Causes of destruction due to improper erection of foundations
Examining the foundations of not only multi-storey residential buildings or massive industrial buildings. It will not be superfluous to assess the structure and condition of the foundation and the acquired private house.
In recent years, the demand for the suburban real estate market has increased. These are mainly low-rise private houses intended both for year-round living and summer cottages. In this regard, the construction of country houses for sale has become a very profitable business. At the same time, in the pursuit of profit, developers often neglect the quality of construction, including carelessly regarding the choice of the foundation structure, completely ignoring the peculiarities of the soil - its composition, density, and other geological features. As a result, the service life of such buildings sometimes does not exceed several years: the foundations begin to crack, sag, and deform.
According to SNiP, each type of soil is best suited to a certain type of foundation foundation.
- Strip foundation. The most popular option and best suited for stable soils with low groundwater levels. These are soils composed of large sandstones and rocks. In the case of a strip base arrangement in an area with a high groundwater level, its base should be located below the level of soil freezing.
- Columnar foundation. The simplest and most budgetary option for the foundation, which is widely used in low-rise construction. Suitable for the construction of houses on sufficiently strong and non-porous soils with a significant slope relative to the horizon. Among the disadvantages of columnar bases is the impossibility of arranging a basement floor or basement.
- Slab foundation. Used to build light structures on heaving or soft soils. By increasing the area of the support, the specific pressure of the building on the ground decreases, which makes it possible to minimize the depth of the foundation subsidence. The disadvantage of this technology is the high financial cost due to the large volume of concrete pouring.
- Pile foundation. A technology specially developed for the construction of massive buildings on soft or water-saturated soils. In this case, the piles are usually buried by drilling or driving down to solid soil. The "hanging pile" technology is used occasionally. The pile foundation allows you to create a solid and reliable support for the structure on construction sites with the most complex geological structure.
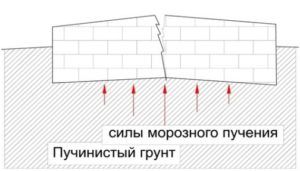 Impact of frost heaving forces
Impact of frost heaving forces
In order for the foundation to last as long as possible, you should follow the recommendations of building codes regarding the conditions for using different types of foundation. Their improper use, sooner or later, will inevitably lead to the destruction of the supporting base, and after it the house.
A strip foundation laid on soft soils will crack and sag; a columnar base, equipped on a site with a high level of groundwater, with the onset of cold weather will be squeezed out of the ground by the forces of frost heaving of the soil.
Checking foundations
A foundation survey is carried out in such cases: establishment of significant deformations of buildings and structures; reconstruction or change of the functional purpose of the house; construction near a new structure; restoration of lost project documentation. Watch a video of how the foundation of a house with a crumbling foundation is examined.
Survey scheme
Inspection of foundations is one of the most laborious processes, therefore, depending on the conditions of the terms of reference, a list of works and survey methods are outlined.
- Get acquainted with the project documentation. It is necessary to find out what soils lie under the object, from what materials the structure was built, structural features, design loads.
- Find out the presence of existing utilities, as well as existing or abandoned basements, wells, tunnels.
-
Obtain permission to open foundations, drill wells.
- During visual inspection, determine the areas of maximum damage to the walls and outline the locations of the pits. Since these damages can be caused not only by the state of the foundations, but also by violations in the foundation, special equipment and diagnostic methods will be needed to find out the real causes of deformations.
- Start digging pits: this will require two excavators, possibly more. The opening of the foundation can be carried out outside or inside, wherever it is convenient. The number of penetrations is determined by the structure of the foundation and the degree of deformation. Also, the condition and area of the foundation can have an impact.
- Inspect the foundation and take samples. Sampling may vary depending on the foundation material. For example, samples of brick and mortar are taken from a brick foundation.
- Fill in pits: layer by layer with compulsory compaction. Restore waterproofing.
- Conduct laboratory tests on the samples taken.
- Draw up a conclusion. It must contain the results of the survey, presented by the relevant documents (defective statements, drawings, graphs, photographs, etc.); assessment of the strength of foundation materials; technical opinion on the impact of additional loads during reconstruction.
