the foundation slab.
Choose the thickness of the backfill individually, taking into account the characteristics of the soil on the site. So, in the case of sandy soil, a 15-centimeter layer will be sufficient, and if the soil is prone to heaving, the thickness of the backfill should be increased to at least 30 cm.
The backfill must be evenly distributed over the entire bottom of the pit and compacted with high quality. An additive in the form of crushed stone (gravel) must be present in the case of arranging the foundation in wet or swampy soil.However, even in normal soils, it is better not to give up crushed stone - such a backfill will improve the moisture protection of the concrete structure.
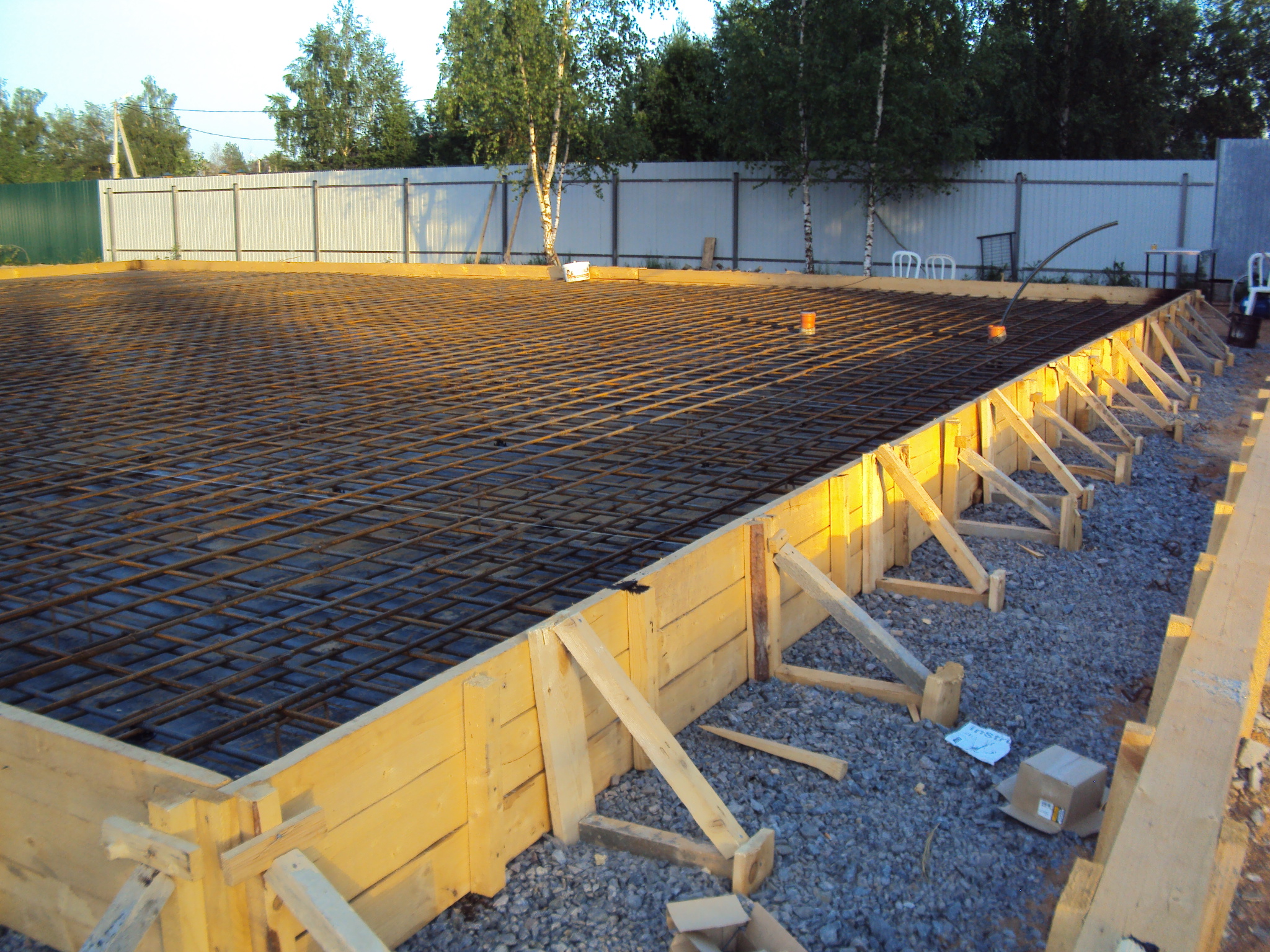
Third stage - formwork
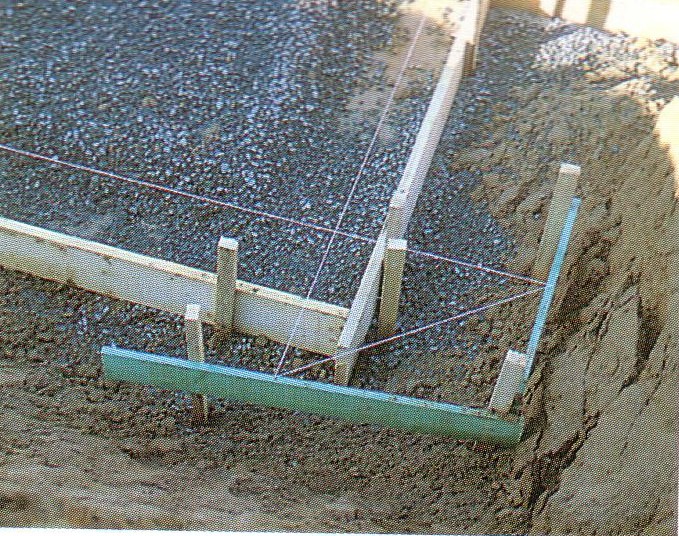

Installation of slab foundation formwork
For the manufacture of removable formwork, use planed boards with a thickness of 2 cm or more. Be sure to fasten the boards at the corners. Use self-tapping screws for fastening. Reinforce the outer surface of the formwork with struts.
If you wish, you can use a fixed formwork. For its manufacture, you need to use a fiberboard. For fixing the fixed formwork, use ties and brackets. The use of braces is also required.
At the same stage, provide for the arrangement of passages for various communications (water supply, etc.). Formwork around them. At the same stage, you can lay the pipes themselves.

Slab foundation formwork
Fourth stage - waterproofing

Warming and waterproofing
Place a thick plastic wrap on the bottom of the pit. Also, materials such as roofing material and geotextiles are suitable for providing moisture protection. Lay the waterproofing material with an overlap and an obligatory approach to the formwork.
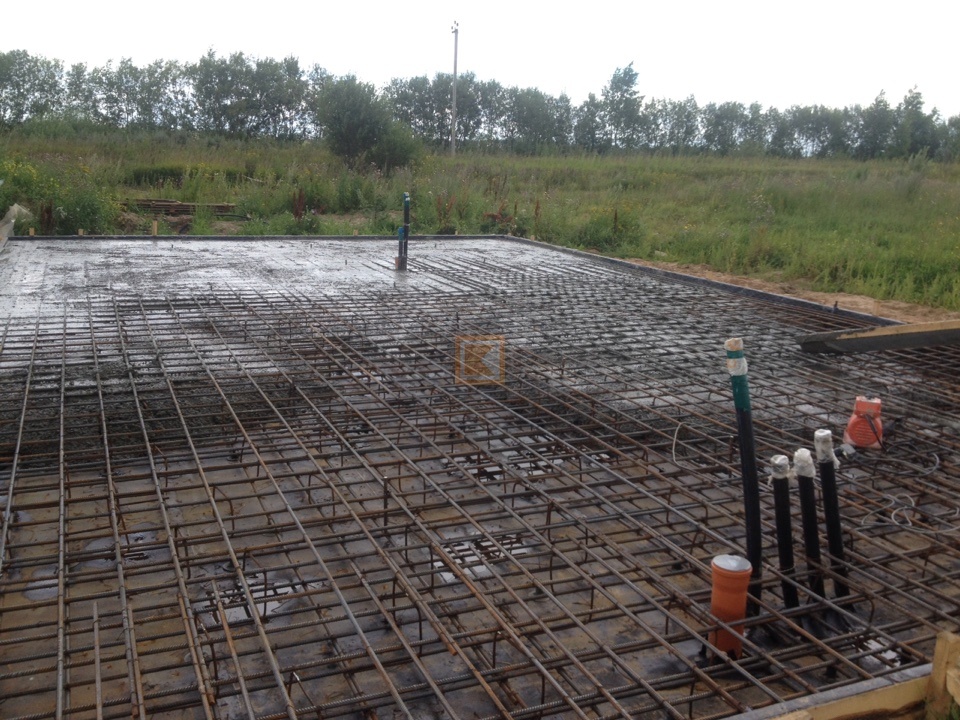
Fifth stage - reinforcement

Reinforcement of slab foundation
Not only the reliability and strength of the foundation depends on the quality of the reinforcement, but also the stability of the building, which will be built on the foundation you are equipping.
If the future structure will have small dimensions and weight, a mesh with cells of 100-150 mm from 8-10 mm rods can be used for reinforcement.

Reinforcement of slab foundation
If the future building will be more massive, reinforcement should be performed using 12-14 mm rods. The rods are also laid out in the form of a grid. Use steel knitting wire to connect the cross bars. It is better to refuse the use of welding.

Reinforcement of slab foundation
If the base will have a significant thickness, the reinforcement is performed in several layers. These moments are calculated and approved at the stage of calculation and design of the foundation.
Sixth stage - filling

Fill
The concrete must be poured in one pass. Therefore, either ensure that you can quickly make a large amount of concrete yourself, or order the material ready-made.
Pour the mixture in an even layer, slowly.

Platen DIY foundation
Be sure to compact the concrete with a vibrator and then with a vibrating bar. This treatment will remove excess air and voids from the concrete. Smooth and level the processed fill.
Leave the foundation to gain strength for 1-1.5 months. In the process of drying the base, make sure that its top layer does not dry out. To eliminate this possibility, regularly pour water over the foundation. However, the concrete should not get too wet either, control this moment.

Slab foundation
After the foundation is completely dry, insulate it with polystyrene plates. Dismantle the formwork if a removable version was used. This completes the arrangement of the slab base.
Happy work!
