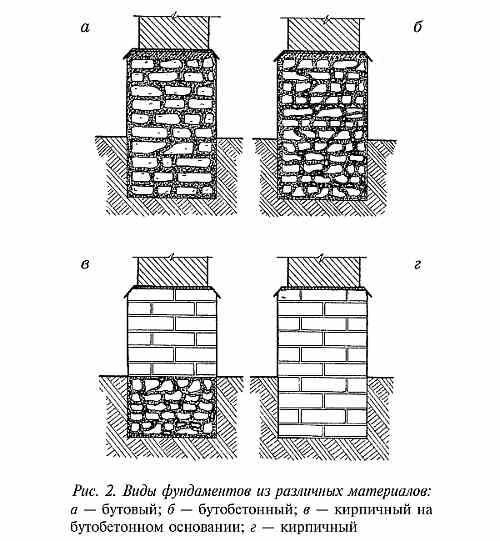
Rubble stone: description and characteristics
Any debris of rock is called a rubble stone. On this basis, the material is divided into magmatic, metamorphic and sedimentary. It can be obtained naturally or artificially. By appearance and purpose, rubble stone is divided into three groups:
- Rounded has a naturally oval shape. It is mined in river beds. Such material is used in landscape design.
- Industrial has maximum strength and frost resistance. Rubble stone of this type is used for the construction of dams and dams or for strengthening the railway track.
- Pastel has two parallel edges - pastels. It is convenient for laying fences, foundations or exterior walls.
It is most convenient to work with pastel rubble stone.
Specifications
The main characteristics of rubble stone are set out in GOST 2173-87. The following properties can be distinguished:
- The weight of the material depends on the rock from which it is obtained. A cubic meter of a light stone weighs 1300 kg, a heavy one - 3 tons. One element can weigh up to 55 kg.
