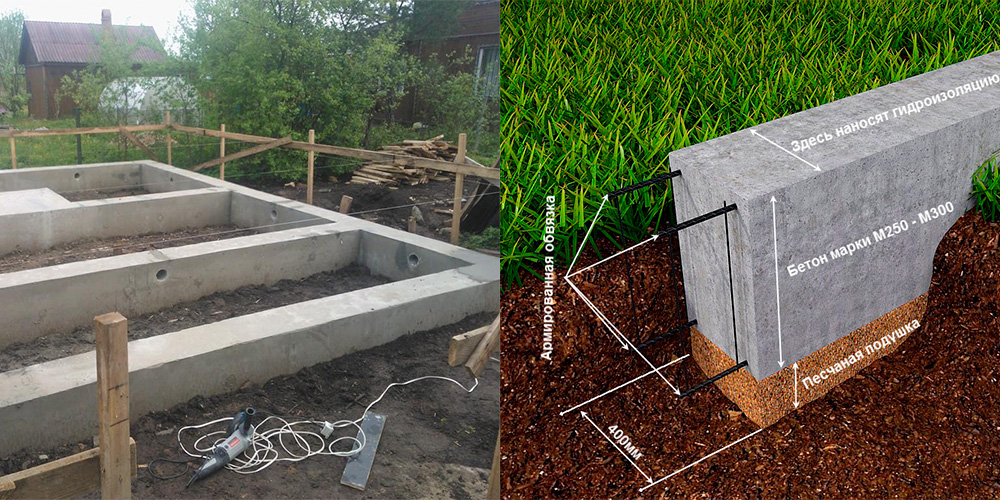
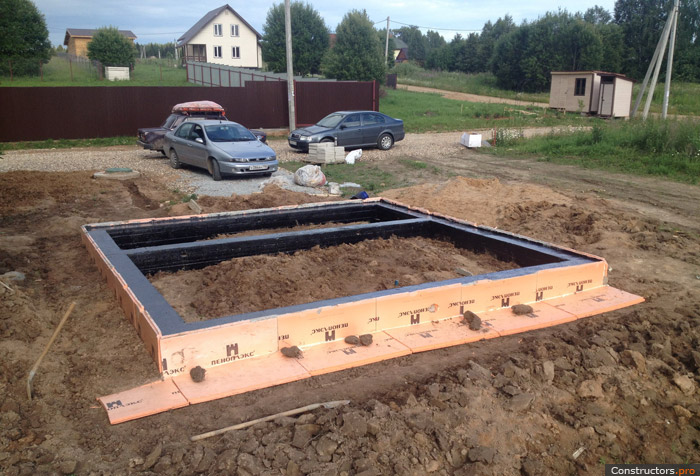
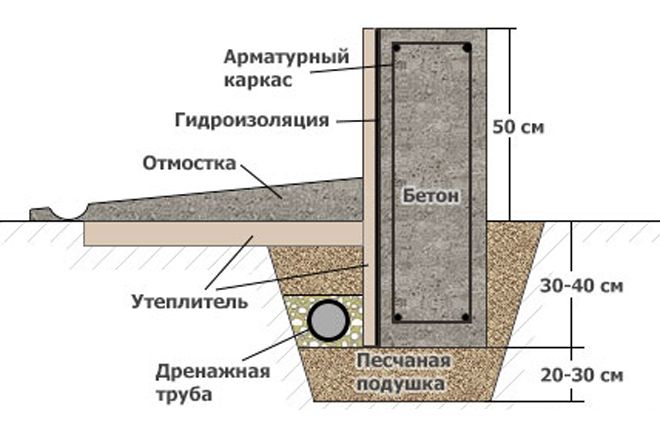
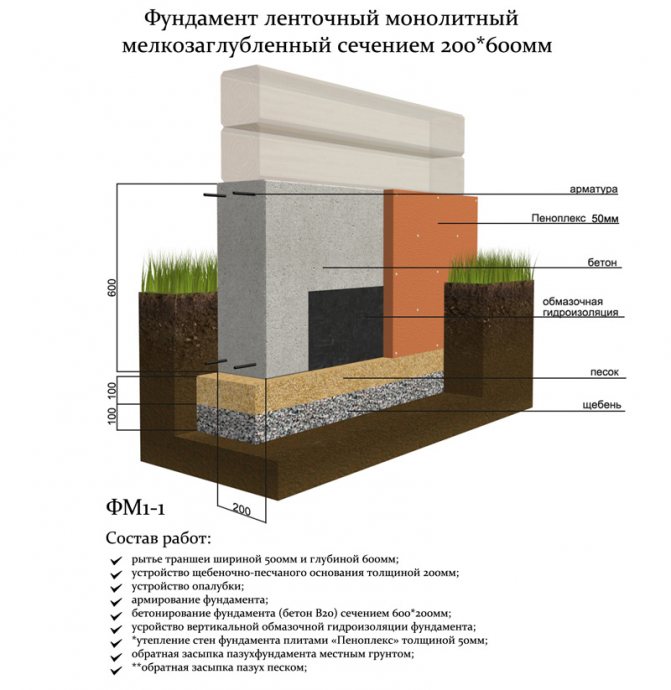
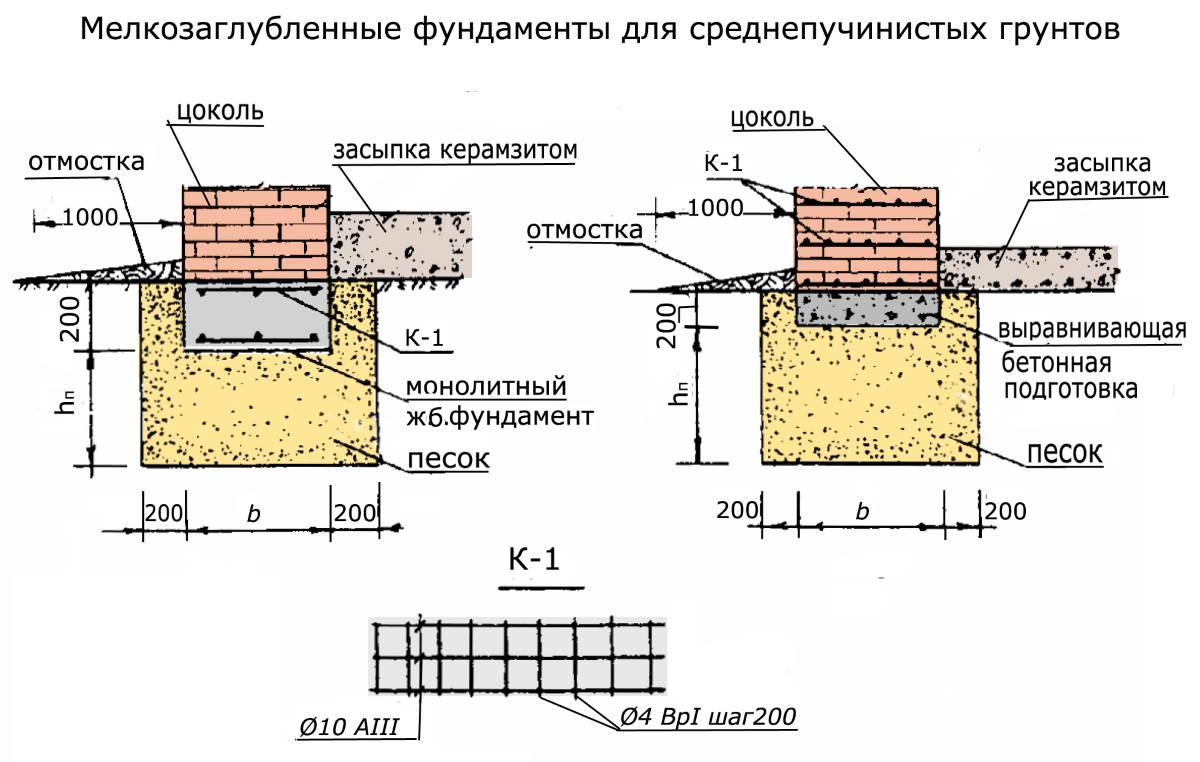
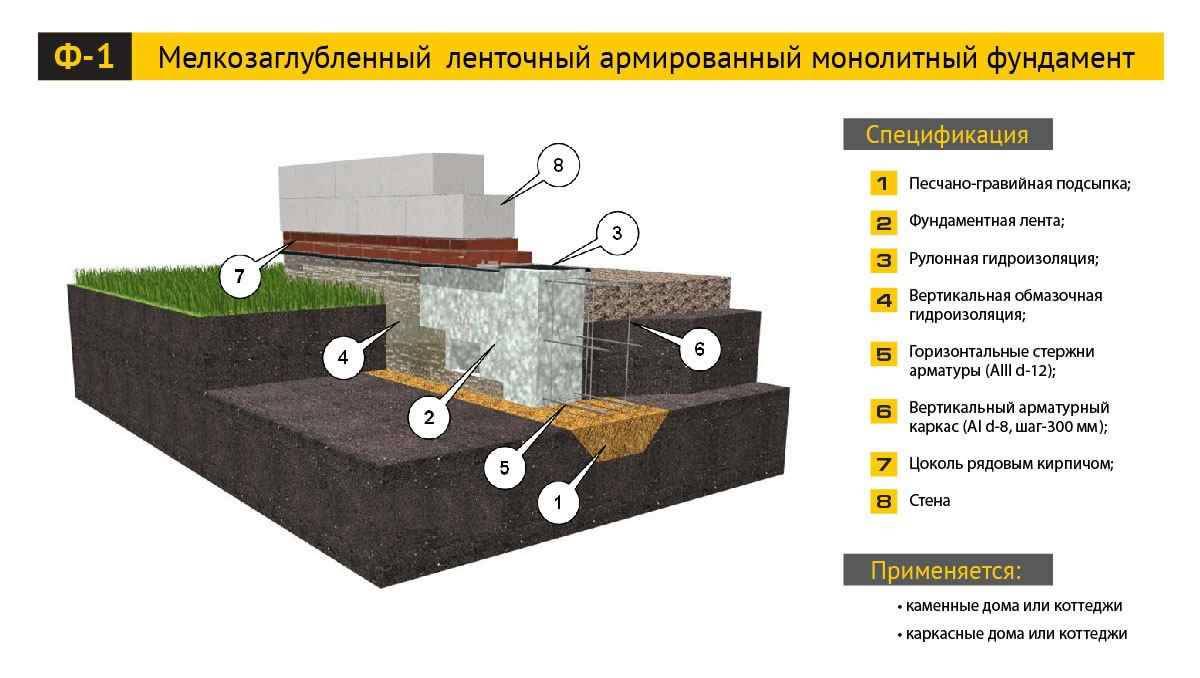
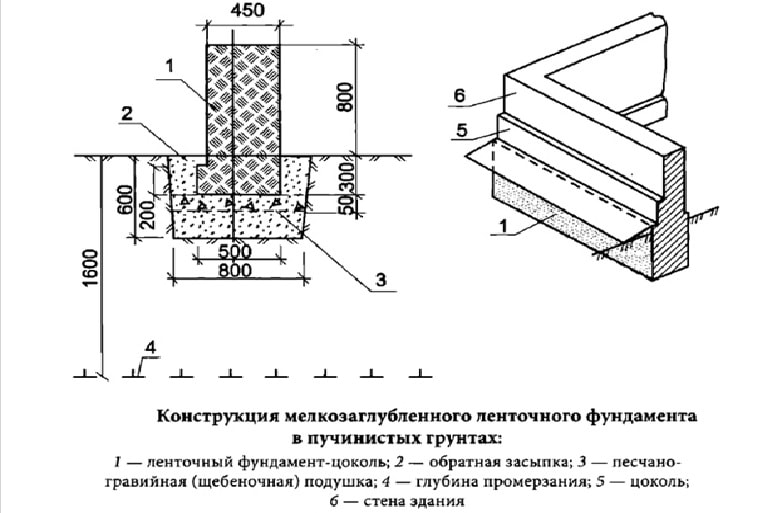
Why insulate the foundation of MZLF
The outer layer of the heat insulator on the foundation tape solves several problems:
- keeps the geothermal heat of the bowels - the soil under the building does not freeze, the forces of frost heaving cannot arise;
- shifts the thermal circuit, the dew point outward - relevant for the technical underground, the operated underground floor, on the outer walls of which moisture is guaranteed not to appear.