Inspection features
 Foundation survey using a pit
Foundation survey using a pit
The peculiarity of the foundation survey is the excavation of pits. Depending on the purpose of the survey, the number of pits may vary. So, for example, during reconstruction or re-profiling, the pits are additionally torn off in the area where the extensions (superstructures) of the house are designed and where the load is expected to increase.
The pits run to a depth of at least half a meter below the foot of the foundation. Length is desirable from one meter
Precautions must be taken when descending into the pit.
The use of the electrometric method for measuring the density and moisture content of the foundation material will help to speed up the results. In case of high humidity, it is necessary to establish its cause. Watch the video on how the foundation survey is carried out.
In the event of significant damage, an examination of the foundations and foundations will be required. For this, static sounding, drilling of wells for sampling, stamping tests, and survey of soils using geophysical methods are carried out.
Diagnostic methods have improved significantly in recent years. Instead of sawing or drilling out cores, non-destructive research methods are used to determine the strength of the material and its integrity on site. For example, it can be ultrasound, sclerometry, a method of radiation flaw detection.
There are nuances when examining foundations on piles. Here the grillage is subject to inspection. Although usually with pile foundations, problems do not arise. If it is necessary to determine the length and integrity of the pile, the method of seismic acoustics will come to the rescue. As an example - the use of seismic stations "Diogenes".
When to inspect bases and foundations
 Broken foundation
Broken foundation
- With a planned increase in the number of storeys of the building;
- Changing the purpose of the building, technical re-equipment of the production building;
- Overhaul or planned repairs of the foundation associated with the appearance of visible signs of deformation of the supporting structure;
- With the appearance of significant cracks, deformations and subsidence of the basement floor, as well as the facade of the house;
- In the event of subsidence, not related to seasonal fluctuations of the soil;
- When designing and starting the construction of other buildings nearby;
- If you need to carry out restoration and restoration work in architectural monuments, sculptures with pedestals and other similar structures.
In some cases, to examine the foundations and obtain a finished result, it will be enough to study the technical documentation for the building. But for old buildings, such projects simply cannot be found, because they do not exist, and no building archives were kept at that time.
Causes of deformation and destruction of building foundations:
- Rainwater that has penetrated deep into the foundation through cracks, pores or damaged drainage system;
- Aggressive groundwater contaminated with chemicals that entered the depth of the base from damaged sewers;
- Groundwater raised above the permissible level;
- When mistakes were made in the design of the foundation, poor quality building materials and products were used that were not designed for the design loads;
- Natural aging of building materials, in particular sandstone, limestone and rubble;
- Through the emergence of external vibration from the side of new industrial and administrative structures, which affects the foundation from the outside;
- Displacement of soil layers, other reasons.
The drilling method allows you to clearly establish the composition of the base, its depth and the composition of the mineral components. When drilling, soil and foundation samples are taken at different depths, a visual inspection of the structure is carried out, and samples of building compositions are taken. Often it is necessary to completely open the foundation in order to examine the condition of the reinforcing layers.
Prerequisites for the survey
 In the presence of serious cracks, it is necessary to inspect the foundation.
In the presence of serious cracks, it is necessary to inspect the foundation.
The prerequisites for the inspection of buildings and structures are:
- the appearance of visible signs of damage to the integrity of structures;
- reconstruction or other changes in structures with increasing loads;
- repurposing or modification of functional purpose;
- detection of deviations in the project, in which the bearing capacity of elements and structures decreases;
- lack of a general plan and other documents;
- restoration of interrupted construction after a certain time;
- deformation of the base;
- damage from a number of facilities under construction;
- fire, natural disasters, man-made accident.
The list shows that the reasons for surveys are quite serious, so only specialized enterprises can carry out this kind of work. They must have the necessary technical base and a staff of qualified workers, use various diagnostic methods. The status of an organization, for example, is confirmed by the presence of a Certificate of the established form.
Assessment of the technical condition of structures
Inspection of buildings and structures involves an audit of building structures: from what material they are made, the declared properties, the identified state. First, it is necessary to visually determine the type of homogeneity violation and the area of its distribution.
At the same time, it is important to find out the cause of the damage, how it will affect the bearing capacity, develop a set of measures to eliminate this cause and restore the integrity of the structure
In the course of the survey, design schemes of structures are made, samples are taken, which are examined by laboratory methods. The figures obtained form the basis for assessing the technical condition of the examined elements.
