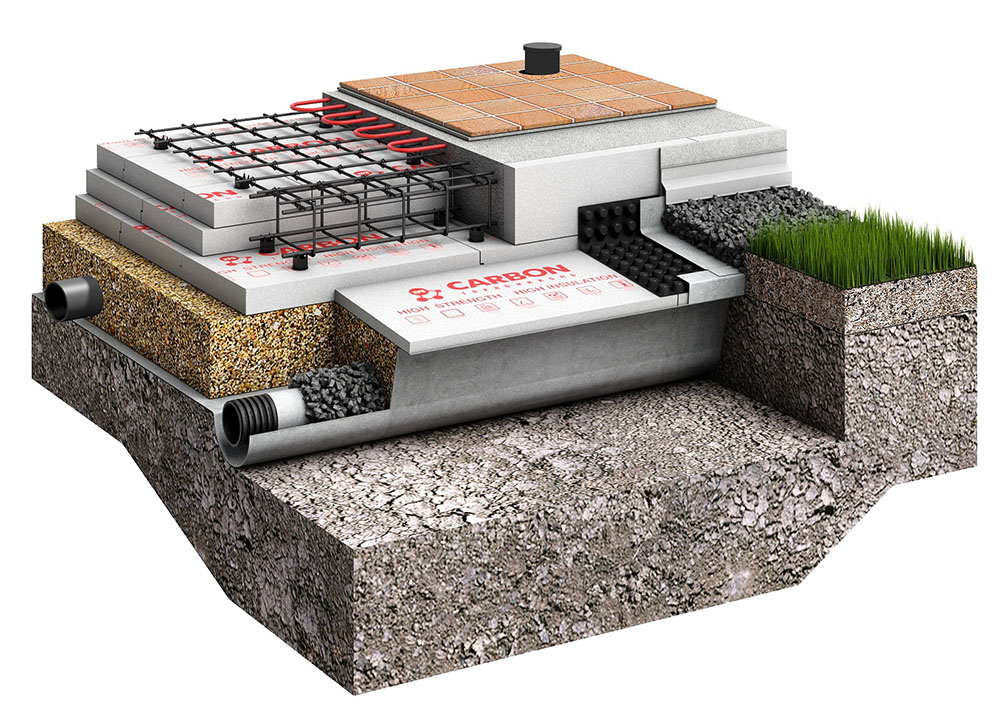
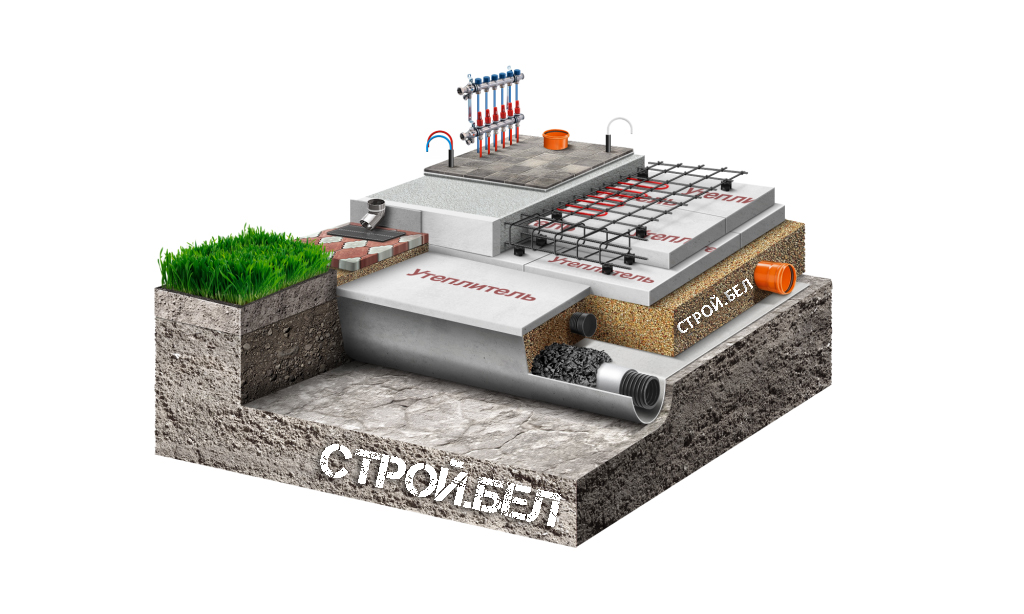
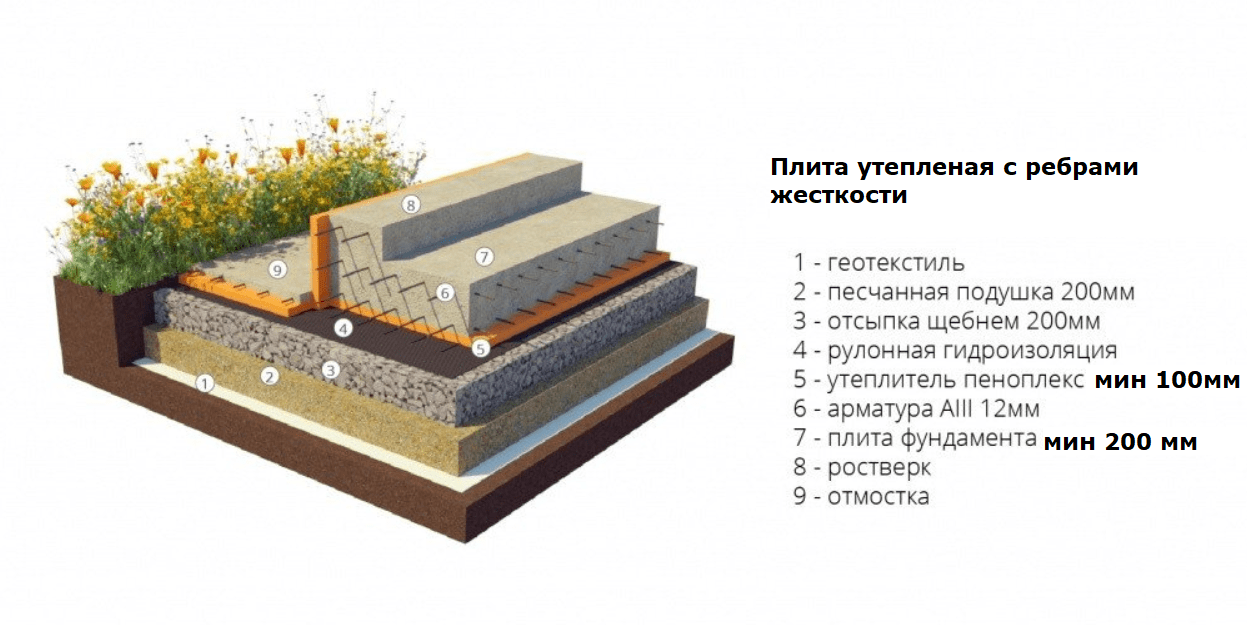
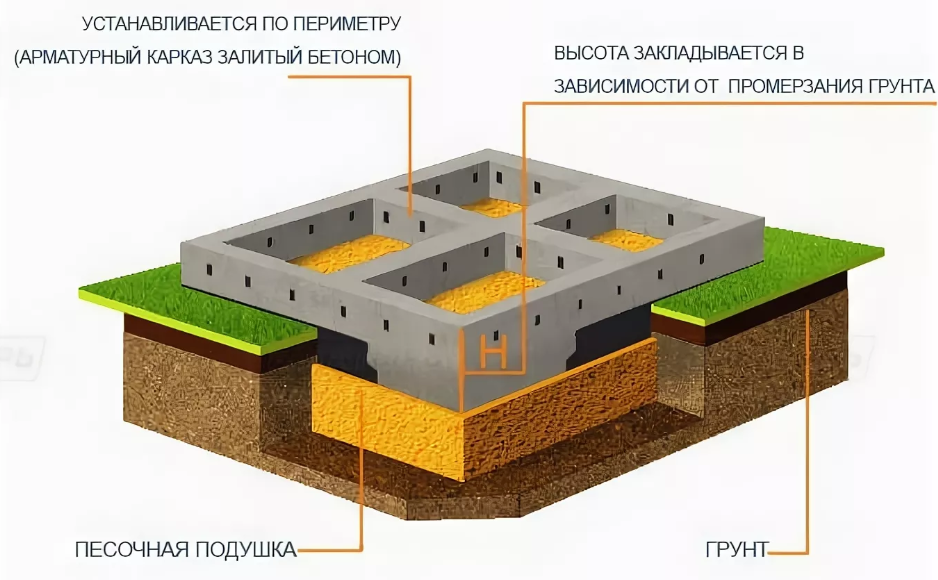
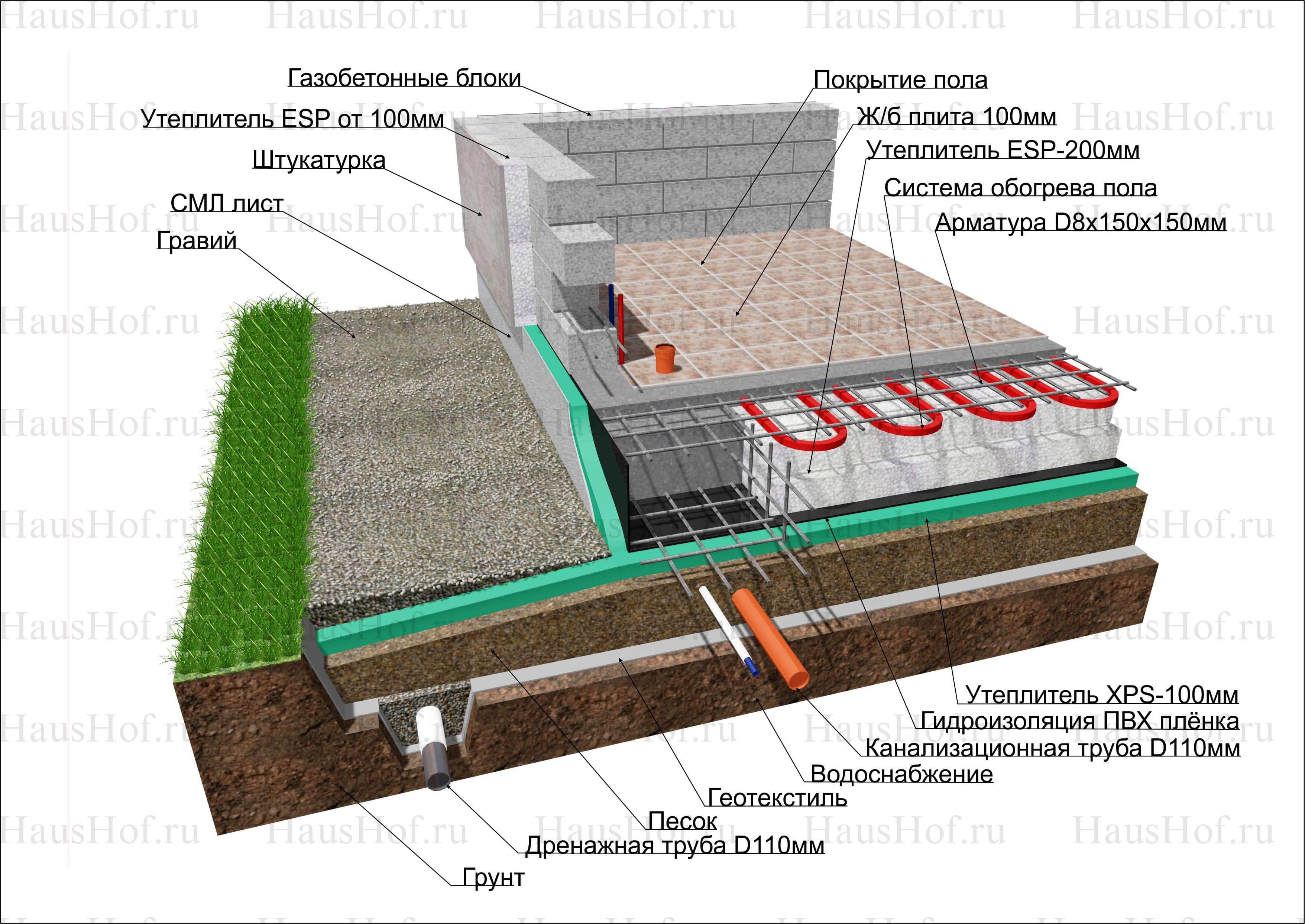
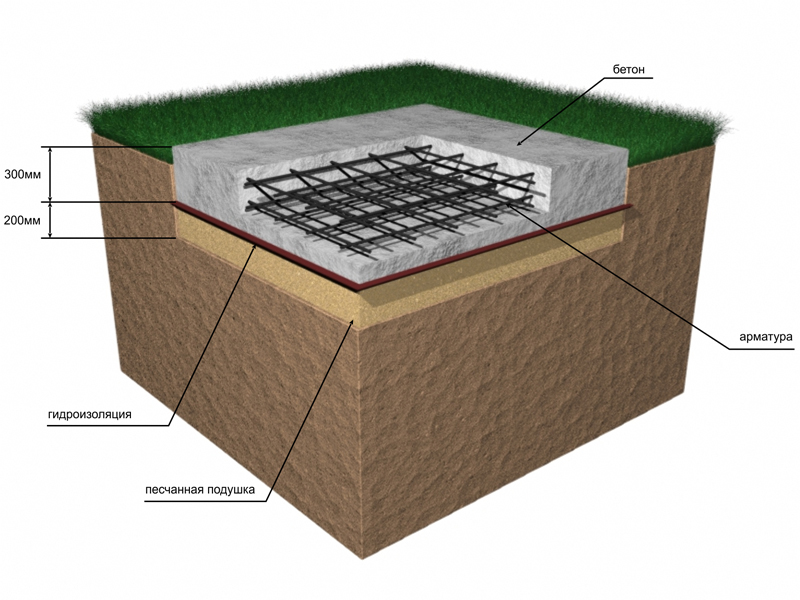
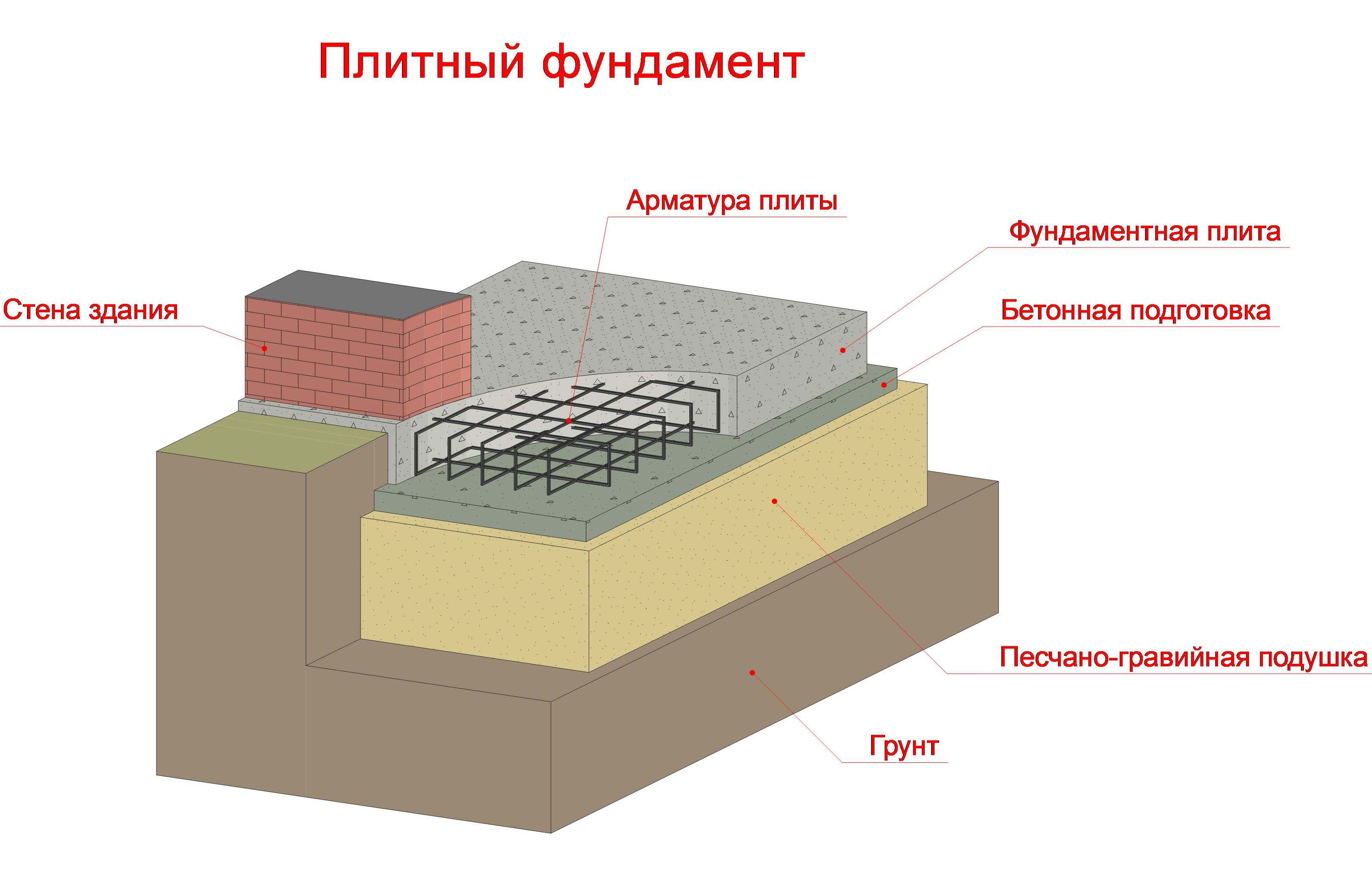
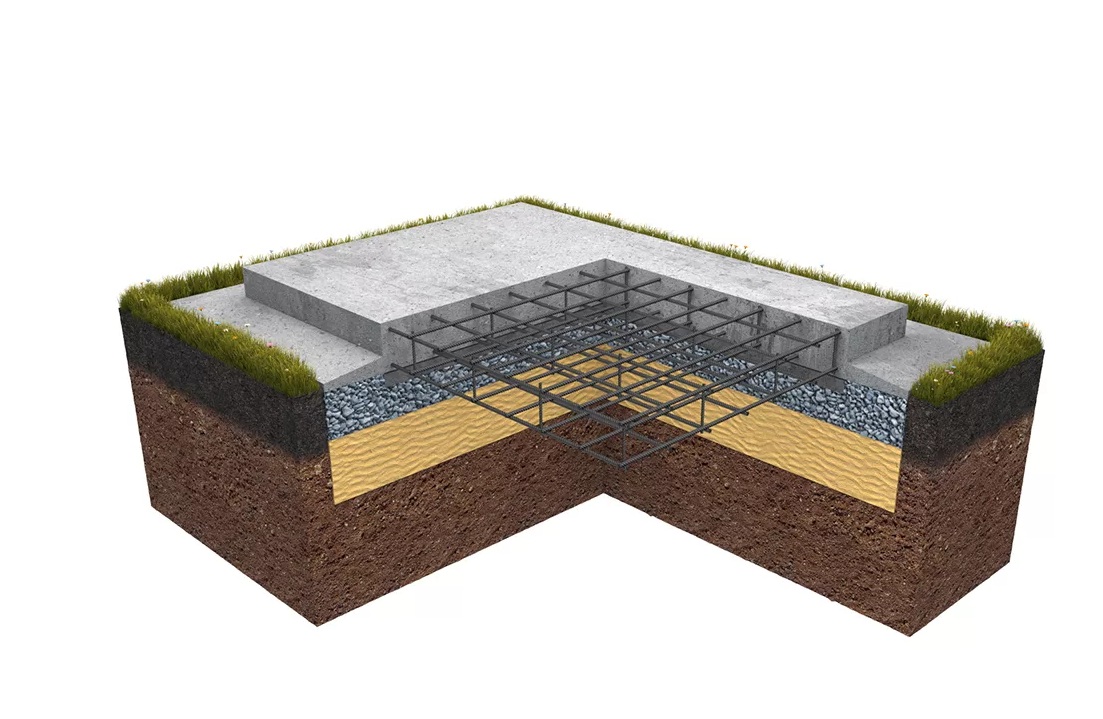
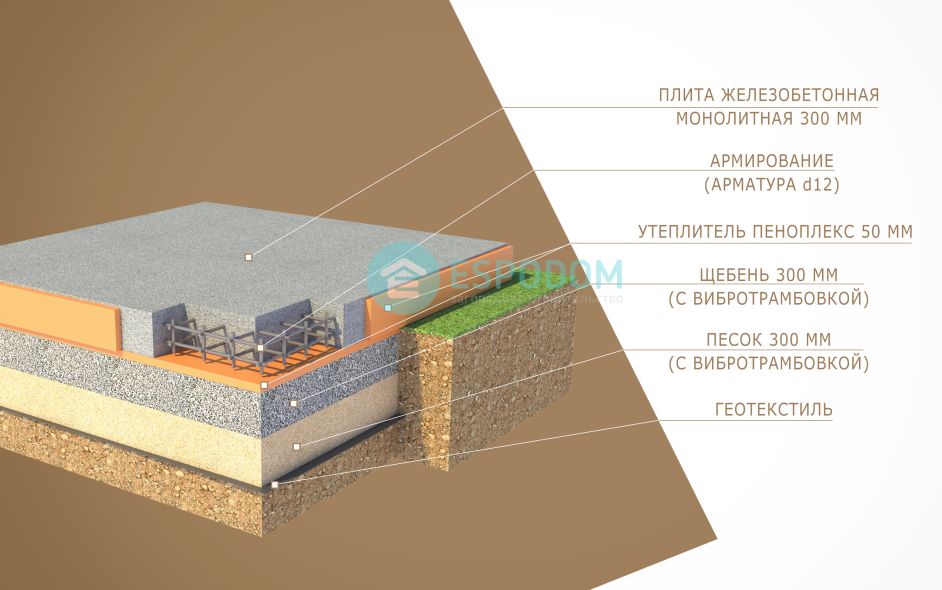
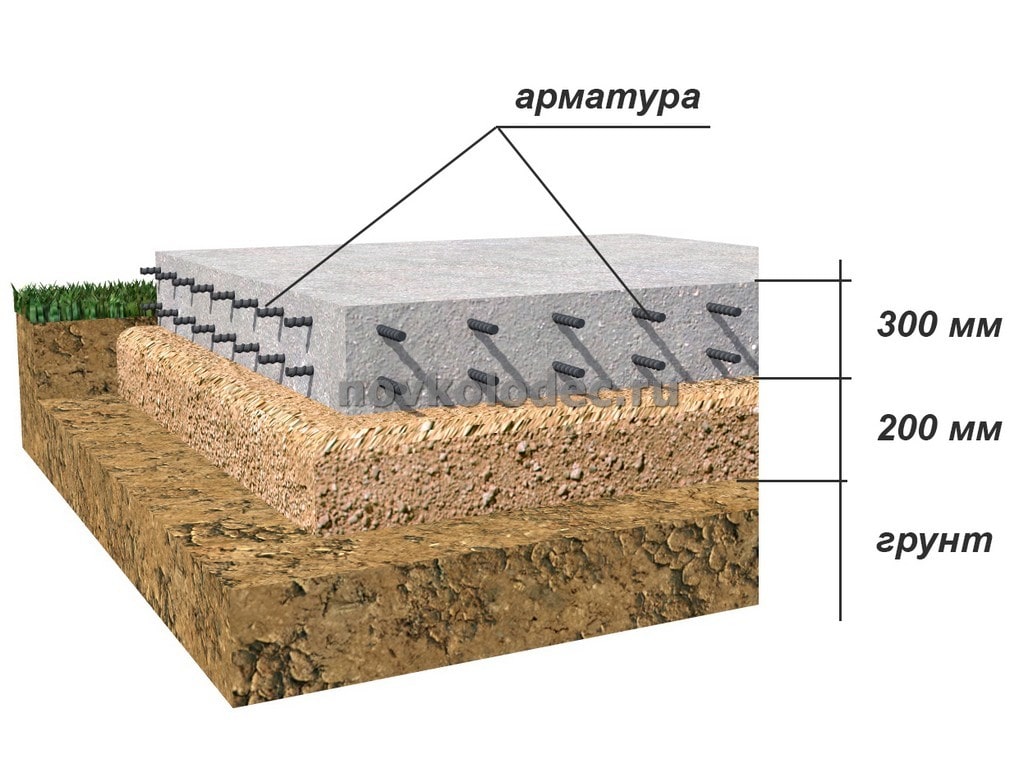
Advantages and features of monolithic slabs
Solid reinforced concrete slabs are widely used in the construction of the foundations of construction projects due to a set of advantages:
- simplicity of design. A solid reinforced concrete base is placed over the entire area of the building at the ground level or with a slight deepening into the soil. Does not require increased volumes of earthworks, it is carried out in a limited time;
- acceptable level of costs. Reducing the estimated cost of concreting is achieved by supplying significant volumes of concrete from vehicles using trays. At the same time, the labor of low-skilled workers is used for tying reinforcement, pouring and vibration compaction of concrete;
- increased bearing capacity. The increased support surface area and the rigid spatial reinforcement frame allow maximum loading of the monolithic foundation slab. The design guarantees the stability of the erected building during soil movements;
- ensuring the integrity of the walls of the building. The monolithic platform for the house does not undergo local deformations, evenly transfers the weight of the structure to the ground, compensates for the swelling of the soil in winter;
- combining the base of the building with the subfloor. The monolithic base serves as a subfloor. It allows you to equip the floor of the lower floor without using reinforced concrete slabs and pouring screed for the floor covering;

Before starting work, soil analysis is carried out
- the possibility of constructing a slab base on difficult soils. The absence of the need for deepening into the ground reduces the labor intensity of earthwork in areas with closely located aquifers, as well as in areas of deep soil freezing;
- versatility. The solid foundation slab can be used for light structures as well as buildings with heavy brick or concrete block walls.
