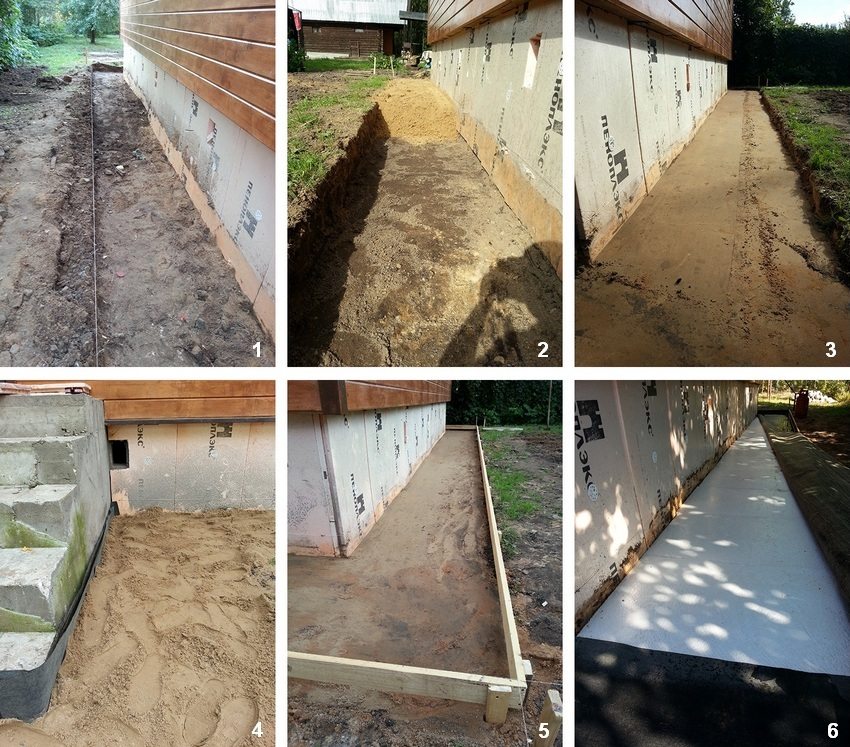
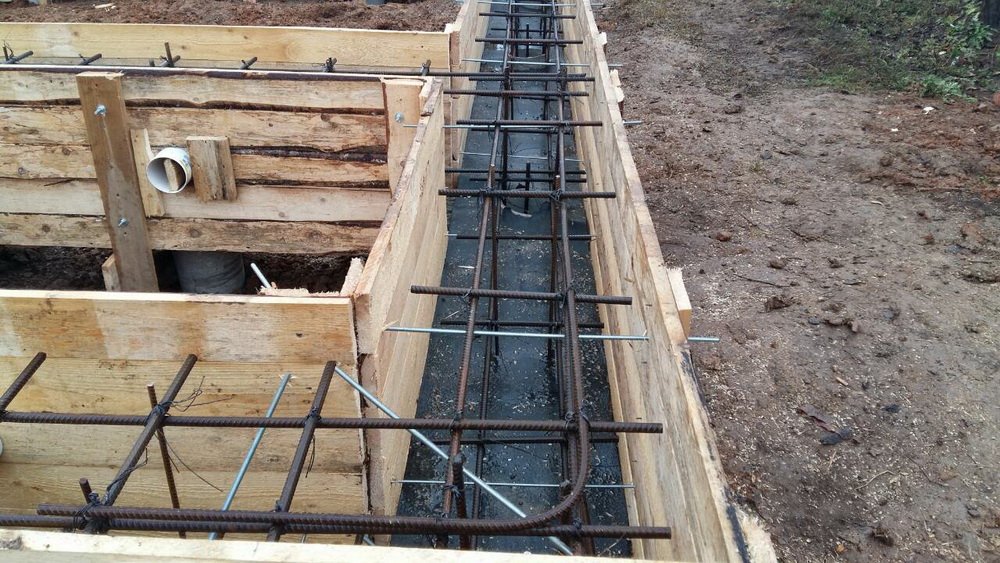
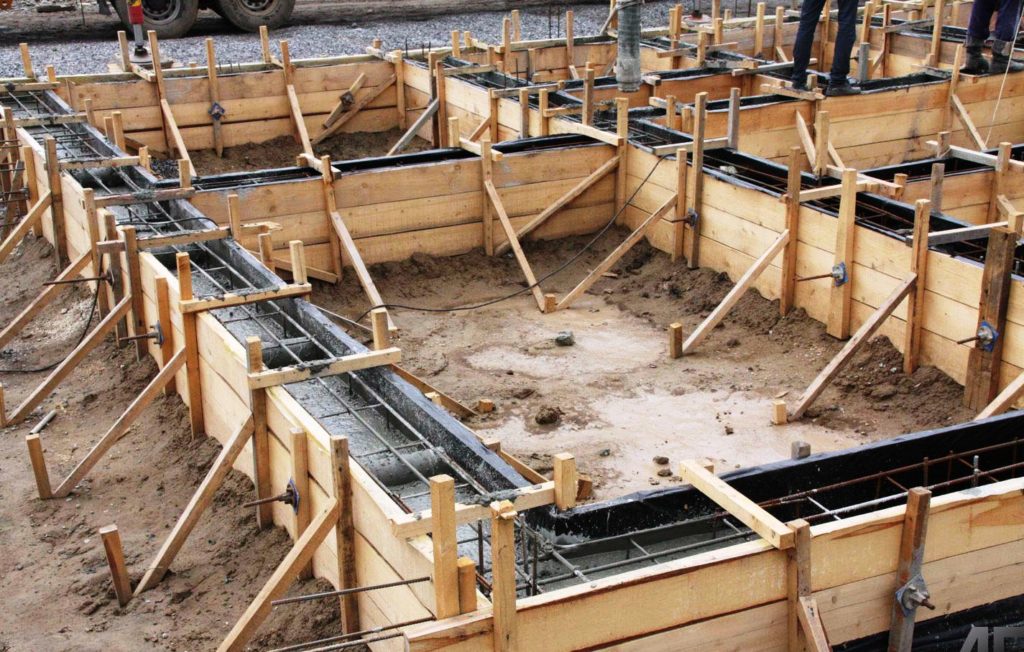
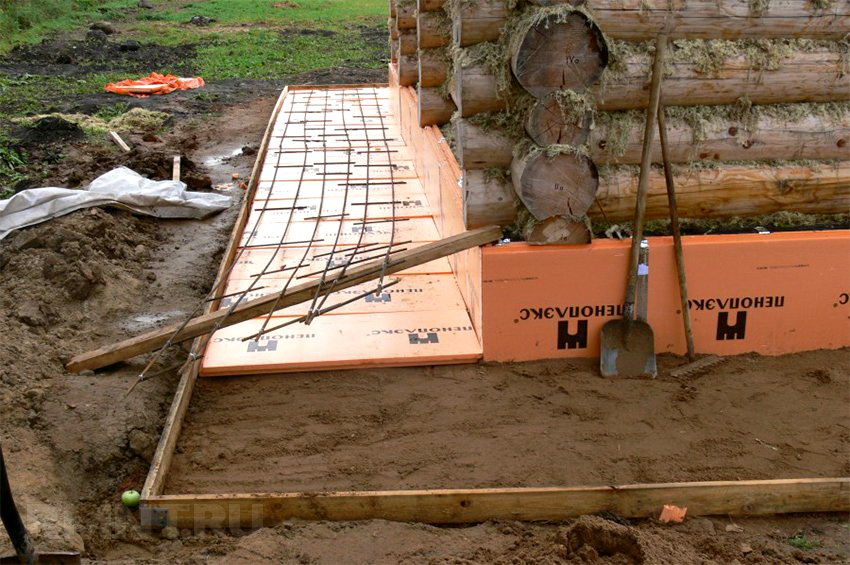
General Provisions
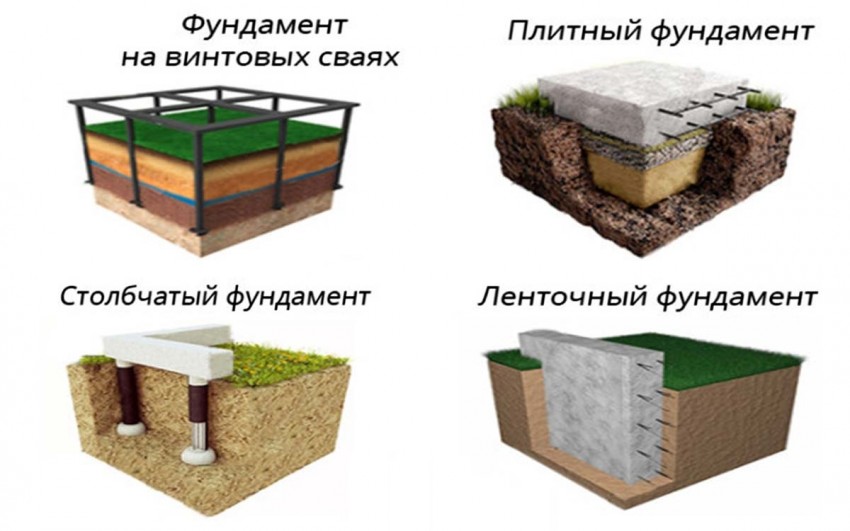
For the construction of a private house, you can make one of the following types of foundations:
Which one is the best is difficult to say, since the choice of one or another type of base must be made depending on the characteristics of the soil and structural features. The cheapest foundation will not always be the best.
When deciding what foundation to make for a private house, you should be guided by general recommendations. It is also necessary to take into account the construction conditions, namely:
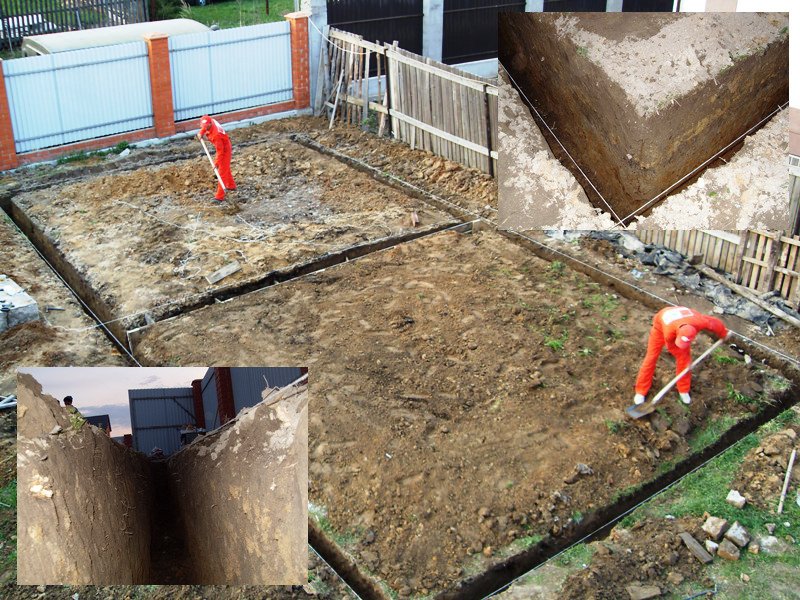
Before building a house, you need to conduct geological surveys in order to know the type of soil, its composition and characteristics.
Depth of groundwater
These data can also be obtained in the course of conducting hydrogeological studies.
For the construction of any houses and buildings, you need to know the depth of soil freezing.
It is also necessary to know the total load from the structure in order to correctly calculate the structure of the base and select the appropriate materials.
It is important what kind of house you will make, with or without a basement or basement.
You also need to take into account the materials for making the house, as well as the material of the foundation.
The presence or absence of underground communications .. If you make the foundation with your own hands, then you should be aware of the common mistakes:
If you do the foundation yourself, then you should be aware of the common mistakes:
You should not lay a shallow foundation for light buildings on heaving soils. In this case, the forces of frost heaving will cause deformation of the structures.
The foundation must rest on solid ground
It would be a mistake to make the base of the house on unconsolidated loose soil.
Do not forget about the lateral pressure of the soil on the walls of the base, as well as the destructive effect of groundwater.
It is important to use all measures that allow water to be diverted from the foundation structures.
Let us consider in more detail the features of the device and the design of each type of foundation, which you can do yourself for a private house.