 Unacceptable vehicle of the building
Unacceptable vehicle of the building
Such an assessment means assigning a category of technical condition to structures, which will affect the order of their further operation:
- serviceable vehicle - normal operation of the accepted loads without restrictions;
- operable vehicle - the same service, but with probable periodic inspections;
- limited serviceable vehicle - control of the technical condition of the structure, possible limitation of loads, performance of work to strengthen or protect against destructive factors;
- unacceptable vehicle - safety work, carrying out restoration measures and strengthening the structure;
- emergency vehicle - prohibition of operation, performance of emergency work.
In what cases the foundation is examined
Clarification of the state of the supporting structure and the base located under it is necessary in a number of situations:
- the number of floors is increasing at the facility;
- technical re-equipment of production is carried out;
- major repairs are planned, after which the load forces will increase;
- large cracks appeared on the facade, the openings were warped;
- unacceptable problems have developed;
- it was necessary to erect a new foundation in the immediate vicinity of the object.
Quite often, the presence of problems associated with the condition of the underground structure is judged by the external damage to the walls, determined by the visual method. In addition, doors located in the common plane, which have begun to jam, are considered a clear sign of a base defect. In such situations, experienced specialists unanimously state that deformation processes occur at the object, and the main reason for this is the weakness of the base or its premature destruction.
Sometimes it is enough to study the project documentation. But if it is absent, or significant subsidence of the object is observed, the excavation of pits is mandatory for examining the foundations.
Deformation, distortion or subsidence occurs for various reasons, which appear immediately, after a certain time, or with seasonal heaving of the soil. As a rule, such problems are associated with:
- atmospheric precipitation falling into the soil and moistening the concrete base;
- groundwater, gusts in the sewage system, heating main or water supply;
- poorly compacted base;
- freezing or washing out the soil;
- ground shift.
Impact on the technical condition of the foundation

Technical condition data for strip foundations.
Instrumental examination of the foundation of a house is a complex undertaking. Assessment of the state of the building foundation is carried out as follows: by digging a pit along the structure, coring is taken from the foundation body; determine the diameter of the laid reinforcement; an examination of the geometric parameters of the foundation is carried out; identify and fix defects. In addition, samples are taken from the soil at home for testing in laboratories. Based on the data obtained from the laboratory of the surveyed object, as well as analysis, taking into account the current situation, archival data, calculation of the bearing capacity of the foundation soils under the foundation, and other calculations on the terms of reference, a technical report is prepared with conclusions, conclusions and recommendations.
As you know, the foundations of houses are used underground. The foundation absorbs loads and forces from the structure of the house, and transfers them to the surface of the subgrade. The foundation soil, in turn, also affects the foundation. As a result, the technical system between the ground and the structure is in balance. If this balance is violated, deformation and gradual destruction of the structure occurs. In the calculations, when designing, force factors are mainly taken into account. And during the operation of a structure, its foundation is influenced by a variety of other physical processes, such as, for example, temperature drops (seasonal and daily); wandering currents; fluctuations in groundwater; heterogeneity of different types of soils and their physical properties.Such factors are taken into account using a system of special coefficients.
In certain cases, foundations experience special effects, mainly associated with vibrations during earthquakes, underground workings, etc. Impacts of this kind are seismic. At the same time, they are taken into account by dynamic calculations, involving the determination of the frequencies and modes of vibration of the system from the building to the ground.
What is drilling. How to dig.
Greetings to all visitors to the treasure hunter blog. I continue the topic of searching for treasures, because each of us dreams of finding a treasure, digs through tons of earth in the hope that now there will definitely be a treasure, and not an old bucket Today I will tell you about one way to search for treasures and coins, when your metal detector simply by virtue of its digital data will not be able to see the treasure or coins.
So, punching, what it is and when it is used. Pitching comes from the word pit, to lay a pit, that is, to dig a trench for something. Let's look at the example of finding treasures and coins. For example, we have a weak device that hits a maximum of 25 cm. We hear a barely audible signal, but our intuition tells us that there is something valuable under the coil. we are not lazy, digging, digging into the signal source and baa, what we see is a silver ruble. With joy the hair stands on end on the head, the heart stops and we continue our search with convulsive waves, but alas, there are no more signals. And this signal was barely audible, as they say, on the verge of the power of the device. As a rule, silver rubles do not come across one by one, most often it is a small treasure. So to be sure that there is no more ruble, you need to break through everything to the end. This is where drilling will help us, it really helps to look for treasures in a promising place.
