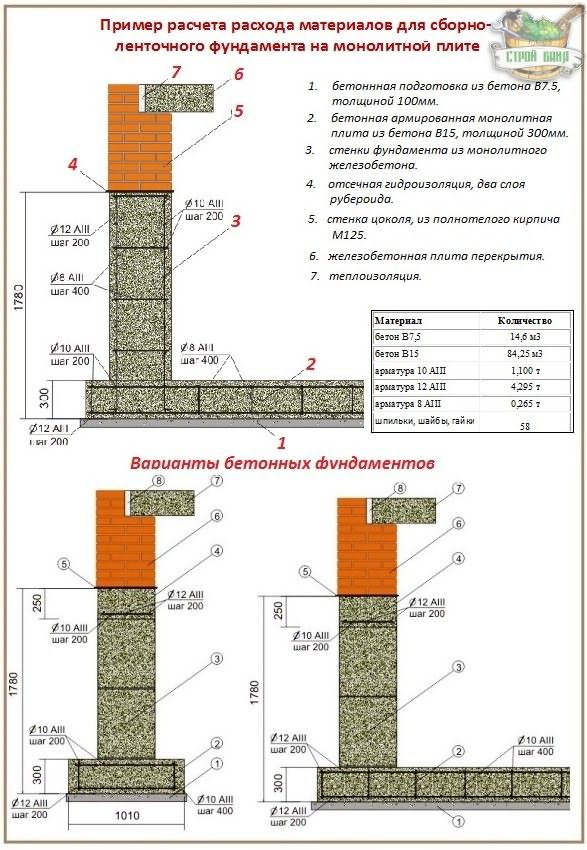
Grades and strength classes
Concrete is marked with the letters M and B. M is a material grade that indicates the average load per square centimeter that a given sample can withstand under compression until complete destruction.
In construction, mainly brands from M100 to M500 are used:
-
М400-М500 is a concrete used for the construction of bridges, tunnels, hydraulic structures and other large objects with increased strength requirements.
- M400 is a material intended for industrial construction and the construction of foundations for low-rise buildings on wet and soft soils.
- M350 - used in the construction of swimming pools, multi-storey buildings, various high-rise structures.
- М300 - used to create reinforced concrete structures, as well as for the arrangement of road slabs and staircases.
- M200 - concrete for private construction. It is used for the construction of light foundations and interior works.
- M100 is an auxiliary material used for the preparation of the foundation base, the arrangement of outlet drains, thin screeds.
B is the class of concrete. It denotes the actual compressive load that a given species can tolerate.
The strength class is determined by breaking a cube of hardened concrete with a side of 15 cm with a special press.
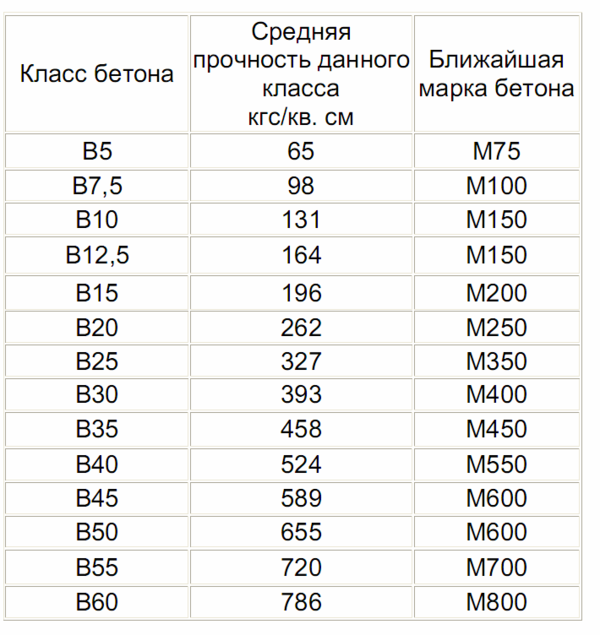
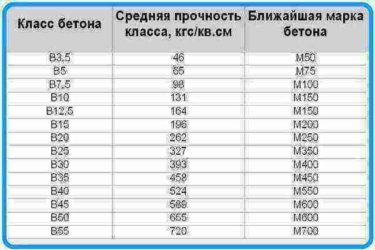
Brand and class are not the same thing. But each class has a brand that is as close as possible in strength. This is shown in the table:
| Class | Average strength (kg / cm2) | Brand |
| AT 5 | 65 | M75 |
| B7.5 | 98 | M100 |
| AT 10 | 131 | M150 |
| B12.5 | 164 | M150 |
| B15 | 196 | M200 |
| IN 20 | 262 | M250 |
| B25 | 327 | M350 |
| B30 | 393 | M400 |
| B35 | 458 | M450 |
| B40 | 524 | M550 |
| B45 | 589 | M600 |
| B50 | 655 | M600 |
| B55 | 720 | M700 |
| B60 | 786 | M800 |
The brand and class of concrete - what are the differences, the video will tell you:
Frost resistance
This indicator is marked with the letter F. It determines how many freezes and thaws concrete can overcome without receiving more than 5% destruction.
Different grades of concrete can go through 30 to 300 freezing cycles.
Water resistance
The letter W is used to denote water resistance. It shows how much water pressure a concrete coating can withstand without letting water through the pores.
To determine the correspondence of the indicators of water resistance and frost resistance of concrete to brands and classes, a special table is used:
| Concrete grade | Concrete class | Frost resistance F | Water resistance W |
| m100 | B-7.5 | F50 | W2 |
| m150 | B-12.5 | F50 | W2 |
| m200 | B-15 | F100 | W4 |
| m250 | IN 20 | F100 | W4 |
| m300 | B-22.5 | F200 | W6 |
| m350 | B-25 | F200 | W8 |
| m400 | B-30 | F300 | W10 |
| m450 | B-35 | F200-F300 | W8-W14 |
| m550 | B-40 | F200-F300 | W10-W16 |
| m600 | B-45 | F100-F300 | W12-W18 |
Indicators of workability of the solution

Workability is the ability of concrete to fill the mold evenly when poured and, after compaction, to form a homogeneous dense mass.
There are three workability classes of concrete:
- P - spreading mixtures;
- P - movable;
- F - tough.
Within each class, there is a division according to the degree of manifestation of characteristics. So, spreading mixtures are divided into categories from P1 to P6. The higher the indicator, the higher the ability of the material to self-fill the mold without vibration compaction.
Mobility is indicated by the letter P. There are 5 degrees of concrete mobility. Mobility is determined by laying out concrete in a shape with a cone with a height of 30 cm, a lower diameter of 30 cm and an upper one - 10 cm.
The higher the number, the more mobility. After removing the cone, the concrete gradually loses its shape. The degree of shrinkage of the mold determines the mobility of the mixture.