- Frost resistance indicates the number of freeze / thaw cycles that a rubble stone can withstand. The maximum indicator is F400. This material is suitable for the most severe climatic conditions.
- Strength directly affects the service life of the rubble stone. The lowest indicator is M200. This material can only be used for decorative purposes. The highest is М1400. This type of stone is suitable for the construction of roads or bridges.
- Bulk density is important for the correct calculation of the required amount of material. The normal rate is 1.4–1.9 t / m3.
- Radioactivity is a material safety parameter. Only first class rubble stone is suitable for use in residential areas.
Rubble stone is perfectly combined with other building materials
Features of the device
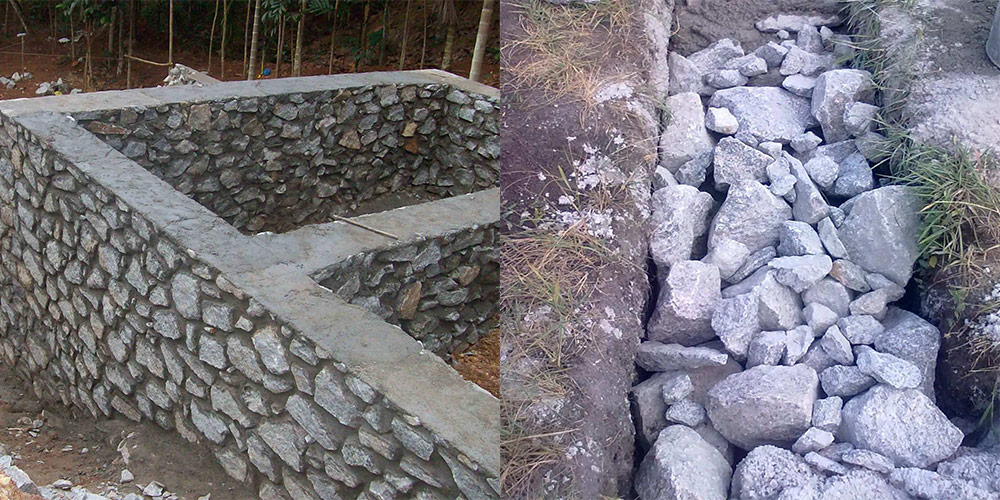
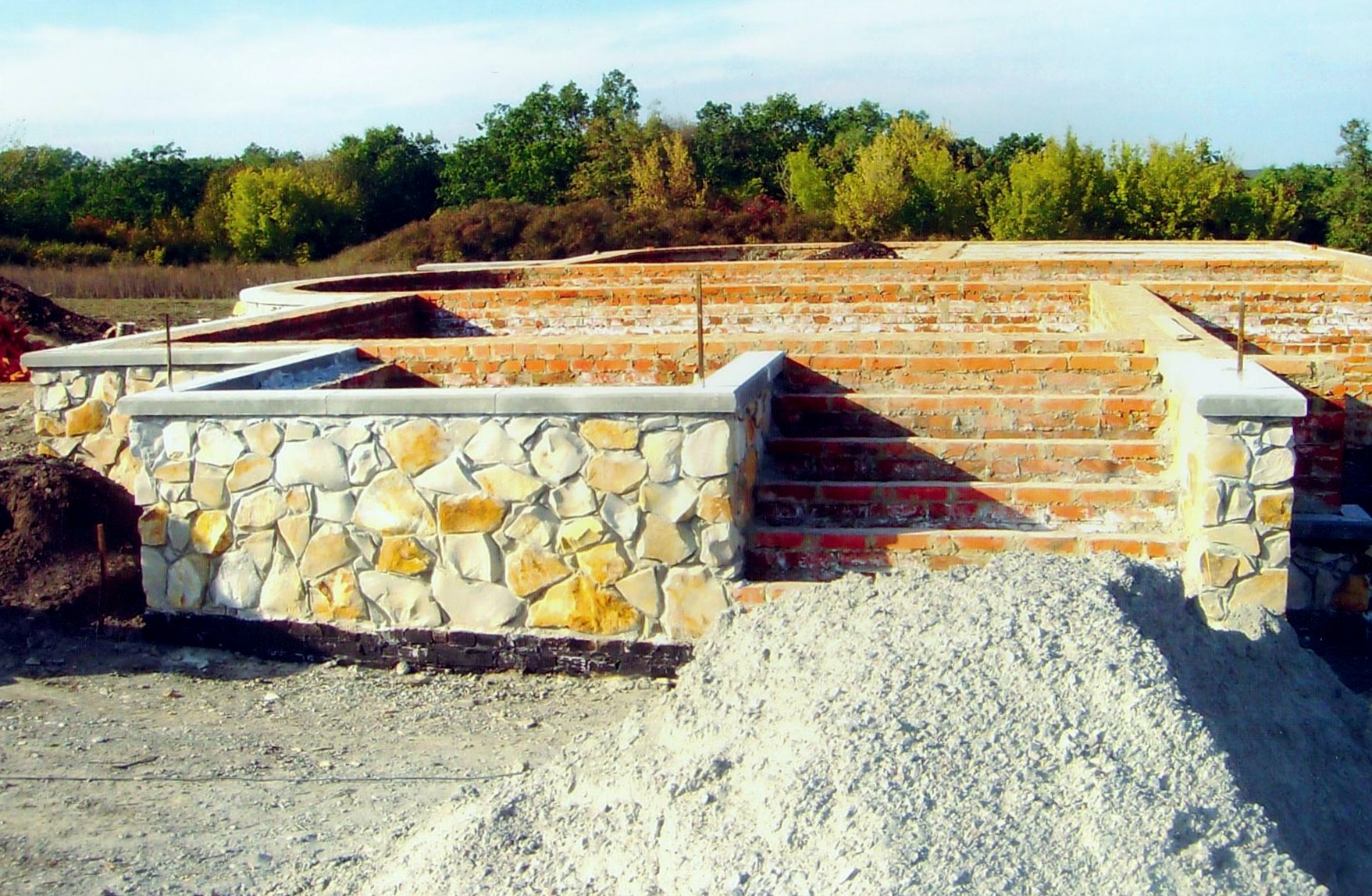
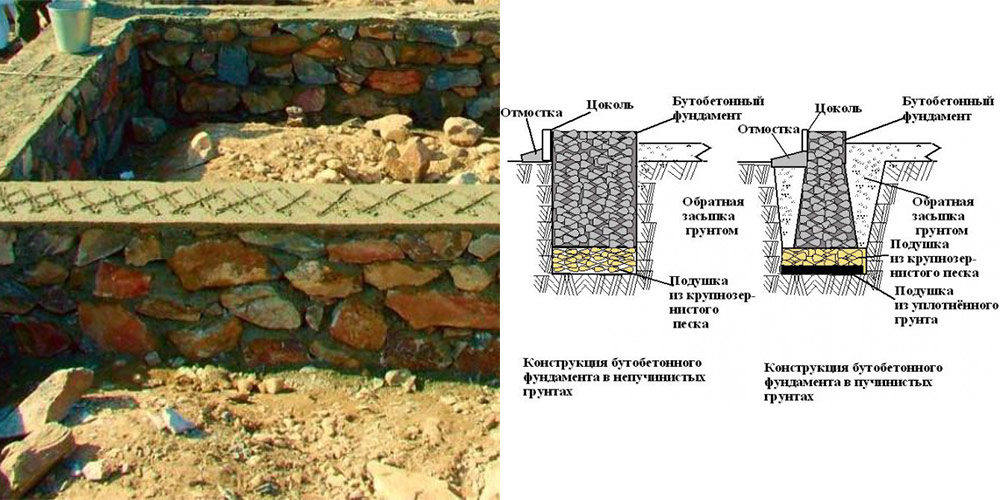
Since rubble is a large-sized stone, you will not be able to make a foundation less than 35 centimeters wide from it. Consider this point before starting excavation work. The optimal width of the "tape" made of rubble (the stone is laid in two parallel rows) is 45-55 cm.