Monolithic tape frame
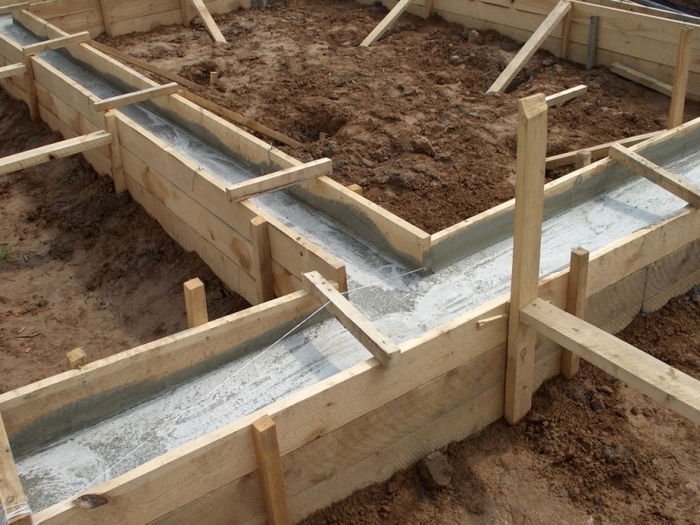 It is better to start the construction of a strip foundation if the soil on the site for a house made of gas blocks is calm enough
It is better to start the construction of a strip foundation if the soil on the site for a house made of gas blocks is calm enough
It is better to start the construction of a strip foundation if the soil on the site for a house made of gas blocks is calm enough and not subject to seasonal heaving, frequent erosion by groundwater, etc.
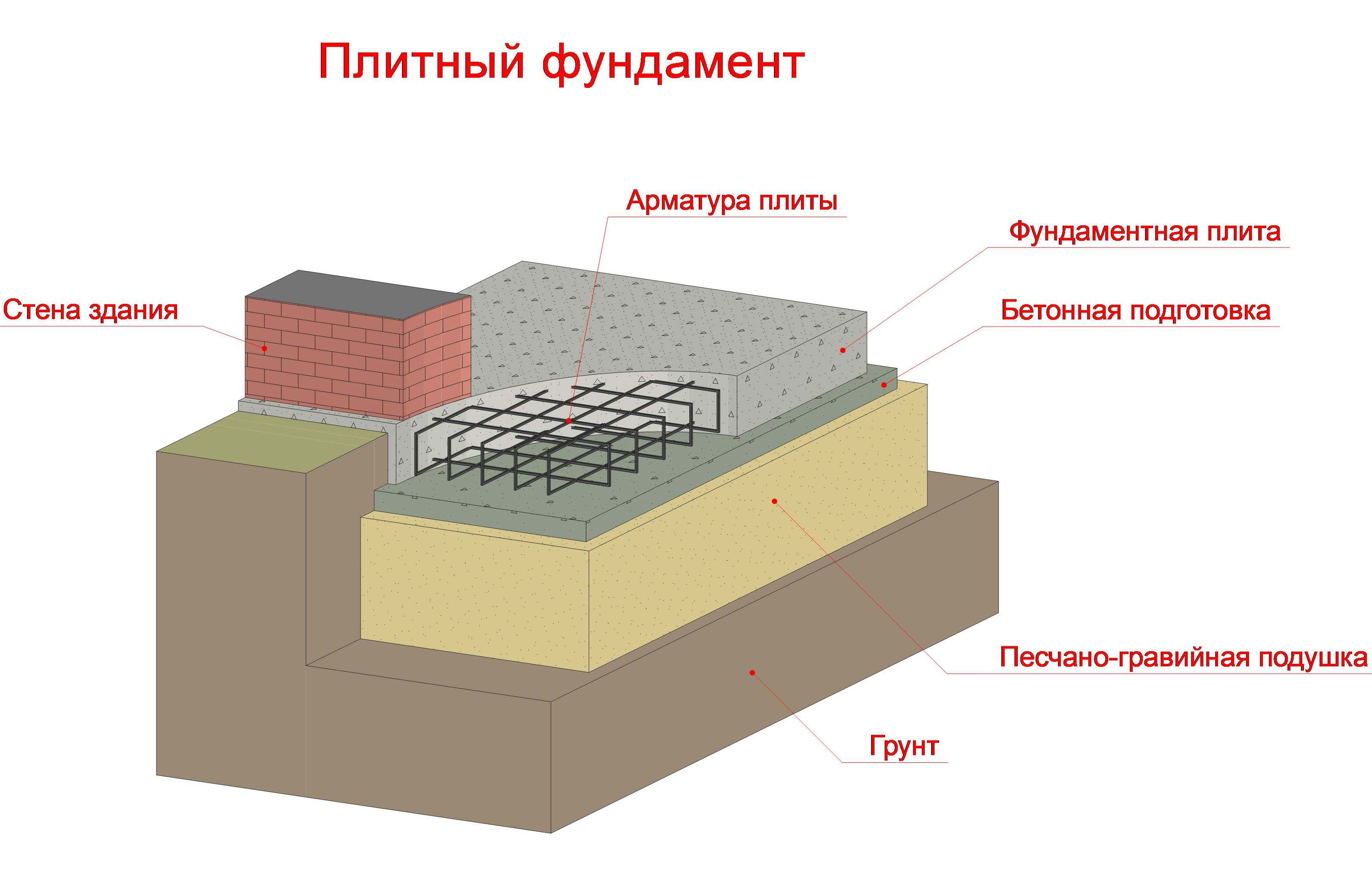
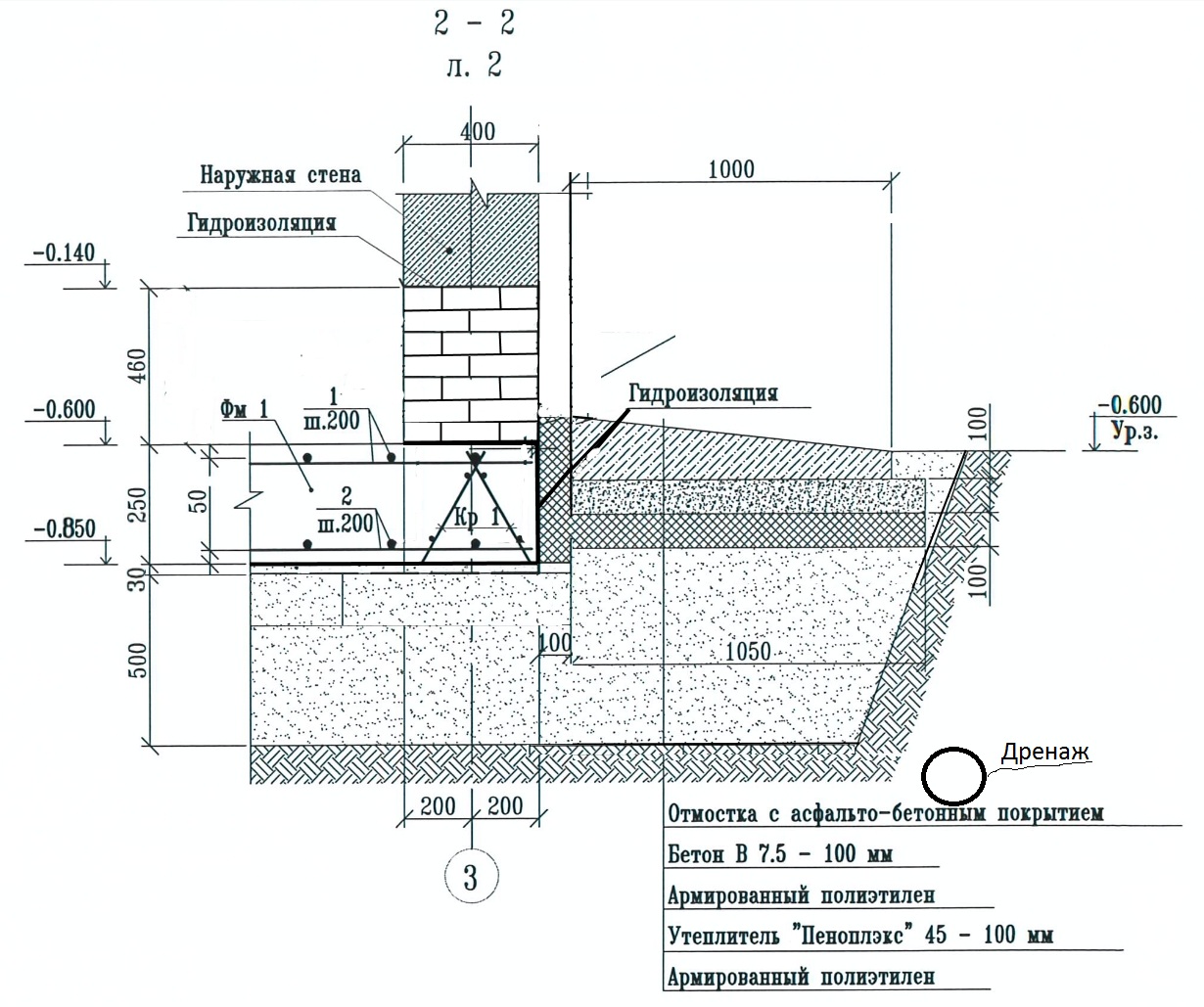
According to the project, the strip foundation for a block house can be made of small thickness. That is, you can make it shallow due to the low specific weight of the blocks. So, m3 of gas block is only 600-700 kg. Therefore, even if the construction of a two-story house is envisaged, the height of the strip foundation can be only 1.3 m.For greater reliability, you can make an expanding sole at the bottom of the frame. It will further reduce the force of pressure on the frame at home.
The principle of building a strip foundation is as follows:
- A pit of the required depth is being dug along the perimeter of all load-bearing and internal walls.
- The bottom of the pit is compacted and covered with a layer of sand 15-20 cm and the same layer of rubble. All the ingredients of the cake are tamped well.
- After that, the formwork is mounted, equal to the width of the projected base.
- Iron reinforcement is installed in the formwork and the ready-made solution is poured.
Installation methods
The foundation structure, depending on the requirements of the project and the specifics of the installation operations, can be constructed using various technologies.
The following mounting methods are possible:
monolithic. It provides for the execution of operations for the assembly of the formwork structure, the preparation of the working site, the implementation of reinforcement work and concreting. The one-piece version has increased strength, does not require the use of special lifting equipment, and allows you to form a slab of the required thickness. Weaknesses of a solid base - an increased level of financial costs associated with the need to use an increased volume of concrete solution, as well as reinforcement;

Installation of a monolithic foundation slab and technology during construction
composite. The prefabricated slab base is assembled from industrially manufactured reinforced concrete elements. Their installation is carried out on a previously prepared surface with a crushed stone-sand cushion, followed by pouring concrete mortar into the joint areas. The disadvantage is the need to use special lifting equipment, the use of standard products with a constant thickness, which does not allow the formation of a thickened base, and also insufficiently high strength compared to the monolithic version.
What is a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab?
Diagrams of the device of non-buried monolithic and precast-monolithic foundation slabs.
The design of a reinforced concrete monolithic slab refers to one of the options for the construction of a shallow or.
A shallow foundation is used for lightweight buildings, the installation of which is made of wood or foam concrete, small brick or frame buildings. It is advisable to use it on slightly heaving soil. laid in depth about 50-70 cm.
Heavy houses with bulky floor slabs are built on buried foundations. This type of foundation is used on heaving soils, as well as in the case when it is planned to equip a basement or basement in the house, for example, for a utility room or garage. The foundation is deepened 20-30 cm deeper than the soil freezing mark. Dwelling on such a design, it should be understood that its device will entail a large consumption of materials and labor costs.