Depending on how mobile the mixture is, its purpose is determined:
| P1 | Pouring concrete cushions under the foundation, floor screeds, creating concrete slabs without reinforcement, foundations with a small amount of reinforcement. |
| P2 | Slab foundations with lightweight reinforcement cage, concrete beams. |
| P3 | Dimensional columns and supports, horizontal concrete structures with full reinforcement, high foundations. |
| P4 | Any reinforced concrete structures with dense reinforcement stacking, equipped without vibration. |
| P5 | Constructions obtained by pouring concrete with sealed formwork. |
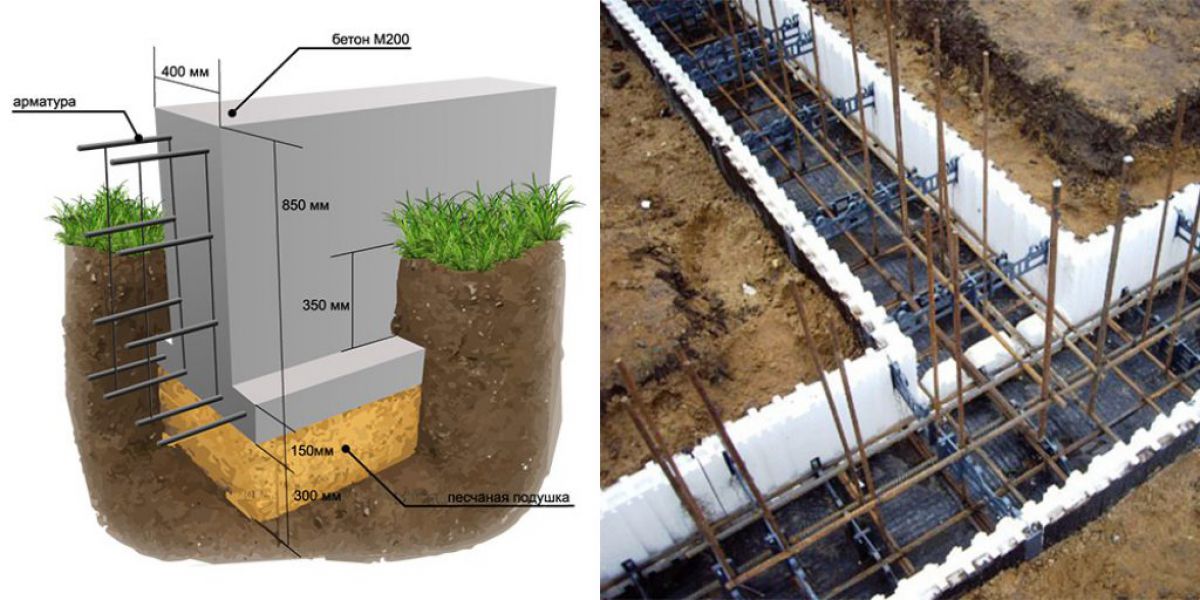
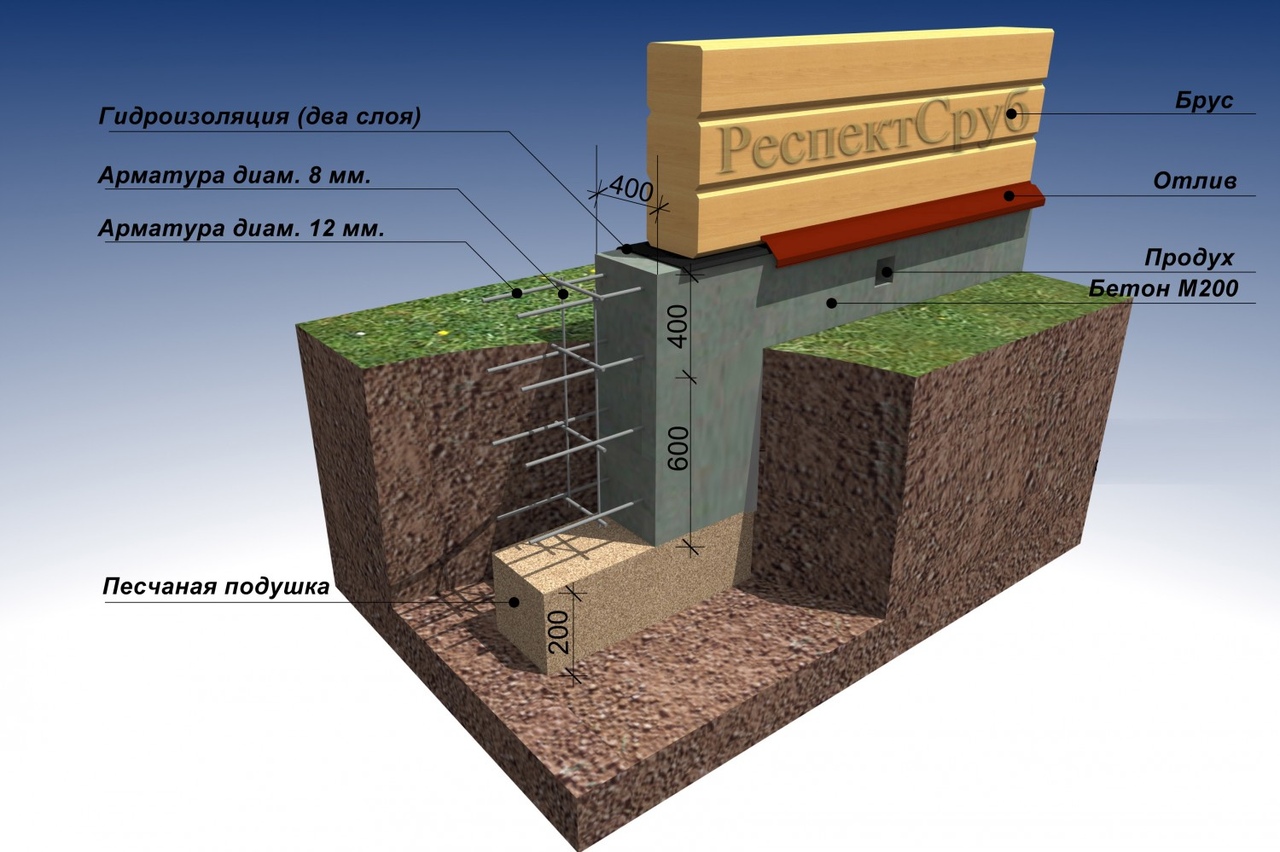
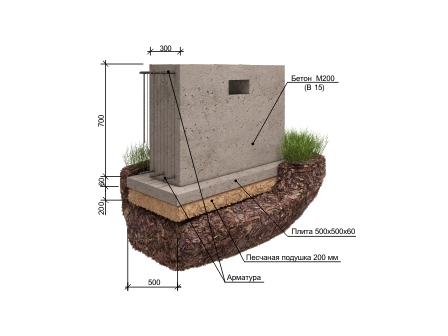
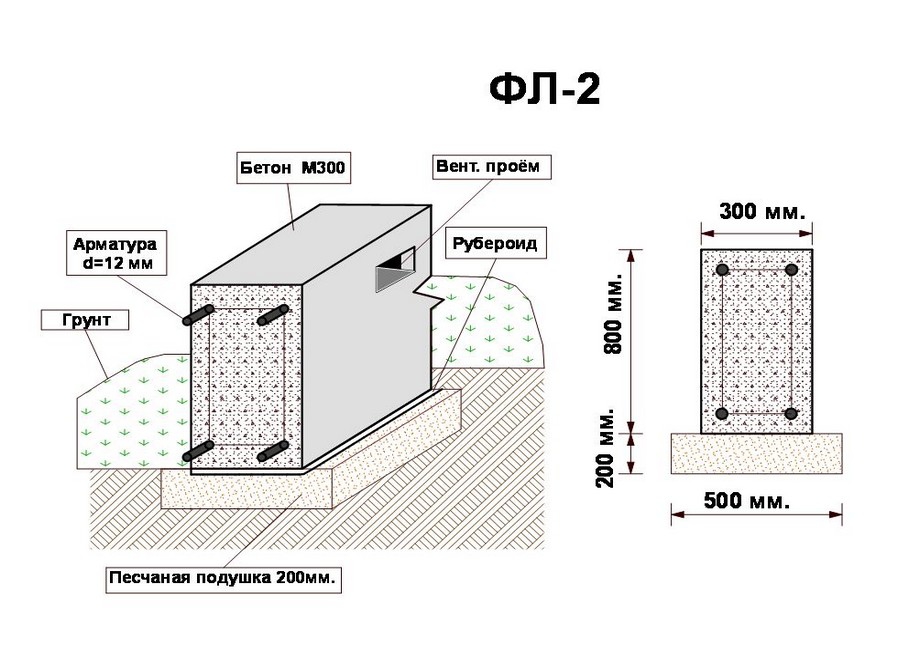
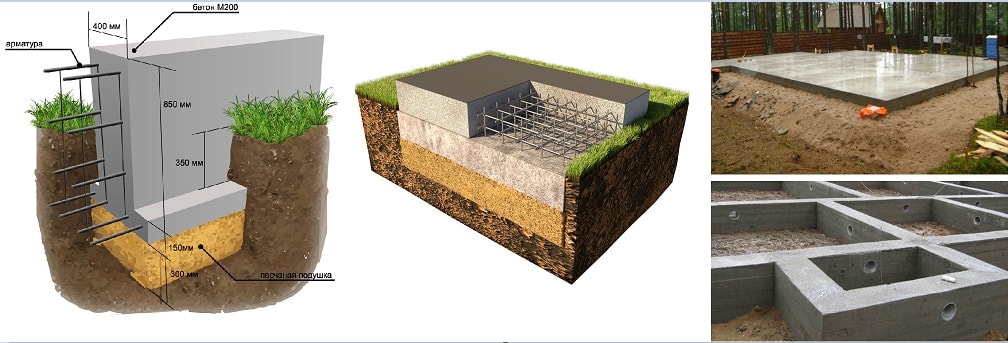
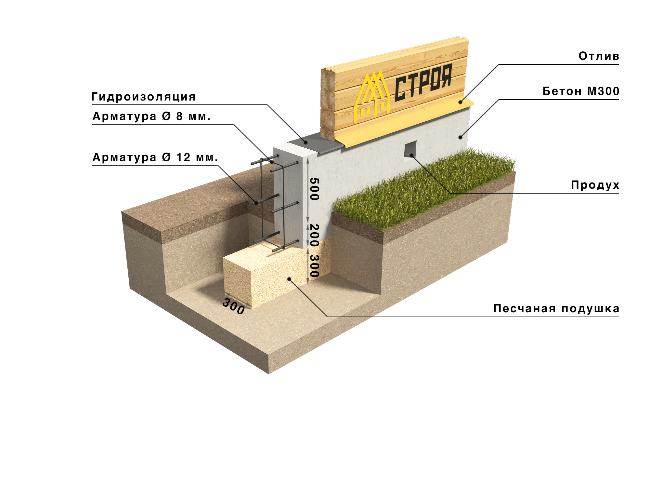
Foundations for private houses
There are the following types of foundations;
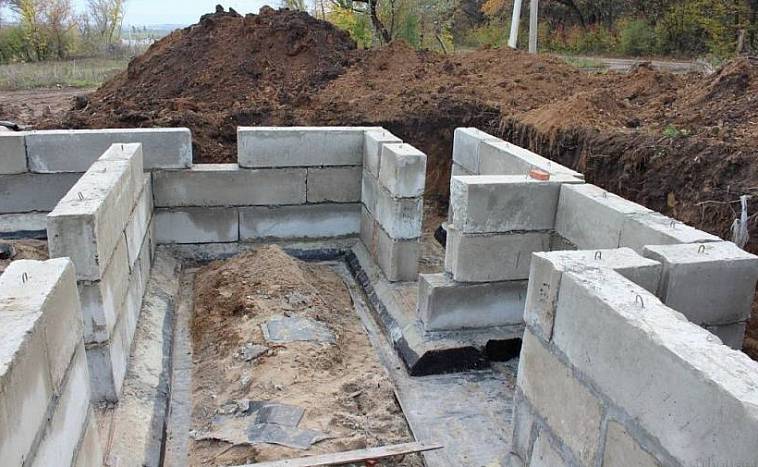
