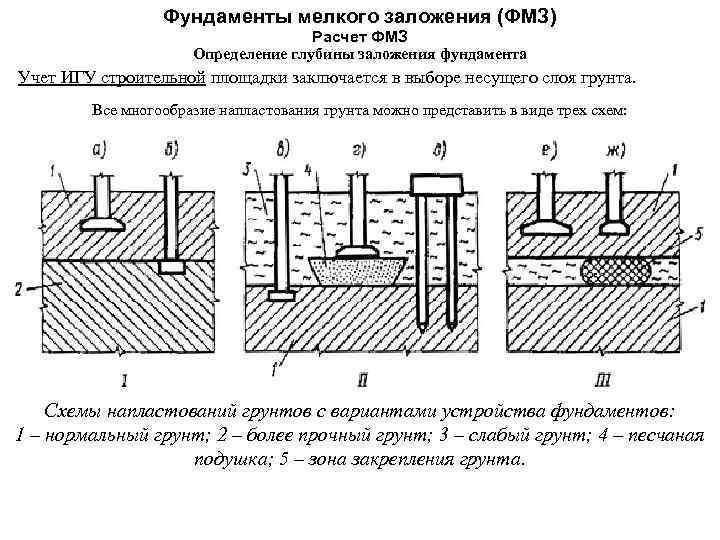
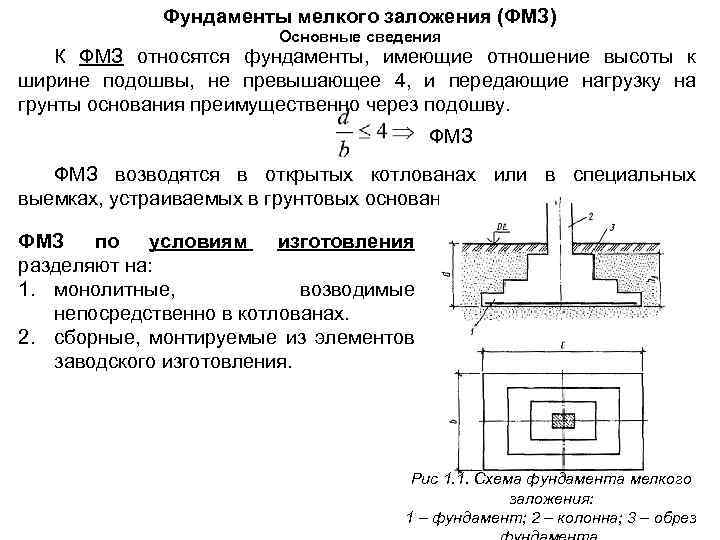
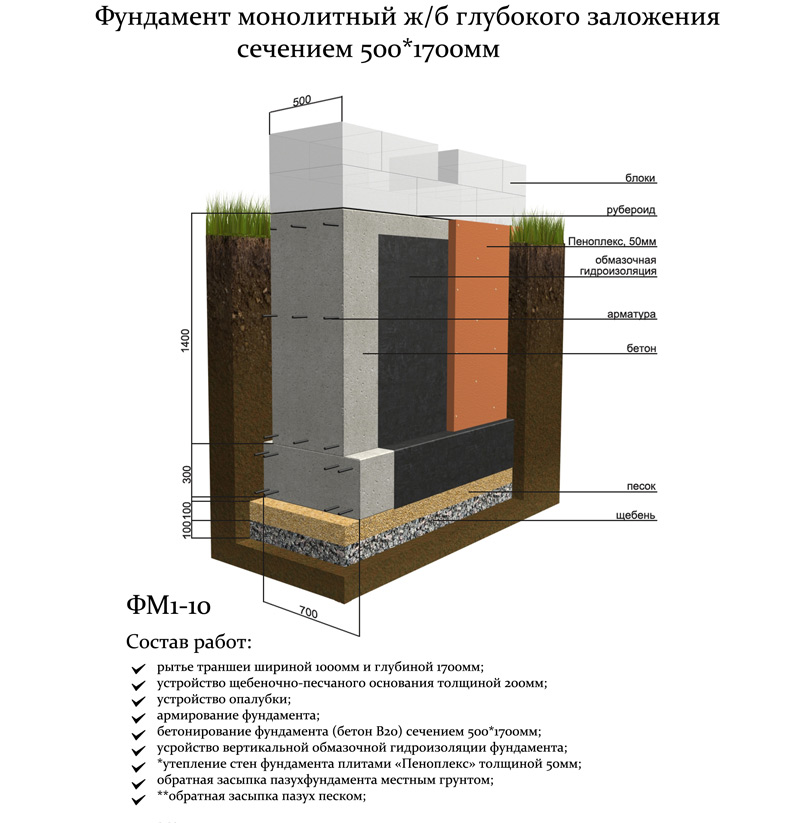
How does the depth of the foundation affect the bearing capacity of the foundations?
 Sketch of uneven lifting of the pit bottom due to incorrect calculation of the bearing capacity of the base
Sketch of uneven lifting of the pit bottom due to incorrect calculation of the bearing capacity of the base
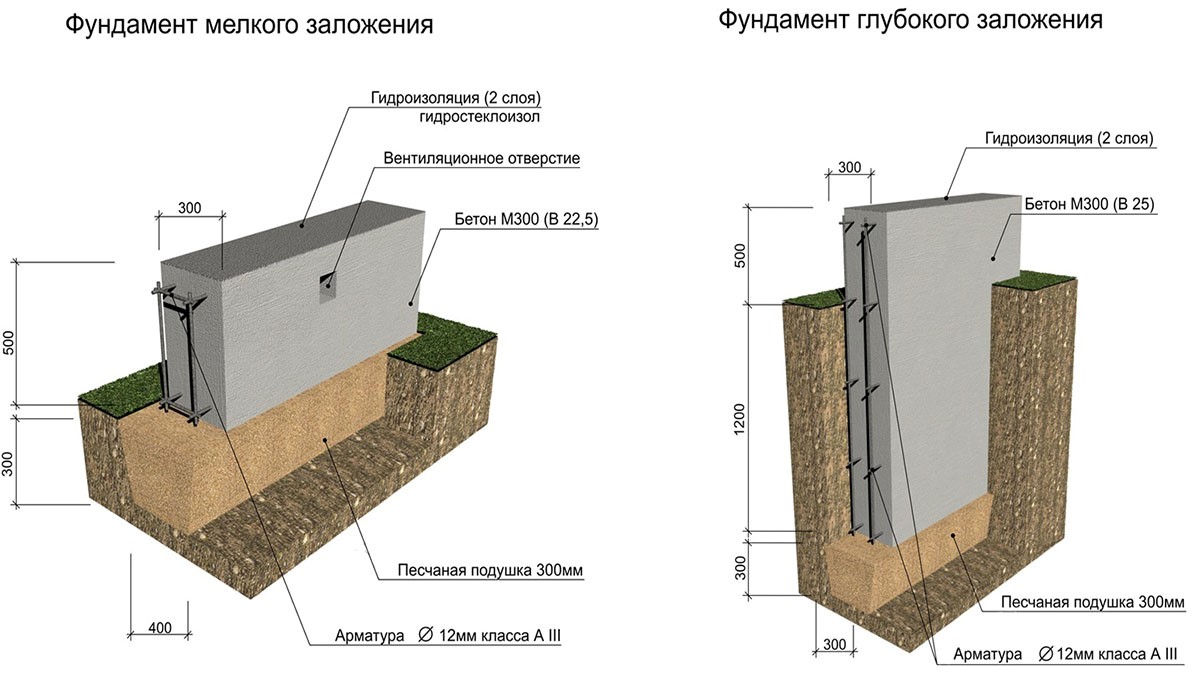
Why are deeply buried foundations less prone to failure than shallow ones? After all, small foundations must be strengthened, the optimal pile design must be selected and complex calculations must be made. The reason for this lies in the nature of the behavior of soils at different depths.
So for sandy foundations, an increase in the depth of the foundation immersion leads to a decrease in settlement, but the bearing capacity increases sharply. A similar situation is observed with any other soils that contain large quantities of sand.