Diagram of the foundation slab device.
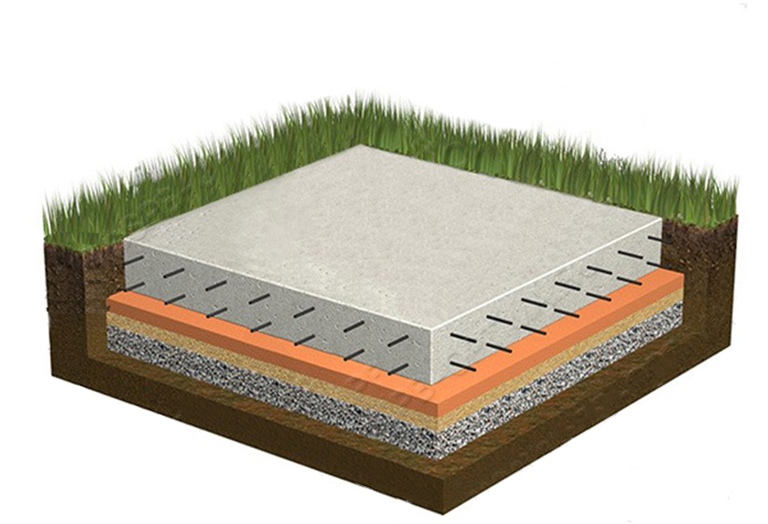
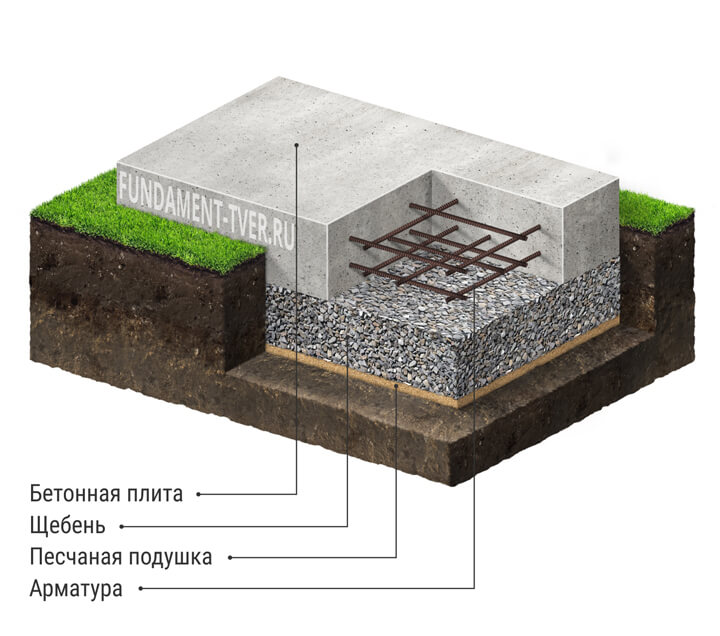
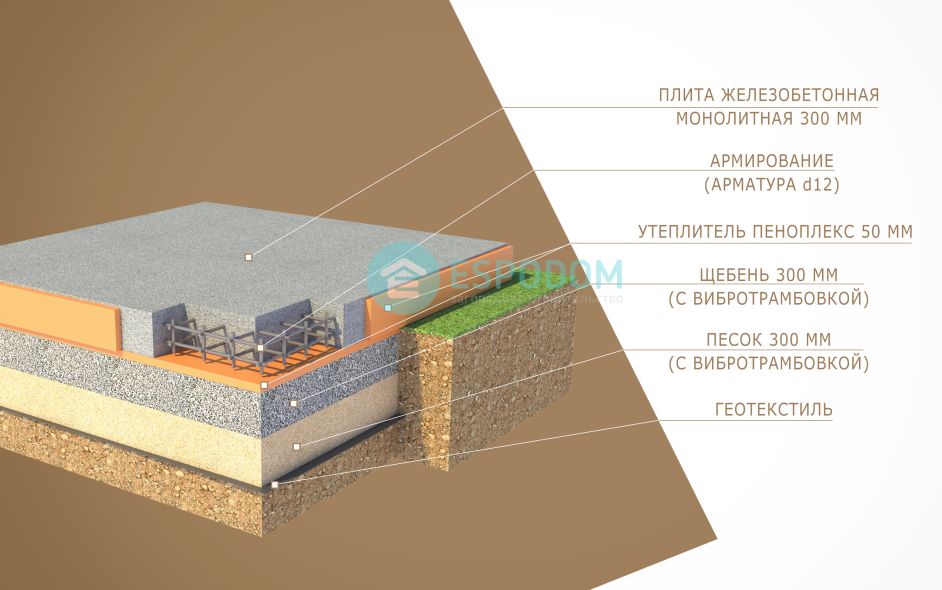
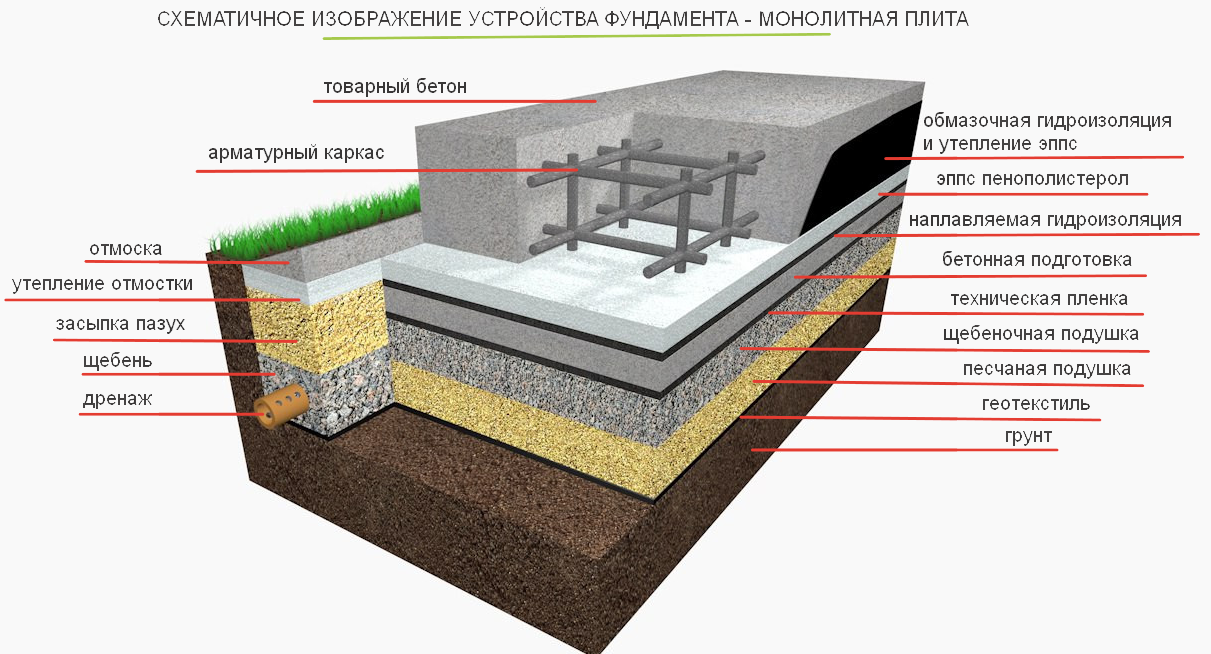
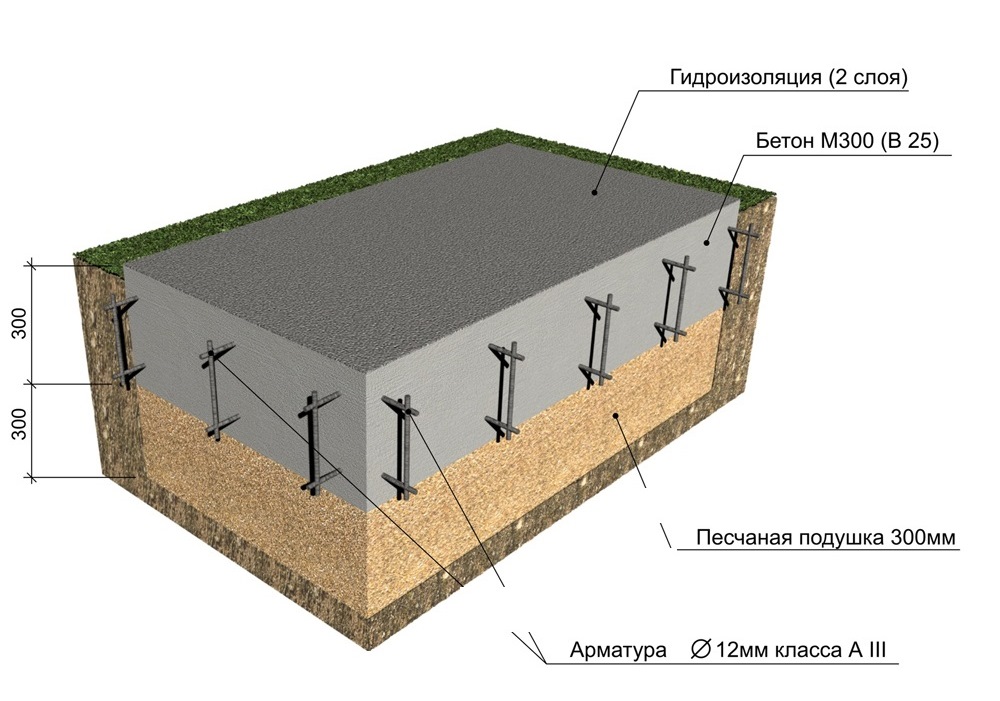
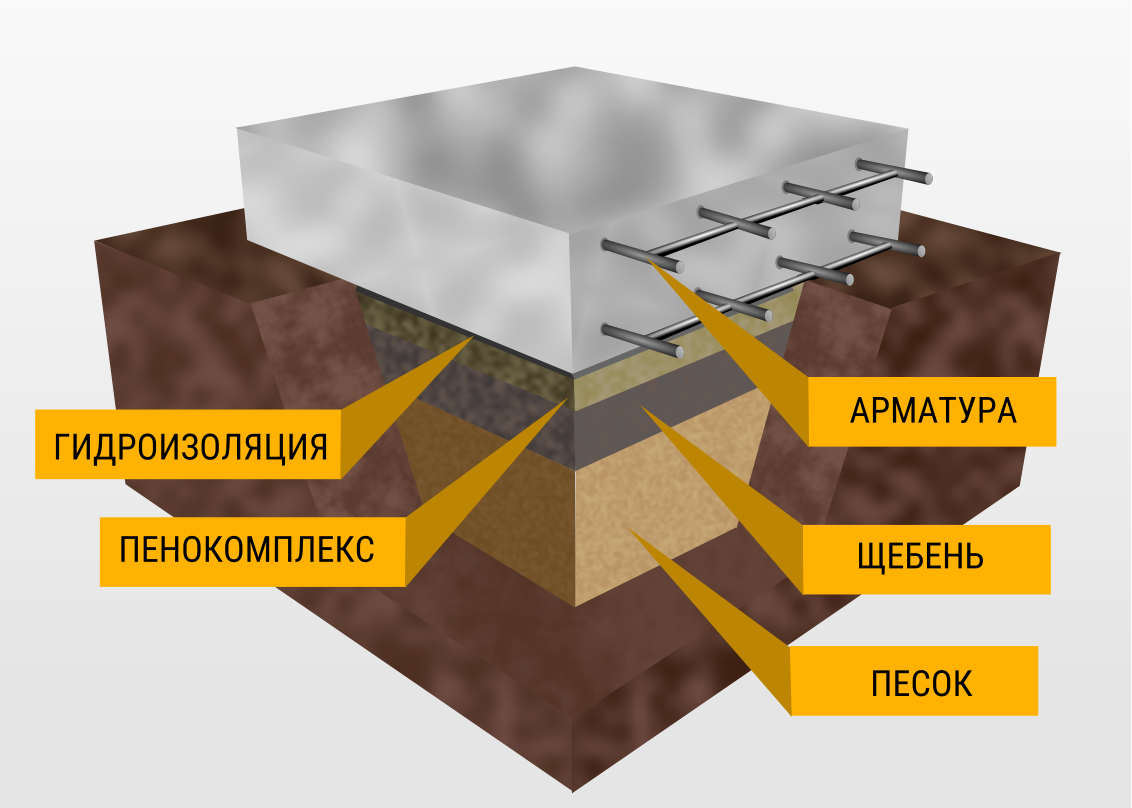
What is a monolithic slab? This is a slab of reinforced concrete, under which a cushion is laid from a layer of tamped rubble or sand 10-30 cm. The crushed stone cushion is placed on the mainland soil, in another way - the earth, which was not subjected to mechanical stress (loosening and digging).