How to drill? We are digging a trench 5 meters long, width, depth of about 30-40 centimeters at the place of the found ruble. The work, of course, is titanic, but it needs to be done, because we are looking for treasure or plowing. We carefully dump all the excavated earth next to the trench, call it a metal detector. In this land, most often, nothing comes across. We are interested in the bottom of the trench, so we call it with the utmost care. Imagine, we went 40 cm deep and then another device rang at 30, a total of 70 cm is obtained. This is drilling, we laid a hole and pierced its bottom, it turns out that we rang 70 centimeters down to the width of the trench. Not a bad chance to find something.
If coins began to come across at the bottom of the trench, then you can safely take a day off at work and begin global drilling of the entire area until the coins stop coming across. Most often, they dig the scales, but this is not a panacea, they dig when the place is promising, when there is information that a treasure is buried here, or they just dig when there is nowhere to put their strengths.So it is advisable to dig with a coping partner, because the work is hard and it is unrealistic to dig alone hard. Finding old coins by punching is very difficult.
If there are a lot of people, then several pits can be laid, which will increase the chances of success. Trenches are laid at a distance equal to the width of the pit, that is, if the width of the trench is 40 cm, then after 40 cm, lay the next trench. Drilling allows you to punch the area as efficiently as possible for the presence of coins and treasures, but you will also have to work decently. So if the place is promising, then be sure to dig, the result will be simply amazing. Happy cop, colleagues.
The essence of the process
Any foundation research begins with the signs of the beginning of destructive processes appearing on the house. At a glance, it is impossible to determine the exact place of violation of the integrity of the structure. You need to understand the cause of the problem so that you do not have to redo the foundation over and over again.
In order to gain access to the walls of the base, it is required to create a recess near the damaged section of the structure. It is impossible to drill wells, the risk increases that the rate of concrete disintegration will increase.
A pit will help - a deep rounded pit, which is created with maximum depth. The excavated space is located outside or inside the base.
The second name of the pit is a viewing pit through which a detailed inspection will be carried out.
When it is difficult to identify the exact area with damaged concrete, restoration of the structure is carried out, more than 10 pits can be dug around the perimeter of the building.
The indentations are placed in compliance with the symmetry relative to the surface. It is much more difficult to carry out excavation inside the foundation, often pits are made on the outside of the structure.
The size of the excavated space is different, the main thing is to provide a sufficiently convenient access for a specialist to carry out the manipulations necessary in a particular case. Often the parameter depends on the size of the person - you need to make it so that it is comfortable to sit down, bend over to take a sample.
When deepening the base to 60 cm, dig a hole about 80 * 80 cm. If the base is laid deeper, dig up a space of 100 * 100 cm (length, width), the depth depends on the state of the concrete building. It is recommended to deepen 10-20 cm below the sole of the base, but this is impossible if the foundation is in poor condition, too old, and the soil is too loose.
The base repair can be seen in the following video:
At the end of the foundation survey:
- You will learn the causes of foundation defects and deformations.
- You will know the actual physical and mechanical properties of the foundation materials.
- We will determine for you the depth of the foundation and the state of the waterproofing
- Experts will provide you with recommendations for restoring the foundation to a working condition.
- You will receive recommendations for further safe operation
As a result, the customer receives a document with an expert assessment of the state of the foundation. This is not only a legal basis for continuing the operation of the facility or carrying out major repairs in it, but also a technical conclusion with recommendations on the composition of further construction work.
The survey of foundations is one of the most difficult activities in the list of engineering and survey works. It requires the involvement of several specialists in different directions, and it can only be produced by licensed specialists in accordance with existing regulations.
When it is necessary to inspect the foundation of a building
A survey of foundations involves the study of the foundations of buildings in order to identify factors that affect the state of ground structures. It is necessary:
- With a partial or complete reconstruction of an object with the replacement or strengthening of individual load-bearing elements, deepening the basement, adding side buildings or several floors that increase the load on the base.
- When carrying out a major overhaul of a structure without additional load on the foundation.
- When building new facilities near existing ones.