The slab design, along with the advantages, has a number of disadvantages:
- The problematic arrangement in sloping areas where there is a high likelihood of soil shifts. The problem is solved by pouring in one piece with the base of the ribs at the bottom of the inclined section, which fix the site.
- Increased estimated cost associated with the involvement of construction firms in the performance of work on a contractual basis. Self-construction can significantly reduce costs.
- Increase in the volume of work on excavation and concreting during the construction of the basement room. This is due to the need to pour the concrete base below the zero mark at the bottom of the pit.
The features of the slab base are associated with the different location of the site relative to the zero mark. One-piece basis can be performed:
not buried. Set up without excavation on a pre-planned soil surface;

The standard monolithic slab is most in demand in buildings with a basement
- shallow. The base of the building is immersed in the soil to a depth of 30–40 cm until the supporting surface coincides with the zero mark;
- buried. It is used in the construction of buildings with basements and basements. Construction is associated with the implementation of significant volumes of earthworks, a sharp increase in costs.
The slab foundation differs in design and method of formation:
- Monolithic is poured into the formwork with the reinforcement cage installed. The entire structure is cast in one step, forming a solid base. The design is characterized by increased strength.
- The prefab consists of individual reinforced concrete slabs, which are laid on a crushed stone pillow.The gaps between them are concreted, and the surface is leveled with a small layer of mortar. The prefabricated version of the base loses to the monolithic one in terms of strength characteristics.
To build a solid foundation, you need:
- use high-quality steel reinforcement;
- comply with the recipe in the manufacture of concrete mortar;
- adhere to the technology of performing work.

A more durable base is a plate that has stiffeners
Compliance with these requirements will allow you to form a reliable base of the building, to avoid the appearance of cracks on the walls.
Formation and concreting of the slab
The whole process of work on the construction of a monolithic foundation can be divided into four main stages. It:
- Geodetic part of the work (breakdown of the axes along the contour of the slab).
- Arrangement of seams - but this is in the case when the volume of work is too large and cannot be completed in one day.
- Concreting.
- Concrete hardening control and maintenance.
The following mechanisms and devices are involved in the work process:
 Jib crane
Jib crane
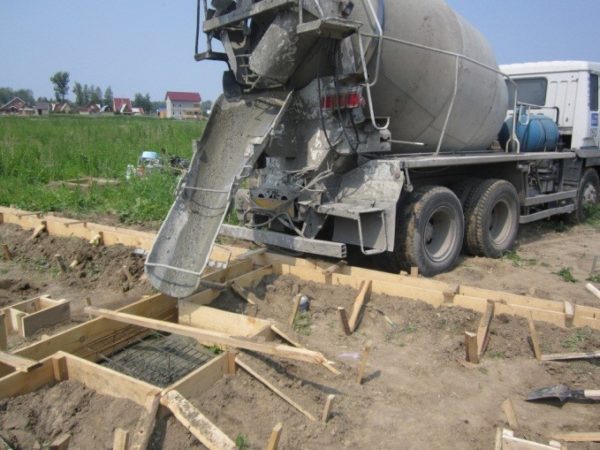 Concrete mixer truck
Concrete mixer truck
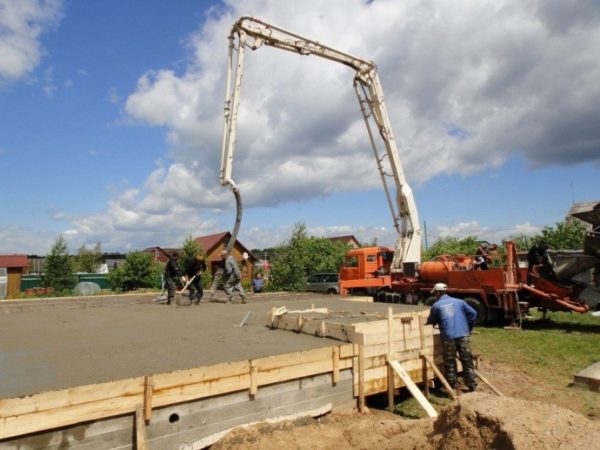 Concrete pump
Concrete pump
 Gasoline vibrating screed
Gasoline vibrating screed
Organization of work
Any large-scale work requires solving a large number of organizational issues. It is necessary to find qualified workers, install a change house for them, arrange an access road to the construction site and protect it, provide the object with materials in a timely manner, select and deliver mechanisms to the site. Only after that you can proceed directly to the construction.
Table 2. Installation instructions
Steps, photo
A comment
Step 1 - breaking down the contours of the pit
It is impossible to start such important work as the construction of a monolithic slab without a drawing. On its basis, a breakdown of the contours of the pit is made, and the transfer of marks to its bottom, and the formwork is exposed.
Step 2 - excavation
The soil is sampled along the marked contours.
Step 3 - arranging the sand cushion
Sand is delivered to the object and distributed to the bottom of the pit with the obligatory pouring of water and layer-by-layer compaction with a vibrating plate.
Step 4 - compacting the sand with crushed stone
To achieve the highest density of the bulk base, a layer of crushed stone is poured over the sand and tamped again. At the same time, a small formwork is being set up, along which the foundation will be poured.
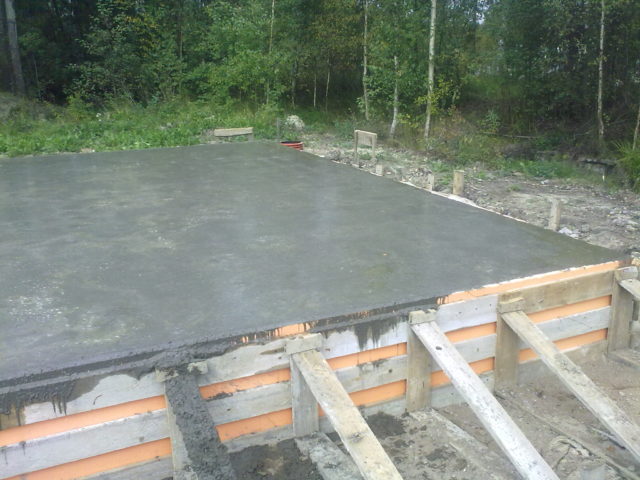
Step 5 - pouring the foundation
Concrete preparation is performed on top of the coarse-graded bedding
A layer of lean concrete is poured to a thickness of 5 or 10 cm (depending on the thickness of the main slab). Please note: the area of the preparatory concrete layer should be slightly larger than the area of the main slab - from all sides by 10 cm.
Step 6 - installation of a waterproofing layer
After 3-4 days (depending on the weather), when the foundation has hardened well, you can start waterproofing. The most reliable option is a two-layer one, when the rolled bitumen material is glued to the mastic (or fused).
Step 7 - assembling the formwork under the slab
On the foundation, according to the specified dimensions of the slab, the formwork is assembled, and its walls are lubricated with used oil
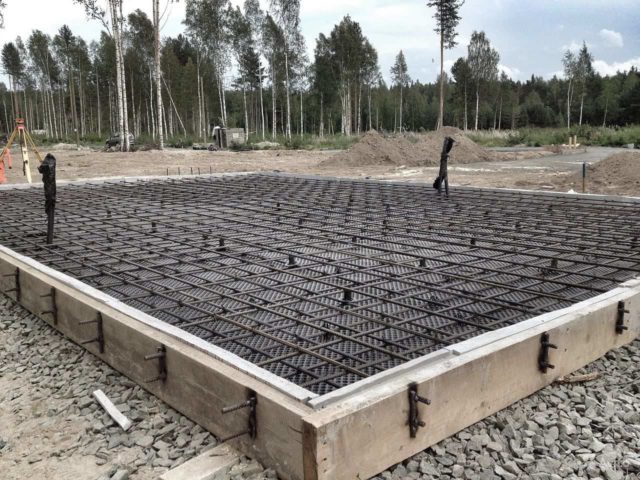
If the foundation has a small thickness, a reinforcing mesh is laid on the bottom, on special supports.
Step 8 - knitting the frame
With a slab thickness of more than 150 mm, the frame is made three-dimensional. Therefore, the next stage is transverse knitting of reinforcement with a step of 25 * 25 cm.
Step 9 - concreting
The main condition for the correct operation of the slab in the future is its continuous pouring. In any case, the area of even a large private house is not so large as not to have time to concrete the foundation in one day. The main thing here is to organize well the supply of ready-mix concrete to the object.
Step 10 - compacting and smoothing the concrete mass
Fresh concrete is immediately compacted and its surface leveled.
Step 11 - waiting for curing
Now, in order to continue working, it is necessary to wait until the slab reaches at least 70% of its design strength. It depends on the temperature of the concrete. At +20 degrees, this happens already on the seventh day.
But all this time, concrete must be properly looked after. In hot windy weather, in order to exclude the rapid loss of moisture, the stove can be covered with plastic wrap, or you will have to constantly water it with water.
Step 12 - stripping the slab
The formwork is removed when the concrete reaches 50% strength. At the same +20 degrees, this happens on the third day after pouring. After removing the formwork panels, the side walls of the slab are treated with bitumen mastic.
Step 13 - plinth formwork
If there is a need to fill in the monolithic base as well, then the formwork is exposed for the third time - now under it.
Step 14 - fill the base in layers
The whole process of installing the reinforcement cage, pouring, tamping and waiting for strength is repeated. As a result, the foundation will look like this one in this photo.
Pros and cons of slab base
The slab foundation is a shallow foundation, which ensures the reliability of the building when the ground moves. The base has a "floating" ability, thereby minimizing the risk of distortion of the structure during seasonal freezing or thawing of the soil. Thus, the foundation and the building, installed on it, seem to "float" on the upper layers of the soil. This is optimal for heaving, clayey areas, but such structures are practical on any other type of soil.

The device of the slab foundation is simple, but ensures its stability
The slab foundation has a simple structure, which is efficient in operation. This is due to the following advantages of such a foundation compared to other options:
- the minimum amount of earthwork contributes to savings in the construction process;
- ideal for difficult, heaving soils, as it ensures the stability of the structure;
- the service life of a high-quality slab foundation is more than 150 years;
- the ability to use any material for building a house;
- a simple device does not require a lot of time spent on construction.
In the process of creating a slab foundation, a large amount of concrete, reinforcement and other materials is needed. This leads to significant financial costs, which is the disadvantage of such a foundation for a home. To equip the slab, you need the most even initial surface. Otherwise, the laying of the foundation layers will be impossible or of poor quality. At the same time, all communications calculations are necessarily planned at early stages. The disadvantages of the slab construction are pronounced, but during construction on heaving soils base is the only option.

Slab base suitable for a flat area
The stability of the slab base allows you to build houses with a height of 2 floors. At the same time, it protects the structure from distortions as a result of freezing of the soil, as well as the durability of structures.
