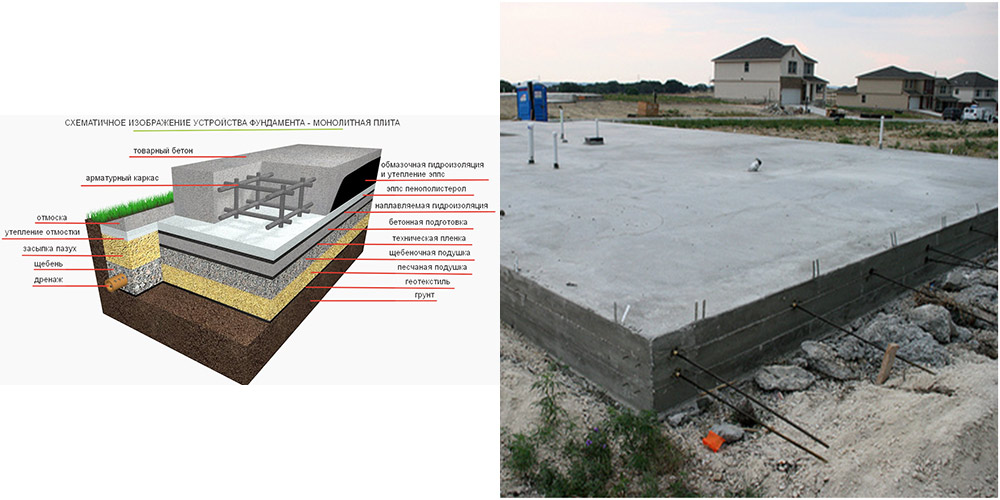
Slab foundation - what is it
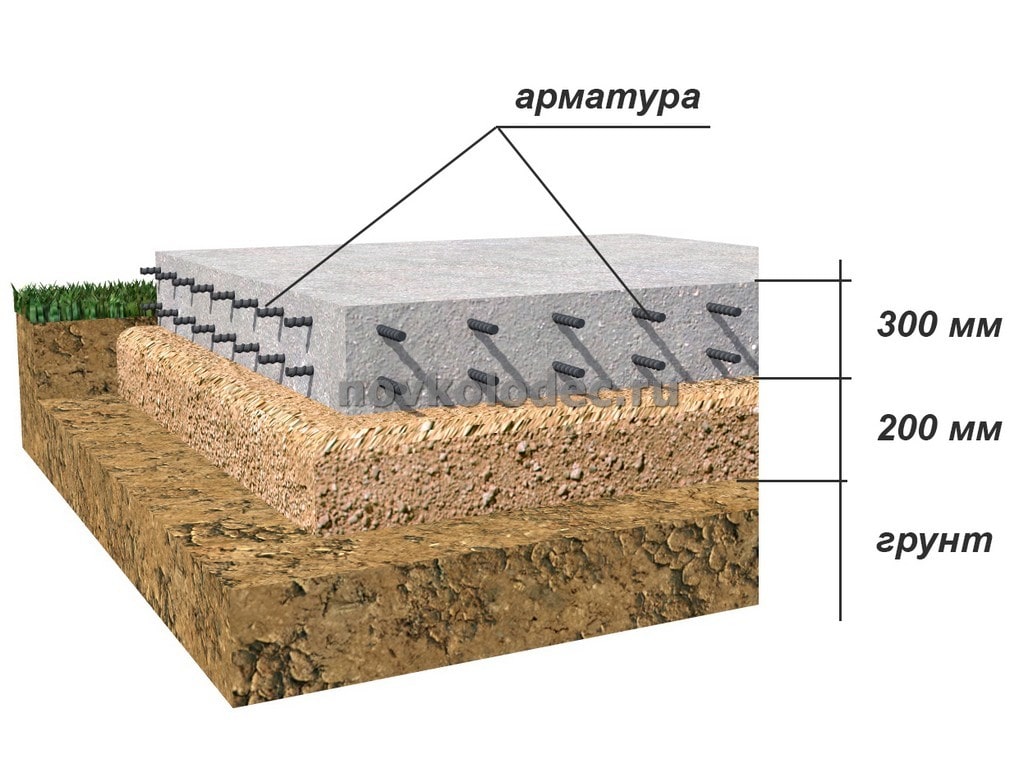
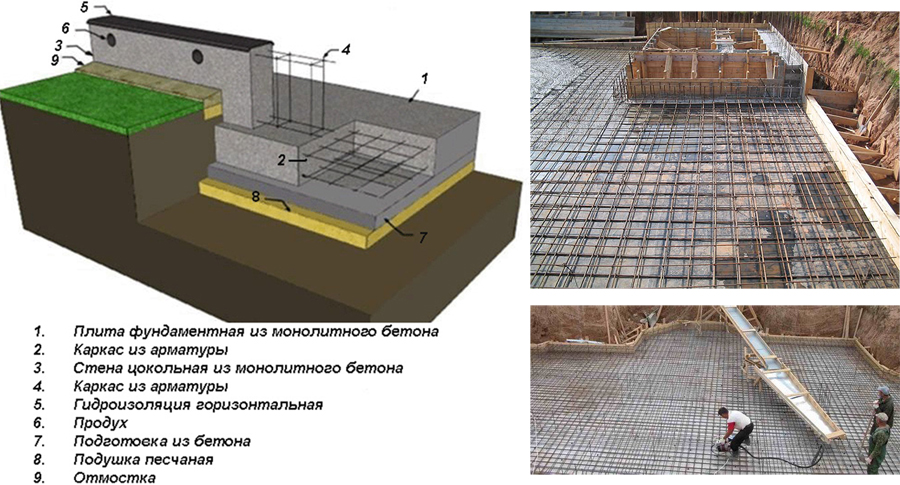
A monolithic slab for a house belongs to floating unburied foundations, there are also shallow foundations. It got its name due to the fact that the reinforced concrete base is poured under the entire area of the house, forming a large slab.
A prerequisite is the presence of a sand and gravel cushion, which redistributes the load from the house to the ground, and serves as a damper in case of frost heaving. Often, such a foundation is the only possible solution. For example, on unstable, loose soils or on clays with a large freezing depth.
The construction of a monolithic slab foundation is simple and reliable, but its production requires a large amount of reinforcement and large volumes of high grade concrete (not lower than B30), because the entire area occupied by the building is reinforced and concreted, and even with a margin - for greater stability. Therefore, such a foundation is considered expensive. In principle, this is so, but it must be considered. In some cases, its cost is lower than that of a deep belt - due to less land work and less concrete.
The depth of the monolithic slab is determined depending on the mass of the house and the type of soil. With shallow depth on heaving soils in winter, the house, together with the base, can rise and fall. With the correct calculation of the reinforcement and the thickness of the slab, this does not affect the integrity of the building. The slab compensates for all changes due to the elastic force. In the spring, after the soil has melted, the house "sits down" in place.
There are four types of slab foundations:
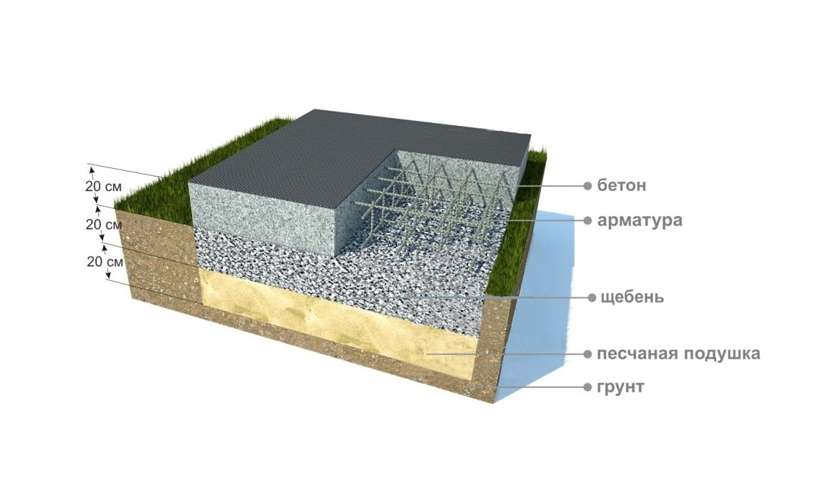
- Classical. A reinforced concrete slab is placed on a sand and gravel cushion with or without insulation. The thickness of the concrete layer is 20-50 cm, depending on the soil and the mass of the building. The thickness of the pillow layers depends on the depth of the fertile layer - it must be completely removed. The resulting excavation can be filled with sand and gravel by 2/3.
