What waterproofing to choose for the foundation - DIY foundation

Groundwater, moisture, weather dampness - all this poses a natural threat to a building if its base is not reliably protected from water.
So that concrete and other materials in the structure of the foundation do not suffer from moisture, creating an atmosphere of dampness in the lower rooms, a number of works must be carried out during construction, the main of which is waterproofing the foundation.
What materials, technologies are better suited for this and is it possible to cope with the process on your own - find the answers below.
What is foundation waterproofing
Any waterproofing is a series of works aimed at warming, protecting the foundation from influence, moisture penetration, and reducing the natural absorbency of concrete. This procedure is especially relevant if the house is on wet soil or has a basement, garage, basement. There are different ways than to process the foundation from moisture:
- bitumen, bituminous mastics are widespread;
- then cement-polymer compositions follow;
- liquid rubber and self-adhesive roll materials are used.
What is waterproofing for?
Concrete is the main component of any foundation, it has a porous, pliable structure, so liquid from the atmosphere and soil always seeps into it, destroying the integrity of the structure, creating and increasing microcracks. Ultimately, this will help lead to such serious consequences as partial destruction, rotting, crumbling of the house at the base.
Waterproofing is necessary for each building in order to increase the period of its safe, guaranteed operation, to protect the house from dampness and its unpleasant components - fungus, mold. Modern waterproofing of the foundation allows you to eliminate all these hazards with the help of functional, affordable building materials and simple technology.
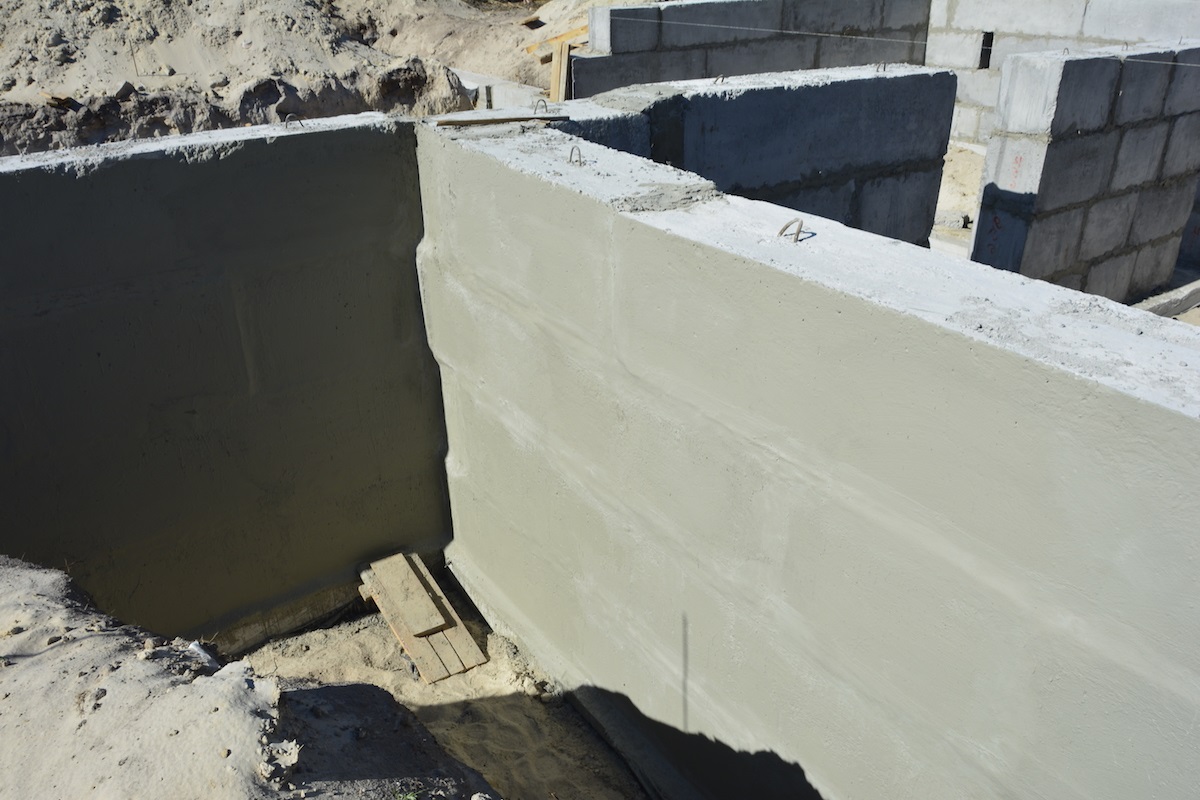
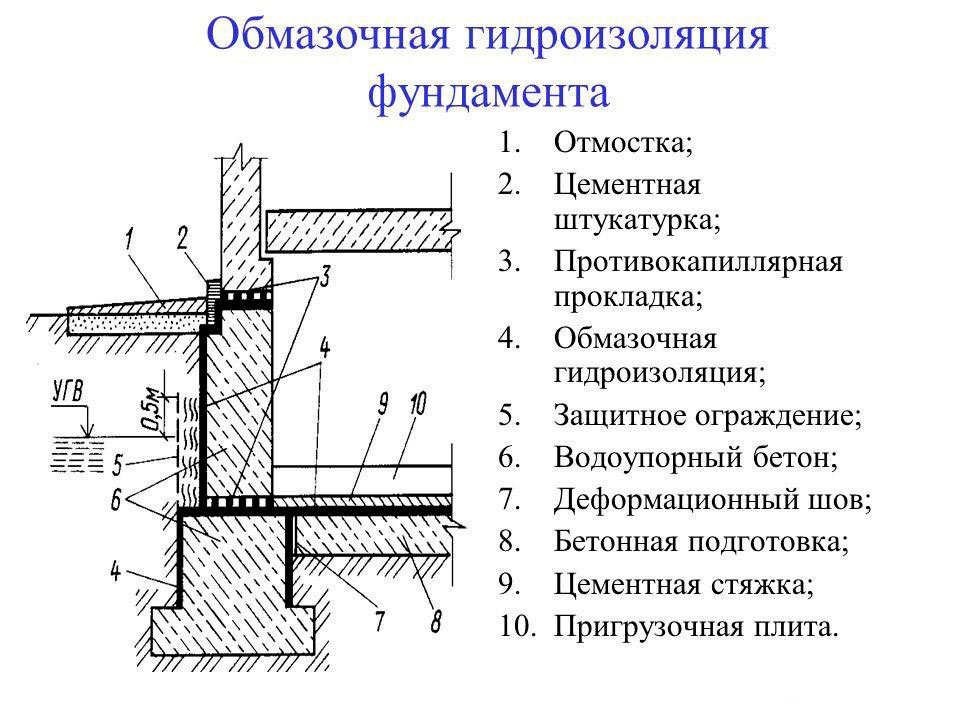
Foundation horizontal waterproofing
Depending on the characteristics of the material and terrain, a horizontal or vertical type of procedure is used.
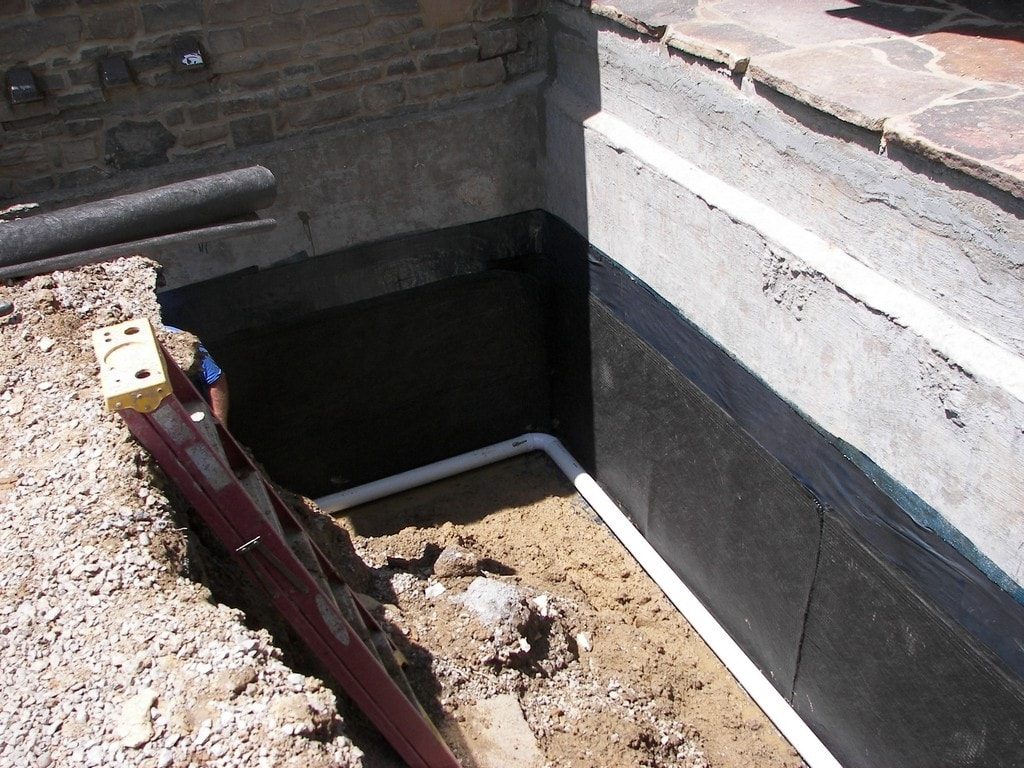
The horizontal one provides good protection of ceilings, walls, basements, terraces and balconies from capillary waters, it is laid along the edge of the foundation, just above the blind area.
For implementation, a roll or impregnation method is used. Horizontal waterproofing of the foundation is carried out at the beginning of construction, before the construction of the walls.
