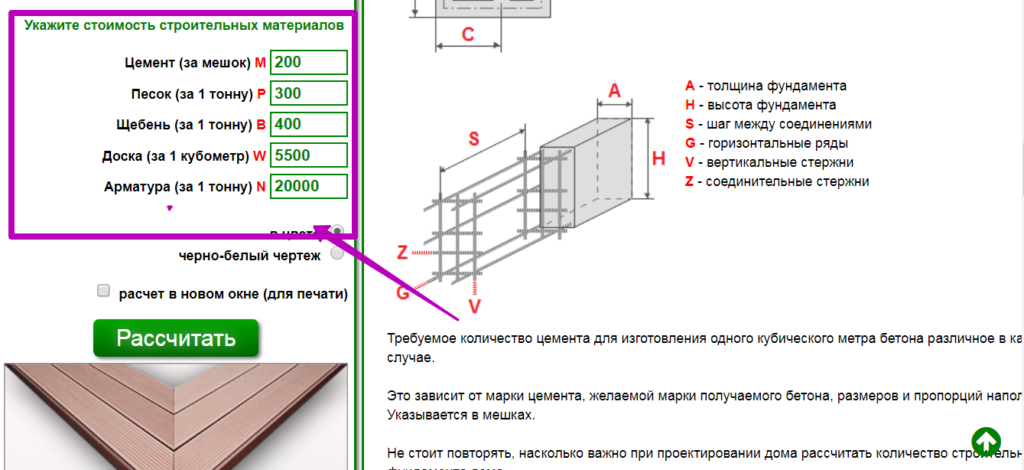
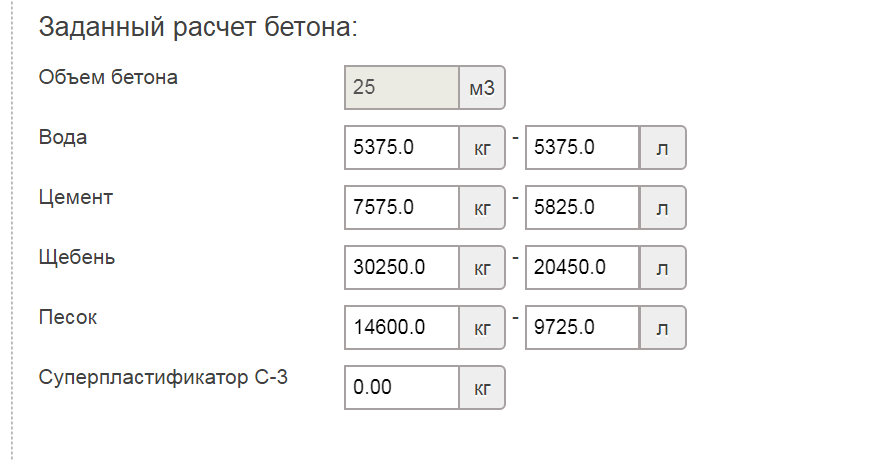
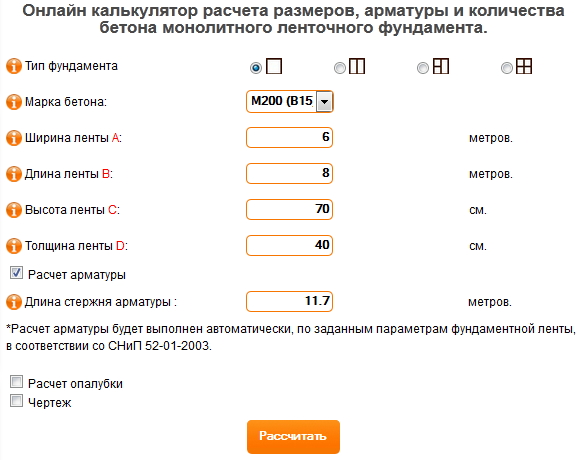
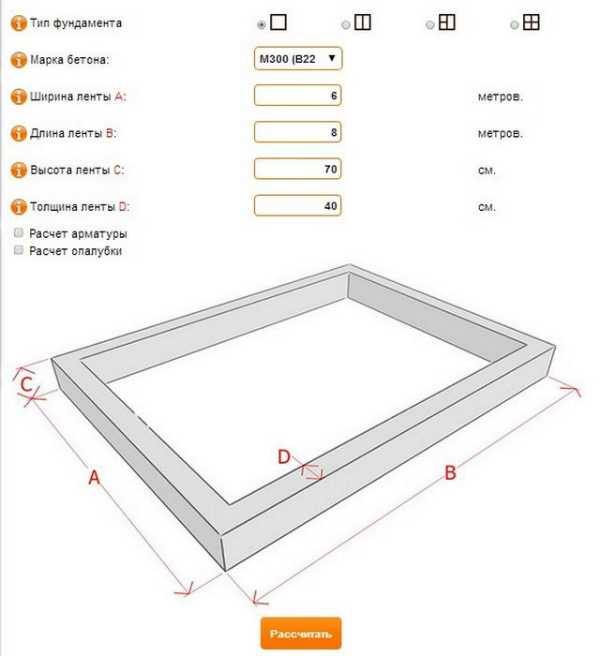
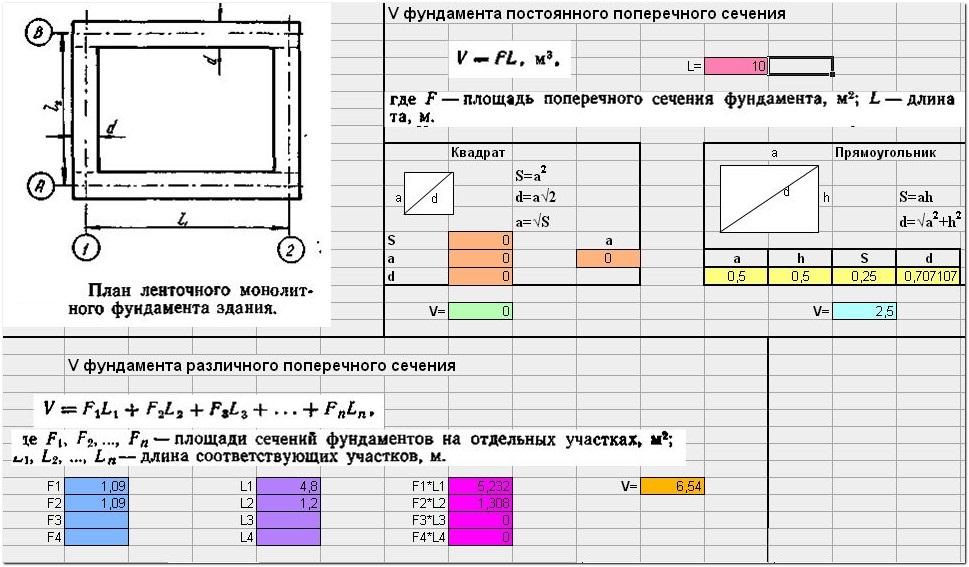
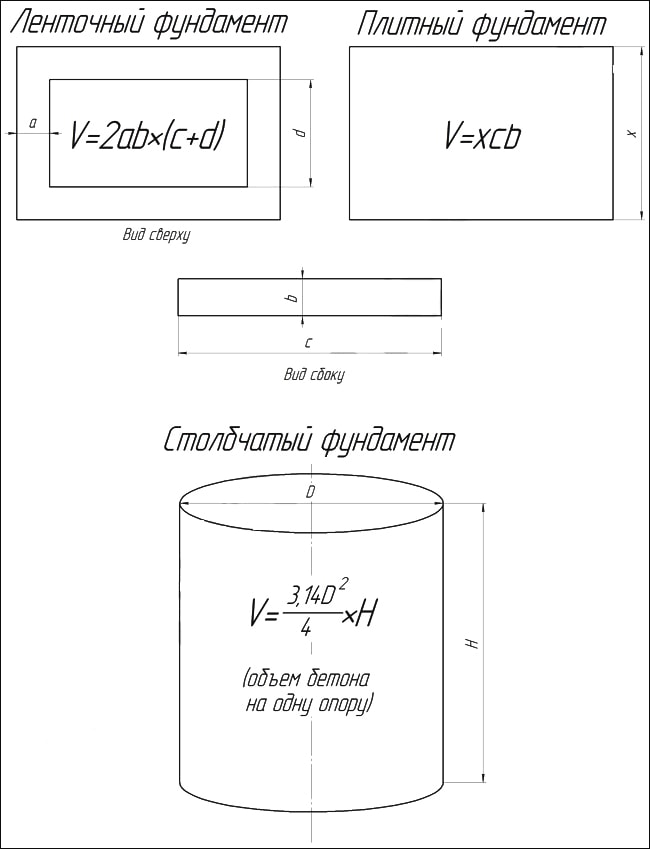
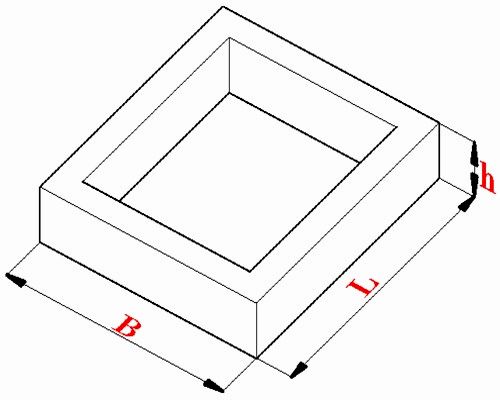
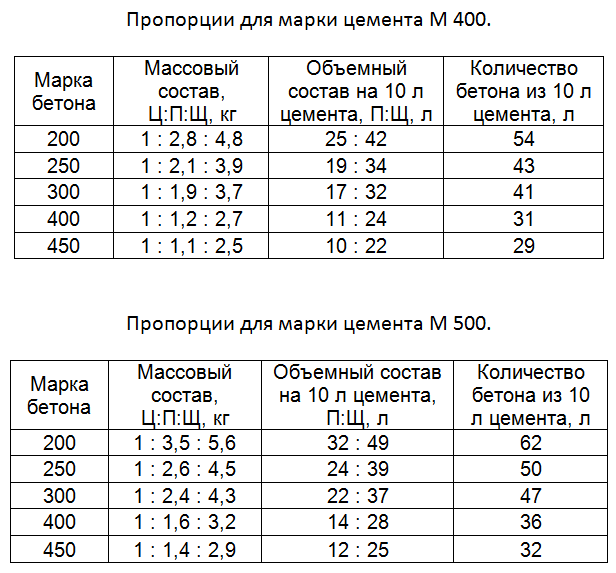
The need for accurate calculations

In the photo - large-scale concreting in industrial construction
Why is it so important to know the volume of the required solution correctly, because if there is not enough material, more can be done? In fact, the maximum strength and durability of monolithic structures is ensured only if the mortar is fed into the formwork for concrete products without prolonged downtime. You can avoid downtime, which can lead to the stratification of concrete, by knowing the exact amount of the mixture that will be required to carry out certain construction work.
To avoid downtime, which can lead to the stratification of concrete, you can know the exact amount of the mixture that will be required to carry out certain construction work.
Actual calculation formulas

In the photo - an installation for the preparation of mortars in limited quantities
At the moment, there are many ways to carry out calculations, for example, you can use a concrete volume calculator. But an online calculator may not be available at the most crucial moment, and therefore we will consider those formulas that can be implemented in practice at any time and under any circumstances.
It is no secret that there are several types of foundations, laid to one or another depth before the start of the main construction work. Depending on the configuration of these structures, their size and, as a result, the volume of solution that will be required differ.
Formula for columnar bases

In the photo - formwork for a columnar (pile) foundation
So how do you calculate the volume of concrete? To do this, you need to measure the height of the structure, find out the area and multiply these indicators. But the approach to calculations in accordance with the formula V = S * H is relevant only to simple structures, while calculating the volume in relation to complex structures will require a different approach.