In order to prevent seasonal fluctuations of the soil from destroying the masonry, a "pillow" is poured on the bottom of the trench, consisting of a layer of sand and a layer of rubble. Its thickness after compaction should be within 15-20 cm.
The rubble foundation is buried in the ground below the seasonal freezing mark in order to eliminate the effect of frost heaving forces.
If the work is carried out in dense soil, then it is not necessary to put the panel formwork in the trench. In this case, the foundation is made using the "vaspor" technology, laying the quarry close to the walls of the trench.
The classic laying of rubble foundation is carried out in layers. Before laying the first layer, experts recommend laying dense polyethylene on a sandy pillow. It will not allow the cement laitance to leave the solution, to reduce its strength. The booth is placed in two parallel lines, leaving a 3-5 cm gap between the stones for pouring the mortar. The upper row is laid with the bandaging of the lower one: the stones should overlap the lower seams.
For the preparation of a strong potting solution, fresh cement of the M-500 brand is used. The proportion is selected in the following ratio: for 1 part of cement, 3 parts of sand. The consistency should be creamy for good penetration into the seams.
Before laying the stones, moisten them a little with water. This will remove dust and improve adhesion to the mortar.
Materials and tools required for the manufacture of concrete foundation
Nowadays, rubble concrete foundations are increasingly being chosen in private construction.
Its benefits are obvious and attract the attention of developers. The production technology of work is deeply studied and it is easy to transform it for a specific object
A special rubble concrete mixture is prepared from prepared components, which must correspond to the brands and quality laid down in the project. Half of the volume of the prepared mixture is concrete, and the second part is a special rubble stone. For each of the ingredients, the corresponding technical requirements are set, which determine the characteristics of the future building.
In the standard construction technology, it is allowed to reduce the component of the stone up to 40% of the volume.
A concrete strip foundation is made of concrete, the grade of which should be M-400 or M-500. Crushed stone is used in small formations, no more than 3 cm. The proportions of crushed stone, sand and cement should be 5 to 3 to 1. With the help of water, they reach the required consistency of the solution. It depends on the future construction technology, as well as on the use of a special rammer or vibrating plate.
The production methodology does not differ from the standard approach to the construction of a strip monolithic base and requires the same tools.
How to make a rubble foundation in the summer and masonry intermittently
Are there possible breaks in the production of rubble masonry?


Breaks in the production of rubble masonry are allowed only after filling the gaps between the stones of the last laid out row with mortar. The solution is used to cover the surfaces of the stones of this row only when the masonry is renewed. In dry, hot and windy weather, the masonry is protected from rapid drying by covering it with shields or roll materials. When erecting rubble concrete foundations, stones and debris from the dismantling of the masonry laid into the concrete mixture must not be contaminated, otherwise they will not have strong adhesion to the concrete. In dry weather, the fragments are poured with water before placing in the concrete mixture. To ensure the solidity of the masonry, work breaks are arranged only after the stones are embedded in the upper layer of the concrete mixture and compaction. During breaks in laying the foundation in dry summer weather, rubble and rubble concrete masonry is moistened 3-4 times a day by sprinkling with water.
What are the conditions for laying foundations in hot weather?


When performing work in summer in hot weather (at an air temperature of 25 ° C above and a relative humidity of the outside air of less than 50%), the following conditions must be observed: the water-removal ratio of solutions prepared on slag and pozzolanic Portland cements must be increased; the water-holding capacity of each of the compositions of the solutions must be installed at the facility at least once per shift, while the value of the indicator must be at least 75% established in laboratory conditions; the delamination value should be no more than 25 cm3 for solutions with a mobility of 10-12 cm and no more than 40 cm3 for solutions with a mobility of 12-14 cm; clay brick must be abundantly wetted with water before being laid in the structure.
What kind of cement can be used at air temperatures above 25 ° C?