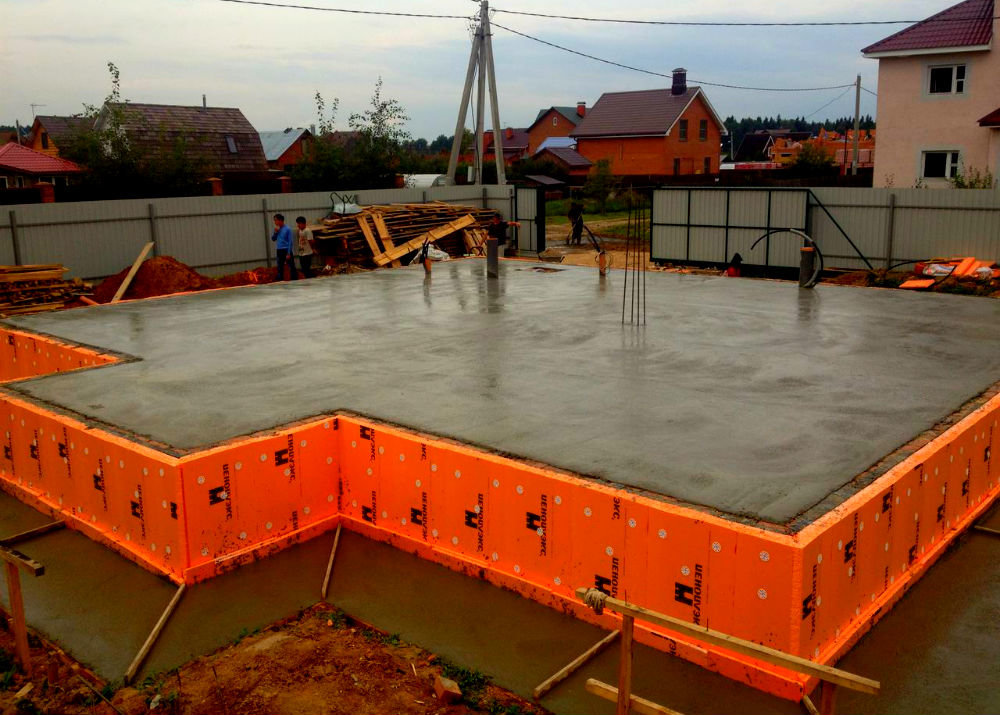
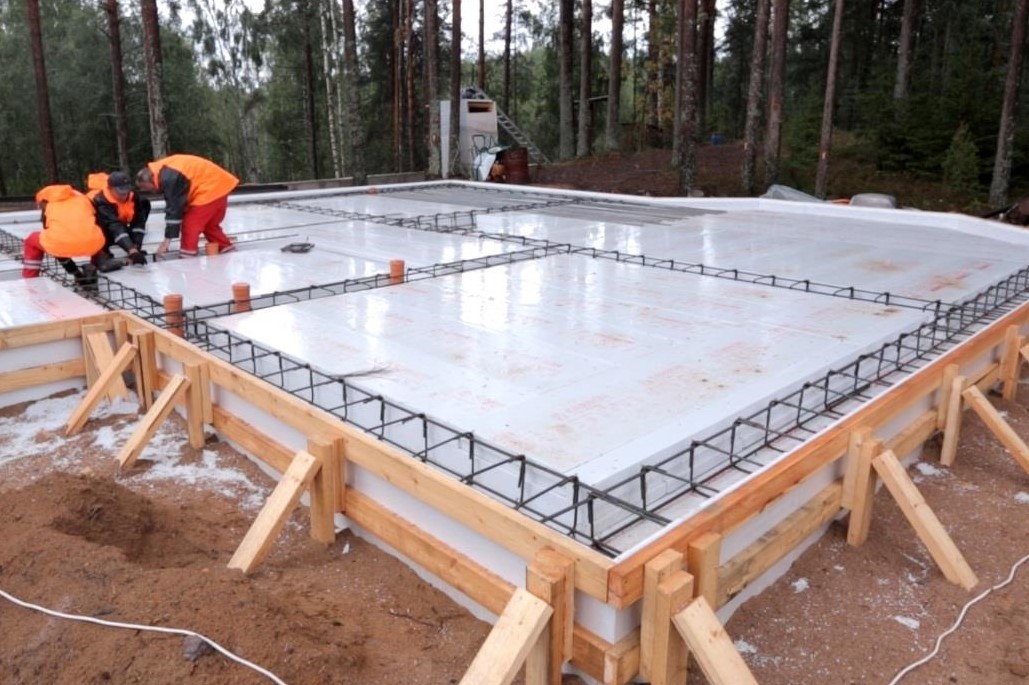
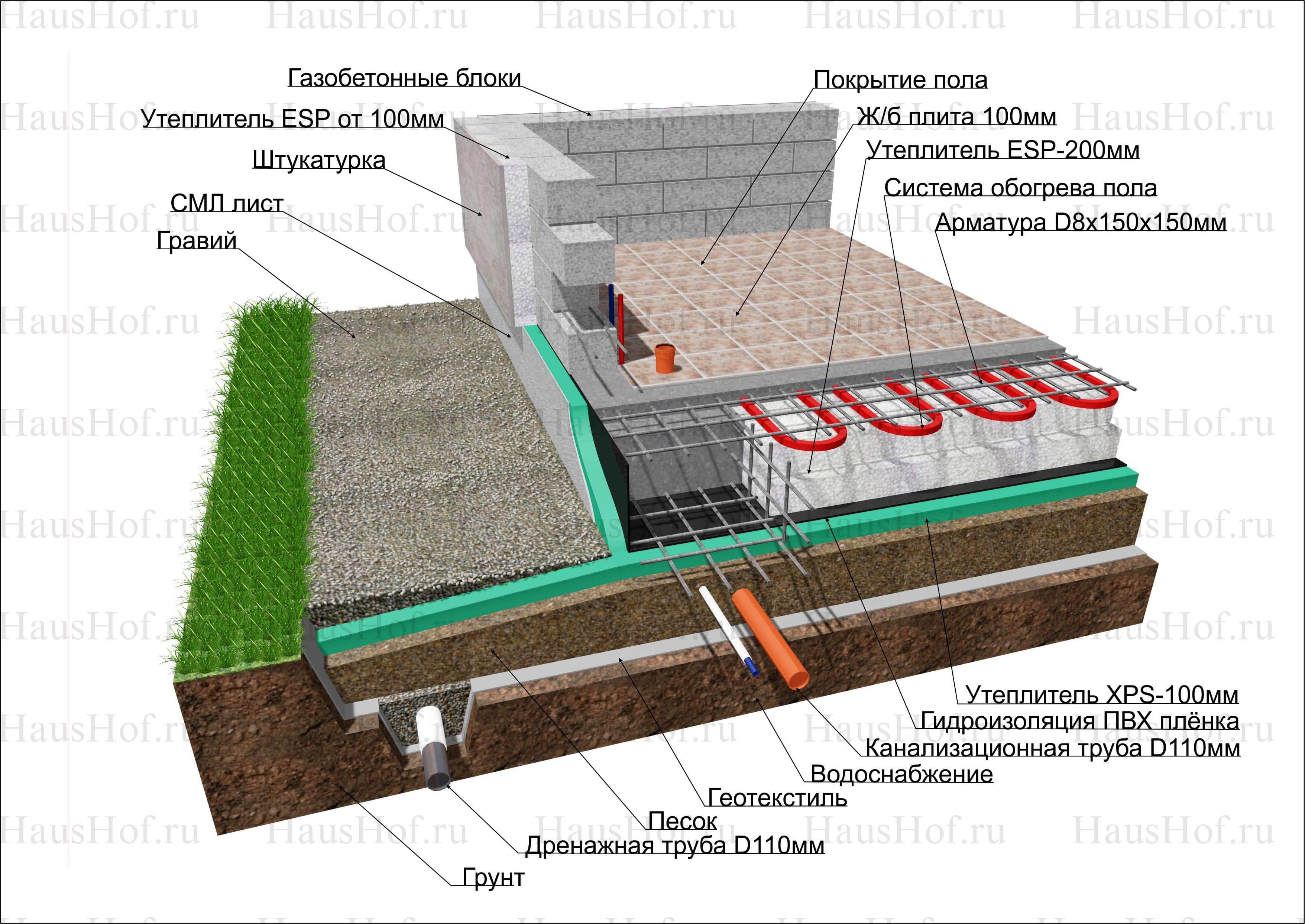
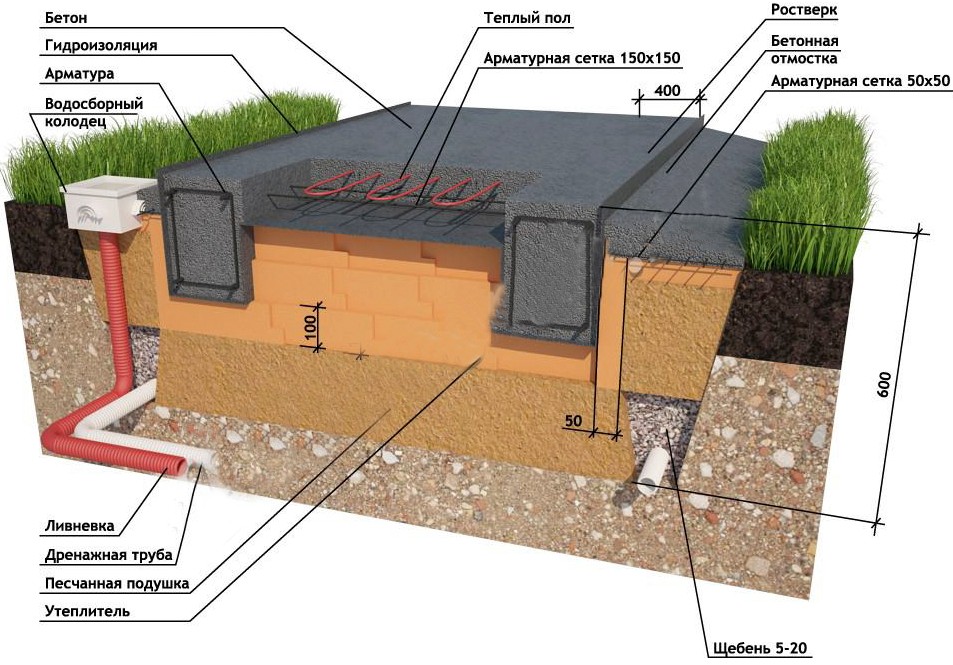
- Insulated Swedish plate (USHP) with built-in underfloor heating. Firstly, it differs in that the slab formwork is non-removable - made of L-shaped polystyrene foam blocks. This significantly reduces heating costs - heat loss is minimal. Also, underfloor heating pipes are laid on top of the insulation, reinforcement is laid on them (sometimes under them) and everything is poured with concrete, the thickness of the concrete layer is 10 cm.All communications, including water supply and sewerage, are laid even at the stage of base preparation - in a sand cushion. That is, after the foundation is made, the heating system is ready and the engineering systems are installed. This approach allows you to speed up construction, but the foundation itself is expensive. This type of foundation requires a competent engineering calculation and the same execution: when calculating and laying communications, one cannot be mistaken, since alterations are impossible. Also, questions arise about the repair of systems embedded in the foundation. It is impossible, therefore expensive materials are laid with a long warranty.
