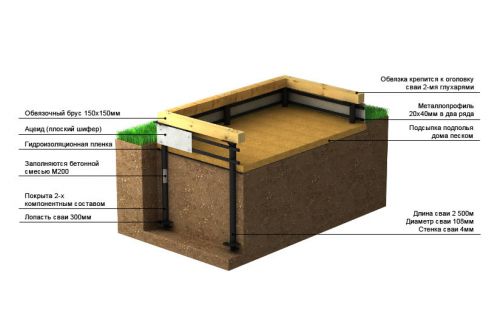
Pile foundation
For a massive residential building made of bricks or blocks with a pitched roof and an attic, a pile foundation should be provided, resting on dense load-bearing soil layers. When constructing two-storey buildings, such a system is economically justified, since it has the best bearing capacity.
 SVF plan.
SVF plan.
The basic arrangement of the foundation in a swampy area for a residential building should be based on a standard calculation and installation of the required number of concrete, bored or screw piles. Connected by a grillage into a single bearing system, they will provide reliable support for the entire building structure on solid layers below the bottom of the swamp.
The cost of a foundation on swampy soil using concrete piles will be significantly higher than that of tape and "floating" slab systems, since special construction equipment will have to be used to perform the work. But, depending on the type and number of piles installed, such a scheme will be able to withstand the weight of a two- or three-story brick residential building without subsidence for many years.