When performing concrete work at an air temperature above 25 ° C and a relative humidity of less than 50%, fast-hardening Portland cements should be used, the grade of which should exceed the grade strength of concrete by at least 1.5 times. It is impossible to use pozzolanic Portland cement, slag Portland cement below M400 and alumina cement for concreting above-ground structures, except for the cases provided for by the project. The temperature when concreting structures with a surface modulus of more than 3 should not exceed 30-35 ° C, and for massive structures with a surface modulus of less than 3 should not exceed 20 ° C.
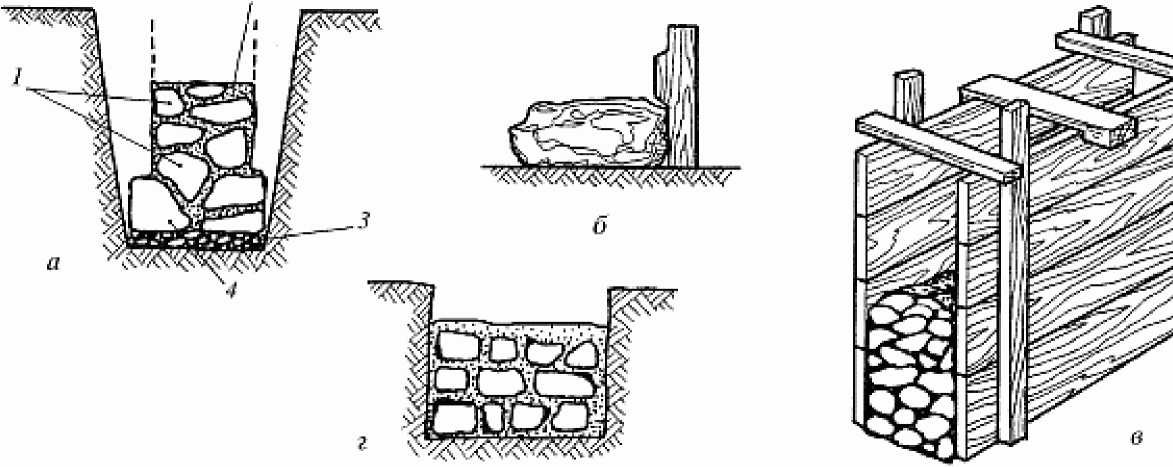
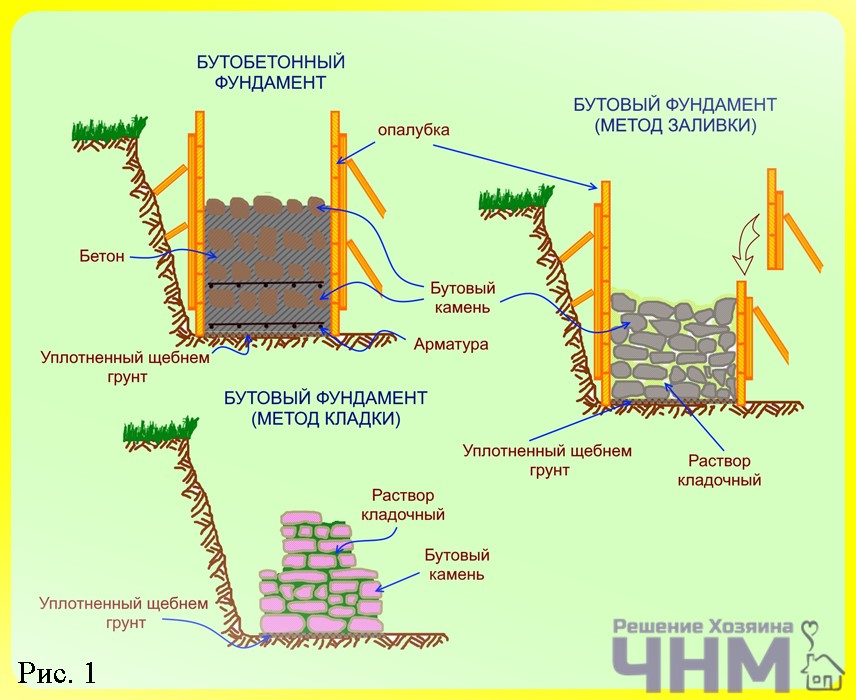
Laying stone under the bay
There are several ways of laying natural rubble stone.For a rubble strip foundation, 3 types of masonry are suitable: under the bay, under the bracket and under the scapula. Let's consider the first method first. It is suitable for small buildings with a height of no more than 10 m and always with good, stable ground. The first step is to install the formwork.
Table of design resistance of collapsing soils.
This is followed by the laying of natural rubble stone. Torn and cobblestone is used as it. The selection of a stone is not carried out. The first layer is laid without mortar. A layer of rubble is placed on it. The layer is carefully rammed. The thickness of the crushed stone can be 5-10 cm.