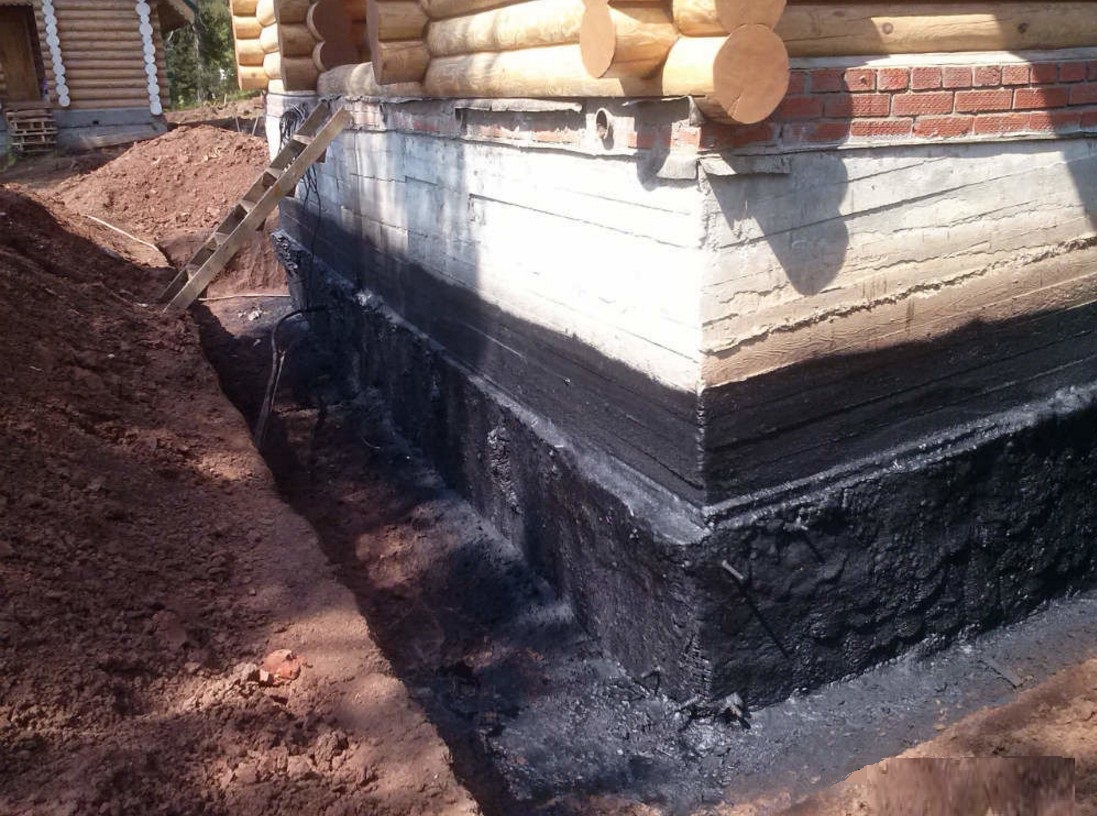
Penetrating materials for waterproofing
Penetrating waterproofing materials differ from others in that they change the structure of the components of the foundation, and do not isolate its surface from moisture. For this purpose, mixtures are used that penetrate deep into the concrete structure. This can significantly reduce the exposure of the foundation to capillary moisture.
Penetrating mixtures can be applied with a brush
The principle of operation of such isolation is simple. The components of mortars and waterproofing mixtures interact with aluminum and calcium ions contained in concrete, forming complex type crystalline hydrates. The pores in the concrete base are gradually filled with needle crystals, but very small gaps remain. Water molecules can penetrate through them in the form of steam. Capillary moisture penetration is impossible due to the presence of surface tension of the droplets.
Liquid formulations
For arranging waterproofing with penetrating compounds, liquid mixtures are often used that are easy to use. They are optimal for new foundations without cracks or defects. In this case, the concrete base can be processed both from the outside and from the inside.
Penetrating waterproofing is timeless
The technology for applying liquid penetrants for waterproofing a foundation is simple. The complex of works includes the following mandatory stages:
- Cleaning the surface from dust and dirt. It is possible to process with a hard brush and then with a strong jet of water.
- Material preparation. The dry mixture must be diluted with water according to the instructions. The result is a composition with the consistency of a very liquid sour cream.
- Material application.Do this with a wide brush. The first layer is kept for about 6 hours, and then the next one is applied.
-
Cracked foundation treatment. To do this, you need to dilute the powder to a thick consistency, and then apply the composition to the surface with a spatula.
- Decorative processing of the foundation. It is possible at least 21 days after waterproofing.
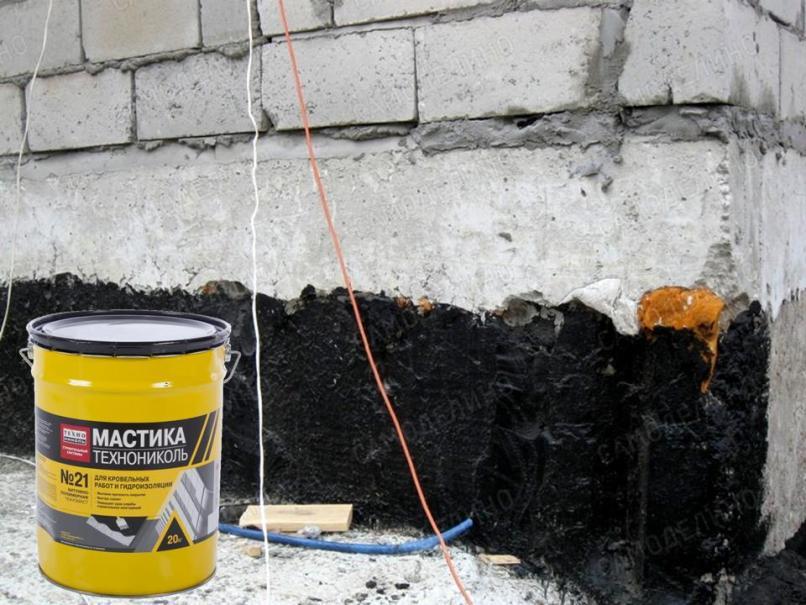
This method is distinguished by simple technology, and the choice of funds is very extensive. For example, there is a demand for the Penetron mixture, which is distinguished by its mechanical strength and high quality.
Design features
Foundation design options.
Types of foundations for a private house by type of construction:
- tape;
- columnar;
- pile;
- slab.