The calculation method for columnar bases with round piles is as follows:
- We calculate the area of the base of each pillar, we do it according to the formula S = 3.14 * r², where r is the radius of each individual pile;
- Then we multiply the parameters of the area by the estimated height of the pile and get the volume;
- Then we multiply the resulting volume by the number of piles that will be applied according to the project.
Calculations for slab-type bases

In the photo - slab base formwork
Now let's look at how to calculate the volume in m3 of concrete for a slab foundation.
The instruction in this case is simple, since such a base is a one-piece structure.
- To begin with, we divide the planned perimeter of the foundation into rectangles. This must be done if the shape of the base is complex. If the configuration is simple and is a rectangle or square, we find out the area by multiplying the length by the width.
- Next, we determine the depth of the bookmark and multiply this number by the resulting area.
Calculation of the volume of material for a strip foundation

In the photo - the formwork of the strip base
A strip concrete foundation is by far the most popular type of foundation, as it is characterized by sufficient strength and durability. In addition, choosing this type of base, you can save the solution, since it will not be poured along the entire perimeter of the object, but only under load-bearing walls and partitions.
The calculation of the volume of concrete in this case is not difficult and is performed as follows:
- We measure the estimated width and total length of the tape. We multiply the obtained parameters and get the area of the base.
- Then we determine how deep the foundation will be, and multiply this number by the area and we get the nominal volume of the solution, which is necessary for pouring into the formwork.
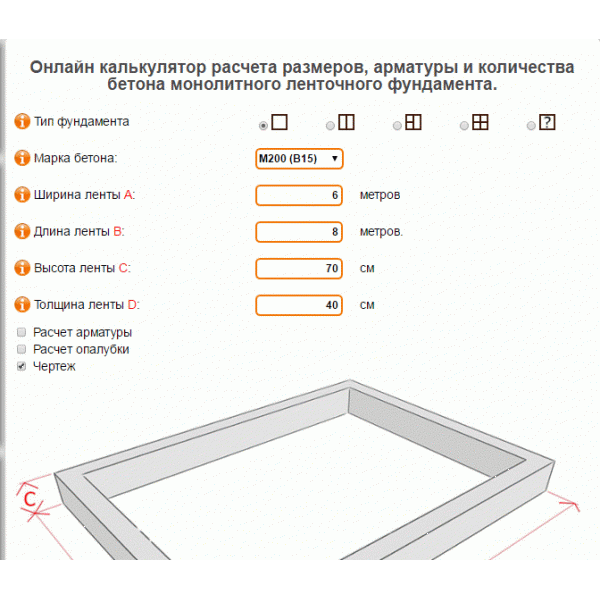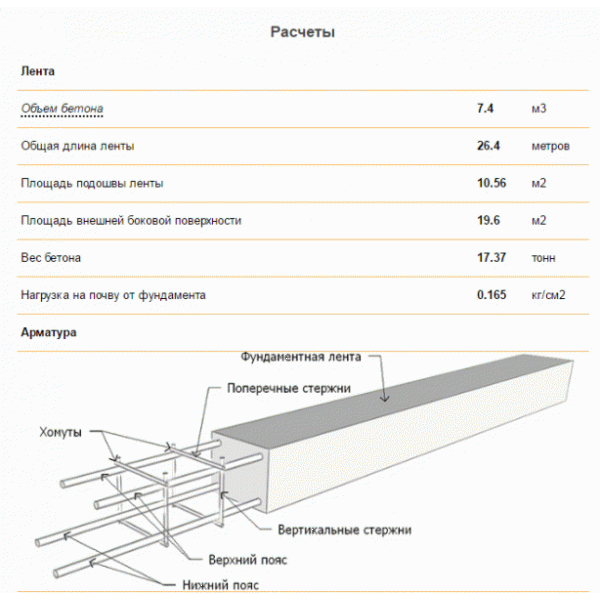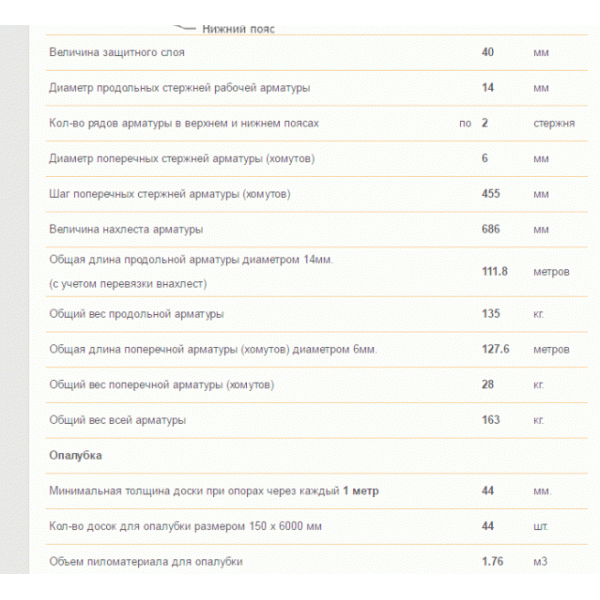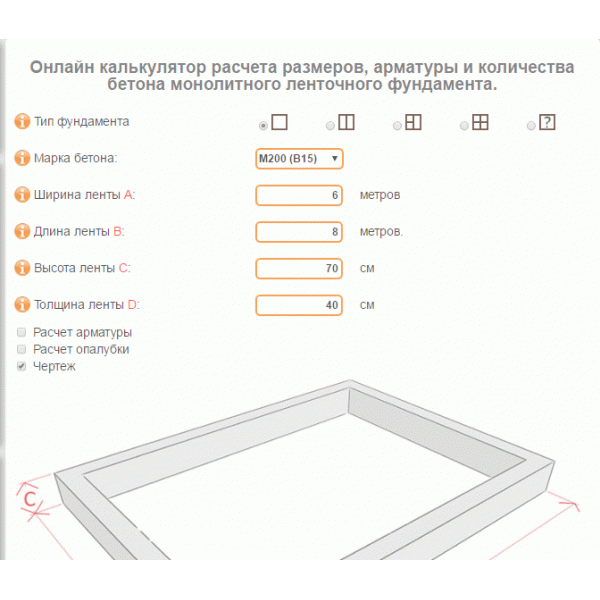
Tiled type of foundation. The amount of rebar and tying wire.