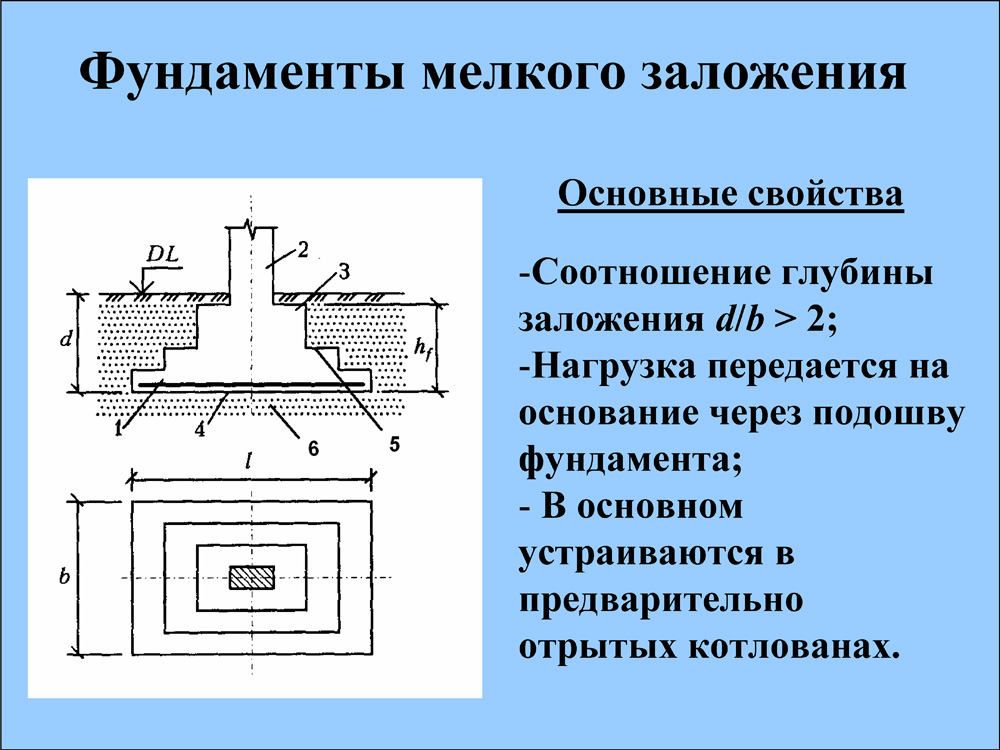
Therefore, depending on the depth of the laying, distinguish between shallow and deep bases. It is clear that for each type you have to use your own building materials and equipment, but the reliability of the structures differs several times.
How does the deformation of sandy soils under the bottom of shallow foundations occur? First, the soil under the sole is enlarged, then it rises with wedges on different sides of the structure and forms a free cavity under the sole. Therefore, even minor shifts and movements of the soil will lead to partial destruction of the supporting structures. Shifts and failures are often observed.
But deep foundations are much more difficult to destroy. The displacement of the soil will be almost completely neutralized by the vertical movement of the soil along the sides of the base surface, and in this case there can only be local compaction of the soil. The destruction of the foundation in the third phase of soil deformation is of a calm nature. The dependence of the depth of the basement on the sediment on clay soils is practically not manifested.
Thus, the bearing capacity of the foundations is an important indicator of the state of the soil and cannot be neglected. If you make the right calculation and take into account all the factors, then according to the finished result you can choose not only the optimal size and shape of the future foundation, but also discover hidden problems in the existing one. And in the future, promptly take measures for urgent repair or reinforcement of structures so that they do not deform from external influences.
Reinforced frame formation
 Reinforcement strip foundation
Reinforcement strip foundation
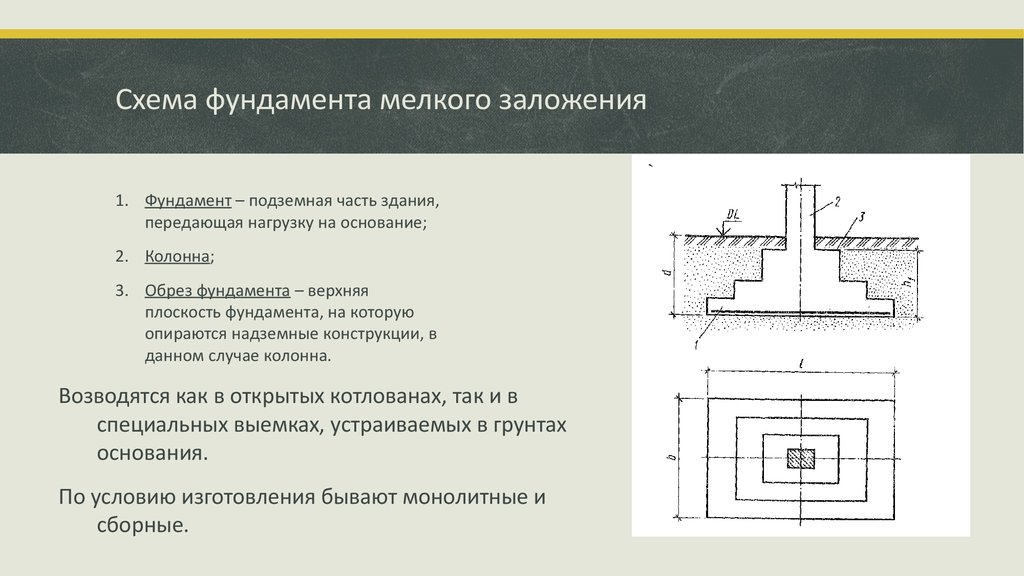
Any foundation is subject to reinforcement, both shallow and deep. Due to the complexity of the work performed, not every developer performs it.
The diameter of the steel rods used for reinforcement depends on the dimensions of the base. The optimal cross-section of the reinforcement is 8–12 sq. mm. Reinforcement of the foundation is carried out on the basis of a metal frame, which can be mesh or consist of belts.
A belt is called a structure formed by horizontal rods fastened together by jumpers. Vertical bridges fasten two belts together, and their length should not exceed half a meter. Reinforcement using a belt is a rare occurrence.
In a separate belt, the rods are connected by horizontal bridges every 10–15 cm. As a result, you will get a reinforcing mesh with square windows, the sides of which will be within 10-15 cm.
This method of reinforcement is considered the best on the one hand and expensive on the other. The formed belts are fastened together with wire or welded using electric welding.
Useful Tips
-
If the technology of insulation with expanded polystyrene is used, the heat-insulating layer must be treated on top with glue for finishing work.This will allow the insulation to maintain its performance for a longer period of time.
- To increase the protective functions of the base of the house, it is recommended to additionally insulate the blind area. In this case, work should be done around the entire perimeter of the building. Any material can be used, including expanded polystyrene.
- The insulation should be laid only after the arrangement of the blind area and drainage cushion, as well as the laying of the waterproofing material.
- On top of the insulation, it is imperative to make a concrete screed. Alternatively, paving slabs can be laid.
- If the construction of the building was carried out on soil characterized by a large freezing depth, it is strongly recommended to take care of additional protection of the thermal insulation layer from various types of mechanical damage. Brickwork over polystyrene foam insulation is best suited for this purpose.
- Insulation should be carried out for all types of foundations, regardless of the type of soil on which the house was built.
- Without a certain construction experience, it is strongly discouraged to insulate the foundation on your own. In such a situation, the best solution would be to turn to experienced professionals who know their business perfectly and are able to perform work of any degree of complexity in the shortest possible time.
When choosing a company for warming the base, you should pay attention not only to its experience in the relevant market sector, but also to feedback from existing customers.
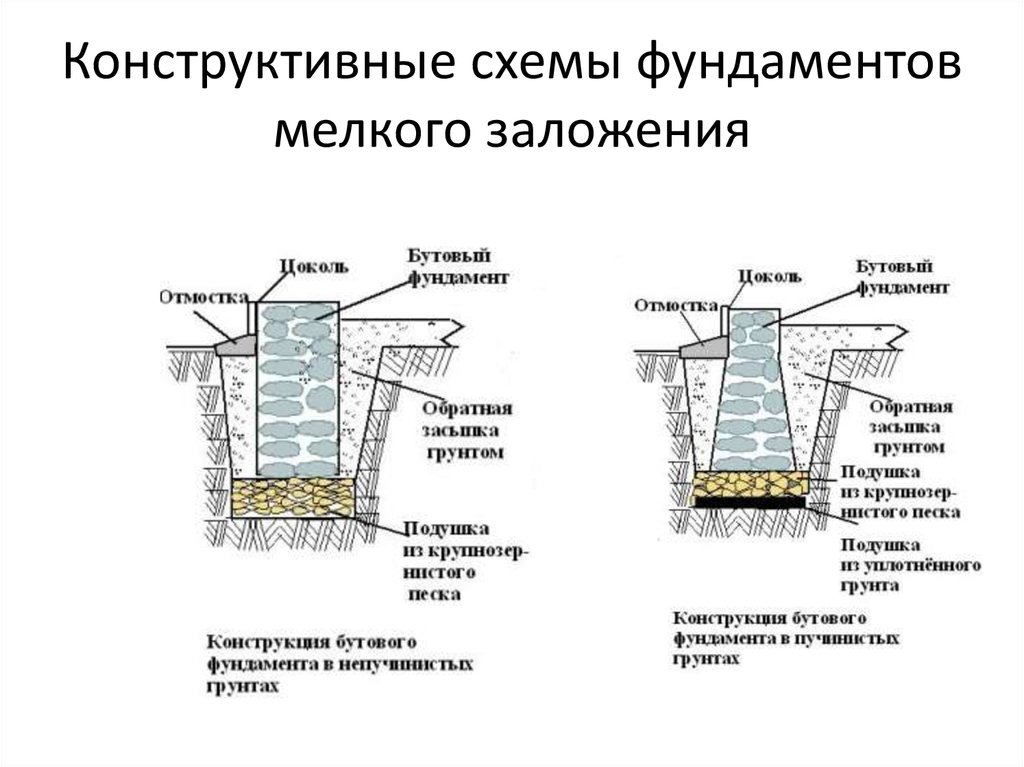
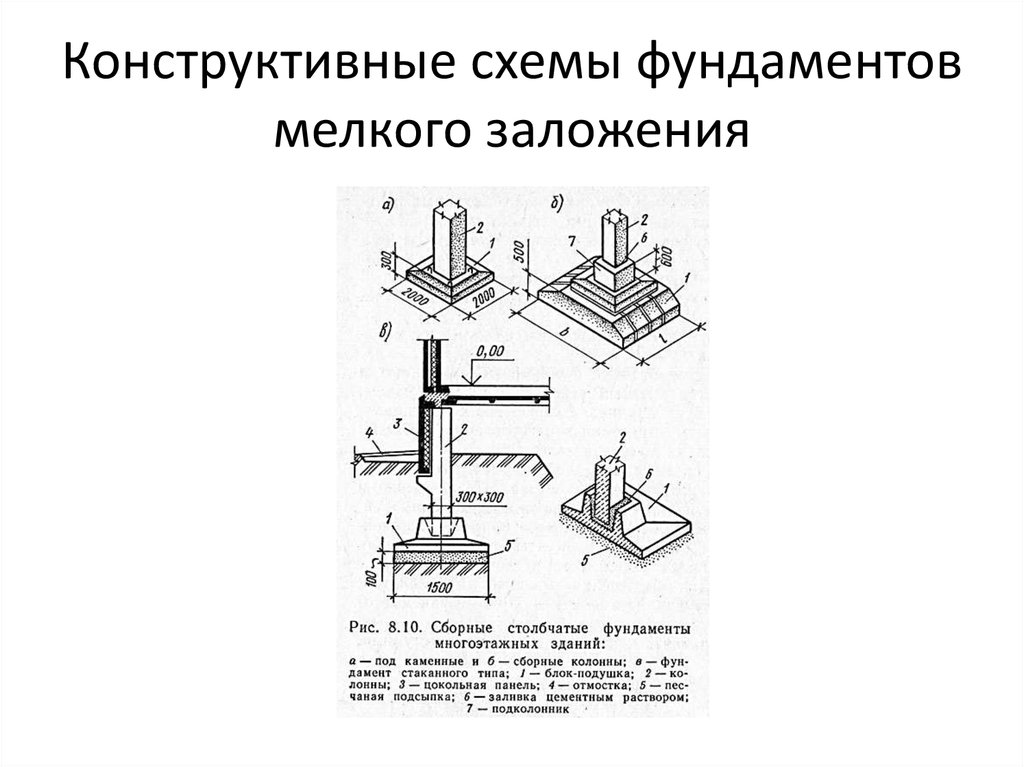
Installation of a shallow columnar foundation
This type of base is suitable for baths and small wooden houses, as well as structures made of light building materials, for example, summer houses made of plasterboard or chipboard. The main advantage of such a foundation is quick construction and minimal construction costs. It includes the following stages:
- Design and calculation of the foundation. Experts recommend conducting a laboratory analysis of the soil in order to determine the exact depth of the pillars, depending on the depth of its freezing.