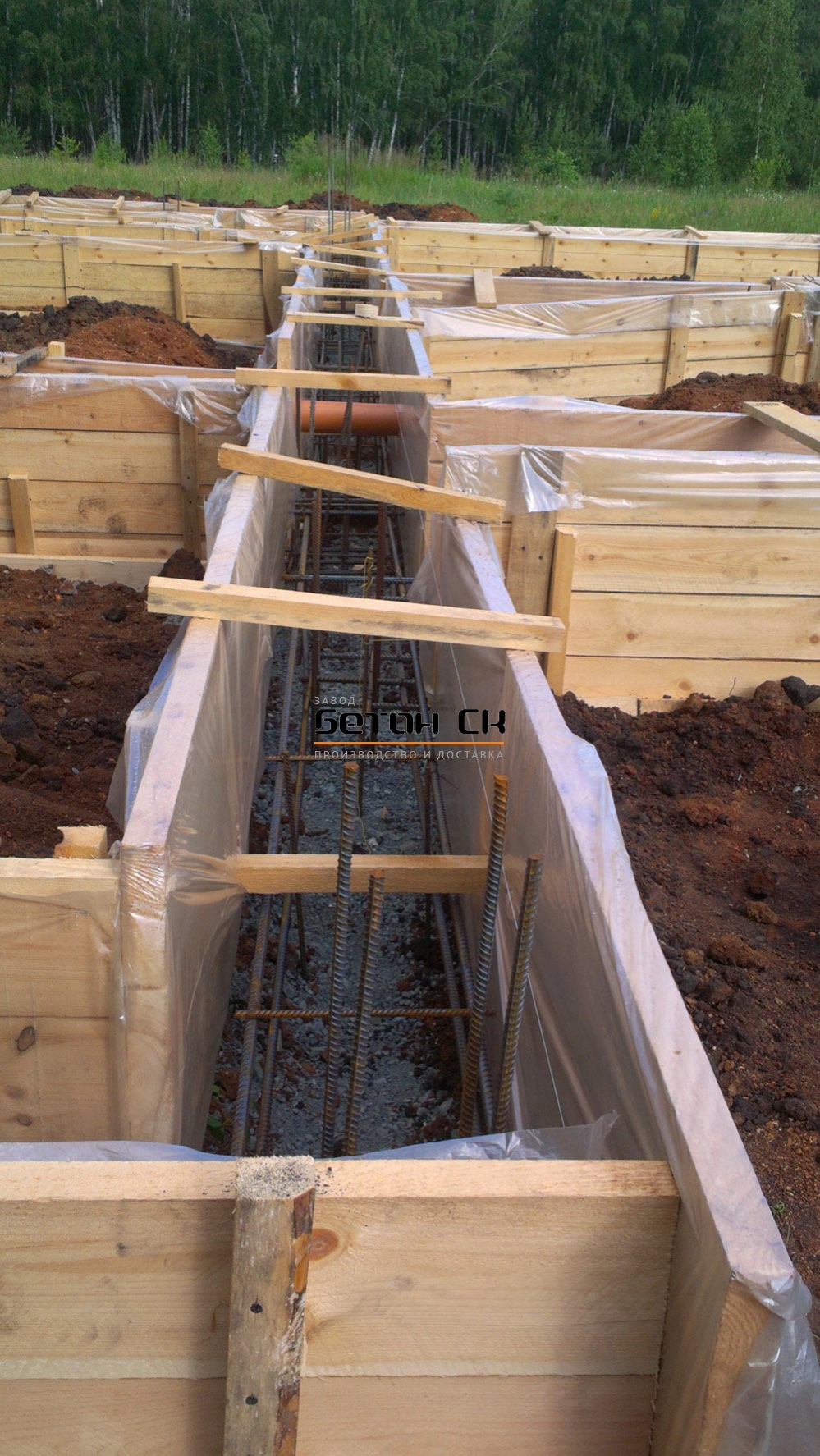
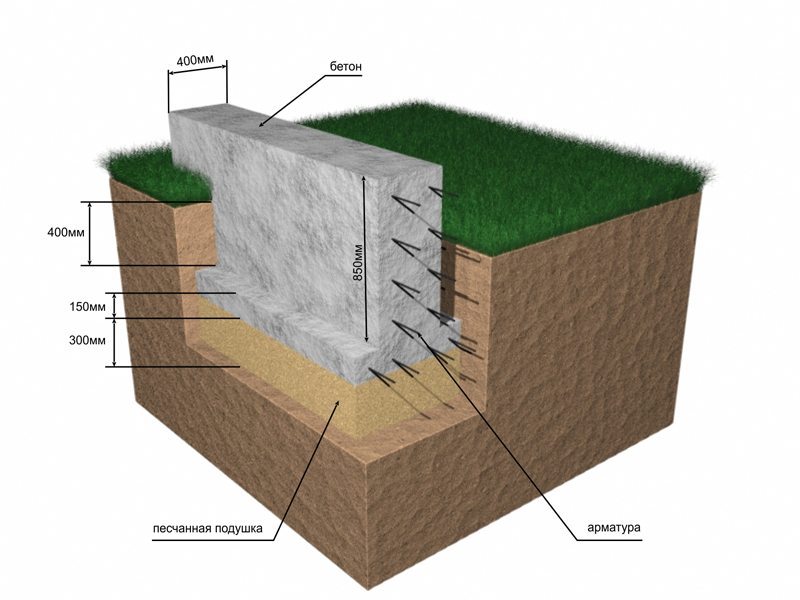
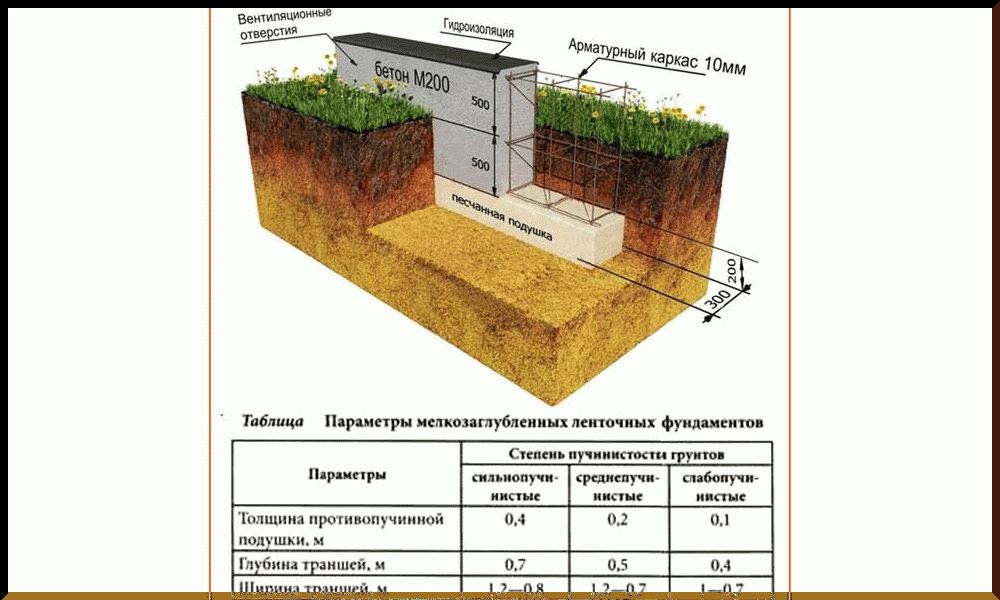
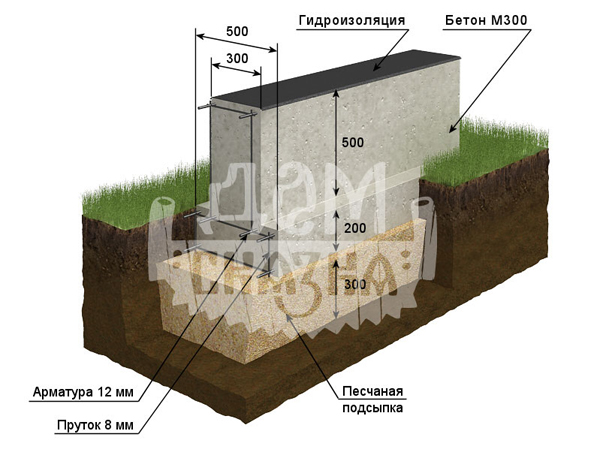
Tape
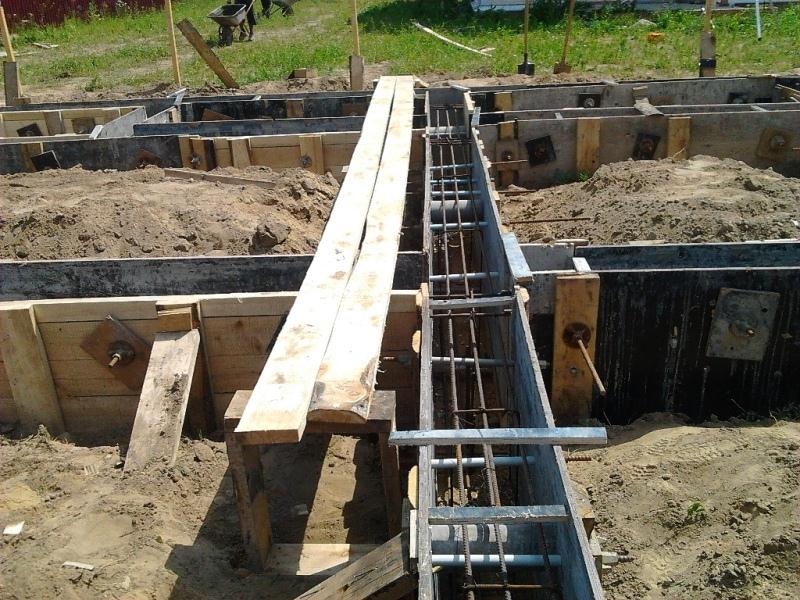
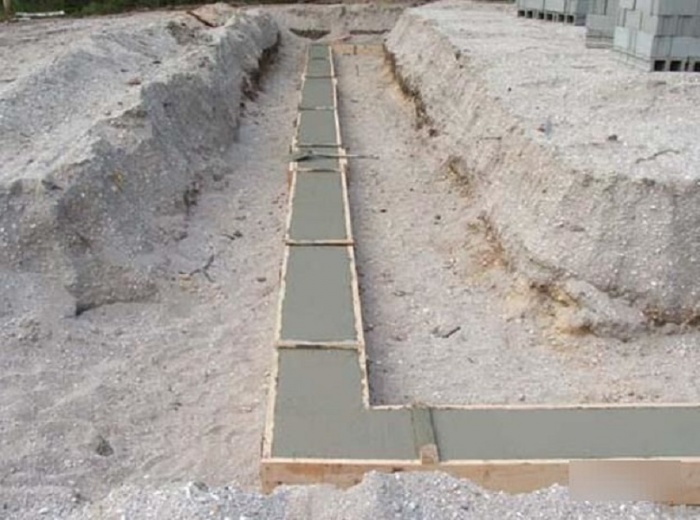
It is especially often used in private construction. It fits under heavy concrete and brick houses. It is a strip of reinforced concrete of calculated width and depth, arranged under the load-bearing walls of the building, usually with basements.