Often, a concrete slab is 20-40 cm thick. In addition to a monolithic slab, precast reinforced concrete from several slabs (for example, road slabs) is allowed. They provide for the installation of a concrete or cement leveling screed over the slabs.
However, a monolithic foundation, representing a device of one slab, is more reliable and durable in operation, since it has a high spatial rigidity, in comparison with a prefabricated foundation of a plurality of slabs.In addition, the cost of the device on site is much cheaper than the purchase, delivery and installation using a crane of road slabs and the installation of a cement screed on top of them.
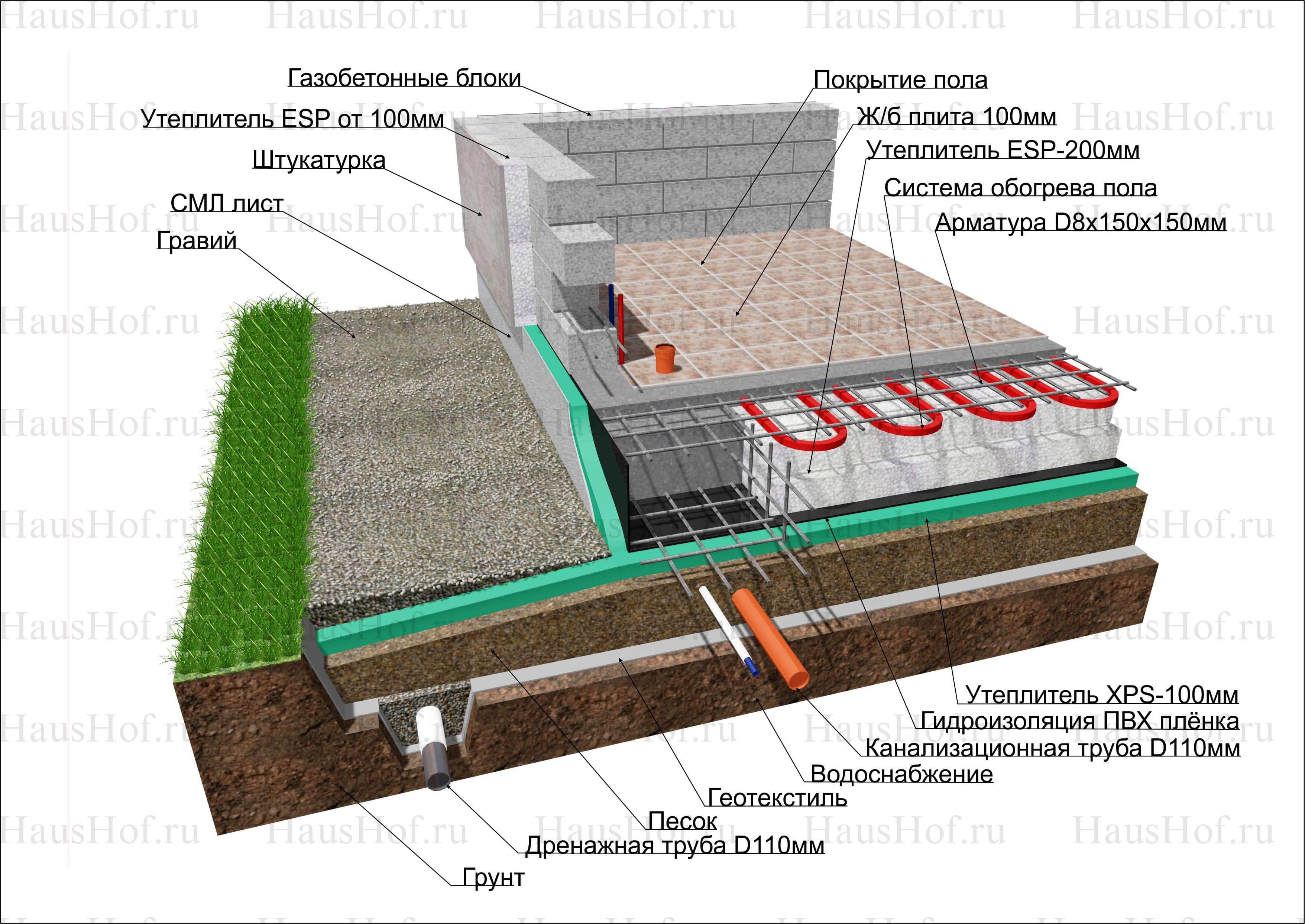
Slab foundation construction technology
It is recommended to deepen the slab foundation, at least a meter deep, and if the building is not heated, then it is worth either insulating it or deepening it to the depth of freezing of the soil.
First, they dig a pit, the dimensions of which should be slightly larger than the slab, since it is necessary to leave space for waterproofing and insulation work. Leveling the soil must be done carefully and manually, since the surface of the soil base must be flat. Then a layer of geotextile is laid
This is an important condition that will not allow the sand and gravel bed to disperse into the ground. A layer of sand and a layer of gravel, carefully leveled using a level, always with careful compaction of a sand and gravel pad, in layers of 10 cm
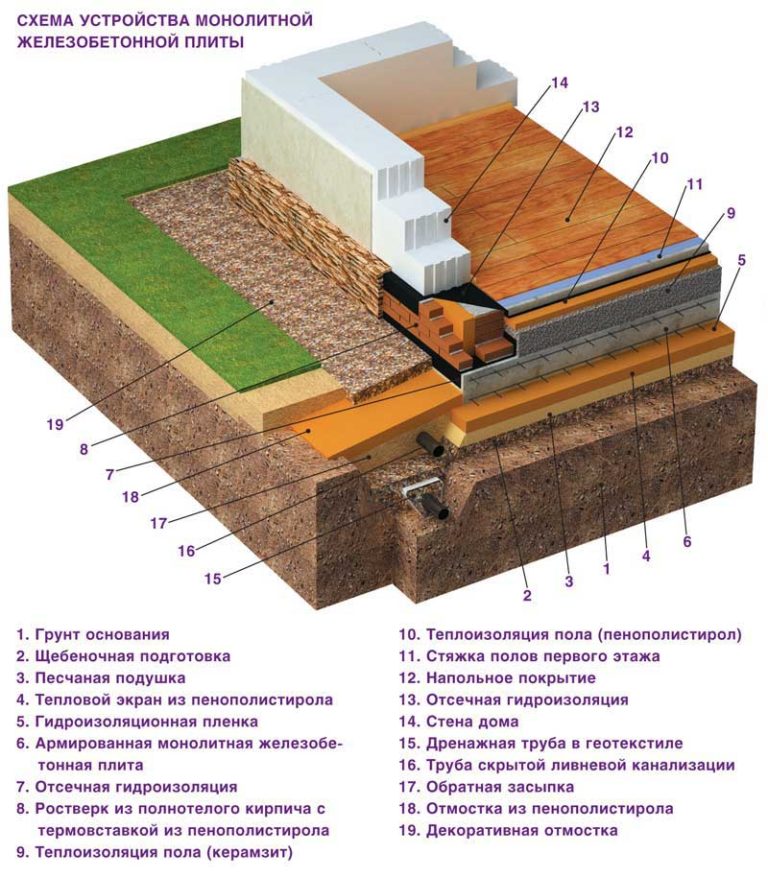
At this stage, you can lay the necessary communications (water, sewage, etc.), if they will run under the foundation. After that, a thin leveling layer of sand and concrete preparation (up to 10 cm) can be laid on the "pillow". Next comes a waterproofing layer made of vinyl film or roofing felt, and a double layer is encouraged.
The waterproofing must be removed (released) outside the slab and, when deeply buried, combined with the waterproofing of the walls of the basement floor. After the waterproofing, it is worth putting a layer of polystyrene foam, for thermal insulation, on top of which a layer of protective vinyl film can be additionally applied. The preparation of the slab foundation cushion is completed and the construction of the slab itself can begin.
This process begins with tying or welding a mesh of reinforcement bars. It is not recommended to place the reinforcement too close to the slab surface. As soon as the reinforcing mesh is completed, the formwork is built and it is imperative to strengthen it, since the concrete pressure will be high. Concrete is poured into the resulting form, which is carefully distributed and compacted with a vibrating tool. The surface of the concrete slab is smoothed and leveled, and then covered with a film to prevent drying out too quickly. The finished slab is settled for three to four weeks, with watering daily, during the first seven days. When the slab is ready, you can wrap the released waterproofing and solder it to the edges of the slab. That's it, the monolithic slab foundation is ready and you can move on to other work.
Slab foundations are very reliable and durable, and their effectiveness in difficult soils has been repeatedly proven in practice. Sandy, weak, heaving, bulk, loose, heterogeneous and other “problem” soils at the construction site can guide you to use this particular type of foundation. With proper planning and strict adherence to technology, there are not so many shortcomings in the slab foundation. If you are building a simple building, for example, a garage, a bathhouse, a workshop or any light outbuilding, then a slab foundation is an excellent solution. But if your building is residential, and has a decent layout or number of storeys, then serious construction calculations will be required to use a monolithic slab at the base of the house.
It is very important that the designer has the appropriate education and that the necessary soil studies are carried out.