- Calculation of the distance between the posts (for monolithic products it is 100-120 cm).
- Performing markup.
- Digging a hole along the perimeter of the foundation, its thickness should correspond to the cross-section of the pillars.
- The pit is covered with crushed stone up to 20 cm thick, it is carefully rammed.
- Execution of a reinforced structure. First, the rods are installed on the width of the foundation, then longitudinal parts are attached to them. The lattice can be mounted both in the pit itself, as well as in a separate area with the subsequent immersion of the structure into the trench.
- Pouring with concrete grade 250.
- Execution of a box from long edged boards, it should not have a bottom.
- attachment of formwork to pre-erected reinforcement structures.
- Filling the formwork with cement mortar of the same brand.
- Production of a filling and a bitumen layer that protects it from moisture ingress.
For the most durable use of this type of foundation, it is worth adhering to a few simple rules:
- correct calculation of the foundation;
- uniform load is not its total area and individual elements;
- selection of exceptionally high-quality materials both when pouring the foundation and when erecting formwork;
- all work should be carried out in summer or early winter.
In the video below, you can understand the basics of how FMZ is performed:
If you adhere to all of the above rules, a shallow foundation will become a very economical and convenient option for creating a foundation for a private building. It should be used in private construction and in certain soil conditions.
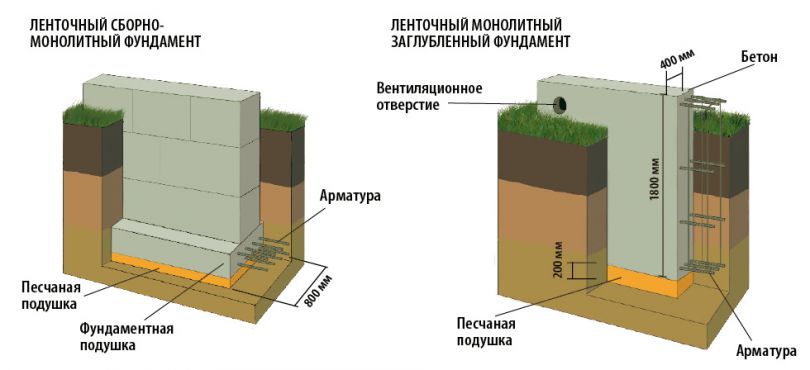
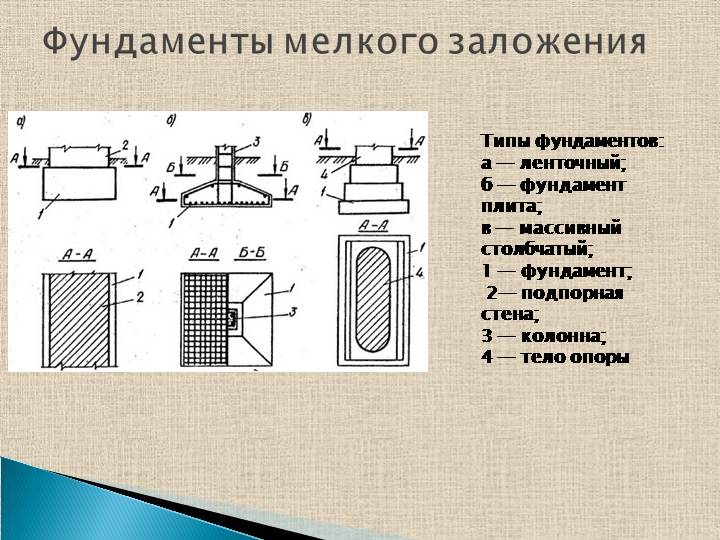
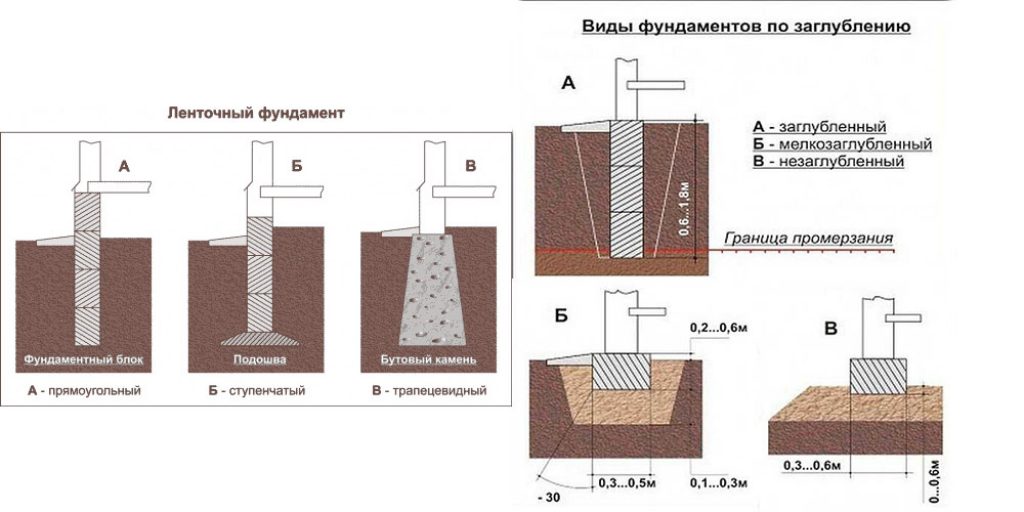
Base types
All types of platforms can be arranged at a short distance from the ground surface. These include:
- Plated.
- Tape.
- Columnar.
There is also a separate type of foundation - a pile foundation, but it is installed below 3 m, and it is rightfully considered a deep foundation option.
1. Stove. The most reliable design of all types presented. It is a reinforced concrete slab reinforced over the entire area. Such a platform is not threatened by climatic and geodetic conditions of the area. In addition, the building on such a base practically does not shrink. The disadvantages include the high cost of the foundation - up to 50% of the total construction. The price includes the necessary participation of specialized equipment and the amount of fittings.
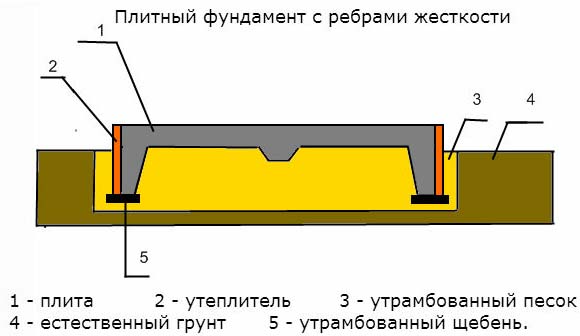
2. Ribbon. A popular option in various constructions. It is represented by two constructions:
- prefabricated monolith with reinforcement outlet;
- block foundation with reinforcing belts - upper and lower.
Requires several stages of preparation before pouring, namely:
- digging a ditch with precise parameters for load-bearing walls;
- the device of crushed stone and sand cushion, serving as drainage;
- reinforcement.