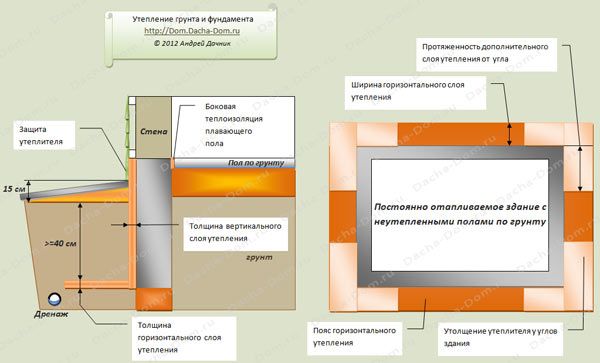
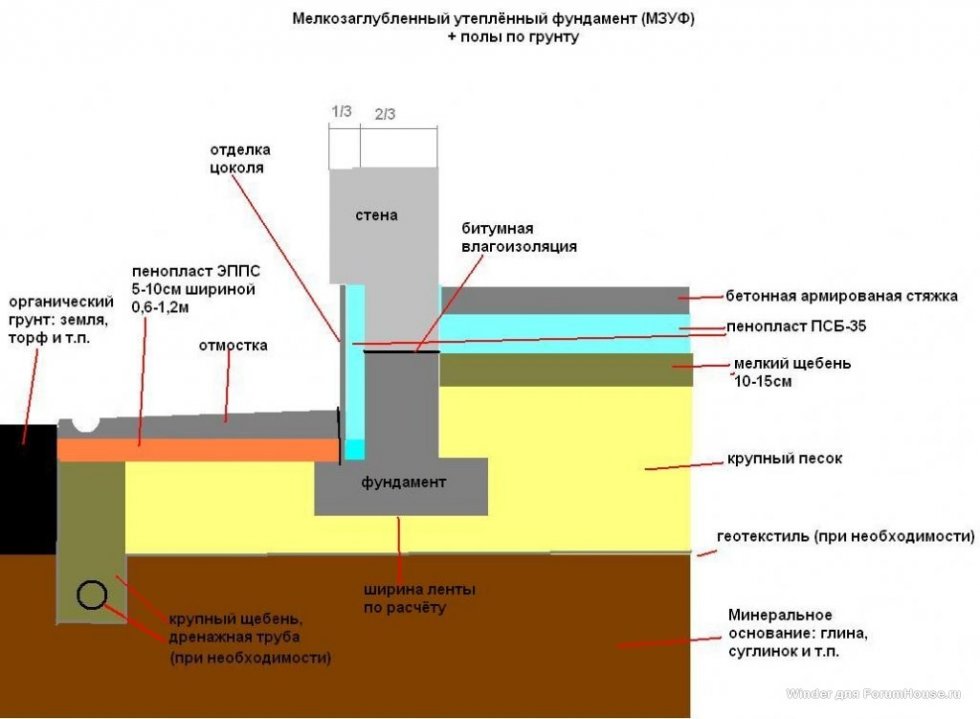
However, it is impossible to keep the heat of the bowels solely by facing the foundation with a heat insulator. The depth of the MZLF is insignificant, therefore, an increase in the perimeter is required. For this, an insulated blind area is often used - concrete over a layer of extruded polystyrene foam with a slope from the wall of the building. However, computer simulation with the built-in real characteristics of structural materials proved the low efficiency of this method:
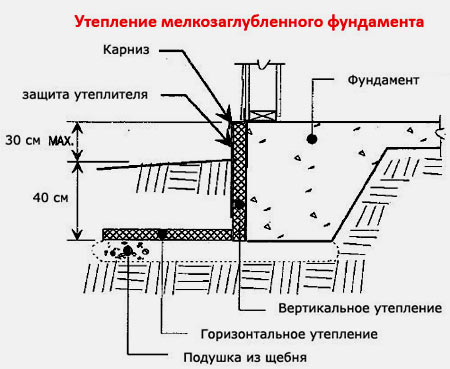
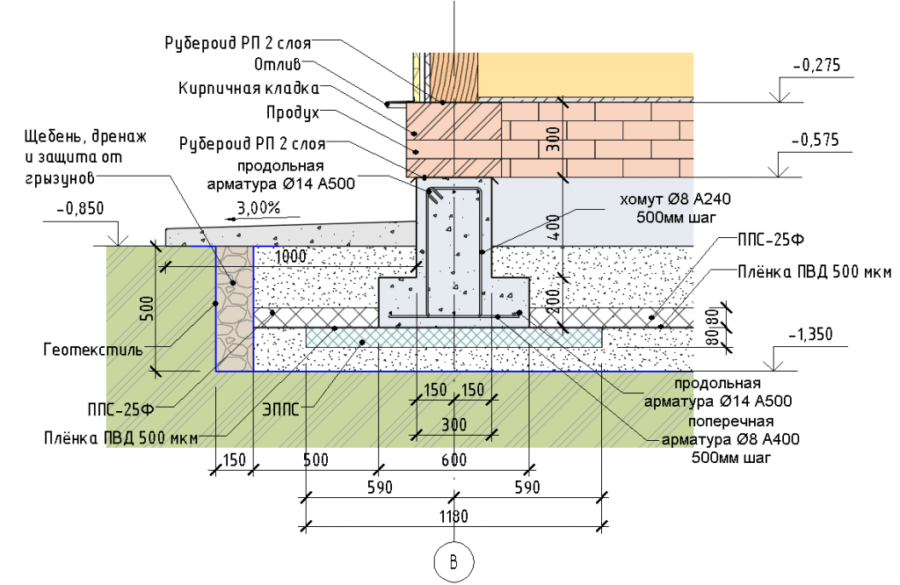
The most economical option for the construction budget is a warm blind area 60 cm wide with a 5 cm thick expanded polystyrene sheet + a 5 cm vertical layer of PSB-S to the height of the basement (from ground level to the beginning of the wall masonry) Fig. 1.
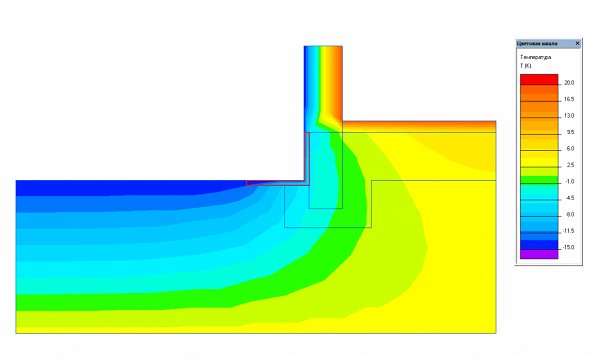
Fig. 1. Scheme of heat distribution when insulating the blind area and the base of the MZLF.
This technology is suitable only for soils with a low clay content, since the residual heaving is greater than 50%;
If you paste over the entire height of the MZLF tape (mark -30 cm) with a heat insulator, leaving the insulated blind area, this indicator will decrease to 40% Fig. 2.
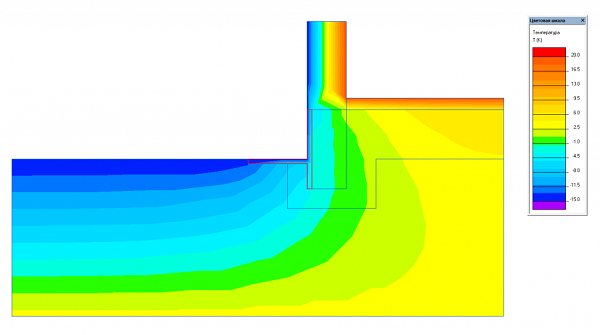
Rice. 2. Scheme of heat distribution when insulating the blind area and MZLF tape to the entire depth.
With an increase in the perimeter of the thermal circuit (90 cm of the blind area from the foundation), heaving decreases by another 5 - 7%, sharply increasing labor costs (expansion of the trench, increased excavation, material consumption). An increase in the thickness of expanded polystyrene or PSB-S also does not eliminate the heaving forces under the sole of the base of the cottage as a whole.
However, if you transfer the insulation to the level of the sole - to line the bottom of the trench by 60 cm around the perimeter, the heaving forces under the reinforced concrete structures disappear completely. Rice. 3.

Fig. 3. Heat distribution scheme for insulating the sole and MZLF tape.