Slab foundation - what it consists of, features
A slab foundation is essentially a monolithic foundation, the material of which is reinforced concrete. Such a foundation is located under the entire area of the building being erected. That is, the total weight of the building will be evenly distributed over the entire area, which in turn will significantly reduce the load on the soil.

The features of this foundation include a calm attitude to various kinds of seasonal changes in the soil. Since such a foundation both rises and subsides entirely. That is, the building being erected will both rise and fall along with its foundation, which will not suffer from seasonal changes in the state of the soil.
Please note that when building such a foundation, a prerequisite is special sand cushions and waterproofing of the foundation. As a rule, the thickness of the slab foundation is calculated based on the parameters and characteristics of the soil and soil, on which the building will actually be erected.
Note that the maximum load directly depends on the soil, which is determined based on the following data:
As a rule, the thickness of the slab foundation is calculated based on the parameters and characteristics of the soil and soil, on which the building will actually be erected. Note that the maximum load directly depends on the soil, which is determined based on the following data:
- The total weight of all building materials that will be used to build the structure;
- The payload that makes the structure heavier includes a variety of infrastructure and furniture
- Climatic loads such as wind pressure or the weight of a snow cover.
As practice has shown, for the construction of sufficiently light household or utility buildings, a monolithic base plate is sufficient, which is only 10 cm thick.
But for the construction of residential buildings, the thickness of the slab foundation is more than doubled and is 25 cm. In addition, such dimensions of the slab allow for full-fledged reinforcement of the base.
The advantages of the slab base
Highest load-bearing capacity in comparison with other popular types of concrete foundations.
- Ease of arranging the slab. Difficulties sometimes arise exclusively at the stage of performing calculations. There are no problems with pouring the foundation.
- Relatively shallow depth. Due to this property, the structure is almost not subject to perceptible deformations during the seasonal freezing and thawing of the soil.
- The possibility of using the foundation as a floor. It is only necessary to insulate the structure with high quality.
- The minimum amount of earthwork. A foundation of this type does not require strong deepening, which can significantly save resources on earthworks.
- It is advisable to use a slab foundation only on difficult soils. Such a base, as already noted, is very expensive, so it makes no sense to use it on normal soils.
DIY foundation slab: step by step instructions
The whole complex of works on arranging the slab base of a house or an outbuilding can be done on your own.
Preparatory stage
The site for the foundation is cleared of debris, trees and shrubs, after which the marking of the future foundation pit is performed
It is important to ensure that the tensioned cords form right angles. For the accuracy of the geometry, check the coincidence of the lengths of the diagonals of the marked rectangular section
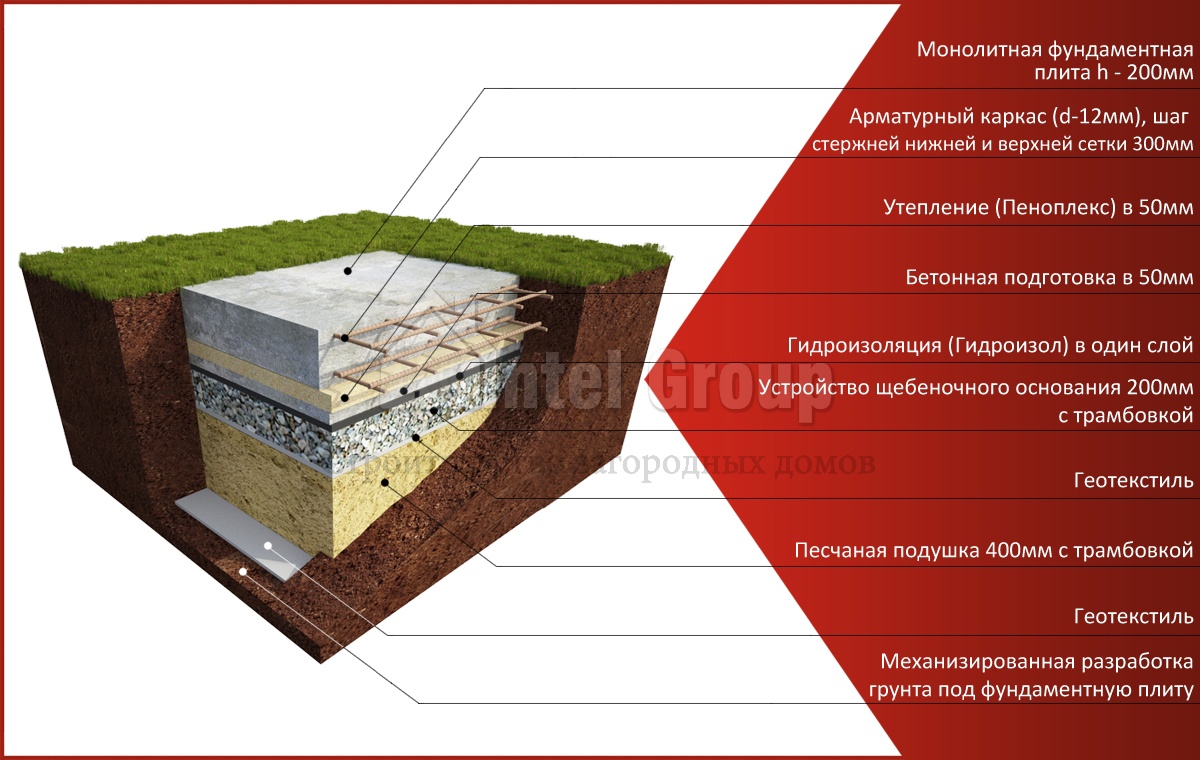
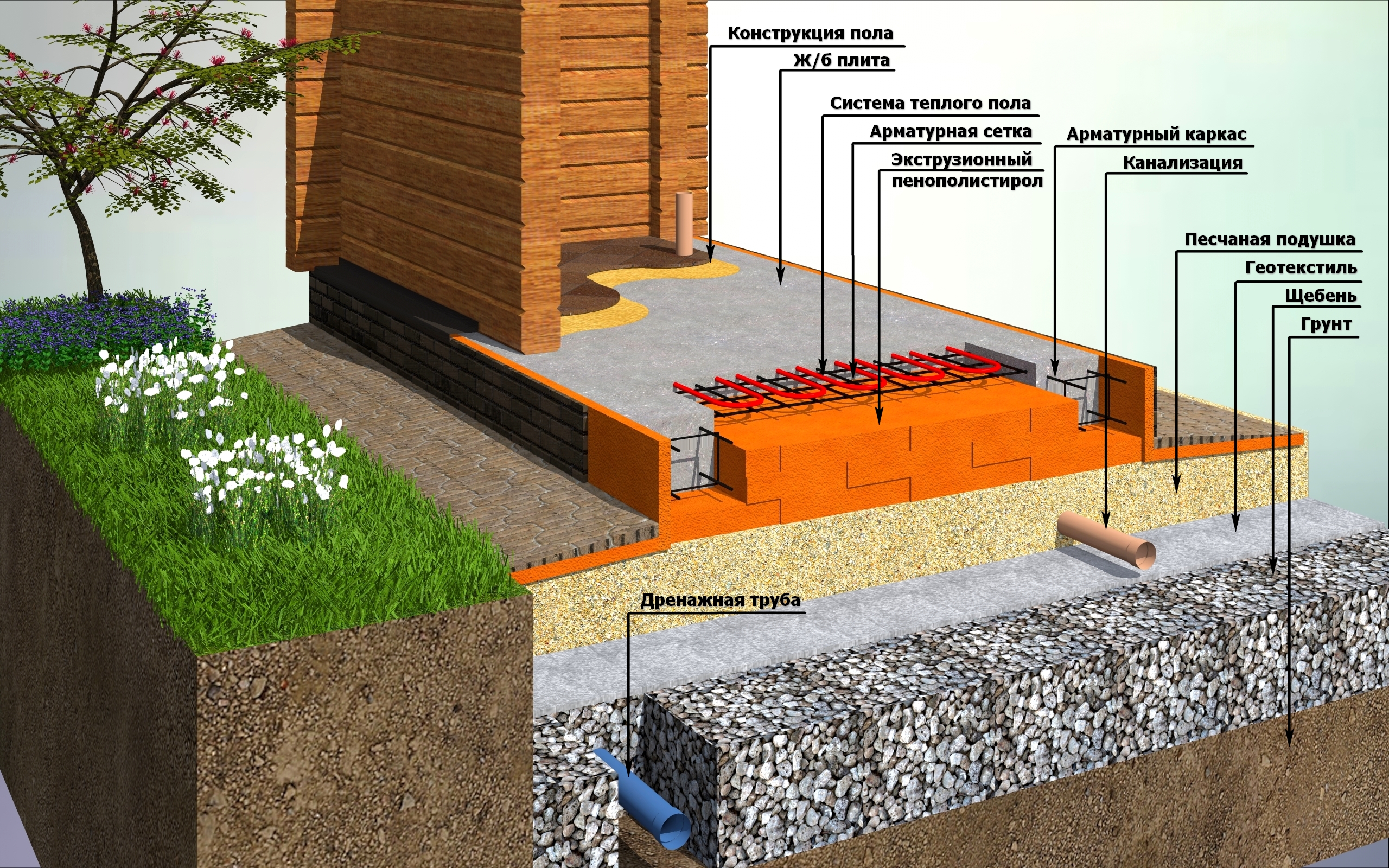
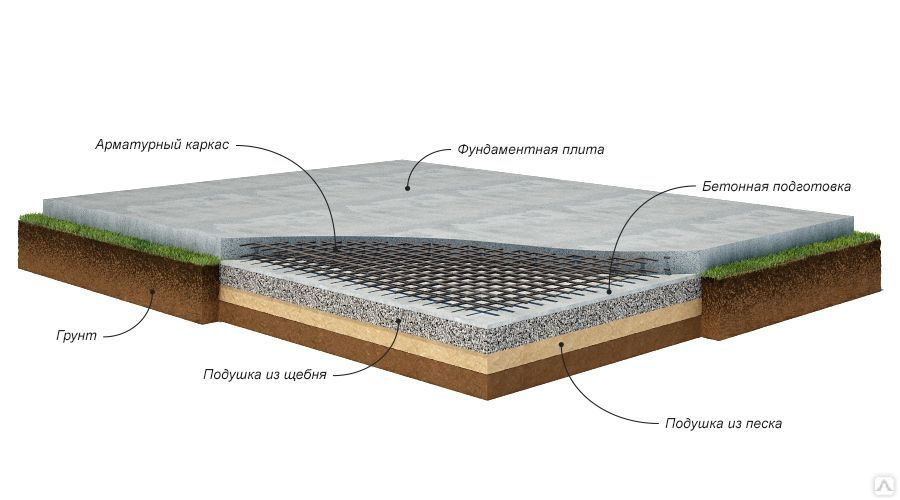
On the marked area, it is required to dig a pit, taking into account the thickness of the sand-crushed stone cushion, footing, waterproofing and the design value of the slab deepening.