 Strip foundation
Strip foundation
The depth of the strip foundation is greater than the depth of soil freezing. For light (usually wooden) houses, shallow strip foundations are sometimes arranged.
Columnar
Supports-pillars at the corners of the structure and at the intersections of the walls.
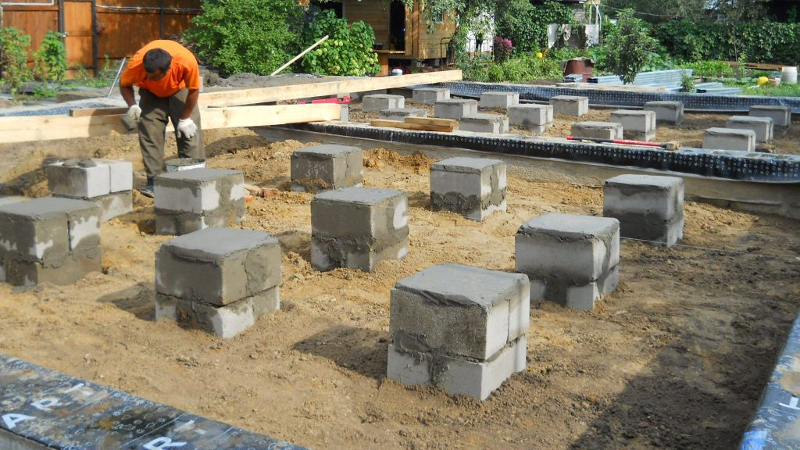 Column foundation
Column foundation
It is being built on stable soils for light buildings. The lintels between the posts can be brick, concrete, rubble. Basements with this type of foundation are not expected. This type of foundation is cheaper than a strip foundation, but it has limitations in use.
Monolithic
It is used on highly compressible soils for light (wooden) structures.
 Monolithic foundation
Monolithic foundation
In case of movement of the soil base, the monolithic slab does not allow the structure to collapse. Construction is done without the involvement of technology, planning possibilities are not limited. The disadvantage is the impossibility of arranging a basement and the high cost.
Pile
It is installed on soft moving soils for structures with high loads. The piles are predominantly reinforced concrete with a bearing load of 2 - 5 tons per unit.
 Foundation piles
Foundation piles
The pile heads are connected to form a support. Convenient in dense urban areas. Reliable and durable, does not depend on the level of groundwater. The method is expensive and is not used in private construction.
Platen
Included in the group of monolithic foundations. The base of such a foundation is the floor of the house.
 Slab foundation
Slab foundation
The foundation is expensive, it is arranged only for small houses. According to its characteristics, it corresponds to a monolithic foundation.
Floating
Such a foundation protects the building from soil deformations.
 Floating foundation
Floating foundation
It is installed on watered, weakly bearing and bulk soils.
Screw
Included in the group of pile foundations - a pile in this case is a pipe with a blade.
 Screw foundation
Screw foundation
It is used on flooded construction sites, on heaving soils, unstable soils with difficult terrain.
Types of foundations
The basis for the construction of buildings is formed taking into account the load, types of soil, structure. Depending on the type of foundation and its volume, the calculation of the need for materials is performed.
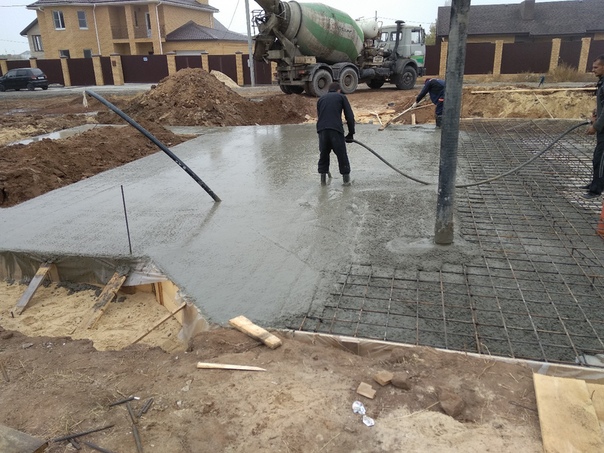
- The strip base is a closed loop made of reinforced concrete, arranged under the load-bearing and internal walls of the building. How to make a tape-type foundation mortar? To calculate the requirements for materials, you must determine the volume of each section and add them. The mixture must be poured continuously, with layer-by-layer compaction and observing the protective layer of the reinforcement.
- The columnar type of base is used for lightweight structures located on dense soils. In practice, a combination of both types of foundation is often used.
- The slab type of foundation is practiced on weak, heaving soils. Made of reinforced concrete. Pouring should be done in one go to prevent delamination of the finished structure. The concrete mixture is distributed evenly with the obligatory compaction with vibrators or bayonet.
- Pile-rammed foundations. The volume of concrete is calculated according to the geometric formula: the cross-sectional area of the well must be multiplied by the depth of the pile and by the number of rods.