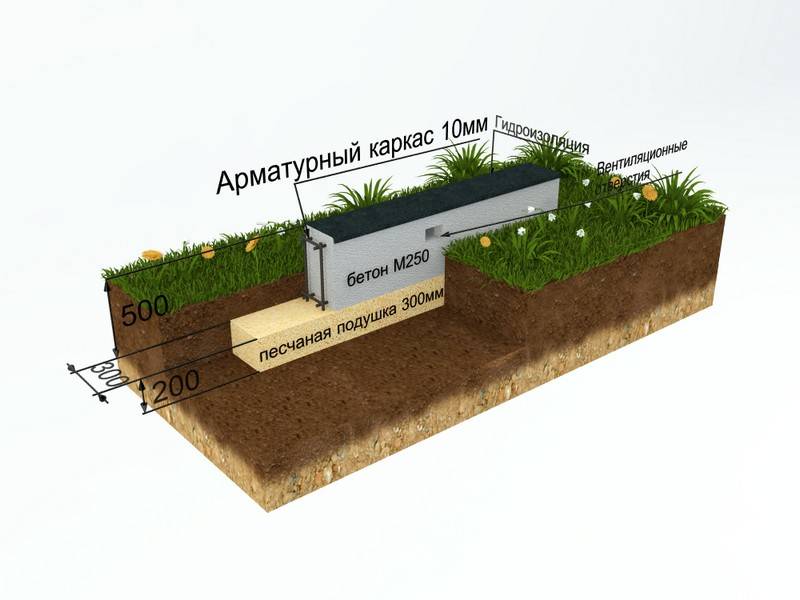
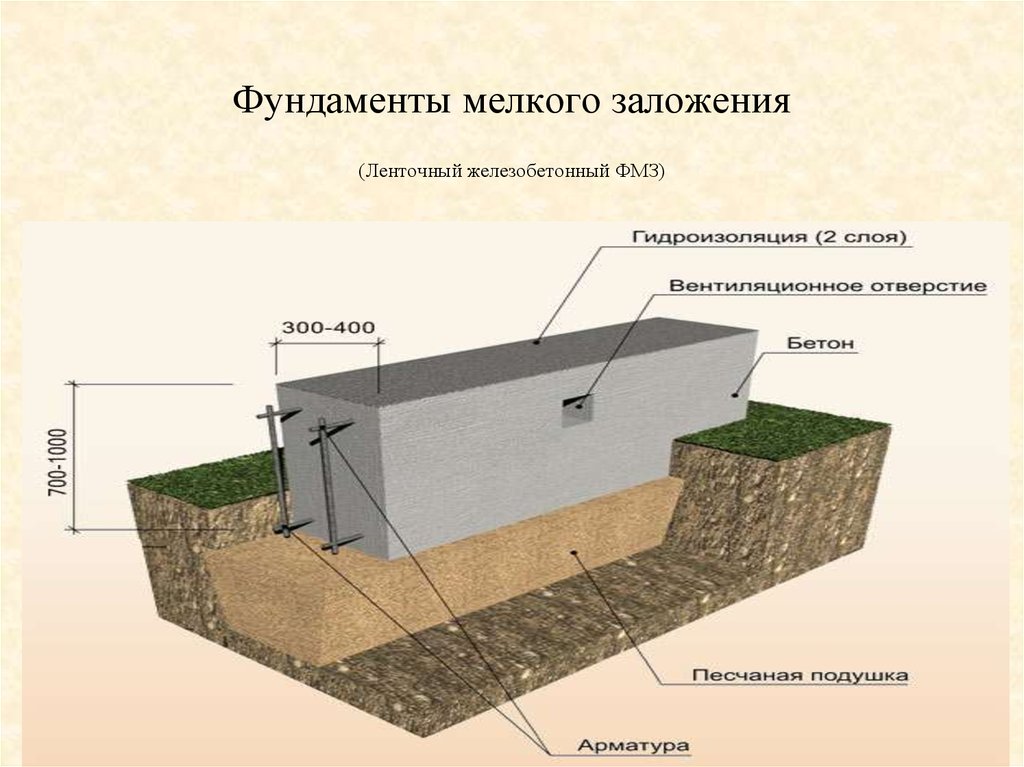
Technology for the construction of a strip shallow foundation
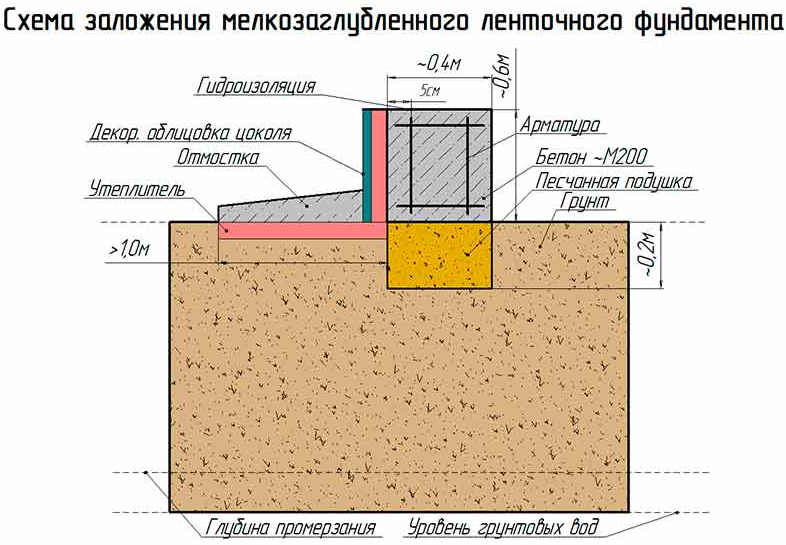
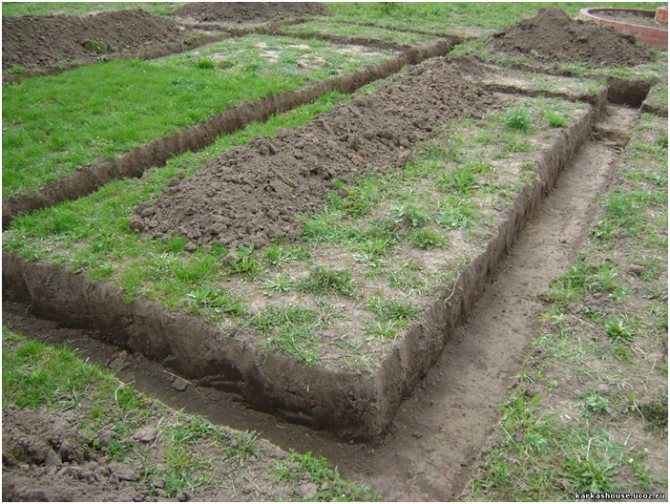
Before you start building a shallow strip foundation with your own hands, it is necessary to carry out the appropriate calculations - width, location and optimal depth. Based on the data received, a diagram is drawn up. It is necessary so that in the course of work you do not have to interrupt to carry out repeated measurements and calculations.
The scheme is drawn up in a matter of minutes, but subsequently it often saves several hours. Designing shallow foundations is simple, so even a layman can handle this work. When the scheme is ready, you can start binding on the ground. Armed with pegs and a strong cord, you need to determine exactly where will be located foundation of the house on plot.
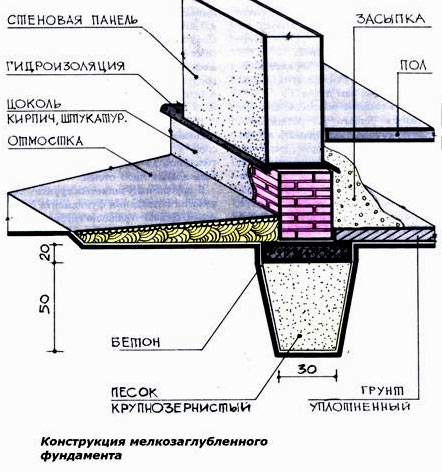
Shallow foundation construction drawing
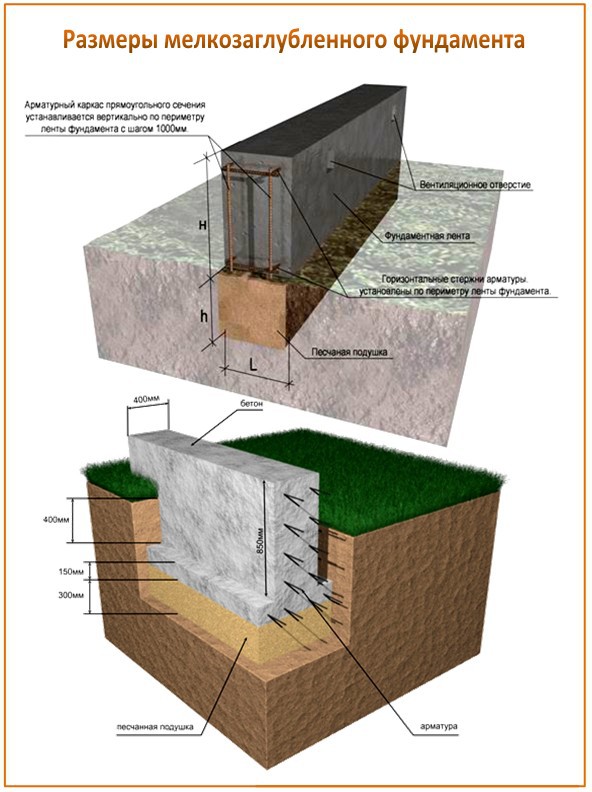
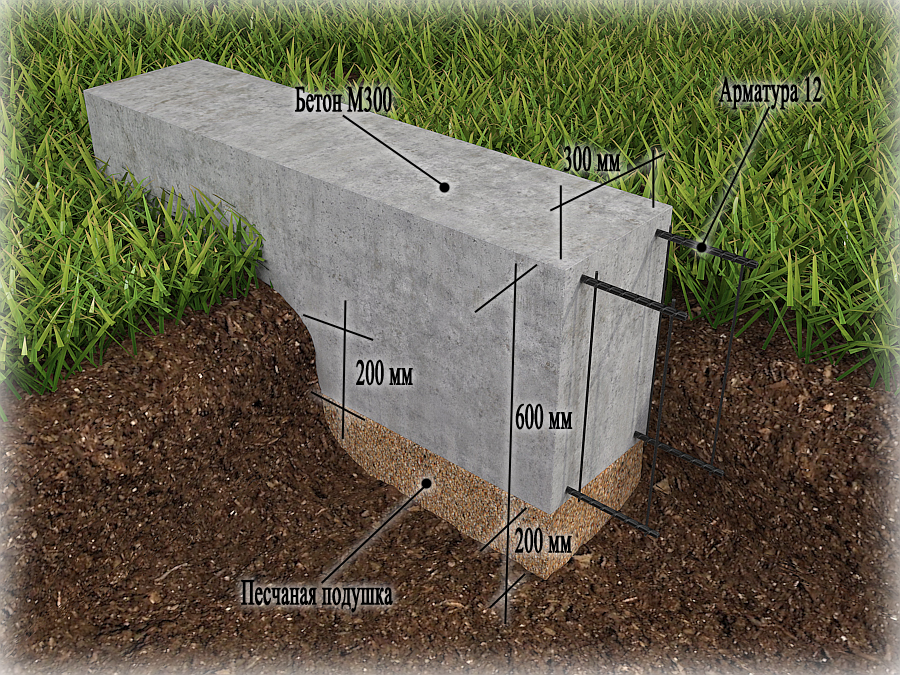
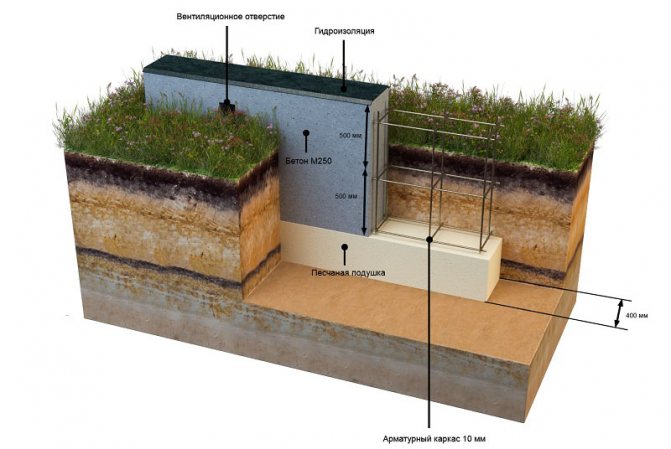
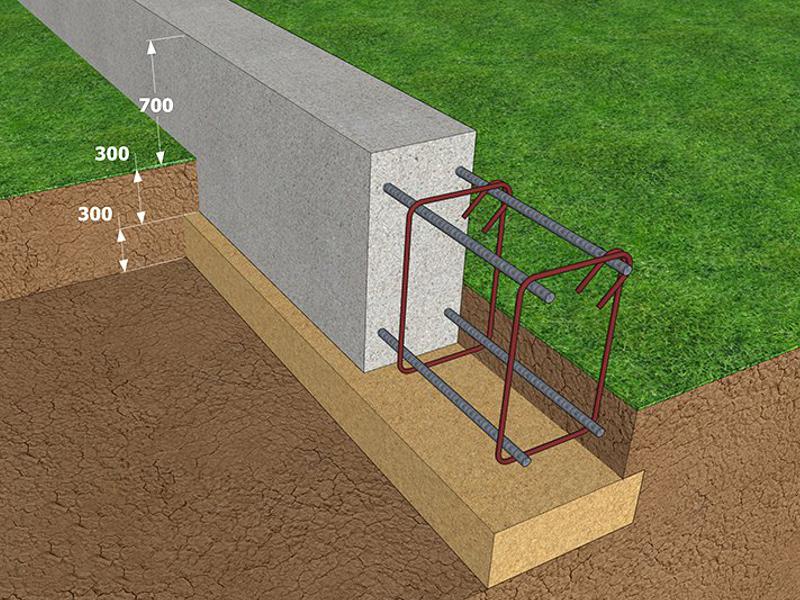
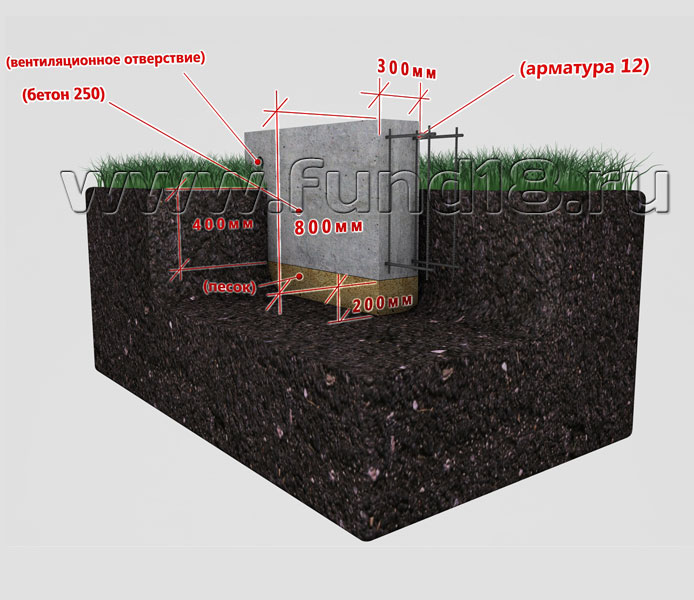
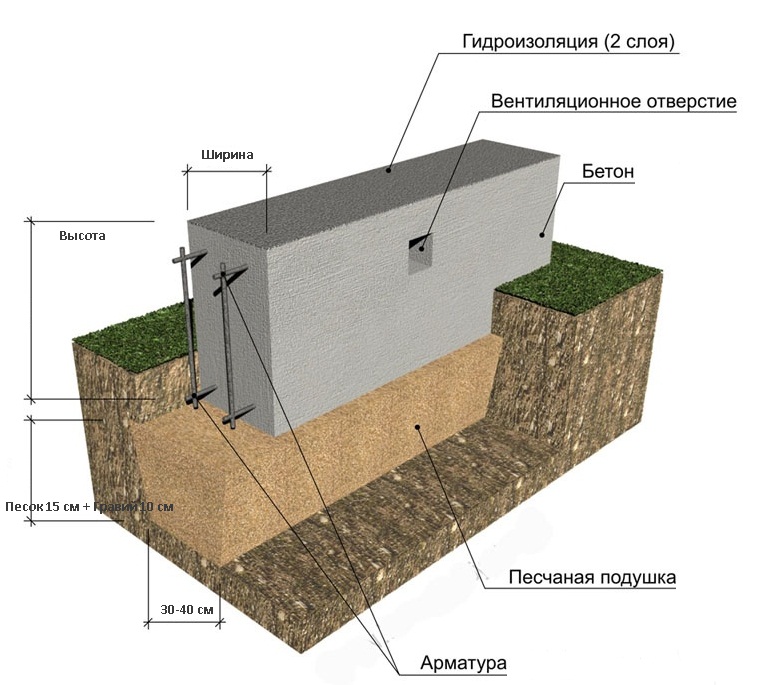
After that, you will have to take up the shovel. Having marked the boundaries of the future trench, it is necessary to dig a ditch 60-80 centimeters deep and about 40 centimeters wide.
More precisely, the width can be determined by taking the thickness of the outer walls of the building, adding 5 cm sides on each side for the stability of the structure on the foundation and another 5 cm for installing the formwork (for this, plywood, boards, profiled sheets and other thin ones can be used, durable materials).
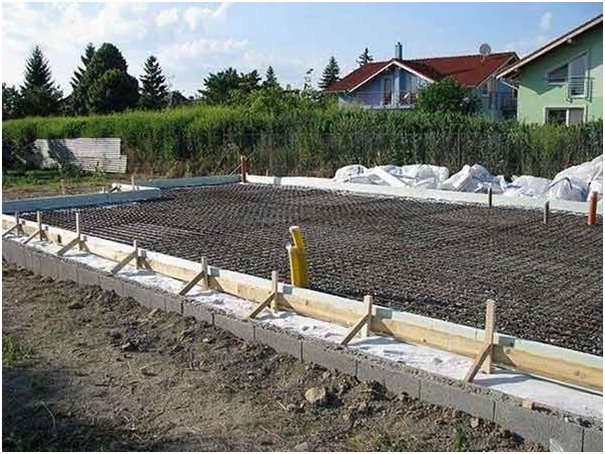
The next stage is reinforcement. From reinforcement with a thickness of 5-7 mm. the base for the foundation is knitted or cooked.A reliable reinforcing base is especially important if shallow foundations are erected on heaving soils. Foundation without strong reinforcement will simply collapse during seasonal fluctuations in soil level. In most cases, this leads to the destruction of the house.
The resulting "skeleton" is installed in a trench and poured with concrete. When it gains sufficient strength, the formwork can be removed.
And the effectiveness of waterproofing roofing material is much higher.
Insulation of a shallow strip foundation
After that, the next stage of construction begins - insulation of shallow foundations
It is very important if you do not want heat loss through the foundation to force you to continuously heat your home during the cold season.
The fact is that the shallow foundation lies above the level of soil freezing. And without high-quality insulation, it will significantly increase the heat loss of a residential building.
Extruded polystyrene foam is most often used as the main insulation. This material has several advantages. It is lightweight, which simplifies the process of transportation and installation. It is able to perform its function perfectly for many years, even when working in high humidity soil, without harm to itself.
And, finally, expanded polystyrene, despite its small thickness, provides high-quality thermal insulation.

When the insulation of the foundation is completed, it remains only to fill up the remaining cracks with earth and compact the soil tightly.
Some experts recommend planting low but dense shrubs along the wall of a house built on a shallow foundation. In the summer season, they give a special freshness and beauty to the house, emphasizing its originality and grace. But there is also a purely practical calculation - additional thermal insulation.
As you can see, the shallow strip foundation, despite its apparent complexity, is nothing extraordinary.
The entire device can be completed in a matter of days by a couple of people who may not even have the skills to carry out construction work, but will seriously study the theoretical part.

An example of reinforcement of a shallow foundation
After the foundation has gained sufficient strength (usually after 10-20 days, depending on the humidity and temperature of the ambient air), you can start building a bathhouse, a house, a gazebo or any other building.
Preservation for the winter
Even most professionals do not know that it is dangerous to leave a newly poured foundation during the winter. The base without load is not able to balance the heaving forces by its own mass. At the same time, there is no heating of the perimeter due to not installed heating equipment.