Features of the floating foundation
A floating foundation is a type of slab structure. Floating is often synonymous with slab base, but they have some differences. The floating version is presented in several types with the following features:
floating lattice - a base that has cruciform stiffening ribs with a step from 1 to 3 m. The method has a lower cost, and during operation, distortions of the building are excluded. The key to the reliability of the structure is the accurate calculation of all parameters, depending on the characteristics of the future structure;
The columnar floating version cannot be created on clay soil, but it is optimal for rocky and gravelly sands when building log cabins, frame or panel houses. Fundamental the pillow is made of sand and waterproofing, which replace the fertile soil layer. The pitch between the posts is 1.5–2.5 m;
the floating slab is a one-piece shallow base
At the same time, it is important to stabilize the condition of the heaving soil by organizing drainage, replace the layer of inert soil, and protect it from freezing. This avoids the violation of the integrity of the building when the slab moves as a result of soil swelling.
A floating foundation differs from a slab foundation in that it can be created in several versions. The choice of a certain one depends on the material of the building, the characteristics of the soil, the weight of the structure. In any case, an accurate calculation of all parameters is needed, otherwise the structure may squirm as a result of soil movement.
Finnish base
The foundation, in which the slab is not connected to the basement / foundation part, only accepts service loads. On the basis, communications in the form of a warm floor do not pass, because they are mounted at the stage of finishing the structure. The Finnish version is designed for the subsequent arrangement of a warm floor. The base is suitable for buildings without an underground floor.
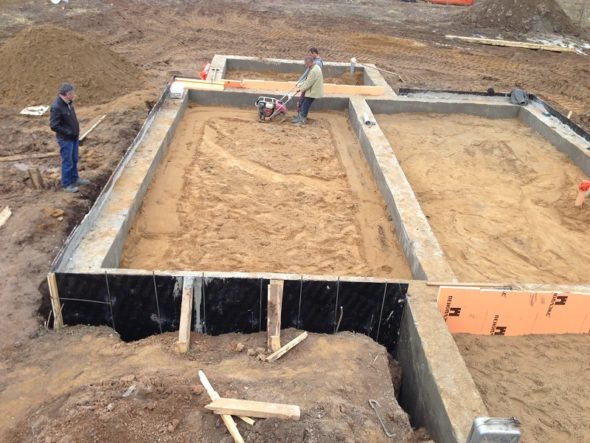

For the Finnish slab, the inner part is filled up separately
The Finnish base assumes insulation with foam or other materials for arranging the foundation. This process is carried out from the inside of the structure. At the same time, the bottom plate does not have thermal insulation, and fused or glued films are used for waterproofing.
Pros and cons of a foundation slab
The disadvantages of the monolithic structure of the base of the structure are the continuation of the advantages and features of its structure.
Advantages
- practically no preparatory work is required, which significantly reduces the construction time of the structure;
- the device of a reliable foundation of the building does not require special qualifications from workers and special tools and equipment;
- the massive homogeneous base of the building is not affected by seasonal temperature fluctuations in the ground;
- the maximum possible strength and durability of a monomorphic structure, which is incredibly difficult to deform, since it has no joints;
- you can save on flooring in the building, because the slab itself is the floor.
Watch all the advantages of the stove in the video:
disadvantages
- the cost of materials and the construction of a monolithic foundation made of reinforced concrete is about a quarter of all costs for the construction of a building;
- the construction of a house with a solid structure of its foundation requires clear preliminary planning, calculation and design of all construction work;
- the impossibility of laying a massive and solid slab structure in those areas that have slopes.
Pros and cons of slab foundation
The slab foundation has many advantages, including:
- The foundation has little ground pressure. This is achieved due to the spatial reinforcement, as well as its large area, which makes it easy to transfer soil movements in different seasons of the year, while the base evenly rises and falls with the structure. This makes it possible to prevent the formation of cracks and gaps in the walls.
- The foundation can be erected without much effort on your own, without the use of special equipment and skilled workers, however, the entire process of pouring concrete must be strictly observed.
- Due to its large area, the foundation slab can withstand heavy loads from the house, especially if it is located on a stable, non-heaving soil.
- The slab seems to "float" on the ground during seasonal heaving, and evenly rises along its entire area with the structure.
- The slab base can be used as a subfloor, which makes it possible to reduce the cost of installing logs, however, the slab floor must be insulated and protected from groundwater.
- A slab foundation is an ideal option if you need to build a house on soils where groundwater is located very close to the surface, on mixed and highly freezing soils.
- The foundation has great strength and seismic resistance, which allows it to be used in seismically active zones.
Among the disadvantages of the foundation, one can note the high cost of funds for its construction, and in some cases, the use of special equipment. Also, when using it, you cannot build a structure with a basement.
The use of various types of monolithic foundations in construction
Which type is better to choose: tape or columnar
Diagram of a removable wooden formwork.
associated with the construction of the following types of foundations of buildings and structures:
- Tape.
- Columnar or pile.
- Plate.
If you plan to build a building with a small number of floors, then the tape type is best suited. When arranging such a base, a large filling depth and too strong a deepening into the ground are not required.
The baseband structure should be wider at the bottom of the sole than at the top.
In general, the depth of soil freezing in the area under the foundation slabs will have a great influence on its bearing capacity. At the same time, the device of a monolithic strip structure of the base should assume the presence of walls of a building or structure with a large thickness. Therefore, this type of construction of the base of the house is a more cumbersome option, which also differs in its higher cost when compared with other types of foundation.
One of the more economical options is a columnar foundation. In terms of the degree of labor intensity in the construction process, it is not more costly than tape. In order to build a columnar foundation, holes are drilled in the soil, where a reinforcing cage is inserted, which is poured with concrete
It is very important to determine the characteristics of soil mobility. If the soil is characterized by horizontal mobility, then the device of a columnar type of the base of the house is not recommended
For low-bearing soil, a columnar foundation is also not suitable if the walls of a building or structure are particularly powerful.
Monolithic foundation slab construction technology
The scheme of a monolithic slab on a strip foundation.
When creating a strip structure, you can use floor slabs. At the same time, it is planned to build buildings with a basement or ground floor. When constructing the foundation, you can use reinforced concrete blocks.
When building a monolithic foundation from floor slabs, special attention is paid to the degree of heaving of the soil on the side surface of each of the walls of the structure. Its sole must be strong, as it will also be affected by heaving forces.
In order to protect against such an impact, the width of the trench increases, and to fill the trench, soil of normal density is used, which is not prone to heaving.
They are very often used in the process of constructing a foundation of a monolithic type of floor. In this case, they are divided into several different subspecies. Monolithic slabs can include:
- Precast concrete slabs.
- Beams.
- Liners.
- Plates.
The foundations of buildings made of reinforced concrete slabs will be of the highest quality if they are constructed using formwork.
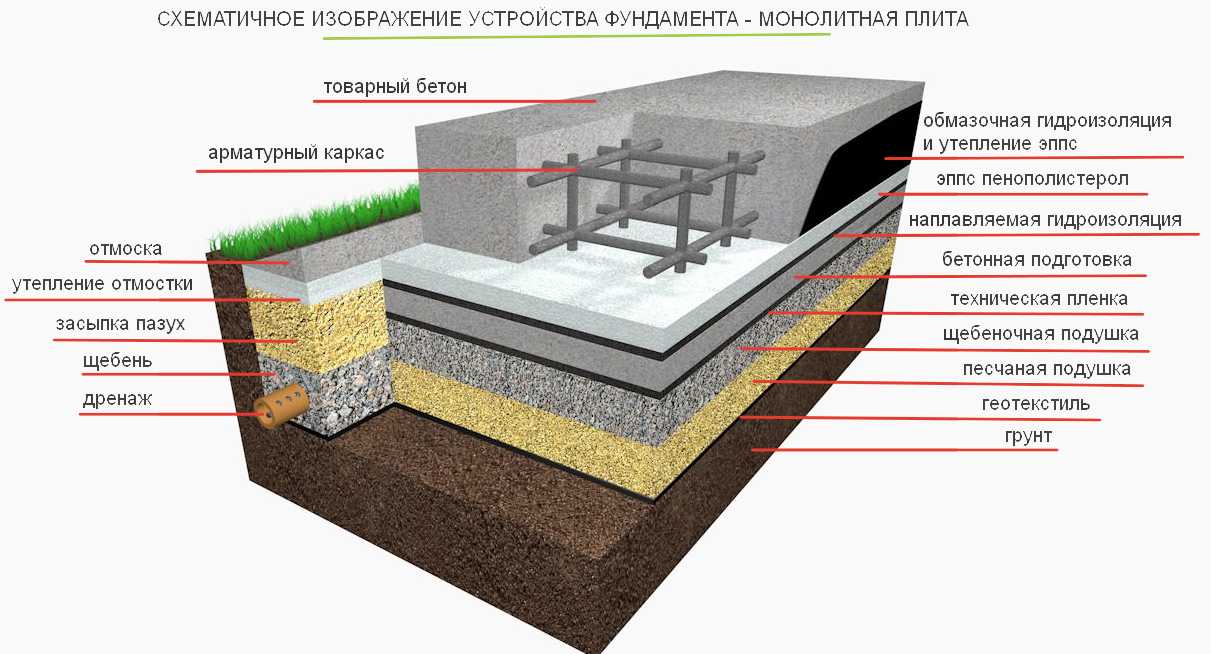
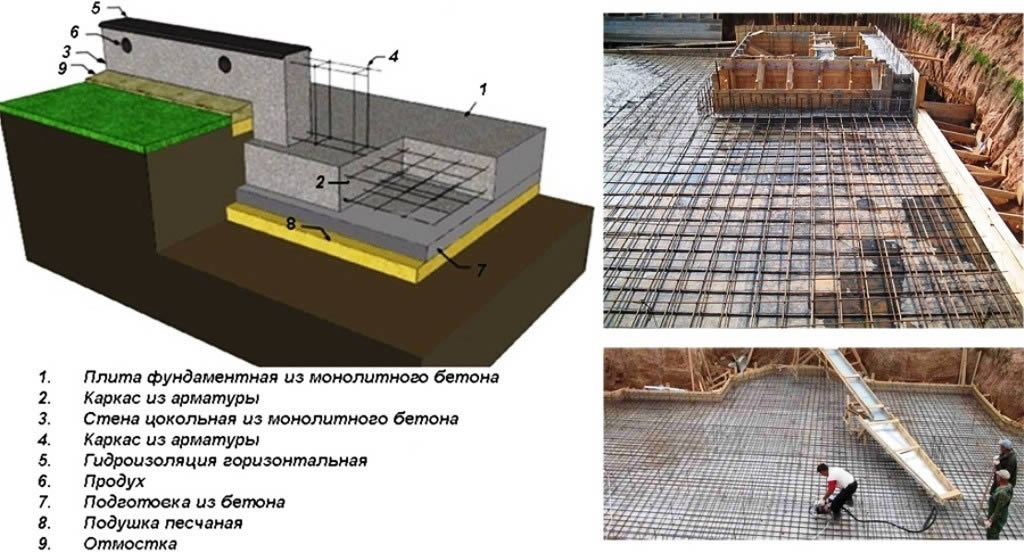
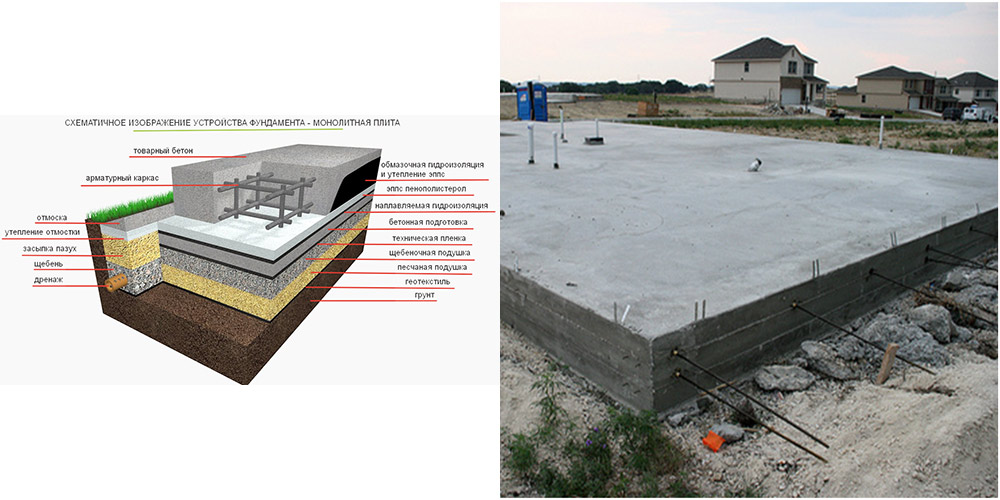
Monolithic foundation device
After the completion of the laying of this type of building foundation, the entire area under the structure will be occupied by a homogeneous structure. These features of the construction of a monolithic foundation must be taken into account even at the design stage, because after the completion of construction, a device under a building, for example, a basement, will be fraught with great difficulties.