Vertical waterproofing
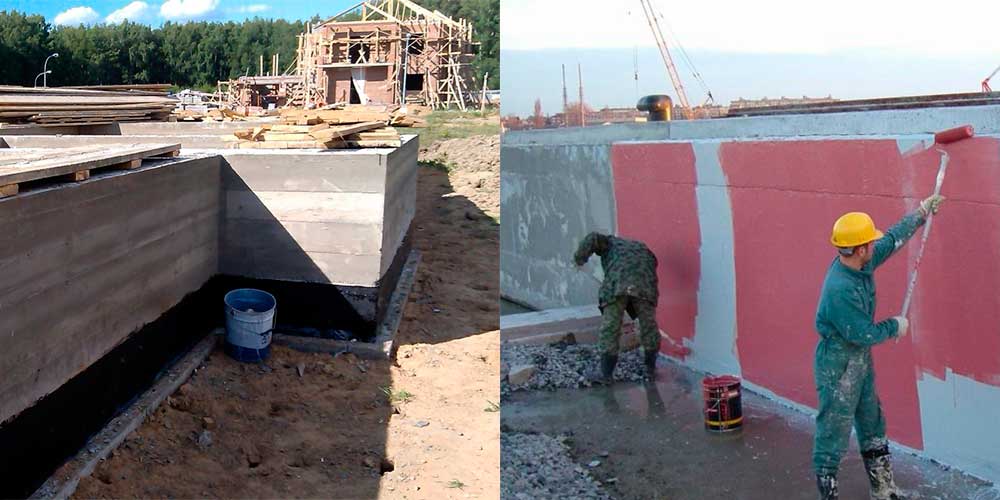
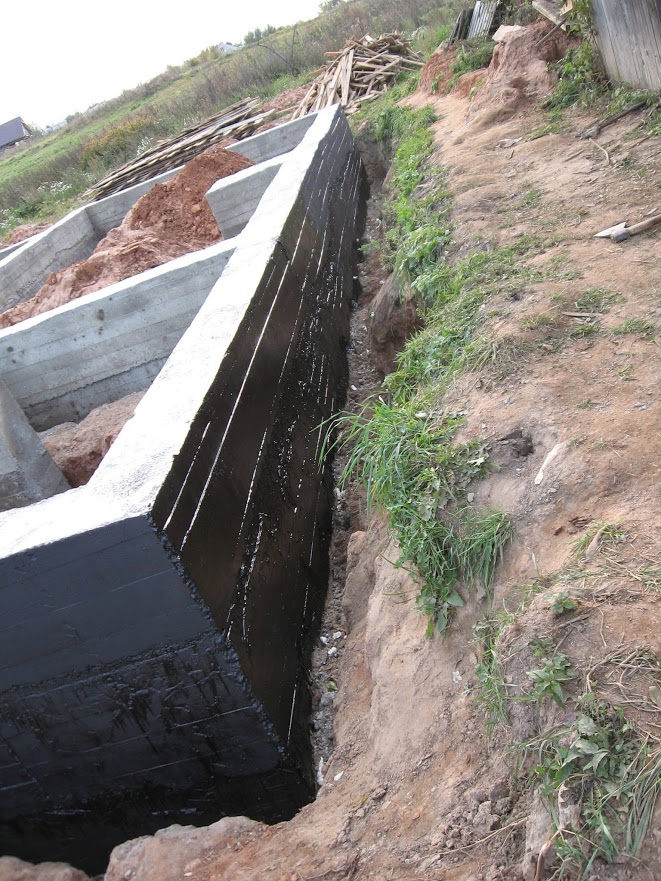
It is better to use light bituminous mixtures for this, which insulate the building and do not weigh down its structure.
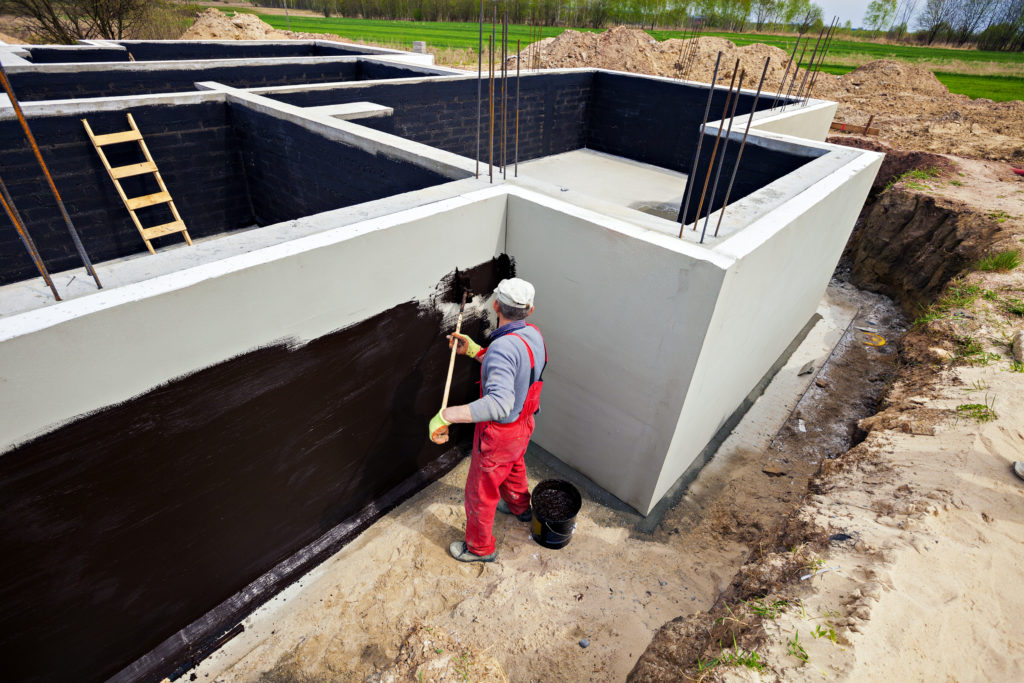
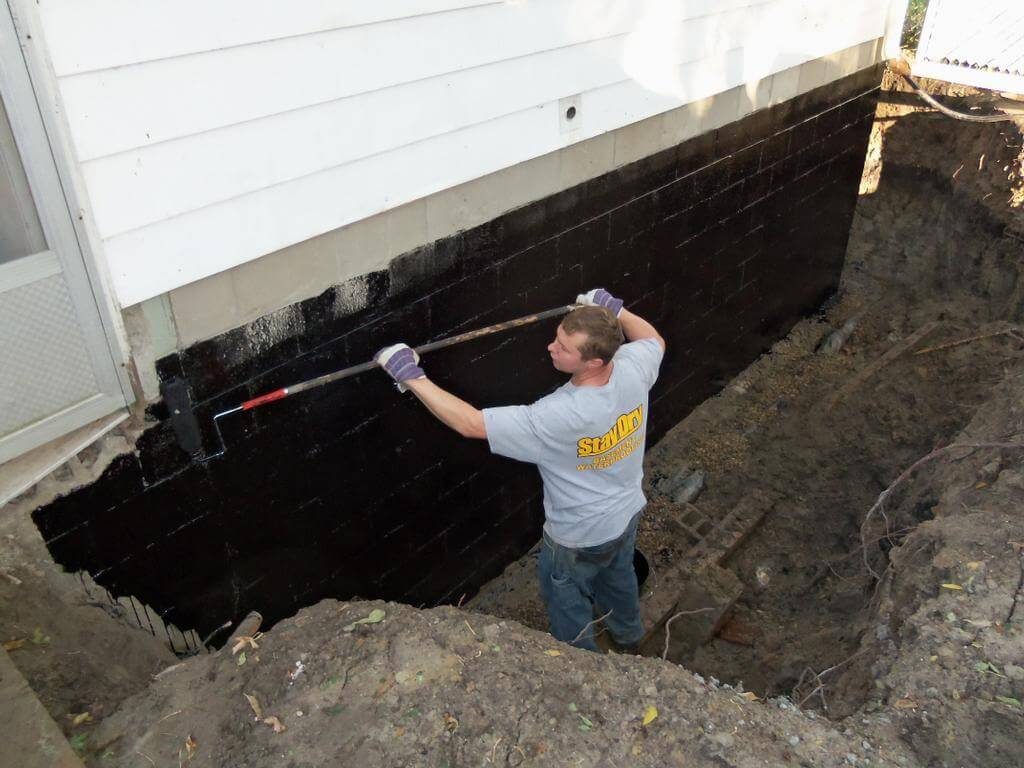
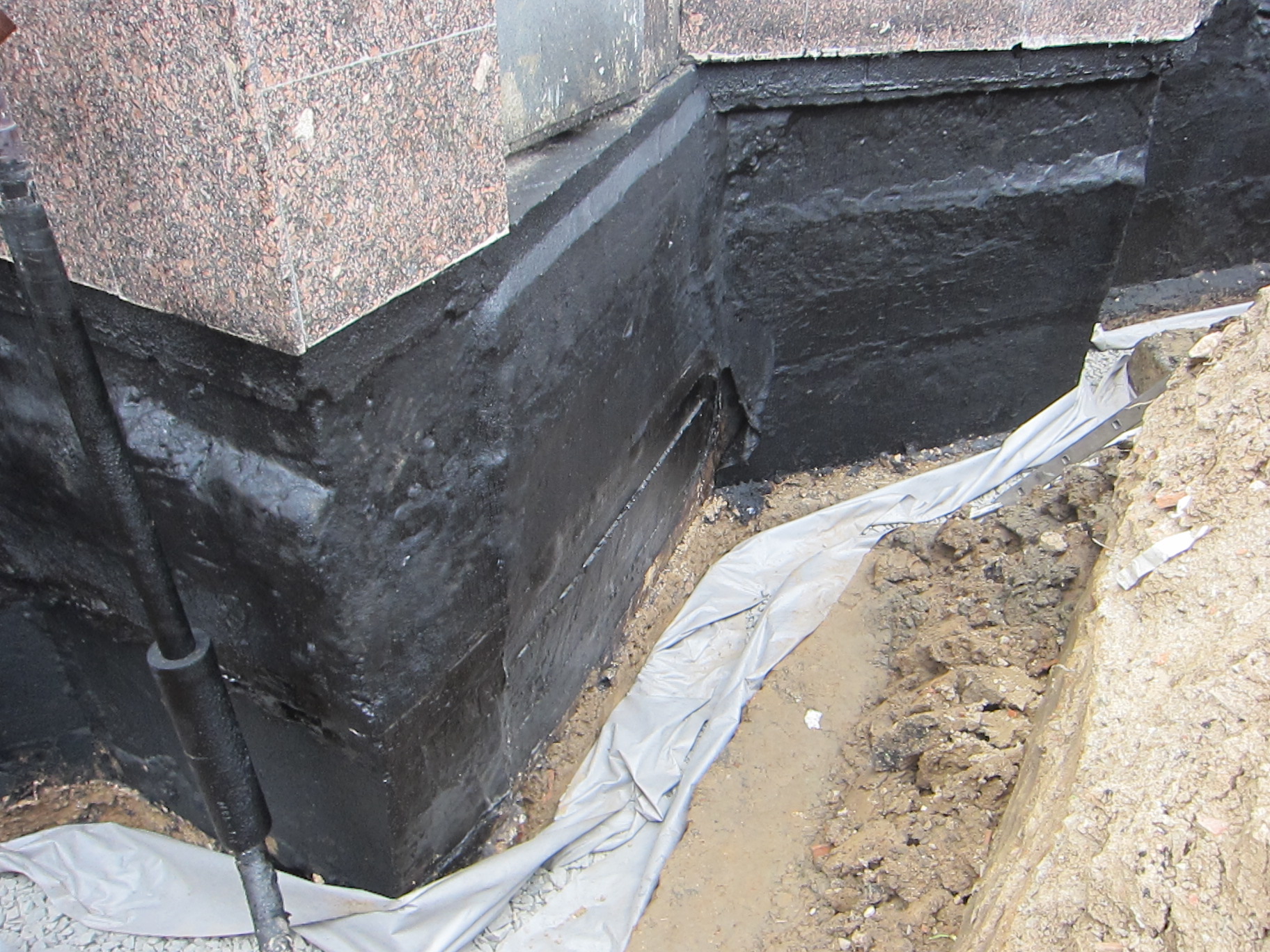
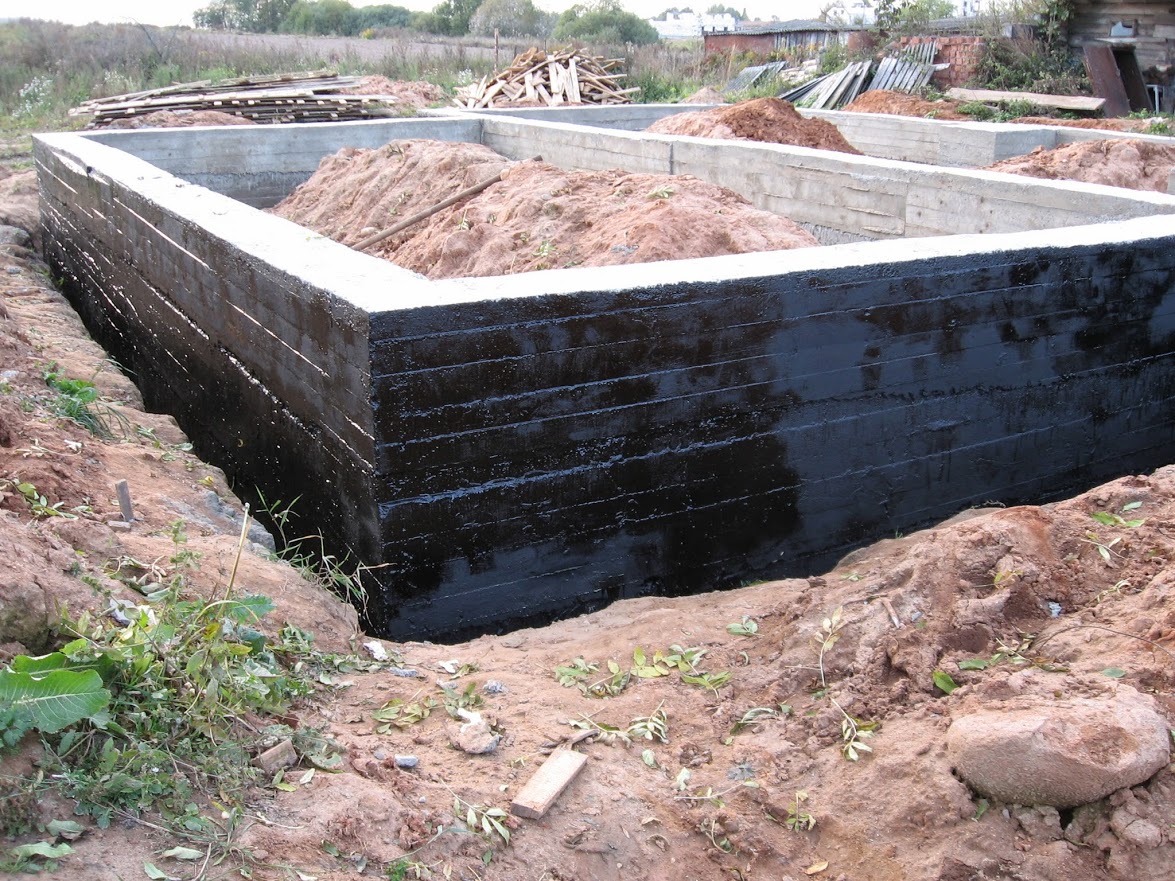
Vertical waterproofing is necessary to protect the side walls, frame, doorway assemblies, underground rooms, from the penetration of surface water.