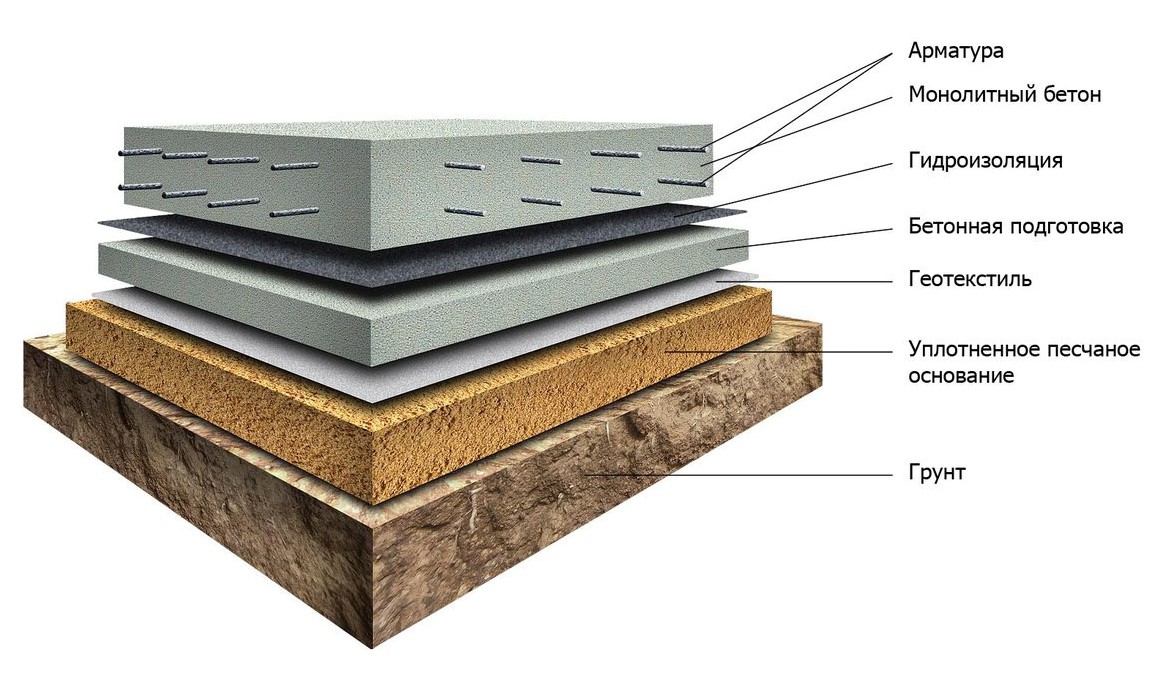
The bottom of the pit should be flat and horizontal, the soil is carefully tamped. The technology of building a foundation-slab can provide for the use of geotextiles to create a barrier between the soil and the sand bed - in this case, the sand does not silt up and is not washed out when the flood groundwater rises. Cloths of geotextiles are laid with an overlap of 30 cm and approaching the walls of the pit.
Arrangement of a pillow
At the bottom of the pit, sand is evenly poured with a layer of 100-120 mm. Then it is moistened with water and compacted with a vibrating plate.Then, according to the same principle, the next layer of sand is poured and rammed. The total thickness of the pillow must be at least 200 mm.
The sand cushion is covered with a layer of gravel or crushed stone 120-150 mm thick. You can pre-lay geotextiles so that the layers do not mix. A layer of gravel is necessary to exclude capillary suction of moisture from the soil.
Waterproofing
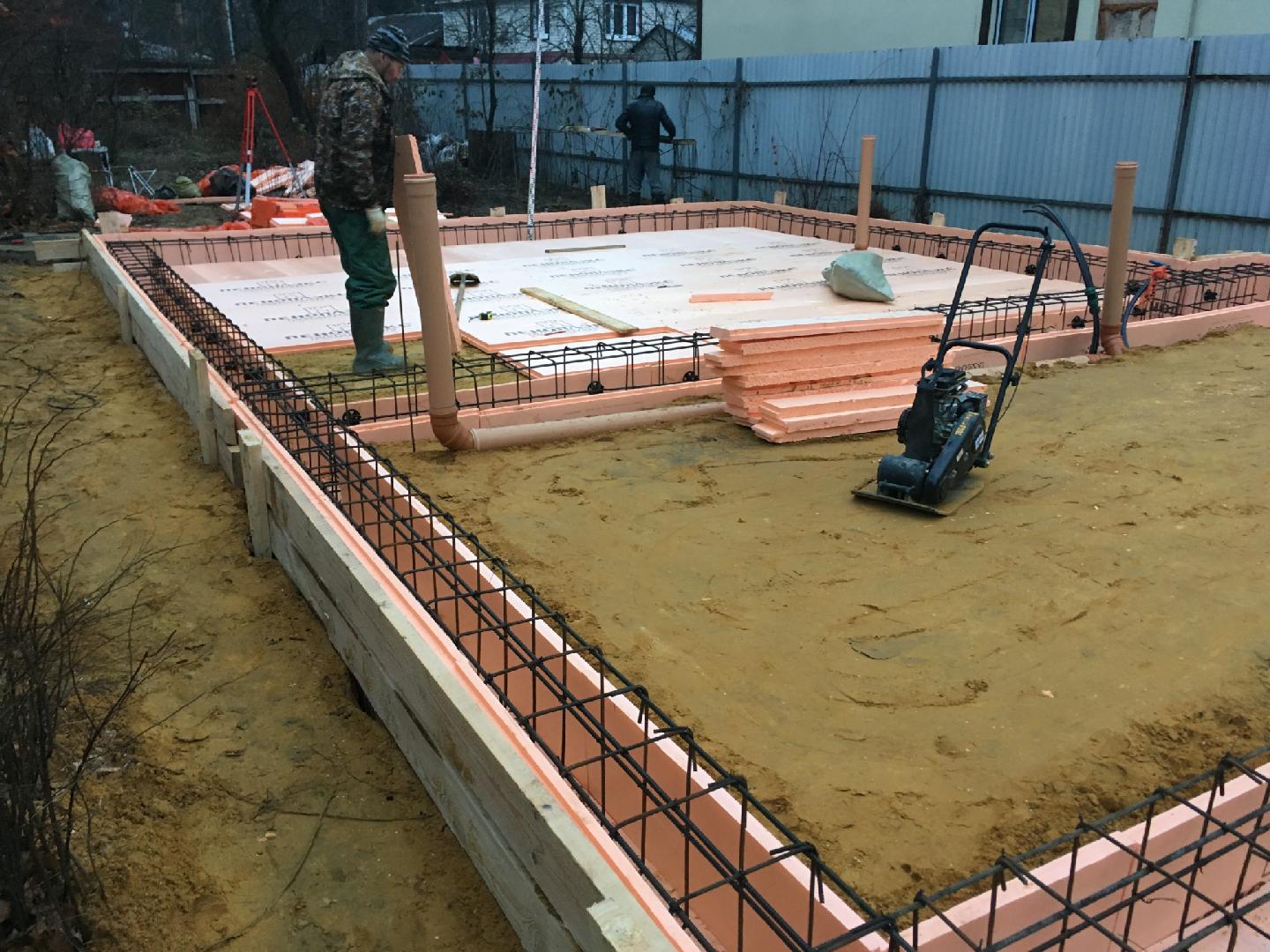
The formwork is mounted on the finished pillow along the contour of the future slab. For rigidity from the outside, the formwork is propped up with spacers. The structure must be sealed so that moisture does not leave the working mixture during concreting.
For reliable waterproofing of the foundation, it is recommended to perform concrete preparation - a thin layer of concrete is poured over the compacted rubble. Layer thickness 50-70 mm, concrete grade M-100.
After the foundation has dried, waterproofing is laid from a special polymer profile membrane or two or three layers of rolled bitumen material. The waterproofing should go to the walls of the formwork, the edges of the sheets are glued together with bitumen mastic or fused, heated by a burner.
Insulation of the foundation
In regions with cold winters, thermal insulation of the foundation slab is practiced when it comes to building a residential building, where it will serve as the base of the floor. Insulation under the foundation slab is laid in an even layer if it is designed flat. When arranging a slab with stiffeners directed downward. From the same insulation, sites are formed in the designed places.