The work on the construction of a monolithic foundation is a fairly simple, albeit painstaking and time-consuming task.
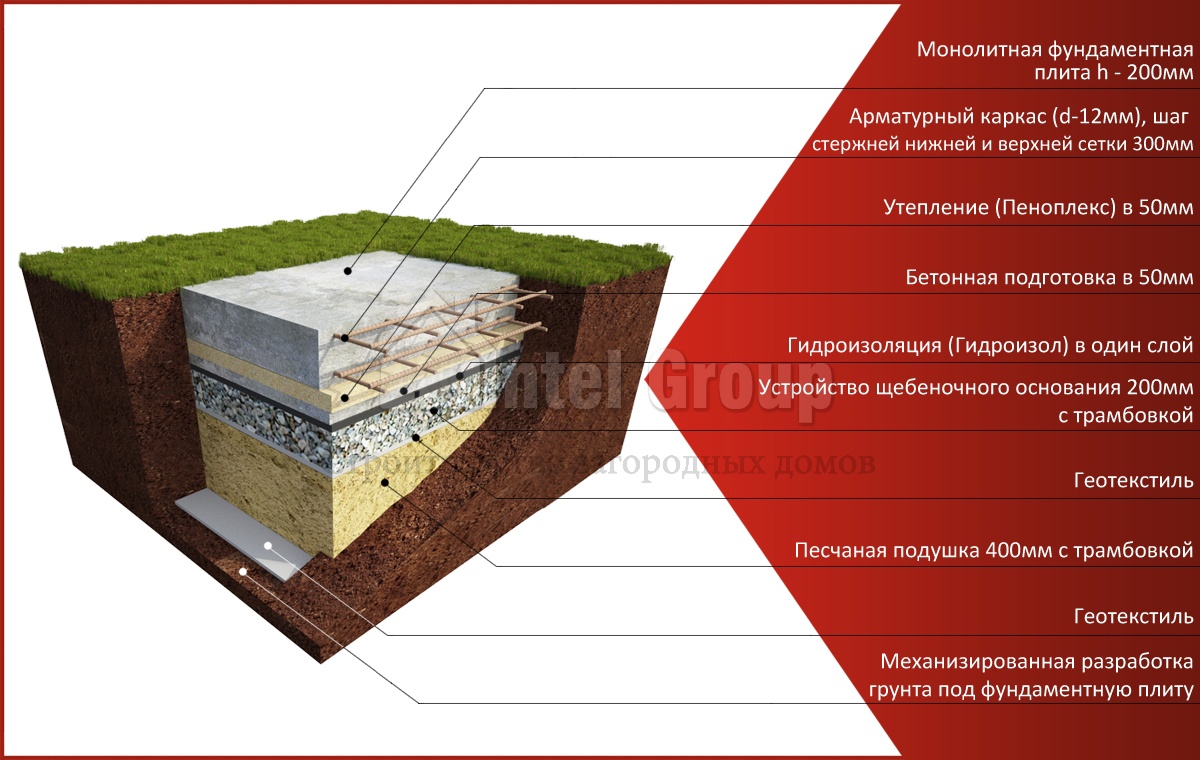
Calculation of the thickness and area of the foundation
 Slab construction
Slab construction
This takes into account:
- the type of soil on which the construction is being carried out;
- the weight of all building materials needed to build a house;
- climatic features and seasonal weather changes (temperature regime, wind loads on the structure, precipitation, snow melting rate, etc.);
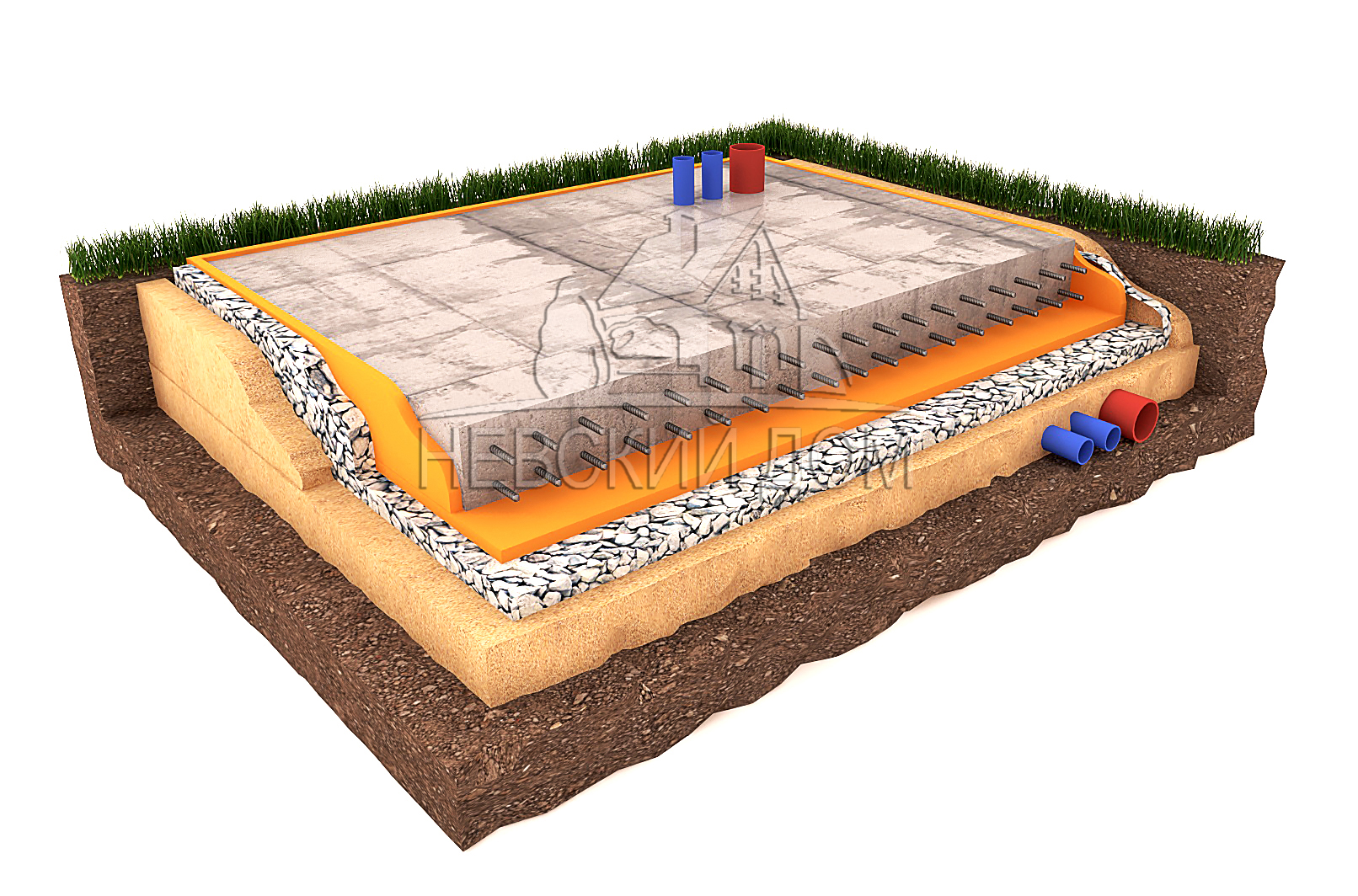
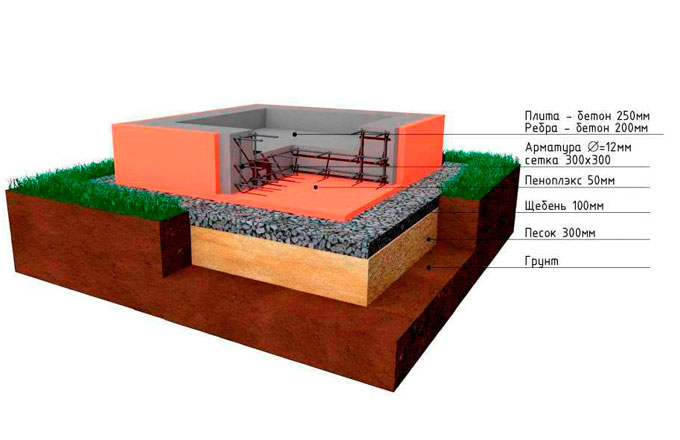
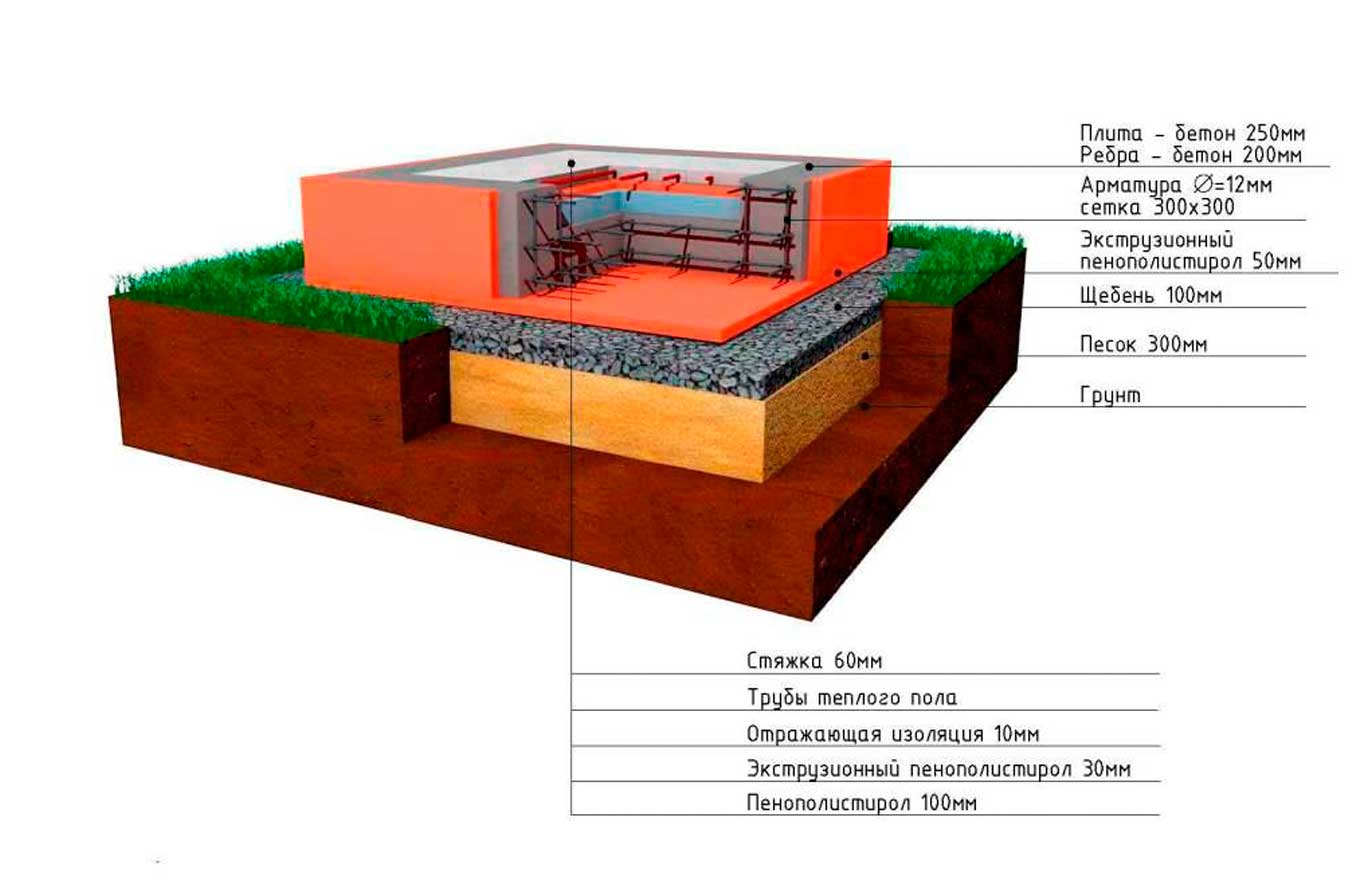
In general, you can give advice: for ordinary outbuildings and garages, it is often sufficient to lay foundation slabs 10 cm thick, and for one-story residential buildings - 25 cm.