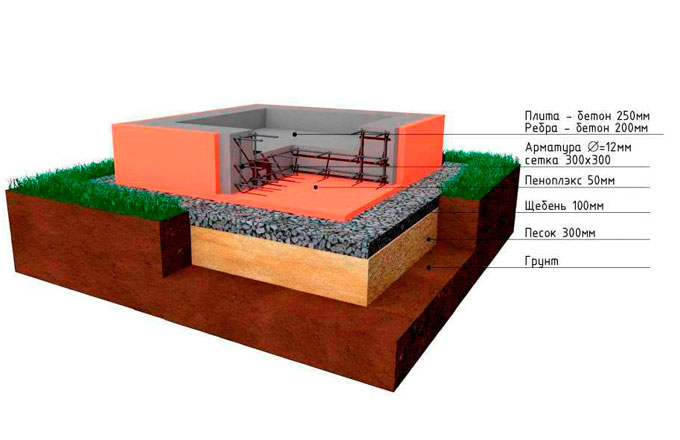
- Russian - plate with stiffeners. To strengthen the structure for heavy houses and in difficult operating conditions (strong frost heaving), Russian scientists came up with the idea of making more massive stiffeners. They are usually arranged under load-bearing walls. At the same time, the complexity of the work increases - stiffening ribs are separately arranged, separately - a slab. But the bearing capacity of such a foundation is much higher, which makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the slab - up to 10-15 cm.
How to make a floating foundation with your own hands
The small volume of earthworks and the possibility of self-production without the use of heavy construction equipment make floating foundations in demand among individual developers for the construction of various light structures, such as low-rise buildings and outbuildings, auxiliary structures and technical facilities.
All work on the construction of the foundation can be divided into several stages: preparatory and the process of performing the work itself.
At the stage of preparation, a drawing of the structure to be constructed is drawn up and the need for the materials used is calculated, after which these materials are purchased, and the necessary tools and equipment are prepared.
 The use of prefabricated concrete and a concrete pump will shorten the time of work and ensure a high-quality pouring of the concrete slab
The use of prefabricated concrete and a concrete pump will shorten the time of work and ensure a high-quality pouring of the concrete slab
When the preparatory work has been completed, you can start performing them in the following sequence:
| Illustration | Description of action |
 |
Marking is carried out at the construction site. |
 |
The pit is dug and the base is rammed. |
 |
The formwork is being mounted. |
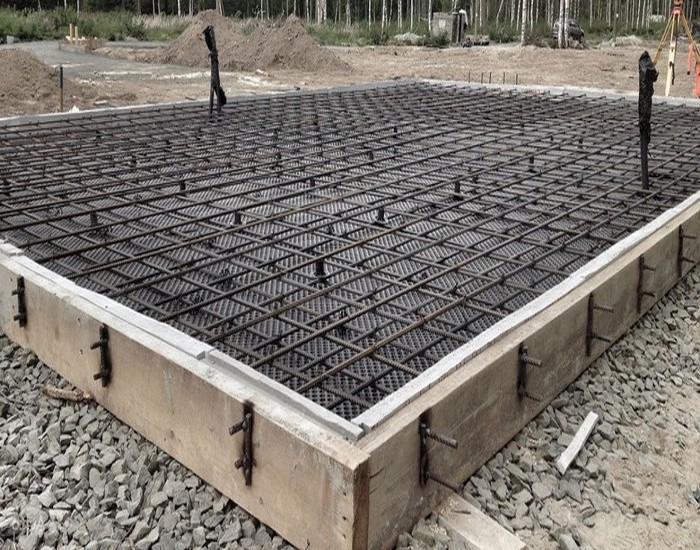
 |
Fittings are being laid. |
 |
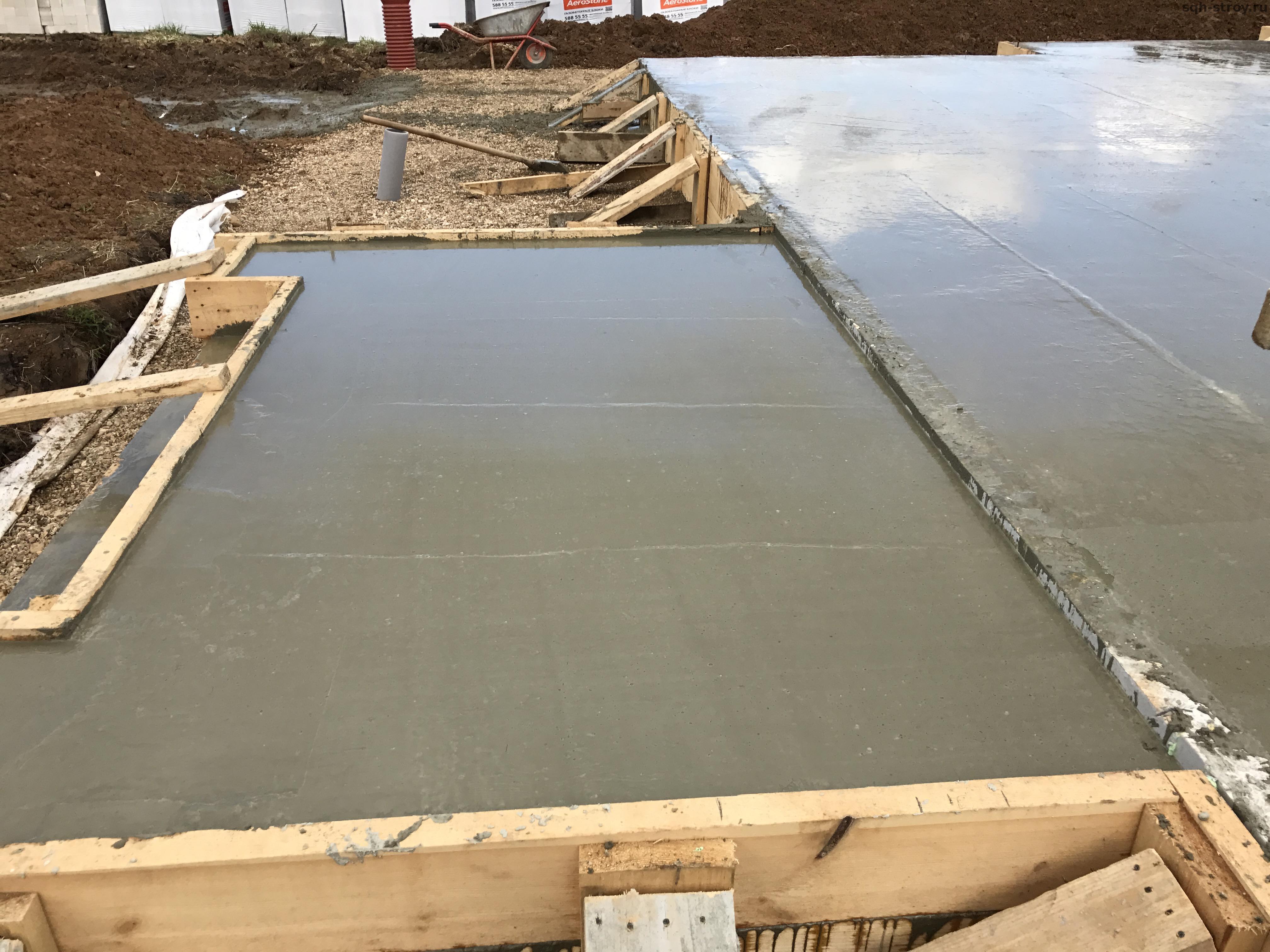
Concrete is being poured. |
 |
The concrete is leveled at the specified level in accordance with the exposed formwork. |
 |
The surface of the slab is smoothed. |
After the slab is poured, it is necessary to give some time for the concrete to harden, after which the installation of the enclosing structures can be carried out.