Since this part of the building is often exposed to external factors, an additional layer must be applied over the main waterproofing layer.
Roll waterproofing for foundation
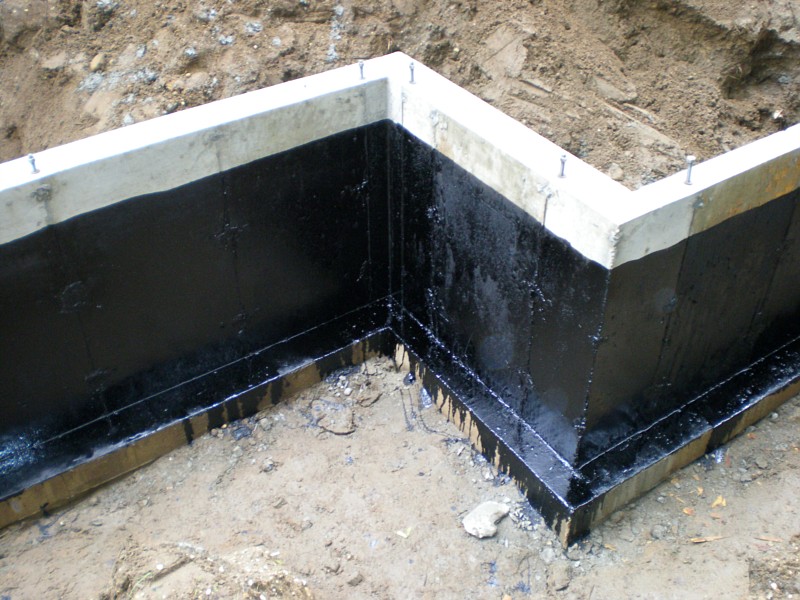
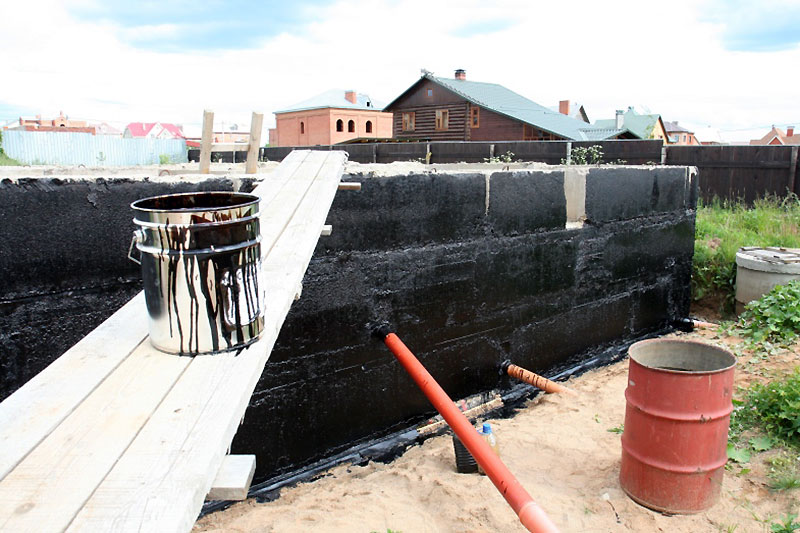
Gluing waterproofing of the foundation is made with the help of materials such as roofing material, glass-fiber insulation, glassine, which are glued in several layers using mastic or special glue.
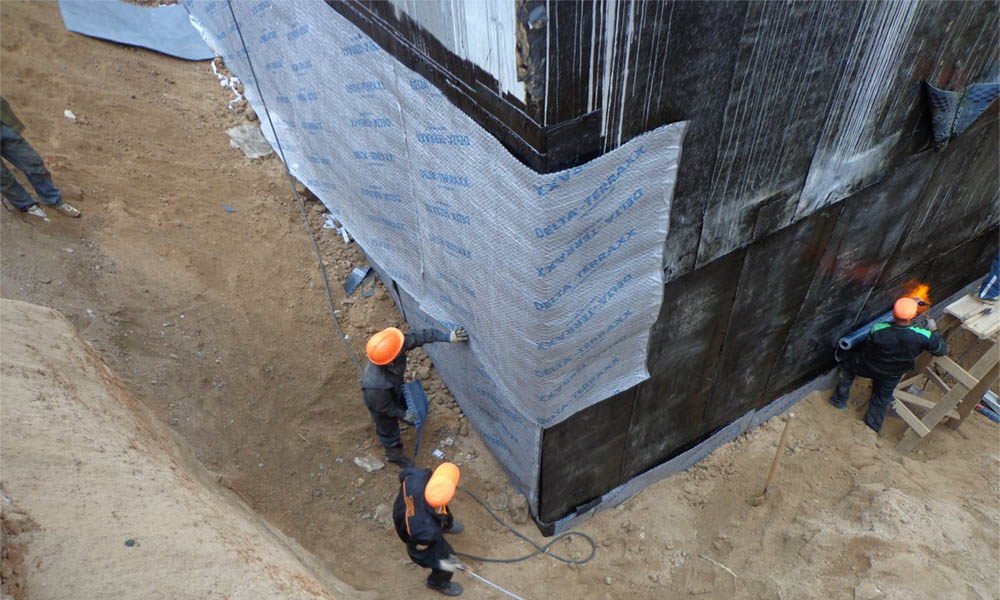
Other methods are film diffusion membranes, which have high vapor permeability and protect the interior of the building well, or bitumen, polymer rolls, hot-bonded, float-bonded (for better connection to the surface).
In advance, you should calculate the amount of material required for horizontal protection from groundwater: the future waterproofing layer should be about 3 mm if the base of the foundation is at least 3 meters.The thickness and quantity of coatings depend on the quality and strength of the material; the recommended standards are often indicated on the packaging.