Temporary protection of MZLF is as follows:
- the perimeter (foundation + 1 m of soil around it) is covered with a double layer of film (polyethylene is not recommended, it is better to choose PVC);
- structures are protected with a heat insulator (expanded clay, straw, mineral wool, slag, sawdust) Fig. 4;
- installation of snow retention elements - shields along the perimeter of the building spot.

Fig. 6. MZLF conservation for the winter.
Soil density can be reduced mechanically by plowing, digging up the soil on the site. A depth of 15 cm (shovel bayonet) is quite enough for this. Rice. 5;
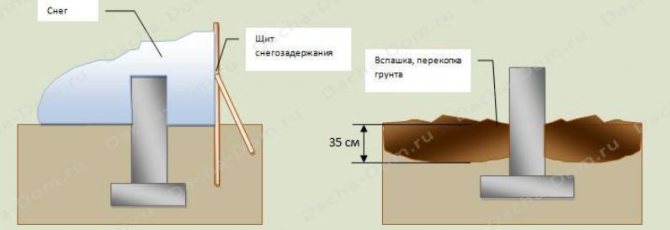
Fig. 5. MZLF conservation for the winter.
Applicability criteria for shallow foundation
The shallow foundation is distinguished by its simplicity of design, but it is also inferior in strength to the buried version
Therefore, it is important to determine the possibilities for such savings and their feasibility. Such foundations are most common when erecting light structures made of stone or frame blocks.
 Low-loamy soils are suitable for the construction of shallow foundations
Low-loamy soils are suitable for the construction of shallow foundations
The main criteria for choosing shallow foundations include the following:
- Soils should have minimal heaving, since there is a high risk of raising the foundation and destruction of the building. With low or medium heaving, it will be necessary to reinforce the concrete in the strip structure with reinforcement. Installation of a shallow basement is prohibited on highly loose soils.
- The depth of soil freezing should not exceed 0.2-0.35 m, since the depth of the foundation is up to 1-0.7 m. That is, the freezing zone should be 30-35 cm higher than the tape, excluding the sand-crushed stone cushion.
- The soil must have sufficient bearing capacity and not be seasonally submerged. This is due to the fact that a shallow foundation must be supported not only from below, but also from the sides of the belt in order to prevent its displacement under load. To determine the composition of the soil, geological exploration is carried out, and to assess the possibility of building an object - engineering surveys.
If the main criteria are met, then you can start preparatory work.
Scope (MZFL)
The shallow foundation is used in the construction of structures on slightly heaving and non-heaving soils with a low moisture content. These are sandy and sandy loam soils.
The main criterion is the water table. It should be 0.5 m below the base depth.
Important! Most of the clayey soils are of medium and high loaminess, therefore, the construction of MZFL on these types is accompanied by problems. Since the shallow-buried type of foundation is between non-buried and buried, the bearing capacity is estimated as average
Since the shallow-buried type of foundation is between shallow and buried, the bearing capacity is estimated as average.
The MZFL technology is used for structures:
- country and frame houses;
- timber structures;
- outbuildings;
- baths;
- sheds;
- fences.
Important! Structures made of foam blocks, gas blocks and brick houses, a small foundation will not work. It can be used in combination with other types of bases.
For example, in combination with piles. For heavy structures, a pile-strip foundation is suitable. the bearing capacity is increased due to the bored supports. The design must comply with SNiP 2.03.01-84 in terms of strength and resistance to deformation.
Tape base
Shallow tape slabs in suburban construction were in great demand. You can use such a device for:
- Buildings made of wood
- If you follow all the rules, you can use it for buildings with heavy stone walls.
When planning further foundation insulation, then you can build foundations on any type of soil. The strip base consists of: a uniform strip of concrete mix, which should also be evenly loaded with further building structures. Types of erections:
- Reinforced concrete with two belts
- Precast reinforced concrete with outlets of reinforcement in a small amount
- Blocks with two belts, lower and upper
- Block with one upper belt.
Advantages of shallow tape base:
- Profitable money savings. Indeed, when erecting foundations with a deep foundation, the prices for such an erection in order exceed the foundations of a shallow foundation.
- Savings on labor costs. All construction work of this type involves a small amount of work. First of all, savings arise when working with earthworks, as well as creating formwork.