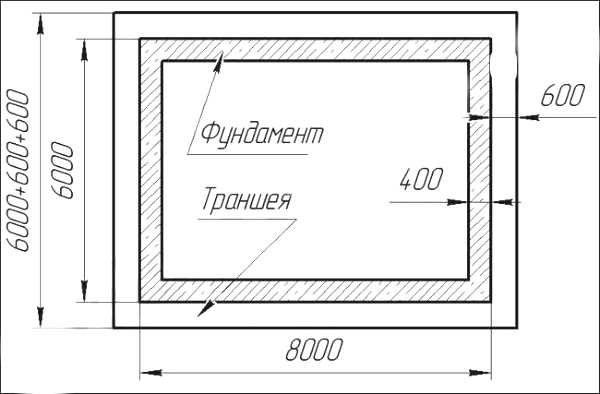
The amount of reinforcement depends on the soil and the weight of the building. Let's say your structure stands on stable ground and has a low weight, then thin reinforcement with a diameter of 1 centimeter will do. Well, if the structure of the house is heavy and stands on unstable ground, then thicker reinforcement from 14 mm will suit you. The step of the reinforcing cage is at least 20 centimeters.
For example, the foundation of a private building is 8 meters long and 5 meters wide. With a step frequency of 30 centimeters, 27 rods are needed in length, and 17 in width. 2 belts are required, so the number of rods is (30 + 27) * 2 = 114. Now we multiply this number by the length of one bar.
Then we will make a connection at the places of the upper mesh of the reinforcement with the lower mesh, we will do the same at the intersection of the longitudinal and transverse bars. The number of connections will be 27 * 17 = 459.
With a slab thickness of 20 centimeters and a frame distance from the surface of 5 cm, it means that for one connection you need a reinforcement rod with a length of 20 cm-10 cm = 10 cm, and now the total number of connections is 459 * 0.1 m = 45.9 meters of reinforcement.
By the number of intersections of horizontal bars, you can calculate the amount of wire required. There will be 459 connections on the lower level, and the same number on the upper level, for a total of 918 connections. To tie one such place, you need a wire that is bent in half, the entire length for one connection is 30 cm, which means 918 m * 0.3 m = 275.4 meters.
Monolithic slab base
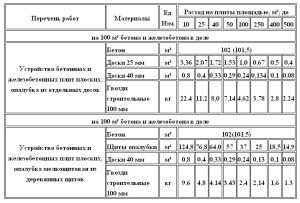 Determination of the volume of materials on a slab base
Determination of the volume of materials on a slab base
A monolithic base is a large rectangular slab immersed at a specific depth in the soil.
And this means that the calculation of the volume of the slab will take a minimum of time, because already according to the ready-made drawings of the bearing walls, you can calculate the length, width and thickness of the structure.
For example: foundation length 12 meters, width 7 meters, thickness 0.6 meters. As a result, the volume of the slab will be as follows: 12 * 7 * 0.6 = 50.4 m3.
But this volume does not entirely correspond to reality, because in any monolithic slab there is a reinforcing mesh. You can also calculate the total volume of all rods and strapping and subtract it from the total volume of the foundation.
Foundation calculation
If you take a responsible approach to calculating the volume of consumables, then there is a chance to reduce your operating costs and make construction less expensive at all levels. Moreover, there are simplified calculation options available to citizens who have never encountered construction engineering.
The homeowner is able to independently make all the necessary calculations that affect the total amounts that will be used for the purchase of building materials and for work. Calculation of costs allows you to competently highlight the key points in the construction process and build a reliable home ownership.
Calculation of materials for the construction of walls
The cost of construction is largely determined by the cost of the materials used, and that is why it is so important to know in advance how much of what will be used to construct the walls. As a rule, walls entirely of concrete are not cast, but a monolithic frame is made in the form of columns at the corners and horizontal beams
Wall blocks, bricks or other masonry materials are laid in the cavity of the frame
As a rule, the walls are not cast entirely of concrete, but a monolithic frame is made in the form of columns at the corners and horizontal beams. Wall blocks, bricks or other masonry materials are laid in the cavity of the frame.
In order to calculate the volume of the frame, you need to draw a diagram of the structure as a whole and break it down into separate columns and crossbeams. Now we have to calculate the volume for each individual element, which will be an order of magnitude easier. To do this, calculate cross-sectional area columns and crossbars and multiply them by the height.
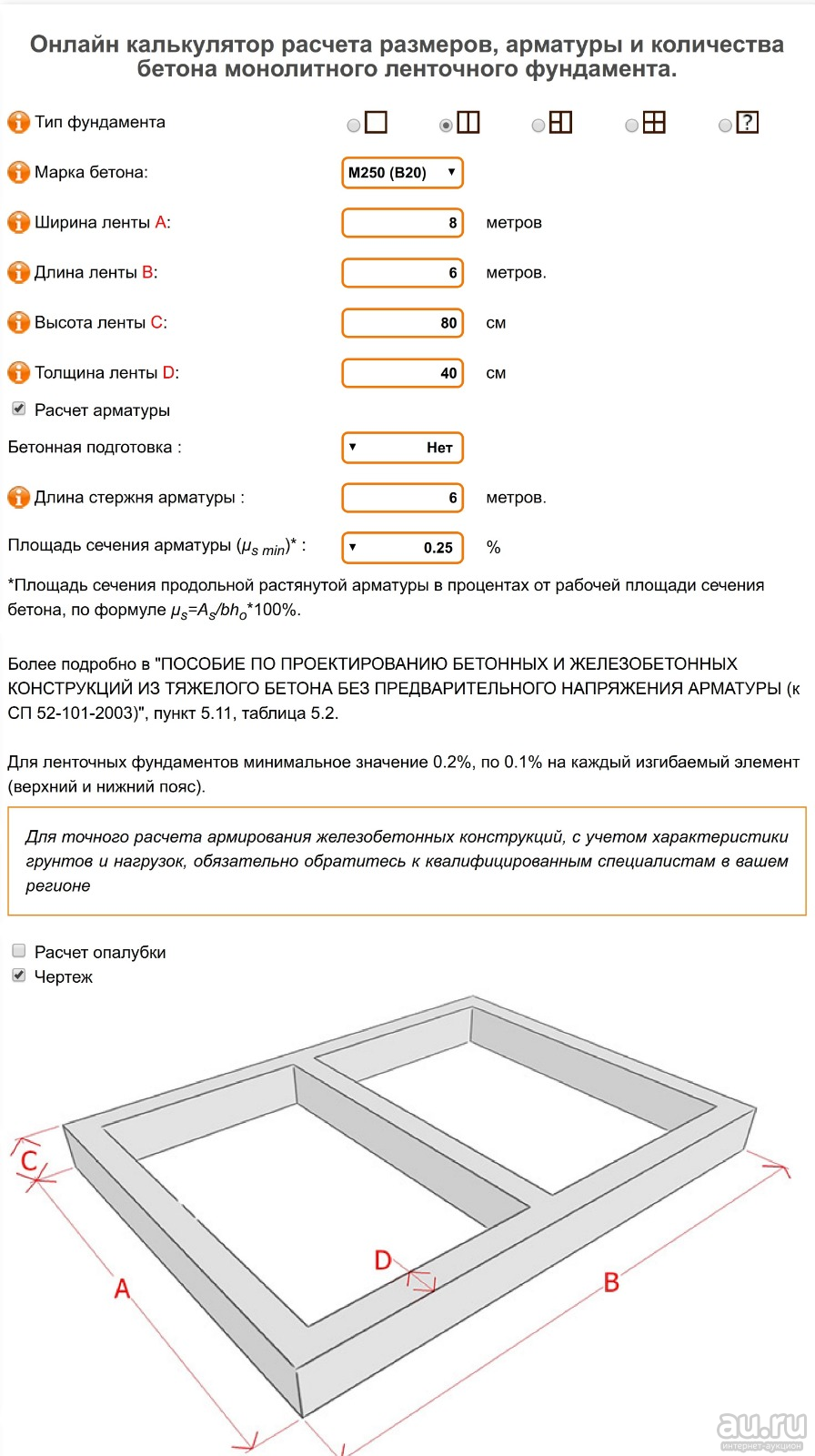
Tape
The most popular basis for the construction of a private house is considered to be a strip foundation.It is a kind of closed concrete tape that runs under all the load-bearing walls of the building.