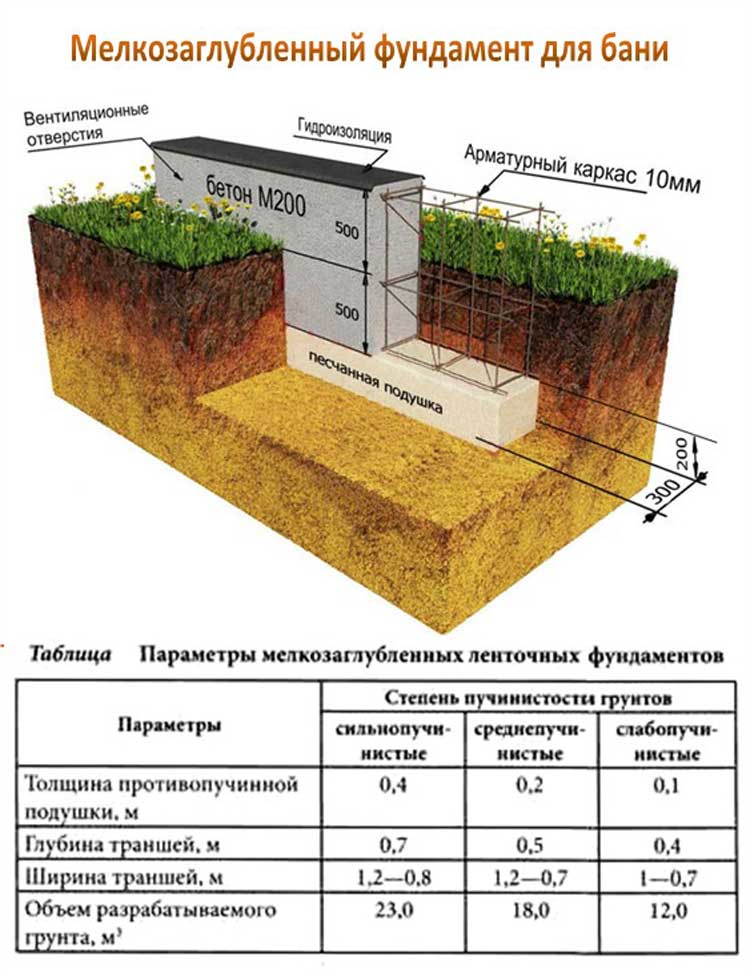
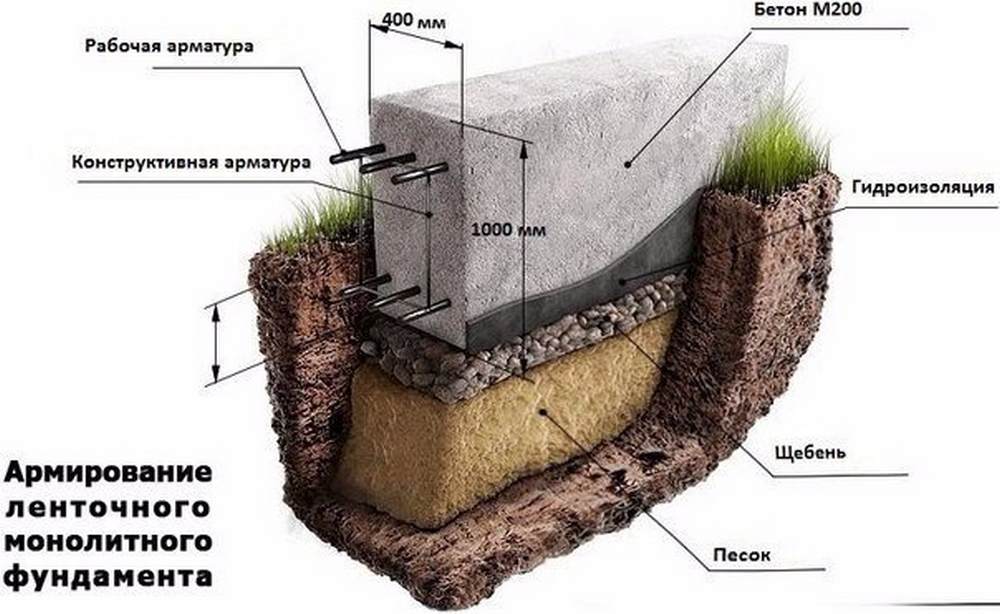
Tape
Tape supports can be made of reinforced concrete, concrete or rubble stone. This type of foundation is suitable if you need a basement in a building. There are three types of tape:
- deep (bearing depth more than 1.2 m);
- shallow (bearing depth from 0.5 to 1.2 m);
- not buried.
Depending on the type of section, tape structures are:
- rectangular;
- T-shaped (with broadening in the lower part to increase the bearing capacity).
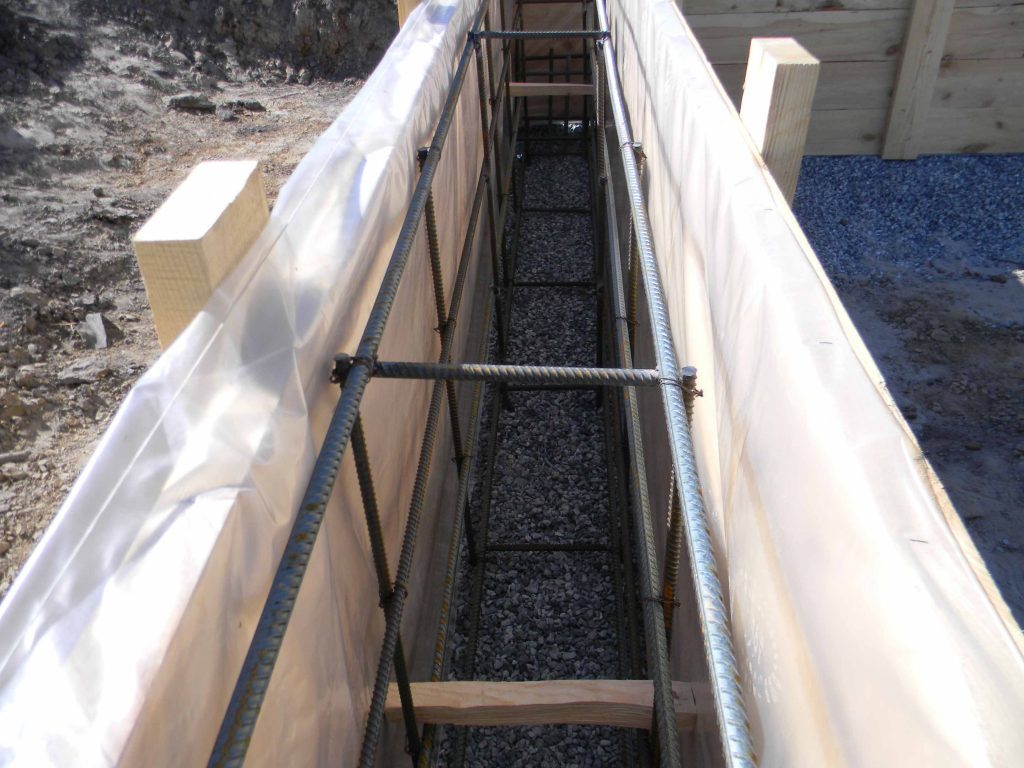
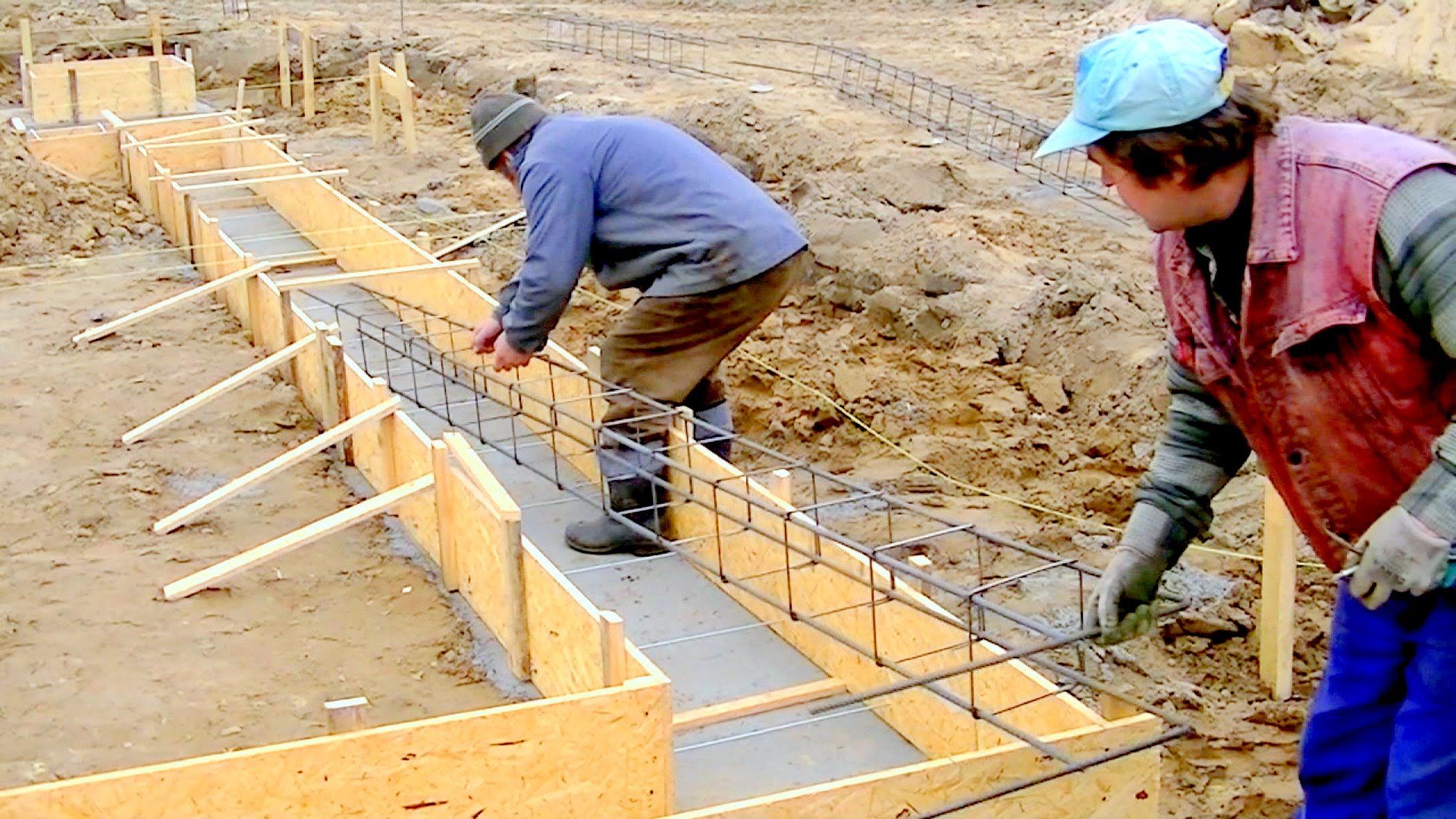
Varieties of the tape-type foundation are also distinguished depending on the method of their manufacture. For private construction, monolithic structures will be an advantageous solution. They do not require the involvement of heavy equipment and workers with specific knowledge. The main disadvantage is the need to wait until the poured concrete gains strength. The exact time depends on the material, air temperature and humidity. On average, it takes 4 weeks for the concrete mixture to harden.