 If the depth of the solid ground does not exceed three meters, then metal screw piles can be used for the foundation.
If the depth of the solid ground does not exceed three meters, then metal screw piles can be used for the foundation.
Their use reduces the cost of the foundation, but reduces the bearing capacity of the structure. In addition, their application is limited by the depth of installation.
As a material for the bearing walls of a residential building on a screw pile foundation, you will have to use aerated concrete, hollow brick or wood, with additional external insulation made of foam. At the same time, using screw piles, you can make a foundation in a swamp with your own hands, without inviting contractors for this.
To install screw piles on a swampy area, the top soil layer over the entire building area, with the addition of 0.5 meters to each outer axis, must be removed to a depth of 50-60 cm. After that, install the piles by screwing them in according to the design scheme. Cover the bottom with geotextile and cover with a crushed stone-sand mixture not below ground level.
Next, it is necessary to connect the screw piles with a powerful reinforced concrete grillage under the load-bearing walls and partitions or paired channels No. 18-24 (depending on the weight load).
Strip and slab foundations
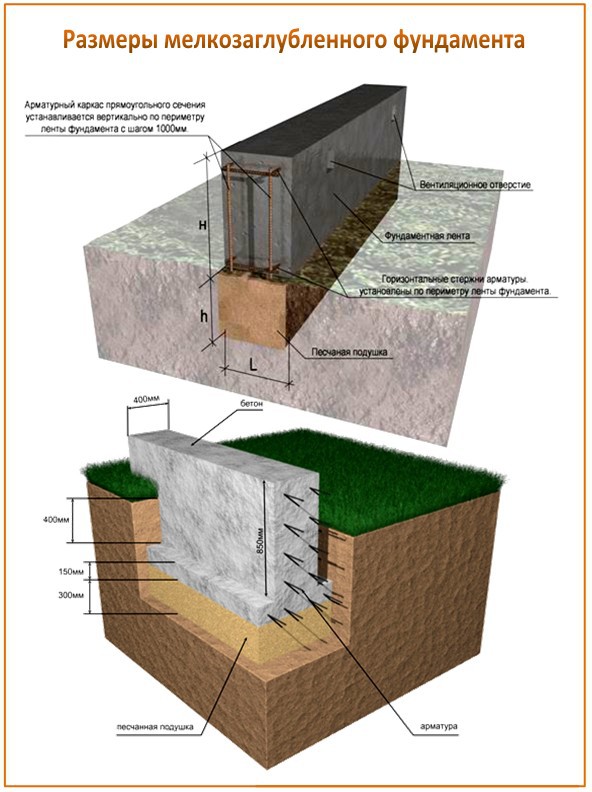
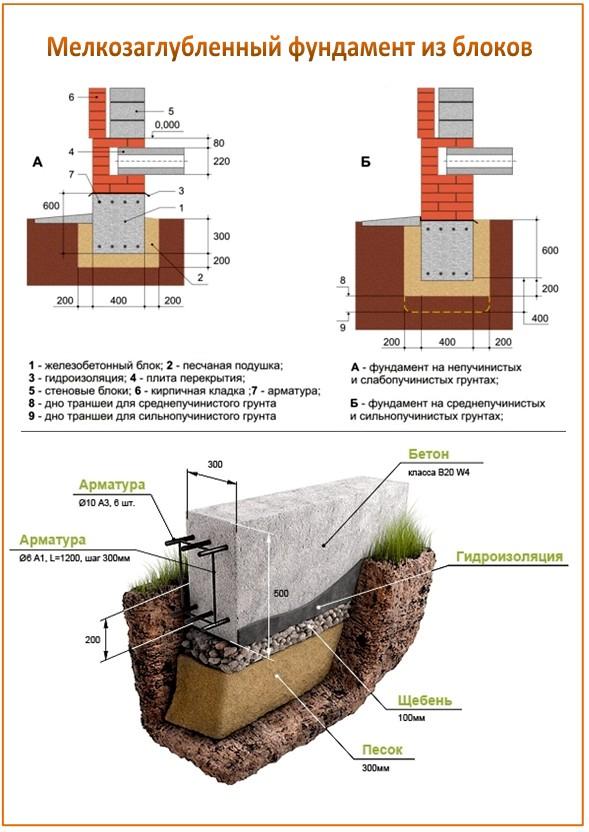
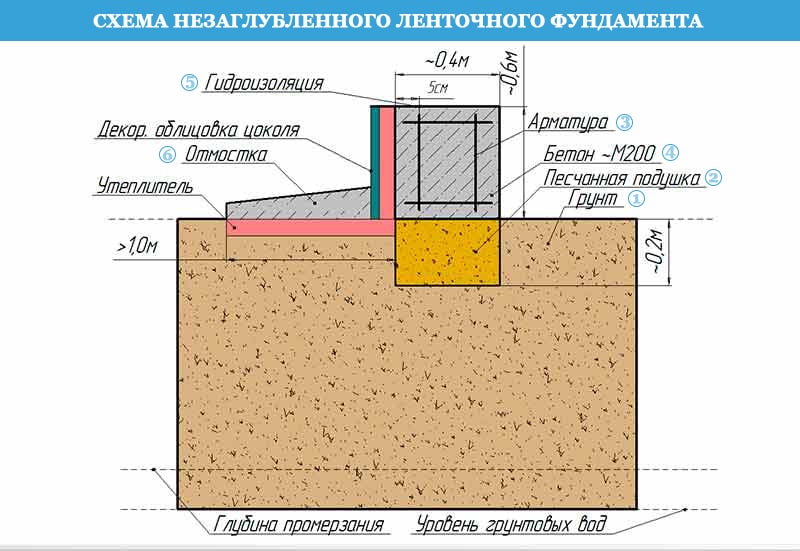
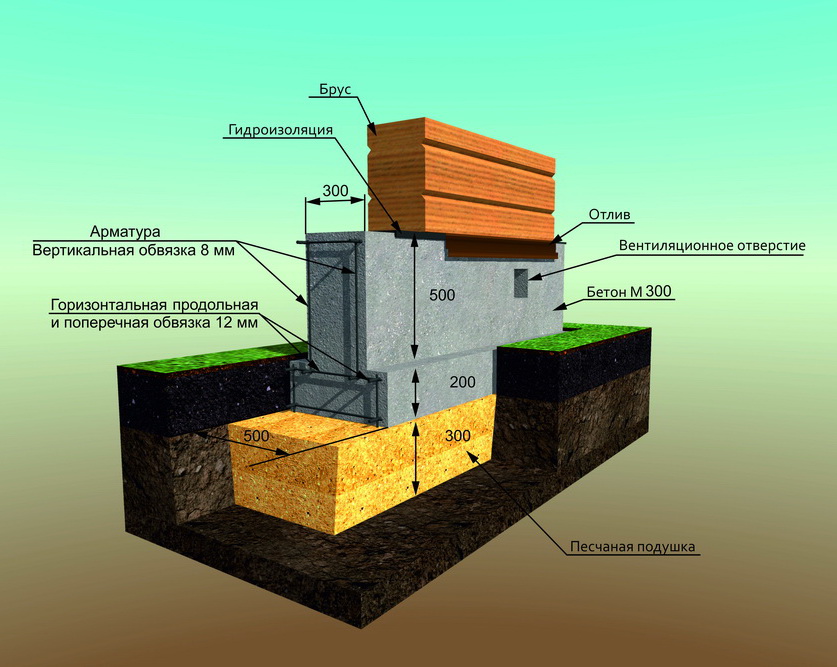
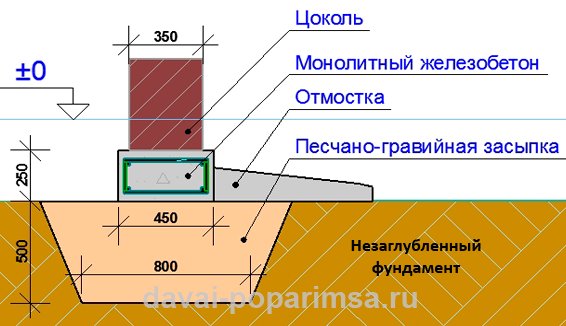
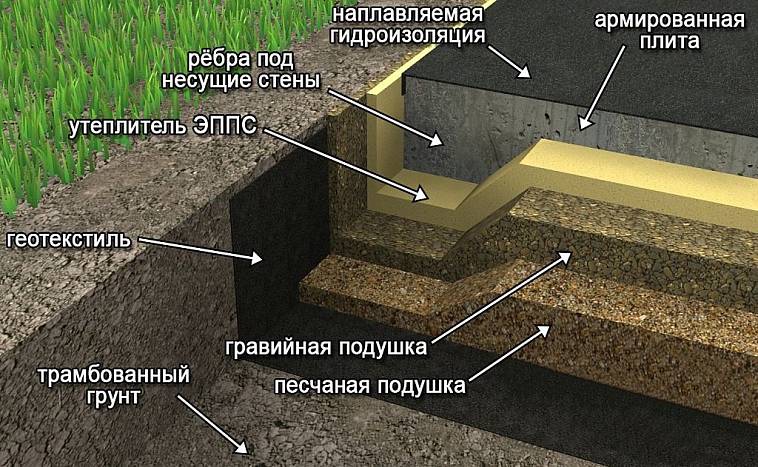
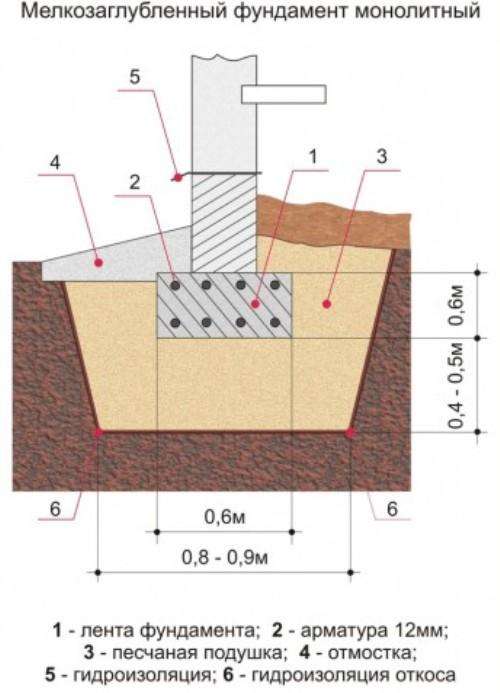
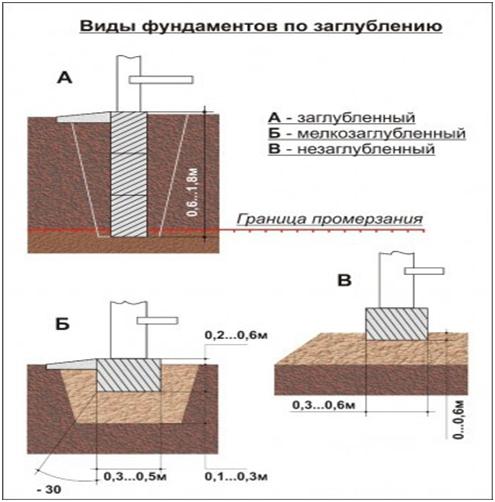
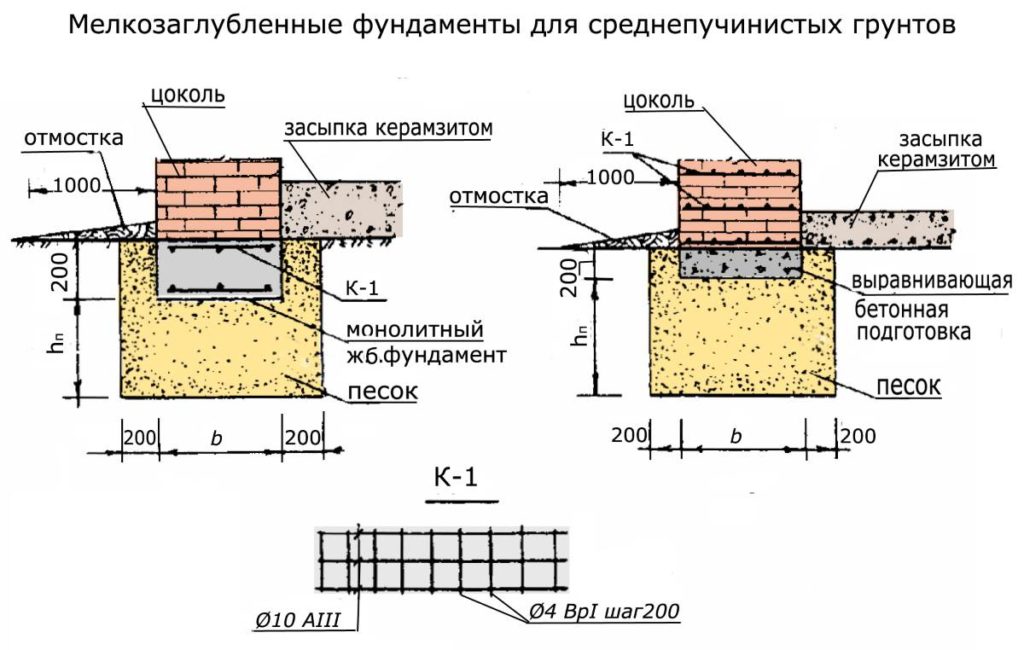
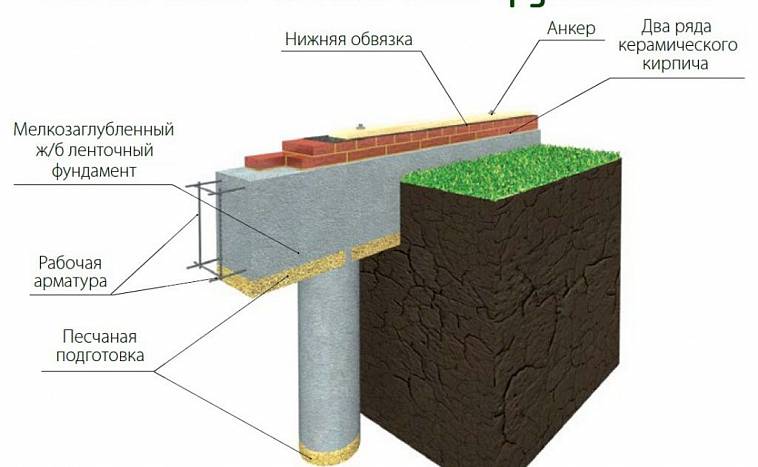
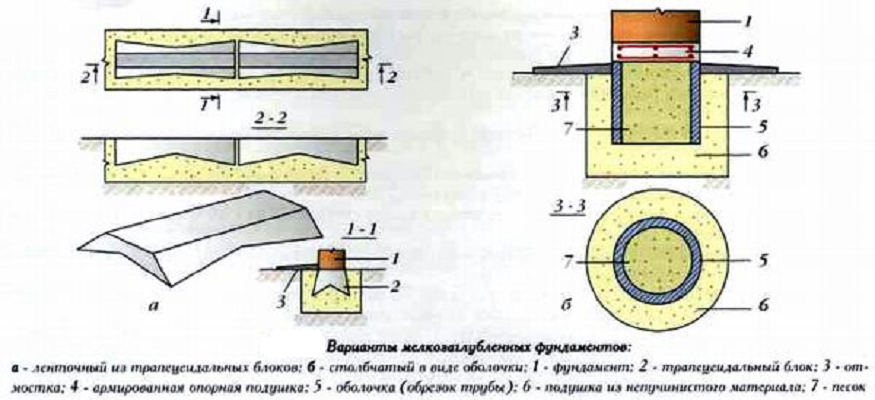
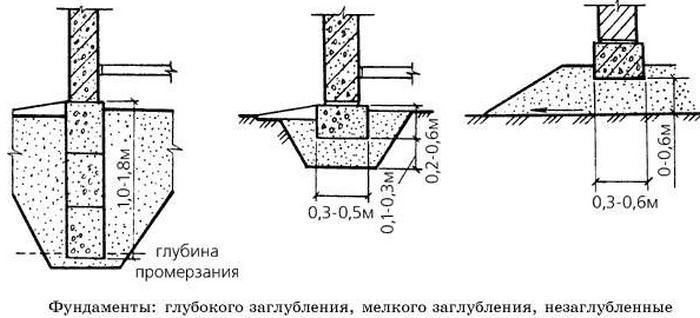
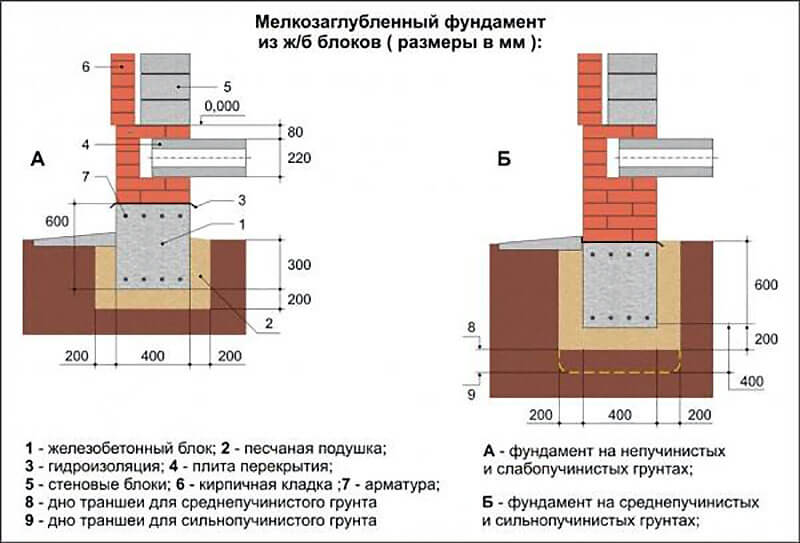
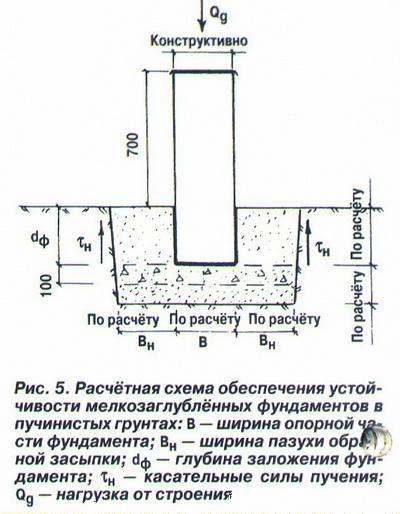
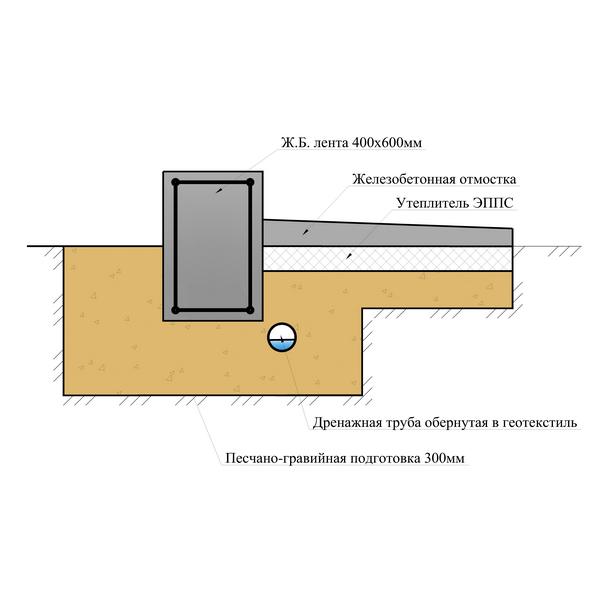
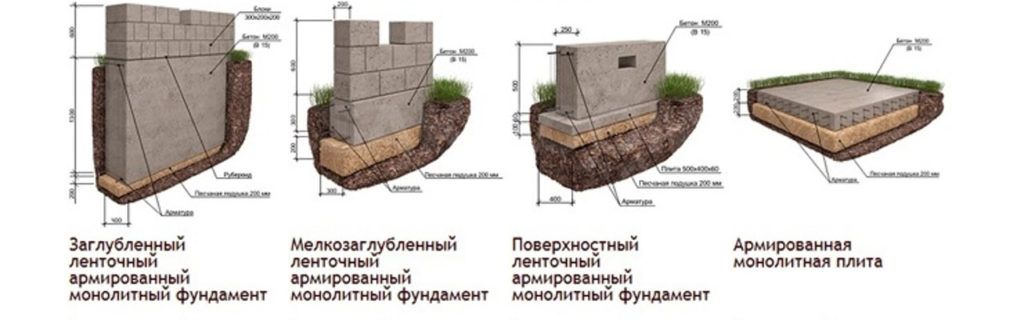
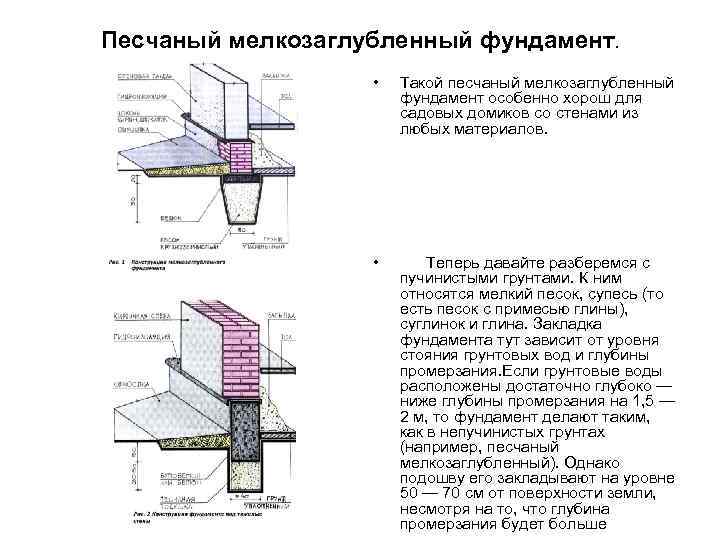
Strip and slab foundations refer to shallow foundations, the design of which involves the installation of a foundation twenty to fifty centimeters deep into the soil.
An shallow foundation requires fewer consumables, but in terms of strength it is in no way inferior to foundations of a conventional foundation, ensuring a long life of a house, a barn or a fence.