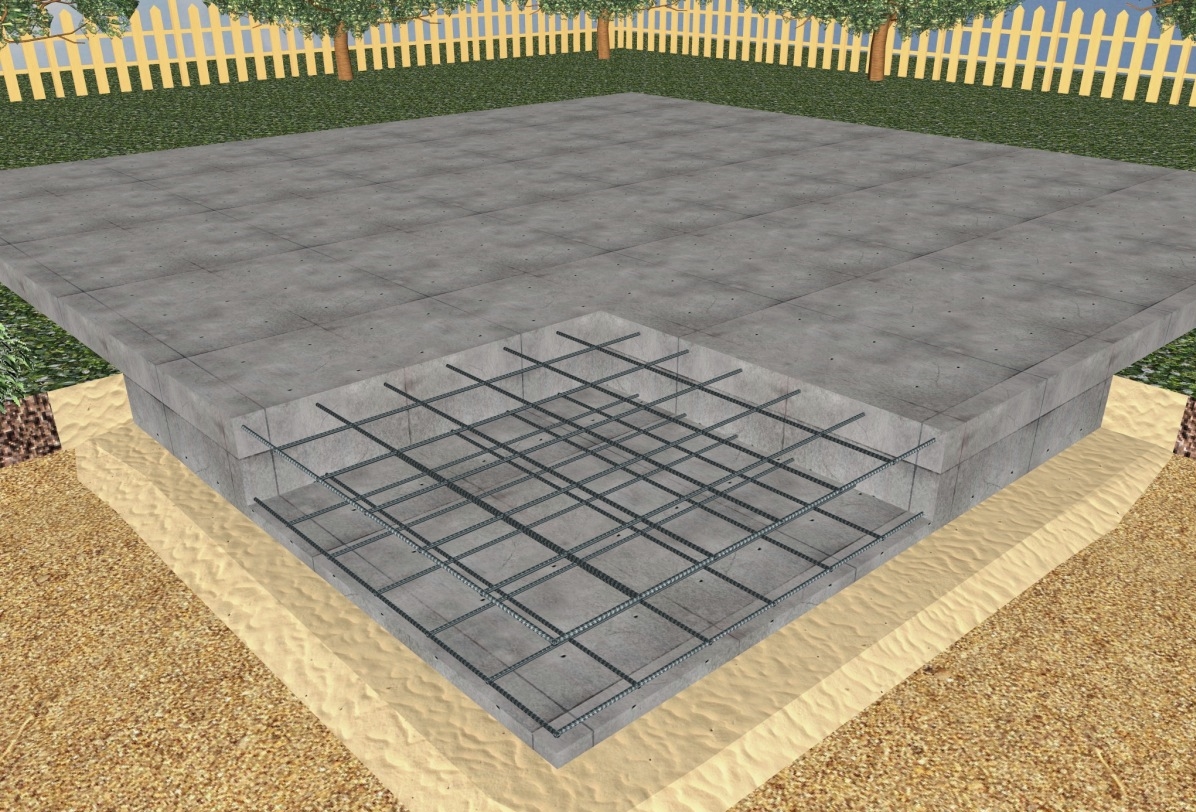
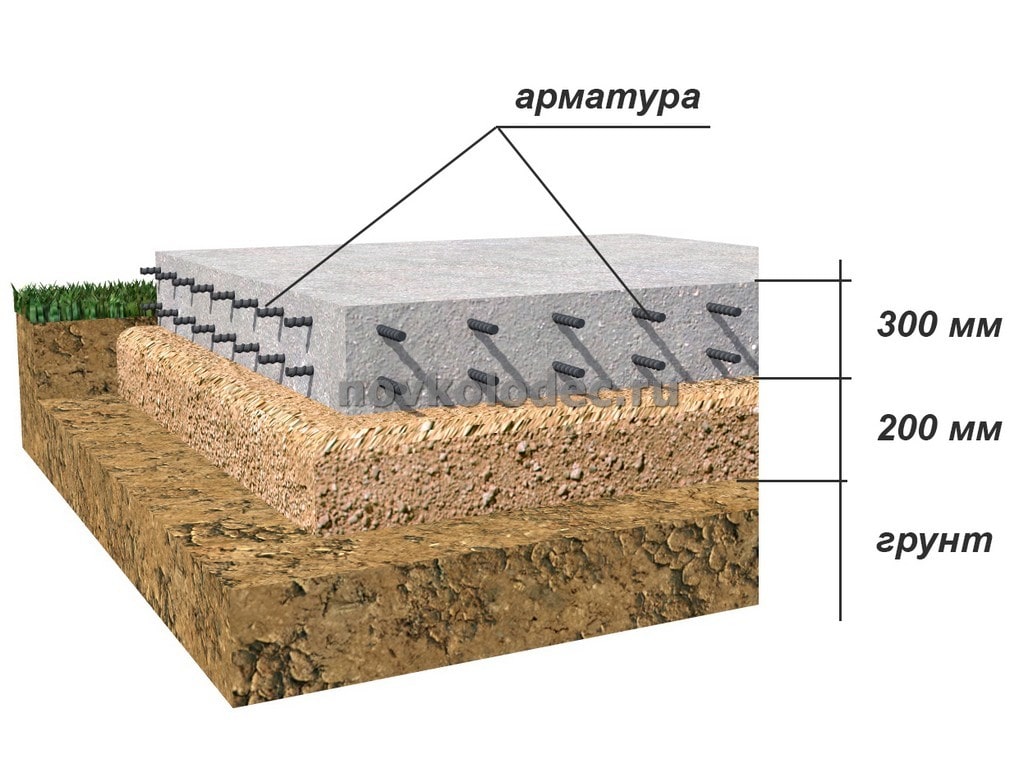
Reinforcement
The installation of the reinforcing cage starts from the bottom mesh. In order to maintain the required clearance of 30 mm from the base, the reinforcement rods are placed on special plastic supports.
First of all, all the longitudinal rods are laid. Then the transverse ones are attached to them using wire twists or plastic clamps. Welding is not used - overheating of the metal at the attachment points weakens the structure.
In order to place the second tier of the lattice at the required height above the lower one, use "spider" stands (they are "frogs") over the entire area (2 pieces per square meter) and U-shaped edge elements.
Concrete works
The pouring of a monolithic foundation slab should be performed within one shift, otherwise it is impossible to achieve the required structural strength. Working mixture requirements:
- concrete grade M-300 (strength class B22.5);
- mobility P3;
- coefficient of water resistance W8 and more;
- frost resistance class F
The mortar fed into the formwork must be immediately evenly distributed over the entire plane. For compacting concrete, eliminating air bubbles, you cannot do without a deep vibrator. The surface is leveled with a rule or with a vibrating screed.
The foundation of a monolithic slab should be covered with plastic wrap to protect it from precipitation, debris and accidental damage. A day later, within 5-7 days, it is required to wet the concrete surface with water. This will prevent the top layer of the slab from drying out and cracking. After 10-15 days, the formwork can be removed - the concrete will have time to gain more than 50% strength. The construction of the walls is started no earlier than a month after pouring - the concrete must be fully ripe.
Knowing how to make a foundation for a slab for a house, you can save a lot of money on the construction of a summer house or a country house, a garage
In order for the foundation to serve for more than one decade, it is important to strictly observe the technology of work and use high-quality materials.
Slab foundation for a private house
The technology for making a slab foundation is quite simple and anyone can handle it. So, first of all, you need to prepare all the necessary materials and tools:
- Fishing line and pegs for marking the territory.
- Rubber hammer or vibrator.
- Technique or shovel for digging a pit by hand.
- Planks and slats for creating formwork and leveling poured concrete.

First of all, the territory is prepared, for this it is cleared of all garbage, weeds and all materials. Then the marking of the area of the future foundation is carried out. Pegs are driven in at the corners, between which the fishing line is stretched.
Then, after the correct marking of the foundation, you can start digging a pit. Its depth is usually about 40 cm, no more. Next, formwork panels are installed around the entire perimeter of the pit so as to form the upper part of the future slab.
It is imperative to make a sand and gravel cushion about 20-30 cm thick. To do this, first fill in a layer of sand, tamp it well, then fill in a layer of gravel, which must also be tamped well. The thickness of each layer should be about 10-15 cm each.
Do not forget about foundation waterproofing. To do this, lay a plastic wrap or geotextile or any other suitable material on top of the rubble. Also, do not neglect the thermal insulation to reduce heat loss. It is carried out over the waterproofing in the form of extradited polystyrene foam.
An important stage in the construction of a foundation slab is its strengthening with reinforcement. To do this, on the bottom of the pit, on top of the insulation, 2 layers of reinforcement are laid, which are interconnected and have cells of about 25x25 or 20x20 cm.
After completing the reinforcement, you can start pouring concrete and it is best if a concrete mixer is used for this purpose. Pouring of concrete should be carried out at one time, in order to exclude delamination of its layers. In addition, concrete must be tamped using a construction vibrator to eliminate air voids.
In conclusion, the surface of the future foundation is leveled using a rule or a wooden lath, after which the foundation is left until it hardens completely. Typically, the curing period is about 4 weeks, and during this time the foundation must be periodically moistened with water and covered with plastic wrap to prevent cracks on its surface. The formwork is removed within a week after the concrete is poured.
Do-it-yourself foundation plate - we disassemble the scheme step by step

Installation of a monolithic foundation
Knowing the order of the layers, the foundation slab can be quickly built with your own hands.
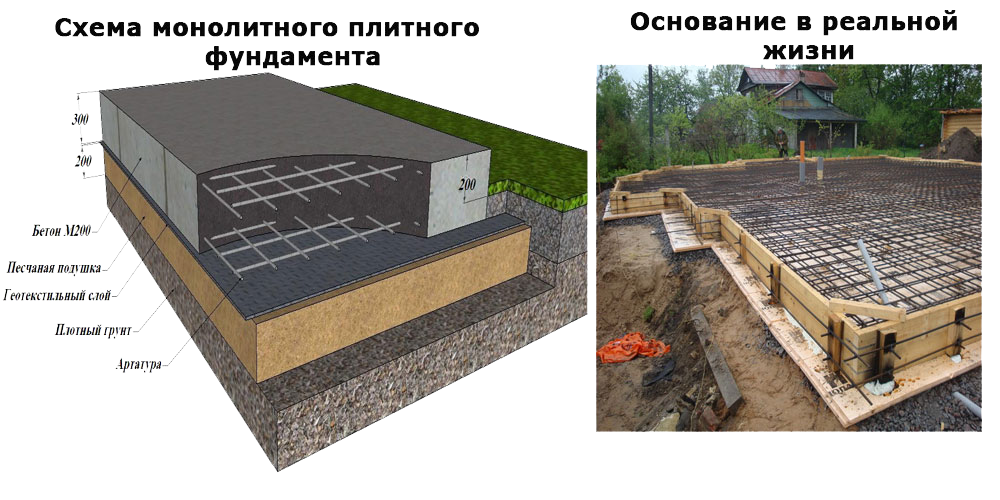
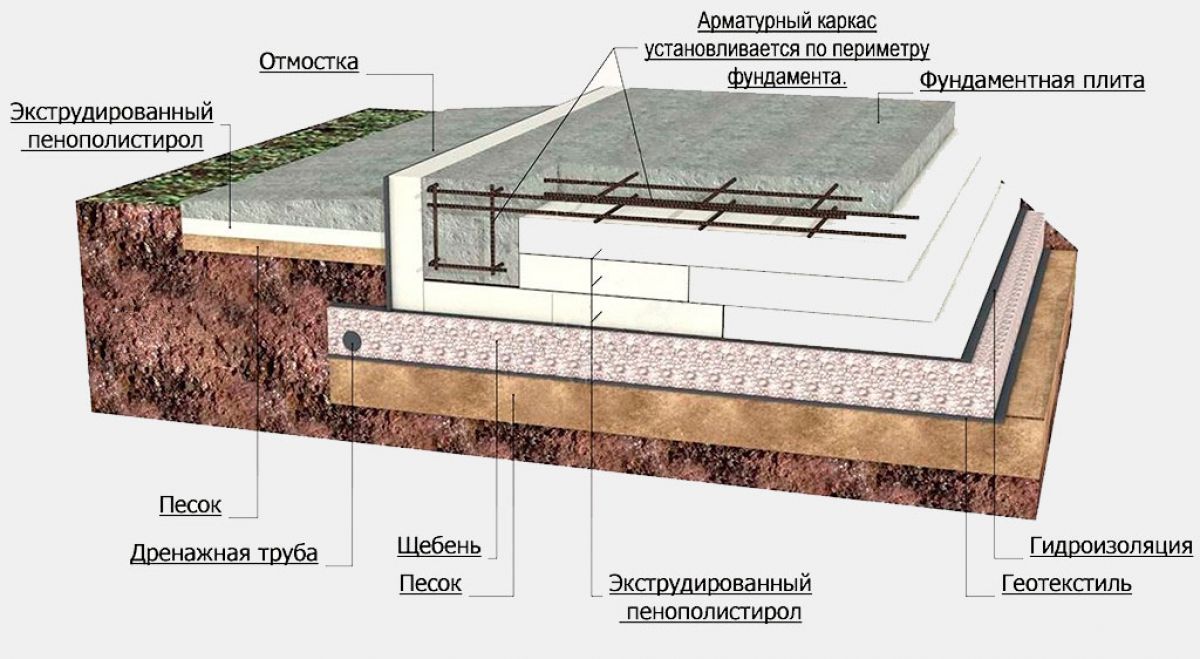
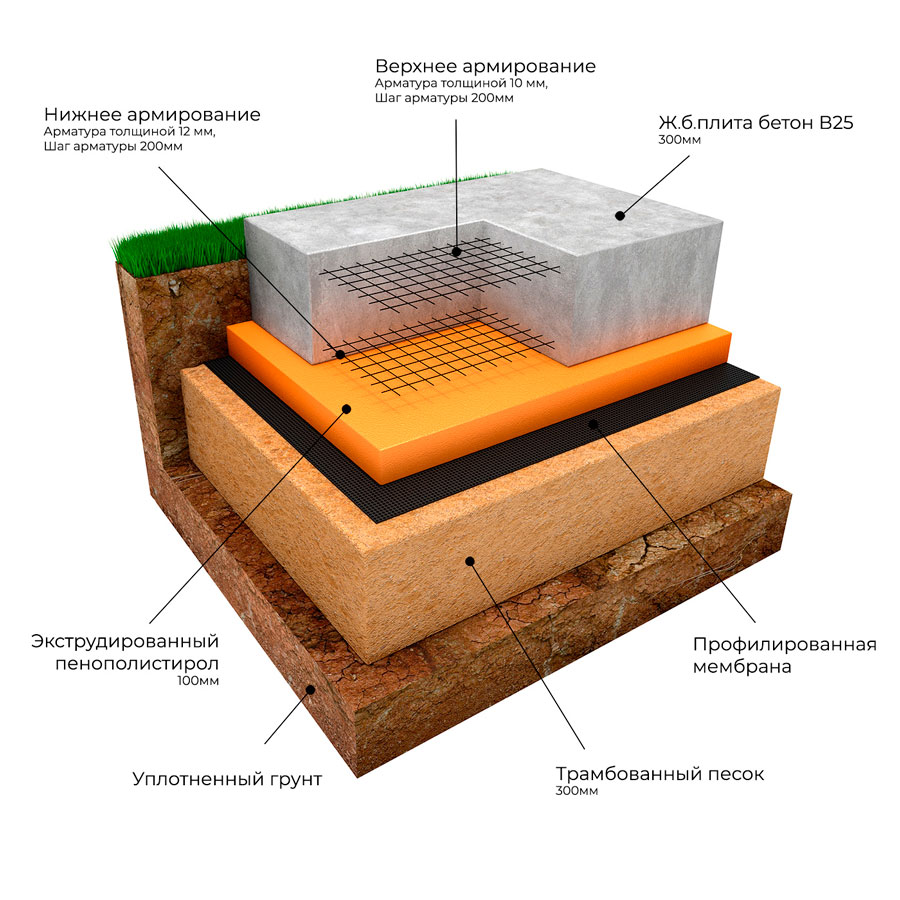
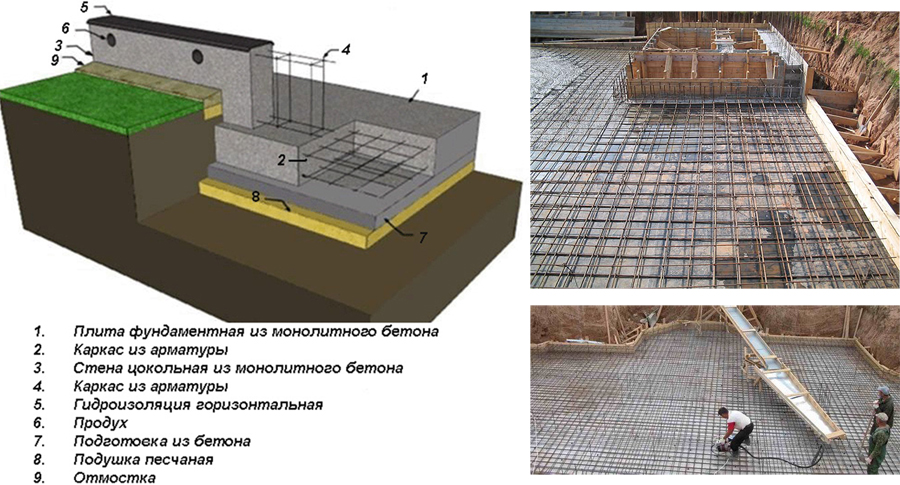
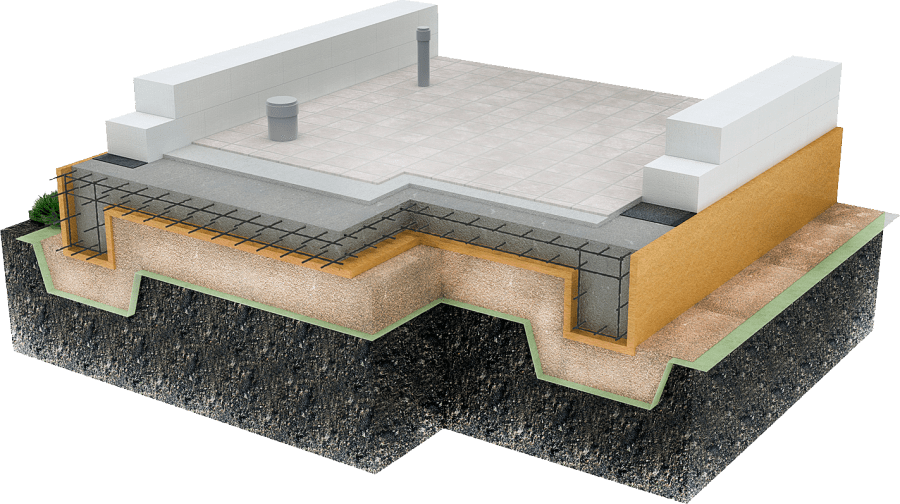
Step by step consider the device of a multi-layer foundation, starting from the bottom layer:
- geotextile fabric. Differs in increased filtering capacity. It is laid on the surface of the soil, making it difficult to mix the sand and crushed stone bedding with the soil;
- pillow. It is carried out from a compacted mixture of sand with gravel or crushed stone. It restrains the swelling of the soil, levels the site and allows you to place drainage lines in the compacted array;
- concrete. A thin layer of concrete mortar, poured onto a pillow, is called a footing by builders and is poured to level the base under the main slab. The concrete increases the load capacity;
- waterproofing material. It makes it difficult for groundwater to penetrate to the foundation surface, and also prevents moisture leakage from the concrete solution. This increases the strength properties of the monolith after hardening;
- thermal insulation. A heat-insulating layer is laid for additional insulation of the room or for arranging underfloor heating;