Materials for coating waterproofing
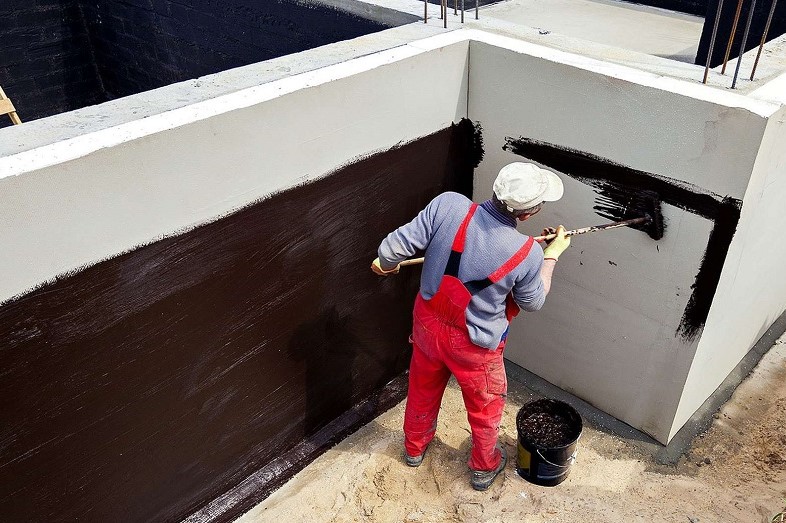
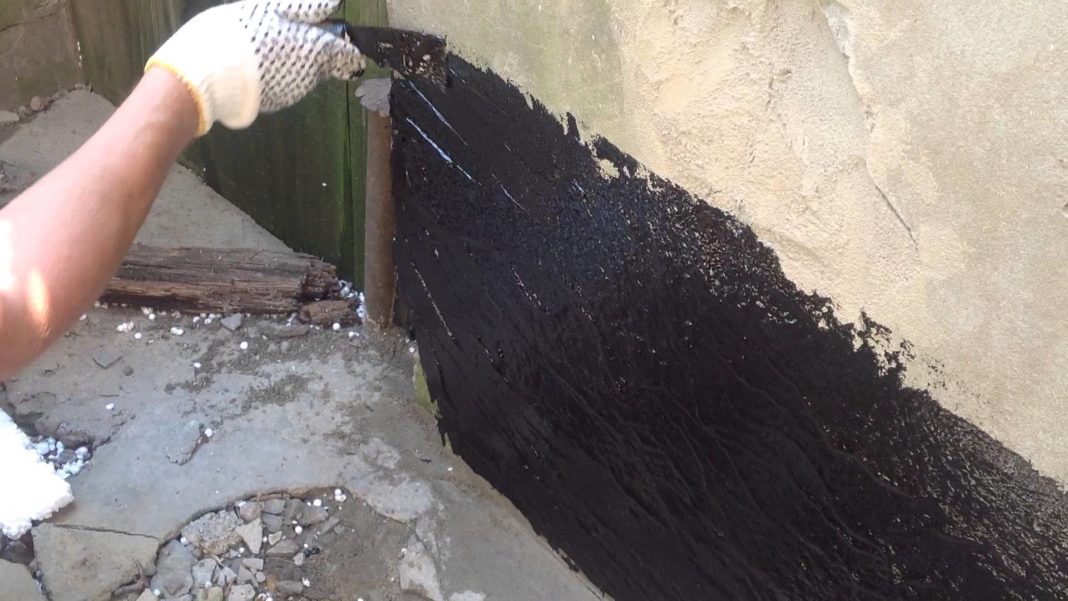
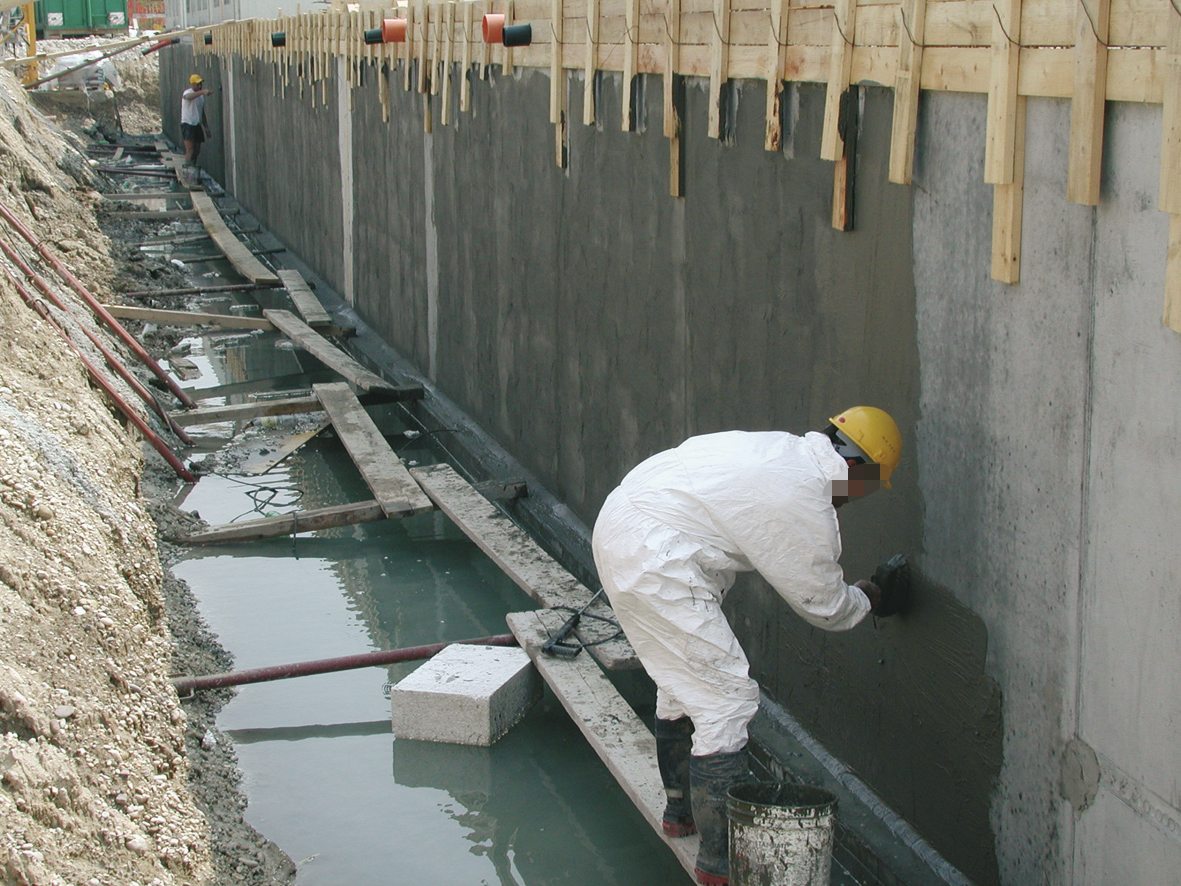
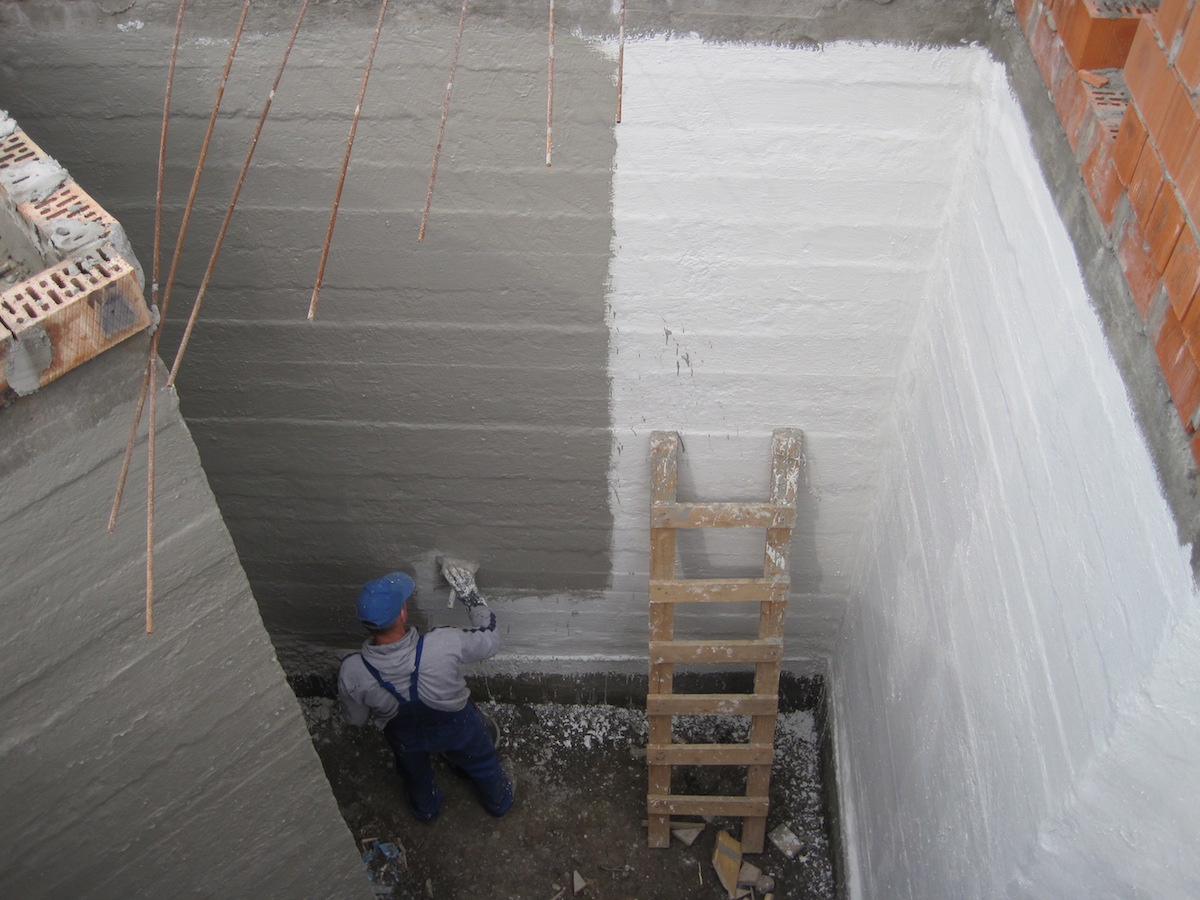
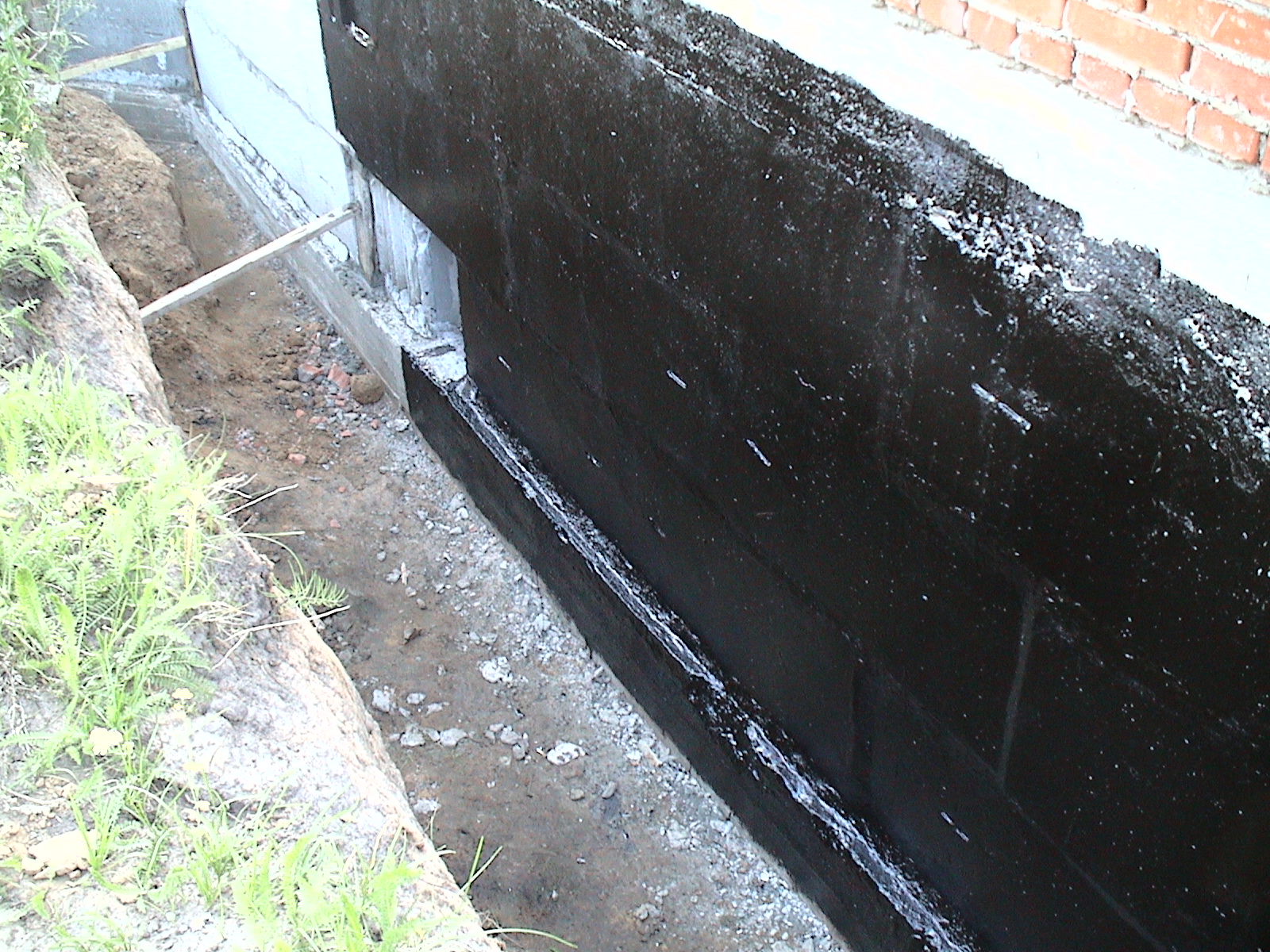
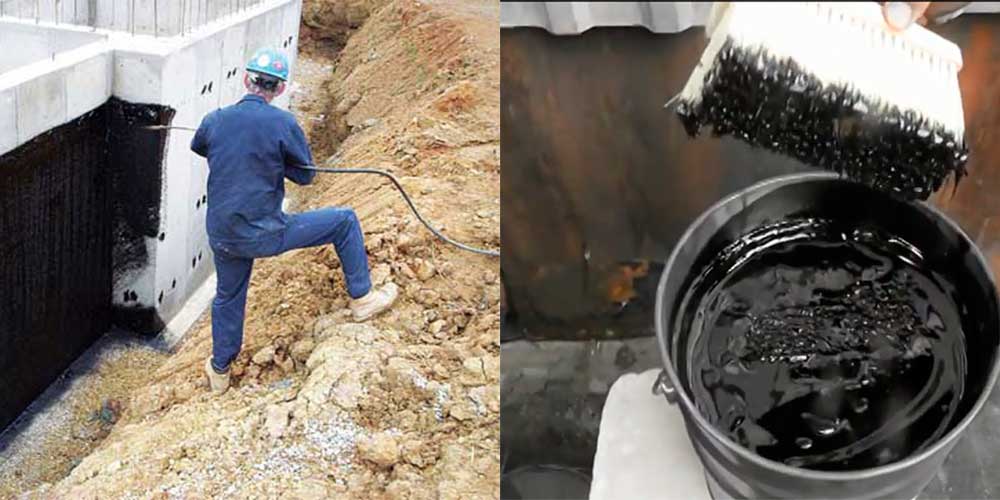
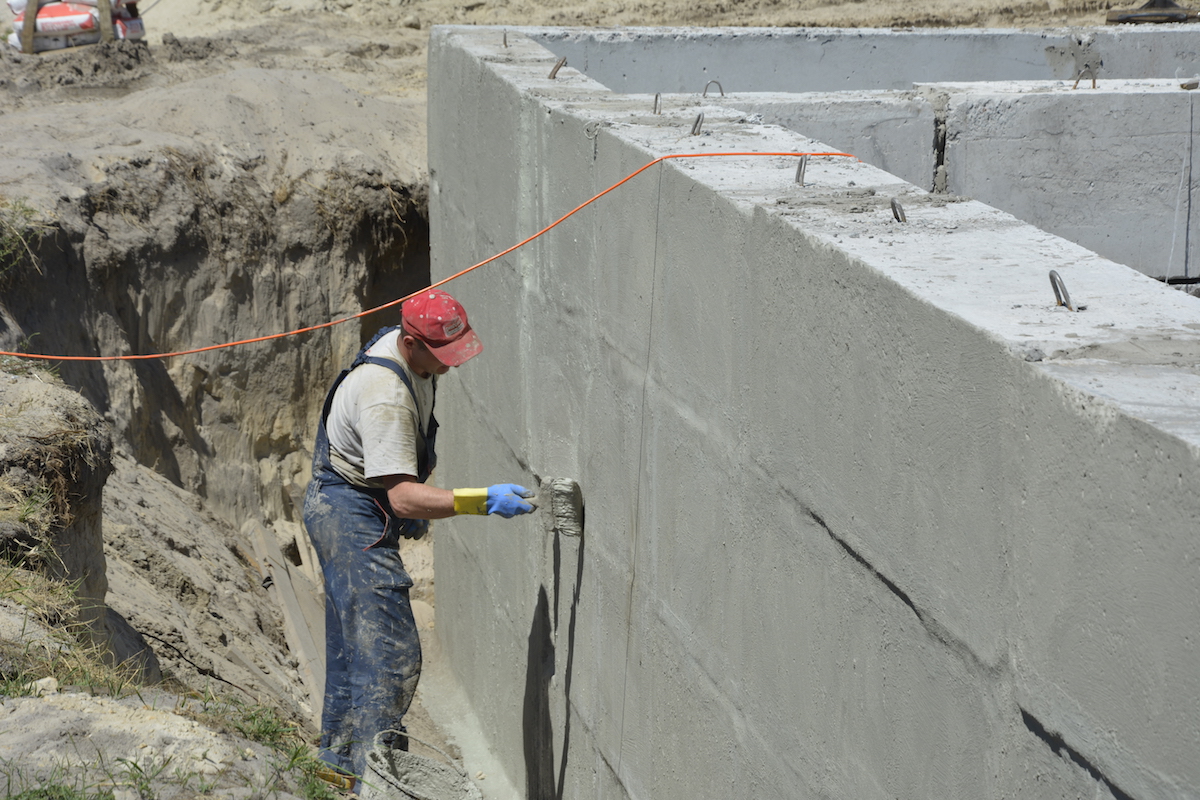
For the installation of coating waterproofing of foundations, special mastics are used based on bitumen, bitumen, cement-based compounds, as well as polymer materials.
Materials containing bitumen
In this group of waterproofing materials, bitumen is in the first place, but since when it is used, it needs to be warmed up, then due to the emergence of new materials, its use is reduced.
 Hard bitumen will need to be warmed up before application
Hard bitumen will need to be warmed up before application
Various plasticizers (rubber, silicone) and sealants are added to the composition of bitumen-based mastics, which improves their physical properties, performance indicators, as well as the conditions for performing work with their use. Bitumen-polymer mastics do not require preliminary heating, but before applying them, it is required to treat the surface to be coated with a special composition - a primer-primer.
 Primer for bituminous mastic
Primer for bituminous mastic
Primer - the primer is applied in order to improve adhesion, strengthen the base to be treated and close the pores on its surface. Primer-primers are made on mineral, bituminous, alkyd and acrylic bases and for various types of bases (concrete, brick, wood, etc.).
Mastics are available in one-component, which can be used without additional preparation, and two-component - for the use of which you need to prepare them.
For various types of bases, various brands of mastics are produced: for foundations and floors, under tiles, for roofs, as well as for parts of buildings and structures in contact with the ground.