After the surface is compacted, the filling is carried out with the previously prepared mixture (cement mortar). This is necessary for greater tightness and filling of voids. Each row is placed on the previous one in a dry state and only after tamping with a sledgehammer is it poured with a solution. The thickness of each layer is 20-25 cm. It is advisable to use a device such as a vibrating compactor, with which it is possible to distribute the solution to a greater extent over all voids. All this increases the strength and reliability of the foundation.
Construction of rubble concrete foundation
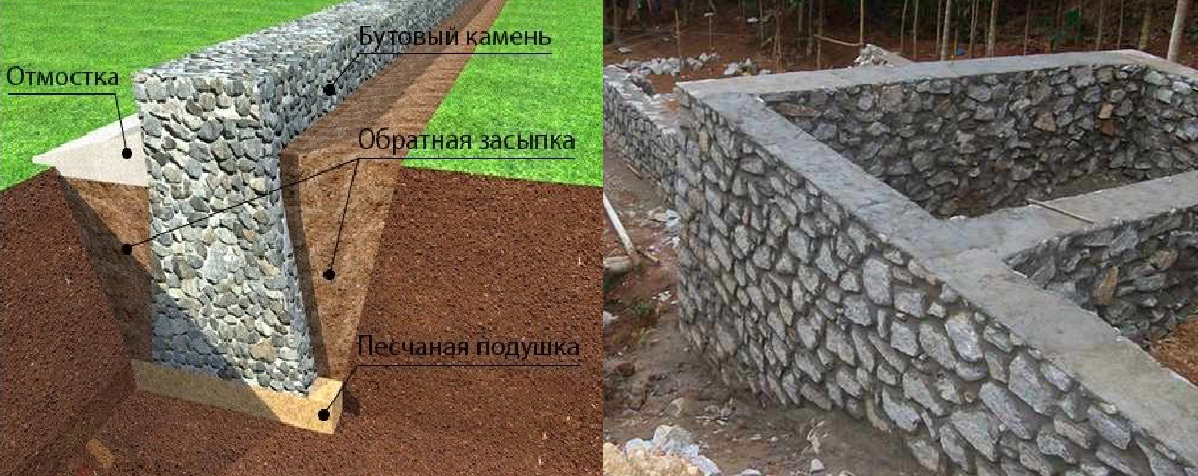
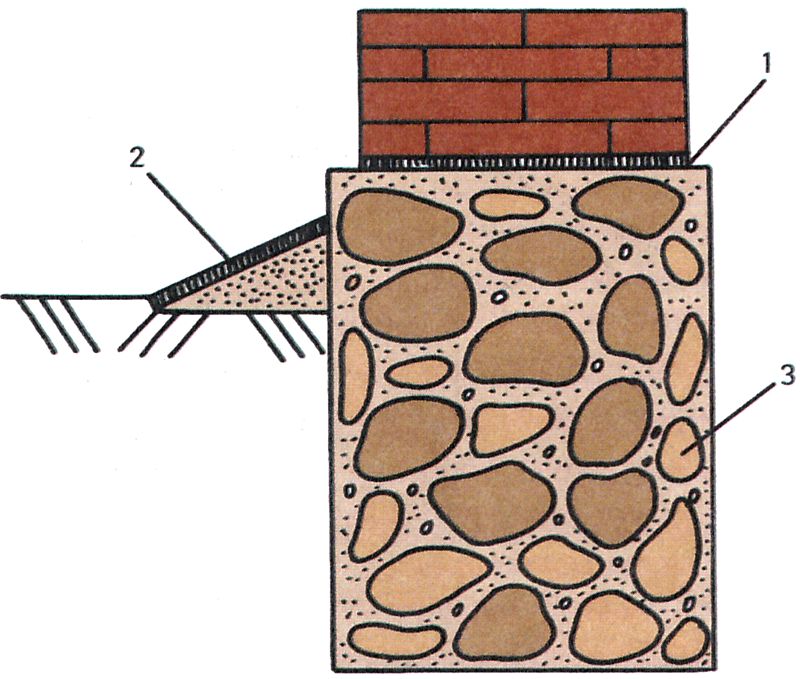
A concrete foundation differs from rubble in that it is made from the same mortar from which concrete is made. But instead of crushed stone, brick battle, rubble stone, half-bricks are added to the mixture. The rubble concrete foundation is also laid in layers - first a layer of mortar 10 cm thick, then a layer of filler 15-20 cm thick, etc.
A diagram of the construction of a concrete foundation for brick walls is shown in the figure below:

As you can see, a sandy sand cushion is arranged here, which makes it possible to more evenly redistribute the loads from the structure to the base soils.