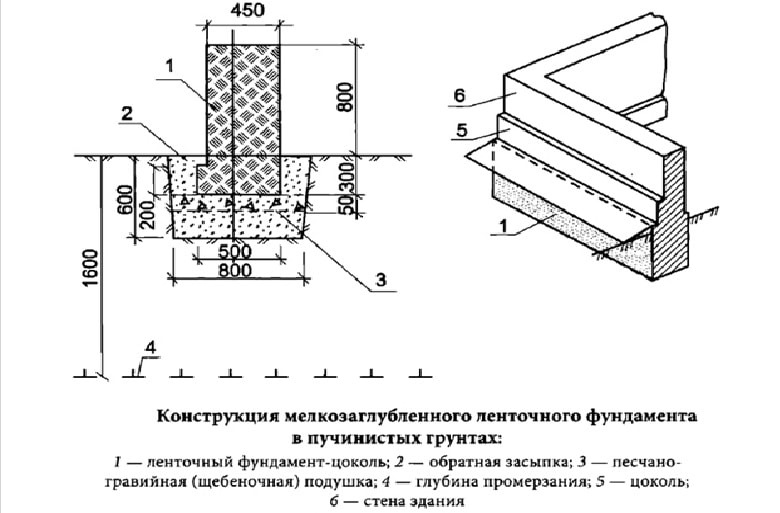
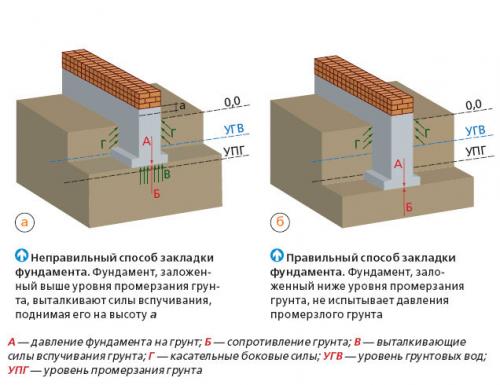
A strip foundation is one of the most reliable options, along with a columnar foundation. As with the columnar, the base of the strip foundation is laid below the freezing level, which allows it to withstand the seasonal expansion of the soil.
Photo:
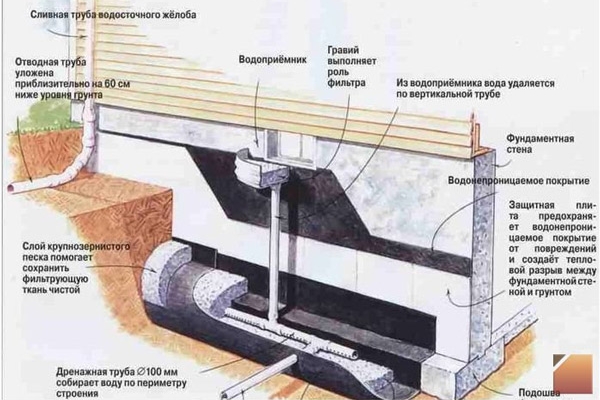
Device diagram
Among others, there is also a structure called a slotted foundation. Its manufacturing technology consists in placing concrete without using trench formwork.
It is important to remember that the success of the construction of such a foundation directly depends on how well the various measures are taken, depending on several criteria. Important indicators are the degree of deformation and solidity, i.e.
all parts of the foundation must be in clear contact with each other, which will allow the structure to resist stress near the side surface
Important indicators are the degree of deformation and solidity, i.e.all parts of the foundation must be in clear contact with each other, which will allow the structure to resist stress near the side surface.
The structure is strengthened with reinforcement, steel wire or metal rods.
A shallow slab foundation is actually one of the most reliable, along with a columnar one.
However, it is also the most expensive, because the technology for its manufacture requires a fairly large amount of materials.
The fact is that the slab itself, on which an unburied foundation for a house, barn or fence is being erected, is in fact nothing more than a concrete cushion covering the entire area of the pit.
Video:
Such a pillow, of course, is able to cope with heaving of any scale, but it also requires colossal infusions of various kinds.
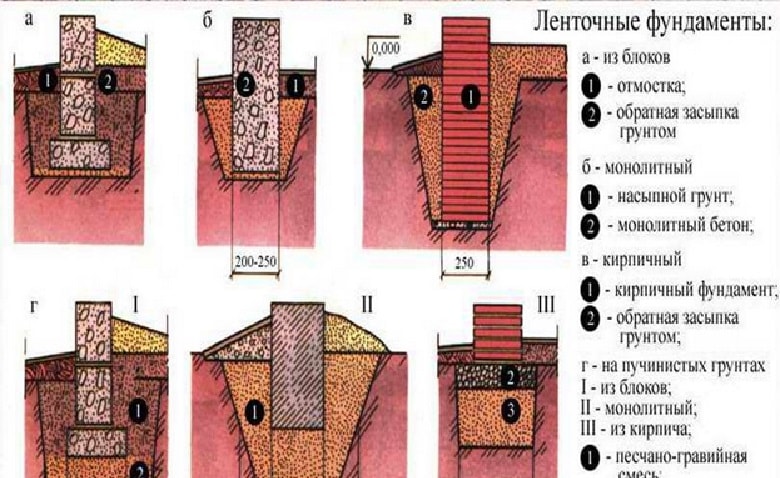
The strip foundation is often attractive because it is quite possible to lay it on your own, which is why it is most often installed for the construction of a house or a fence.
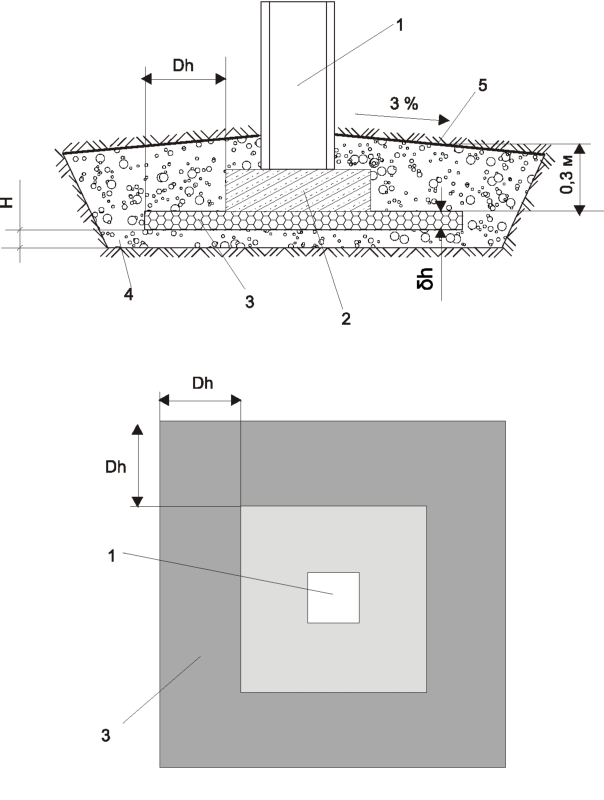
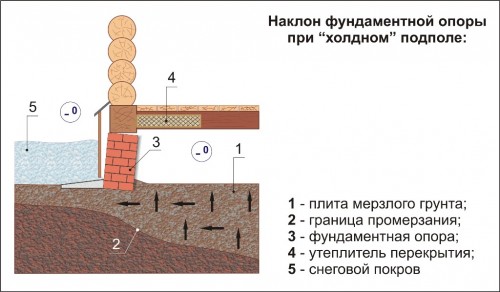
On heaving ground, it is possible to build only an unburied version of this structure.
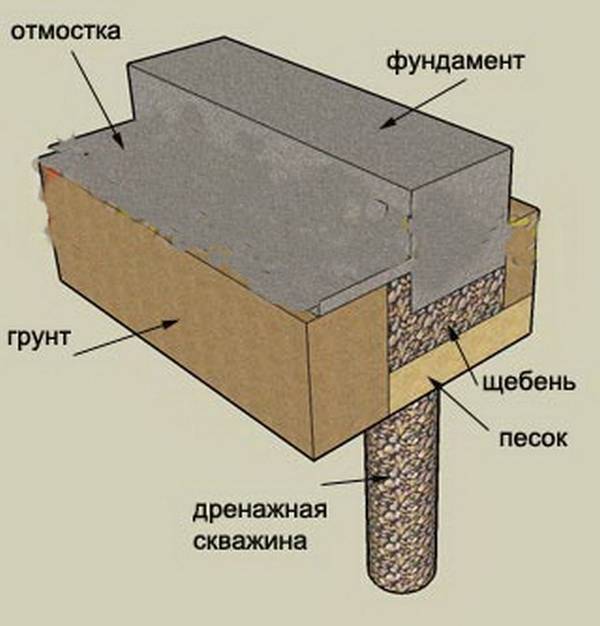
But even though this type of foundation is shallow, the foundation must still lie at a depth sufficient to avoid freezing the soil, which makes the depth variable depending on the climate.