 Low-temperature bitumen mastic
Low-temperature bitumen mastic
Cement based materials
Cement-polymer mastics include Portland cement, mineral fillers and polymerizing additives. These are two-component formulations that require water or a special emulsion to prepare.
In addition, the industry produces mixtures, which, in addition to cement, include resins and inert fillers, as well as organic additives.
These materials are somewhat more expensive than those made on the basis of bitumen, but due to the fact that during the production of work with their use, the total volume of construction and installation work is reduced, the total cost of construction is almost identical for both versions.
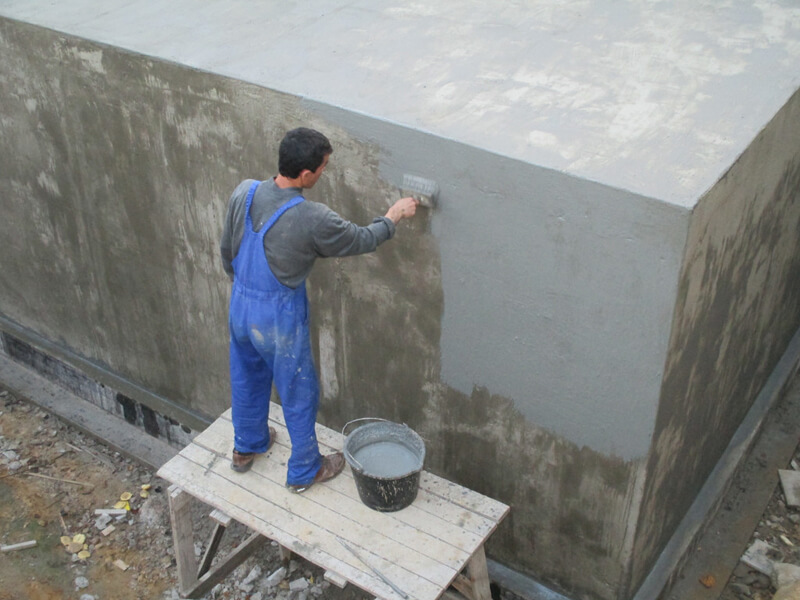
The reduction in the volume of work is due to the fact that the cement-based waterproofing layer serves at the same time as a screed for the finishing coating of the treated surface.
Polymer materials
This group of waterproofing materials includes mastics made from synthetic emulsions, rubber, plasticizers and other technological additives.
Polymer mastics are much more expensive than materials based on cement and bitumen, but due to their technological characteristics, which are significantly superior to these materials, they are becoming more and more widespread.
The advantages of polymeric materials are:
- High adhesion to the coated surface.
- Elasticity.
- Absolutely waterproof.
- Fire safety.
Waterproofing under the foundation
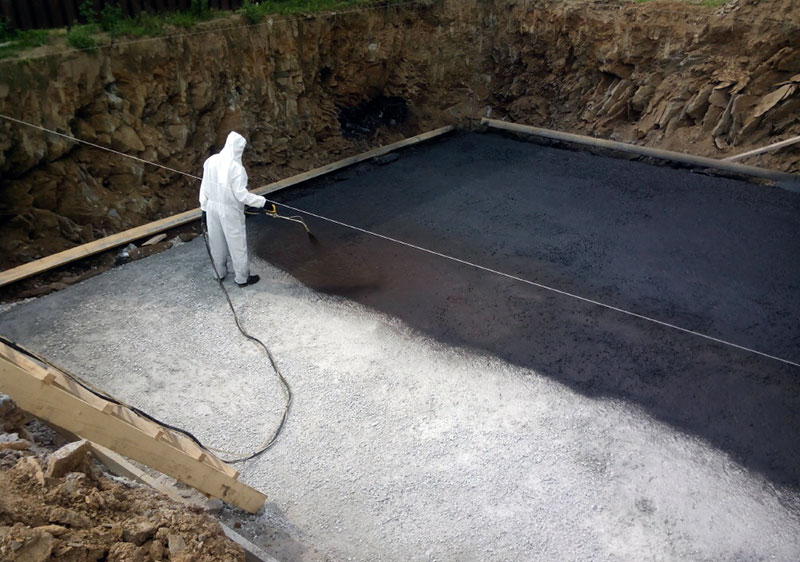
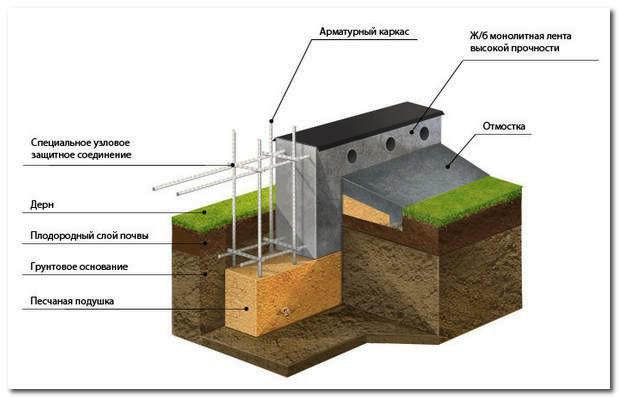
To prevent moisture from penetrating into the concrete structure through the sole, a special waterproofing layer must be laid under the foundation base. It can be done in two ways.