Prefabricated foundations are suitable for the construction of apartment buildings and large objects. They are constructed from prefabricated concrete blocks and concrete pads. This option allows you to increase labor productivity. But the construction will require lifting equipment and skilled workers to secure the elements to the crane hook and set them to the design position.
Deep-laid tape.
Each of the above structures has its own scope.
Related article: Step-by-step instructions for strip foundations.
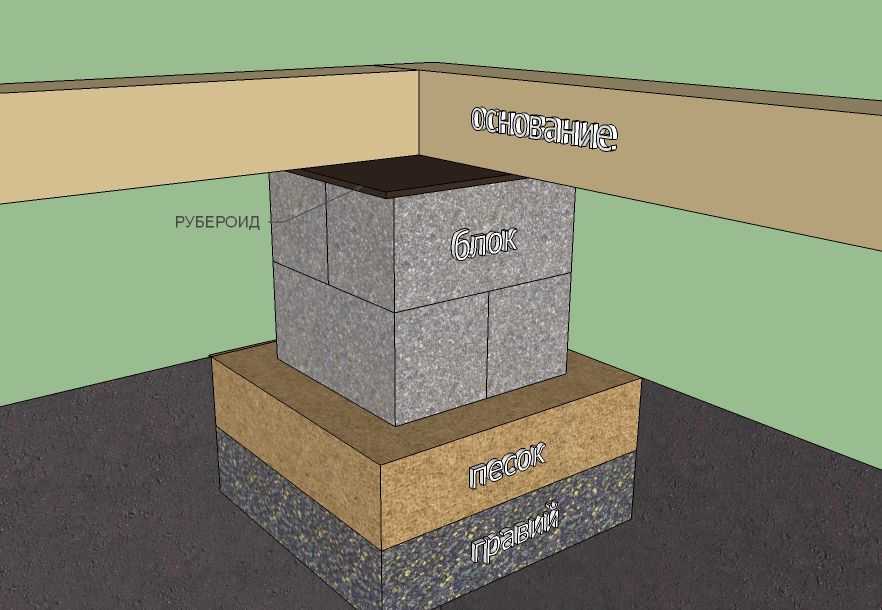
Columnar
Columnar bases are used for the construction of buildings on a metal or reinforced concrete frame. They serve as supports for free-standing columns. For the construction of industrial buildings, glass-type columnar foundations are used. For private construction, you can find simpler rectangular or square structures. They are made from concrete or reinforced concrete. Just as in the case of the tape, the types of foundations are distinguished according to the depth of the laying:
- recessed;
- shallow;
- not deepened.