To get a shallow foundation, a frost-resistant foundation like a tape, it will have to be insulated with styrenes along the inner walls. The basement floor will not do without additional gaskets.
3. Columnar bases. Recommended for small, one-story, mostly wooden buildings. They are pits with reinforced concrete rings, filled with mortar at all corners of the future structure and its bearing units with a step of no more than 2 m. They can be made of brick, or asbestos concrete by factory molding with the release of reinforcement. After installation, the pillars are cut to the level, after which the grillage is installed on them.
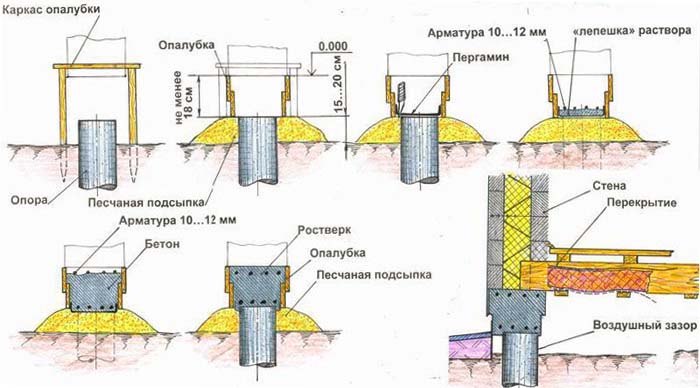
Shallow columnar foundations are unpopular due to their shortcomings:
- too dependent on the behavior of the soil - the level after shrinkage may change;
- the bottom of a residential building becomes accessible to all winds;
- restriction in construction materials - a lightweight version is selected;
- you will have to forget about the basement or basement as a usable area.
As it follows, having evaluated your own financial and physical capabilities, you can choose a platform suitable for your own construction or give such a task to specialists on the grounds in a specific region.
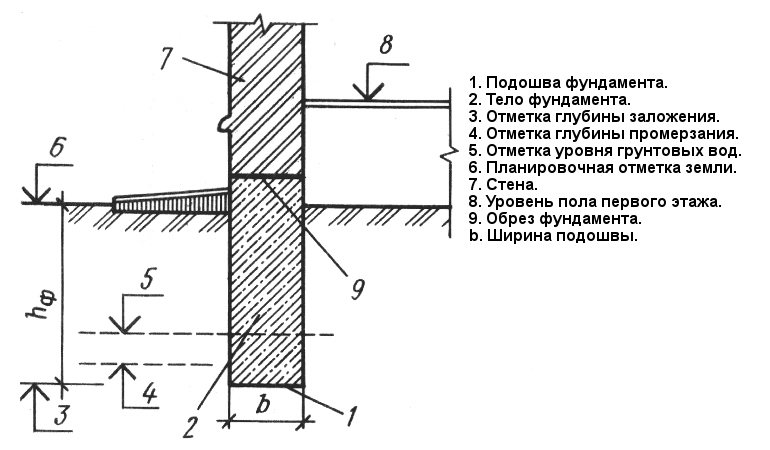
The choice of depth and the device of a sand and gravel cushion for the foundation
The design of turnkey houses provides for the type of foundation in advance. Before the device of a particular variant, three parameters are analyzed:
- The construction of the finished house - area and material of manufacture. The definition is necessary to find the maximum load on the platform surface - kg / m2.
- Climatic conditions of the area. At strong subzero temperatures, there is a reason to think about a reliable deepening in order to avoid damage to concrete.
- Soil composition and moisture level. Capricious lands can cause shrinkage and defects in the finished structure.
For example, in the project there is a wooden or cinder block house with an area of 157 m2. The terrain has a clayey soil of medium movement. The average temperature in winter is around -15-20⁰. The waters lie below 2 m. Thus, the best base would be a tape reinforced version up to 1 m below the basement + drainage.
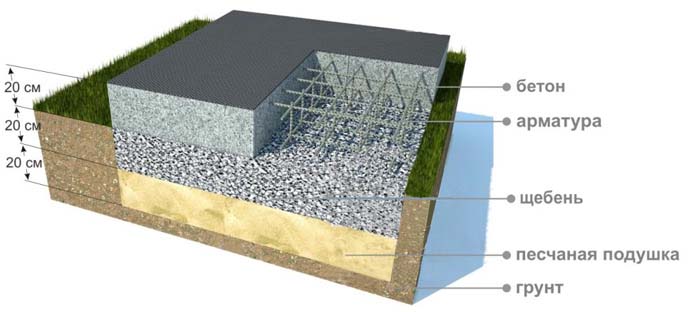
Platform protection
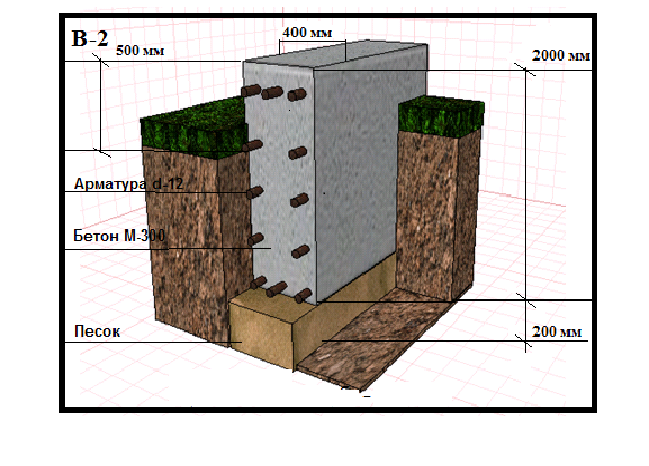
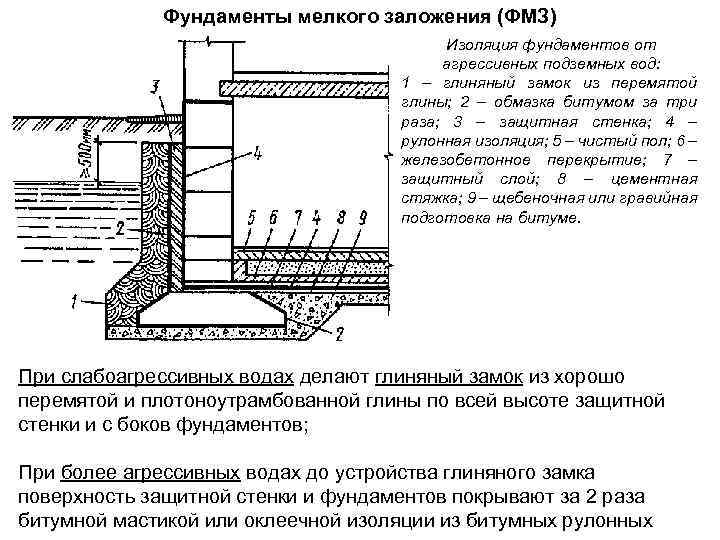
Different foundations can be shallow and deep, but none of them is complete without a so-called sand and / or gravel cushion. It serves as protection against harmful waste fluids located near industrial plants that can interact with the base and create destructive processes relative to the chemical composition of concrete. Each layer that protects the platform from moisture is carefully compacted, spilled with water and calculated to a height of at least 15 cm. After that, the foundation is reinforced and poured. The drainage must contain coarse sand, crushed stone or expanded clay. All three components can be used with a total height of 30 cm.
The correct choice and arrangement of a platform for private or other type of construction is the key to a durable and comfortable stay.
Formwork
 Formwork strip foundation formwork
Formwork strip foundation formwork
Formwork for a deep foundation is mainly made from edged boards, but you can also buy a plastic kit. The formwork is made to fit the size of the base, while the boards are hammered into shields. There should be no gaps in the shields.
In order to prevent the shields from sliding apart when pouring concrete mixture from the outside, they are fixed with the help of slopes. To fasten two opposite walls of the formwork, U-shaped jumpers are installed every 50 cm.
Before proceeding with the installation of the formwork, you must first form a sand cushion at the bottom of the trench under the freezing line. Roofing material is laid on the bottom as a waterproofing layer.
It is important to know: before pouring the cement mortar, wooden boards must be abundantly moistened with water so that they do not absorb it from the mixture itself
How a tape deep foundation is built
Using the example of a strip structure, let's see how the deep foundation is laid.
For the construction of such supports, additional work must first be carried out. This is necessary to prepare the future site. After that, you can start marking work. This can simply be done using the pegs and rope method. It is believed that you need to mark out in two lines. After the successful completion of the marking, the earthworks are carried out. Here the whole task is to trench the required depth.
Often, the depth depends on the soil, the depth of the groundwater and the depth of freezing. It should be calculated based on the degree of need for serious bearing qualities. If the building is heavy and the soil is weaker, then the depth should be great. To determine the width, the bearing properties of the soil should be calculated. As a result, the necessary trench is pulled out.

Reinforced post installation
The next stage includes formwork. It can be made either by hand or use an industrial version. Self-made formwork, most often from wood. Outside, it must be secured with slopes. They can be made from fittings or from rails.
Small nails are hammered inside the resulting structure. The technology provides for them at a certain height from the lower edges. The height of the support will depend on this height. You need to try to protect such a base as much as possible from excess moisture.