- At the bottom of the prepared pit, a layer of crushed stone and construction sand is leveled and carefully rammed. Then geotextile, membrane waterproofing film, again a layer of geotextile and ordinary polyethylene film are laid, which will protect the material from the penetration of liquid cement.
- The bottom of the pit is covered with a thick layer (at least 20 cm) of oily clay, which must be well leveled and tamped. Next, a layer of concrete with a height of 5-8 cm is poured.After waiting for the concrete to completely harden, this "pillow" is waterproofed with bitumen mastic, a layer of roofing material is laid, a layer of mastic is again applied on top of it, a second layer of roll waterproofing is laid. Next, a five-centimeter layer of concrete is poured, which, two to three hours after pouring, is sprinkled with fine cement sifted through a sieve and leveled. After the concrete is completely dry, the foundation itself can be poured.
The size of the waterproofing layer
To carry out the work, a coating technical map of foundation waterproofing is used. The document indicates the type of material used, the technological sequence of the work, the calculation, the schedule of actions, the requirements for safety and labor protection.
In the operating instructions, it is recommended to apply several layers of waterproofing. The repetition rate depends on the depth of the base of the construction object. It is recommended to use the values from the table.
| P / p No. | Foundation depth, meter | Protective coating thickness, centimeter |
| 1 | less than 3 | 0,2 |
| 2 | from 3 to 5 | 0,2-0,4 |
| 3 | more than 5, as well as concrete piles | 0,5 |
A new waterproofing coating can only be made after the previous layer has dried. To determine the degree of dryness, it is enough to run your palm over the base. The surface will be flexible and soft to the touch.
You can check the readiness in another way. Take 1 square meter of plastic wrap and place on the base. If no condensation forms on the inside within 24 hours, you can continue working.
The process time depends on several factors:
- type and composition of waterproofing;
- humidity of the base area;
- climatic temperature.
Screen isolation

A relatively new way to protect foundations, somewhat reminiscent of the erection of a clay castle. With such waterproofing, bentomates are used, which tend to swell on contact with moisture due to the formation of a waterproof gel. The basis of bentonite mats is special clay granules. The reliability of screen insulation is equivalent to a clay wall 1 meter thick. The mats are fixed to the surface using dowels.
Based on the features of the structure and their capabilities, each developer decides which waterproofing is best suited for the foundation specifically in his case. The main points for choosing a specific technology are the presence of a basement and its depth, the type and amount of groundwater, as well as the design features of the foundation.
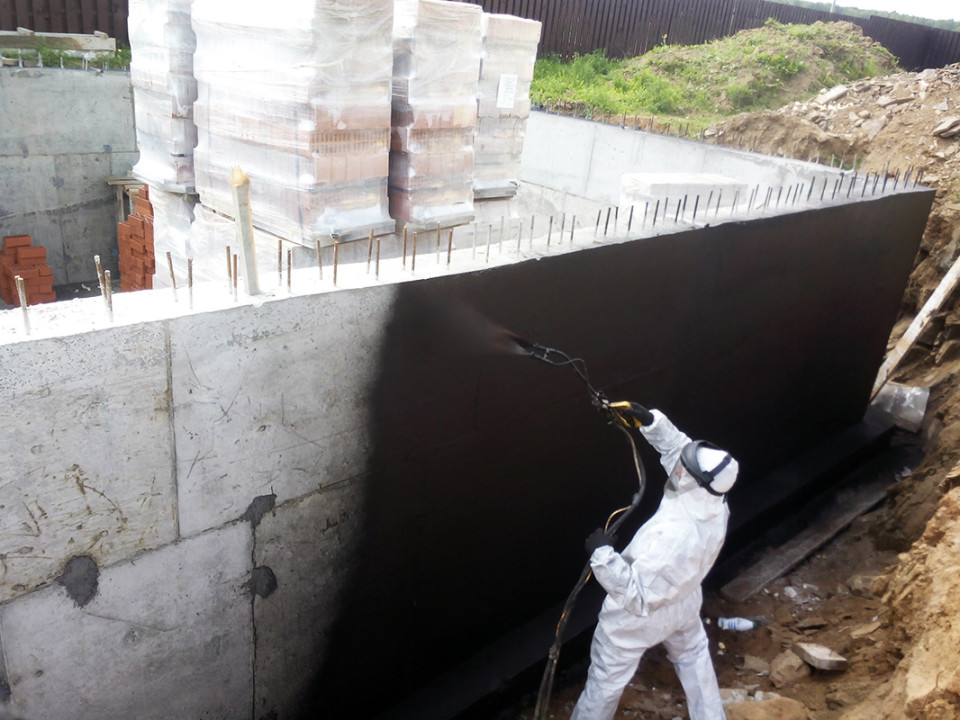
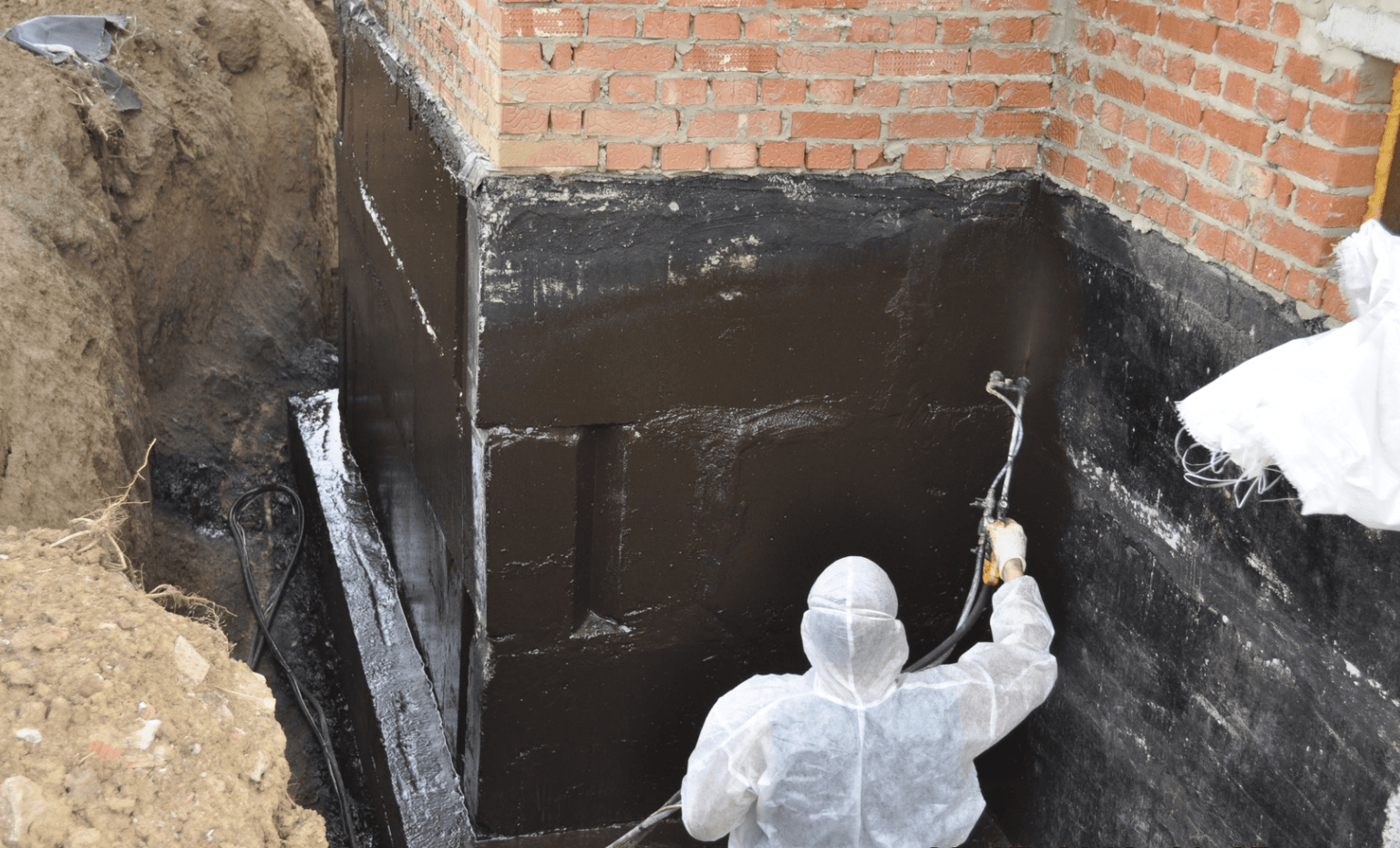
Technology for performing coating waterproofing
-
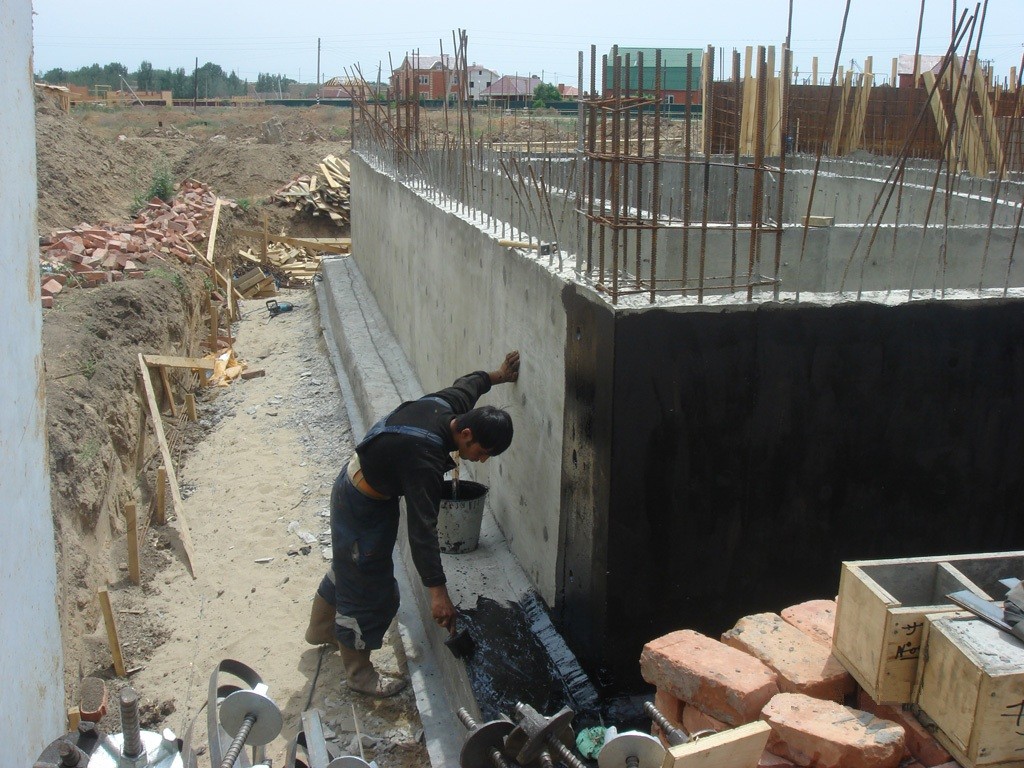
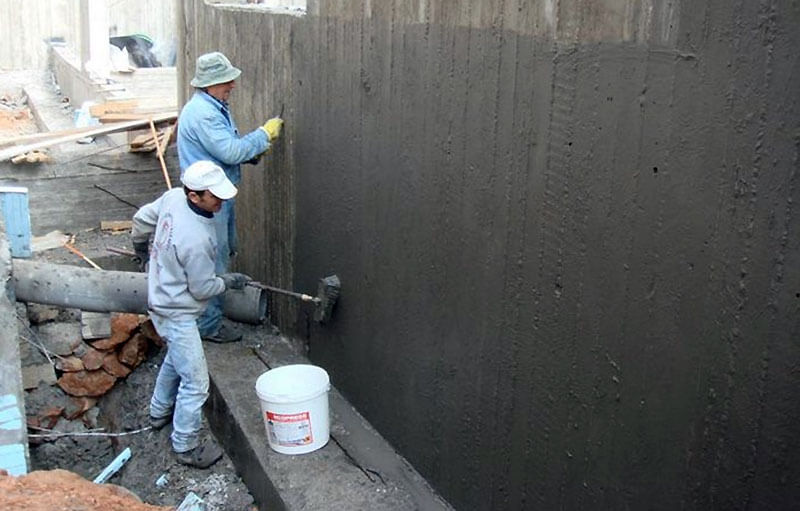
The surface of the foundation is cleaned from dust and dirt. Sharp protrusions, corners and edges must be rounded off to a radius of at least 3 cm using a grinder, otherwise, under mechanical pressure of the soil or structures, the waterproofing layer will be damaged. If the inner corners are to be coated, it is necessary to make fillets of a triangular cross-section - with their help, the backfill pressure on the waterproofing layer is reduced. Cracks and seams are sewn up to a solid base, sealed with cement mortar. The sinks are also covered with cement mortar - when they are coated, air remains in them, and after a while bubbles form, at the rupture of which the continuous waterproofing layer is broken.
