What is the best foundation to equip on the sand
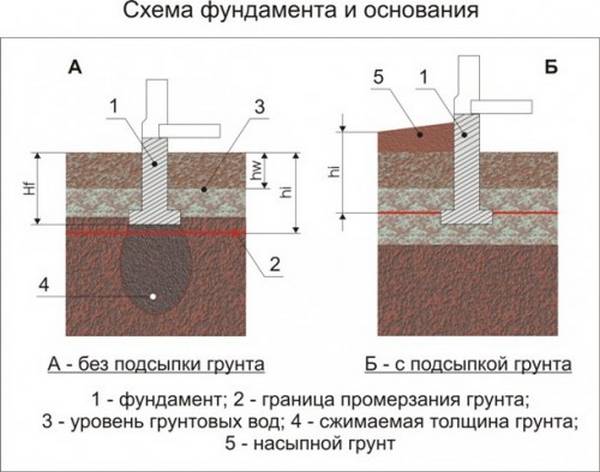
The type of foundation for the house is selected depending on the type of sandy soil.
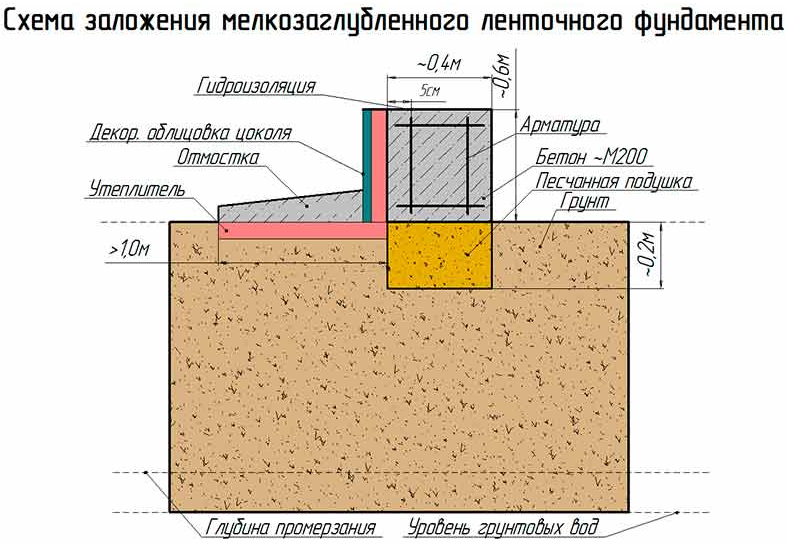
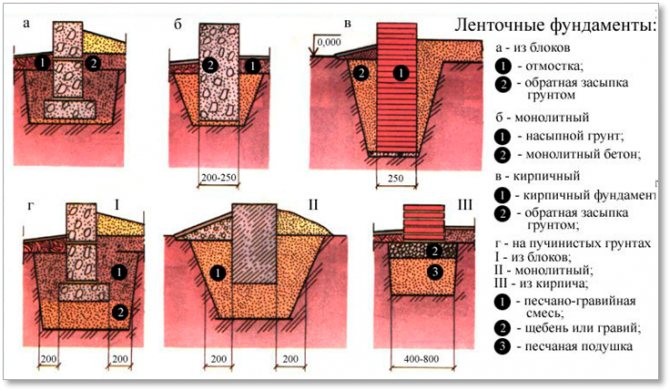
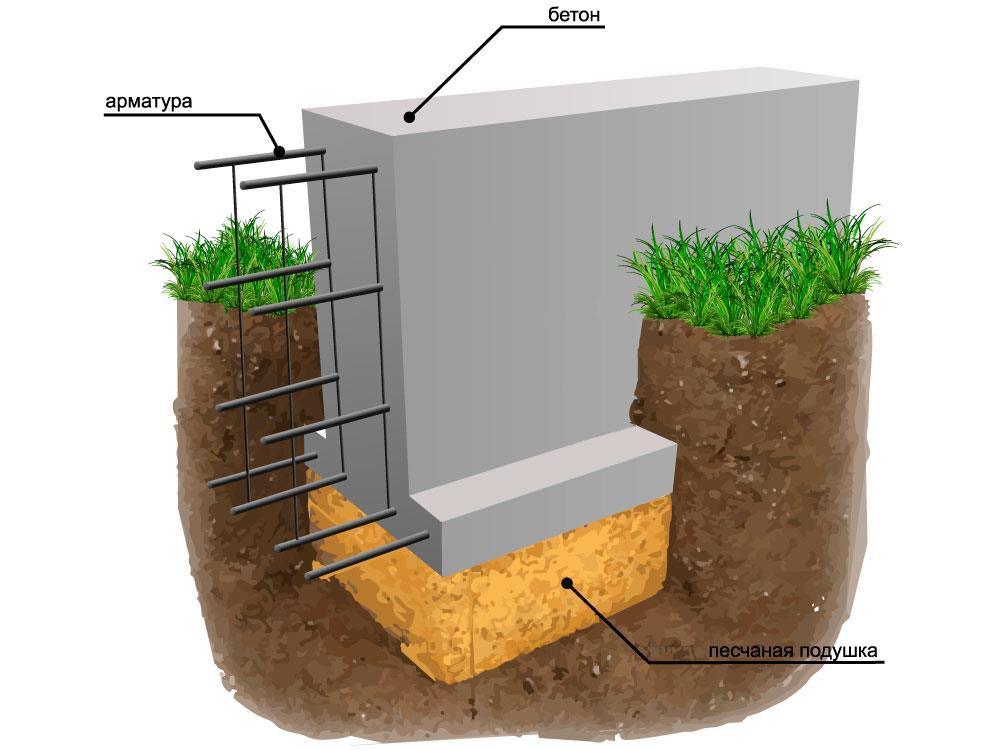
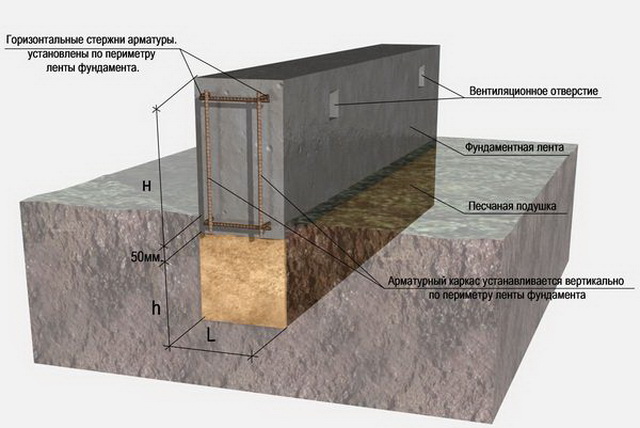
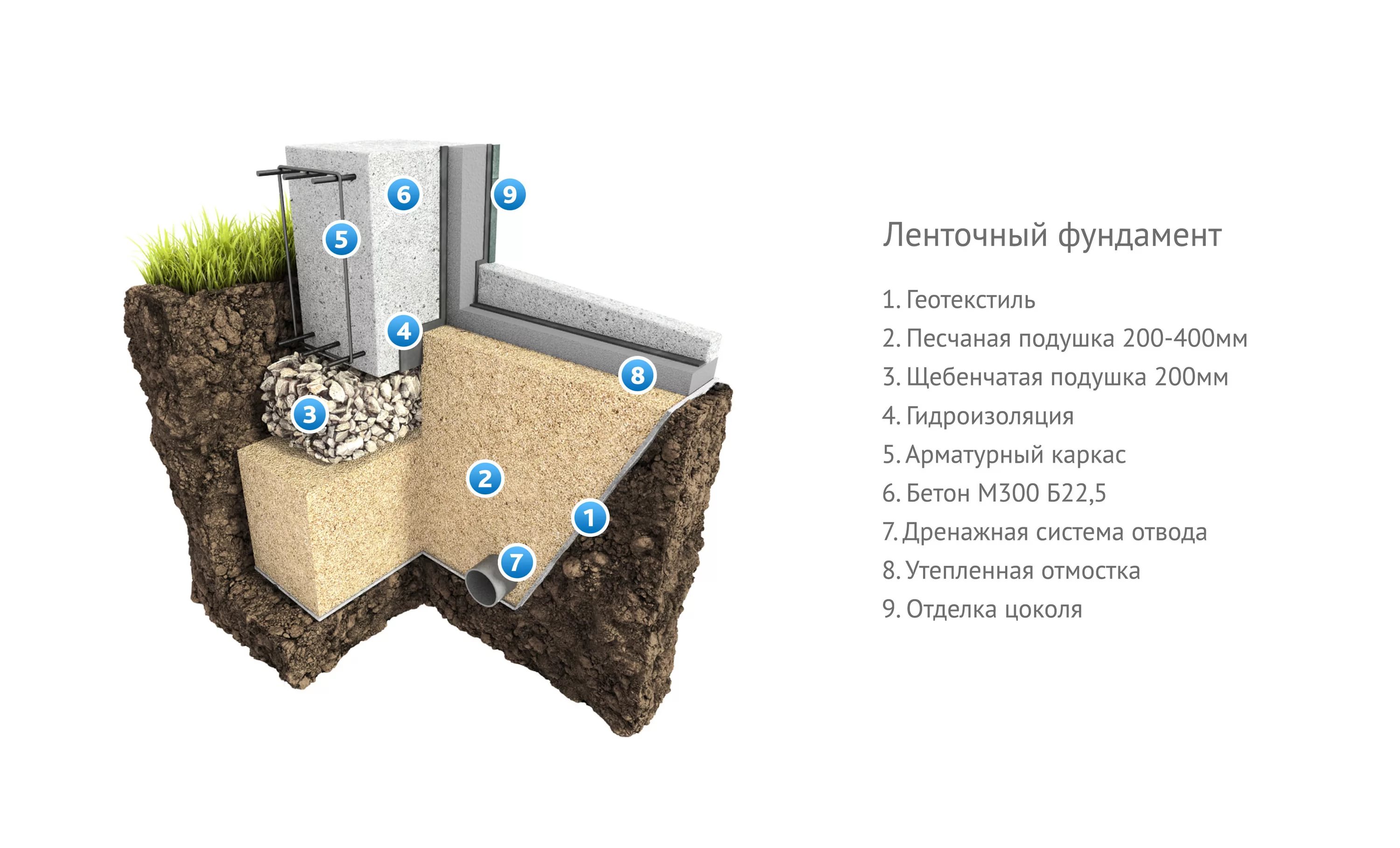
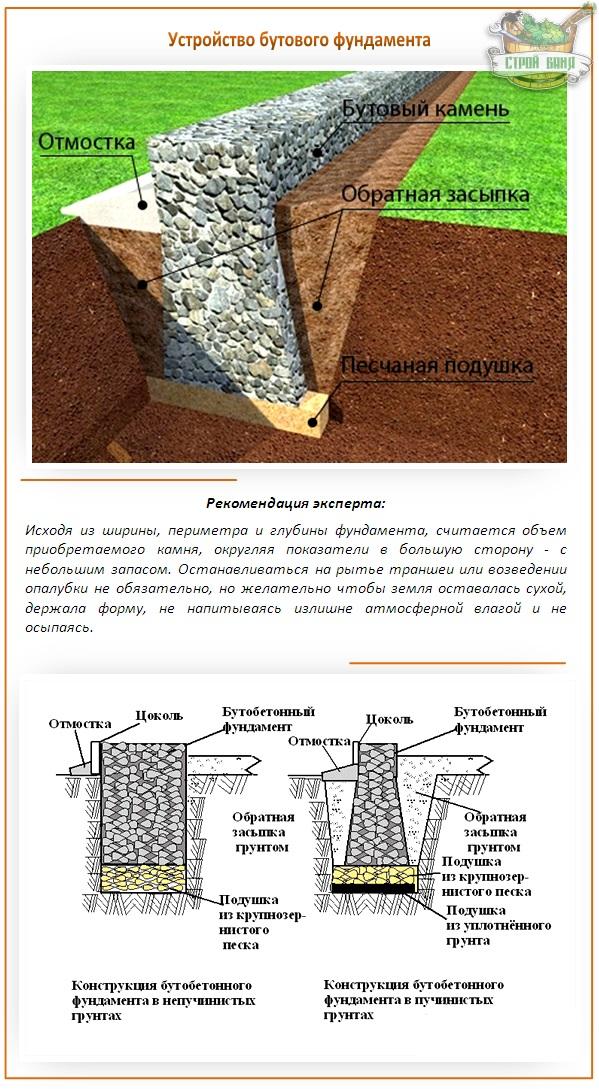
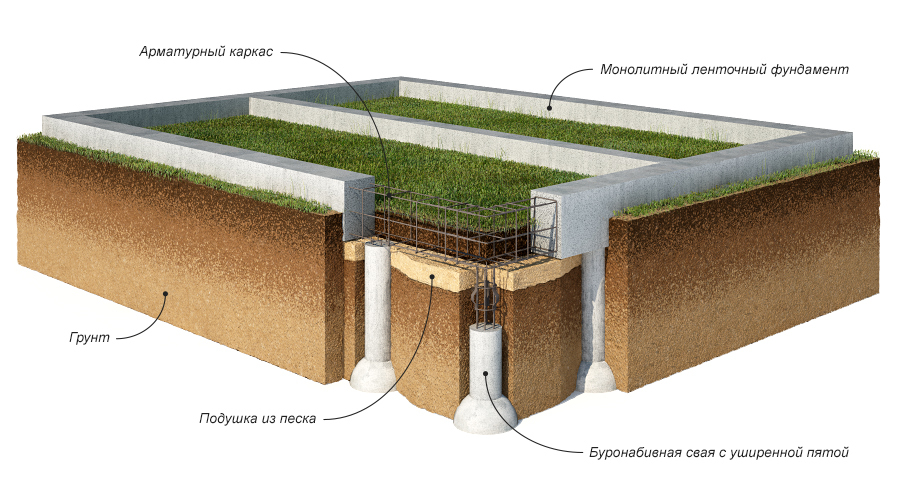
Ribbon base
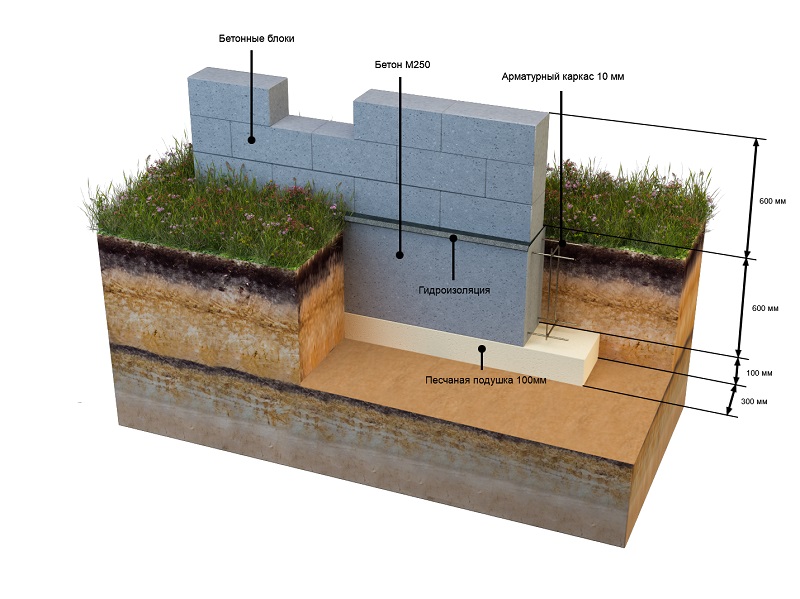
The tape type foundation is very often used in Russia. Arrangement of the belt on sandy soil cannot provide high strength characteristics. Errors made when erecting structures on silty soils can lead to cracks and deformation of the base. As a result, both the foundation and the entire structure are destroyed.
Columnar base
The main elements of such a foundation are separately set posts. The strength of the foundation depends largely on their correct installation. Construction on dusty and shallow soil requires a large deepening of the main elements of the foundation. If this condition is not met, it is possible that the columns diverge or skew, which threatens the formation of cracks in the walls of the building. In addition, with frost heaving of the soil, the pillars of the base may be pushed out, and during thawing, their lowering can be observed. As a result, the structure is deformed and destroyed.