Construction technology

If you plan to use a slab foundation as the floor of the first floor, then the structure must be carefully insulated
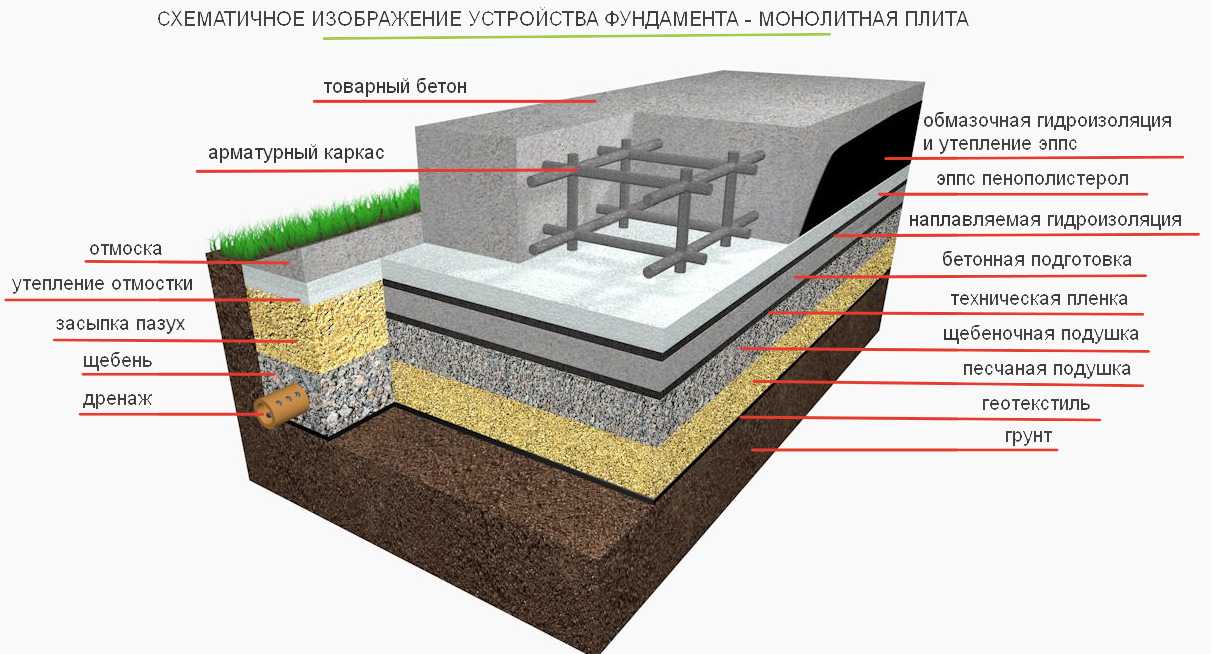
The floating foundation is built in several stages. First of all, it is necessary to prepare the construction site: remove unnecessary green spaces, clear the site of debris and carry out markings. After that, a pit of the required depth is dug. In this case, do not forget that below the base of the slab there will be a layer of sand and gravel. If the volume of work when digging a foundation pit is significant, then it is better to involve construction equipment.
After that, the work is carried out in this order:
- The bottom of the pit is leveled and carefully tamped. The permissible drop is at least 50 mm. If there are more significant differences in height at the bottom, then at the maximum load on the base, the slab structure can crack and begin to collapse.
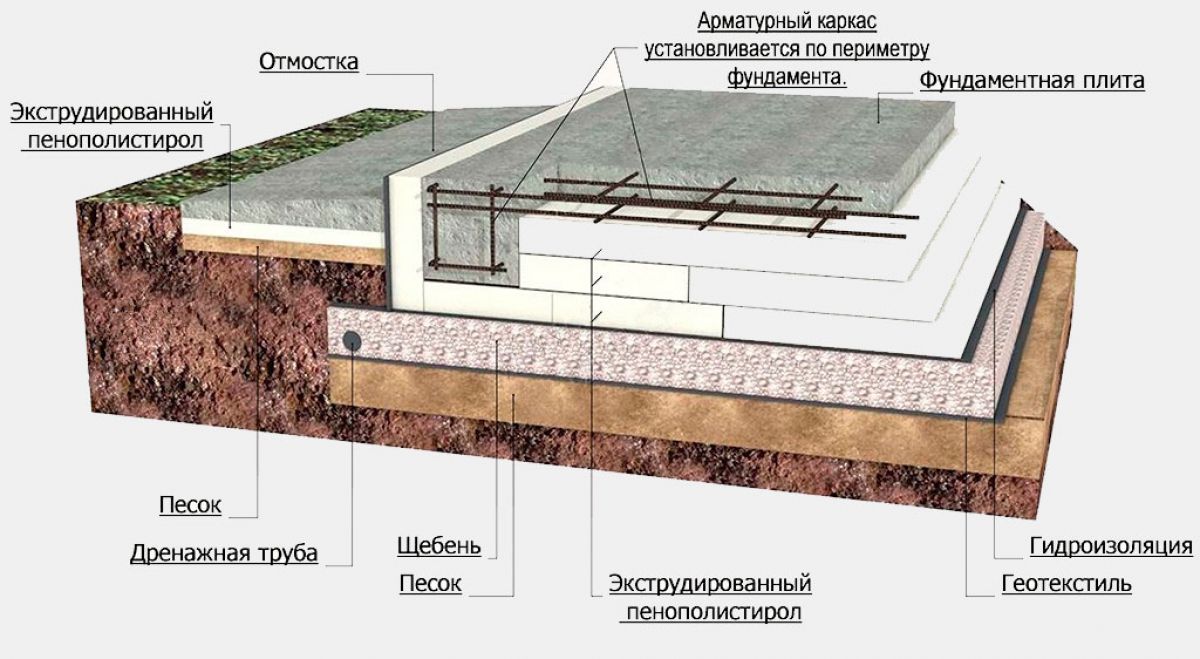
- It is also recommended to additionally perform a drainage system at the bottom of the excavation and cover the surface with geotextiles. So you can protect the gravel-sand cushion from being washed away by groundwater.