Columnar base.
Related article: Step-by-step instructions for building a columnar foundation.
Pile
The closest relative of the columnar foundation is the pile foundation. It is worth distinguishing between piles for private construction and for the construction of apartment buildings, office buildings and industrial facilities. The latter are distinguished by their large diameter and rather high cost. In the private sector, two types of piles are commonly used:
- metal screw;
- reinforced concrete bored.
They differ in material and manufacturing technology. The first ones are produced at the plant and delivered in finished form to the construction site. The second ones are poured on the spot.
A pile foundation is practically the only way out when working on swampy soil. They are able to work on soft soils with high water content
But it is important to remember that such elements are suitable only for non-massive structures made of wood or lightweight concrete.
According to the type of work, piles are divided into hanging and racks. Hanging ones provide bearing capacity only due to the lateral surface. Rack piles rest on the ground at the bottom.Hanging elements are used if the soil layer with good strength characteristics is too deep.
Hanging piles and racks.
To ensure the joint work of freestanding piles or pillars, a grillage is made. It is a tape that ties the upper parts of the supports. The grillage can be metal, wood or reinforced concrete. The choice of material depends on the type of building walls, the distance between the foundation supports and other factors.
Pile-screw foundation for the house -photo.
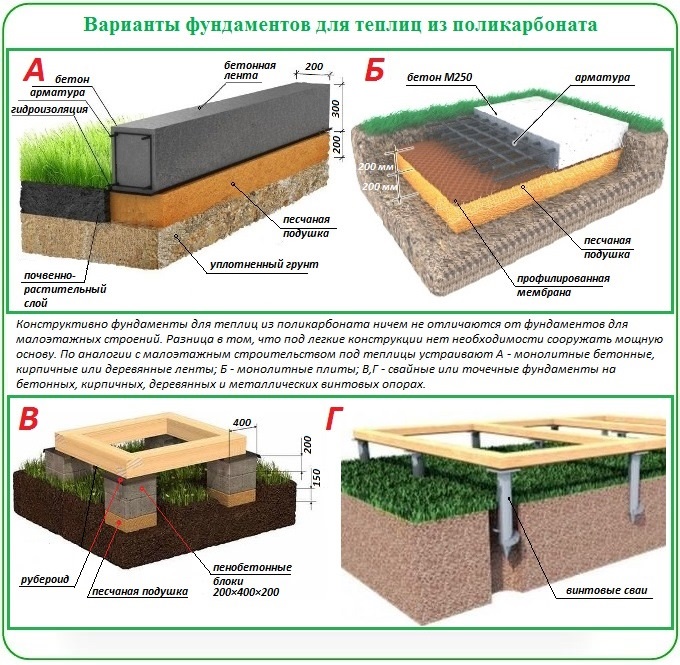
Platen
Recently, slab base is gaining popularity in the private sector. The structure is made of reinforced concrete. The slab can be buried, slightly buried, or not buried. The easiest way is to make a non-recessed structure. This does not require complex soil development measures.
Reinforced concrete slab.
Related article: Step by step device manual slab foundation.
Plinth finish
A variety of materials are used to finish the basement. The main requirement is that they are strong enough and withstand being in water.
Optimally, the foundation cladding is carried out with a special siding for the basement or closed with a profile metal sheet. Siding imitates the classic stone materials used for the basement - rubble stone, brick, flagstone, etc.
Decking in dull colors for the basement will also look pretty beautiful. Their main advantage is that they can be easily washed from dust and dirt, and your base will always have a presentable look. Siding can be metal, plastic. It is better to use a special siding for the basement, siding for the walls will not work here.
Before starting work, it is necessary to install the crate. It is made from wooden blocks with a cross section of 50x50, which must be treated with a composition against rot and fungus, or special plastic guides. Since the bars will be in a humid environment with poor air circulation, it is imperative to treat them with special compounds!
The bars are attached to piles or a monolithic basement of the house using self-tapping screws. The fastening step depends on the type of siding panels. Usually, large-sheet siding is used with a pitch of 30 cm for fixing the bars, the same rule applies to corrugated board. Then a metal corner is fixed at the bottom. The corner should be higher than the blind area, so it can be done in advance and align the inner perimeter under the corner.
After that, siding or corrugated board is attached to the bars, cutting it along the lower corner, and a straight line is maintained from above. The corrugated board is fixed with an overlap of sheets in two waves. Close up the corners, make out the windows with slopes. At the end of the work, an ebb is installed in the upper part so that water does not get under the siding.
Defects of building foundations and their causes
The reasons for defects in foundations, due to which buildings can lose their strength, are the following:
- old age;
- substandard materials;
- poor quality of construction work.
The main defect in building foundations is uneven subsidence. Outwardly, this is expressed in the appearance of cracks of various shapes and different directions, both on the foundation itself and on the walls of the house, various distortions of the house itself.
Also, the following are considered as the causes of foundation defects:
Incorrectly chosen foundation depth. It is very difficult to fix this defect, and sometimes it is impossible at all. If the subsidence is insignificant, it is possible to add soil along the entire perimeter of the foundation, thereby artificially increasing the depth of laying.
The rise in groundwater is difficult to predict, but it can be corrected, perhaps by arranging drainage systems or planting varieties of plants that effectively draw moisture from the soil. Drainage systems are best laid at the same time as the foundation.
Uneven Uneven load on the foundation from the side of the building.For example, when the main house is much heavier than the veranda. If the house has already been built, then in order to avoid further deformation, it is necessary to separate the foundations of the veranda and the house. To do this, lay boards impregnated with bitumen between the foundations.