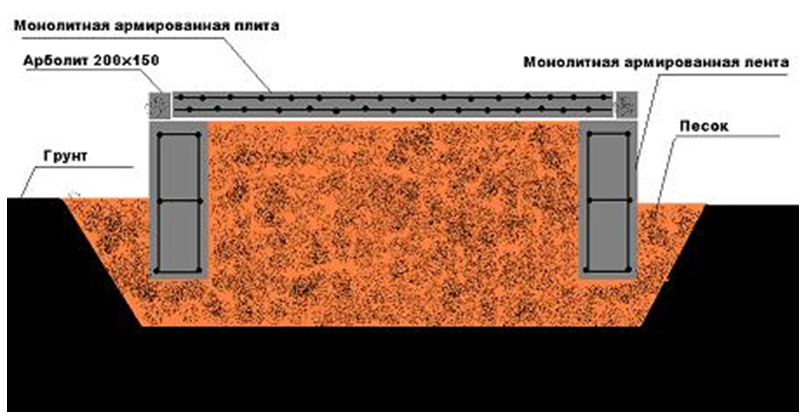
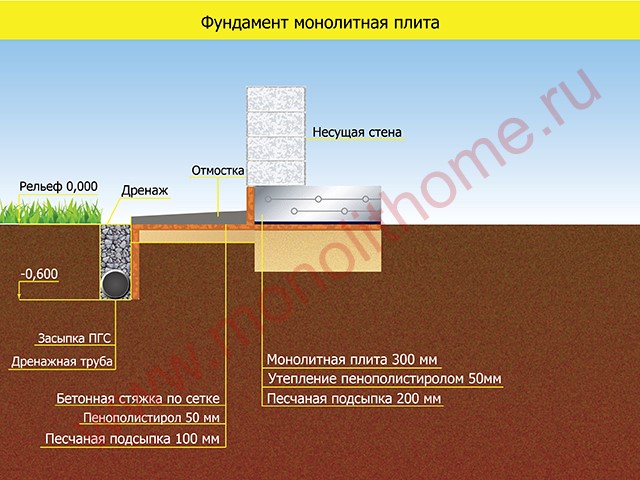
Monolithic slab base

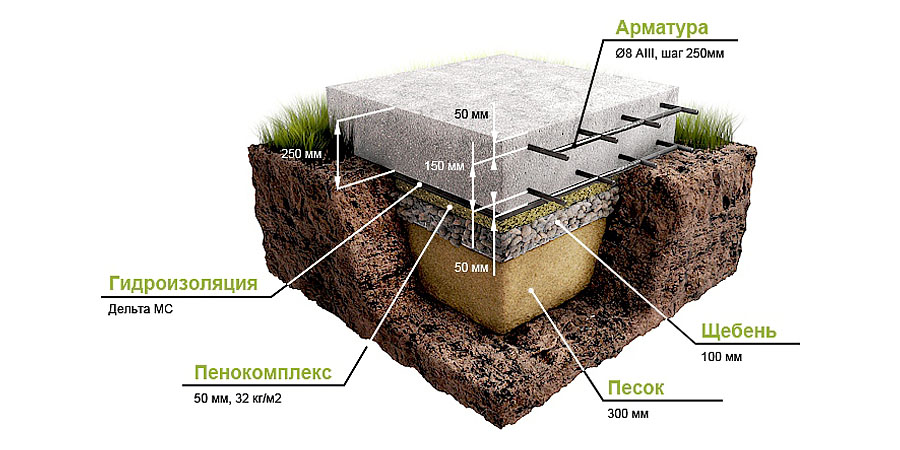
Slab foundation on sandy soil
The slab foundation has a larger support area, which gives it high strength even when building on sandy soil. Additional reinforcement of the base plate increases its strength several times. Therefore, in areas with sandy soil, it is best to use a monolithic base in the form of a slab. However, the cost of such a foundation is quite high, so they resort to arranging it only in rare cases.
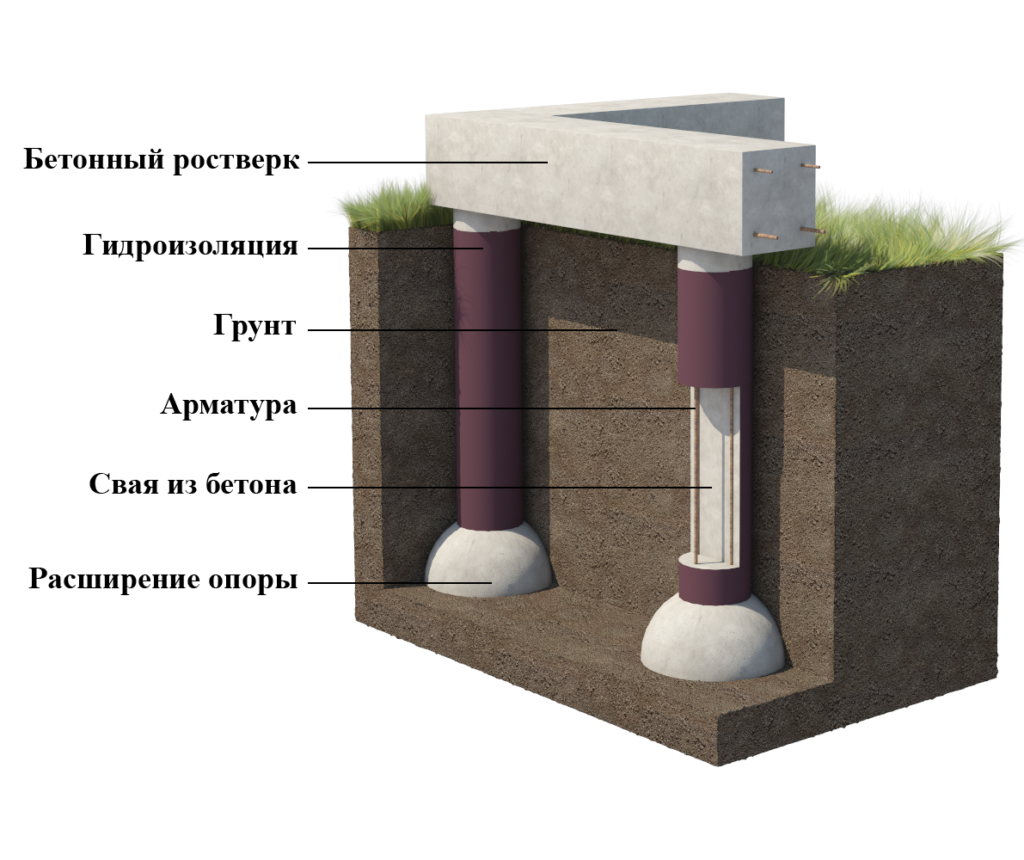
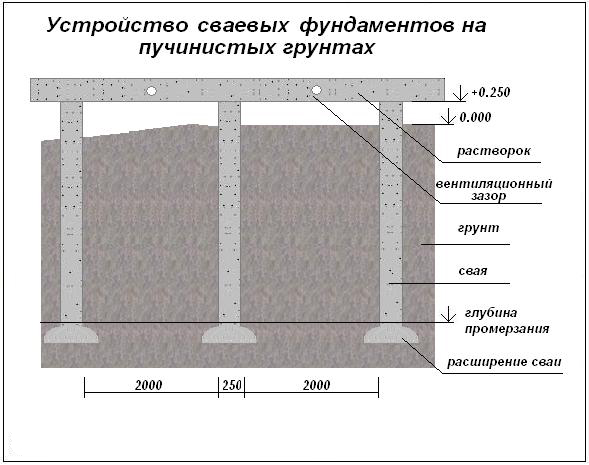
Foundation on piles
Arrangement of a pile foundation on sand is an ideal solution. Such a base is highly durable and reliable on any type of soil. However, in the construction of massive structures, additional calculations are required.
FILLING WITH SOLUTION
A monolithic structure requires the simultaneous pouring of a large mass of concrete, and therefore it is preferable to use a ready-made concrete mixture. The use of a special technique allows the concrete mixture to be poured evenly, in a very short time.
To improve the structure of the monolith, concrete is compacted using a deep vibrator.
After filling the mold, the concrete is allowed to stand and only after it has gained a certain strength is the horizontal surface of the slab checked.
The formwork from the monolith is removed 10-12 days after pouring, the integrity of the slab is inspected and the embankment is checked for deformations - soil subsidence, displacement, swelling. The absence of these phenomena makes it possible to judge the correct work on the preparation of the embankment. The rest of the construction work is recommended to be carried out after the concrete has gained the necessary strength, that is, not earlier than after 28 days.
What foundation is suitable for clay soil
Layers of foundation laying for loamy soil with waterproofing.
After accurately determining the type of soil on the site and the depth of the groundwater, it is necessary to decide what kind of foundation can be built. Clay soil limits the choice of the base of the house, so you can use only two options: build belt or pile foundation. Which one to choose, we will try to find out further.
If the soil is more or less homogeneous, then a strip foundation is suitable for it, a pile foundation is used in cases where stones are found in the soil.