Then - the stage of reinforcement. This must be done with ribbed steel reinforcement. This stage is performed in two belts. Then the belts will be fastened together with reinforcing wire. Both the top and bottom chord should be mesh. These are several rods that are stacked in parallel. They are fastened with jumpers. The racks are fixed to these jumpers, which are then again attached to the jumpers, but already of the upper belt.
Now all that remains is to complete the concrete pouring work. Experienced builders recommend doing this job in one go. If for some reason this is not possible, then you should not fill horizontally in layers, but apply the method of vertical parts. So, the system is split into parts using shields.
As a result, the structure will be durable and reliable. If the soil moves, then the base with a horizontal seam may delaminate. After one part of the concrete has been poured, it is necessary to tamp. This can be done by tapping on the formwork.
After pouring, waterproofing is done over the entire plane. Before doing this, a thin screed is made at the edge. Its task is to align the plane of the tape. For waterproofing, either roofing material or polyethylene is suitable.
Finally, you can move on to the final stage. The formwork is removed here. This can only be done after the concrete has hardened. Backfilling is performed with higher quality soil.It is produced along the entire length and as evenly as possible. The backfill layer should not exceed 40 cm.
So, all the work is not so complicated and time-consuming, but the result will be the most reliable, durable and effective support, on the basis of which even the most difficult buildings can be built.
You can choose the appropriate option in each specific case only on the basis of the type of this or that soil, the volume of the budget and many other parameters. If all work is carried out strictly according to technology, reliability is guaranteed.
The need to perform thermal insulation
This technology has significant differences from the method used for deep foundations, since in this case there is a much smaller amount of area on which thermal insulation works are carried out. The main goal is to create such operating conditions under which the base of the building will not be subjected to huge loads from the heaving soil, which means it will not lose its quality and reliability. The use of modern technologies and thermal insulation materials allows you to protect the main part of any building - the foundation.
Materials (edit)
The most acceptable material for this type of work is extruded polystyrene foam, which has the following technical characteristics and features:
- light weight of the slabs;
- high thermal insulation properties;
- low water absorption;
- non-exposure to low and high temperatures (range from -50 to + 75 ° C);
- ecological cleanliness;
- high compression rates;
- easy installation;
- low cost and economy;
- durability.
The process of carrying out insulation works
In order for the shallow insulated strip foundation to serve for a long time, it is necessary to correctly and competently perform heat and waterproofing.
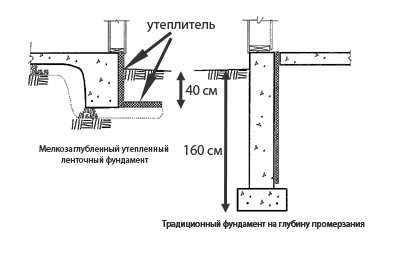
The whole process begins with outdoor work. Fastening of plates of extruded polystyrene foam with a thickness of at least 50 mm is carried out on the side surfaces of the base using special glue or plastic dowels-nails. In the lower part of the foundation and along its entire perimeter, sheets of foam are laid (horizontally), the width of the insulated soft blind area is from 1 to 1.5 meters. In the corners, reinforcement is made from several layers of material, and glue is used to connect the sheets "in the lock". After the installation and laying of the foam is completed, backfilling with soil, ramming and the creation of a concrete blind area are performed.
The effect is improved by carrying out internal thermal insulation. For these purposes, foam sheets with a thickness of 3 cm are used, which are laid directly on the ground base. Such a thickness of the slab will not interfere with the flow of heat from the side of the room, which will exclude the heaving of the soil inside the room. The laid sheets of thermal insulation are covered with other layers of building materials.
Knowing all the features and the procedure for carrying out the work, it is not difficult to make a shallow strip foundation with your own hands, the insulated house will be cozy and comfortable for living.
Calculation of the index of flexibility of building structures
1. Index of flexibility
building structures l is determined by the formula
,(1)
whereEJ - reduced stiffness on
bending of the cross-section of building structures in the foundation-plinth-belt system
reinforcement - wall, tf.m2, determined by the formula (4);
WITH - stiffness coefficient
foundations with heaving of the soil for the bases of strip foundations;
L —
length of the wall of the building (compartment), m;
,(2)
for reasons
columnar foundations
,(3)
Here pr, hfi, b1 - the same designations as in paragraphs. -;
Af - the area of the foot of the columnar foundation, m2;
ni - the number of columnar foundations within the length of the building wall (compartment).
2. Reduced stiffness at
bending of the cross-section of building structures in the foundation-plinth-belt system
reinforcement-wall, tf / m2, is determined by the formula
[EJ] = [EJ]f + [EJ] z + [EJ] p + [EJ]s,(4)
where EJf,
EJz, EJp,
EJs - accordingly, rigidity
on the bending of the foundation, basement, reinforcement belt, building walls.
3. Flexural stiffness, tf / m2,
foundation, base and reinforcement belt is determined by the formulas
f= gfEf(Jf+ Ayc2);(5)
z = gzEz(Jz+ Azyz2);(6)
p = gpEp(Jp + Apyp2);(7)
where Ef, Ez, Ep - respectively, deformation moduli tf / m2,
foundation material, base and belt;
Jf, Jz, Jp- respectively moments
inertia, m4, cross-section of the foundation, base and reinforcement belt
relative to its own main central axis;
A, Az, Ap- the area of the transverse
section, m2, foundation, base and reinforcement belt;
y, yz, yp - respectively, the distance, m, from the main
the central axis of the transverse cross-sections of the foundation, base and reinforcement belt up to
conditional central axis of the section of the entire system;
gf, gz, gp
- respectively, the coefficients of the operating conditions of the foundation, basement and belt
gain, taken equal to 0.25.
Bending stiffness
a foundation consisting of blocks that are not interconnected is taken equal to
zero. If the basement is a continuation of the foundation or their joint is provided
work, plinth and foundation should be considered as a single constructive
element. With no reinforcement belts EJp
= 0. In the presence of several belts of reinforcement, the bending stiffness of each of them
is determined by formula (7).
4. Flexural stiffness, tf / m2,
walls made of bricks, blocks, monolithic concrete (reinforced concrete) is determined by
formula
s = gsEs(Js
+ Asys2),(8)
where Es - deformation modulus
wall material, tf / m2;
gs
- coefficient of working conditions of the wall, taken equal to: 0.15 - for walls made of
bricks, 0.2 - for block walls, 0.25 - for monolithic concrete walls;
Js- the moment of inertia of the transverse
section of the wall, m4, is determined by the formula (9);
As
- cross-sectional area of the wall, m2;
ats—
distance, m, from the main central axis of the cross-section of the wall to the conditional
the neutral axis of the section of the entire system.
Moment of inertia of the cross-section of the wall
is determined by the formula
,(9)
where J1 and J2 - respectively, the moment of inertia of the wall section
along openings and walls, m4.
Cross-sectional area
walls are determined by the formula
,(10)
where bs - wall thickness, m.
Distance from center of gravity
the reduced cross-section of the wall to its lower edge is determined by
formula
,(11)
5. State from main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation to the conditional neutral axis
systems foundation-plinth-reinforcement belt - the wall is determined by the formula
,(12)
where Ei, Ai- deformation modulus and area, respectively
cross section i-th structural element
(base, wall, belt);
ji - coefficient of working conditions ith constructive
element;
yi - distance from the main central axis of the cross section ith
structural element to the main central axis of the cross-section
foundation.
6. Flexural rigidity, ts.m2,
walls made of panels is determined by the formula
,(13)
where Ej, Aj- respectively, the modulus of deformation, tf / m2, and the area of the transverse
section, m2, j-to communication;
m —
the number of links between panels;
di- distance from j-that connection to the main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation, m;
y - distance from the main
the central axis of the cross-section of the foundation to the conditional neutral axis
foundation-wall systems of the building, determined by the formula
,(14)
wherein n —
the number of structural elements in the foundation-wall system.
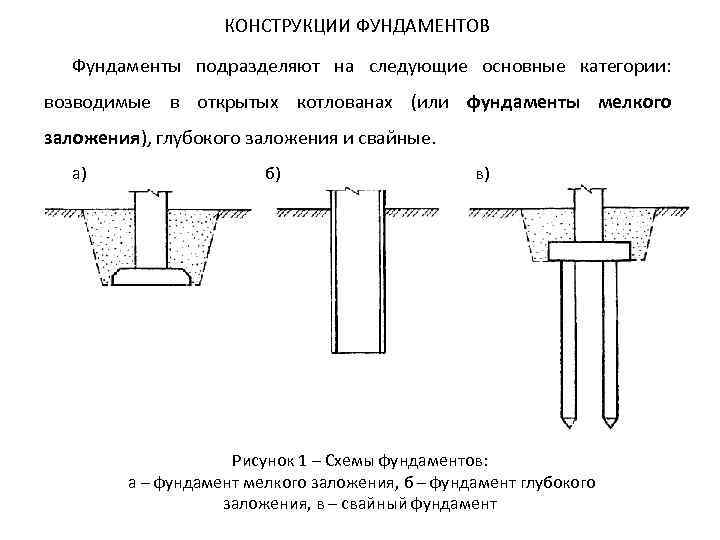
Deep foundations classification
There are several types of deep foundations, different in shape, method of construction, depth of laying, design features and materials used. Some types are used to create a solid and durable foundation for heavy buildings, others allow you to build a buried structure with underground rooms, and others reduce horizontal loads on the structure.
