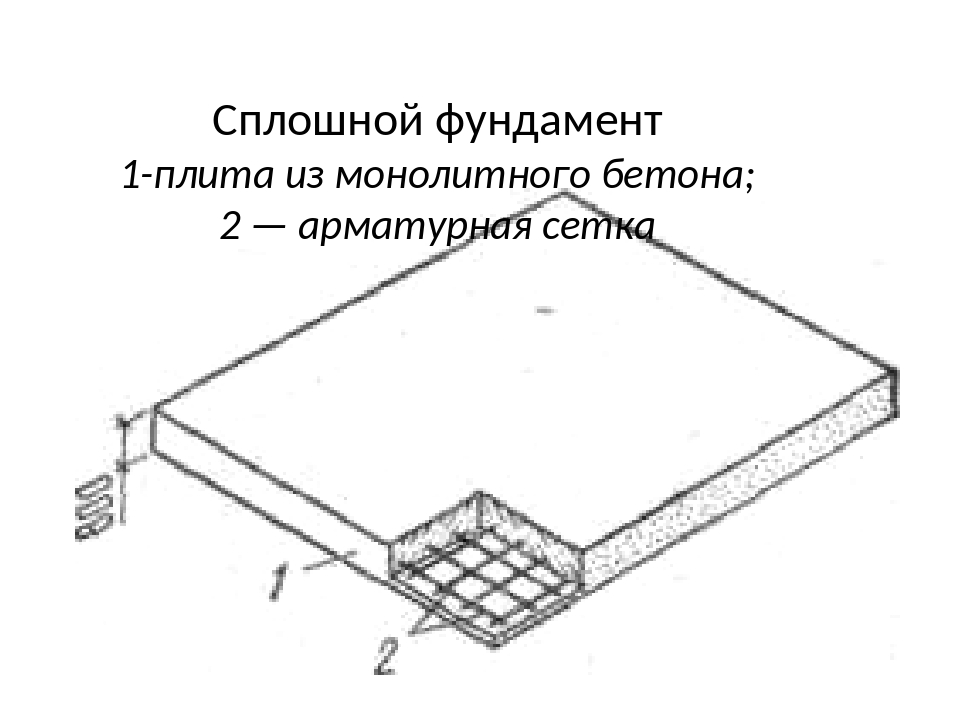
Subsequence
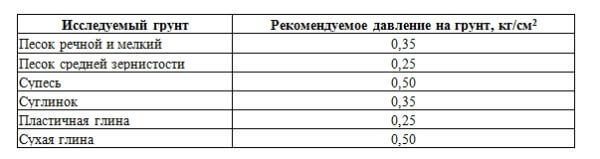
1. If you have chosen a slab foundation: the scheme of work says that the first step is to determine the type of soil by the method described above.
The table shows the permissible specific pressure for it.
2. Calculate the total load of structures planned for construction on the foundation, per unit area. This includes the load from the bearing walls of the future home, the load of interior partitions, ceilings, windows, doors, roofs, furniture and possible snow decking on the roof.
For this, the area of all surfaces is calculated and multiplied with the load indication of one square meter of material taken from this table.
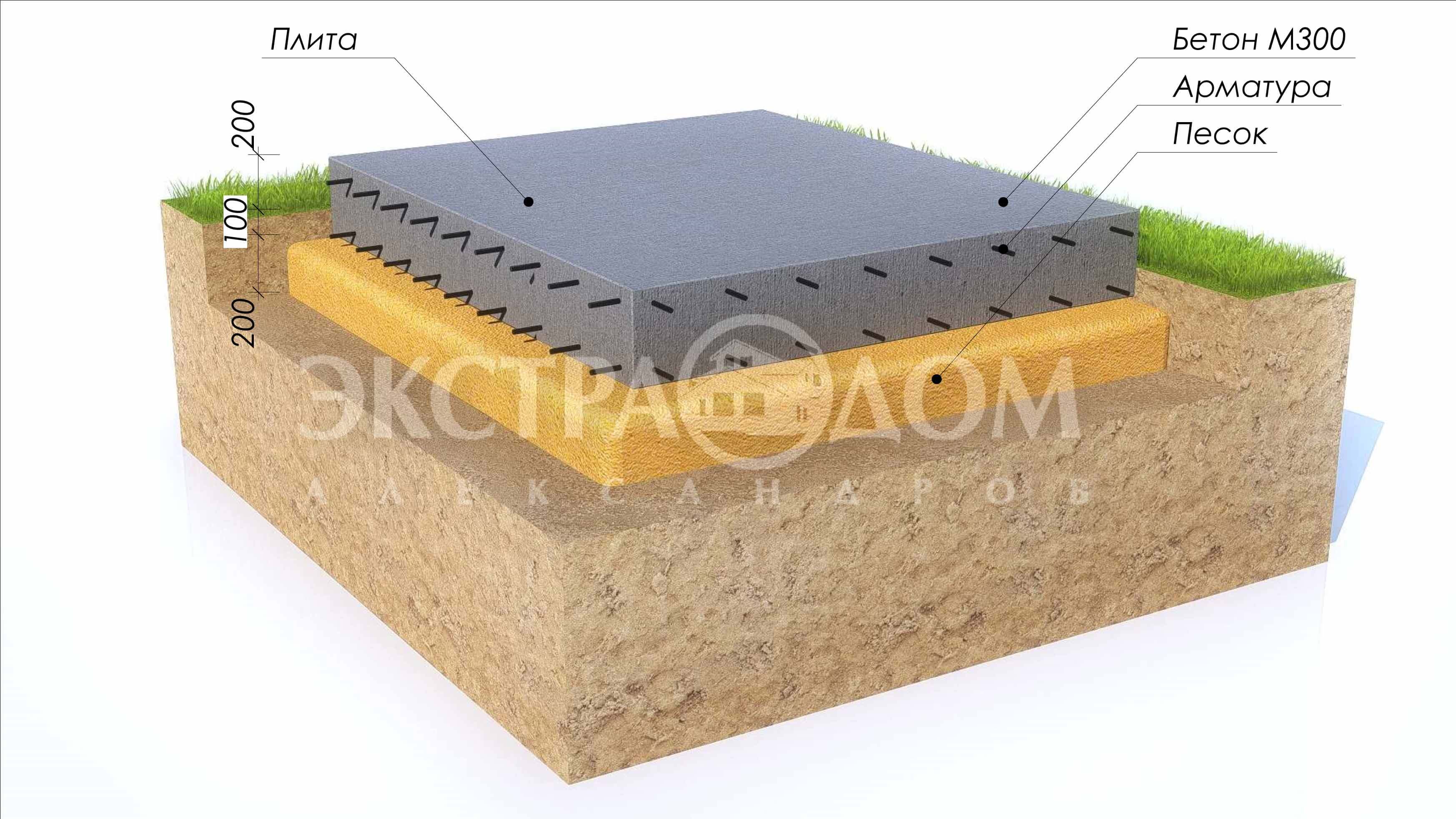
Monolithic slab foundation: thickness calculation (load parameters):
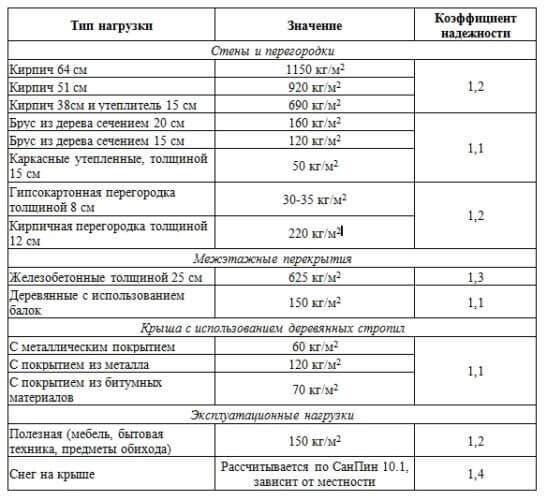
Important! Load data for other materials can be found in building codes. The third column "Safety factor" in this table shows by what value the final load must be multiplied to ensure the required margin of safety for the foundation
The third column "Safety factor" in this table shows by what value the final load must be multiplied to ensure the required margin of safety for the foundation.
The final formula for calculating the total ground load looks like this:
P1 = M1 / S,
where М1 is the total load of the structure, obtained by adding the load of all structural elements, multiplied by the reliability factor, S is the area of the foundation base.
3. We calculate the difference between the standard value of the permissible load from the table and the total load of the house:
Δ = P-P1,
where P is the tabular value of the load.
4. We find the maximum mass of the foundation, the excess of which can have adverse consequences in the form of subsidence of the entire slab and structure:
M2 = Δ * S,
where S is the area of a concrete slab.
5. The next step is to find the maximum thickness of the concrete slab for the foundation:
t = (M2 / 2500) / S,
where t is the thickness of the concrete layer, 2500 is the density of reinforced concrete, expressed in kilograms per cubic meter.
The result is rounded down to a multiple of 5.

6. We carry out the compliance of the slab thickness with the conditions under which the difference between the obtained pressure and the tabulated pressure on the ground should not exceed 25%.