It is not easy to build a foundation on loam, but if you understand all the nuances of this work, you can do it.When erecting a foundation on loam, problems such as breaking off, swelling and subsidence of the structure can arise. Most often this happens due to insufficient depth of laying the foundation or at high pressure that can be exerted on it. Problems can arise at a house whose foundation was built on loam, if small stone was used during its construction, or the walls were built from foam blocks.
Diagram of a strip foundation for clay soil.
To avoid all of the above problems, building a house should be accompanied by choosing the right type of foundation. In this case, the blocks can be sifted out immediately, since a reinforcing frame device will be required in the role of a connecting element. The bottom of the base should be wider than the top. If there are concerns about soil pressure, the base will need to be coated with machine oil or wrapped in PVC film, which will not let water through to the foundation during a thaw. It will be useful to insulate the top layer of the earth, for which you can use expanded clay or crushed stone.
The choice of the type of foundation. which can be erected on loam is also influenced by the material used in the construction of the walls of the house. If it is a brick, then you should stop your choice on a strip foundation that can withstand a heavy load.
If it is planned to build a barn or a summer greenhouse, then it is better to choose a pile foundation that is capable of providing the necessary degree of monumentality of the structure being erected.
On clays and loams also you can use bases in the form of a monolithic slab, which must be installed on a sand cushion. Its advantage lies in its buoyancy, which means it can easily withstand any ground movements. Another advantage of the monolithic foundation is the absence of the need for global land works.
Foundations on coarse and medium-grained sands
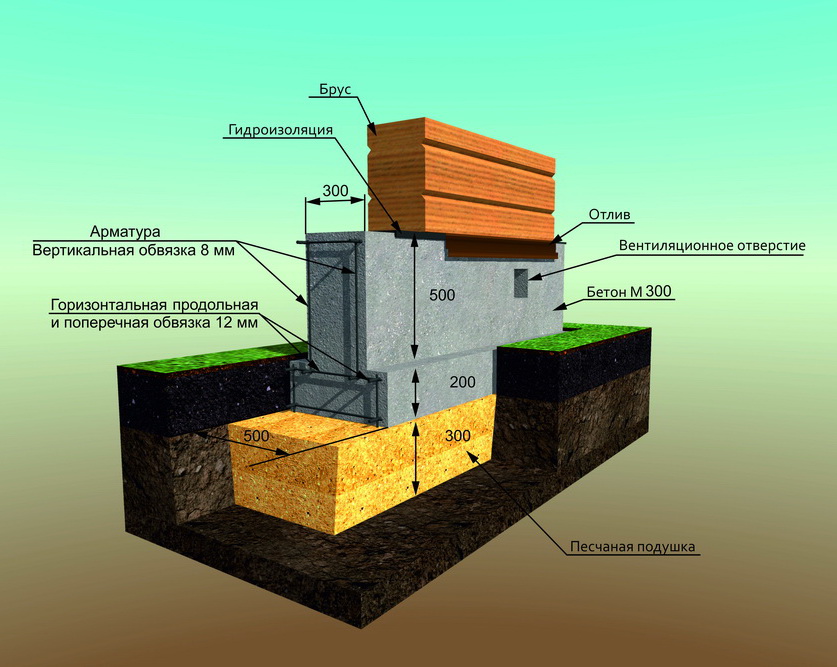
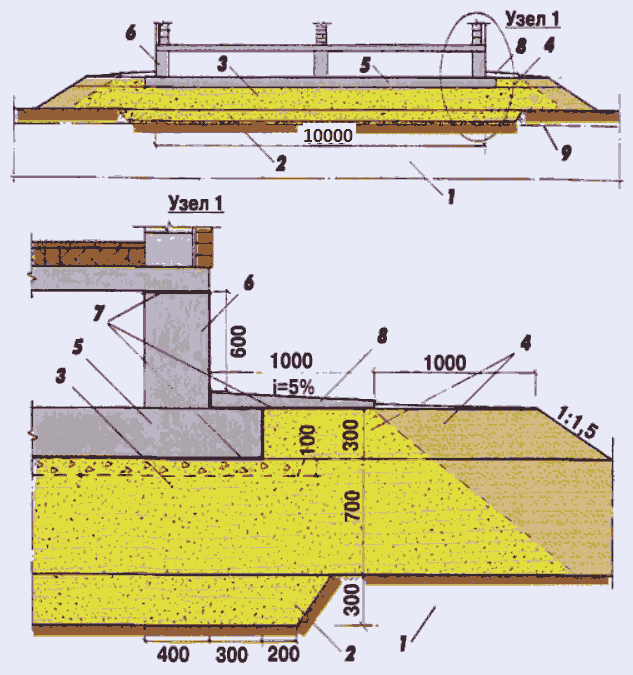
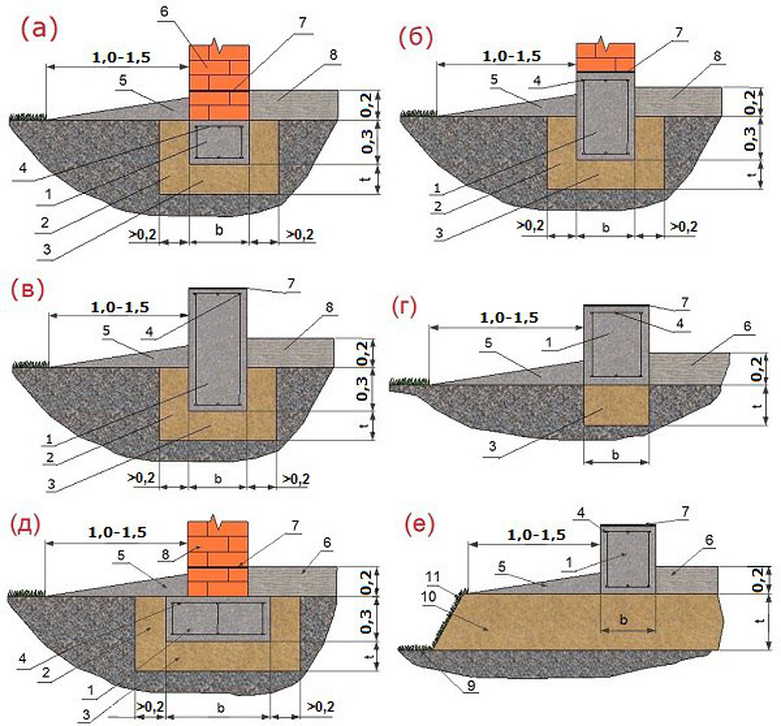
The case is simple, and any type of foundation will do. If the groundwater flows low, at a depth of 1.80 m or more, the optimal foundation is a tape, columnar, or their combinations. Monolithic reinforced shallow tape (MZLF) or foundation from precast concrete blocks FBS suitable for houses made of stone, brick and blocks of several floors and with a basement. For lighter frame houses, or one-story buildings made of lightweight concrete blocks and beams, a support-column foundation, brick or block, will be sufficient.