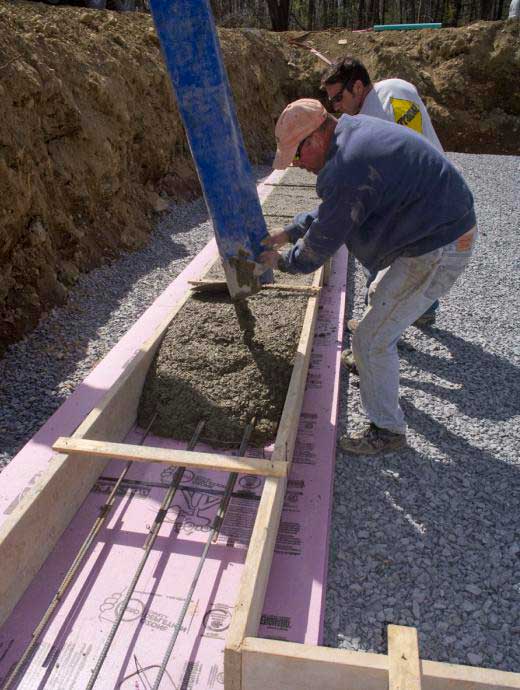
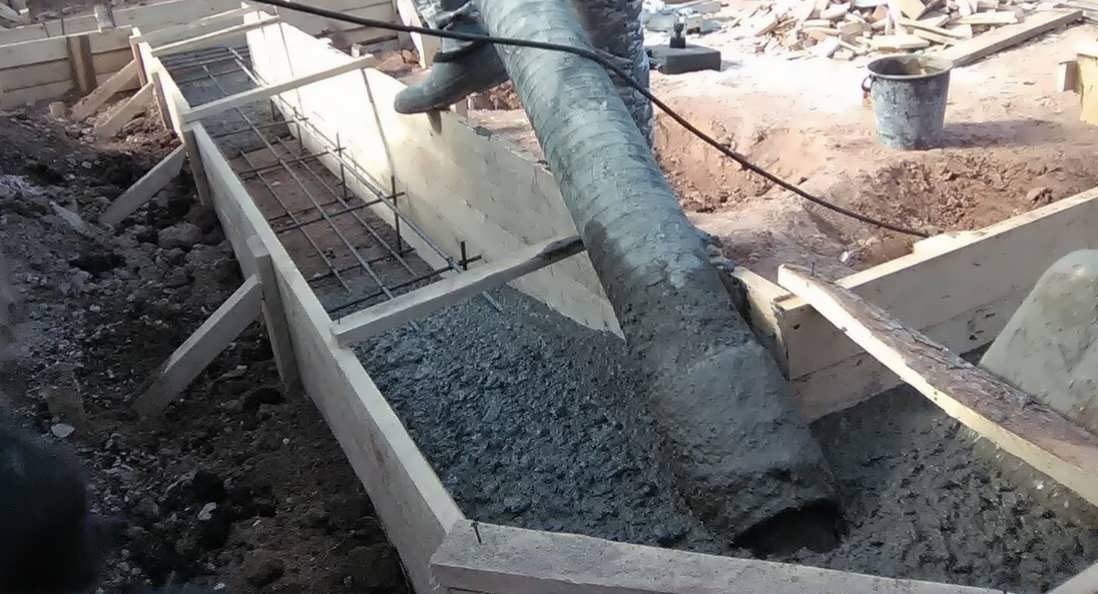
After pouring into any type of base, the concrete mixture requires moistening, otherwise the structure may crack due to the rapid drying of the top layer. The first week should be regularly watered and covered with a film or tarp.
DIY foundation concrete
You can use the materials separately or ready-made sand and gravel mixture (proportions in buckets: 1 volume of cement for 5 volumes of the mixture).
Components for 1m 3 of concrete must be mixed in the ratio:
- cement - 300-350 kg;
- crushed stone - 1200 kg;
- sand - 600-700 kg;
- water - 150-180 liters.
Calculation of the amount of cement and sand, crushed stone and water should take into account the properties of materials, their qualitative composition, the value of strength, the presence of impurities (clay particles may be in the sand).
To correctly make a cement mortar for pouring the base, dry components are poured into a concrete mixer, mixed for 2-3 minutes. Then, without stopping to interfere, water is poured in portions. It is better to dissolve the necessary additives in water first. The mixing process should not be long, 5 minutes is enough.
Methods for calculating materials
The concrete recipe for the foundation includes the following components: cement, sand, gravel or crushed stone as aggregates, water. Each component is responsible for quality. In order for the final result to meet regulatory requirements, you need to correctly perform the calculation and determine the required number of components, observing the proportions.
Calculation of components and preparation of concrete for the foundation in buckets is relevant for small volumes of construction work, where 1-4 m 3 of mortar is required. The basis for this calculation is usually the volumetric value of the cement.
What should be the ratio of sand and cement for pouring the foundation
Each component of the concrete mix differs in volumetric weight, therefore, in practice, the following proportions are used: 5 buckets of sand are taken for 2 buckets of cement and 9 are crushed stone or gravel.
The preliminary calculation of ingredients can be done using the online calculator in liters or kilograms. The calculation of emergency situations is carried out taking into account the requirements for concrete and the characteristics of the main materials.
For example, to obtain 1 m³ of concrete grade M200 in the presence of a concrete mixer for 180 liters, cement M400, sand and crushed stone, you will need:
- water - 215 l;
- cement - 233 l;
- rubble - 818 l;
- sand - 389 liters.
Under the given conditions, the calculator will calculate the need for materials for 1 batch and the number of downloads.
When it is necessary to adjust the consumption of raw materials, taking into account the operating conditions of the structure being erected, the type of mixture, the use of a plasticizer, the value of the coefficient of expansion of concrete particles, it is necessary to use the correction table.
Concrete composition for the foundation
Concrete is a material consisting of:
- Astringent. Most often it is cement (Portland cement). There is also non-cement concrete, but it is not used for foundations.
- Placeholders:
- sand;
- crushed stone or gravel.
- Water.
The grade of concrete is determined by the proportions of all these components, as well as by the conditions of its hardening (setting). Optimal conditions for concrete to gain strength are created at a temperature of + 20 ° C. Under such conditions, the process is very active in the first 7 days. During this time, concrete gains about 50% strength. With such parameters, it is already possible to continue construction further. The design strength, which is taken as 100% in design, under such conditions is recruited in 28-30 days. In reality, the process continues further, but at a very low speed. The strength gained after 30 days is not taken into account anywhere - it goes "in reserve".

At what strength can the construction be continued depending on the grade of concrete
With a decrease in temperature, the setting time increases significantly (at + 15 ° C it takes about 14 days to reach 50% strength). At a temperature of + 5 ° C, the process practically stops, and under such conditions, winter concrete is already needed - with appropriate additives and / or measures to increase the temperature (wrapped, heated in a mixer, heated through the formwork or heated directly by attaching heating cables to the formwork from the inside ).
For the manufacture of concrete, various types of Portland cement are used. The most common are:
- Portland cement - begins to set no earlier than 3/4 hours and no later than 3 hours after mixing. The end of the setting is in 4-10 hours.
- Slag Portland cement - after mixing, depending on the temperatures and parameters of the solution, it begins to set in 1-6 hours, finishes in 10-12 hours.
- Pozzolanic Portland cement - hardening begins in 1-4 hours, ends in 6-12 hours.
- Alumina cement - begins to harden in 1 hour, finishes in 8 (but not later).

The cement grade is needed for the foundation, usually M400 or M500
Any of these types of binder can be used to prepare concrete. Only you will need to take into account the setting time of the solution - you need to lay and vibrate it before hardening.