-
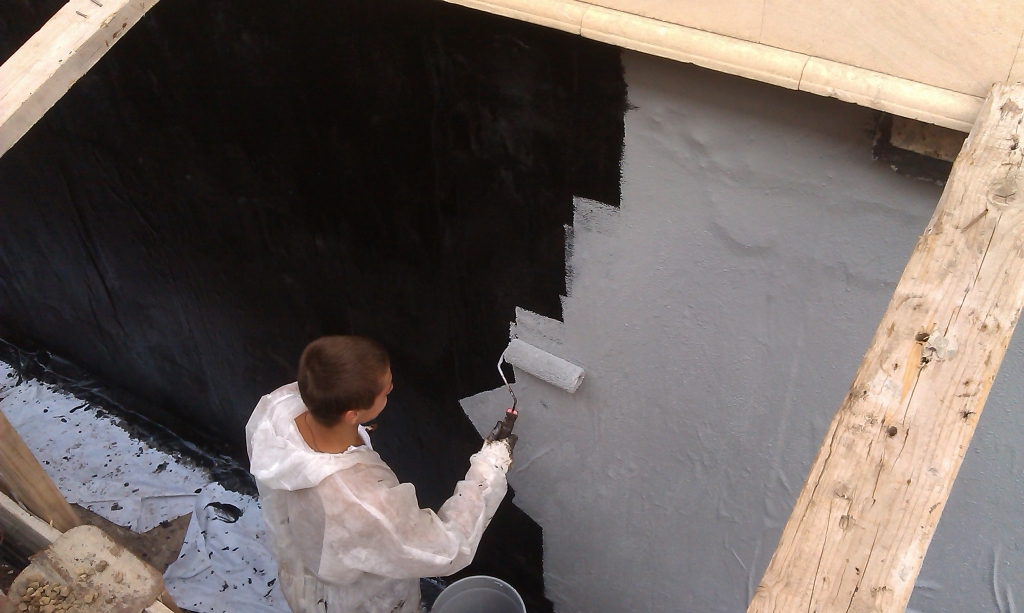
To improve the adhesion of the waterproofing film to the base, so-called primers are used - primers designed for a specific type of coating. For bituminous mastics based on organic solvents, primers with the same type of solvent are used, for water-based compositions - water-soluble primers. The primer is applied to the dust-free base using a roller, the corners are additionally coated with a brush. Drying time for a primer usually does not exceed a few hours.
-
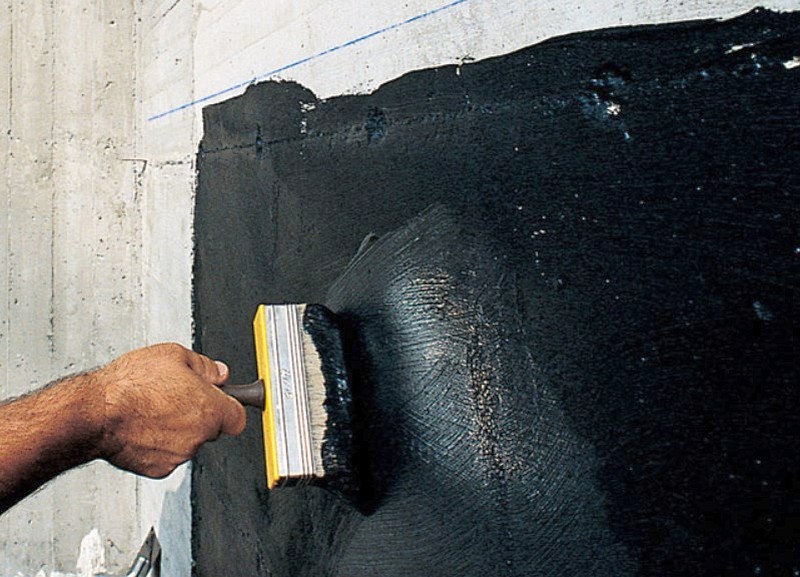
Under bituminous and bitumen-polymer mastics, a fast-drying bitumen varnish is applied in the first layer, which ensures good adhesion.The varnish is applied with a brush, vertical strokes, or spraying, over the entire surface of the foundation. They are waiting for it to dry completely.
-
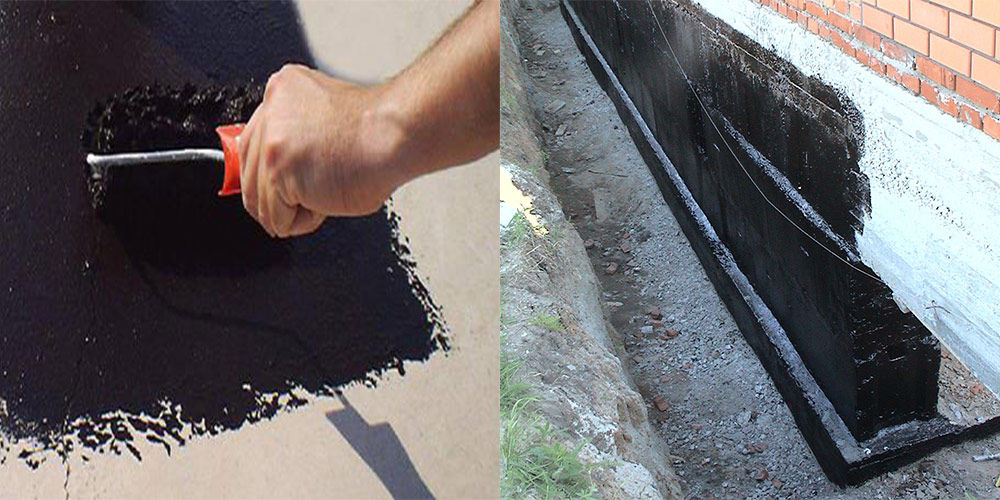
Prepare the mastic for application. The one-component is stirred and, if necessary, diluted with an appropriate solvent. The two-component mastic is mixed according to the instructions on the package.
-
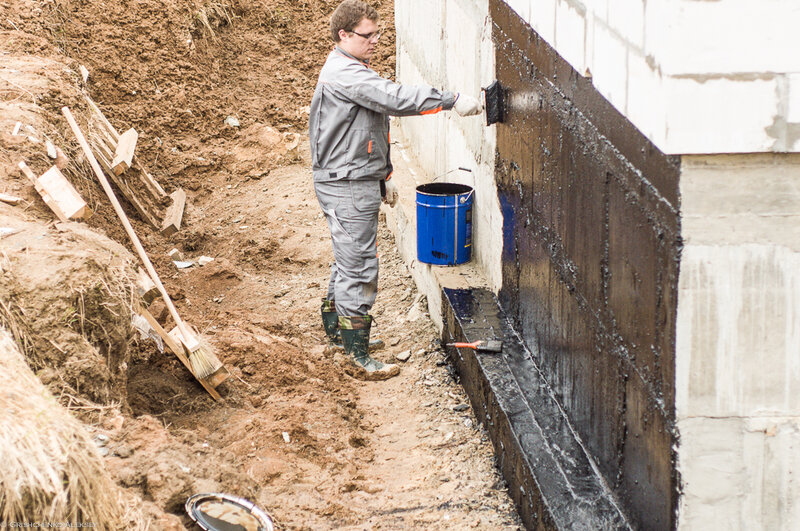
The first layer of mastic is applied with a wide brush, roller or spatula. The mastic is applied without gaps, carefully smearing the corners to form a solid and tear-free coating. The direction of the strokes is vertical. In a similar way, two or three layers of mastic are applied, necessarily waiting for the time of its complete hardening. When working in subzero temperatures, the mastic must be slightly heated to improve its plasticity.
-
In the case of new buildings, the waterproofing must be reinforced to avoid damage by shrinkage. To do this, use fiberglass, fiberglass, sticking them on the first layer of mastic so that they are completely moistened with it. It is also necessary to reinforce the corners, fillets, sharp projections with beveled edges with fiberglass.