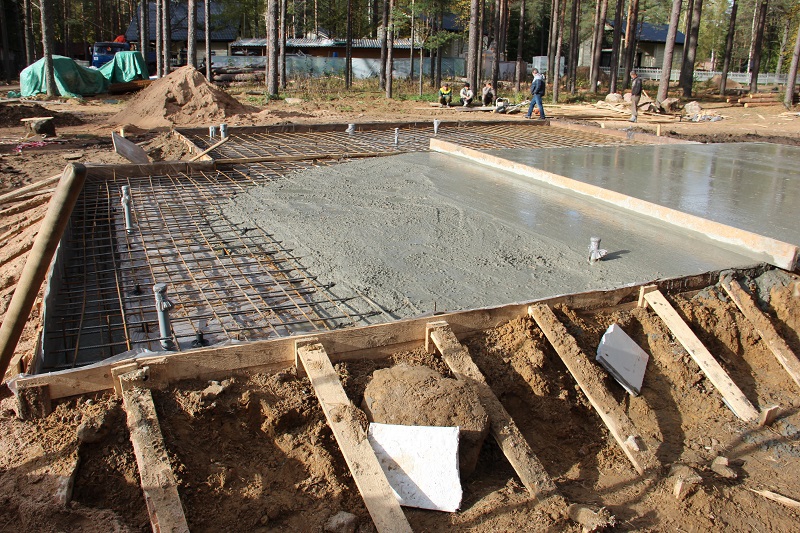
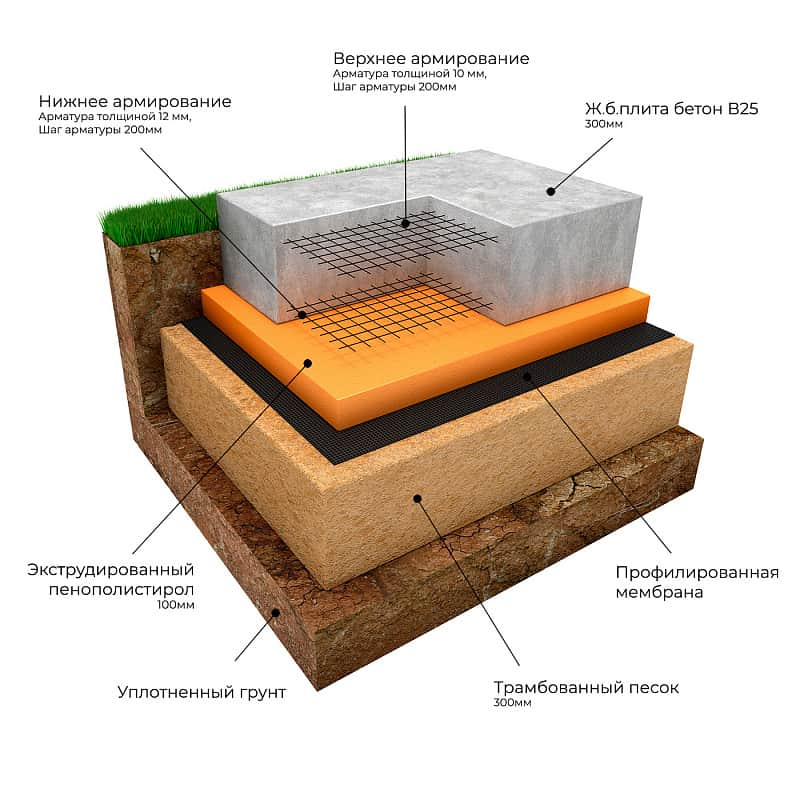
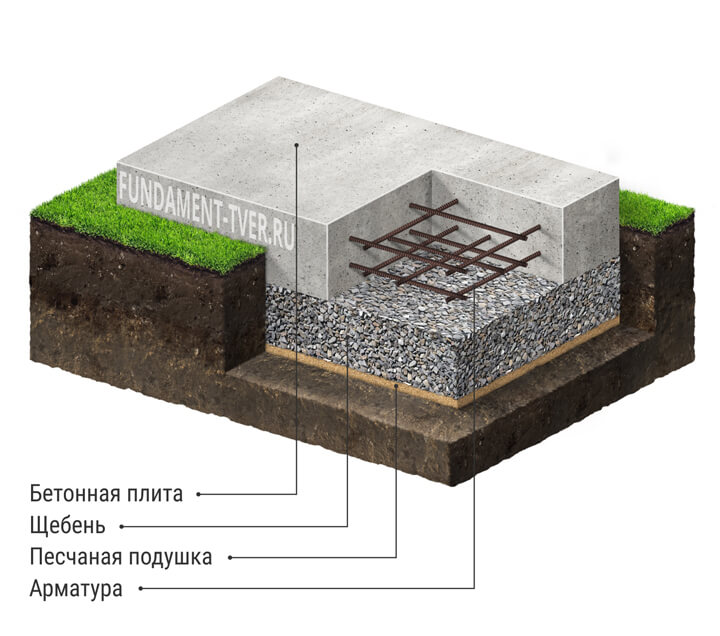
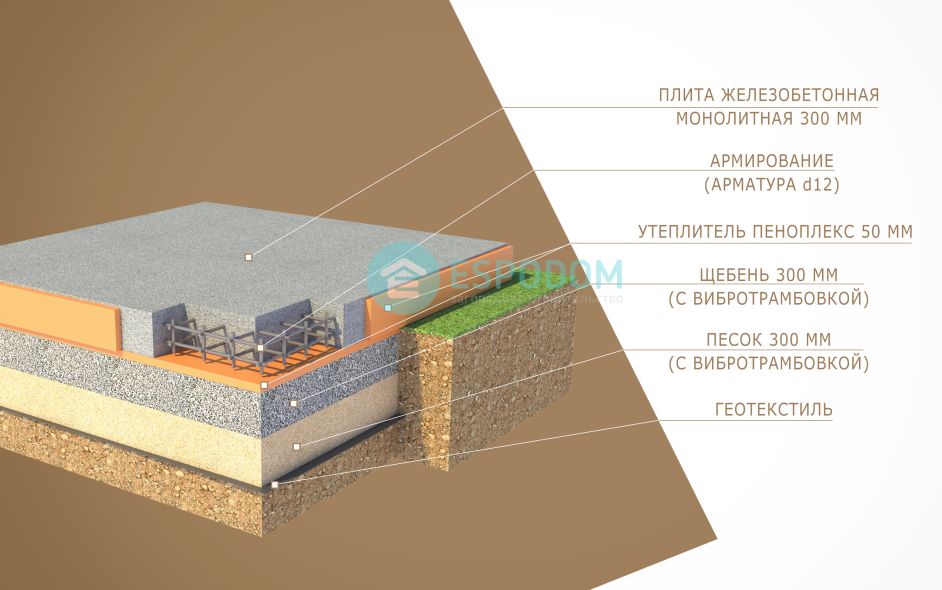
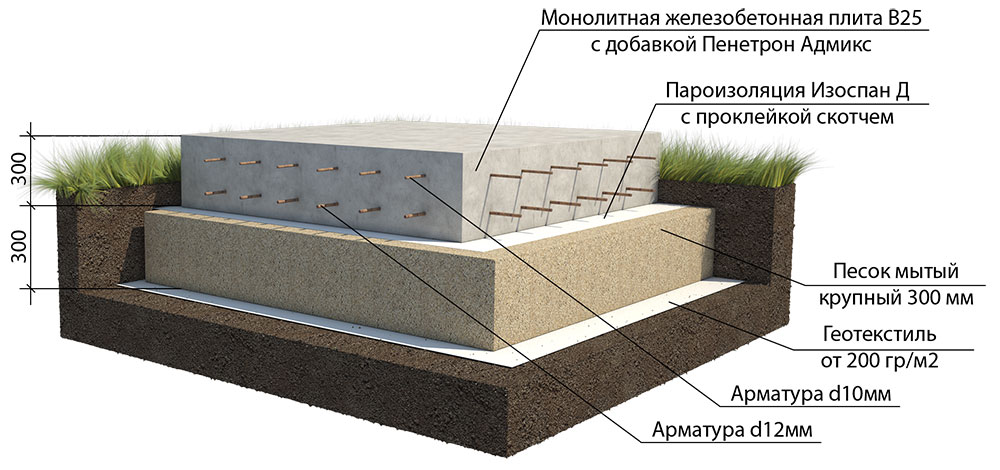
- Now we start making a pillow for a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. For this we use coarse sand or crushed stone. You can also use a mixture of these materials. Usually the height of the pillow is 100-400 mm. The thickness of this layer depends on the calculated height of the foundation slab and the characteristics of the soil. After filling in the sand or mixture, the interlayer is moistened with water and rammed well.
- If you plan to use a slab foundation as the floor of the first floor, then the structure must be carefully insulated. This should be done at this stage. For this, a dense polyethylene film is spread on the rammed pillow. Then a layer of extruded polystyrene foam is laid. The thickness of the material slabs depends on the climatic conditions of the region and is determined on a case-by-case basis.