How to calculate how many cubes of concrete are needed for a foundation? Calculators that help determine the consumption of cement-sand mortar for pouring are available on many construction sites, one of which is presented at the end of this material. To calculate the volume in cubic meters, you need to know the linear dimensions of the structure: height, width and total length of the base.
The strip base is concreted by pouring the ready-made cement-sand mixture into a wooden formwork with a pre-installed reinforcing mesh. Large fractions (gravel, crushed stone) are added to the solution to acquire higher strength characteristics of the foundation.
The dimensions of the base depend on the dimensions of the building to be erected. Usually, the width of the foundation tape has a size of at least 300 mm, the height of the ground part is from 400 mm, and the depth can reach 1500-2500 mm, depending on the availability of groundwater, the depth of freezing and the desire to equip the basement. It is not recommended to install strip foundations on heaving soils if the formwork is deepened less than the freezing depth.
The length of the foundation will be equal to the total length of all external walls, including the internal load-bearing wall, under which the foundation is also installed. As a result, having received all the required values, it is possible to calculate the volume of concrete for the foundation. In this case, a calculator may not be required - it is enough to multiply all the indicators in meters and get the required number in cubic meters.
The calculation formula looks like this:
V = h * b * l, where:
- V is the volume of the solution in m3;
- h is the height in m;
- b - width in m;
- l is the length of the tape in m.
For example, for a building measuring 6x6 m and one internal load-bearing wall, with a foundation height of 2 m and a width of 0.4 m, the volume of the filling solution will be: V = 2 * 0.4 * 30 = 24 m3. With the same width and height of the foundation, for a 10x10 house and two load-bearing internal walls, the calculation will look like this: V = 2 * 0.4 * 60 = 48 m3.
This calculation allows you to calculate an almost exact cubic capacity of the solution, but it should be remembered that during transportation, part of the concrete is lost, and also with loose formwork, part of the concrete solution may leak out, but at the same time there is an additional internal volume occupied by the reinforcing cage. Therefore, it will be correct to enter a correction factor in the direction of increasing the calculated value by 2%.
As a result, we get a more accurate formula for calculating the volume of concrete for a strip foundation:
V = h * b * l + 0.02 * (h * b * l)
The resulting value is rounded to the nearest whole number. For our examples, the refined calculation will look like this: for a 6x6 house V = 24 + 0.02 * 24 = 24.48 (25) m3, for a 10x10 house V = 48 + 0.02 * 48 = 48.96 (49) m3 ...
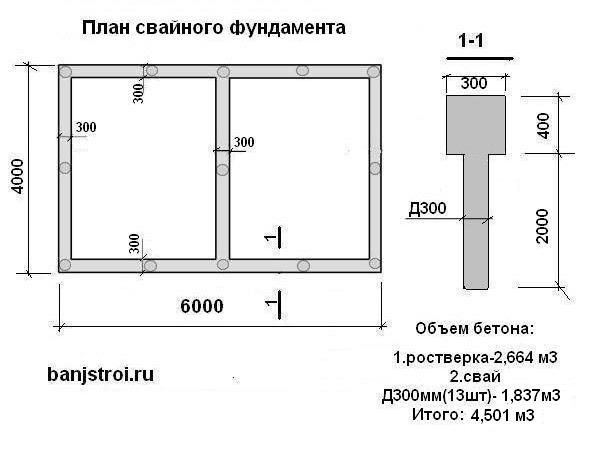
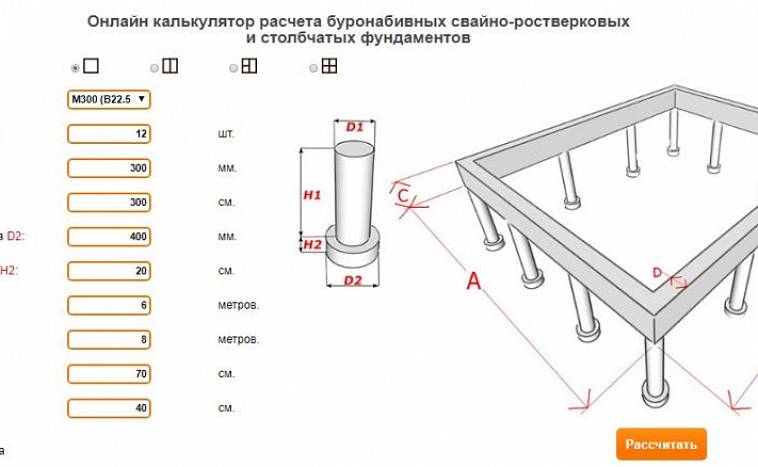
Pile-grillage and screw foundation
 Diagram of a pile concrete foundation
Diagram of a pile concrete foundation
The total cubic capacity of such bases is the summation of the volumes of the pillars and grillage slabs.
In other words, this is a combined option for calculating a strip foundation and a columnar foundation.
Only here, the calculation takes into account the cubic capacity of the column cylinder.
Attention, if factory bored piles or screw metal structures are used, then only the tape part of the grillage is calculated, and the parameters of the pillars are not used. They can only be used when calculating the required number of earthworks
They can only be used when calculating the required number of earthworks.
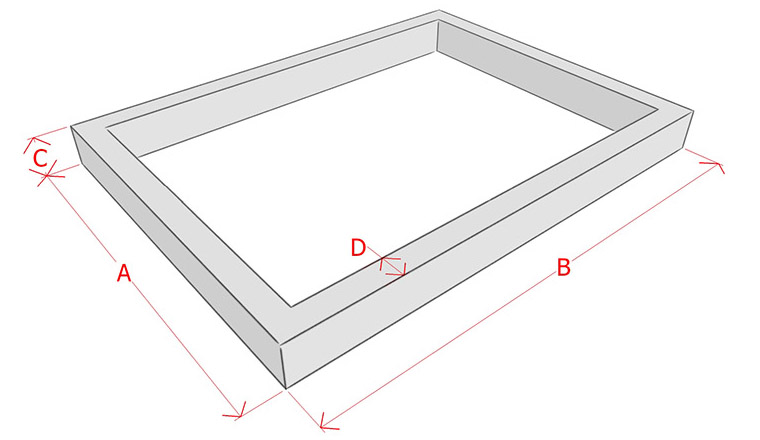
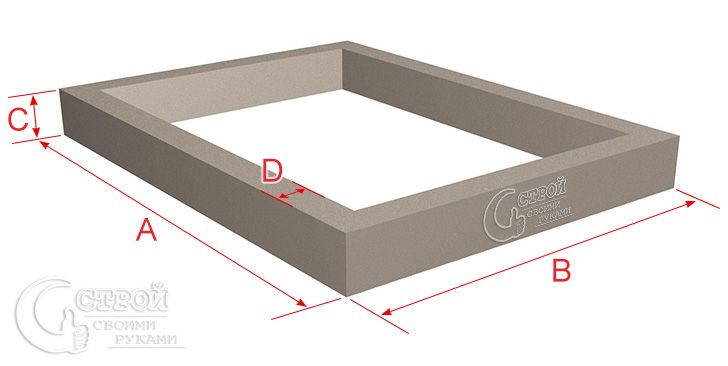
Determination of the volume of the strip foundation
In general, you can calculate the amount of concrete for pouring the strip base yourself. To do this, you need to know the height, width and length of the tape... If the foundation has the same width and height along the entire length, then you can use a simple geometric formula:
V = S * L.