Deep foundations classification:
- drop wells;
- caissons;
- thin-walled shells;
- drilling supports;
- walls in the ground.
We propose to talk about each of the types in more detail.
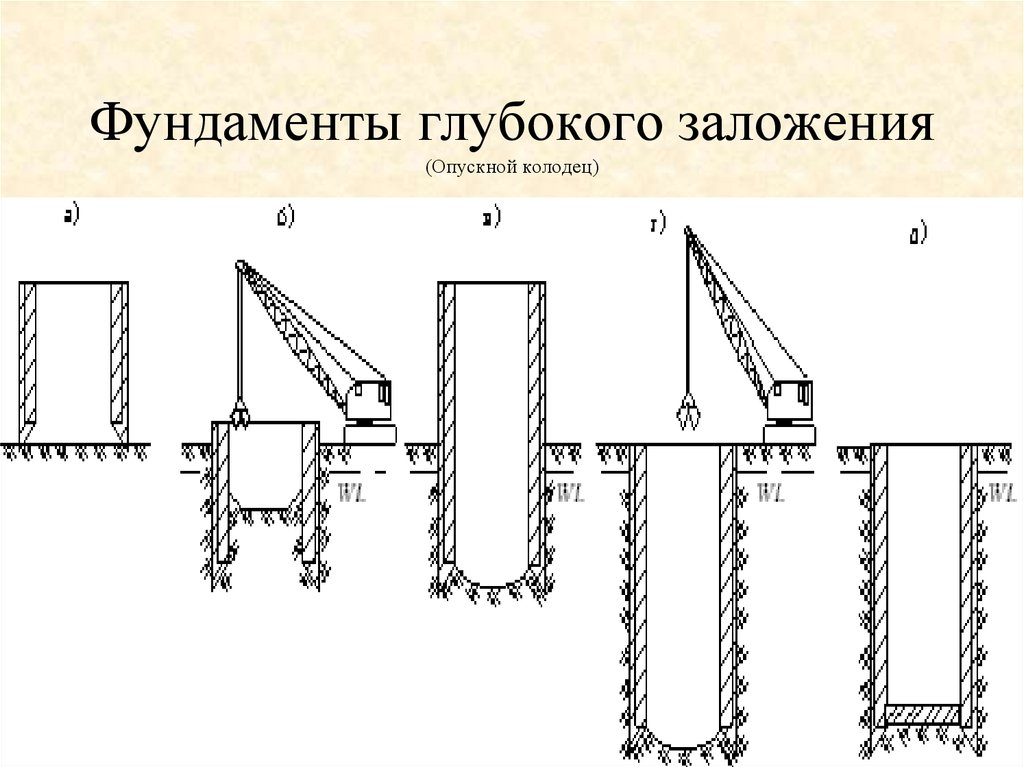
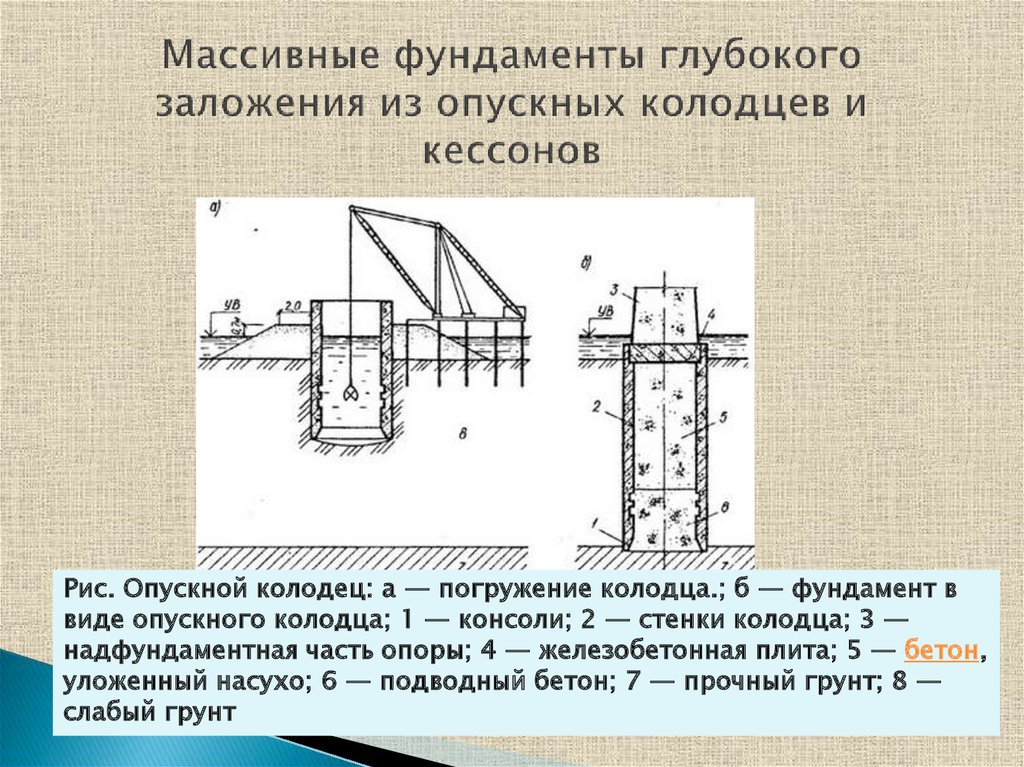
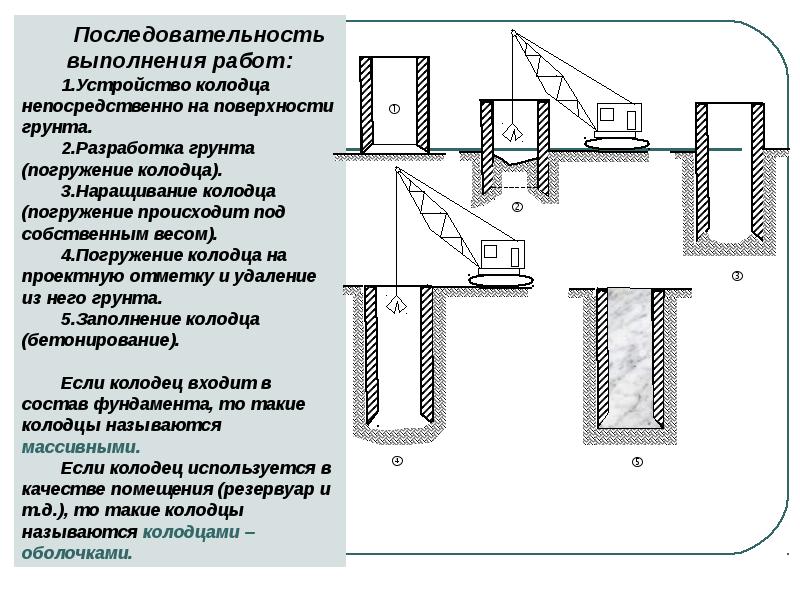
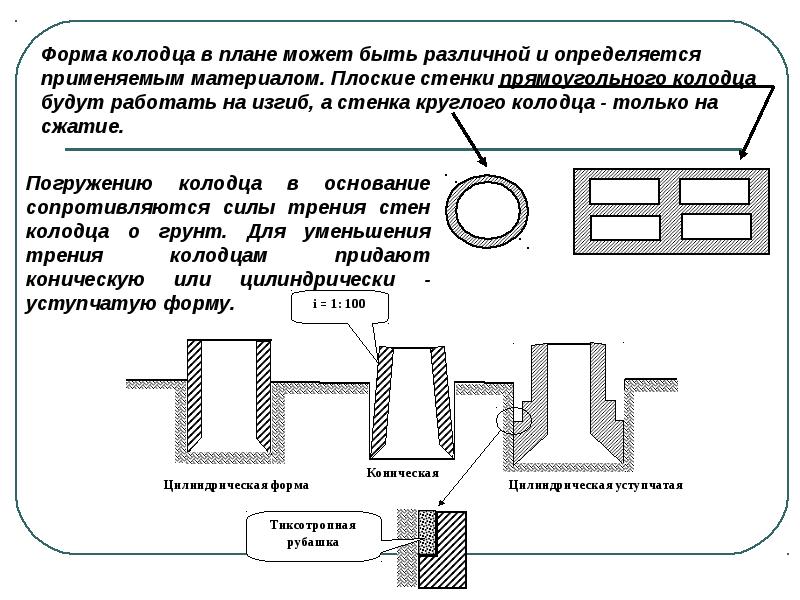
Drop wells
The sinkhole is a closed and, as a rule, symmetrical, through-type structure. It is placed in the ground in its entirety or collected from several sections, after which it is carefully concreted.