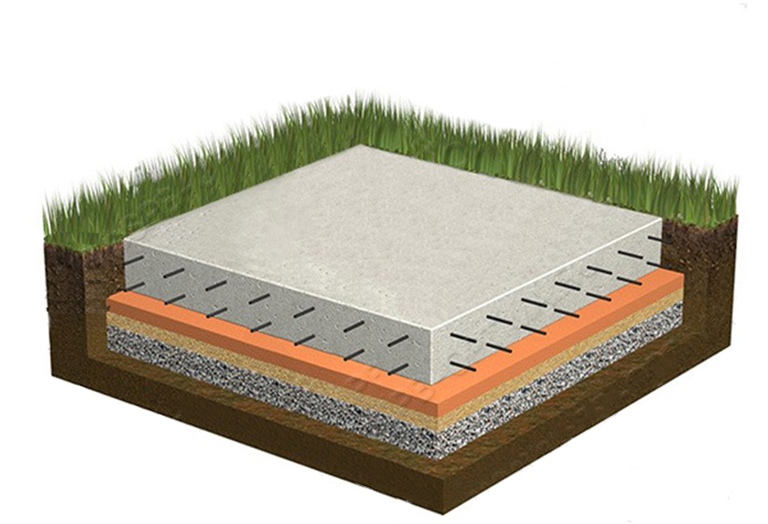
Excavation and preparatory work
- a pit is pulled out, the dimensions of which should be 0.5 meters larger than the length and width of the future building;
- the bottom of the pit is leveled and the pit is given the appearance of a strict rectangle;
- backfilling, filling with water and compaction of a cushion of sand and gravel is performed;
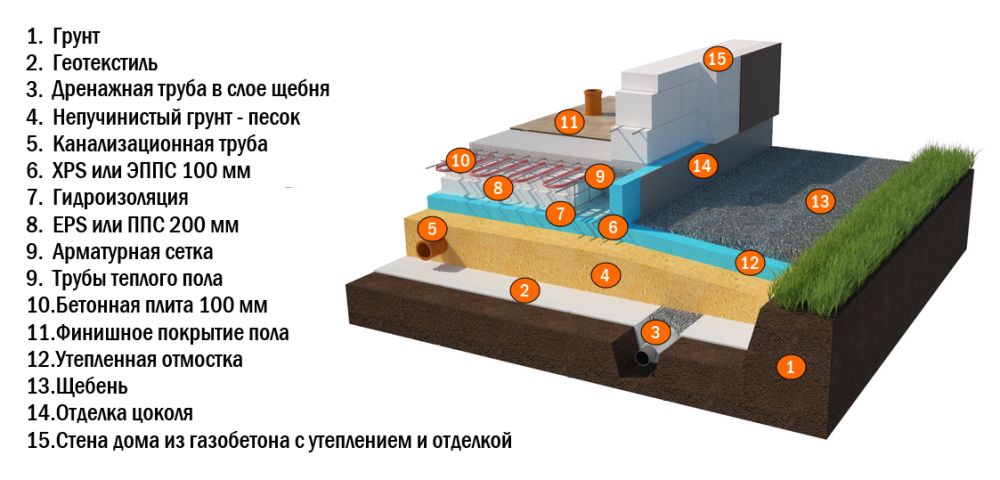
- the calculation and connection of communications (sewerage, water and gas pipelines) is carried out, since after laying a reinforced concrete slab it will be rather difficult to bring them to the building.
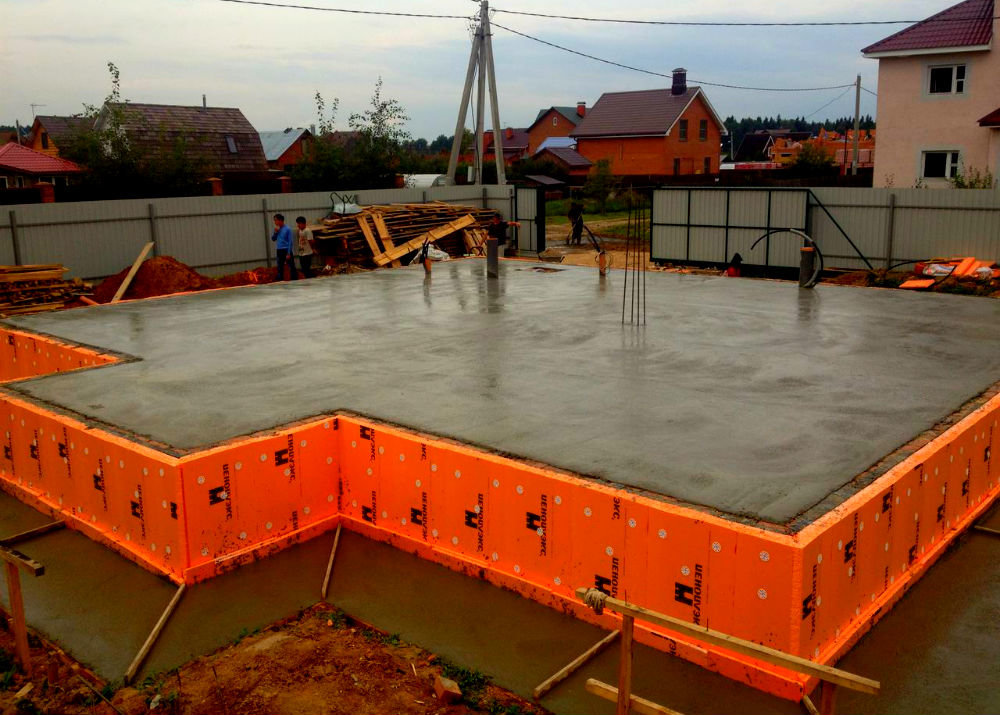
Waterproofing device
- waterproofing sheets are overlapped and in two layers;
- it is advisable to fill the bottom of the pit with a thin layer of concrete before covering with waterproofing sheets;
- sidewalls are also waterproofed using bituminous bridges;
- a concrete blind area is created to prevent rain and melt water from flowing under the foundation body.
Not pleasant features of both concrete and reinforced concrete are that they have high thermal conductivity and hygroscopicity. Therefore, it is advisable to additionally add heat and waterproofing additives to the concrete solution.
The video below describes the whole process:
Formwork device
- for formwork, boards from 2 cm thick and more are used; they are fixed on support pillars driven into the ground along the perimeter of the pit;
- the corners of the rectangle and the lengths of the diagonals are checked so that the rectangle of the future concrete slab is correct.
At this stage of the laying, it is necessary to decide what the monolithic structure of the building base will consist of:
- from solid reinforced concrete;
- solid concrete; or
- from industry-standard slabs?
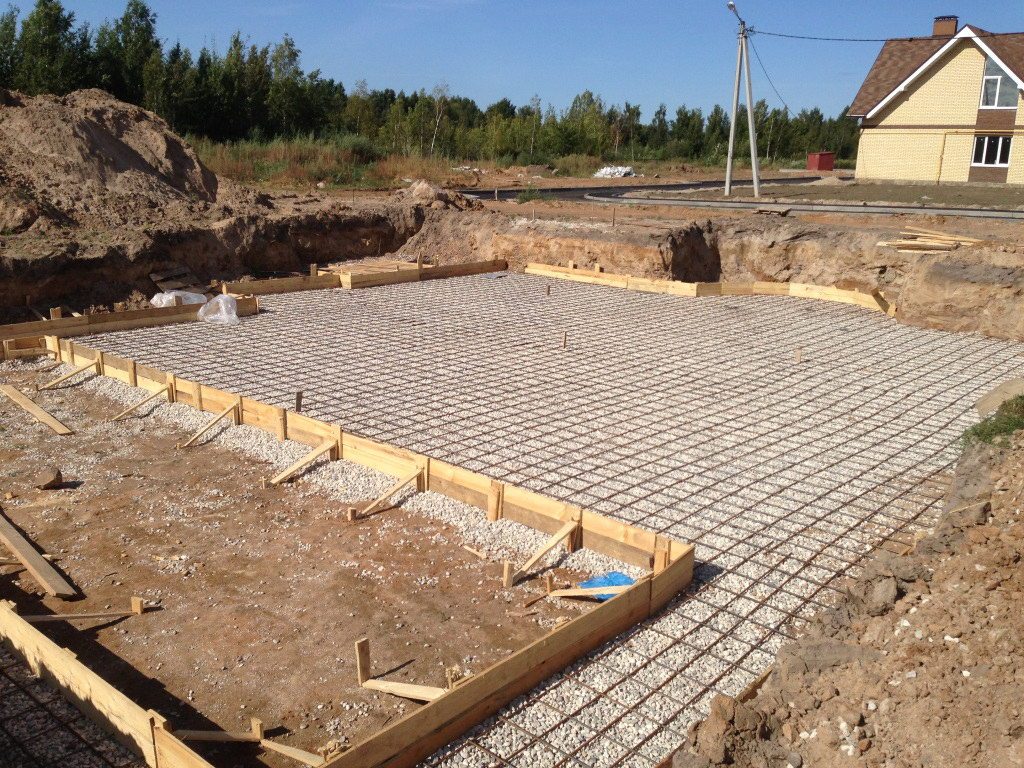
In the first case, it is necessary to make the device of the reinforcing mesh of the future base plate of the building with rods with a diameter of 12-16 mm. (In the construction of industrial and multi-storey buildings, more powerful fittings are also used). At the intersection, the rods are connected with special clamps or welded.
Filling the foundation pit with concrete
 Pour concrete after reinforcement
Pour concrete after reinforcement
- the recommended concrete used for pouring foundations in central Russia is concrete with a resistivity of a static load of 300 kg / cm2, with a frost resistance of 200 cycles and a water resistance of 4 units;
- pouring is carried out either in one step with subsequent processing of the plate body with vibrators to remove air inclusions, or in layers;
- to speed up the pouring process, it is advisable to use a special technique - a concrete pump with a concrete mixer, since concrete is a highly mobile mixture;
- after pouring, they begin to level the surface of the structure;
- after the concrete dries, the construction of the monolith of the base of the house ends.
Complete hardening of a monolithic structure with a thickness of 25 cm occurs in 25-28 days, and 80% - in 10-11 days. If excessively dry and hot weather is established, then it is advisable to carry out additional moistening of the surface of the concrete mixture so that its surface does not crack with intensive evaporation of moisture.
Advantages and disadvantages
The foundation slab has high strength and reliability indicators. Moreover, you do not need to possess special construction skills for its independent creation.It is enough to know how to hammer together wooden formwork panels and mix concrete.
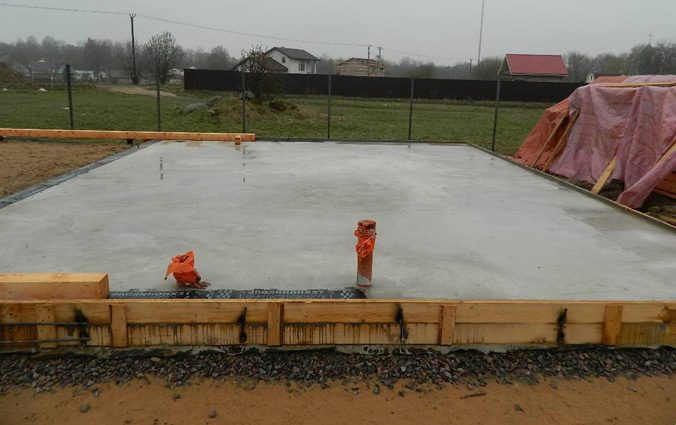

Over time, concrete only gets stronger, so do not be afraid to leave it "brew" for a season or two
Almost all types of cottages can be safely installed on a slab reinforced concrete foundation. For the construction of buildings on it in one or two floors, aerated concrete, ceramic and gas silicate blocks, as well as all types of wood (profiled timber, logs, etc.) are used. The wall masonry, for which a gas block or brick is taken, on such a monolith will definitely not crack from swelling of the soil. On the slab, you can put both wooden or concrete houses, as well as frame or frame-panel houses.