Increasing the load on the foundation due to the superstructure of the upper floors:
- due to an incorrect assessment of the capabilities of an already existing foundation. Elimination of this defect will cost the owner of the house a decent amount, and this even if circumstances allow strengthening the foundation by increasing the bearing area of the foundation;
- the load-bearing capacity of the soil has been incorrectly estimated; it can be increased by pouring the soil under the foundation with "cement milk".
Insufficient strength of foundation materials or loss of strength over time.
For brick foundations, stacked on a lime mortar, over time, a violation of the adhesion of the mortar to the brick is characteristic (moisture ingress into the foundation, freezing, load on the foundation). Major repairs are required, replacement with a new one. To do this, you need to unload the old foundation by transferring the weight of the house to temporary supports. Wooden beams serve as temporary supports. They are placed next to the old foundation and, by means of steel beams, transfer the load of the house to wooden beams.
Characteristics and merits influencing the choice
In order for the consumer to make the right choice of material, manufacturers apply a special label to each package of goods. The available abbreviation shows not only the quality of the product, but also where these raw materials can be used.
The marking reflects the composition of the additives as a percentage and the permissible loads on the cast base. When choosing a product, you should knock on the bag in order to determine the flowability of raw materials. If you feel fossils, then it is better to refuse to buy a product.
The presence of lumps signals a too long or incorrect storage period. And also when choosing raw materials, it is necessary to take into account the resistance to the influence of aggressive factors. Quality products should have the following parameters:
- Resistant to high humidity. This criterion is especially important when reinforced concrete structures are included in the foundation.
- Durability. It is better to choose a material with a high rate.
- Anti-corrosion properties. Raw materials must resist rusting and have sulfate-resistant properties.
- Air resistance and frost resistance.
When choosing a product, it is necessary to take into account some of the advantages of mixtures. The purchased powder for a long period of use must have:
Resistance to low temperatures. Such a criterion will allow pouring in different climatic conditions and performing repeated defrosting and freezing of the composition. The number of such procedures depends on the brand of raw materials.
Rust resistant. Characterizes the material's ability to withstand aggressive environmental conditions.
Excellent indicators of water resistance.
Sulfate resistance. This criterion determines the degree of resistance of the solution to the effects of sulfate ions. These indicators are of particular importance in the process of construction of hydraulic structures. Depending on the selected brand of raw materials, strength indicators will directly depend.
Transportability
With long-term storage and transportation of raw materials over long distances, the ability to maintain the original characteristics in the open air is of no small importance.
Change in volume. The shrinkage characteristics of the material and its ability to swell depend on this criterion.
These properties are important for calculating the final weight and outdoor curing time.
Foundation finishing stages
Before starting to plaster the foundation, you must:
- Make notches over the entire area of the base. This aspect applies exclusively to the concrete foundation.You can make notches with a screwdriver or some other durable metal object.
- Align the surface.
- Prime the surface.
- Moisten masonry joints and any other damage with water, and then fill with a mortar based on cement and sand.
-
Shoot a fine-mesh mesh Rabitsa to the foundation. In this case, staples or dowels will help.
- Install beacons in the corners and every 1.5-2 meters.
Beacons are installed as follows:
Using the hydro level, a flat strip is drawn on the ground near the foundation
It is important that the indentation from the foundation is almost invisible (2-3 cm), the strip should run close to each other. At the place where the corner of the wall with the strip will intersect, the peg is installed strictly vertically, and the height of the peg must correspond to the height of the base
The distance between the peg and the foundation should be filled with mortar. A vertical bump should form, the alignment of which should be done using a building level
Such beacons should be made in all corners, as well as every 1.5-2 meters. 3 nails should be driven into the pegs intended for corner beacons, on which it is necessary to pull the lace. This lace will work as a reference point for plastering the foundation under the stone. Accordingly, after pulling the lace, 3 lines will appear: below, in the middle and on top of the base
It is important to remember that between the laces and the beacons themselves, there is an opening of 1 mm
How to plaster the foundation? There is nothing complicated in the further process.
- First of all, you should wait until the lighthouses dry out, after which it is necessary to spray the foundation. First of all, it is wetted with water. After that, using a ladle or trowel, the cement mortar is sprayed, prepared in advance according to the above rules. The permissible layer thickness varies between 5-9 mm.
- After the "spray" has dried, a more liquid primer should be applied on top of it.
- After the primer has set, the covering composition should be applied - thicker and more plastic. It is this composition that is a plaster mortar with waterproofers and plasticizers.
- The last stage involves mashing the surface. This process achieves the smoothest surface possible and also allows it to be leveled. Grouting is carried out using a special grater, which has a fine metal mesh. You can also use foam or some other special tools. The most important thing is to choose the right moment for mashing. In this case, the plaster should not be completely dry, but it should already be seized. You can make plaster in a variety of ways - under a stone, or give it a relief surface.
What foundations are
Foundations differ structurally, according to the material of manufacture, etc. Consider and determine what types of foundations are suitable for DIY construction:
Tape: widespread, ideal for 1 or 2 storey buildings.
Columnar: they drill or dig holes below the freezing level. They are placed in the corners of the house and at a distance of 1-1.5 meters between themselves. The pillars at the top are connected with a 40 * 40 cm belt made of reinforced concrete.
Slab (monolithic slab): the most time consuming and expensive, but works well on quicksand and other soft soils.
Pile: Several rows of piles are used, on top of which a slab is poured. It is used on soft soils, withstands high loads.
Tape and columnar types of foundations are the most common, suitable for do-it-yourself construction.
Cheapest types of foundations
The price for installing the foundation is formed not only from the amount spent on the purchase of building materials, but also from the total weight of the finished house. It is for this reason that a light and economical frame on poles or piles can be made for a frame or wooden house. Below we consider options for foundations that will be economical options in each case for a particular building.
Foundation for a wooden house
For such a house, it is quite possible to mount a shallow columnar frame with a wooden grillage. The financial benefit in this case will be in the following parameters:
- No need to dig a full-fledged pit;
- Possibility of using improvised means (blocks, bricks, wood) as a building material for foundation supports;
- Minimum labor costs during installation, that is, the base can be built even with your own hands without the involvement of professional craftsmen.
- The cost of such a columnar frame on average in Russia is from 40 USD. for one pillar.