- As a supplement, you can spend the savings on building a basement.
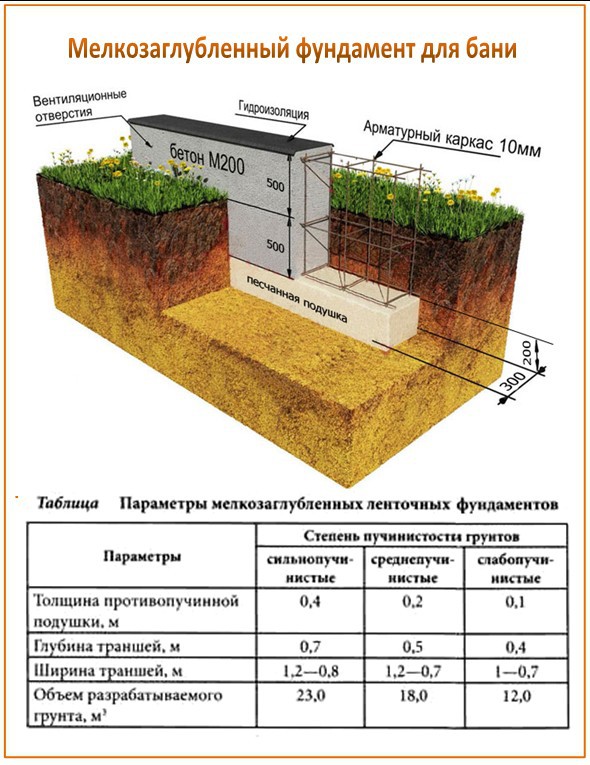
As practice has shown, the installation depth of the strip base can correspond to the freezing depth and the depth of the vegetation layer. Construction books give a figure of fifty centimeters. With such a depth, all the forces of frost heaving are concentrated in this place, therefore such a depth is considered the most dangerous.

Calculation of the base
Counting small foundations is considered an important step in construction. The service life of the foundation and the house as a whole will directly depend on the correctness of the work done. With all this, it turns out to reduce the cost of the main construction of the structure. When calculating shallow foundations, the first step is to determine the size and type of structure. The main properties include the size of the sole, as well as the level of depth. Several factors affect the level of foundation laying depth, one of which is the type of construction of the planned building, for example:
- The type of material used for the construction of the roof
- What walls are planned from
- Will there be a basement in the building or not
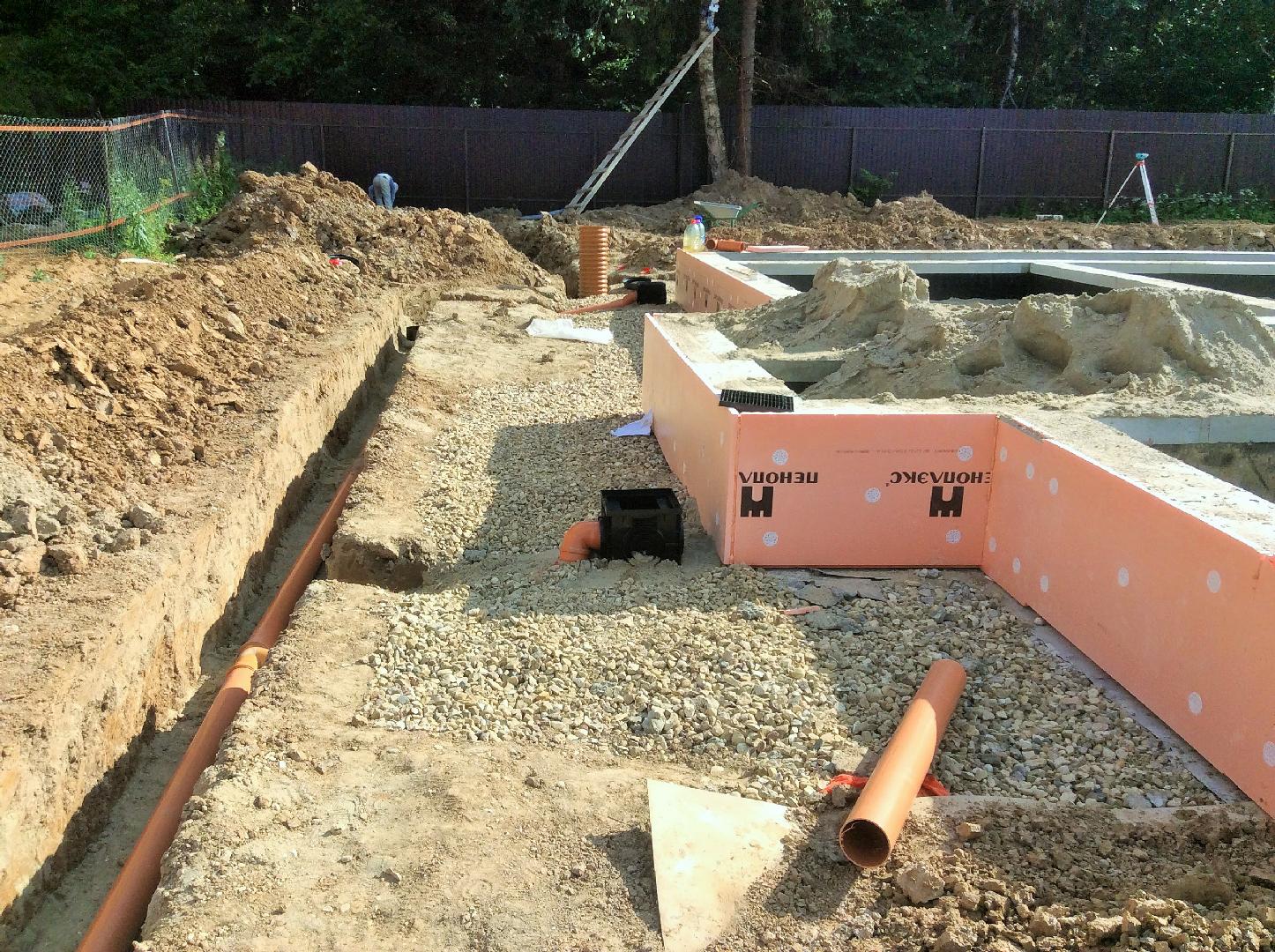
In addition to these factors, the properties of the soil on the construction site also affect groundwater level... In the event that water appears on the soil surface, it is necessary to completely dry the construction site. After carrying out drainage work, it is necessary to devote time to laying engineering communications.
After completing the preparatory work and choosing the required dimensions of the foundation, you should smoothly proceed to its calculation. The ultimate strength and deformation that the base structure can withstand is calculated. After completing the theoretical work, you should take up the practical part of the construction, that is, engage in the construction of the foundation structure.

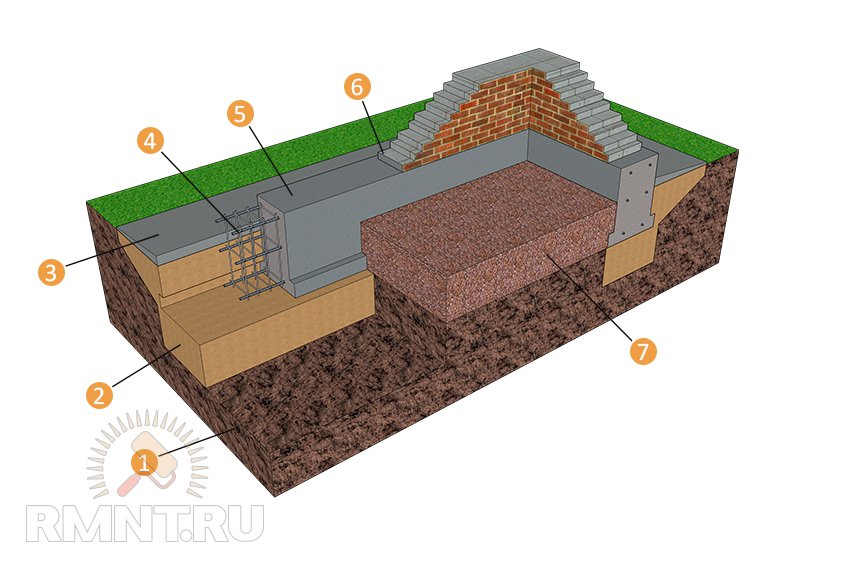
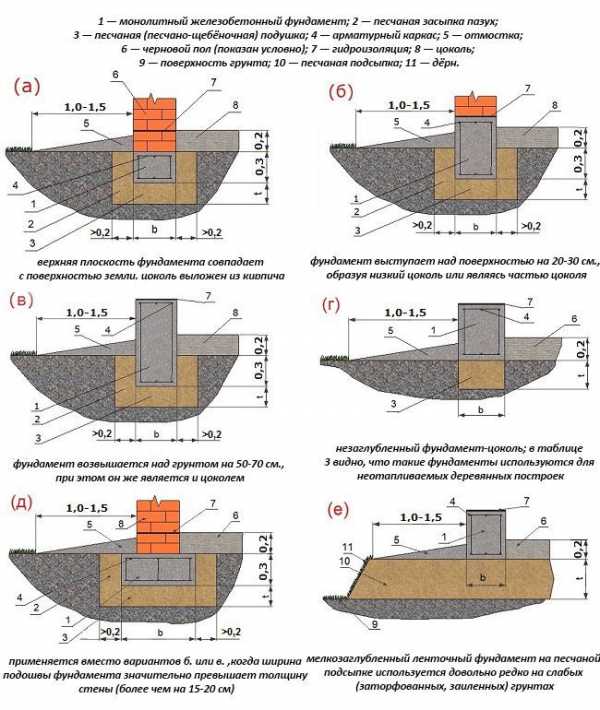
Base device
The bases, which are slightly deepened, are partly not subject to deformations arising from the heaving of the soil. For this reason, this method of installing the foundation is widely used in practice. Most often they are used in the construction of small houses, summer cottages and frame structures. Buildings with light weight cannot withstand the heaving of the soil, so the foundation deepens to a small level.
The structure, which shallow foundations are able to, consist of a monolithic frame. A frame with a reinforced concrete base can easily resist the heaving of the soil, not only seasonal, but also constant.
Foundations that can be used at the time of installation on shallow depths:
- Columnar base
- Tape view of the foundation
- Reinforced concrete slab
These types of foundations have a common component, such as a reinforced concrete foundation. The dimensions of any of the bases are chosen only by the strength calculation. It is based on the weight of the structure when it touches the ground. Although the large area reduces the pressure, the maximum size of the site does not justify the construction costs. For this reason, all calculations must be equal to the values in construction, that is, all buildings must be leveled to the area of the foundation.