In this formula, the letter "S" stands for the cross-sectional area of the foundation, which can be calculated by multiplying the width of the foundation by its height. The letter "L" indicates the total length of the concrete tape.
For example, consider the following option:
The strip base for a house measuring 10 * 8 meters has a width of 0.4 meters and a height of 0.8 meters. First, the cross-sectional area of the foundation is determined:

Concrete for casting strip foundations
S = 0.4 * 0.8 = 0.32 m2.
Next, calculate the total length of the concrete tape, which is equal to the perimeter of the house:
L = (10 + 8) * 2 = 36 meters.
Now you can safely calculate the volume of the strip base with the same section along the entire length:
V = 0.32 * 36 = 11.52 m3.
Therefore, for pouring a tape-type foundation under a house with a size of 10 * 8 needs about 12 cubic meters of concrete solution.
If the foundation has different widths in individual sections, then the calculation is carried out separately for each section, then the obtained values are summed up.
It is also important to take into account those parts of the foundation that are located under all load-bearing partitions, calculate their volume and add to the overall result
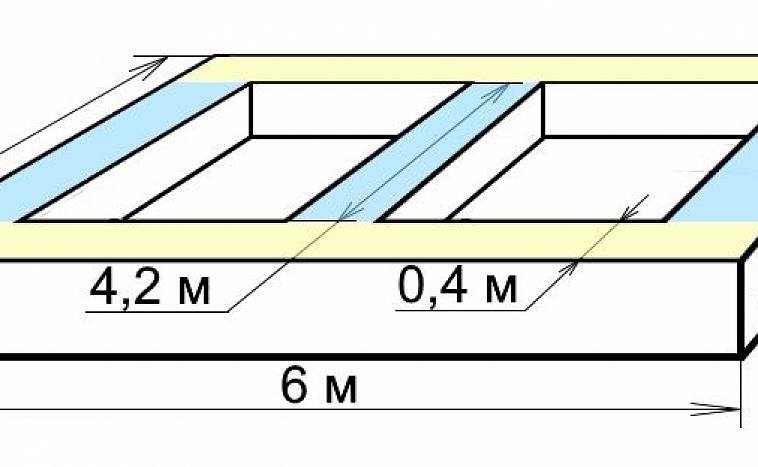
Tiled foundation.
The slab foundation is a monolithic structure, poured under the entire area of the building. To make a calculation, you need basic data, that is, area and thickness. Our building has dimensions of 5 by 8 and its area will be 40 m 2. The recommended minimum thickness is 10-15 centimeters, which means that when pouring the foundation, we need 400 m 3 of concrete.
The height of the base plate is equal to the height and width of the stiffener. This means that if the height of the main slab is 10 cm, then the depth and width of the stiffener will also be 10 cm, it follows that the cross section of 10 cm of the rib will be 0.1 m * 0.1 = 0.01 meters, then we multiply the result 0.01 m, for the entire length of the rib 47 m, we get a volume of 0.41 m 3.
Strip foundation
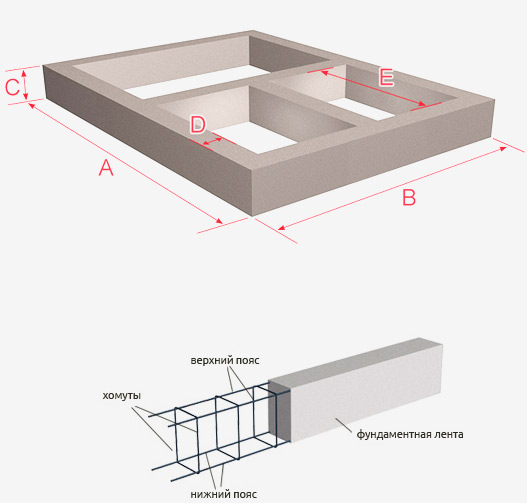
In terms of this type of base structure, it is a tape contour of a rectangular or more complex shape with internal sections for partitions. To calculate the volume of concrete on a rectangular foundation, you need to subtract the volume of the parallelepiped along the inner contour from the volume of the parallelepiped with dimensions along the outer contour. The result will be the volume of the foundation tape itself. Internal partitions can be divided into sections of the same section for the calculation of each section separately. To determine the total volume, the volumes of all such areas are summed up.
Example 1.

Strip foundation plan for an example of calculating the volume of concrete.
- The volume along the outer contour will be equal to 10 x 8 x 2.4 = 192 m³
- The volume along the inner contour is 143.63 m³.
- The volume of the outer part along the perimeter will be 192 - 143, 63 = 48, 4 m³
- The volume of the inner part (8.8 + 6.2) x 0.6 x 2.4 = 17.72 m³ is the product of the cross-sectional area by the total length in m.
- In total, 66.13 m³ of concrete will be required for pouring.
Calculations in this case were made according to the drawings. When determining the volume of concrete in the installed formwork, actual measurements of the formwork should be made and the necessary calculations should be made in the same way.
Calculation of the foundation for a private household
Let's figure out how to calculate the cubic capacity of the foundation - a concrete structure with a minimum thickness. The formula is used:
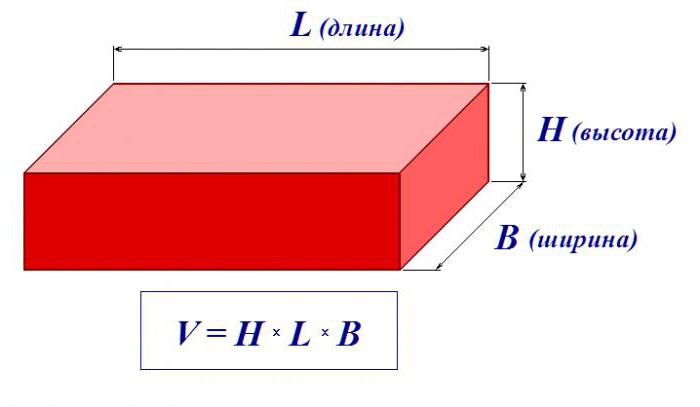
V = A × B × C, where the total is volume and the rest is length, width and height. Thus, it is easy and quick to obtain the cubic capacity of this type of foundation, you just need to know the initial data.
This foundation structure is considered the most durable and stable, because there are no joints on it, which somewhat violate the integrity.
For example, a building has an area of 10 × 10 meters and the structure will use 20 square-section supports. The arrangement of the pillars will be as follows:
- 4 in the corners,
- 16 in the rest of the area around the perimeter of the object.
The concrete pillar has a cross section of 300 × 300 mm and a height of 2 meters, the sole has a cross section of 500 × 500 mm and a thickness of 20 centimeters. The cubic capacity of the soles of concrete pillars is 20 × 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.2 = 1. And the volume of the supports: 20 × 0.3 × 0.3 × 2 = 3.6. And if you add up the results of the calculations, it turns out that 4.6 cubic meters of foundation is required for this building object. For round pillars, the formula is applied:
V = π × r2 × h, where the height of the support and its diameter are involved. When the volume of one column with a circular cross-section is determined, you need to multiply by the number of supports.

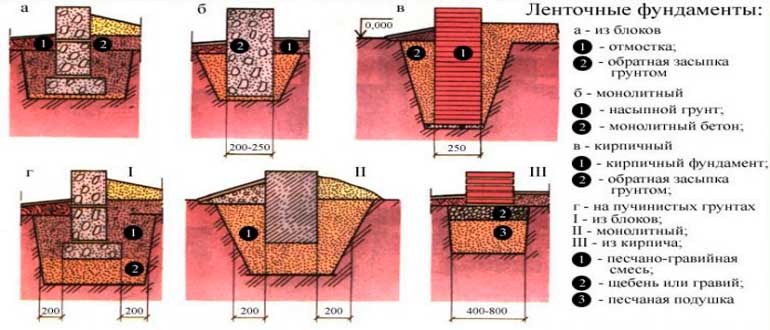
Strip foundation from blocks or stone
 Finished strip foundation trench
Finished strip foundation trench
The calculation of the tape structure resembles a monolithic one, only there are already a number of features. To begin with, there is always less concrete solution here, because the strip base has bearing side and intermediate edges, and the inner surface is empty. So, what quantities are needed to accurately calculate the tape structure:
- Length of all load-bearing walls and intermediate load-bearing partitions;
- The width of the foundation pit, taking into account the thickness of the walls and the allowance for the formwork;
- Foundation depth;
- Base type: monolithic concrete or prefabricated from blocks, rubble natural or artificial stone.