Foundation for a brick or block house
Heavier buildings also require a more powerful base with a high load-bearing capacity. In this case, the most economically viable option would be a shallow or medium-depth columnar monolithic foundation with the same reinforced concrete or beam grillage. Ideally, a tape frame should be built under a stone house. Especially if the soil on the site is complex. When building a tape frame, you can save on building materials if there are deposits of buta (natural stone) near the site. The rubble strip foundation is strong and reliable enough and has a high bearing capacity.
Foundation for a monolithic house 1-2 floors
In this case, a full-fledged strip base or a concrete monolithic slab is arranged. The latter option is especially good for moving soils with high groundwater levels. Moreover, if it is planned to install a strip foundation, then in the case of moving soils on the site, it is necessary to mount a support sole under the frame tape. The expansion will reduce the mass of the house on the base and increase the bearing capacity of the foundation.
You can save on the construction of a strip base if you assemble it from concrete blocks. This will reduce the cost of work by about 30%. The cost of a strip monolithic base will cost about 111-126 USD / running meter. A monolithic concrete slab will cost from $ 48 / m2. But depending on the depth of the base.
Pile foundation
The most economical and at the same time durable type of frame. The base on metal screw piles can be arranged on difficult moving soils, in rocks, with a high level of groundwater. The only condition for a pile foundation is a structure that is lightweight. This can be a frame or panel house, a garage or a utility room such as a barn.
The savings here are as follows:
- No need for complex earthworks;
- Do-it-yourself installation without the involvement of professionals;
- Relatively low cost of building materials (piles and channels for grillage).
- The price of a pile foundation is on average from 72 USD. for one pillar.
TISE technology foundation
This is a type of pillar or pile foundation, the supports of which have a cross section of 25 cm. At the same time, a special expansion with a cross section of 60 cm is arranged under the pillars of the base. It is called a shoe or sole. Such a pillow is capable of significantly reducing the pressure of the mass of the house on the columns of the frame, which means it can prevent the soil from sinking under its weight.
The TISE technology foundation is good for any house (brick, block, frame, stone). In addition, it is this type of foundation that can be arranged on almost any soil, such as sand, clay, loam, high ground level, etc.
An important link in the construction of the base using TISE technology is a strong grillage - a frame encircling the posts. It is most often made of rolled metal or monolithic concrete. The cost of such a foundation (including work) will be from 64 USD / running meter.
Foundation slab
It is also called a floating base. Such a monolithic concrete pad goes deep into the soil by 1.5-1.7 meters. In this case, the concrete fill is reinforced with a rigid frame.
A slab foundation can hardly be called an economical base arrangement, but such a frame will withstand any load on the most difficult soils. The slab foundation is not afraid of seasonal heaving of the soil, or a high GWL, or moving layers or difficult terrain.
Soil mechanics
The choice of the foundation primarily depends on the characteristics of the soil: its composition, the depth of freezing and groundwater, and only then - on the structure of the house and its materials.
The type of foundation is selected depending on the soil
Soils
Before designing a house, it is better to order a professional site survey. Moreover, you should not use the results of your neighbor: sometimes even neighboring plots differ greatly in their characteristics. But you can do it yourself: dig a hole from half a meter to a meter deep, then make a two-meter well with a garden drill, studying the soil from different depths.
If the site is located in an inhabited village, then it is good to talk to the owners of neighboring sites, to look at their sites. This will help a lot.
According to the reference book “Soils. Foundations. Choosing the optimal foundation ”soils are of three types:
- rocky - massifs of homogeneous crystalline rock (rock) and sedimentary layered rock: dolomite, shale, sandstone, limestone;
- conglomerate - any soil with a large percentage (more than half) of fragments of crystalline or layered sedimentary rocks;
- non-rocky, which, in turn, is subdivided into
- related - loams and clays;
- unbound - sands and sandy loams.
Soil classification is well shown in the diagram.
The cohesion of the soil also changes with moisture. Independently, soil connectivity is determined visually - by the angle between the slope of the soil ejected from the pit and the horizontal.
It is non-rocky soils that are characteristic of our strip.
If your soil is virgin sandstone or gravel, then you are in luck (even more fortunate if it is still rocky). Sand is a wonderful home base. It is quite reliable if the soil is plastic, dense and dry loam, or gravel, or even caked construction waste. The trouble is that clays are never completely dry, and wet clay tends to swell and swell.
| Position | Characteristics of the soil | Minimum depth of foundation (cm) |
| 1 | Sand | 50 cm |
| 2 | Clay | 70 cm |
If this is an easily and unevenly shrinking soil - forest, or garden fill soil, or, much worse, swampy soil, then your construction will cost you much more due to the forced compensation of these problems. In the case of quicksand (resembling dust or flour) or silt, building a house is generally impractical.
Freezing
In addition to the composition of the soil, you need to know to what depth it freezes in winter. In our "latitudes" the depth of freezing is usually from eighty to one hundred centimeters.
Ground water level
This is also an indicator on which not only the "model" of the foundation depends, but also the depth of its laying; it is estimated in relation to the depth of soil freezing. If in winter the water does not rise below 2 meters to the freezing depth (for brevity we will designate it with the letter Q), and your soil is fine and silty sand or hard clay, then the depth of the foundation will not depend on the freezing depth in principle.
Table: dependence of the depth of laying the foundation on the depth of groundwater
| Position | Ground water level | Groundwater level (m) | Foundation laying depth (m) | Note |
| 1 | Short | Below Q + 2 m | Not less than 0.5 m | |
| 2 | Higher | Above Q + 2 m | To the depth of freezing or below | The foundation must be installed on a sand and gravel drainage pad |
But if the soil on the site is mixed, and sand or peat lies on top of the clay, then after precipitation so-called "lenses" appear inside the soil - moisture seeps from above through the permeable layer and lies on the impermeable clay. And this is very dangerous for the foundation because of its unpredictability.
The scheme of the soil permeable from above, in which internal, very dangerous for construction, "lenses" of water are formed
Therefore, it is better to order a complete survey of the site from professionals and get a number of necessary documents on the condition of the soil in your hands. They should include the following information:
-
Topographic plan with curves of occurrence of soil waters and different types of soil.
- Mechanical properties of soils: the possibility of subsidence and sliding, heaving, cohesion, the ability to withstand the foundation without special efforts.
- Physical and chemical properties of soils - freezing depth, wetting ability; what substances it releases when wetted, and how they will affect the foundation material.
-
Diagram of the depth of groundwater and its changes depending on the season and temperature.