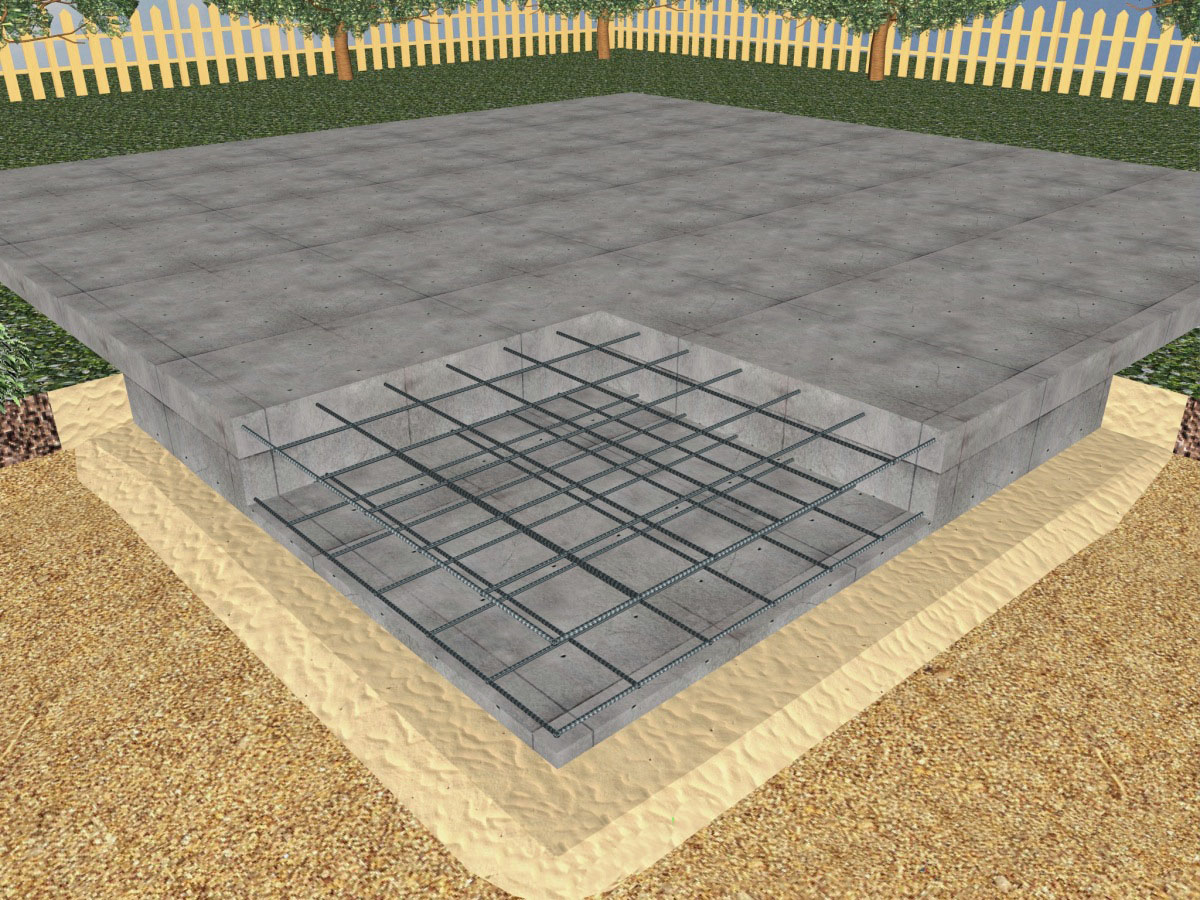
- After that, you can proceed to the manufacture of the formwork. For this, it is better to use laminated boards, since the edge of the base will be smoother, and the products can be reused. A smoother edge of the slab will facilitate the installation of the insulation. Laminated boards are fastened together with self-tapping screws. For rigidity, spacers are installed on the reverse side every 0.5-1 m.
Next, we move on to reinforcement.

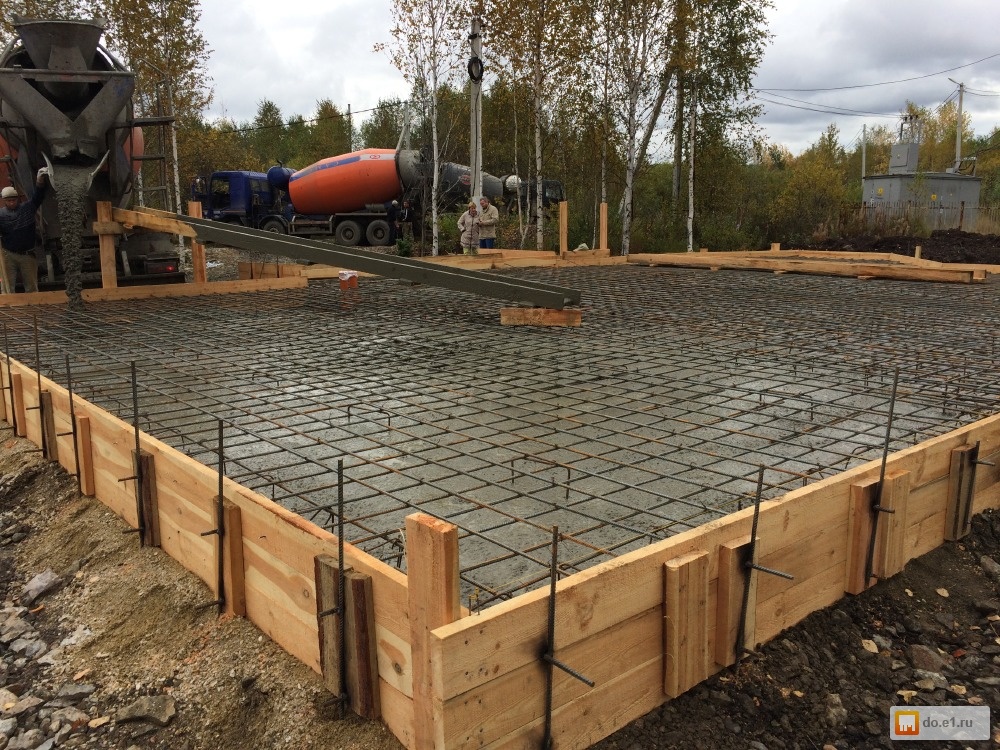
The steel frame is made in the form of a spatial structure from a bar of the required thickness
The steel frame is made in the form of a spatial structure from a bar of the required thickness (usually the 3rd class reinforcement with a diameter of 12-14 mm is used). It is better to use wire to hold the bars together, rather than welding, in order to provide more flexibility and not create additional stress at the joints.
Since the reinforcement cage on all sides must be protected from corrosion by a layer of concrete of at least 5 cm, first, concrete is poured into the formwork with a layer of 50 mm.After it has solidified, a reinforcing cage is installed. During installation, the frame should not come closer to the formwork surface by more than 50 mm. Now we fill in the rest of the concrete mixture.
The poured concrete composition must be tamped using special equipment.
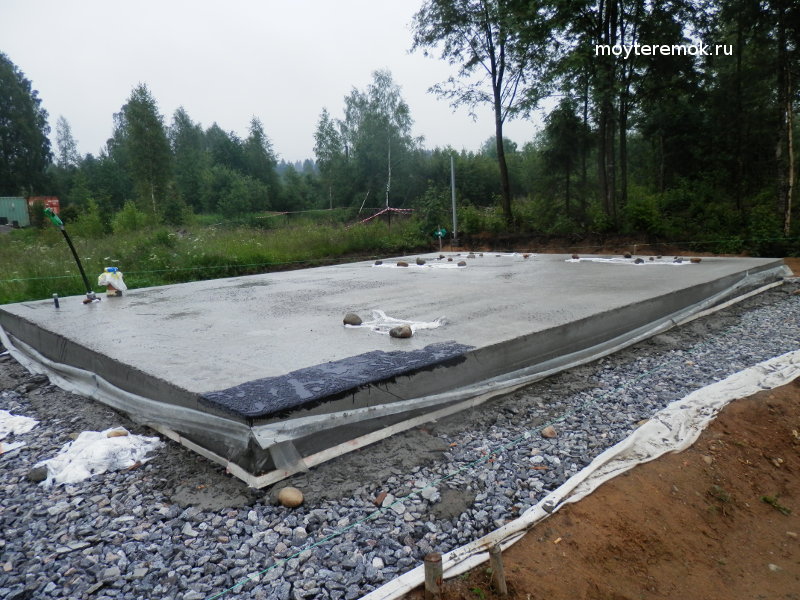
Finally, the surface of the concrete slab should be checked for evenness using a level. If irregularities are noticed, they are corrected. After that, the surface of the base is covered with plastic wrap for a couple of weeks. In the first few days, the concrete surface is moistened with water. This will ensure more uniform evaporation of moisture from the concrete and its high-quality hardening.
After removing the formwork, the side walls of the slab foundation can be insulated with polystyrene.
How to build a bath on a "floating" stove?
In the standard version, the arrangement of the floating foundation is very simple - a reinforced concrete monolithic foundation located under the entire building area at once. It is done on normal soil, buried, and where there is a lot of sand underfoot - shallow.
How can you build a floating foundation with your own hands for your bath:
Stage I. The entire layer of vegetation is removed from the entire place where the bathhouse will be, plus 1 m for the blind area. The removed layer is transferred to the garden. A pit is dug - under the design mark. It is better to hire an excavator for this.
It is important not to dig, otherwise the foundation may simply burst at the dig site. This is a very serious mistake.
So that the edges of the pit do not crumble, it is better to dig them with a slight slope.
Stage II. A layer of crushed stone 10 cm thick is filled in, it is laid in several stages, it is well rammed (for example, with a log with a handle). Then - a layer of sand that fixes the rubble and does not allow it to "walk". And its resistance to frost helps the new foundation to resist the cold.
Stage III. A waterproofing layer is laid - usually a dense, expensive plastic film. It is necessary so that moisture does not then seep into the foundation, and valuable concrete "milk" does not leak during the pouring of the solution. Then a small layer of concrete is poured - M-100.