Then you get a pillow that protects the structure from the influence of heaving from below. On the sides, it will be protected by waterproofing. A cushion of sand and crushed stone, in turn, is the basis for a layer of concrete, which is distributed between the reinforcement segments that limit it.
There is a procedure that must be followed in order to build the strip foundation correctly.
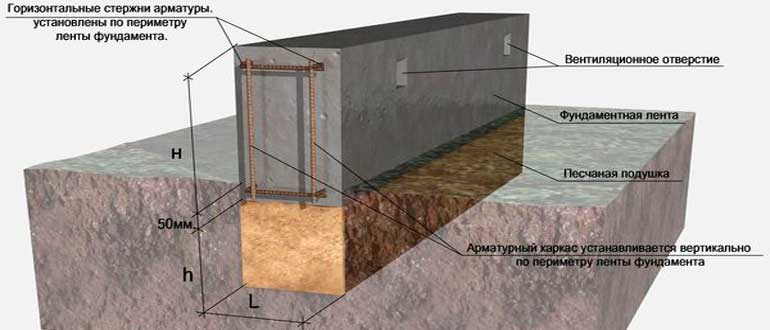
First of all, you should dig a pit with a depth of half a meter to 70 cm, then finish its edges with waterproofing.
Photo:
Correct laying of the foundation
Then a pillow is poured, each of the layers of which should be 20 - 30 cm, and their thickness should be that after tamping.
On top, in turn, it is also insulated with waterproofing, and then the entire structure, thus protected from silting and dampness, is surrounded by reinforcement and poured with concrete.
After the concrete is poured, the upper reinforcement is laid, necessarily - on the not dried concrete so that the materials can grab together.
In general, a strip foundation, which is successfully a rather attractive option when building a house or a fence, requires adherence to a small but important number of rules. As it became clear from the article, even heaving soils cannot interfere with the construction of a house, a fence, or in general any light construction, and some types of unburied foundations are even easy to erect, which makes it possible to build independently
As it became clear from the article, even heaving soils cannot interfere with the construction of a house, a fence, or in general any light construction, and some types of unburied foundations are even easy to erect, which makes independent construction possible.
But, of course, the most important thing is to take into account the type of soil and strictly follow the technology.
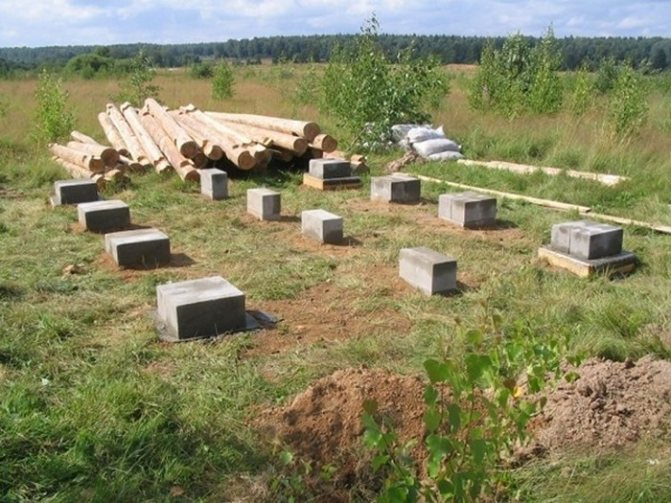
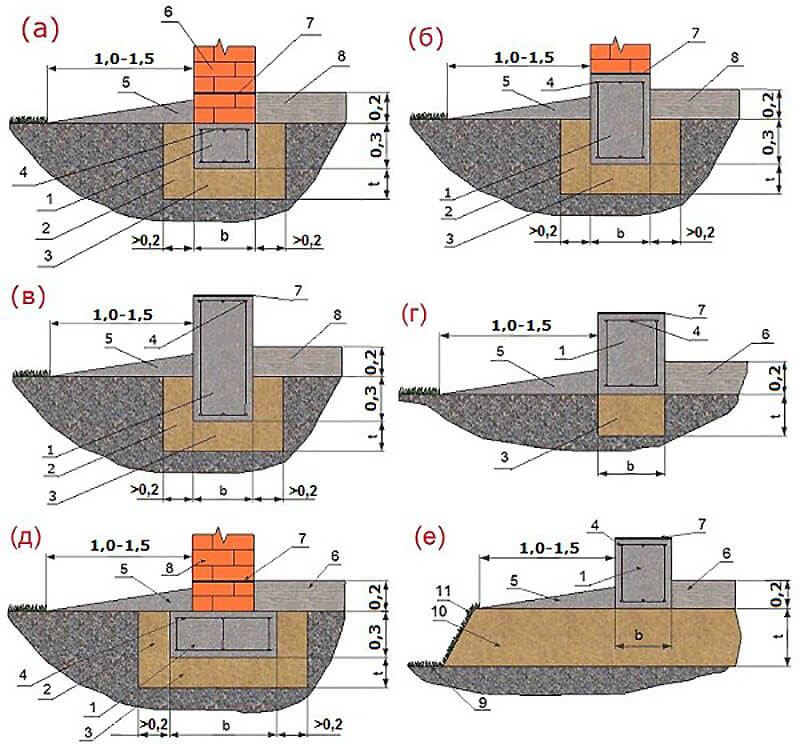
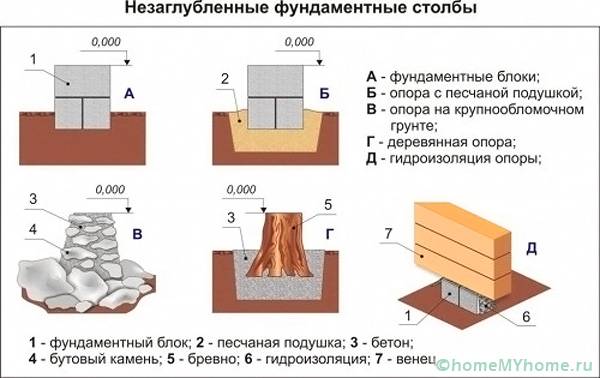
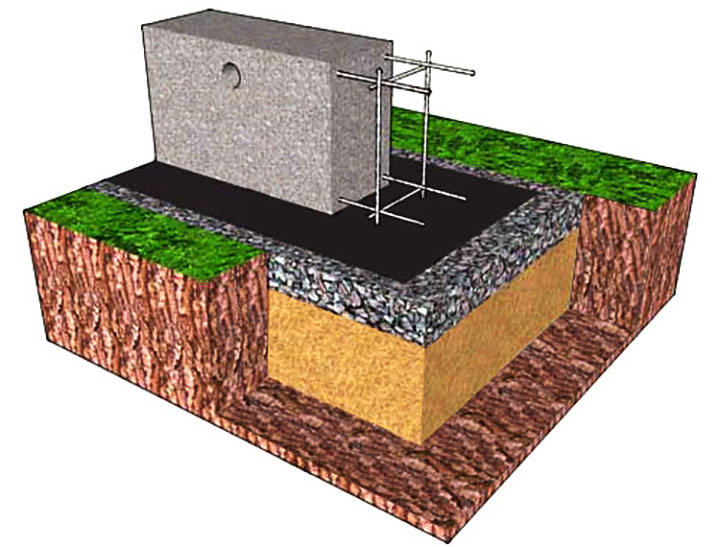
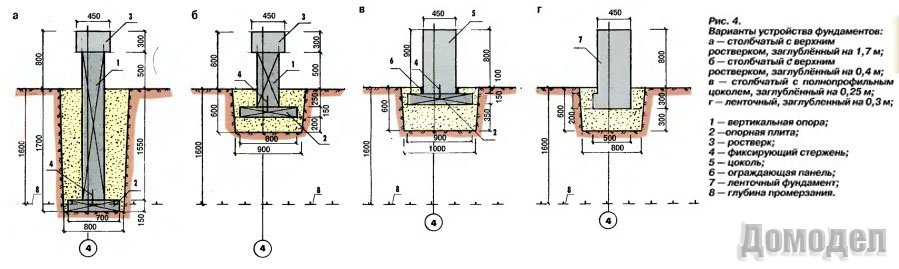
Arrangement of a shallow columnar foundation on piles (bored or flooded)
Another high-speed type of construction of the foundation of a light house is the construction of a columnar foundation on piles. Here, the role of pillars is performed by flooded or ready-made factory piles, which, using a special installation, are driven (screwed) into the ground to the required depth. The small amount of time spent on arranging the piles compensates for their high cost. Installation of this type of foundation is not a cheap procedure, which, when self-built, nullifies the basic idea of saving.