One of the main problems of such a monolithic foundation is communication. Plumbing and sewerage for the home must be designed in advance. All pipes must be laid before the concrete is poured. Then it is difficult and impossible to break the monolith. Plus, on a slope, such a foundation with your own hands or with the involvement of professional builders will not work. It needs a flat area.
What is a slab foundation?
Due to its massiveness and strength, a monolithic foundation in the form of a single slab is able to withstand serious local impacts from below from the soils without destruction and deformation. With strong heaving in winter, it evenly and all rises with the house on it, and in the spring it also drops. If such a base under the building is made exactly according to the technology, then it is durable and strong.
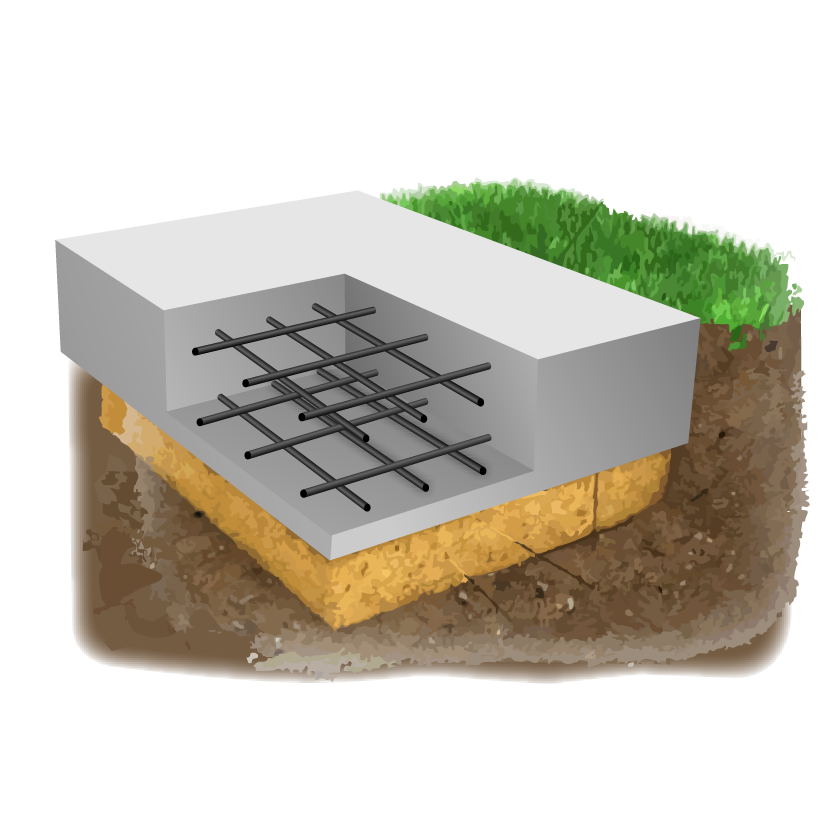
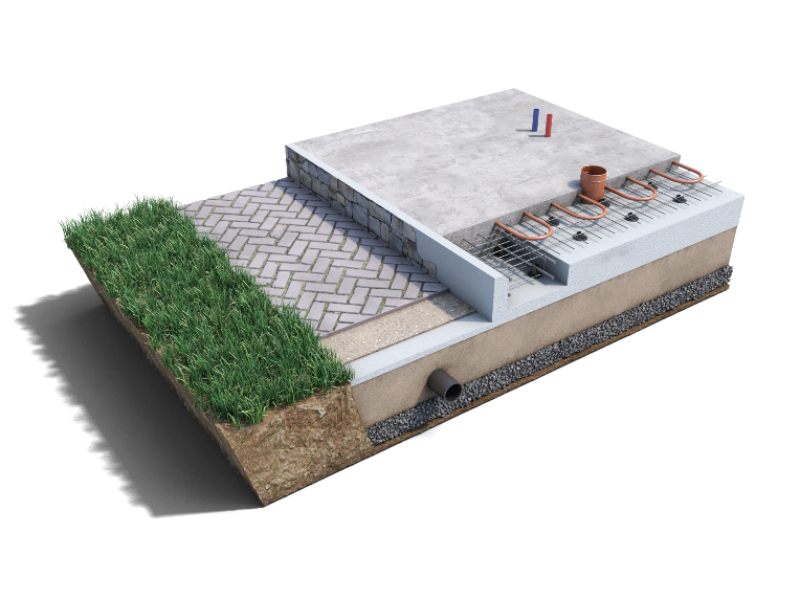
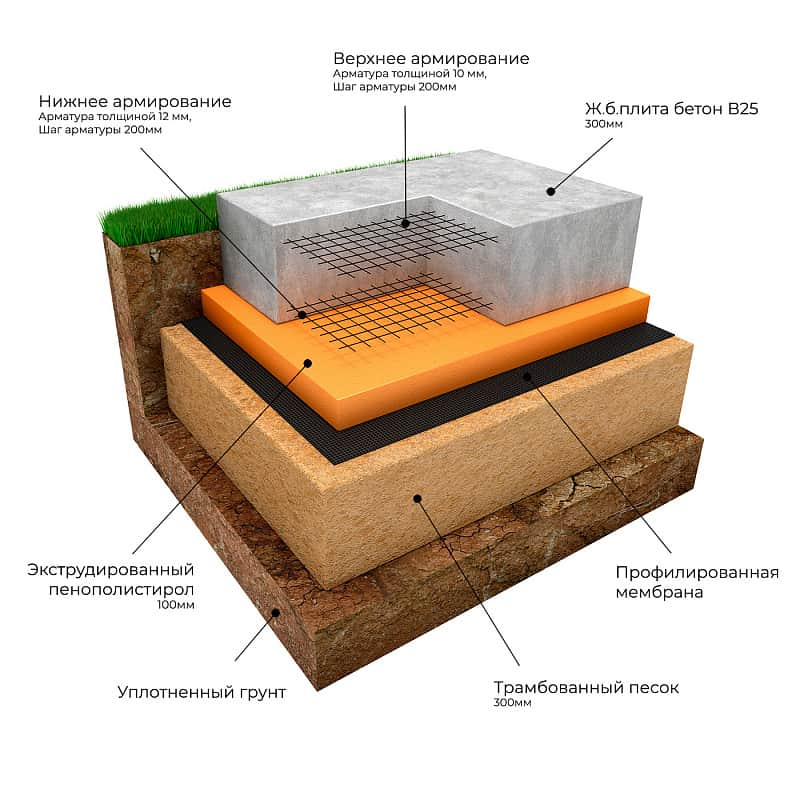
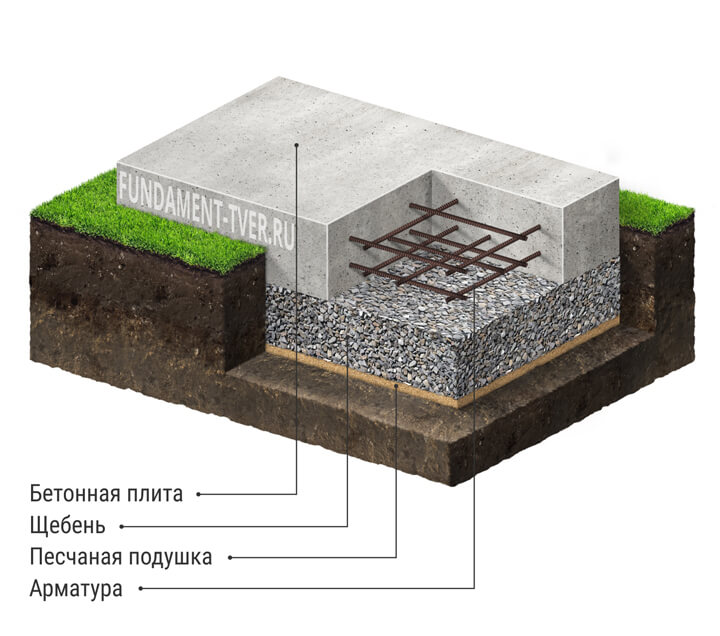
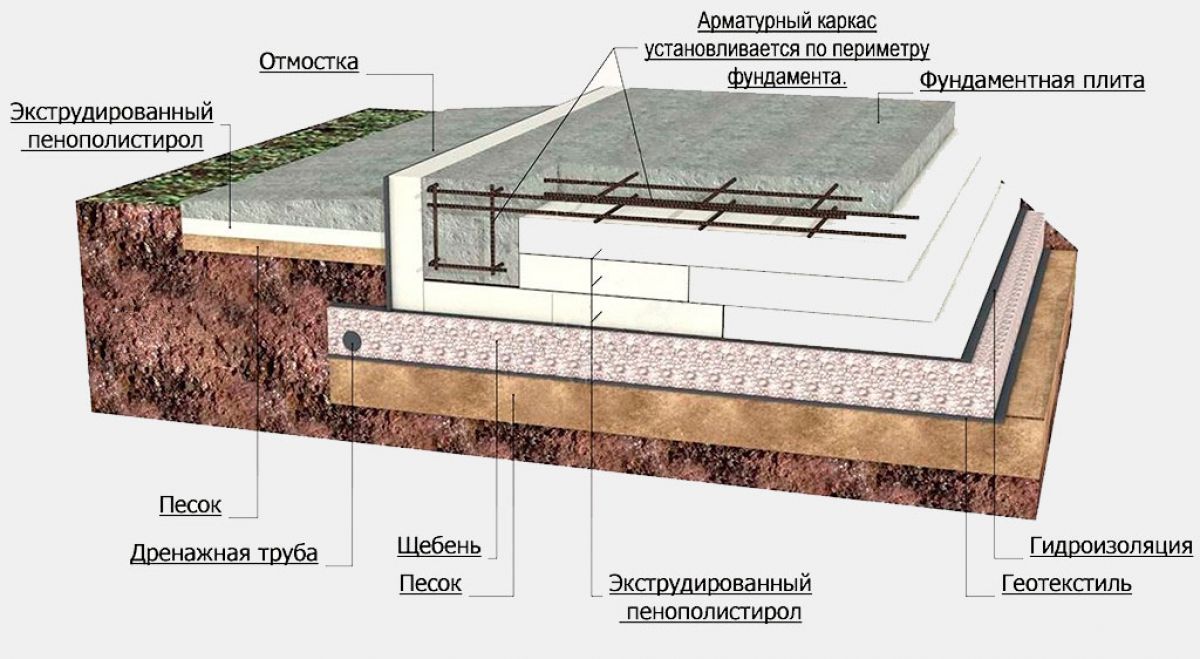
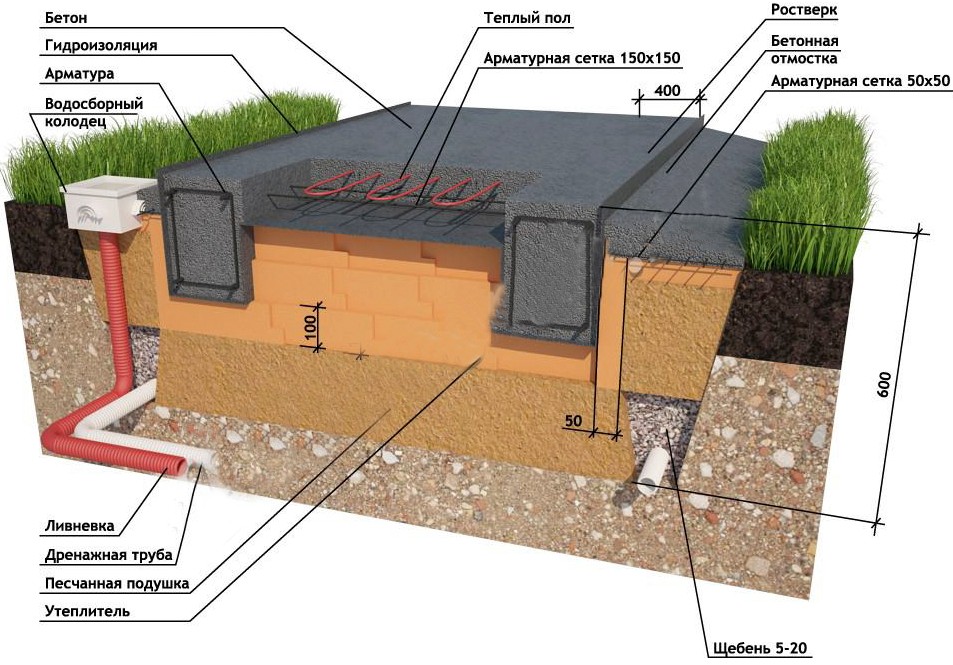
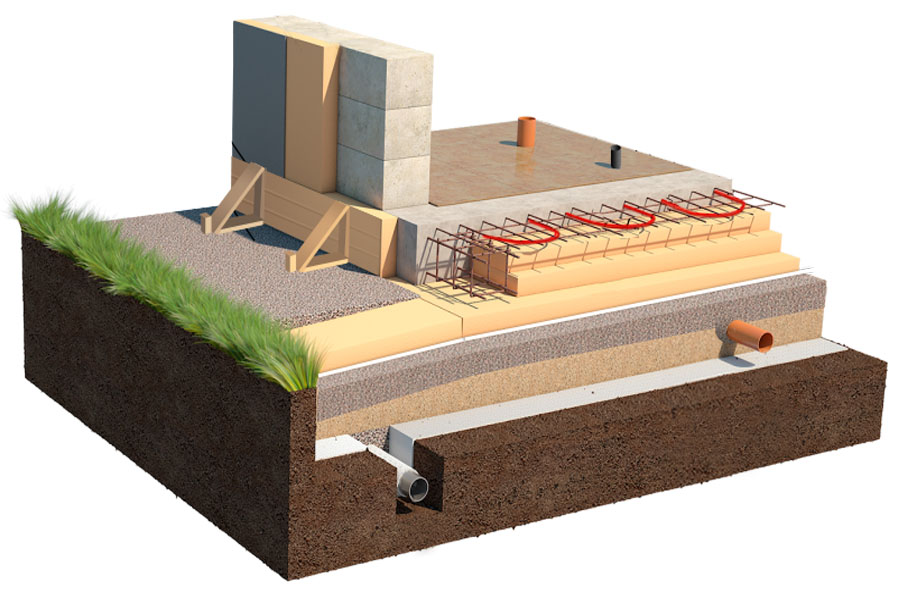
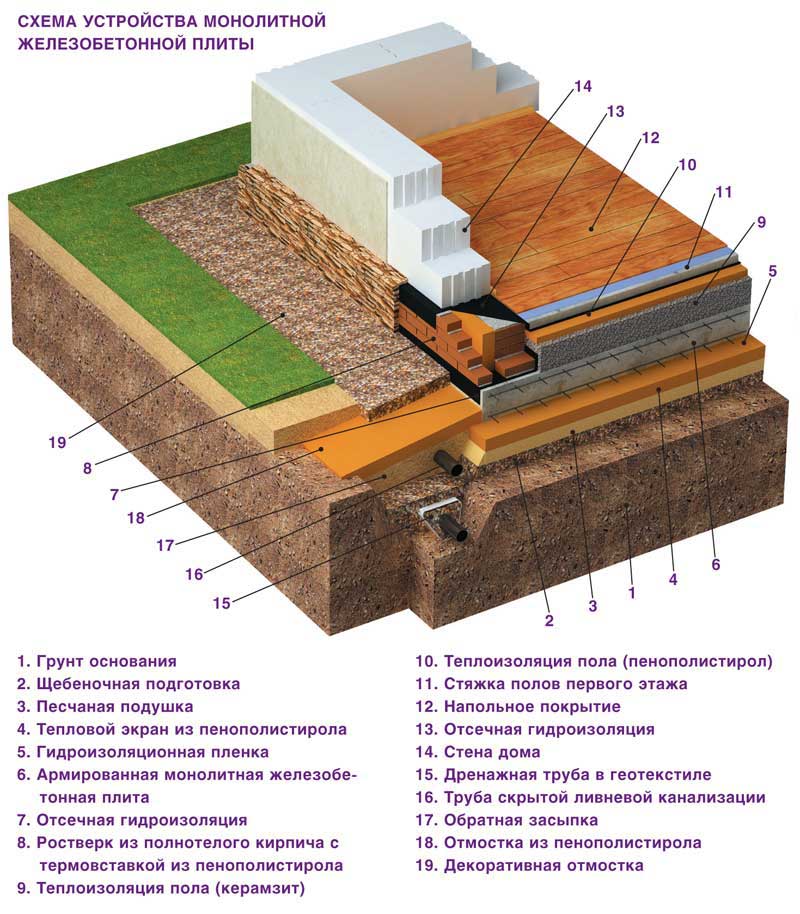
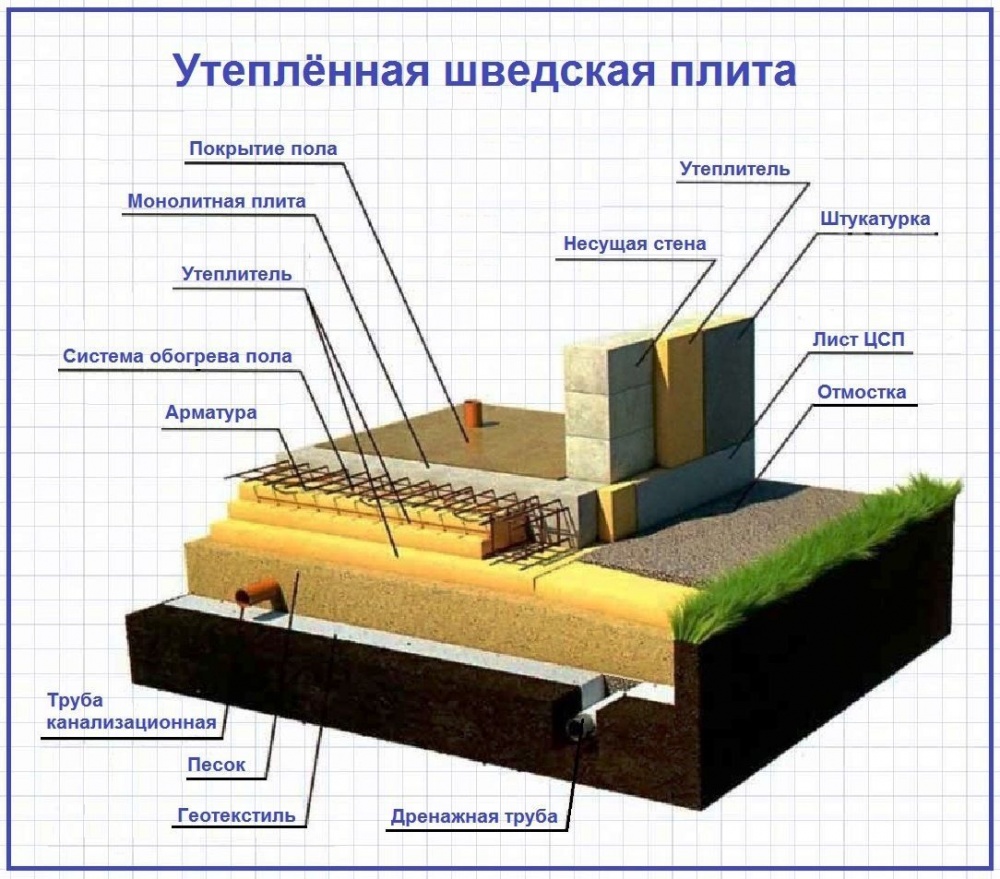
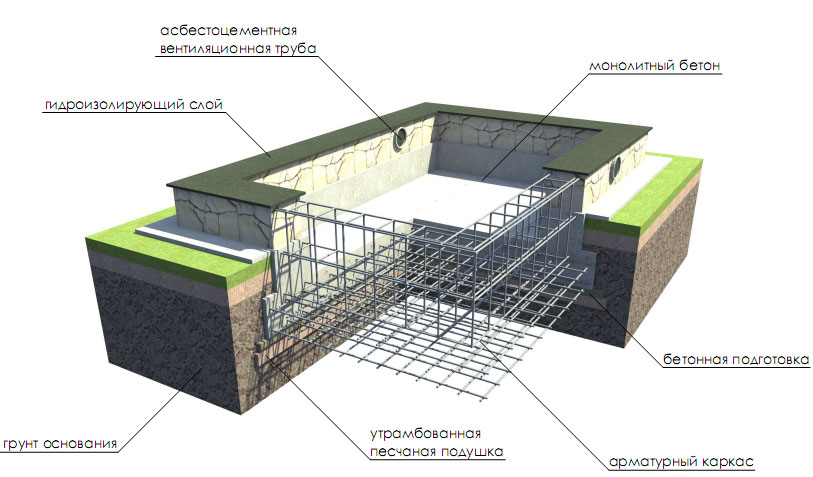
Device diagram
Such a foundation for a low-rise building consists of three layers:
-
A pillow made of sand with gravel.
-
Waterproofing.
-
Reinforced concrete slab.
It should be clearly understood that this is not a panacea for every occasion. Yes, it can be set up on difficult terrain. But if the site is swampy or located in northern regions with severe winters, then for a private house it is better to prefer an analogue from piles. The stove will be of little use in such situations.
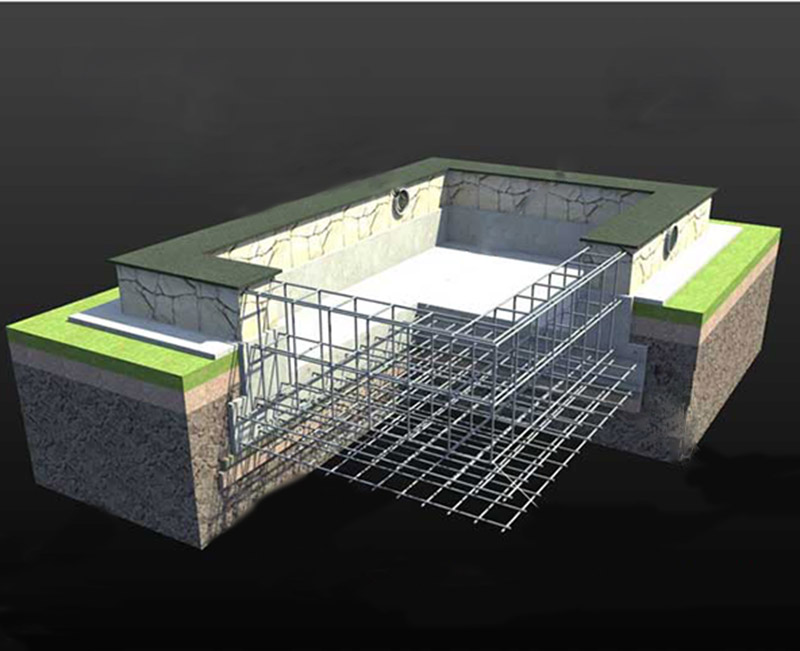
Differences with and without a basement
In the case of a simple monolithic strip foundation without a base, the work algorithm is quite simple.
It consists in marking the site, digging a pit, filling a gravel-sand cushion, installing formwork, reinforcing the foundation and filling it with concrete.