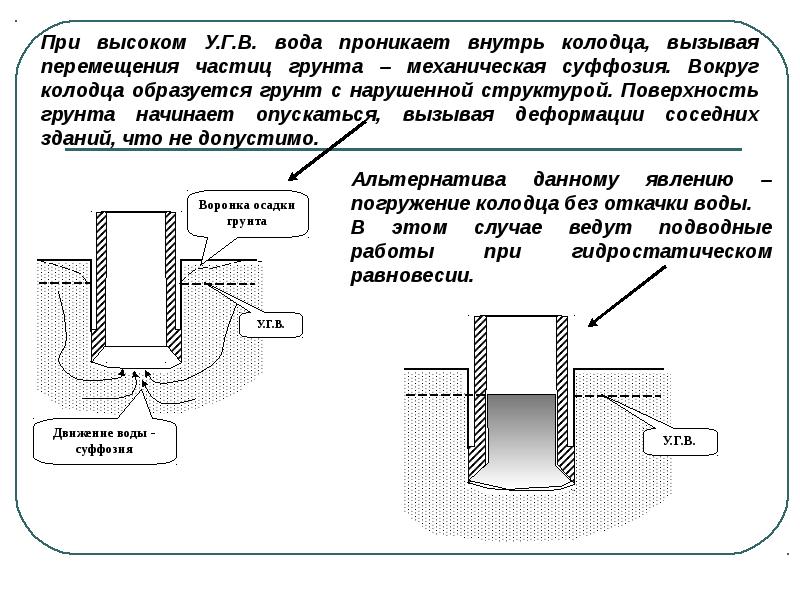
Typically, fall wells are installed using their own weight, but in some cases, vibrations are used to secure them firmly. The main rule is adherence to the strictest verticality when diving. As the well sinks into the ground, the soil is gradually removed from under it, using a hydraulic washing machine or a grab excavator for this purpose.

Falling wells are made from a variety of materials, including reinforced concrete, masonry or masonry, and sometimes metal and wood may be used. The lower part of the structure is equipped with a cutting part with corners or channels. It is reinforced more than the entire body of the well. The outer walls can be stepped or vertical with a decreasing diameter towards the top.
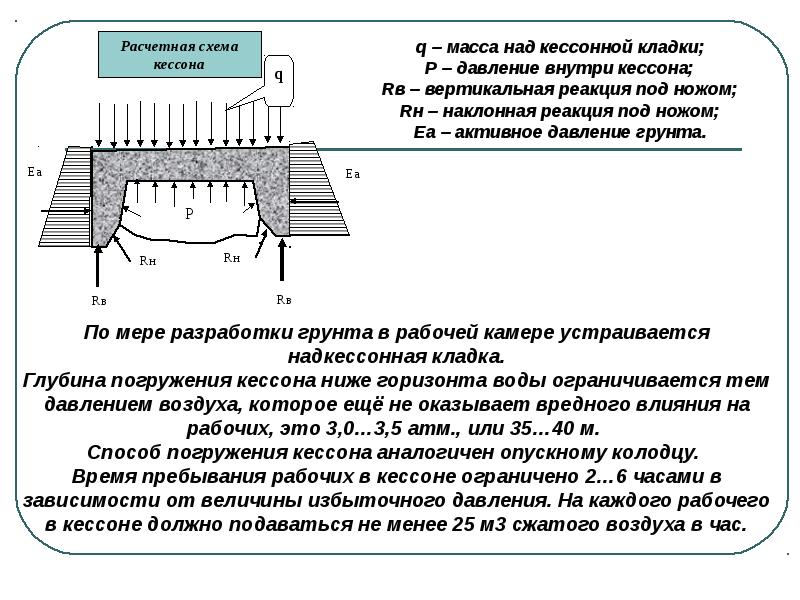
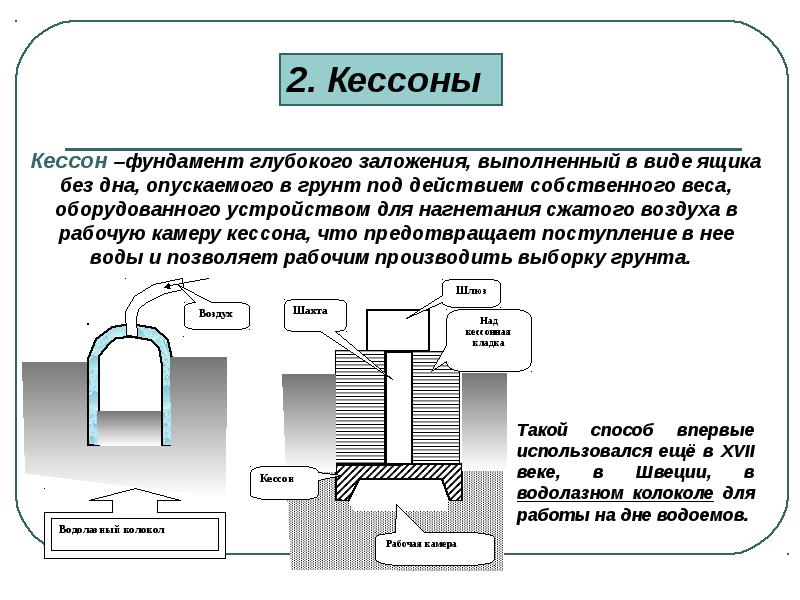
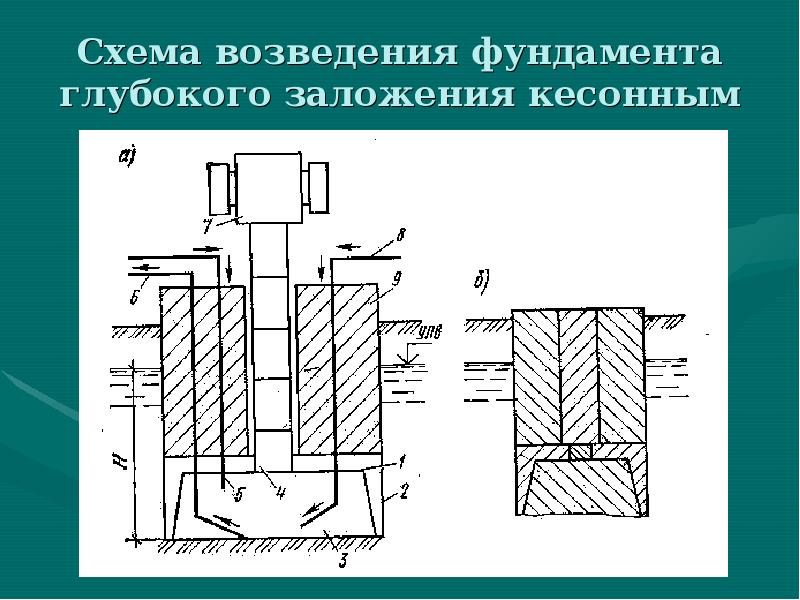
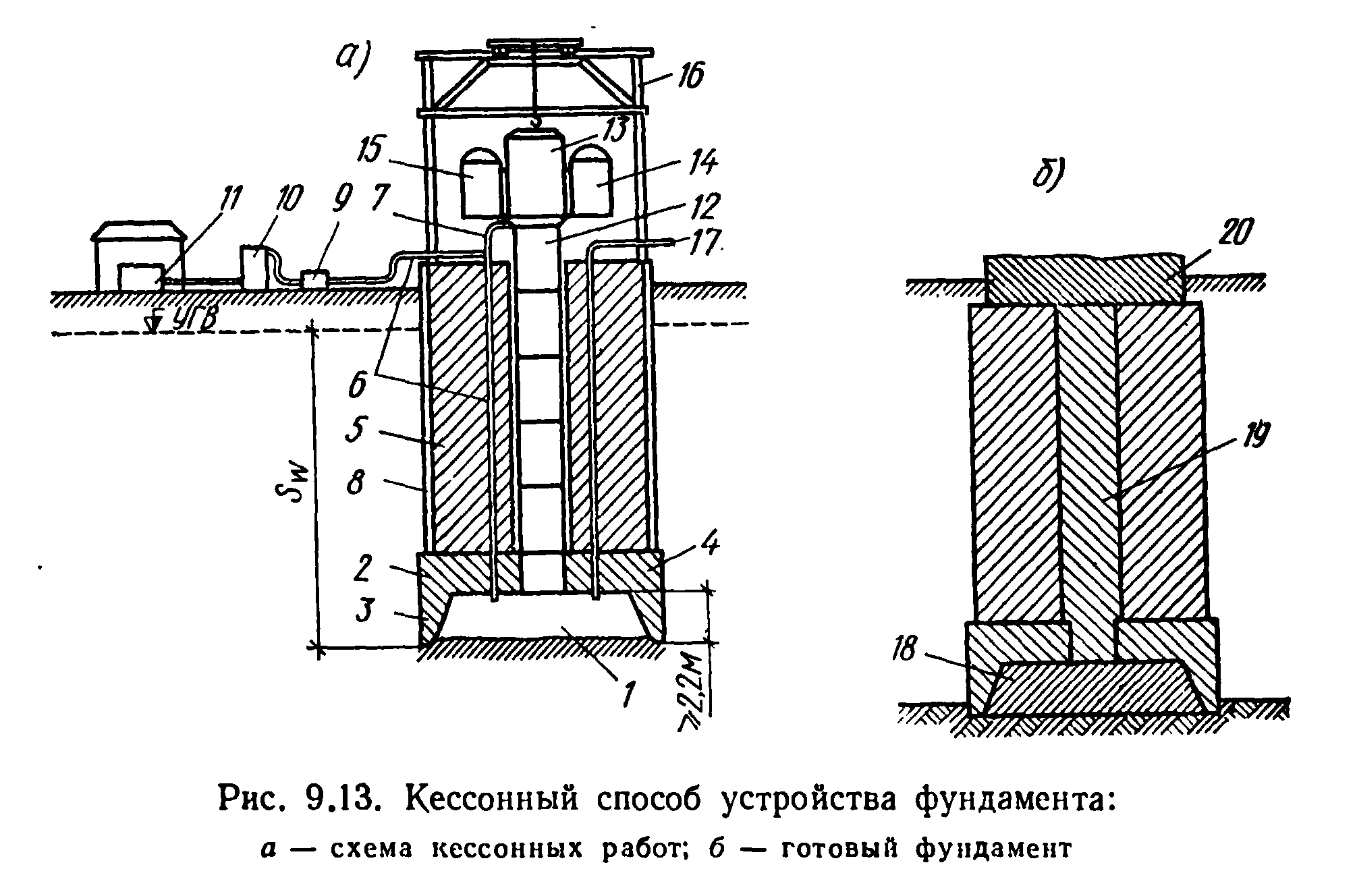
Caissons
Caissons are used in cases where a deep foundation has to be mounted below the groundwater level. The caisson is a kind of chamber with forced air that dries and pushes out the soil for development. When the caisson chamber is lowered into the ground, it is poured with concrete.