- formwork. The formwork structure allows the concrete mortar to retain the required shape and prevents moisture loss during hardening. Its design can be stationary or dismantled;
- fittings. To increase the strength characteristics of the concrete mass and prevent the formation of cracks, reinforcement with steel rods is performed. They absorb bending forces and increase durability;
- concrete. This is the final layer of the foundation structure, located at the top of the "pie".The concrete mass, reinforced with a reinforcing lattice, absorbs the force from the mass of the structure.

Slab foundation device diagram
Pros and cons of a monolithic foundation
Despite the fact that there are much simpler and cheaper types of bases in arrangement, the technology of a monolithic foundation is actively used throughout the country, since it has a unique set of advantages:
- the possibility of arrangement on those types of soil where the construction of another version of the foundation is impossible. These are, for example, fine sandy and dusty soils, bulk and water-saturated, weakly bearing and clayey soils;
- durability is higher than that of other types of foundation, and reaches 150 years, provided that all the intricacies of its arrangement are observed;
- record bearing capacity. The monolithic slab foundation can withstand enormous loads. For private construction, this means that a 3-storey brick house can be built on it;
- the loads on the base are evenly distributed, because it is monolithic. The absence of seams and joints will save the structure from the appearance of deformations and destruction during ground movements, which means that the house will not be distorted and will not be covered with cracks;
- during seasonal heaving of the soil, the base rises evenly with the house, and then it also drops evenly, while there are no deformations at all;
-
a monolithic base greatly simplifies the arrangement of the subfloor. After minimal preparation, you can already put laminate, tiles or linoleum on it;
- a monolithic slab becomes an excellent protection against soil moisture that can penetrate into a house built, for example, on a strip base;
- the minimum amount of earthworks, since the monolithic slab foundation is deepened by about 2/3 of its thickness and belongs to shallow foundations. Therefore, preparatory work is minimized, which allows you to reduce time and financial costs;
- relative simplicity and speed of arrangement. It will be difficult to do without special equipment, but it will take a minimum of time to prepare such a reliable foundation. In addition, almost any master will be able to level the site, fill in the sand and gravel mixture and tamp it, if the necessary equipment is available.
As a result, we get a unique foundation that can be used almost always and everywhere, but, alas, it cannot do without drawbacks:
- price. To fill the base under the entire future building, it will take a lot of concrete and reinforcement, and this is a big waste;
- pouring must be done at once, and in order to prepare such a large amount of concrete, you will have to use special equipment (the best option is an automatic mixer), and this is an additional cost;
- it is better to entrust the construction of a monolithic foundation to specialists. Of course, you can try to do it on your own, but you will have to rent special equipment;
- it is impossible to equip a basement or cellar under the house;
- when building a monolithic foundation in areas where the temperature reaches record lows, it is necessary to additionally equip a layer of thermal insulation, which increases the cost of building a foundation;
- a monolithic foundation is not suitable for areas where landslides are often observed. Also, it is better not to use it on soils with a thick silty or vegetative layer. Another limitation is steep terrain;
-
it is necessary to think over the location of all communications in advance.
Foundation calculation
The construction of slab foundations begins with some preparatory work. These include the definition of the foundation pie and the method of reinforcing floating slabs. In addition, it is necessary to select waterproofing materials for the lower sections of the wall structures and to calculate the armored belts.
Scheme for calculating the slab foundation.
In order to make the correct calculation of a monolithic foundation, the following must be taken into account.First you need to decide on the thickness of the slab, the total area of the slab and the depth at which it will be laid. The area of the foundation should be slightly larger than the area of the building. This will help improve the strength characteristics of the building and reduce the likelihood of house sinking.
The calculation of the area of the foundation is made according to the formula:
S> γn F / γc Ro,
where,
γ = 1,2 - coefficient of reliability;
F - load on the foundation (total weight of the house and payload);
γc - coefficient of working conditions, depends on the type of soil (for plastic clay it is 1.0, for low-plastic clay, low-moisture sands - 1.2, for coarse sands 1.2, for fine sands - 1.3,);
R0 is the conditional soil resistance of the foundation for shallow foundations (determined according to special tables).
Table of indicators of soil resistance.
Do not forget about the load inside the building. It should be borne in mind that the building will contain furniture, household appliances, and people will also live. Therefore, it is necessary to add another 150 kg per m2 to the obtained result of the calculation.
According to their properties, slab foundations belong to the category of shallow and shallow foundations. The thickness of the slab depends on the characteristics of the soil and the type of building.
After all the calculations are completed, it is necessary to divide the resulting number by the area of the building under construction and correlate with the bearing capacity of the soil. Despite all calculations, stiffeners should be provided under the base floors and walls.