-
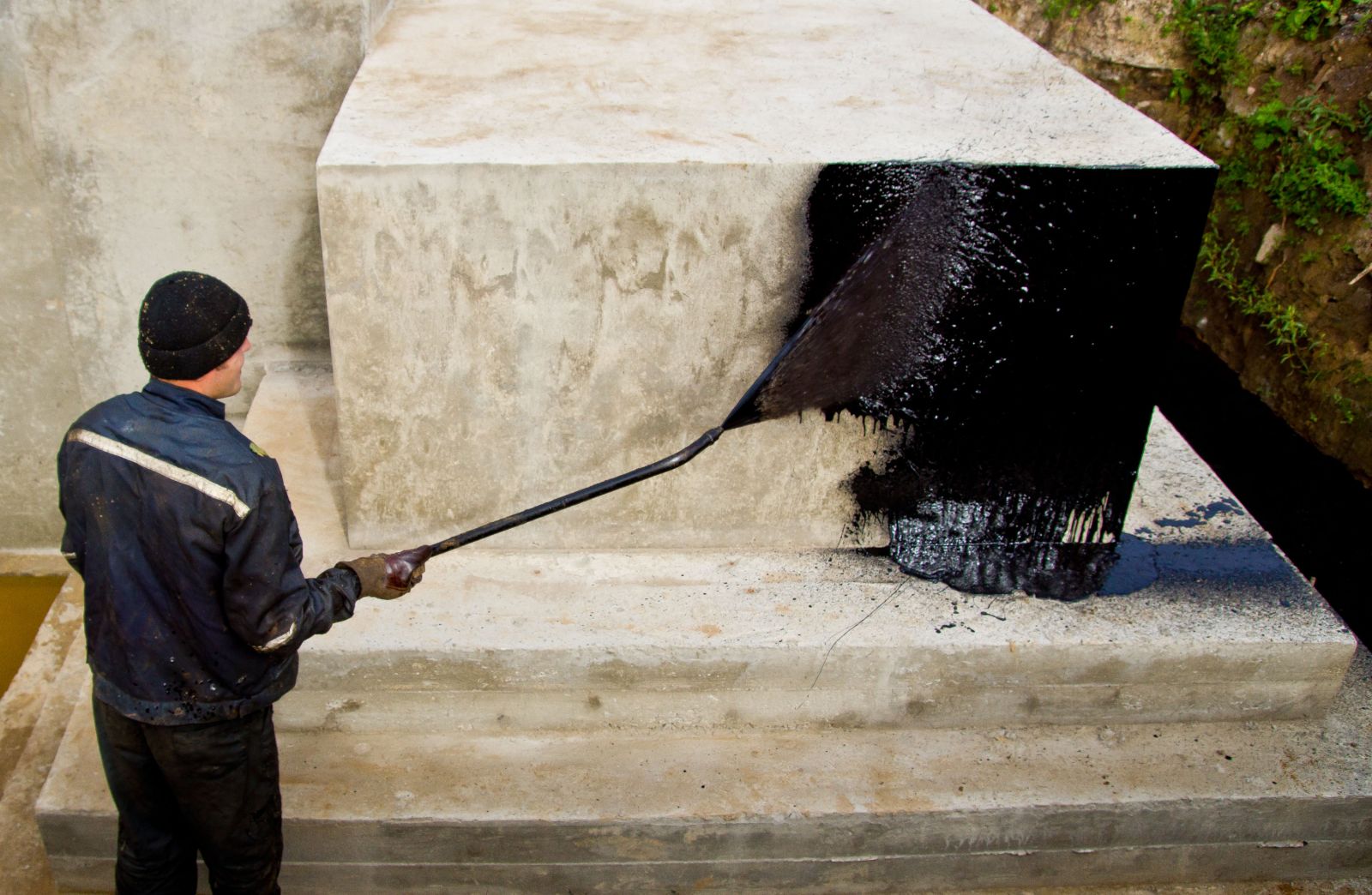
Bituminous mastic for hot application must be preheated to a temperature of 160-180 degrees in a metal container. Apply it with a spatula, leveling with a stiff brush. Hot bitumen mastic is usually used for horizontal waterproofing of the foundation, where a thicker layer and faster hardening of the bitumen layer is required.
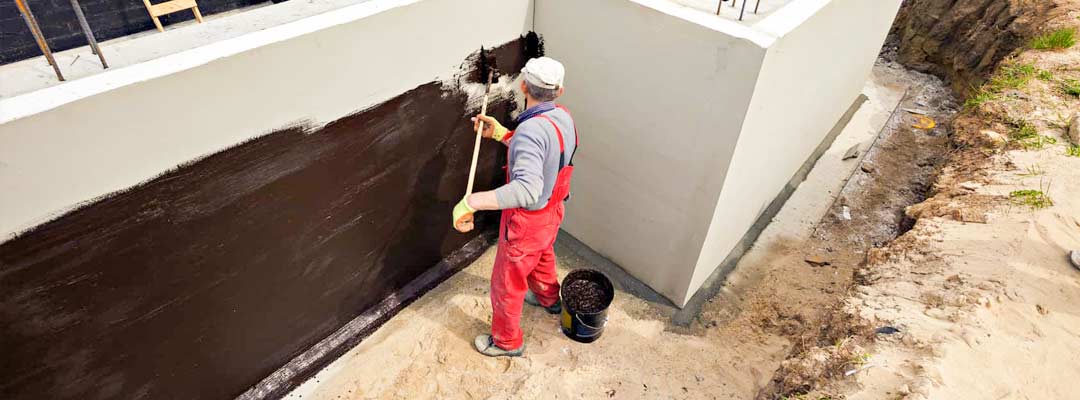
- After the mastic has completely dried, they begin to warm the foundation or backfill the soil. For backfilling, use sand without foreign inclusions - they can damage the waterproofing layer. To reduce stagnation of moisture at the walls of the foundation and to reduce hydrostatic pressure in areas with a high level of groundwater, drainage is performed before backfilling.
Lubricated waterproofing is also used as additional protection of the foundation and an underlayer for glued waterproofing. In this case, the preparation of the foundation surface is carried out in the same way, including rounding off sharp corners and making chamfers, filing, as well as priming and coating with varnish or the first layer of mastic. Next, glued waterproofing is performed.
Mastic and primer for additional protection are chosen depending on the roll material: for bitumen-coated roofing materials - bitumen-based mastic, for polymer materials - water-soluble mastic based on rubber and dispersed petroleum products, since bitumen is an aggressive material in relation to polymer coatings and can cause their destruction. Also, you cannot use bitumen mastics based on organic solvents as an unprotected waterproofing before insulating the foundation with foam and polystyrene. It is better to choose a water-based polymer-based composition or cover the waterproofing with a cement primer.
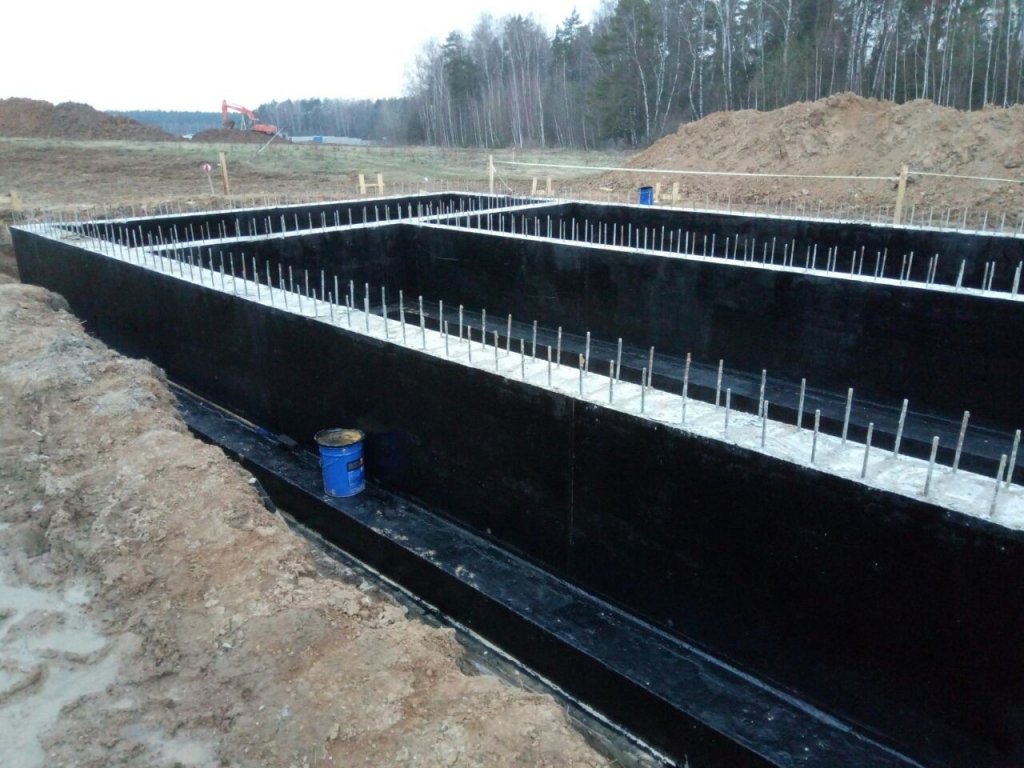
Insulation of the pile-strip foundation
The work includes two stages: high-quality processing of all piles and covering with an insulating layer of tape. Various methods and materials are used to protect the supports - bored piles can be poured into tubes made of a special waterproof material, and driven piles can be protected where possible. But manufacturers usually make modern supports from moisture-resistant concrete (with special additives), so they are not afraid of moisture.
For processing the tape, you can also choose different options - coating (bitumen, tar), roll (roofing material), spraying with a rubber-bitumen composition, using polyurethane foam, etc.
The material is chosen in accordance with the relevance of its cost, requirements for the level of protection, structural features of the foundation and the ability to implement this or that technology.
Types of coating waterproofing
The main requirements for waterproofing protection are the continuity of the layer, the maximum turnaround time.As a coating waterproofing, mastics are used, classified in accordance with the state standard GOST 30693 of 2000 according to the following features:
- composition - polymer, bituminous, combined, one- and two-component;
- solvent - organic or water;
- hardening - non-hardening, hardening by solvent evaporation or due to a chemical reaction;
- method of use - cold, hot.
Cold mastics are more convenient to work with, they do not need to be heated with special equipment. Hot are only bituminous mastics or combined mixtures in which rubber crumb or polymer granules are added to the bitumen.
Mastics of the following modifications are most in demand:
- polymeric - does not destroy polystyrene foam glued on top of it to insulate structures;
- bitumen-polymer - plastics improve the properties of the film, for example, the tensile strength of such a material is 300% compared to the usual one;
- bituminous rubber - filled with EPDM crumbs, there are hot, cold mixtures;
- bitumen-emulsion - ready to use, quickly hardens.

The film obtained from pure bitumen without modifying additives has low mechanical strength, therefore it is not used in foundations.
Mastics are ideal for protection against capillary groundwater. With a hydrostatic pressure from groundwater within 5 m, polymer modifications should be used, within 2 m - bituminous mastics. The thickness of the layer depends on the depth of the structure, is 2 - 4 mm for 3 - 5 m foundations, respectively.
The one-component mixture has an almost unlimited life (time to application). In two-component mixtures, after mixing the compositions, a chemical reaction begins, so the entire volume must be completely used up before setting.
The industry produces three categories of cold sealing waterproofing materials:
- budget - cost 20 - 30 rubles / kg, consist of tar, construction bitumen;
- standard - have a strong unpleasant odor, contain BN 70/30 or BN 50/50 bitumen; with average characteristics, a naphtha fraction is used as a solvent, they cost 50 - 85 rubles / kg;
- class Premium - the composition includes rubber-modified bitumen BN 90/10 or BN 70/30, hardening within 12 - 18 hours, the cost of the mastic is 100 - 140 rubles / kg.
Important! Budget mastics, despite the presence of packaging and the manufacturer's brand, do not meet the requirements of GOST. Therefore, you should not save on the quality of the waterproofing layer, you should buy either standard coatings or Premium class products .. Products based on tar hardens up to 5 days, flows down from the vertical walls of the foundation under their own weight in the heat, since these materials have practically no heat resistance
After 8 weeks of operation, elasticity decreases sharply and unpredictably
Products based on tar hardens for up to 5 days, flows down from the vertical walls of the foundation under its own weight in the heat, since these materials have practically no heat resistance. After 8 weeks of operation, the elasticity decreases sharply and unpredictably.