Thus, a typical calculation of a tape structure with overall dimensions of 10x12 meters, a tape width of 0.4 meters and a depth of 2 meters, as well as one longitudinal tape for an interior partition with a thickness of 0.5 meters, can be calculated as follows:
- Solid parallelepiped with voids: 10 x 12 x 2 = 240 m3.
- Empty sections inside the structure: (10-0.4-0.4) * (12-0.4-0.4) * 2 = 206.08 m3.
- The difference in volumes that will go to all external and internal walls is: 240-206.08 = 33.92 m3. Immediately you need to round off this value to an integer larger number, because there is also the thickness of the space for the formwork.
- Interior tape (10-0.4-0.4) * 0.5 * 2 = 9.2 m3.
- Total. The total cubic capacity of the strip foundation with the given parameters is 33.92 + 9.2 = 43.12 m3 (44.0 m3).
What to look for when constructing a foundation
In some cases, the cost of installing a foundation foundation reaches a third of the cost of the entire construction, so the desire of some developers to save money turns into sad consequences. There are also mistakes due to inexperience and negligence of the performers. We will briefly list what should not be allowed when constructing a foundation:
1. Inconsistency of the base structure with the type of soil on the building site. Strip foundations, in particular, are set up on stable, dry soils. On watered soils, pile or slab structures are preferable. If there is no design solution, specialists should recommend the type of foundation.
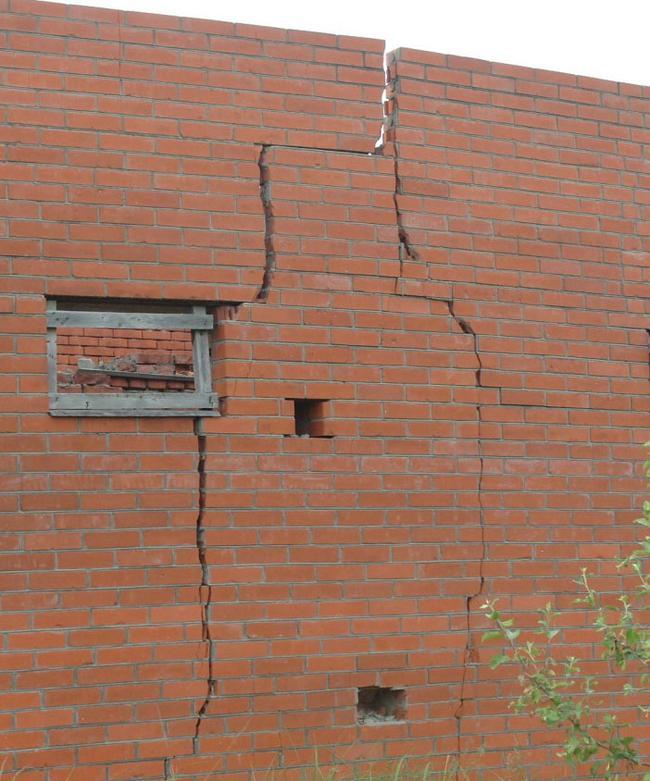 Wall cracks from foundation settlement
Wall cracks from foundation settlement
2. Incorrect arrangement of the sole under the strip foundation. Often, the sole is arranged casually, because unscrupulous builders do not consider it necessary to carefully carry out work, the result of which is difficult to control. As a result, the distribution of the load on the sole turns out to be uneven, the foundation “creeps” in it, and then cracks appear in the constructed building.
3. Incorrect installation of the formwork and, as a result, an insufficient outer layer of concrete in order to guarantee the covering of the reinforcement cage, corrosion of the reinforcement. Insecure formwork fastening.
4. Lack of calculation of the cube of concrete. Such a calculation must be done when pouring it yourself. Since the constituents of concrete have different properties, the cube of concrete should be calculated in order to accurately determine the volume of materials for the foundation device.
5. Inaccurate observance of the geometry of the structure. Uneven corners in rooms are not the biggest nuisance that can be the result of irregularities. The consequence of such an error may be, for example, a shortage of the length of the slabs for the floor device.
6. Lack of reinforcement or "economy" on diameters and quantity threatens that the foundation will not withstand the load.
7. Incorrect dressing (or lack thereof) of foundation blocks when constructing prefabricated types of foundations.
Types of foundations
Engineers accept the foundation constructively using detailed calculation formulas. What is taken into account when choosing:
- House weight;
- Temporary loads;
- Soil type;
- Ground water level.
Having compared a number of factors and the results of calculations, experts accept one of the types of foundations:
- Tape;
- Pile;
- Plate;
- Columnar (only for light houses);
- Combined (a complex design that can only be accepted as a result of professional calculations).
The most common type of base is tape. This design can be adopted for a house with any parameters for all types of soil, except for floating ones. To calculate such a foundation, you need to know the height and width of its wall to the basement (it is part of the foundation), as well as the perimeter of the house and the length of all internal walls.
It is advisable to choose bored piles for private housing construction - they are practically not inferior to finished factory products, but it is much easier and cheaper to install such piles. The construction of the pile foundation also includes a strapping grillage, which must be taken into account when calculating concrete.
The slab is a solution for construction on floating ground. This is a kind of pillow that is able to maneuver on the foundation during seasonal soil liquefaction and during periods of its instability.
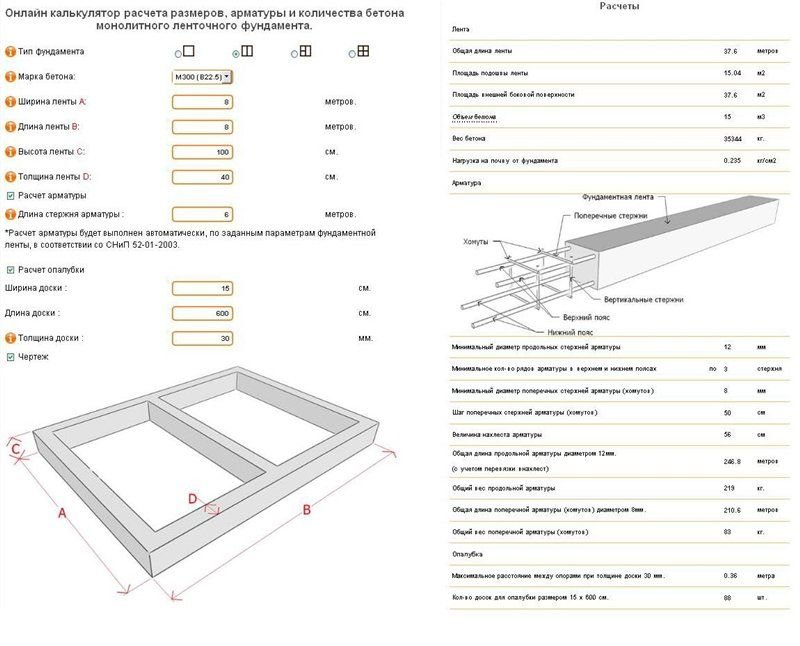
Formula for calculations
The required amount of concrete must correspond to the formwork parameter. Therefore, in order to calculate the volume of concrete for driving a foundation, it is necessary to know the geometric dimensions of the form. Armed with a tape measure, we measure the already set form, and rely on the necessary parameters:
- width;
- height;
- length.
As the long-term construction practice shows, relying on the calculations for the ready-made formwork, you can get more accurate calculations than guided by the dry numbers of the working drawings. In addition, making repeated measurements, you can identify errors in the installation of the foundation mold and eliminate them in time.
In the case of simple shapes, the calculation formula is as follows:
When performing calculations, the values should be brought into a single calculation system - cm, m. In relation to concrete, the parameter is most often used - m 3, less often liters. When converting a unit of measurement between values, the proportion is used: 1 m 3 of concrete = 1000 liters. At the same time, the density of the composition does not affect the quantitative indicators. A mixture compacted, for example, by vibration, corresponds in its cubic capacity to the displacement, as well as materials for concreting made using conventional technologies.