First option
Concrete mixture preparation scheme.
A shallow trench is being dug along the perimeter of the future house. Wells are drilled in it and piles are poured. The upper part of the piles is covered with a waterproofing material. Sand is poured into the bottom of the trench between the ends of the piles.It should be placed flush with the ends of the piles. Then roofing material is laid on top of the sand. Then the formwork is mounted, which is upholstered from the inside with glassine or tar paper. This is done so that concrete does not stick to the formwork panels. Supports are made outside. The outer walls of the formwork are connected with transverse beams. This is due to the need for maintaining the integrity of the formwork structure when the concrete solution is poured. Further, a reinforcing cage is installed in the inner space of the formwork. It is tied to the outlets of the reinforcement from the ends of the piles. When this is done, concrete is poured. When pouring it, you need to pierce it with a steel bar to get air out of the concrete and ensure its density and strength. After the concrete dries, the formwork is removed, the sand is removed. In this case, a gap of 20 cm remains between the grillage and the ground. The grillage is ready.
Second option
Scheme of a columnar shallow foundation made of reinforced concrete blocks.
At a short distance from the ground between the ends of the piles, a formwork is installed like a box with a bottom. It is in it that the reinforcement frame is mounted, concrete is poured. The rest of the work is the same as in the first version. There is a distance between the soil and the concrete. In order to insulate this structure, you need to make a pick-up. It will serve to insulate the underground and will prevent the ingress of dirt and snow.
The next stage is the waterproofing of the grillage. When erecting it, one should not forget about the device of ventilation holes - air vents. Their location, number, dimensions must be planned in advance, before pouring concrete.
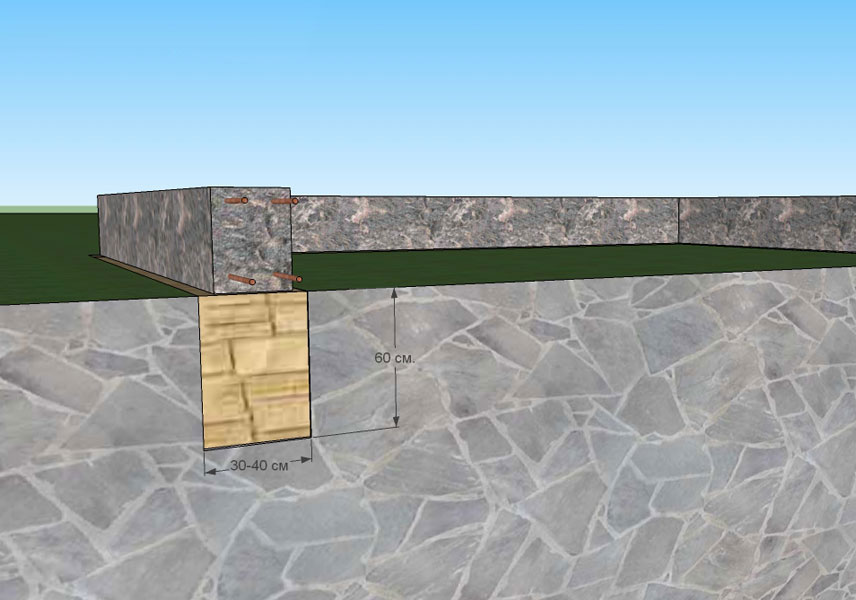
The finished grillage, after the house is fully built, it makes sense to decorate it with stone, brick or other material in accordance with the general style of the facade of the house.
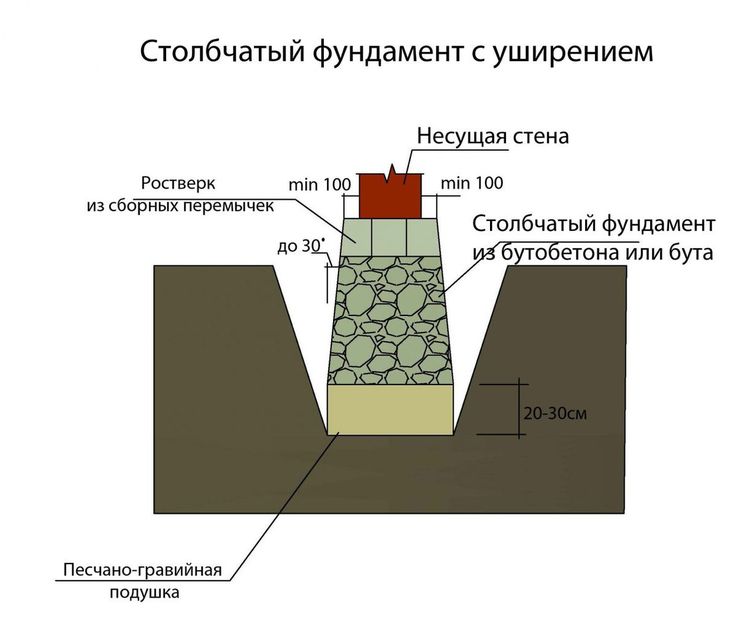
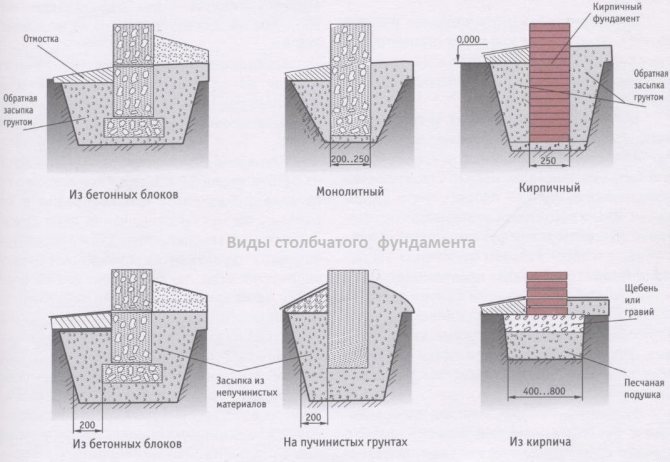
Columnar non-recessed base
Shallow columnar foundation is used quite often.
The shallow foundation of a columnar type is used quite often. It can settle down on slightly heaving and heaving soils, provided that the structure being erected has small overall dimensions and weight. As for rocky, coarse-grained rocks and soils, which are not characterized by movement, such bases can be used under a large house made of timber or logs.
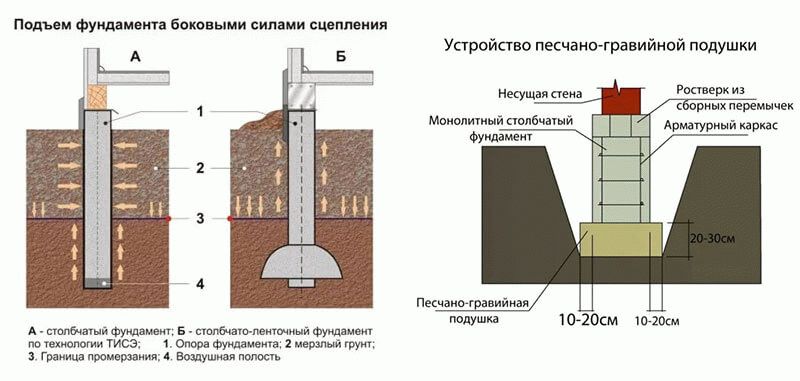
The shallow foundation on the supports can also be used in the case of reducing the effect of heaving on the building. To achieve this, the soil under the supports must be replaced with a sand layer.