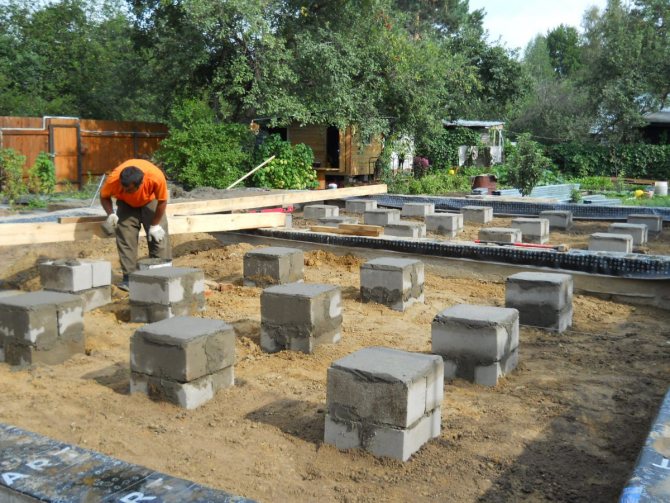

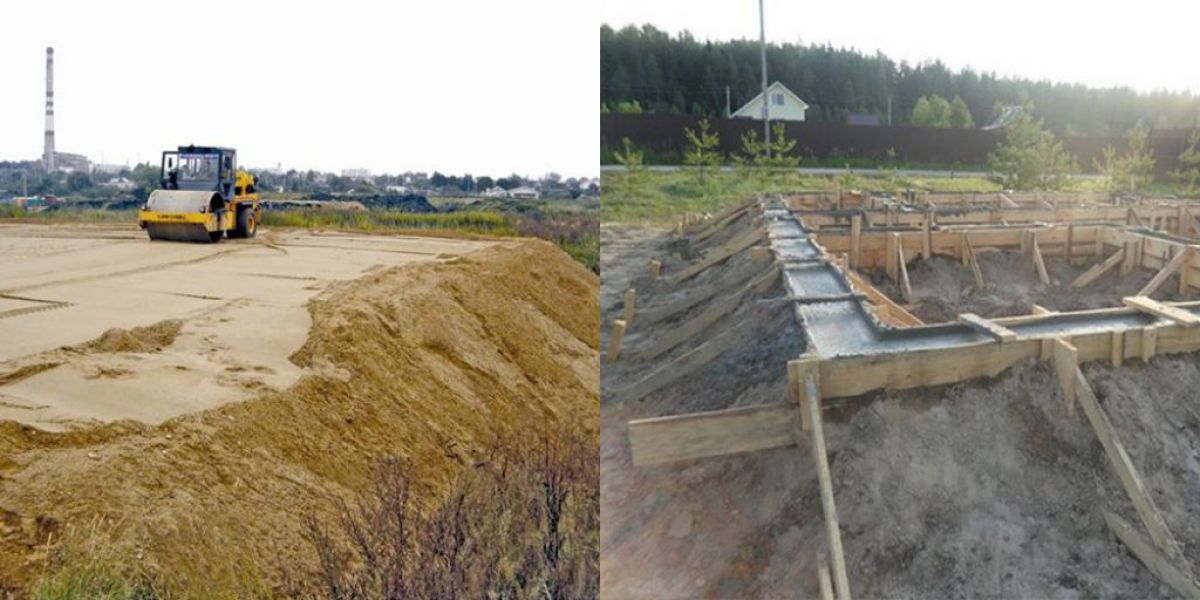
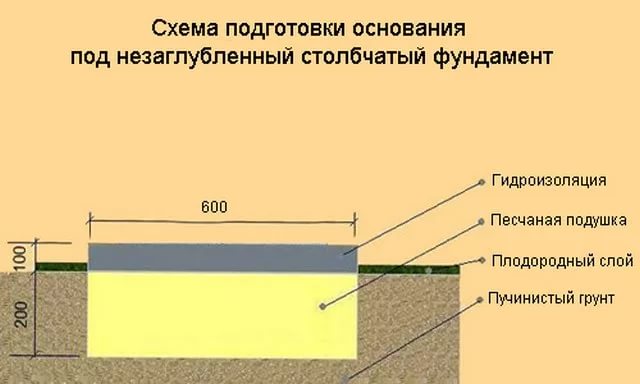
Before starting construction, they always lay out the site and remove all the debris, and then cut the vegetation layer of the soil to a depth of about 20 cm.
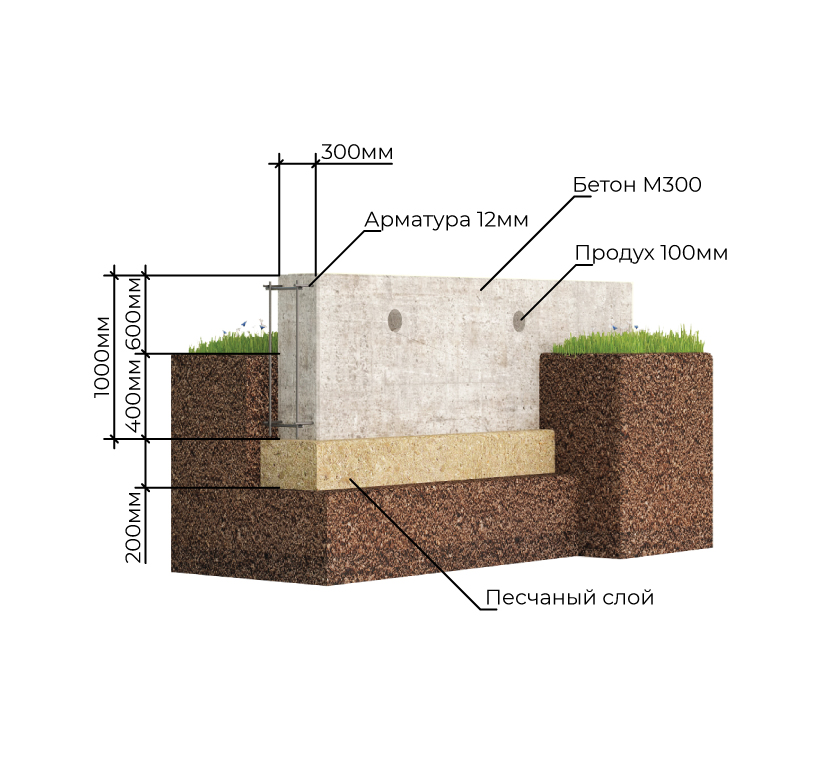
Columnar foundation does not require complex technology. materials - concrete, rubble concrete, sand concrete, blocks are possible. Application foundation blocks of size 200 * 200 * 400 mm allows you to do work with your own hands, without the involvement of equipment. When using bricks for laying support pillars, remember that silicate bricks and red bricks with low frost resistance characteristics are unacceptable for foundations.
The foundation is started with clearing and marking the site. Supporting foundation pillars are placed in the corners of the house, at the intersections of the load-bearing walls, that is, at the points with the maximum load. The plan of the house is transferred to the locality by means of mounting racks, marking the points by driving in pegs, along which the cords are pulled - the axes indicated on the plan of the house.
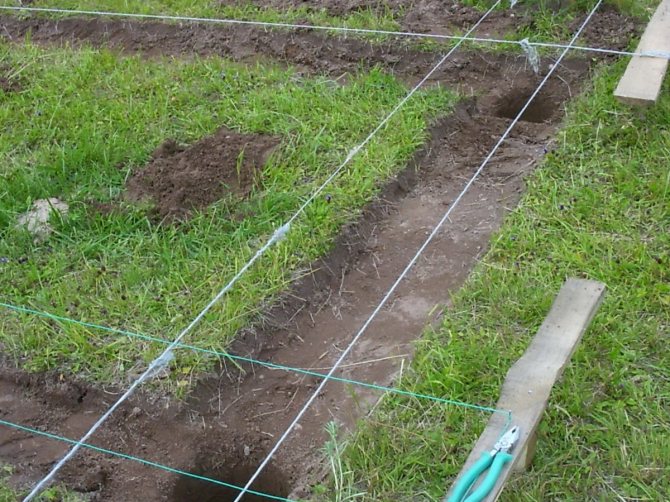

Pits for support pillars are dug strictly along the axes. For a monolithic version, after installing a crushed stone or sand gravel cushion, roll waterproofing is arranged, formwork and reinforcement cage are installed, then concrete is poured with a seal with a vibrator or bayonet. A grillage is arranged on the top of the supports.
For a columnar version made of brick or in a block design, trenches are deepened up to 400 mm under the pillars, and a crushed stone pillow is made to exclude capillary suction of ground water. Waterproofing from roll material is arranged on the pillow. The laying of the support pillars is done with obligatory dressing, the size of the pillars and depends on the thickness of the future load-bearing walls. The finished masonry is coated twice with bitumen or bitumen mastic. Vertical waterproofing - cut-off is performed with roll material. Then proceed to the construction of the walls.
Varieties of clay soils
Before determining the type of foundation, it is necessary to clearly understand on what type of soil the construction will be carried out.
Loams are widespread in central Russia
Depending on the amount of clay content, soils are of the following types:
- sandy loam - loose rock containing sandy and silty components in combination with 5-10% clay;
- loam - soil, in which the clay component is present in the amount of 10-25%, and the rest is occupied by sand;
- clay is a fine-grained sedimentary rock with a high percentage of clay matter from 30%.
The main distinguishing characteristic of clay is its weakness in front of moisture, due to which it quickly turns into a pasty mass and prevents further seepage of liquid into the soil. The layers of the studied rock can be located at a significant depth, which increases the risk of soil swelling in winter due to freezing of stagnant water.