In the case of building a foundation with a complex configuration, the object is conventionally divided into simple shapes - parallelepipeds or other simple elements (circles, cylinders, etc.). The calculation is made for each element separately, the obtained values are summed up.
Calculation of foundation area and weight.
The most important factor is the soil under the foundation, it may not withstand high loads. To avoid this, you need to calculate the total weight of the building, including the foundation.
An example of calculating the weight of the foundation: You want to build a brick building and have selected a strip type of foundation for it. The foundation deepens into the ground below the freezing depth and will have a height of 2 meters.
Then we calculate the length of the entire tape, that is, the perimeter: P = (a + b) * 2 = (5 + 8) * 2 = 26 m, add the length of the inner wall, 5 meters, as a result we get the total length of the foundation 31 m.
Next, we calculate the volume, in order to do this, you need to multiply the width of the foundation by the length and height, let's say the width will be 50 cm, which means 0.5cm * 31m * 2m = 31 m 2. Reinforced concrete has an area of 2400 kg / m 3, now we find the weight of the foundation structure: 31m3 * 2400 kg / m = 74 tons 400 kilograms.
The reference area will be 3100 * 50 = 15500 cm 2. Now we add the weight of the foundation to the weight of the building and divide it by the support area, now you have a load of a kilogram per 1 cm 2.
Well, if, according to your calculations, the maximum load has exceeded these types of soils, then we change the size of the foundation in order to increase its supporting area. If you have a strip type of foundation, then you can increase its support area by increasing the width, and if you have a columnar type of foundation, then we increase the size of the column or their number.But it should be remembered that the total weight of the house will increase from this, therefore it is recommended to re-calculate.
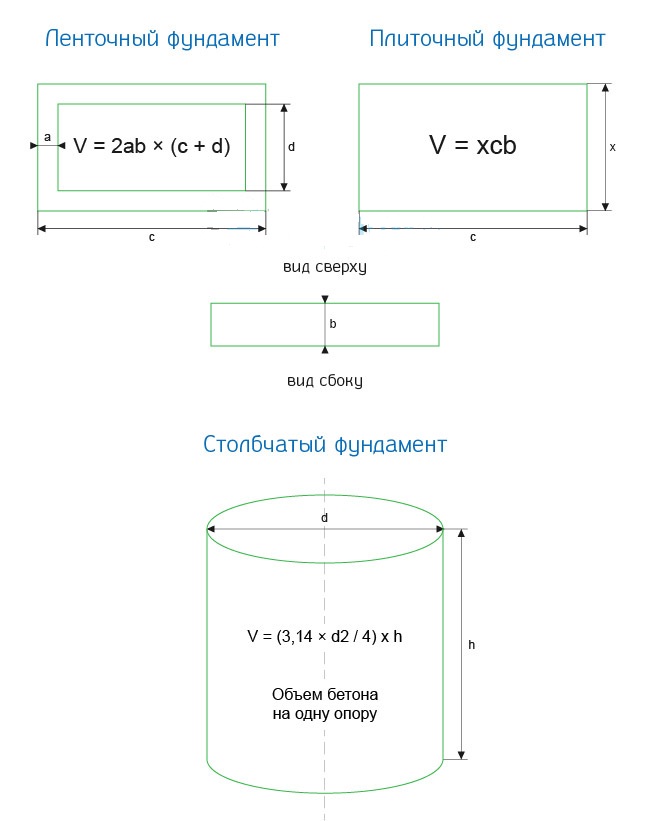
Calculation of cubic capacity depending on the type of foundation
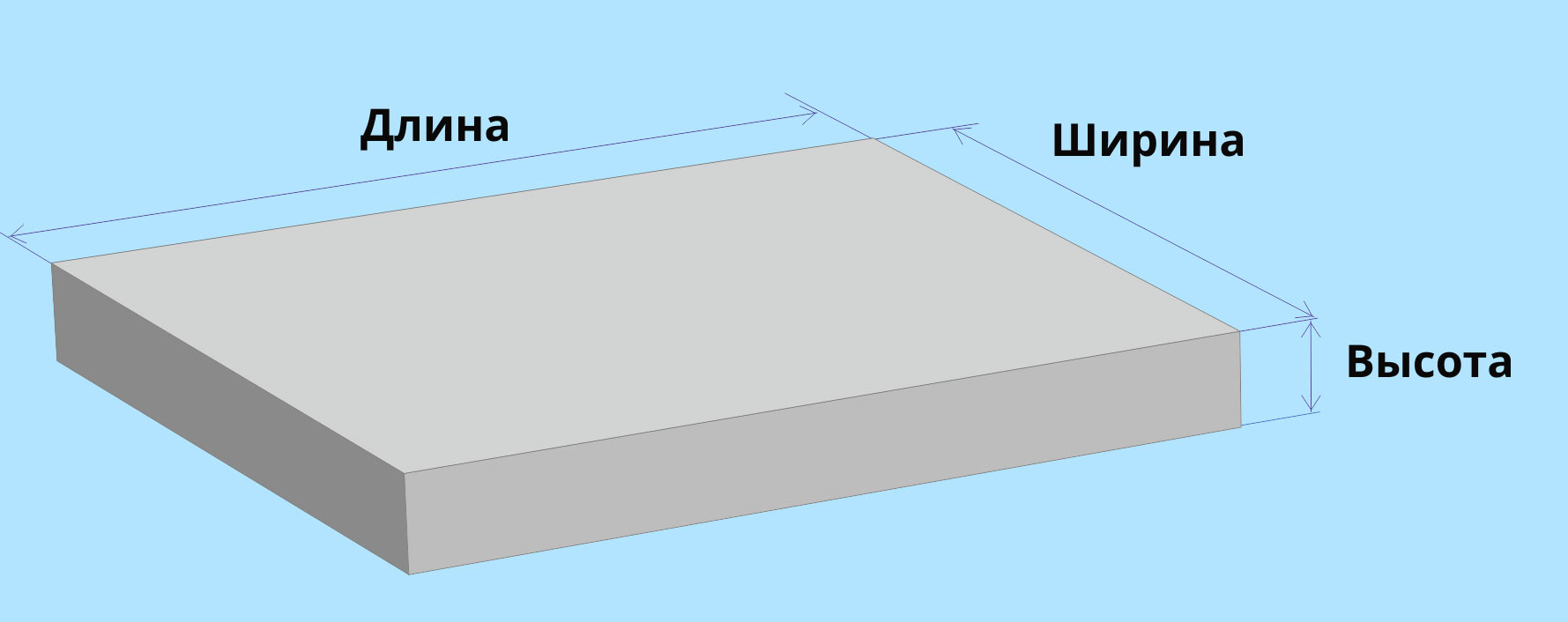
From the course of school algebra, the volume of any body can be calculated by finding the product of its height, length and width. However, the calculation of the cubic capacity of common types of house foundations predetermines the consideration of their individual characteristics.
Counting the volume of a monolith
The base of this type has the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped, the edges of which can be found by comparing with a sketch at the planning stage or by actually measuring the erected formwork.
When measuring the height of the formwork, it should be borne in mind that marks of the required level of concrete are made on it, and it is being erected with a margin of 10-15 cm.
Watch a video in which an expert tells you how to correctly calculate a monolithic slab.
The volume of the presented base is calculated according to the general formula: H x A x B, where H is the height, A is the length, B is the width. For clarity, it is worth giving an example. So, with a foundation depth of 0.8 m, a length of 10 m and a width of 10 m, the cubic capacity of the required concrete is 0.8 x 10 x 10 = 80 m3.
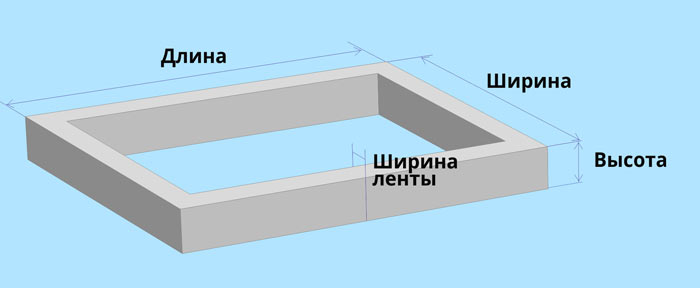
Counting the volume of the tape
Calculation of the cubic capacity of the strip foundation of the house also comes down to calculating the volume of a rectangular parallelepiped minus the internal hollow areas. Despite the apparent complexity, this indicator is easy to calculate in practice.