Subsequent processing of the base
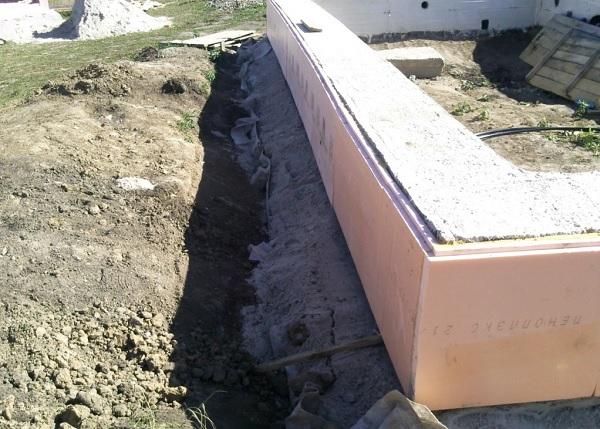
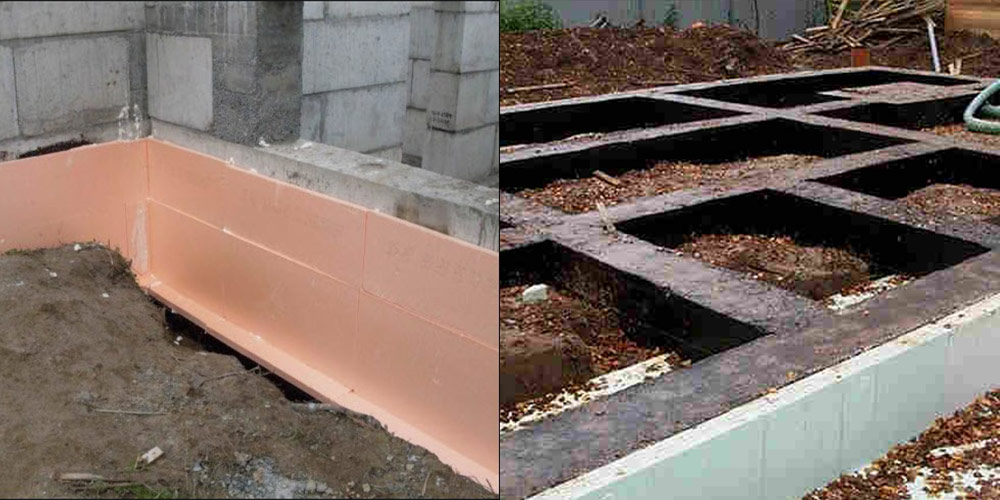
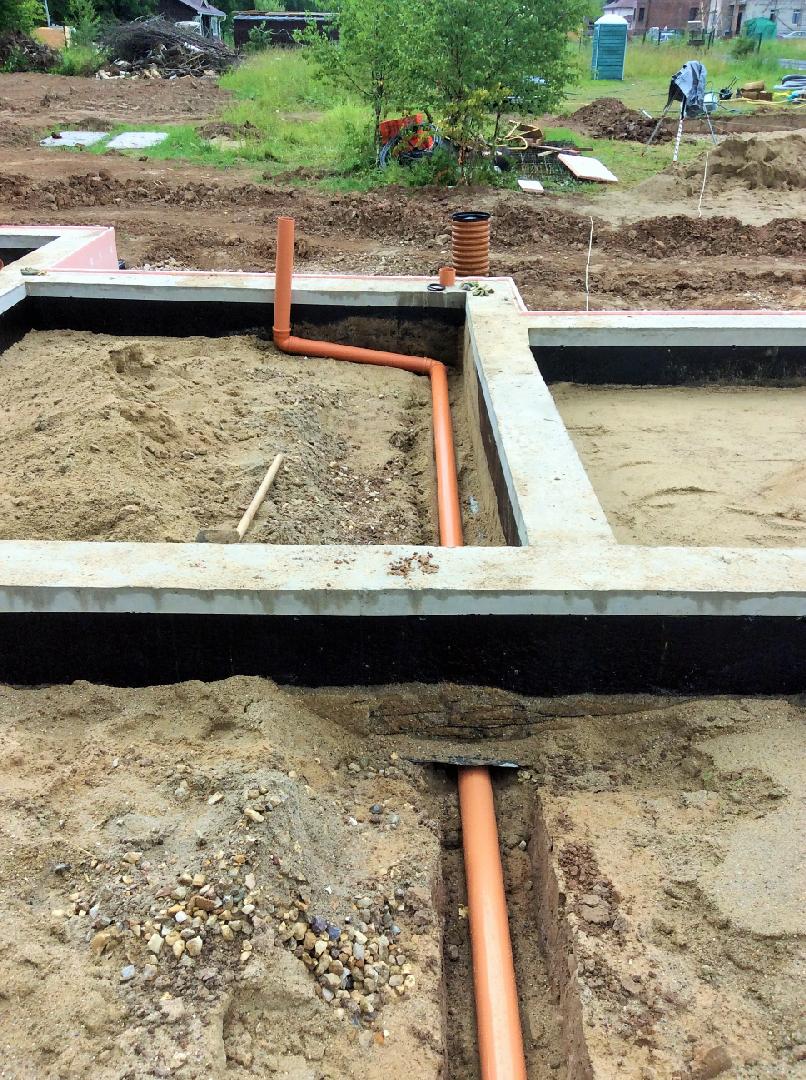
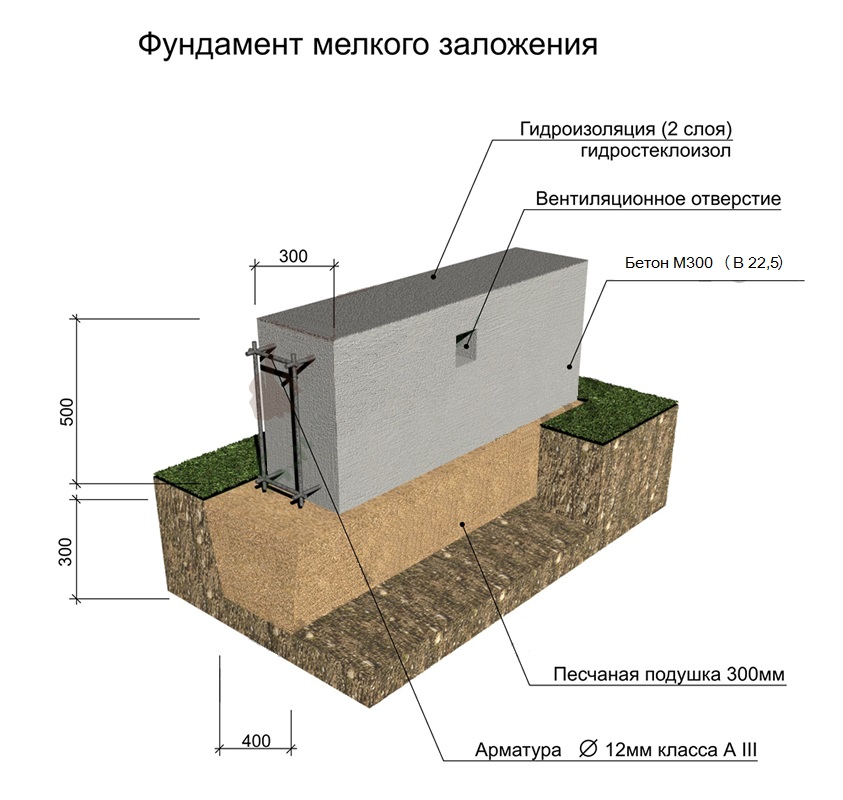
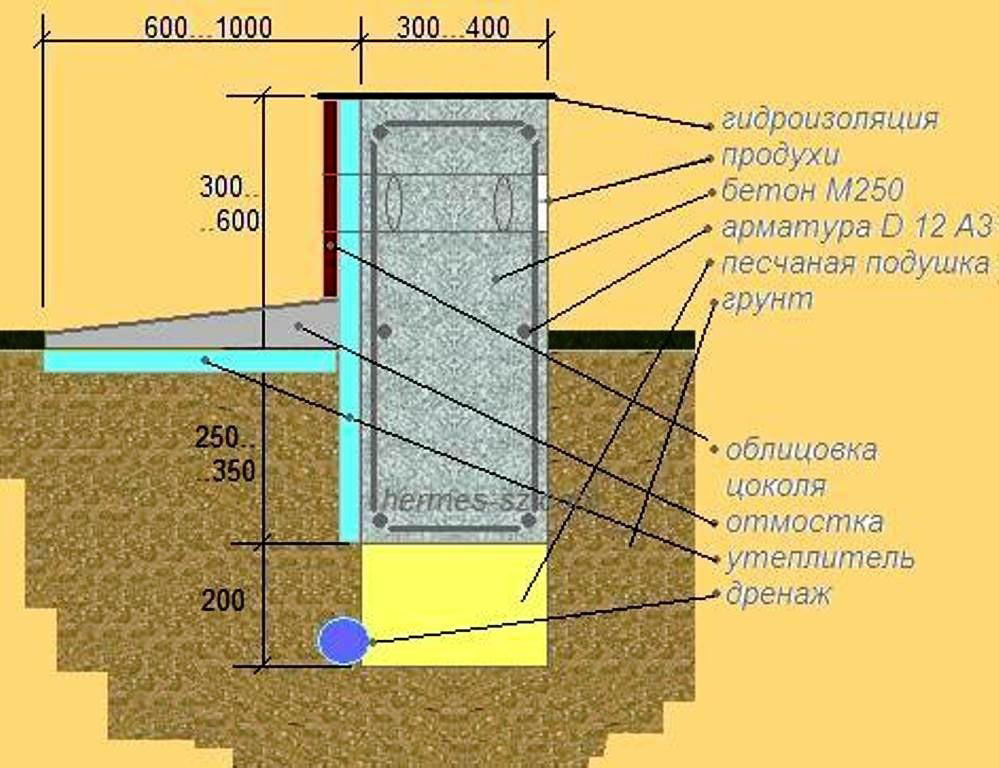
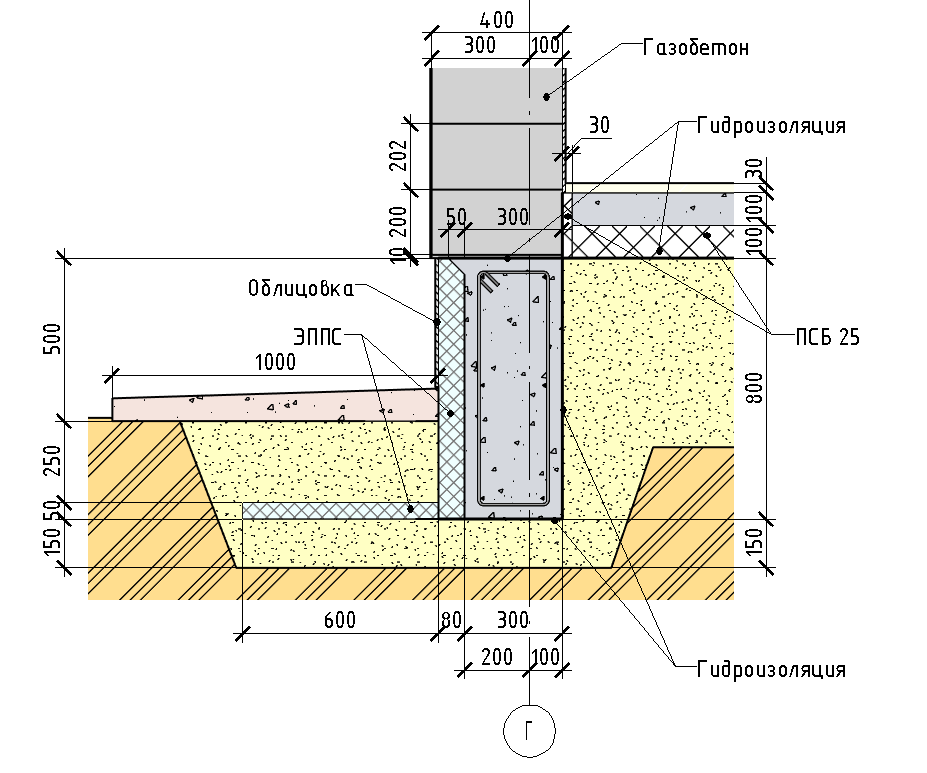
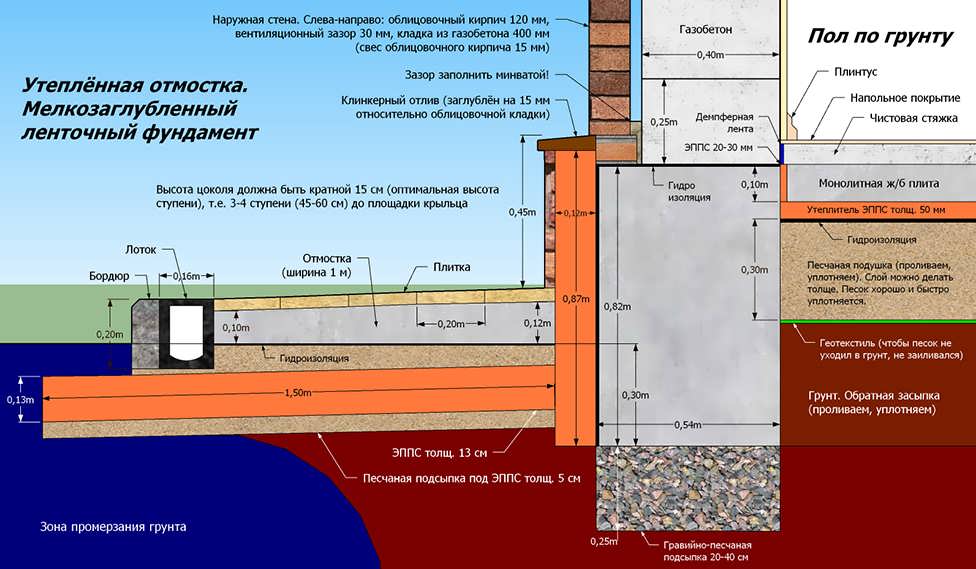
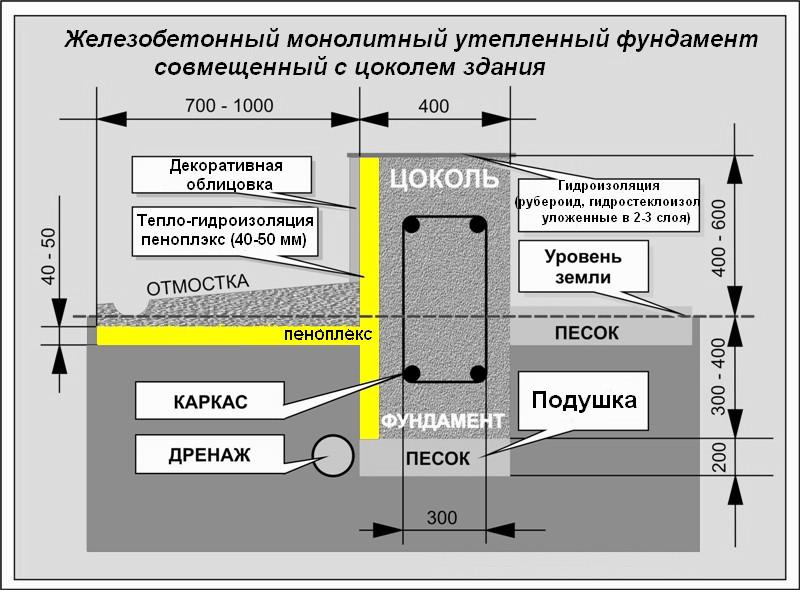
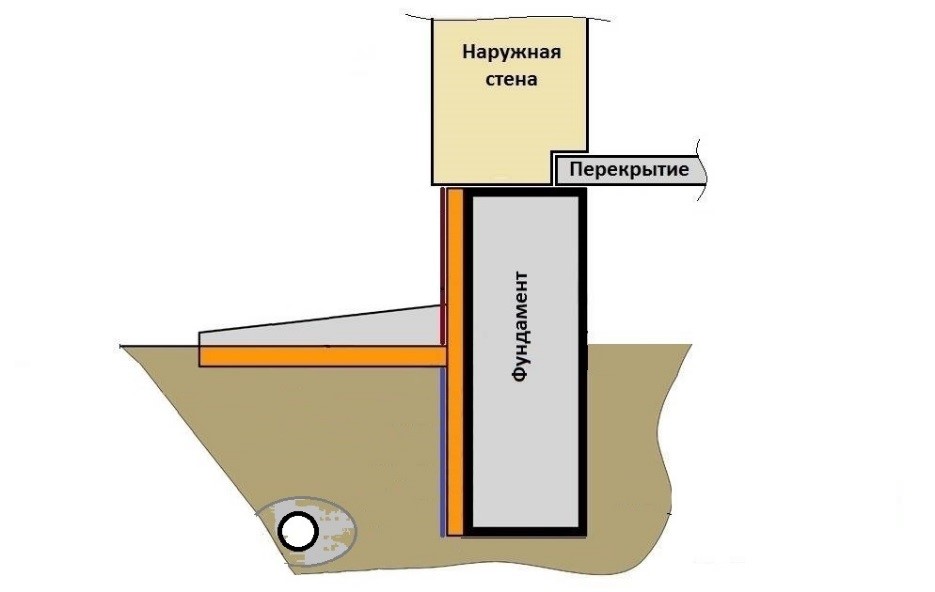
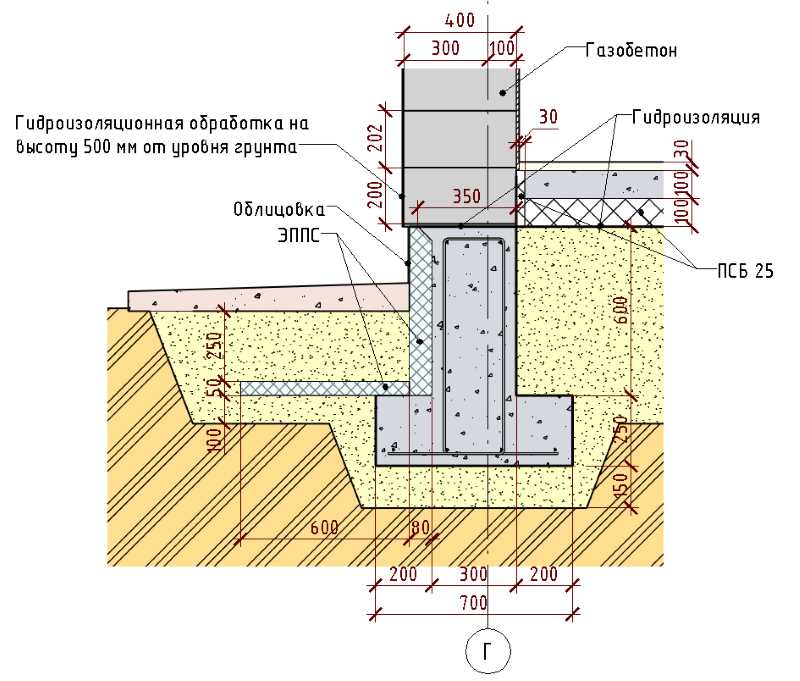
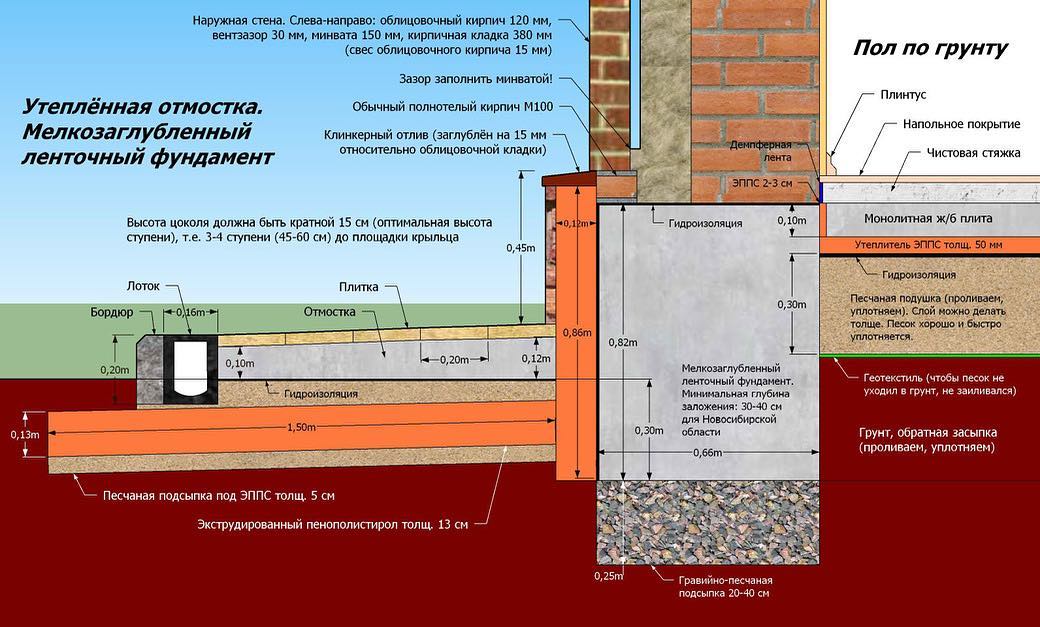
When the MZLF is ready, they begin to protect it from destructive factors: moisture, temperature extremes. For this, hydro and thermal insulation of a concrete tape is used. The blind area also plays a role in protecting the structure.
Waterproofing a shallow foundation
To protect the shallow strip foundation from moisture, it is covered with hydrophobic compounds. There are two types of waterproofing used for MZLF: vertical and horizontal. The first type consists of two layers of roofing material, which are fixed to each other using bitumen mastic. The lower surface of the foundation is insulated even before the installation of the reinforcement, the upper surface - after the concrete has completely solidified. Vertical waterproofing is applied to the side surfaces of the foundation. For this, special impregnations, coatings or gluing materials are used.