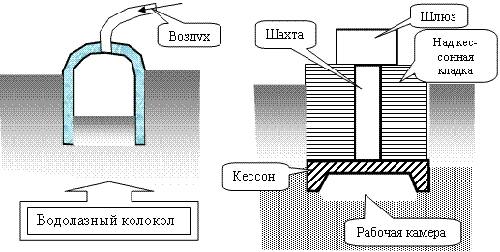
The caisson consists of the following structural elements:
- mine;
- camera;
- compressors;
- gateway devices.
The use of deep caisson foundations is associated with high labor and financial costs. This method is rather difficult to execute, and therefore in modern construction it is practically not used, replacing it with alternatives.
Thin-walled shells and drill supports
Thin-walled shells are hollow metal cylinders, the diameter of which can vary from 3 to 6 m. The length of one section can reach 6-12 m, and, if necessary, they are increased by bolting and strengthening the fasteners by welding.
A vibrating device is used to submerge long metal sections into the ground. Like sinking wells, thin-walled shells have knife parts in their lower part. After installing the elements in a strictly vertical position, the internal voids are poured with concrete mortar.

Drill pads are similar to thin-walled shells, but made entirely of concrete. They are installed in a previously drilled vertical shaft. The body of the concrete support is reinforced, and a slight expansion is made in the lower part of it. It significantly reduces the load on dense soil, and also prevents the heaving forces from loosening the supports and other unfavorable phenomena.
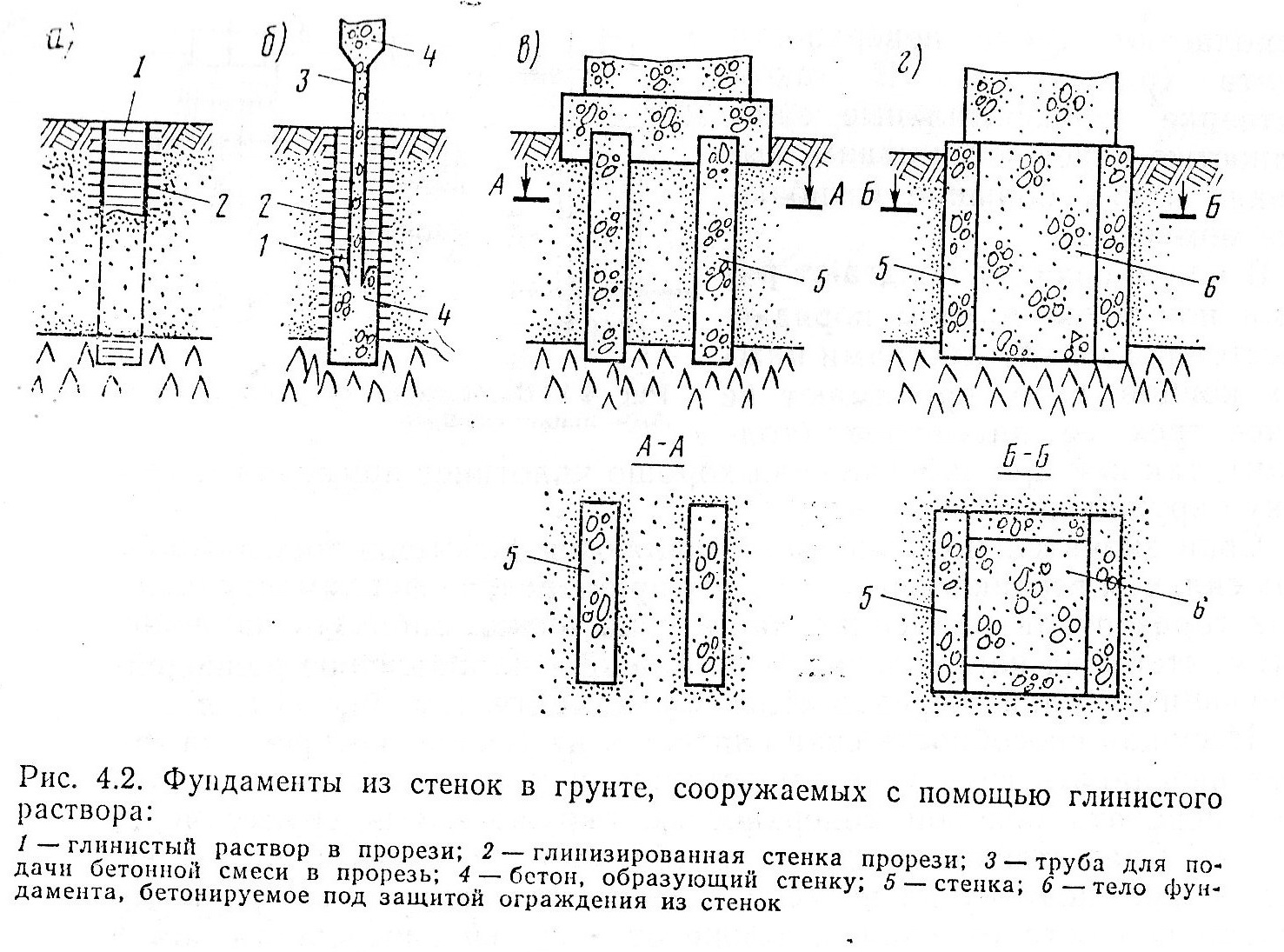
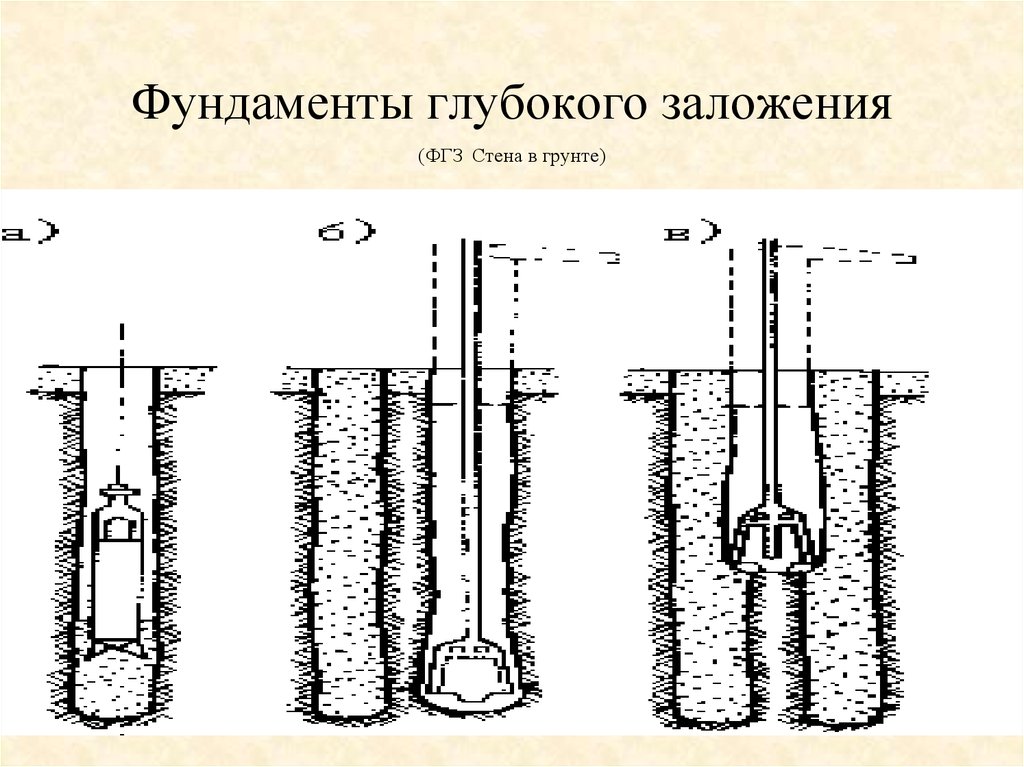
Wall in the ground
Walls in the ground as foundations are erected mainly for the construction of buried structures. First, they outline the outline of the building, after which, in accordance with the markings, they dig a narrow and very deep trench (as for a strip foundation, only much deeper). Then this trench is filled with pre-prepared reinforced concrete sections, or poured with concrete mortar.

Such a deep foundation is used for the construction of residential multi-storey buildings with underground parking, walkways, warehouse, work and production facilities. This method is relevant for densely populated megacities, where developers are forced to fight for every free cubic meter of space. In recent years, houses with underground levels are being erected more and more often in view of their obvious practicality.