For the calculation, it is necessary to calculate the volumes of the external and internal parallelepiped according to the drawn drawing, find their difference, and then add the cubic capacity of the internal tape elements to the result.
We recommend watching a video on calculating a monolithic base tape.
So, with the dimensions of the foundation 12 x 15 m and a tape width of 0.5 m, deepened into the soil by 1.5 m, with an internal additional tape 0.6 m wide, the cubic capacity of the base is calculated as follows:
- We set the cubic capacity of the external parallelepiped: 12 x 15 x 1.5 = 270 m3.
- We determine a similar indicator for the internal figure: (12 - 0.5 - 0.5) x (15 - 0.5 - 0.5) x 1.5 = 231 m3.
- We find the difference between the obtained values: 270 - 231 = 39 m3.
- We calculate the cubic capacity of the inner tape: (12 - 0.5 - 0.5) x 0.6 x 1.5 = 9.9 m3.
- The total volume of the strip foundation pouring: 39 + 9.9 = 48.8 m3.
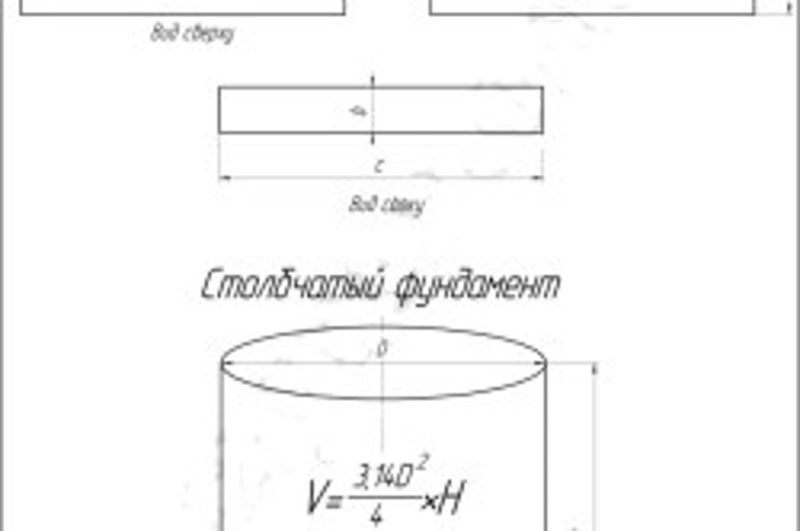
Counting the volume of a columnar foundation
The volume of columnar bases is calculated as the sum of the volumes of two geometric bodies - the parallelepipeds of the column and its foot, multiplied by the total number of supporting elements.
In numerical terms, for calculating a columnar foundation for a structure of 8x8 m with a total number of pillars with a 2 m pitch in 16 copies (4 corner and 12 auxiliary), the soles of which are 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.3 m, and the body pole supports 0.4 x 0.4 x 1, calculated according to the following principle:
- Total volume of the sole: 16 x 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.3 = 1.73 m3.
- The final cubic capacity of pillar supports: 16 x 0.4 x 0.4 x 1 = 2.56 m3.
- The final volume of required concrete: 1.73 + 2.56 = 4.29 m3.
Watch the video how to do it right do-it-yourself calculation of a columnar base.
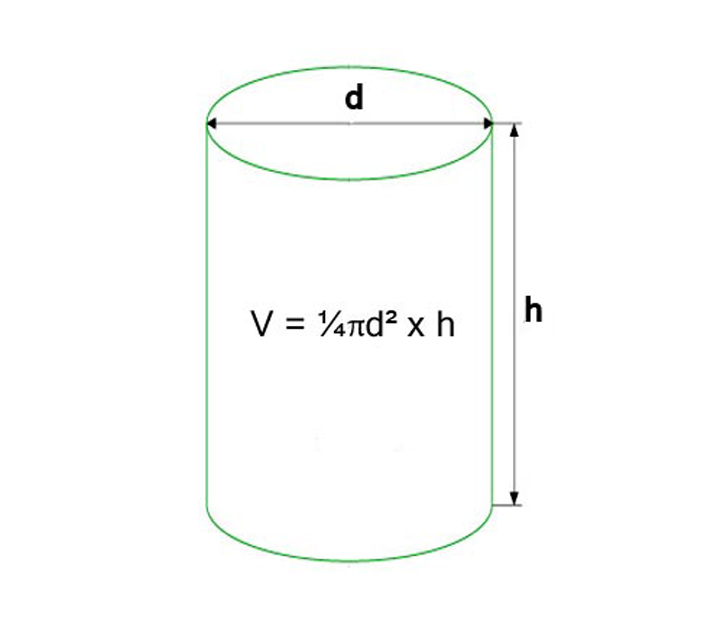
Calculation of the volume of a bored foundation with a solid grillage part
The total cubic capacity of the presented type of foundations of the house is set as the sum of the volumes of bored pillars (cylinders) and a monolithic slab of the grillage part (classic parallelepiped). Just as in calculating the cubatures of the bases presented above, to calculate the total volume of concrete, you will need to break the figure into its constituent elements, set the volume of each of them, and sum the obtained values.
In this case, it must be remembered that the volume of a column or any building element of a cylindrical shape is calculated as the product of the area of the base and the height. In this case, the sole area is found by the formula:
where π is a mathematical constant (3.1415 ...), D is the diameter of the circle (sole).
For clarity, we will give an example, the total volume of the base on 20 supports with diameters of 0.5 m and a depth of 2 m in the soil, supporting the grillage part with dimensions of 10 x 15 x 0.5 m, is set according to the following principle:
Cubic capacity of pillars: 20 x (3.14 x 0.5 x 0.5 / 4) = 7.85 m3.
- Cubic capacity of the grillage part: 10 x 15 x 0.5 = 75 m3.
- Total volume: 7.85 + 75 = 82.85 m3.
Tiled type
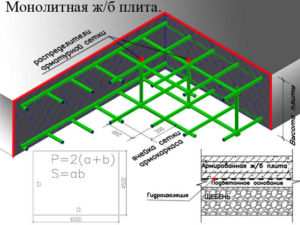 Schematic calculation of slab foundation
Schematic calculation of slab foundation
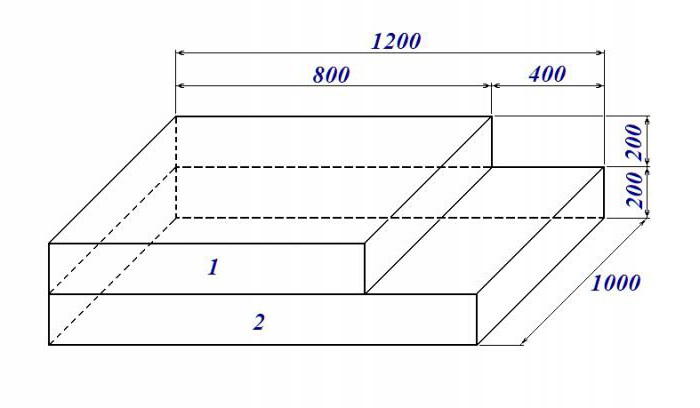
The slab design has the easiest way to count, but it will require more materials as well. In this case, the edge of the foundation slab should protrude beyond the boundaries of the walls of the house by exactly the same distance, which is equal to the height of the slab.
Accordingly, knowing the exact cubic capacity of the required foundation, it will already be possible to calculate and the volume of materials, which will make it possible to understand how much cement, sand and other components are needed. To begin with, you should bring all the data to one unit of measurement, and here meters are most often used, but you can choose any other unit.
Then the length, width and height of the desired slab are simply multiplied among themselves, eventually giving cubic units of volume. It will be more difficult if the base is not rectangular in shape.
Then the cubic capacity can be calculated by dividing the parts of the complex shape of the plate into simpler components - a circle, a semicircle, a triangle, a square, a rectangle. Further, the area of each part is considered separately for further calculations. In this case, mathematical formulas from the school curriculum will come in handy:
The area of a circle is S = πr ^ 2, where r = 3.14 is the default and r is the radius of the desired circle. The area of a semicircle is half the area of a circle. The area of the triangle is hc / 2, where h is the length of the height of the triangle, and c is the length of the base.
The area of the trapezoid can be calculated using the formula h (a + b) / 2, where a and b are the lengths of the upper and lower bases. Further, the volume is considered similar to the volume of rectangular slabs.
In most cases, it is permissible to neglect the volumes that the metal frame occupies, since it is negligible in comparison with the volume of the plate itself, and does not affect the required amount of the mixture.