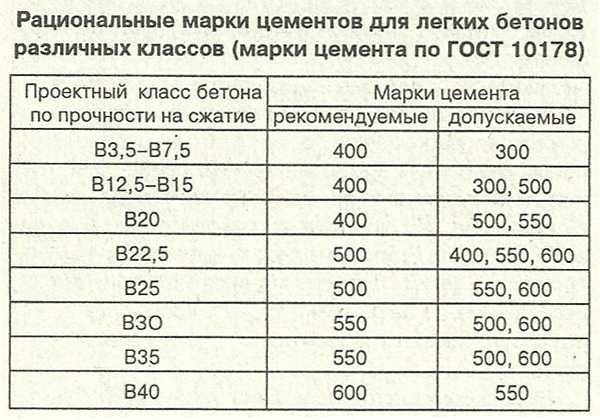
Recommended grades of cement for concrete
Placeholders
Aggregates also influence the quality of concrete. It is necessary to adhere not only to the recommended proportions, but also to quality indicators - moisture and graininess.
Depending on the size of the grains, the following types of sand are distinguished:
- large size of grains of sand 3.5-2.4 mm,
- medium - 2.5-1.9 mm,
- fine 2.0-1.5 mm;
- very small 1.6-1.1 mm);
- thin (less than 1.2 mm).

One of the components of concrete is sand
For backfilling, mainly large and medium ones are used, less often small ones. The sand should be clean - not contain any foreign inclusions - roots, stones, plant residues, pieces of clay. Even the content of dust and silty substances is standardized - they should not be more than 5%. If you decide to "extract" the sand yourself, check the amount of pollutants.
To test 200 cc. centimeters of sand are poured into a half-liter container (can, bottle), filled with water. After a minute and a half, the water is drained, poured again and the sand is shaken. The procedure is repeated until the water is clear. If there is 185-190 cubic meters of sand left cm, it can be used - its dust content does not exceed 5%.
You also need to pay attention to the moisture content of the sand. All proportions are based on dry components.
Even dry and loose sand has a moisture content of at least 1%, ordinary - 5%, wet - 10%. This must be taken into account when dosing water.
Crushed stone and gravel
Crushed stone is obtained by crushing rocks. Depending on the size of the fragments, the following fractions are distinguished:
- extra small 3-10 mm;
- small 10-12 mm;
- average 20-40 mm;
- large 40-70 mm.

Crushed stone must be used in several fractions
For the preparation of concrete, several fractions are used - so the distribution of crushed stone over the volume is more uniform, and the strength increases. The size of the largest fragments is normalized: it should not be more than 1/3 of the smallest size of the structure. With regard to foundations, the distance between the reinforcement rods is taken into account. SNiP also determines the amount of small crushed stone: it must be at least 1/3 of the total volume.
Gravel has approximately the same fractions and sizes, but when it is used, the water-cement ratio (water / cement or w / c) increases by 0.05 (5% more water must be poured).
For the preparation and watering of concrete, potable water is used. Including the one that can be drunk after boiling. Sea water can be used with Portland and alumina cement. Any other industrial water is not suitable.
What brands of concrete to choose for the foundation of a 2-storey building
A two-storey house is no longer a symbol of the fact that its owner has a high social status. For some time, an increasing number of householders prefer to build exactly two-storey residential buildings, thus saving the area of their land.
And when the construction of a two-story building is completed, its owners have a fairly large housing area and a spacious adjoining territory. But there is one nuance here - in all multi-storey buildings, including two-storey ones, a high specific load is created on their foundation.
That is why developers must first of all find an answer to the question that arises - which concrete is preferable to use in order for the base of a two-story mansion to be strong and reliable, to last a long time?
Deciphering the main characteristics of concrete
Regardless of the price and the manufacturer's firm, the main characteristics of concrete include:
- Mobility.
- Waterproofing.
- Frost resistance.
- Brand and class.
In concrete marking, the number is indicated after the letter "M" and denotes the strength factor, that is, the load that the mortar can withstand.This characteristic is very important and should be considered in more detail. So what kind of concrete is needed for the foundation of a two-story house?
The use of various grades of concrete in construction:
- M100 - Known to all "weaving". In fact, this is the worst class that can be used in private construction. For serious construction, such as laying a reliable foundation for a two-story building, it certainly will not work. So we immediately "throw" this option aside. If it can be useful for anything in home construction, it is when laying the foundation of small outbuildings or for the foundation of a fence. It is also used as a 10 cm cushion before placing the base mortar. In this situation, it can be used when erecting the foundation of a suburban 2-storey building.
- М150 - Practically no better than the previous version. For our main purpose, it is also not suitable, since the future construction will be quite heavy. It is useful for building a small summer house or garage from lightweight materials. Much may also depend on the nature of the soil that is available on your site. In the case of rocky ground, it is quite realistic to use this brand of concrete for the foundation of a 2-storey building. However, it is better not to save money and not take risks and move on to considering the following options.
- М200 - М250 - This type of concrete is often selected for construction. But its use is acceptable only when erecting structures from light materials: foam block or frame-shield. A prerequisite for the use of concrete of this brand is rocky or sandy soil, as well as the condition for a small rise in groundwater.
- M300 - Universal concrete for all types of strip foundations. On stable soils, not heaving and not floating, it can be used for the construction of 3-storey houses, if they are not heavy and bulky. Otherwise, if the construction is planned to be too massive, it is necessary to use concrete of a grade not lower than M350 for the foundation. It is very durable, not sensitive to humidity and temperature extremes.
- M350 and above - Rarely used in private construction. Their high strength is indispensable in industrial construction. In individual construction, for houses up to 2 floors, such concrete is simply not in demand. Concrete of such grades has a very short setting time, therefore, only specialists can cope with them. The price for such concrete is much higher than for M300. In our case, concrete of grades M350 and higher is not an option.
Summing up, we can say that for frame 2-storey houses it is recommended to use concrete of the M250 brand. If the house will be built from a bar - M300.
Aggregates - crushed stone and sand
The composition of concrete is determined by those functions and characteristics of concrete that are necessary during its operation. The most common are sand and gravel. They are subject to no less stringent requirements than the quality of cement. Sometimes pebbles are used, but only if they have sharp edges, and not round ones. In the presence of broken lines, the adhesion of the aggregate to the mortar is better, as a result, the strength of the concrete is much higher.
Sand
Construction sand can be river or quarry. The river is more expensive, but it is usually cleaner and has a more uniform structure. It is better to use it when drawing up concrete for pouring the foundation, screed. For masonry or plastering, it is appropriate to use cheaper quarry sand.
In addition to its origin, sand is distinguished by fractions. Large or medium-sized ones are used for construction work. Small and dusty ones are not suitable. The normal size of sand grains is from 1.5 mm to 5 mm. But optimally in solution, it should be more homogeneous, with a difference in grain size of 1-2 mm.
The sand should be clean, preferably with the same grain size
The purity of the sand is also important.It definitely should not contain any extraneous organic inclusions - roots, stones, pieces of clay, etc. Even the dust content is normalized. For example, when mixing concrete for a foundation, the amount of contamination should not exceed 5%. This is determined empirically. 300 ml of sand is poured into a half-liter container, everything is filled with water. A minute later, when the grains of sand settle, the water is drained and poured again. This is repeated until it is transparent. After that, it is determined how much sand is left. If the difference is not more than 5%, the sand is clean and can be used when mixing concrete for the foundation.