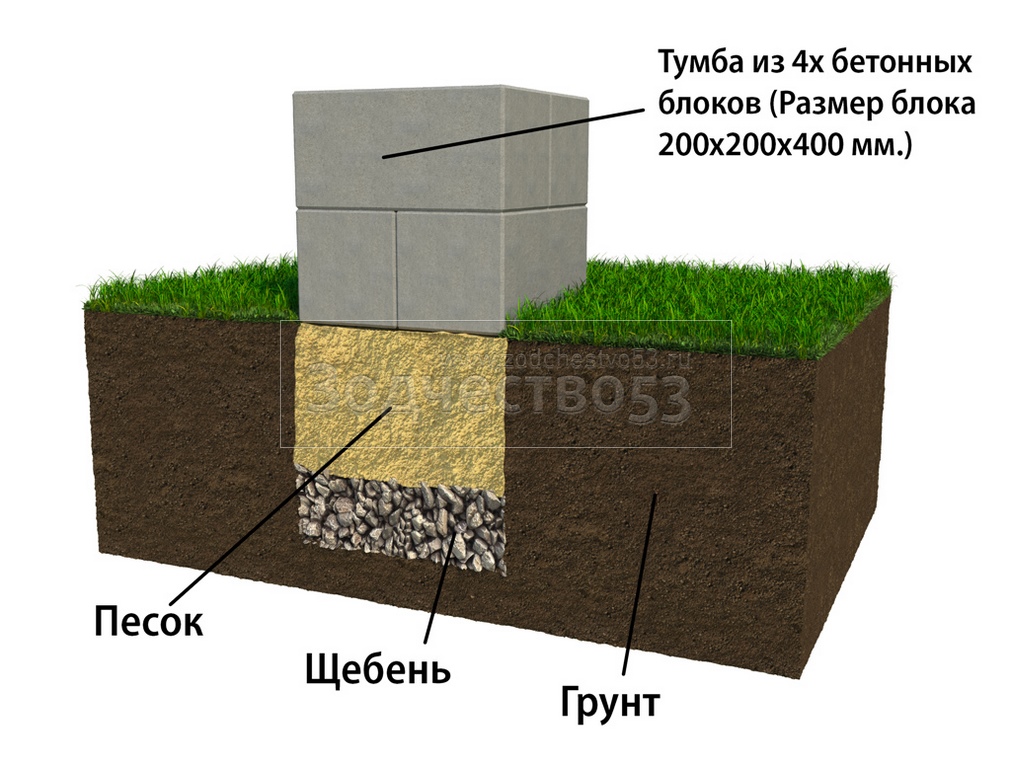
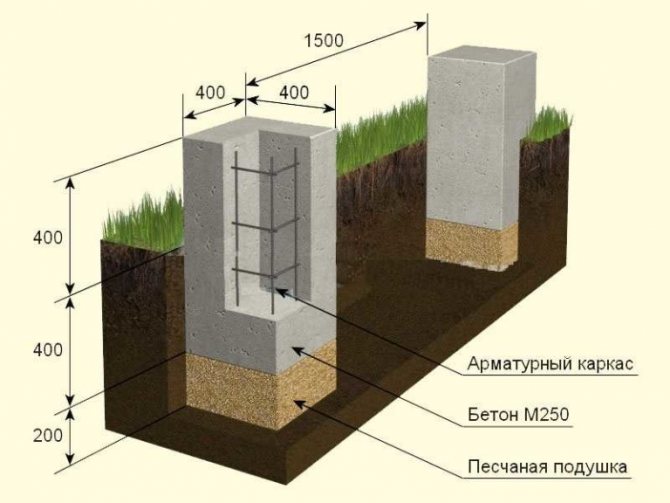
Pillars can be made of reinforced concrete, rubble concrete, stone, sand concrete and concrete foundation blocks. Usually blocks measuring 0.2x0.2x0.4 m are used. If you decide to use a brick, then silicate products and ceramic material with low frost resistance are not suitable for these purposes.
The work is carried out in several stages:
- First, the construction site is cleared of debris, the fertile layer is removed, and a breakdown is performed.
- Then a hole of the required size and depth is dug under each support.
- At the bottom of each pit, a sand cushion is arranged.
- After that, you can lay out the supports from the blocks. Usually two rows of 4 blocks each are made. A thick cement mortar is used to hold the blocks together. The open part of the supports is plastered.
- On the part of the supports that will dock with the house, waterproofing is required. For this, bituminous mastic, roofing felt, roofing material or glass insulation are used.
Shallow base
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction.
This is the most popular type of columnar foundation, since a minimum of money and effort is spent on its construction, and the scope of use is quite wide. Such structures are suitable as a basis for a wooden bathhouse and a frame house.
Usually the pillar is made of pipes, inside which the frame is installed and concrete is poured.Since the main load is taken up by the concrete filling, the material of the pipe does not matter much. It acts more as a permanent formwork. Usually plastic or asbestos sewer pipes are used.
The choice of pipe diameter depends on the purpose of the building. For light arbors, a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm is sufficient, and for log buildings, a pipe with a cross section of 250-300 mm is suitable. The volume of concrete is calculated taking into account that for every 10 m of a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm, 0.1 cubic meter of concrete is required, and for a product with a diameter of 200 mm, 0.5 cubic meters are consumed, for a pipe with a cross section of 300 mm, 1 cubic meter of concrete solution is required.
The order of work is as follows:
- After preparing the site and performing the breakdown, using a hand drill, holes are made in the ground to install the poles. It should be remembered that the depth of the pit should be 200 mm more than the length of the post for making a sand cushion.
- After completing the pit, sand is poured onto the bottom, poured with water and rammed. To protect the concrete mixture from moisture loss, layers of roofing material are laid on top of the sand cushion.
- Further, pipe sections are lowered into the pits, which should have a 10-centimeter headroom. The pipes are leveled and fixed in the well with wooden blocks.
- After that, a little concrete-gravel mixture is poured into the pipe. Immediately after this, the pipe is lifted and fixed in this position until the mixture completely solidifies at the bottom of the pit. Thus, we will get a solid foundation that will well resist the forces of heaving of the soil.
- When the concrete hardens, the pipe is wrapped with roofing felt to perform waterproofing.
- The well is backfilled with sand with layer-by-layer water pouring and ramming. During these works, the position of the pipe must be checked using a level.
- Then reinforcement is installed inside the pipe and concrete is poured.
- Further work can be done in 28 days. At the same time, the foundation is isolated from the main part of the structure using a bituminous or polymer solution.
Calculation for a shallow foundation
An example of the calculation of shallow foundations on heaving soils should be given. For example, a one-story house is being built with the following dimensions:
- height - 4 meters;
- width - 5 meters;
- length - 10 meters.