A few words about bulk soil
The properties of natural soil and bulk soil differ. First, the natural foundation has been compressed over the years, reaching its maximum bearing capacity at this time. In turn, the fill soil compresses itself over a comparatively short period of time, it is heterogeneous, so it is very difficult to predict its behavior during foundation construction. In the table below, we have given the approximate values of the bearing capacity and the time for self-compacting of some types of bulk soils.
| Types of bulk soils | Estimated time required for soil self-compaction, years | Approximate bearing capacity with additional compaction, kg / cm2 |
| Clayey | 2÷5 | 1,5÷2,5 |
| Sandy | 0,5÷1 | 2÷3 |
| Large dairy | 0,2÷1 | 2,5÷3,5 |
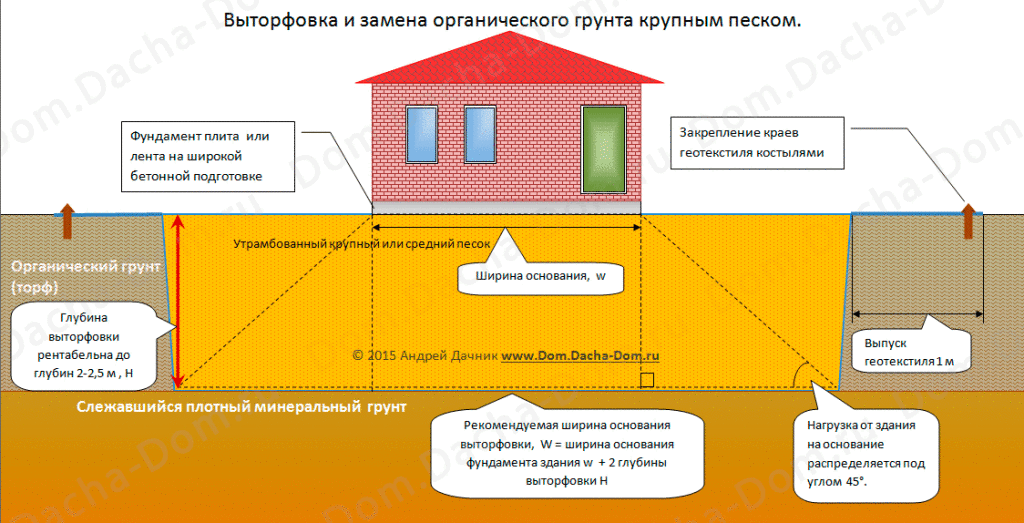
Filled soil is used in two cases:
- when it is necessary to change the relief of the site. If you bought a suburban area that was partially covered with bulk soil, you will have to additionally conduct geological studies of the soil. Indeed, in this case, it is not clear whether the base was compacted artificially, or whether it self-compacted over time. A great danger is the heterogeneous composition of the soil, therefore, it is subject to the most careful analysis;
- when the soil on the building site does not meet the requirements for bearing capacity. For example, it is planned to build a foundation on peat, which can hardly be called an ideal foundation for a house. If the peat layer is small, then it can be replaced with another material, for example, sand or gravel.
Measures to improve the characteristics of filled soil
You must understand that the characteristics of any soil can be artificially changed. As a rule, it all comes down to increasing its bearing capacity and leveling heaving phenomena:
- allow time for the soil to compact itself. The option is not the fastest, but economical;
- compact the bulk soil with special equipment;
- rather expensive methods involve strengthening the base by carburizing it, silicatization and other processing technologies;
- drain, insulate the base to reduce the depth of freezing and lower the level of groundwater;
- if necessary, arrange sand, gravel and other cushions - carry out the replacement of soil in situations when it is necessary to build a foundation on collapsible soils;
- an extreme option is the use of a pile foundation, the base of which lies below the layer of bulk soil
The choice of foundation for construction on bulk soil
Considering the fact that the fill soils belong to the complex group, in the absence of experience in calculating the foundations, it is better to entrust the construction of the foundation to specialists: they will evaluate the soil and will be able to choose the best option for the foundation. At the very least, serious companies will give a guarantee for the work performed. If you decide to do everything yourself, then the options for foundations may be as follows:
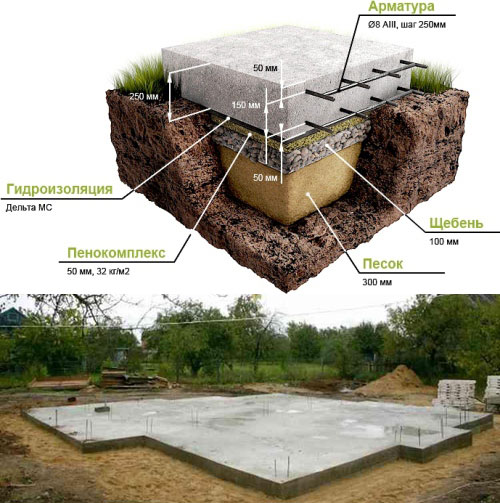
- a slab foundation that allows you to use the entire building spot, create the maximum footprint and protect the house from uneven deformations. A slab is an expensive pleasure, it requires careful reinforcement of the foundation, which naturally increases the cost of the monolith;
- the device of the strip foundation requires a serious analysis of the soil. Take the time to dig a couple of pits and assess the condition of the bulk soil layers. After carrying out the calculations, you can think about the construction of either a shallow-buried or a rigid reinforced concrete tape buried below the GPG. It should be noted that the construction of the tape is more laborious than pouring the slab;
- do not neglect the use of a columnar (pile) foundation. Most often, this option is used on bulk soil, which has already compacted and at a certain depth has acquired sufficient bearing capacity. It is possible to build such supports and provided that the thickness of the layer of bulk material is known, by deepening the piles into the thickness of the "native" soil
It turns out that almost any type of foundation can be built on bulk soil. The only thing is to provide for the amount of shrinkage and choose an option in which local deformations will not lead to a violation of the integrity of the foundation. Of course, provided that the bulk material was planned to be filled and compacted in your presence, all work on the foundation is simplified and future changes in the soil can be predicted.
Frosty heaving of soil
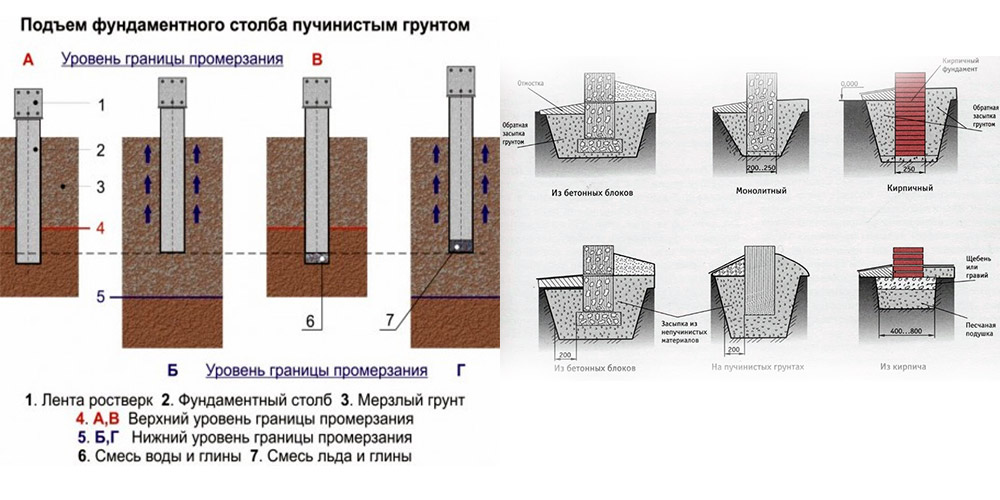
Each building differs in its weight, which exerts loads on the base of the building. The soil begins to resist these loads. If the force of such resistance is higher than the load from the house, then in this case the building will be stable and will stand for many years. If the resistance of the soil is lower than the loads from the weight of the house, then gradually the structure will begin to "sink" in the ground and will inevitably collapse. This is due to the fact that part of the house begins to sink, while the other side remains in place. This provokes cracks and deformations.
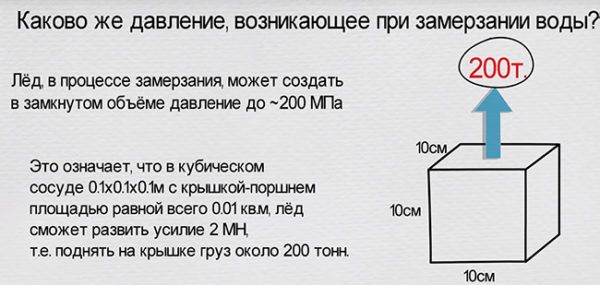
In winter, there are also more loads on the foundation. When the moisture in the soil freezes, it begins to expand and presses against the base with tremendous force. This phenomenon is called frost heaving of the soil.

With this pressure, even the heaviest building can rise. Therefore, it is completely useless to deal with frost heaving. We'll have to adapt.