Warming
The use of thermal insulation allows you to avoid condensation on the surface of the concrete tape, freezing of moisture inside the foundation itself, dampness and cold on the ground floor.This work is especially relevant if a basement is planned in the house. For a shallow strip foundation, external or internal insulation is used. The first is considered mandatory, the second - if there is a basement. Different materials are used for thermal insulation:
-
Penoplex. It is characterized by an optimal price-quality ratio.
-
Expanded polystyrene. Cheap material, but with lowered technical qualities.
-
Polyurethane foam. Expensive sprayed insulation with a long service life.

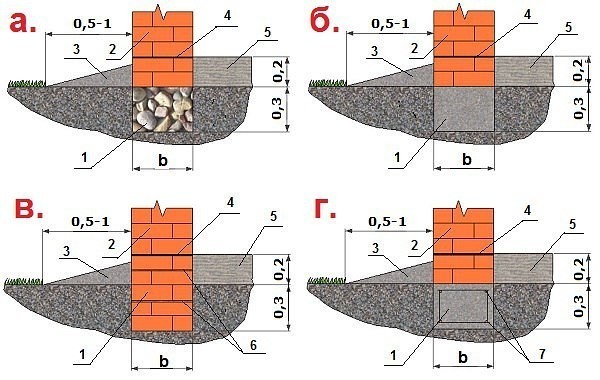
Blind area
At the final stage, the sinuses on the outside and inside of the tape are covered with sand or other material with good absorbent properties. The sand is covered in layers, tamping each one. Next, proceed to the blind area. In the future, it will protect the foundation from water flowing down from above. Installation of the blind area is carried out according to standard technology, taking into account the need for its insulation.