Unfortunately, the construction expertise of foundations is often ordered after the appearance of serious defects in the structures - after the appearance of unacceptable deformation, cracks in the load-bearing walls, water in the basement. Since the causes of these defects are associated not only with violations during construction or operation, but also with the work of soils and groundwater, a technical examination of the foundation of a building is a comprehensive analysis necessary not only to determine the causes of the formation of defects that have arisen, but also to identify the optimal way to eliminate them. ...
Inspection of building foundations occupies a special position in engineering work.
The complexity and responsibility of the assignment provide the value of the assignment. The purpose of the survey is an objective assessment of the current state of the foundation and the identification of existing or potential threats, for the timely elimination of possible consequences of their impact on the structure as a whole. The need to conduct a survey of the foundations of buildings arises in the following cases:
- reconstruction, affecting load-bearing structural elements, when expanding basements, when erecting additional side buildings or floors that can put a load on the base;
- overhaul, even if there is no additional load on the foundation;
- expansion of the construction area with the construction of new structures next to the existing buildings.
Technical due diligence is especially effective when done well in advance. In practice, unfortunately, the procedure is addressed after the formation of defects: deformations, cracks in load-bearing elements, accumulation of water in basements. Establishing the causes and finding ways to eliminate the impact of the problems that have arisen seem to be a complex solution that requires a comprehensive analysis and assessment of the impact of possible violations during construction, during operation, or related to the state of the soil surface and groundwater.
The main task of examining the foundation of a building is to study and assess its bearing capacity, determine the magnitude of the load provided by it during ground movements, vibration and the destructive effect of groundwater.
The main parameters in the course of the examination are considered:
1. Soil properties. The analysis reveals the physical and mechanical features of soil samples and their bearing capacities. Research is carried out at the place of work and in specialized laboratories, with the involvement of existing methodological developments and appropriate tools.
2. Geometric shapes, sizes and proportions of foundations. Based on the data obtained in the process of measuring the width, length and depth of the base, the necessary calculations are performed to determine the errors that have arisen in the deviation of its shape from the permissible design standards.
3. Strength characteristics of foundation materials. Sampling of concrete base for the assessment of mechanical parameters in laboratory conditions and at the site of the object is carried out exclusively by non-destructive methods.
4. Condition of the reinforcement of the building structure
When assessing reinforcing elements, attention is paid to the degree of their corrosion wear, retention of dimensions and location.
5. Waterproofing. The presence, quality of waterproofing, and the level of groundwater are subject to verification. Based on the research, an expert opinion is made with the necessary recommendations.
There is a certain peculiarity in conducting surveys of basements and basements. At the first stage, experts make a visual assessment of the object, study the design documentation, the results of geomorphological and hydrogeological examinations of the state of the construction site. During the second stage, instrumental studies of the foundation are carried out to identify the level of compliance of the existing characteristics with the required parameters. Inspection of the foundations of buildings and foundations of foundations is of a selective nature using the method of sampling pits. The choice of the location of the excerpts and the number of pits are determined taking into account the influence of the structural features of the building, accessibility to the intended place of work and the location of the identified defects. As the laboratory studies are carried out, the necessary control calculations are carried out, the final conclusion is worked out. The results of the examination make it possible to determine the bearing capacity of the foundation, identify the causes of cracks and defects that have arisen, ways to eliminate them, and determine the possibility of using the existing foundation in the future.
Pit construction rules
The pit is a dug hole that exposes the wall of the strip, the support of the columnar or the side of the slab foundation. The locations of the deepenings are determined based on specific conditions.The priority areas are problem areas, and if it is necessary to inspect long zones, the choice is left to the sites that can least of all become an obstacle for passers-by or people living nearby.
When marking pits, builders should not rely solely on the convenience of working conditions and the availability of the territory. Research is almost always carried out in populated areas, so it will not be possible to get rid of the presence of pedestrians near the object. But those around you also need to remember that the foundation survey is only temporary, and the measures taken are necessary, expedient and not critical.
Without fail, the pit should be laid in places where the deformation of the walls is clearly visible. Also, drilling can be carried out:
- in the busiest areas of the building;
- in each independent part of a multi-section house;
- in the areas where additional supports are located.