Sandy soil is different
We think there is no need to explain what a sandy soil is. In a dry state, it is free-flowing, but moisture does not make it plastic. At the same time, depending on the size of sand particles and their percentage, five types of sandy soils are distinguished:
- dusty. Of all sandy, silty sand is the most unsuccessful type of foundation for a foundation. its load-bearing capacity is largely determined by moisture content. When moistened, its properties begin to resemble clay. The content of particles larger than 0.1 mm does not exceed 75%;
- small. With an increase in humidity, the bearing capacity also decreases, but not to the same extent as for silty sands. When pouring the foundation, it must be borne in mind that such soil does not retain moisture, therefore, the foundation pit (trenches) should be waterproofed with plastic wrap.The content of particles larger than 0.1 exceeds 75%;
- medium size and coarse sandy soil contain more than half of the particles larger than 0.25 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively. They are distinguished by high indicators of bearing capacity and serve as an excellent foundation for a home;
- gravelly sandy soil contains more than a quarter of particles, the size of which exceeds 2 mm. At the same time, a foundation made of such soil is ideal for the construction of any type of foundation.
About the foundation and the bearing capacity of sand
An important characteristic of sandy soil for construction is its bearing capacity, which largely depends on its moisture content and compaction of layers. The denser the soil, the greater the load it can carry without significant settlement
At the same time, an increase in water content in it negatively affects the bearing capacity (this statement does not apply to gravelly soil and coarse sand). Sand with larger particles for building a foundation on such a basis is better suited than fine or dusty sand. As with any other soil, with an increase in the depth of the rock, its resistance to compression also increases: the deeper the base of the foundation, the less the house will subsequently settle. A set of measures to protect the base of the house from moisture deserves special attention. Even though sand does not retain water, foundation waterproofing is indispensable.
Foundation options
In most cases, sandy soils can be considered non-porous, because they practically do not retain moisture and do not increase in volume during freezing. For this simple reason, almost any type of foundation can be built on them. And even if the groundwater level at the site is high, the drainage device and insulation of the perimeter of the base of the house will easily solve the problem.

Some nuances
It is necessary to understand that sandy soil can differ in a heterogeneous structure: first, there is a layer of the middle fraction, and deeper - silty sands or sand with clay. Accordingly, the calculated resistance of such soil will differ at different depths. Therefore, before construction, we recommend digging pits to a depth of at least 2 m and assessing the nature of the soil in your area.
Finally
In most cases, the presence of sandy soil at the construction site can significantly save on the construction of the foundation. As a rule, the water table is low, and you do not need to worry about the change in the bearing capacity of the foundation over time. Equally, freezing of the soil does not pose a particular threat, because normal sand does not belong to the category of heaving soils.
Features of the technology of building a foundation, depending on the type of soil
With the help of the correct type of foundation and adherence to the technology for building the base, you can create a solid support for construction on any kind of sandy soils.
Dusty and fine-grained
To build a house on dusty and fine sand, due to the extreme instability of the layers, it is necessary to create the most solid foundation. In such cases, the construction of a slab foundation is permissible. To do this, remove the fertile soil layer and cast a concrete slab, the scale of which is slightly larger than the area of the planned building. The structure does not collapse under the influence of seasonal changes in the soil, since this type of foundation is able to move with the ground, therefore it is called a floating foundation.
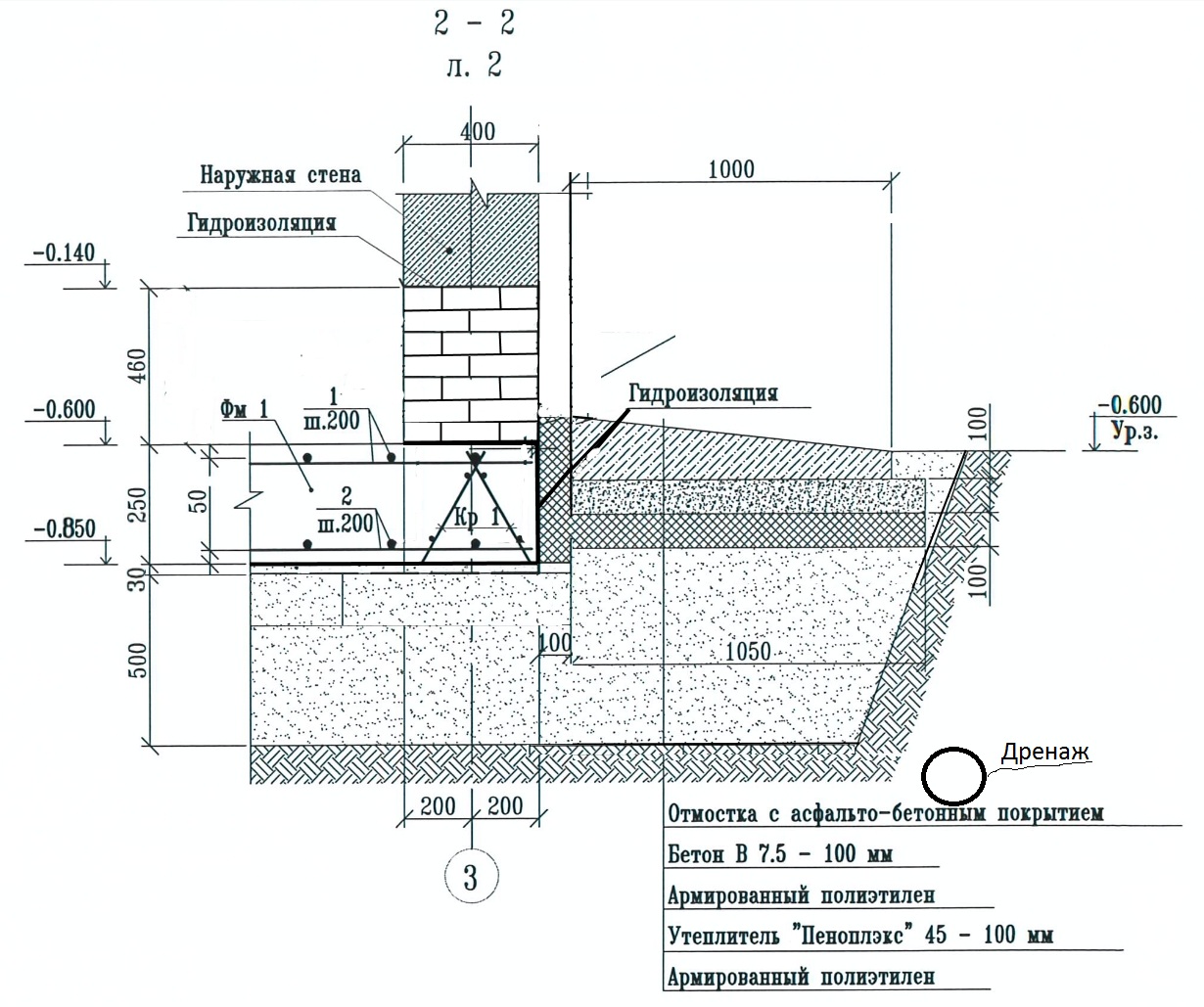
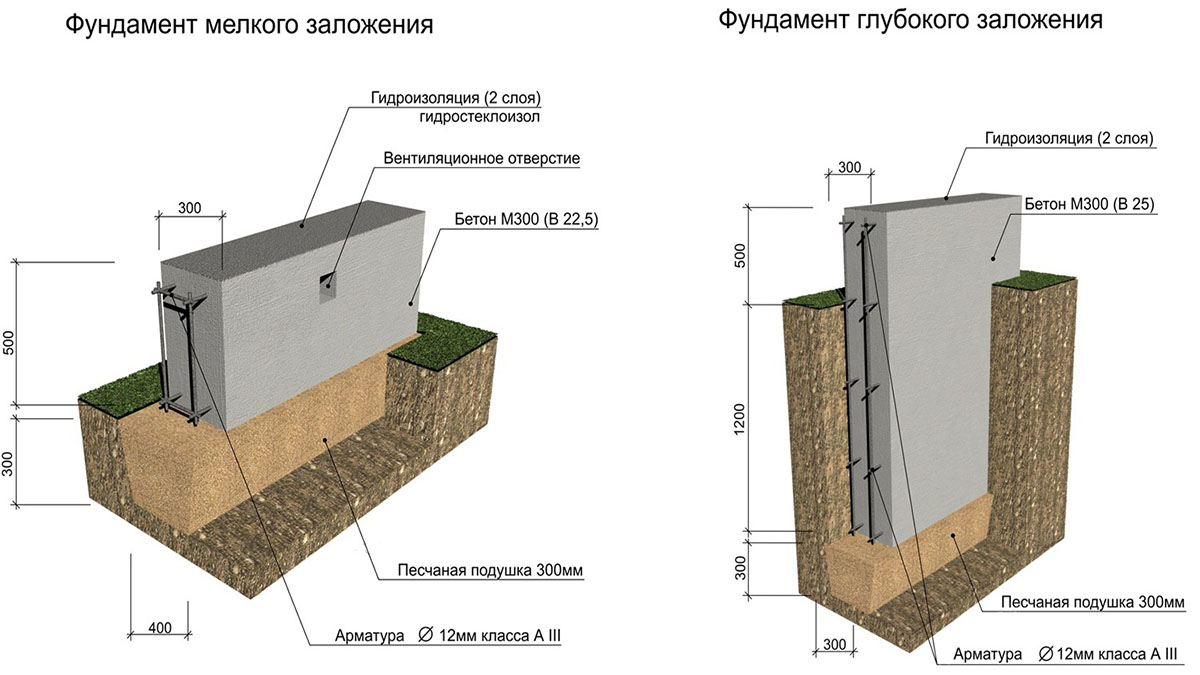
Another more common way to create a solid foundation for a building on silty and fine sandy soil is to use a monolithic strip foundation of a shallow type. It is recommended to make it trapezoidal with lines expanding downward. This contributes to a significant reduction in the influence of frost heaving on the base of the house.