However, attention should be paid to the composition of the base soil when arranging such a sand bed. If the soil filters groundwater well, then bedding will be an excellent solution, helping to remove excess moisture from under the base and redistributing the loads from the building
However, if the building is being erected on a clay base that does not filter water well, the bedding should be minimal or abandoned in order not to create a pocket where moisture will accumulate, washing away the foundation soils, and in winter such an accumulation of moisture can become a factor that increases the value heaving. Be sure to remember this!
Choosing a stone for the foundation
Before building a strip-rubble foundation, you will need to select the main building material. Choosing a stone is an easy task
It is important to know that a natural stone with a bearing capacity of at least 100 kg / cm² is suitable for these purposes. For rubble natural stone, some features are characteristic
Firstly, it means any natural stone that has an irregular shape, weighing up to 30 kg, used in the construction industry. Secondly, it has found wide application not only for this type of work, but also for the construction of basement walls and retaining walls. Thirdly, the advantages of the stone include its high bearing capacity and great strength, and the disadvantages - the difficulty of laying.
Construction of rubble foundation: masonry "under the blade", "under the bracket" and "under the bay"
The foundation of a house made of rubble stone is usually performed in the following ways: "under the shoulder blade"; "Under the bay"; "Under the shoulder blade".
What are the requirements for laying foundations "under the blade"?


Rubble masonry "under the shoulder blade" is performed in horizontal rows 25 cm thick with the selection and pinning of stones, cleaving (filling) of voids and bandaging the seams. The first bottom row is laid on a prepared base dry from large bedded stones facing down with the bed. In order for the stones to fit snugly to the base, they are upset with a rammer.
Then the voids between them are filled with small stones or crushed stone and poured with a liquid solution (with a cone draft of 13-15 cm) until all the voids between the stones are filled. When laying rubble stone, the chipped stone is also compacted by ramming. Further, the laying is carried out in order, observing the dressing on a plastic solution. The mobility of the masonry mortar should correspond to the immersion of the reference cone by 4-6 cm.
In what order are rubble foundations "under the shoulder blade" laid out?
Each subsequent row begins with stacking versts. Before the construction of the inner and outer versts at corners, intersections and every 4-5 m on straight sections of the wall, lighthouse stones are laid on a solution. On them, on both sides of the masonry, the moorings are pulled, along which the horizontal row and straightness of the front surface of the foundations and walls are checked. Stones for verst rows, selected in height, are first laid out dry in order to find the most stable position in the masonry. Then the stone is lifted, a layer of mortar with a thickness of 3 ... 4 cm is laid and the stone is finally installed, settling it with a hammer.
What is Cyclopean rubble masonry?


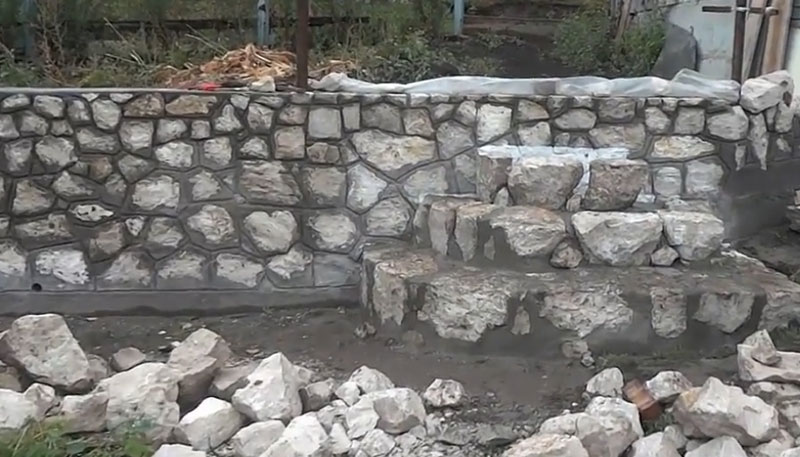
To create a decorative surface when constructing a rubble foundation, a cyclopean masonry is used, which is performed using the "under the blade" method. Specially selected stones are placed in the front surface of the masonry, placing them in vertical rows so as to create a pattern from the seams between them. These seams are also made convex (2-4 cm wide) and embroidered. In this case, roughly hewn stones are used for laying the corners, tying them up with the masonry of the wall.
How do you lay the foundations "under the bracket" and "under the bay"?


Masonry "under the bracket" is used for the construction of walls and pillars. This masonry is a kind of "under the shoulder" masonry, it is made of stones of the same height, selected using a template.