Special attention should be paid to sites where the condition of the soil or foundation is determined as emergency. In this case, in addition to the problem area, they examine the safe zones where the pit is arranged, after which the results of the study are compared. For the foundation of the reconstructed object, the drilling and inspection of the structures together with the base are carried out at the places where the bearing columns and walls are installed. And in the case of a partial superstructure - only in the area of reorganization.
The number of pits depends on the initial purpose of the foundation revision. When reconstructing or overhauling a building that does not provide for an increase in loads, it will be enough to perform 2-3 control pits. When eliminating the flow of water in the basement or on the first floor, holes are dug in each of the watered areas, and when the basement is deepened, one hole is made near all the walls. In the most loaded zones, it is allowed to perform double-sided pits.
Each pit is dug half a meter below the foundation depth. Depending on the tightness of the territory and the size of the deepening, the pit walls are made with slopes or reinforced with vertical shields with struts. The minimum area of the pit bottom relative to its depth is:
- 1.25 m2 - up to 1.5m;
- 2 m2 - from 1.5 to 2.5 m;
- more than 2.5 m2 - from 2.5m.
In buildings with basements, drilling is carried out from the inside, which significantly reduces labor costs when performing earthwork. Pits, in this case, have, as a rule, a depth of 0.8-1.2 m and dimensions along the bottom - 1.0 * 1.0 m.

As a result of the foundation survey, they find out or specify:
- the depth of the underground part;
- overall dimensions in plan;
- type and strength of the structure;
- the presence of defects and destruction;
- class of concrete and grade of stone (based on samples - in the laboratory);
- condition of the waterproofing layer;
- violation of the position relative to the vertical axis;
- the fact of the presence of any gains.
The state of the artificial and natural foundation is determined by a soil sample taken in the same pits. In some situations, additional drilling is required.
Secondary detrimental factors
In addition to the wrong choice of design, the following factors can serve as the cause of the destruction of the supporting base:
- Incomplete construction, when the concrete pouring of the foundation was thrown in the open air for several years without conservation, for example, if the drainage system was not equipped around the perimeter of the foundation with a high level of groundwater. The blind area was not poured to protect the concrete structure from melt and rain moisture.
- Non-compliance with technologies and deviations from the project allowed during construction. Suppose, according to design calculations, specific grades of concrete for pouring, reinforcement for creating a frame, etc. But during the construction process, in order to reduce the estimated costs, building materials were replaced with cheaper ones: low grade concrete, thinner reinforcement was taken.Also, the cause of the destruction of foundation foundations can be excessive haste in construction, when a load in the form of load-bearing walls and ceilings is given to the concrete pouring, which has not yet gained full strength.
- Reconstruction or reconstruction of a building, carried out without carrying out the necessary engineering calculations - for example, an add-on of another floor, a residential attic, an extension. Increasing or shifting the weight of a building can cause the concrete to settle or crack unexpectedly.
- Vibration loads can also shorten the life of the foundation. Thus, buildings located near railway and tram tracks should have a more massive and solid foundation. The same can be said for houses along a busy highway or city street. Nearby construction can also cause vibration damage to the substructure.
- Water is not only the enemy of wood and metal - constant contact with it leads to the gradual destruction of concrete. Filling the smallest cracks and pores, water accumulates in them. With the arrival of winter, it freezes and, turning into ice, increases in volume. As a result, the cracks widen from year to year, which leads to cracking and destruction of the concrete foundation.
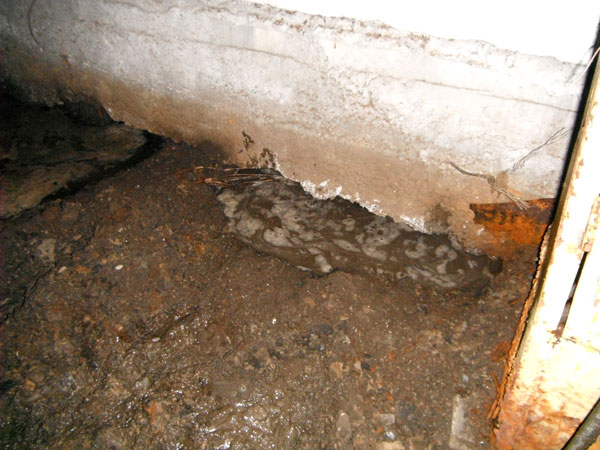
 Blurred base of the building
Blurred base of the building