Finishing
In order for the protruding part of the base to have a more attractive appearance, it is advisable to cover it with finishing materials. In addition to the decorative role, the cladding also provides additional protection of concrete from adverse factors.
There are different cladding options. The easiest and cheapest way is plastering and painting. Another option for finishing is DSP panels and bricks. Such coatings are reliable and durable. Natural stone stands out from the more expensive materials. To save money, but get an aesthetic look, they use imitation of natural materials - artificial varieties of stone and brick.

Materials for thermal insulation of the foundation
When choosing a material for thermal insulation of the base, you should pay attention to several points:
- Insulation must have low thermal conductivity.
- The material should not absorb moisture.
- Thermal insulation must be resistant to temperature changes and mechanical stress.
- Materials for insulation of the foundation must be resistant to an aggressive environment.
- The service life of the insulation and the operational period of the building should be comparable.
Thermal insulation materials, presented on the modern market in a large assortment, meet all of the above requirements. To make the right choice, you need to know the advantages and disadvantages of the material for insulation. The most popular are several types of insulation.
Polyfoam can be considered a reliable heat insulator due to its composition and ability to retain its properties in any climate. On the positive side, the foam is characterized by the following qualities:
- Good thermal insulation;
- Waterproof;
- Ability to resist contact with asphalt and cement.
- Fire resistance.
- Resistance to harmful effects of sunlight.
Extruded polystyrene foam is the most common material for insulating shallow strip foundations. Its main advantage is its low thermal conductivity. The high compressive strength of the material can protect the waterproofing of a shallow-buried strip-type foundation from damage. The low rate of water absorption increases the resistance of the material to severe frosts. Such insulation will reliably protect the base from moisture penetration, sudden temperature changes and corrosive chemicals. With proper operation, expanded polystyrene will last for 50 years.
Polyurethane foam is a new generation material. It combines several main functions: thermal insulation, waterproofing and soundproofing. The material is applied to the surface to be insulated by spraying. In such a heater there are no gaps and seams, which serve as a kind of cold bridges. Therefore, there is no possibility of penetration of cold and moisture into the base of the house. The advantages of polyurethane foam insulation include:
- Reliability;
- High adhesion;
- Long operational period;
- Low rates of thermal conductivity and vapor permeability;
- Seamlessness;
- No need for waterproofing works.
The main disadvantages of polyurethane foam are considered to be high cost and poor UV resistance. In addition, the application of the material to the surface requires special equipment and experience, which can also cause some difficulties.
Expanded clay and earth are considered the cheapest and most affordable materials. At the same time, they are able to significantly reduce heat loss during the cold season. This method is most often used when insulating a strip foundation. The use of earth and expanded clay as insulation prevents freezing of basements in private houses. Expanded clay as a heater for a shallow strip foundation is able to hold back cold air outside. It also absorbs moisture well, which helps to protect the base of the house from waterlogging. However, the use of expanded clay alone does not give a meaningful result. Additional use of waterproofing materials will help reduce heat loss when heating a house.
Shallow Foundation Calculator
Examples of how to calculate this type of important construction project, designed for those who are building or are about to build their own home. The use of special formulas and data will help for accurate and good quality calculations of the strip foundation and the durability of the entire structure of the room.
What you need to know:
- The name of the total length of the tape. It includes information around the entire perimeter of the foundation. You must know the real numbers that are taken after probing the object.
- The area of the sole zone. Determination of the reference area for the future base. It must match the dimensions of the waterproofing system or material chosen.
- Lateral outer surface area. It is assumed to be equal to the insulation zone for the outside.
- The name of the required concrete solution and its quantity. This is the amount of concrete needed to build a foundation for a specific purpose. It is determined only by the independent production of concrete mortar.
- The amount of concrete mass of the solution. Calculated for the average density of cement-concrete mortar.
- The load on the ground on which the foundation will be calculated. This shows the size of the load distribution over the total area.
A real example of calculating a strip foundation
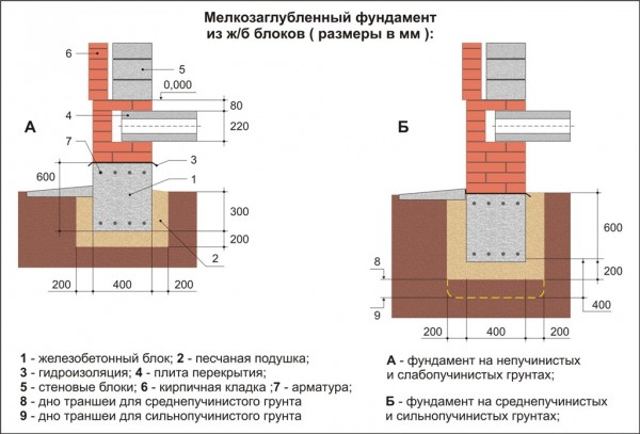 Data used: monoblock concrete mounted on granite. For a better understanding of our own actions, we will draw up a diagram of the scheme.
Data used: monoblock concrete mounted on granite. For a better understanding of our own actions, we will draw up a diagram of the scheme.
1. Data for calculation:
- Shallow strip foundation, base, size: 6x3 m;
- Height: 0.2 m;
- Bottom: 0.25 m
2. Real characteristics of the premises for the construction of the strip foundation:
- The walls are 400 mm thick.
- Soil containing crushed granite
- Two-storey house.
Calculation of gravity when constructing a shallow strip foundation
- Gravity is measured in Newtons, a unit of force that is calculated by taking the weight of a structure in kilograms and multiplying it by 9.81, a number that is actually the maximum gravity of the pressure.
- To build a strip foundation, you need to know the severity of the room, and this is measured in three ways:
- Deadweight: This is the force attributed to the overall structural mass of a building, as mentioned above, roofs, etc. This will be the weight of all materials multiplied by 9.81 to calculate in Newtons.
- Load created: This is the force that will be imposed on the room, including people, furniture, and more. Snow loading (snow load) will also fall into this category.
- In all cases, the final decision on the width and depth of strip foundations is a general rule that the depth of the foundation should be equal to or greater than the distance from the front edge of the wall to the edge of the foundation.But the concrete thickness will be at least 150mm. In some cases, reinforcing steel can be inserted into the foundation strip to reduce the depth of the concrete. It should also be remembered that when constructing a foundation when working on blocks and / or masonry, space must be found in the trench. It is considered normal practice, based on the required strength or better, to build a 600mm wide and 250mm deep concrete strip foundation. This will cover almost all possible cases. Installation outside the building is much easier if the foundation expands rather than narrows and does not allow for errors in the work. It is also worth noting that 600mm is the standard bucket size of an earthmoving machine!
- The choice of filling a foundation trench with concrete is now used in most cases. And in most cases it is much cheaper to do so. The cost of labor involved in laying bricks and blocks to ground level, together with the materials included, is usually greater than the cost of pouring concrete to the required height, which, in most cases, is in two rows of brickwork of the finished foundation.
- The walls built below are subject to earth pressure in both directions and are considered retaining walls.
- Pipes passing through concrete must pass through a special tube to remove the possibility of pressure from any other surface resting on the pipeline.
Varieties of FMZ
Tape
It is the most popular in suburban construction, as well as among individual developers who carry out construction work on their own.
It is used both for the construction of wooden and heavier stone structures. Such a shallow structure is a continuous strip of concrete uniformly loaded by the walls of the structure.
There are several options for its construction:
- reinforced concrete block with an upper reinforcing belt;
- reinforced concrete block with lower and upper reinforcing belts;
- monolithic with two reinforcing belts;
- prefabricated monolithic with reinforcement outlets.
Columnar FMZ
It can be used in the construction of wooden, log, brick and stone buildings.
It consists of pillars that are installed at every corner of the house, as well as at the junction of internal and external walls. The "step" between the posts should not exceed 2 meters.
For the construction of a shallow columnar base, a pit is made, the depth of which should be about 1 meter, after which reinforced concrete rings are placed in it, subsequently compacted with sand and covered with concrete slabs.
Features of the device
If you are choosing a foundation for a frameless house or a bathhouse on clay soil or black soil, then the device of a shallow strip foundation is best for you.
Types of strip foundations from aerated concrete blocks or FBS slabs are convenient for their design and method of transferring forces. They directly take the loads on themselves and transfer them to the soils that lie below. However, unlike foundations for a bath with a solid slab, concrete for the production of FBS blocks from aerated concrete takes much less time, as well as time.
Let's give an example when a shallow foundation is mounted directly under the load-bearing elements of a house or bath. If the house has a basement, then the loads are transferred between the block walls, floor slabs, and then the foundation.
If the house does not have a floor slab, and the floors of the house or bathhouse are filled with a conventional screed over pebbles, then the structural loads are transmitted directly through the walls of the house or bathhouse. In any case, the shallow columnar foundation of the building is considered universal. Even SNiP recommends building standard low-rise buildings or baths on tape bases from FBS blocks of aerated concrete.
Appointment
Let's take an example, when a shallow foundation of aerated concrete blocks on clay soil or black soil differs from the usual one in that it has much smaller dimensions.
An example and calculation of a shallow strip foundation of FBS blocks made of aerated concrete shows that in this case, a slab on clay soil will be deepened by 60-70 centimeters, and the rest of its walls will serve as a basement. Such a solution can aggravate the problem of installing a basement for a house or bath. After all, the entire floor slab will not cover the space of blocks 1-1.5 meters high. But solving it is very simple.
You just need to finish building the missing part of the brick walls to the slab, and then insulate the shallow strip foundation from aerated concrete blocks (FBS). At the same time, the use of combined fences will help you avoid many problems that are associated with the excessive rigidity of the base of the house.

Schematic drawing of a shallow foundation
How many cases, when most of them are not even taken into account, however, houses made of blocks on heaving soils often face the problem of pushing or shrinking certain structures from the slab.
In this case, a deep reinforced rigid monolithic foundation made of FBS blocks can play a cruel joke with you. After all, his device will not allow him to extinguish the load, but rather will lead to the appearance of cracks.
Shallow strip foundations are placed on clay, sand, soft and hard ground. You have almost no limitations in this regard.
But immediately we note that if you plan to work on sandy soil or soil with a weak structure, then the calculation of shallow foundations does not recommend unnecessarily overloading the base by using a too heavy slab.
Anyway, shallow aerated concrete foundations are ideal when you need to build a relatively light house with a single solid floor slab.
For large cottages, you should still select more reliable and expensive options from FBS blocks. However, an accurate calculation will help you to choose how many to choose, it is better to turn to it.
Let us turn to the main pros and cons of such structures made of aerated concrete. They also matter, and quite serious.
Main pluses:
- profitability;
- practicality;
- the ability to extinguish loads from unstable soils;
- simplified calculation;
- construction is carried out using a simpler technology.
The main cons:
- not suitable for the arrangement of large, heavy buildings;
- in some cases it shrinks due to unstable freezing of the soil.