For those works where the presence of clay or lime is only a plus - when laying or plastering - there is no need to take special care of the cleanliness of the sand. There should be no organic matter and stones, and the presence of clay or lime dust will only make the solution more plastic.
Crushed stone
For responsible construction - floors and foundations - crushed crushed stone is used. It has sharp edges that adhere better to the mortar, giving the structure more strength.
Crushed stone fractions are standard:
- extra small 3-10 mm;
- small 10-12 mm;
- average 20-40 mm;
- large 40-70 mm.
In the batch, crushed stone is used in several fractions - from small to large
Several different fractions are used simultaneously in concrete. The largest fragment should not exceed 1/3 the size of the smallest element of the structure to be filled. Let us explain. If a reinforced foundation is poured, then the structural element that is taken into account is reinforcement. Find the two closest elements. The largest stone should not be more than 1/3 of this distance. In the case of filling the blind area, the smallest size is the thickness of the concrete layer. Choose crushed stone so that it is no more than a third of its thickness.
Fine crushed stone should be about 30%. The rest of the volume is divided between medium and large in an arbitrary proportion
Pay attention to the dustiness of crushed stone. Lime dust is especially undesirable.
If there is a lot of it, the crushed stone is washed, then it is dried, and only after that it is poured into concrete.
Storing placeholders
It is clear that the construction site is not the cleanest and most equipped place, and sand and rubble are often dumped directly onto the ground. In this case, when loading, it is necessary to ensure that no earth gets into the batch. Even a small amount of it will negatively affect the quality. Therefore, it is advisable to pour aggregates onto solid areas.
It is also necessary to protect them from precipitation. In concrete formulations, the amount of constituents is given in terms of dry components. Taking into account the moisture content of components is learned with experience. If you don't have one, you have to take care of the condition and cover the sand and rubble from rain and dew.
Requirements for the components of the concrete mix
The composition of concrete contains four components: cement, crushed stone, sand, water. The main thing is that the concrete must exactly match its brand in terms of strength. Briefly requirements for each material:
Cement
Active component of concrete. For foundation concrete, cement M400 or M500 is used (not to be confused with the concrete grade!).
 Cement
Cement
The selected cement should have a minimum shelf life (for a month of storage at a temperature of 20 ° C indoors, M400 cement loses its properties by a quarter, when stored outdoors - by half).
Crushed stone
A filler that provides concrete strength. For a reinforced structure, which is the foundation, according to the norms, a crushed stone fraction of up to 40 mm is needed. To select the desired fraction, you need to take into account the minimum distance between the reinforcing bars. The selected crushed stone of the maximum fraction should not exceed this distance by more than ¾.
 Granite crushed stone
Granite crushed stone
It is preferable to use crushed granite or crushed gravel 5 - 20 mm for pouring the reinforcement cage and 20 - 40 mm for pouring over the ground. Limestone crushed stone can only be used to prepare concrete for foundations on dry soils.
Sand
Quarry sand is suitable - it should be washed and sieved with a minimum amount of clay impurities.
 Building sand
Building sand
River sand is finer and usually contains a lot of clay, which is undesirable for concrete production. If there is no choice, then the river sand should be thoroughly sieved and washed.
Water.
Clean water without biological impurities, petroleum products, oils. Typically tap water is used.
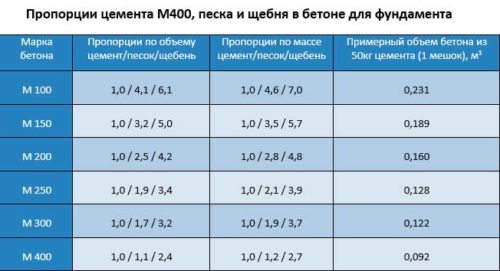
The ratios of the components of the concrete mix of various brands are shown in the table:
Making concrete at home can be seen in the video.
The main characteristics of concrete
- class / brand;
- water permeability;
- frost resistance.
Based on these indicators, the abbreviations of the class and grade of concrete are deciphered. The number following the letter "M" means its strength factor, that is, the load that it is able to withstand.
The first concrete grade used in construction is M100, called "weaving" in everyday life. This concrete with the lowest characteristics, which is allowed to be used in the construction of private buildings on sandy soil.
However, given that the required brand for a two-story house is currently being selected, it should be noted that such material cannot meet the reliability requirements. It is needed rather for the foundation of a fence or small ancillary buildings made of lightweight materials. It is also used when installing a cushion of a shallow strip base before pouring the base solution. Such a thickness of the base for a two-story house is quite possible.
Ready-mix concrete (М200)
Concrete 200 - 250 is a material that is often chosen for foundations on a sandy base. If the building is supposed to be on a sandy or rocky area and is erected from foam blocks or shields, then this is the best option for concrete. An additional condition for this choice is a slight rise of water in the ground.
Concrete grade 300 is universal for the construction of tape-type foundations. It can be used even for the construction of buildings with a higher number of storeys on sandy soil, provided that its thickness is calculated, and the soils are not heaving and not floating.
In the case of designing higher structures, a higher grade is chosen - M350. It tolerates temperature changes well, does not react to fluctuations in humidity levels and has a good strength indicator - 327 kgf / sq. Cm.
Higher grades are rarely used for individual development. This material has excellent strength characteristics and is successfully used in industrial scale construction. It quickly grasps and requires the knowledge of professionals to work with it. In addition, the use of such a mark may incur additional costs.
Output
 For the foundation under a small frame house it is preferable to choose concrete M250 with your own hands. For a two-story building made of timber or foam blocks, it is advisable to use a brand of at least M300, and for a monolithic or brick structure - at least M350.
For the foundation under a small frame house it is preferable to choose concrete M250 with your own hands. For a two-story building made of timber or foam blocks, it is advisable to use a brand of at least M300, and for a monolithic or brick structure - at least M350.
There are a few more points that must be taken into account when choosing the appropriate material for the foundation of a two-story brick house, especially if you plan to independently mix the mortar:
- The release date of the cement should be checked before purchasing. In case of violation of the conditions or storage time, the material can significantly reduce its characteristics.
- It is necessary to check crushed stone and sand for impurities. Their high content can lead to a decrease in the quality of concrete.
- Thoroughly mix all loose components in dry form and only then mix it with water.
- Use water without third-party additives.
And finally, the worse the soil on the building site, the more carefully the thickness and depth of the foundation for a two-story house should be calculated.In addition, for houses with several floors, higher requirements for the characteristics of the concrete mortar must be made. If your site is located not on sandy, but on clay soil, then the threat of heaving is likely, which means that concrete of a higher grade should be selected. If the soils are sandy, then M250 will be enough.
The last, but very important factor in the selection of concrete for a two-story brick cottage is the identification of the presence of salts. In order to cope with the aggressive effects of these components, a special additive is added for additional resistance to sulfates.
Despite the fact that this component is quite expensive, it should not be neglected. The resulting solution will resist well the destructive effect of soil salts and will preserve the foundation for a two-story house.