Stage IV. Formwork is under construction. When the foundation was submerged in the ground, then the walls of the pit can fulfill this role, but they must also be waterproofed. For formwork, boards with a width of 25 mm, which are 50-100 mm thicker than the height of the foundation, are well suited. A control cord is laid along the upper edge of the formwork, only one side of it is fixed in it, while the second, with a tied load, is lowered from the other side. At the time of pouring the solution, you can remove the cord.
Stage V. Reinforcement is laid - this is the most critical stage. Metal rods should look out of the foundation at the places where the walls are built, this is necessary to achieve a strong connection with the base. However, such fittings cannot be cooked, they can only be tied with soft wire. The rods in the corners are closed in a semicircle, their ends are inserted into the side walls of the foundation, and a one-piece flexible structure emerges.
Stage VI. At this stage, the base is concreted: the mortar is laid in layers up to 15 cm, then it is carefully leveled and rammed by bayonetting.
It is necessary to pour concrete in one step, for which it is better to use a concrete mixer. It is better to use the recipe as follows: for 1 part of cement - 1 part of sand and water. It is necessary to tamp the concrete until a wet layer appears on the surface. Then a wooden lath is taken and everything is leveled.
On the first day, the foundation is wetted every 4-5 hours, then covered with a film so that no cracks appear. The next day they are moistened only 3 times, then - only in the morning and in the evening. And when it dries up, the formwork is removed, and after a month you can continue the construction of the bathhouse, or even better - after a year.
Concreting
In the process of concreting the base, the mortar must be laid in several layers, the optimal thickness of each is about 15 cm. All layers must be carefully leveled and tamped with a bayonet.
You can level the top layer using an ordinary smooth wooden lath. In this case, the concrete must be tamped until a wet, shiny layer appears on the surface.
The formwork can be removed already on the fourth or fifth day, but further construction work can be continued only after 1 month, although, according to the technologists, the optimal time limit should be 1 year.
Conditions affecting the choice of foundation
Brick strip foundation device: a - foundation; b - base; c - blind area; 1 - sand pillow; 2 - brickwork; 3 - backfilling; 4 - bituminous coating; 5 - plaster; 6 - waterproofing (roofing material); 7 - facing brick; 8 - adobe masonry.
A floating base device is advisable in such cases:
- looseness of the soil, heaving, lack of dense areas;
- the need to absorb water and retain it for a considerable time;
- high groundwater pressure;
- the depth of soil freezing is quite high and constitutes a threat when erecting a strip monolithic foundation.
The presence of water and the quality of the soil is determined with the help of geodetic instruments or examinations, their assortment includes a technology for their determination, although you can do without expensive research - just look at the neighboring buildings and assess their condition.
The size of the floating foundation is determined by the size of the residential building itself and is added up to 60-80 cm on all sides. The choice in his favor occurs when the soil is not very dense and there is no possibility of using any other. This type of base differs from others in the way of laying.
Foundation formwork concreting
The final stage is the concreting of the foundation formwork. The concrete mixture is poured in several layers, while the thickness of each layer should not exceed 15 cm.
Each layer is carefully leveled and rammed using the bayonet method. The ready-mixed concrete is poured in one step, therefore, it is better to use concrete mixers or concrete pumps to perform the work.
The concrete is rammed until a damp shine forms on the finished surface. To level the top layer, you can use special wooden slats.
On the first day of pouring, it is recommended to moisten the base with water every 5 hours, then cover with polyethylene. This will prevent cracking when the concrete dries quickly. In the following days, the foundation base is wetted only 2-3 times a day. Dismantling of the formwork is carried out after the concrete is completely dry.
Now every individual developer knows what floating foundations are and on what types of soil they can be erected. Due to their practicality and durability, such foundations are becoming more and more popular and in demand in private residential construction.
The principle of operation of the slab foundation
Situation
The building density is growing, people increasingly have to build on "bad" soils (weak, constantly wet, heaving, frozen ...).
Modern projects of country houses have become much more complex in terms of architectural and planning solutions: different parts of the building are built at different heights (one and a half floors, attached garages, special solutions for staircases and landings ...), uneven distribution of load-bearing walls over the building area. Houses are now bigger, higher, heavier.
Problem
On top of the foundation and on the natural foundation, there are uneven influences from the house. From below, complex soils either tend to form local dips under the structure, or they push the building out with the forces of frost heaving, and then, thawing, they sink.There is a risk of deformations and destruction of supporting structures.
Solution
- Increase the supporting area of the foundation by reducing the load from the house on the natural foundation.
- Maximize the spatial rigidity of the foundation, evenly redistribute the pressure “from top to bottom”.
- Separate the heated rooms from the ground under the house with a heat insulator - thus, eliminate the uneven freezing under the building (in winter, the ground under the slab does not thaw).
All these methods of dealing with "irregularities" are based on the principle of the operation of an insulated monolithic slab. This is a kind of a single platform under the house, which is not subject to local bends (with proper design), and without deformations can actually move with the ground - "float".
Types of foundations in construction
There are several types of foundations in construction. Each of them is intended for a specific case. Let's talk about each of them in more detail:
Strip foundation. The most common in low-rise and private housing construction. They are reinforced concrete tape. It is located around the perimeter of the entire building. This foundation is perfect for houses with foreseen basements and garages. On such a foundation, you can build both heavy brick houses and light ones made of wood. In the first case, it will be buried, and for the construction of light structures, a strong deepening is not required.

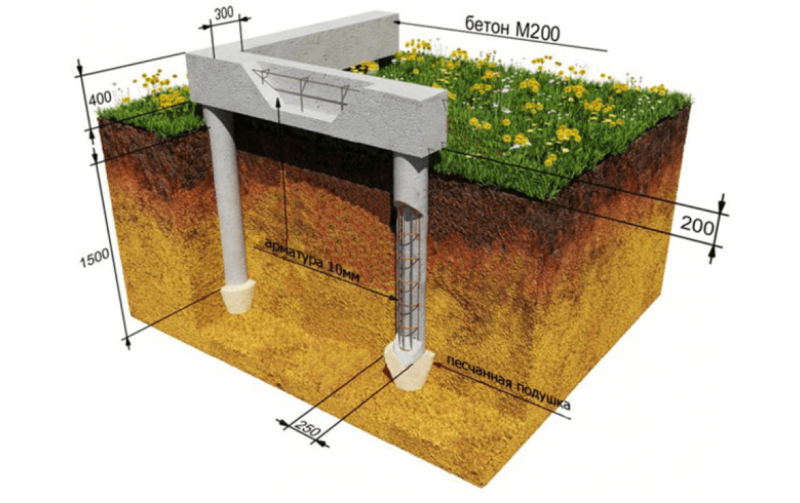
Columnar foundation. The name speaks for itself. It is erected by placing pillars at the corners of the building and at the intersections of the walls. Bridges are made between the pillars of concrete, brick or rubble masonry. With such a foundation, it is impossible to build a basement in the house. Moreover, it is suitable for the construction of light houses. It is best to erect a columnar foundation on stable soils.
 Monolithic. It is a single slab cast in concrete with reinforcement. This option gives freedom of planning and protects the structure from deformations during soil subsidence. For its installation, no special equipment is required, which allows you to carry out the work yourself.
Monolithic. It is a single slab cast in concrete with reinforcement. This option gives freedom of planning and protects the structure from deformations during soil subsidence. For its installation, no special equipment is required, which allows you to carry out the work yourself.

Knowing the strengths of each type of foundation, you can easily choose the right one for the construction of your house.
Types of monolithic slab foundation
Depending on the characteristics of the soil, the building being erected and the climate of the region, one of the following types of monolithic foundation is chosen:
-
solid or classic. The construction technology provides for the excavation of a fertile soil layer, backfilling of the pit with sand and gravel, and the subsequent arrangement of a reinforced concrete base. The thickness of the latter in private construction, as a rule, is 20-50 cm, but depends on the type of soil and the characteristics of the building being erected. Thermal insulation is carried out if necessary. This version of the foundation is great for highly heaving soils, where movements are possible both in the vertical and in the horizontal plane;
-
Russian, or a monolithic slab with stiffening ribs. In addition to the monolithic slab, stiffeners are arranged from below or from above. They are made at the locations of the load-bearing walls in order to strengthen the structure, but at the same time the complexity of the construction of the foundation increases, because it is necessary to fill not only the slab, but also the stiffeners, but the slab can be made thinner, saving on concrete and not losing strength. Stiffeners are, in fact, an analogue of a strip foundation. They can be cast from concrete or made from blocks. The first option is preferable, since in this case the structure will be completely monolithic. The use of ready-made blocks, moreover, will require the use of special equipment;
-
insulated Swedish plate (USHP). The technology is recommended for areas with a harsh climate, excellent for the northern regions of our country.The peculiarity lies in the use of a floor heating system, which is hidden in a concrete slab. In addition, a permanent formwork made of expanded polystyrene is used, which serves as thermal insulation, and a polyethylene film for waterproofing. It turns out that the base heats up, but at the same time heat leakage is minimized due to the presence of thermal insulation. Naturally, the cost of construction will be higher than that of the classic version.