Laying "under the bay" is made of ragged rubble or cobblestone without the selection of stones and laying out verst rows. For this, formwork is made in the trenches after the end of the earthwork. If the soil is dense, then with a trench depth of up to 1.25 m, it is possible to lay the masonry without formwork with the walls of the trench. The first layer of rubble stone with a height of 20-25 cm is laid on a dry base without mortar, a spar with walls and compacted with tamping. Then fill in all the gaps with small stone and crushed stone. The laid layer is poured with a liquid solution so that all voids are filled. Subsequent laying is carried out in the same way in horizontal rows 20-25 cm high, filling each row of masonry with mortar. Rubble masonry "under the bay" is allowed only for foundations of buildings up to 10 m high and only when building on non-subsiding soils.
Watch the video of laying rubble foundations in the above ways:
Erection
We proceed directly to laying the stone. You will not find any one step-by-step instruction, since there is more than one technology for creating a foundation from a rubble. More precisely, there are three of them: "under the bay", "paddle" and "bracket". Each of them has its own characteristics and - in our case - the right to be considered.

You have probably noticed that in the preliminary work there is no point about creating the formwork. The fact is that not in all cases it is required.
So, in the case of masonry "under the blade", it is needed only when a smooth foundation surface is needed - for example, for finishing or for strengthening the foundation (and this is important when it is created independently). But "for pouring" the formwork is always done
Before telling how to make a foundation for all these technologies, one more detail needs to be mentioned. The long side of the stone is called the spoon, and the short side is called the poke. It is these names that are found both in conversations and in articles.
Now let's move on to the methods. As we said, there are only three of them. There is nothing difficult in them, upon closer examination it will become clear. So, let's begin.
"Under the shoulder blade"
Here the work is carried out as follows:
- First, the butt row is laid dry.
- The stones are rammed, the voids between them are filled with rubble.
- The row is filled with solution.
- The butt row is laid. Its thickness, like the previous one, is approximately 30 cm. The height must also be observed: it should be approximately the same.
"Under the bay"
As already mentioned, in this case, formwork is definitely needed. Here, the size of the boot is not so important. This method is rarely chosen, since such a foundation has a rather low strength. Therefore, fences are often erected on them, the maximum is light frame baths. The technology looks like this:
- The butt row is laid, chipped, rammed and poured with a solution (75% sand and 25% cement, that is, 3: 1).
- A spoon row is laid, then all procedures are repeated.
- The top layer is filled with an approximately half-meter (from 40 to 60 cm) layer of the mixture with a cone draft of up to 6 cm and compacted until the solution can penetrate into the masonry.
Mounting
As already mentioned, you can make a do-it-yourself concrete foundation, it is important to adhere to certain rules and sequence
Preparatory work and foundation analysis. You need to find out about the presence of groundwater, remove the top fertile soil layer, remove all driftwood and roots from the area;
The excavation of the pit should be carried out taking into account the height of the underground part of the structure plus the thickness of the pillow - sand and crushed stone, about 20 cm.At the same stage, in the presence of high groundwater, drainage pipes are laid into the depression with an outlet to a well or a ditch;
Cushion embankment with compaction;
Next, the formwork is installed along the width of the tape under the outer and inner walls.
It is important to make lintels at the top of the form and spacers on the sides so that heavy stones do not change the shape and integrity of the formwork;
The compacted sand and crushed stone must be fixed with M75-M100 concrete with a layer of 2-5 cm. It simultaneously serves as a part of the cushion under the tape and prevents the introduction of rubble stones into the base;
When the bottom layer grasps, cement-sand mortar (cpr) M350-M400 is poured in an even layer of about 20 cm
The first layer of stones is evenly laid so that there is an average distance of 5 cm between them. The booth should protrude about half above the solution. If the stones are small, the thickness of the mortar filling should be made smaller;
The cpr is poured so that the bottom row is closed, and the liquid layer is, again, half the thickness of the next masonry of stones. If necessary, a reinforcing cage is mounted;
The steps are repeated until the top mark, with the final fill level to create a smooth mounting surface. Poured with water.
Secrets of the construction of a concrete foundation:
- Stacking of stones should be carried out immediately after pouring the solution, until it grabs, that is, you need to work at a pace;
- You need to select a bottle in shape so that it evenly fills the volume of the formwork without the formation of voids;
- Poured concrete is pierced with a piece of reinforcement or a wooden stick to expel air bubbles from the mass;
- When working in cold weather, the structure must be well insulated for the first time until the strength gains%, in warm weather it must be watered in a timely manner and kept under a film to avoid drying out.
As you can see, it is not difficult even for a non-professional to equip a rubble foundation, it is important to correctly determine the size of the tape, prepare the stones and seal the cement mortar. The result is a durable and reliable design.