If it is necessary to expand the area of the building and make a basement, everything turns out to be a little more complicated. After tamping the sand-crushed stone cushion, it is necessary to fill in the monolithic base plate, which will become the floor of the basement room.
Along the perimeter of the structure at the edges of the foundation, departing from them by an average of 15-40 cm, leave reinforcement outlets, which are connected by strapping to the reinforcing cage of the walls. This allows the walls and floor to be combined into a single structure.
Important! When pouring concrete into the basement, it is imperative to provide for the presence of ventilation holes at a height of approximately 20-25 cm from the ground. When erecting the walls of the underground floor, fixed polypropylene shields are often used as formwork, which serve as good thermal insulation and provide additional waterproofing
It is imperative to provide for the presence of window and door openings and zones where communication pipes will pass
When erecting the walls of the underground floor, fixed polypropylene shields are often used as formwork, which serve as good thermal insulation and provide additional waterproofing. It is imperative to provide for the presence of window and door openings and areas where communication pipes will pass.
Conclusion
Now it is clear what a monolithic foundation is. As you can see, certain knowledge and skills of carrying out construction work are required for its construction. Considering all the features, you will achieve success, even if you do all the work on your own.
By the way, experienced builders recommend pouring monolithic slabs on piles for small objects to save time and money. In addition, to give the foundation of stability, ribbed monolithic slabs are poured. The foundations located on the stiffeners can normally "work" under the influence of the load forces created by the object and the soil.