Please note that the slab foundation can be either monolithic or prefabricated. All the advantages and nuances of a monolithic base are mentioned above.
The prefabricated foundation is created on the basis of road slabs or FBS blocks, which, after installation, are poured with a layer of leveling screed. Prefabricated slab bases require the involvement of special equipment for the installation of heavy slabs, therefore this is a longer and more expensive solution, but at the same time, the performance is inferior to a monolithic slab foundation.
Why choose a slab foundation
In low-rise construction, which we are, in fact, interested in, this type of foundation for many reasons will be preferable to its competitors (both tape and pile structures). This is explained by the advantages, both of a purely technical and near-construction nature.
Strengths of solid foundations
Versatility in base geology. The floating structure can be correctly applied on all types of soils, including low-bearing, heaving, horizontally mobile, with a high level of groundwater, permafrost ...
There are some restrictions on the relief - it is difficult to build such a foundation on a slope, most likely, piles will be preferable. However, there are American-proven technologies for erecting slabs on hillocks, which in their design (in the lower part of the site) have elements of high monolithic belts. Another “centaur” suitable for such places is a pile foundation with a low grillage in the form of a monolithic slab.
Good load-bearing capacity. This quality is due to the specific mechanics of the "house / slab / ground" interaction. We'll take a closer look at this point in the next chapter. In short - the slab has a large support area, so the pressure on the base soil is very low (from 0.1 kgf / cm2). Therefore, a stone house with two floors on a slab can be erected boldly. They say that the elevator shaft of the Ostankino tower stands on a monolithic slab.
High spatial rigidity. It is due to the absence of seams and joints, the use of rigid reinforcement, massive structure and high material consumption. The slab foundation is perfect for houses with "inelastic" walls, which are very afraid of even the smallest (1-3 mm) movements of the supporting structure - brick, aerated concrete, cinder block, shell rock and other mineral materials.
In the presence of excessively heaving soils and a significant sensitivity of buildings to uneven deformations, it is recommended to build them on shallow and not buried monolithic reinforced concrete slabs, under which pillows of non-heaving materials are arranged.
SP 50-101-2004 "Design and construction of foundations and foundations of buildings and structures."
Good insulating properties. With proper execution, it does not allow water to pass through, prevents heat loss through the floor.
Uncomplicated construction technology, builds quickly. It is simply marked out, a minimum of earthworks, a simplified formwork design, easy to reinforce and concretes. Can be manufactured by low-skilled builders.
Conditional disadvantages of the slab foundation
Technically, it is very difficult to combine a solid slab and a basement in a structure.
It is possible to fill the slab only in favorable weather (it loses a little to prefabricated and pile driven foundations).
High price. The increased consumption of materials (concrete, reinforcement), of course, leaves its mark.But if you look at the problem as a whole, then the picture changes dramatically - we save a lot on other materials, stages of construction, production operations:
- the slab becomes the subfloor of the first floor - no need to overlap;
- in the mass of the slab, you can lay a water heated floor, and not pour a separate screed for it;
- for the manufacture and unfastening of formwork panels, less boards or sheet materials are needed (at least twice as compared to strip structures);
- no need to pay for the removal / planning of a large volume of selected soil;
- the height of the outer walls is reduced, since a lower base can be obtained (and these are expensive materials for finishing the facade, labor costs ...);
- lifting equipment, concrete pumps, excavators, hammer-in drivers, drilling machines are not needed, everything is limited to mixer cars;
- you can build on your own and not hire highly paid professional builders, there is less risk of financially suffering from the "human factor" (technology is simpler).
It turns out that the main disadvantage of slab foundations is the lack of awareness of the domestic developer about their advantages. But in the northern part of the United States and Scandinavian countries, monolithic slabs have become the No. 1 foundation.
Monolithic floating foundation option
What is this type of foundation? In simple terms, this is a slab of reinforced concrete, freely located on a cushion (base) of bulk building materials.
- This type of floating foundation is chosen for the construction of rather heavy structures made of stone, concrete blocks or bricks.
- Another name you may be familiar with is. It is made using a clean solution, without the use of large stones, and gravel or crushed stone of small and medium size is suitable as fillers.
For the construction of such a foundation, formwork will be needed. The most suitable equipment in the compaction process is considered to be a vibrator, it significantly improves the quality of concrete. I would like to note that such a foundation does not require a large base thickness, even 40 cm is enough.
Concrete mixer device diagram.
That's what is important - the size and shape must be in exact accordance with the parameters of the structure. So, where to start with a do-it-yourself floating foundation? The technology of floating foundations provides for the initial steps for laying the cushion (base) under the foundation
So, where to start with a do-it-yourself floating foundation? The technology of floating foundations provides for the initial steps of laying the cushion (base) under the foundation.
To do this, you need crushed stone, soil, coarse sand, or a mixture of them. The thickness of the base should be approximately 40 cm.
Next, proceed to the manufacture of panel formwork with a height of 30 cm. For its construction, any level boards are suitable, which must be fixed with a peg from the outside. The distance between them should not exceed one and a half meters.
Another important point is the filling of the stiffeners. For their device, grooves are dug out and roofing material or roofing material is laid on their bottom. This is necessary to retain moisture in the solution.
Slab floating foundation is subject to mandatory reinforcement. It is carried out after the completion of preliminary work. For this, fittings are laid out along the entire base. Uniformity is the main requirement when performing these works. And do not forget that reinforcement is also laid along the ditches.
After these procedures, you can proceed to pouring the foundation with concrete. What materials are used as reinforcing elements?
Concrete foundation pouring scheme.
These can be thick wire, rods (metal), small pieces of pipes (iron), a profile, and so on.
A mixture for pouring a floating foundation is prepared from M400 Portland cement.It is mixed with crushed stone in a ratio of 1 to 2. When using coarse sand, the ratio will look different - 1: 1: 1.
The strength of your foundation will also depend on factors such as mixing quality.
Therefore, pay special attention to this process.
After the end of the pouring, the surface of the slab is compacted and leveled using a level. If there is a need to level some areas, you need to add a solution.
It is best if at this stage of the work someone will help you, since it is much more convenient to carry out this procedure together. Use a long rule in your work. You can do it yourself or purchase a ready-made factory version (aluminum).
- A very important point - the foundation must be poured simultaneously. If there are doubts about this, it is better to fill the entire area, but not completely, but half. You can continue the next day. It is strongly not recommended to fill the slab in parts.
- After the pouring is completed, the surface of the finished slab is covered with any sheet material or film. 14 days in this state will be enough. Do not forget to do the foundation moistening procedure from time to time, then its hardening will be of higher quality and correct.
- After hardening, the formwork is dismantled, and in its place the brick basement is laid. As with the construction of other types of foundations, the plinth is equipped with special holes for ventilation of the underfloor space.
If there is no ventilation, you are at risk of mold. The size of the ventilation vents should be at least 15x15 cm, and their location is advisable at a distance of 15 cm above the ground.
It is possible to carry out the device of a floating foundation with your own hands, but there is an opportunity to use the services of professional companies. The approximate cost of such work is 4000 rubles per sq. m.
The specifics of the construction of the Swedish slab
The Swedes are renowned for being frugal, resourceful, and environmentally conscious. The famous Swedish stove, which is the best type of conventional floating plate, is their invention. This stove is incredibly popular in Norway, Sweden, Finland. This is not without reason: its technology is that this foundation perfectly withstands serious loads arising on problem soils, while it is thermally insulated. Often, in such a base, they even make warm water floors at the same time, which are just right for a bath.
How a floating foundation is built using Swedish technology:
Step 1. A pit is dug, having a depth of 30 to 40 cm.
Step 2. The foundation pit is filled with crushed stone to the ground level, the body of sand is poured there as well. Sand is poured and rammed to the same level.
Step 3. Lay 10 cm thick foam, which is also called "sexual", it is very strong, 100 units
It is important to check that this foam is exactly 10 cm above ground level.
Step 4. Knitted reinforcement, 15x15 cells is placed on this foundation
You need to put it on special plastic mushrooms - so that it is 3-4 cm in the air. There are enough mushrooms themselves, 5 pieces per square meter.
Step 5. Instead of the formwork, the same polystyrene is placed, reinforced from the outside with some kind of board.
Step 6. Finally, the concrete is poured.
Of course, a floating foundation is not a panacea for all problems, it is only one of the successful solutions. This base option is by no means suitable for every bath, but in some cases it becomes the only possible solution, and not bad at that.