Before laying the walls, the surface of the foundation is covered with waterproofing.
Construction rules and quality control of foundations
What are the rules for making rubble masonry?
Rubble laying of foundations is laborious work, associated with weight lifting. Before and during the laying of foundations, the strength of the fastenings of the walls of trenches and pits is regularly checked.In the absence of fastenings in trenches and pits or with fastenings that are not designed for heavy loads, materials and rolling passages are located outside the soil collapse prism. The distance from the edge of the slope or fastenings of the trench (pit) to the stacks of materials is determined by the foreman or foreman. According to the rules for the construction of foundations, it is not allowed to throw stones into the trench. The stone is fed through the troughs; there should be no workers in the trenches at this time. When working in trenches or pits, make sure that the curbs at a width of at least 50 cm are free of materials. Fasteners of the walls of pits and trenches are removed as the foundations are being erected. The lower struts are removed only after installing the upper ones; at the same time, only one or two fixing boards are removed in height, otherwise the soil may collapse. For lowering workers into trenches (pits), as well as for lifting them on the platform, step-ladders 0.75 m wide or ladders with handrails are installed. In winter, they are regularly cleaned of ice and snow.
How to organize the workplace of bricklayers performing the laying of rubble and rubble concrete foundations?


Before making a rubble foundation, they prepare stones, install boxes for mortar, gutters and shovels for lowering the stone and mortar. When rubble laying foundations "under the scapula" in trenches up to 1.25 m deep, mortar boxes are placed on the edge of the trench 3-5 m from each other, and stacks of rubble stone are placed between them. The stone from the pile is fed into the hands of the bricklayer, and the mortar is thrown with a shovel-bucket directly onto the masonry. For laying foundations in trenches and pits with a depth of more than 1.25 m, stocks of stone and crushed stone are placed next to the edge of the trench, and mortar boxes are placed in the trench directly on the masonry. The solution is lowered into boxes along trays set at an angle of 40-50 ° to the horizon so that it does not fall, but slides smoothly. To lower the stone into the trench, gutters with a section of 40 × 40 cm are installed.
How is the quality of rubble masonry of foundations ensured?


Laying begins from lowered areas. The transition from one foundation depth to another is performed with ledges. In each ledge, at least two rows of masonry must be laid, which, depending on the size of the stone, 35-50 cm. The stones of the upper row of each ledge are tied up with the overlying masonry. The masonry is laid in tiers of 0.8-1 m. The height of the gap at the boundaries of individual sections of the masonry should be no more than 1.2 m. The breaks are laid out in the form of a shelter with ledges having a height-to-length ratio of 1: 2 or 1: 1. The breaks in the masonry between adjacent sections are made in the form of ledges - in layers, as in the case of rubble masonry. Quality control of the foundation made of rubble and rubble concrete is carried out using the same measuring instruments and the same techniques as the quality of brickwork.
Distinguish rubble stone by shape
When choosing a boot for the base, you need to decide not only the type of breed, but also the shape.
Depends on the form:
- the convenience of masonry, which affects the time of work;
- appearance;
- cement mix consumption.
Rounded but

Stone that is mined in the surf zone, in places of glaciers of today or during the Ice Age.
Such a stone has a rounded, rounded shape. Such a boot is poorly suited for the foundation.
Bed quarry

A booth, two sides of which approach parallel ones, are called bedded. It turns out something like an uneven natural brick (if you look uncritically). Thickness not less than 70 mm.
Unlike rounded, bedded quarry is the most convenient for laying, it also allows dry laying (without mortar).
Breeds from which bed quarters are obtained:
- Sandstone
- Limestone
- Layered rocks of a stone
Industrial booth

Natural stone, mined by blasting. After sorting into fractions, it goes into sale. Has a "torn" shape
Types of masonry
The masonry is divided into two types.Rubble consists exclusively of rubble. Rubble concrete masonry implies filling the building material with cement. The type of foundation is preferably strip. Columnar is not used universally, since the process of the necessary raw materials can take a long time.
Reclaimed tape masonry has the greatest advantages over other types:
- maximum bearing capacity;
- increased value of frost resistance;
- great plasticity of the solution.
The tape foundation is laid at great depth. This allows you to naturally increase the moisture resistance and frost resistance of the structure. The large depth of the building excludes frequent repairs and cracks in the base of the house.
The number of additional work performed depends on the choice of the type of masonry. When laying the rubble dry, the building material is selected in the best way. In order to avoid accidents during the operation of the house.
If the structure is filled with mortar, then it becomes necessary to construct formwork. These are additional financial costs. In any form, the stones are rammed with a sledgehammer to avoid subsidence of the foundation and distortion of the walls.