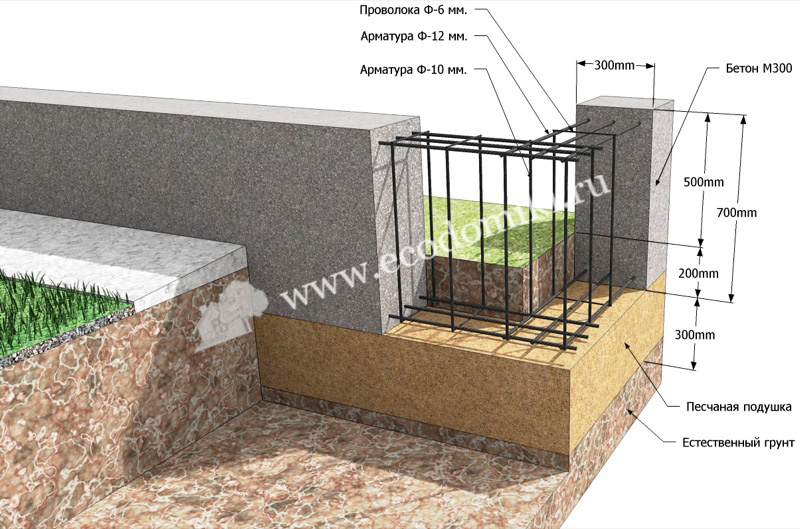
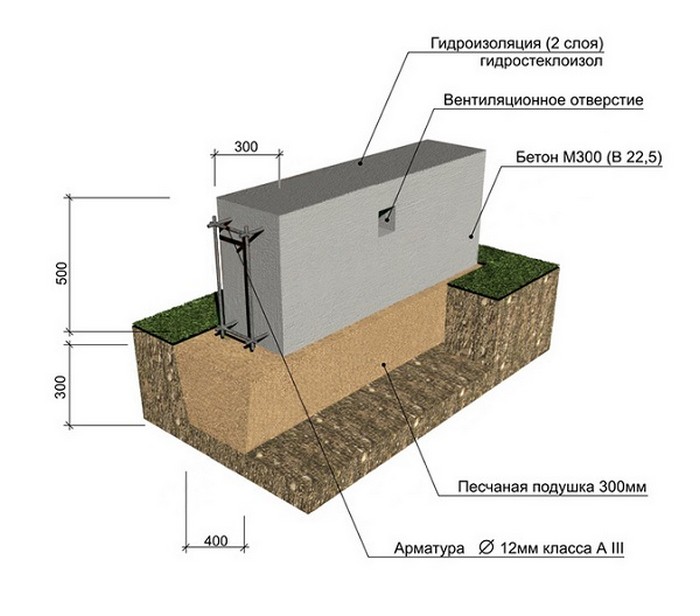
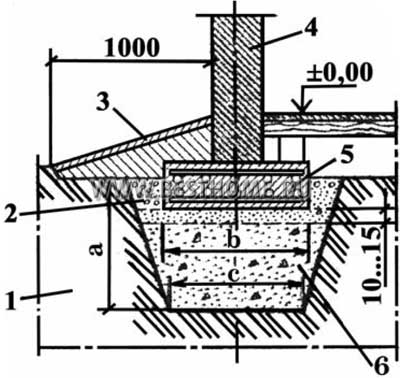
The structure includes two load-bearing internal walls, each 4 m high and 3 m long. The floor does not rest on the foundation, it is poured with concrete. The base will be in the form of a tape with a base width of 40 cm and a depth of 70 cm. The foundation is made of reinforced concrete, for which reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is used. The frame will have two belts, each of which consists of five rods, jumpers with a length of 25 cm.Such jumpers are placed in 50 cm increments.
To find out the mass that the strip foundation will have, it is necessary to determine the following values:
Scheme of a shallow foundation with waterproofing on a baked pillow.
- geometric dimensions of the structure;
- the density of the building material used.
It is quite easy to find out the geometric dimensions. So, the length of the foundation is equal to the perimeter of the future building, that is, you just need to calculate the sum of its sides:
10 + 10 + 5 + 5 + 3 + 3 = 36 meters.
The strip foundation will be poured not only under the external facade walls, but also under the internal load-bearing ones, therefore, they are also taken into account.
Now you can find the volume based on the fact that the height of the tape is 70 cm and the width is 40:
V = 36 × 0.4-0.7 = 10.08 cubic meters.
But this is the total volume from which the reinforcement must be subtracted in order to find out the amount of concrete. Knowing that the strip foundation has two belts of five rods with a dressing, they calculate the length for each:
10-0.5-0.5 = 9 meters.
The length of all belts will be equal to:
2 × (9 × 2 + 4 × 2 + 2.5 × 2) = 62 m.
Each belt has five rods, which means that their total length is: 62 × 5 = 310 m.
Now determine the length of the required lintels for the reinforcement:
Reinforcement scheme for a shallow foundation.
9 / 0.5 + 1 = 19 pcs.,
4 / 0.5 + 1 = 9 pcs.,
2.5 / 0.5 + 1 = 6 pcs.
For one upper belt, the number of jumpers is:
19 × 2 + 9 × 2 + 6 × 2 = 68 pieces,
Since the length of one jumper is 0.25 meters, the total length is:
68 × 0.25 = 17 meters.
For all horizontal frame lintels, the length is:
17 × 2 = 34 meters.
For vertical jumpers, take into account that there are 68 of them on the one side and the same number on the other. That is, it turns out 136 pieces with a length of one of 40 cm.Their total length is:
136 × 0.4 = 54.4 m.
Now calculate the total length of the reinforcement required by the shallow foundation:
310 + 34 + 54.4 = 388.4 m.
To find out the cross-sectional area for reinforcement, use the formula for the area of a circle:
Scheme for the preparation of concrete solution for the foundation.
3.14 × 0.000036 = 0.00011 sq. meters.
To obtain the volume, use the formula:
0.00011 × 388.4 = 0.04 cbm meters.
Now the volume is obtained for reinforcement only:
10.08-0.04-0.04 = 10 cubic meters meters.
A value of 0.04 is taken on the basis that a shallow foundation will be reinforced at the corners as well.
With the help of such a not too complicated calculation, it is determined what requires:
- 10 cubic meters meters of cement (with a density of 2500 kg per cubic meter);
- 0.08 cc meters of metal reinforcement (with a density of 7800 kg per cubic meter).
That is, the total mass of the entire base, which is being erected on heaving soils in the form of a strip foundation, will be:
10 × 2500 = 25000 kg,
0.08 × 7800 = 624 kg,
25000 + 624 = 25624 kg.
That is, the strip foundation has a mass of 25624 kg.
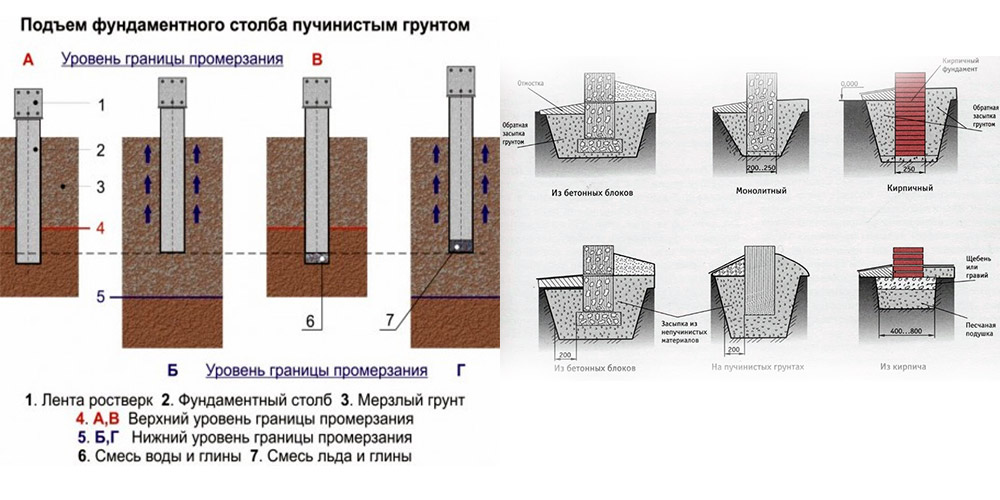
Building a house on heaving soils is not the best option. But if there is no other way out, then it is necessary to carefully calculate the future foundation so that after its construction the structure is not pushed out of the soil during the winter heaving. This is not so difficult to do, but care must be taken so that during operation there are no deformations of the foundation, and therefore the house itself.
The device of a shallow columnar foundation made of pipes
Diagram of the causes of the destruction of the foundation.
With this method, for the formation of pillars, a permanent formwork is made - a steel or asbestos pipe of the required diameter (20, 40 cm, etc.). If the soil has a standard bearing capacity (4 kg per 1 cm²), then it is supposed to simply dig a round recess and insert a pipe of the corresponding section into it. A concrete mixture is poured into the prepared recess a third of the height. In this case, the pipe will slowly rise, and the solution will flow out onto the waterproofing layer laid in advance with an overlap. In this way, a widened base is created - a hydraulic cushion. After the concrete has hardened, work continues. A solution is gradually poured into the pipe up to a distance of 15 cm to the level of the zero boundary (20 cm each and vibropress). From the outside, the "shape" is fixed with compacted soil in order to prevent it from skewing. The subsequent stages of work on the creation of a columnar foundation from pipes are performed by analogy with the previous methods.