Before pouring the foundation tape, the trench is equipped with a waterproofing layer.When laying the sole structure under a structure on fine sand and silty soils, drainage is especially important. Closed systems, which are equipped on the basis of drainage pipes, are recommended as effective methods.
When working on the construction of the base of the base for heavy buildings on fine and dusty sand, it is worth using the pile-tape option for arranging the foundation:
- carry out the markup, dig a pit, install the formwork;
- at the intersections of the tape, wells are drilled to a depth of stable soil layers;
- pipes based on asbestos cement are installed in the wells, the structures are leveled qualitatively, and reinforced with spacers;
- the pipes are poured with concrete solution by 1/3, slightly raised to form a thickening at the bottom. Next, the pipes are filled with a solution, having previously lowered the fittings into them.

Formwork and reinforcement for pile-strip foundations
Piles can be poured without installing pipes, if the environment is not very wet and the wells are not filled with water:
- the lower part of the well is expanded with a special plow;
- reinforcing material is lowered into the well and poured with a solution;
- after the pile structures have solidified, they begin to pour the tape into the formwork.
Experts note that after pouring the foundation on fine-grained and dusty sand, the structure must stand for six months before continuing construction work.
Large and gravelly
Since coarse sandy soils have a reliable level of bearing capacity, any types of foundation structures are relevant here:
- if it is planned to build a house without a basement, the tape version of the shallow type is most often used;
- a columnar base is suitable for a structure made of light materials in the form of frame structures, wooden houses or panel structures;
- for massive buildings with a basement, a strip foundation of a strongly recessed type is performed.

Column foundation for a frame house
When laying a columnar or strip version of the base of the base, foundation blocks or ceramic bricks are also used.
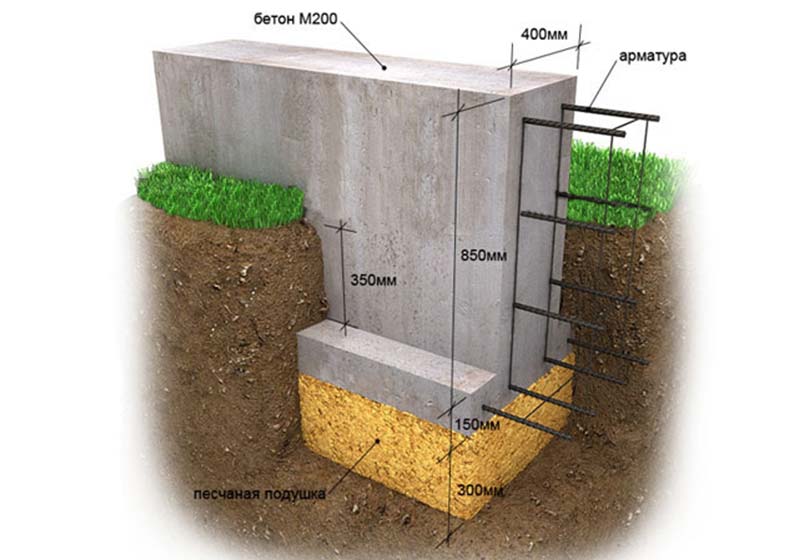
On a shallow strip base on coarse sand, you can put a building made of foam blocks or wood, a frame / panel view of a structure, or a small brick house. At the same time, the depth of laying the sole varies in the range of 40-70 cm.
Do-it-yourself technology for pouring a monolithic shallow tape:
- Site preparation. Having removed the fertile layer of earth, the surface will be leveled.
- Markup. The work is carried out on the basis of the house project.
- Trench preparation. Dig a trench 60-80 cm deep. The width of the recess is equal to the thickness of the planned walls plus 20 cm, that is, 5 cm on both sides of the wall for the stability of the structure and 5 cm for the formwork.
- Filling the formwork with concrete mortar.

Foundation trenches
For formwork, plywood sheets, edged boards, profiled sheets are used, the inner surface is lined with polyethylene, reinforcing materials are used to strengthen the composition.
When constructing massive buildings or houses with a residential basement or basement, a deep foundation tape is laid. Moreover, the sole under the brick house is installed 20 cm below the level of soil freezing. The deeply buried strip foundation is provided with a waterproofing layer on all sides, including the lower surface. Quality drainage is also required.
Types and types of soil for the foundation.

Coarse soils - a mixture of coarse particles (pebbles + gravel) - a reliable foundation for the foundation.

Cartilaginous soils. They freeze slightly, to a depth of about 50 - 100 cm. They are excellent at allowing moisture to pass through; are compacted, rammed. In this soil, the foundation does not lock.

Clay soils. In the case of an excessive amount of moisture, soil erosion and liquefaction occurs; deeply freeze (up to 150cm) and swell.

Loam and sandy loam.They are a mixture of clay mass and sand. Depending on the amount / ratio of components, the soil behaves accordingly.

Peat soils. Bogs, which are usually highly saturated with moisture with a high level of groundwater. Freezing, respectively - deep, very high. In addition, peat contains particles that negatively affect the composition of the foundation.

The depth of soil freezing is very dependent on the type of soil. Naturally: the more moisture there is in the soil, the more it swells and deforms at low temperatures. And this factor, of course, negatively affects the foundation. To calculate the foundation, you can use the foundation calculator.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to influence the properties of the soil, environmental factors and the depth of freezing. The developer may well choose the soil for the foundation even when buying the land itself. The characteristics of all types of soils should be taken into account, as significant construction problems can arise, which will entail high physical and financial costs.
Table of categories and methods of soil development.
|
Soil category |
Soil types |
Density, kg / m3 |
Development method |
|
1 |
Sand, sandy loam, vegetable soil, peat |
600…1600 |
Manual (shovels), by machines |
|
2 |
Light loam, loess, gravel, sand with gravel, sandy loam with construction waste |
1600… 1900 |
Manual (shovels, picks), by machines |
|
3 |
Oily clay, heavy loam, coarse gravel, plant soil with roots, loam with gravel or pebbles |
1750… 1900 |
Manual (shovels, picks, crowbars), by machines |
|
4 |
Heavy clay, greasy crushed clay, shale clay |
1900…2000 |
Manual (shovels, picks, crowbars, wedges and hammers), by machines |
|
5…7 |
Dense hardened loess, grit, chalk, shale, tuff, limestone and rock |
1200…2800 |
Manual (crowbars and picks, jackhammers), explosive method |
|
8…11 |
Granites, limestones, sandstones, basalts, diabases, conglomerate with pebbles |
2200…3000 |
Explosive way |
Types of sandy soils and their features
Sandy soils are divided into types:
- Coarse-grained - these are sands, consisting mainly of particles of coarse fractions. These are the best sandy foundations for the construction of surface foundations. They are distinguished by good cultivation capacity, bearing load and the absence of frost heaving.
- Fine-grained sands, mainly composed of fine and dusty particles. Working with such soil is difficult, since it is difficult to compact. The water permeability of such sand is extremely low; when moistened, it becomes plastic and turns into mud. If the water table is located close to the surface, then such a base can become quicksand. When working with this foundation, calculations should be carefully performed, because reworking a structure can cost more than its construction.
- Sandy loam and loam. Such a foundation is not suitable for the construction of a foundation, since they are loose, unstable, it is almost impossible to compact them and to the required level.
To find out what kind of soil the building site consists of, you need to contact the geological service.