Important! If, according to the calculated data, the thickness of the reinforced concrete slab turns out to be more than 35 centimeters, it is worth considering the option with the construction of a strip or pile base, since a monolithic in this case will be excessive
Scope and types of tape monolithic base
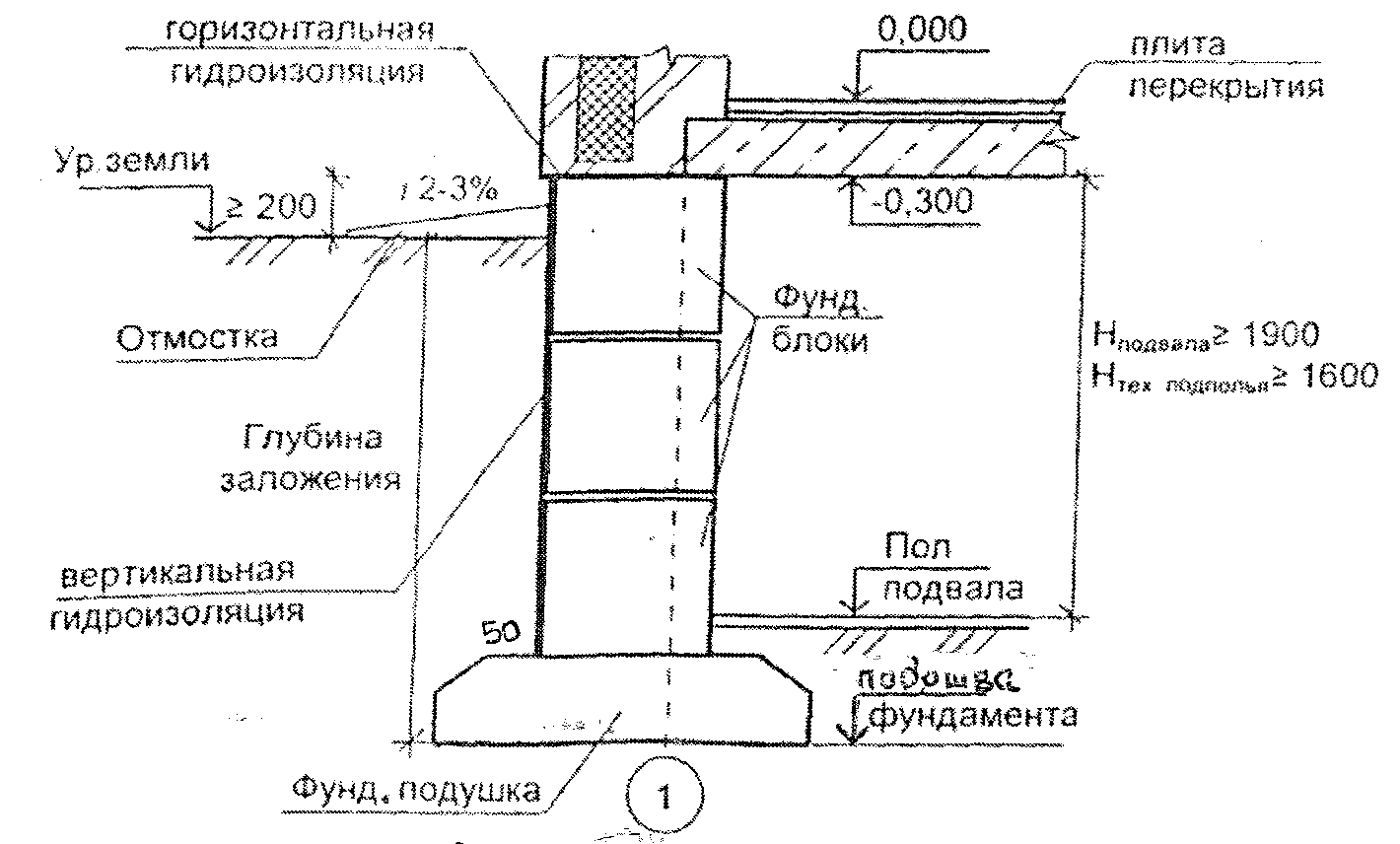
The choice of a specific type of foundation for a future building depends on many factors, the main ones of which are the type of material for building a house, the number of floors, the type of soil and its properties, the level of groundwater passage and freezing of the earth, etc. All these indicators affect the main parameter - the degree of load of the supporting structures on the support and foundation.
When a strip monolithic foundation is being built:
- Large weight of house walls made of stone, brick, concrete
- The presence of heavy floors in the structure - metal, reinforced concrete
- The presence of heterogeneous soils on the site for the construction of the facility (which, in turn, provokes an uneven distribution of loads on the base)
- Bookmark in the project of a basement floor, garage, basement in the future house
The strip-monolithic foundation is a flat horizontal strip of a single shape with a single cross-sectional value. The strip runs along the entire perimeter of the building, as well as under the interior walls.The monolithic structure is made of reinforced concrete - the solution is poured into the formwork with the assembled reinforcing cage inside.
By the type of assembly of the structure, the strip foundation can be:
- Monolithic - concrete is poured into the formwork with reinforcement directly at the facility.
- Prefabricated - made up of blocks produced at the plant, 25% less durable in comparison with the monolithic version.

Monolithic strip foundations by type of deepening and construction:
- Recessed - 50-70% of the base height goes into the ground. This type of construction is relevant for the construction of cottages from different types of heavy materials. The very high bearing capacity makes it possible to equip a good basement or basement in the house. A deep reinforced concrete foundation requires a serious amount of excavation / concrete work, therefore it is rarely used.
- Shallow is the most popular type of construction. The tape is deepened to 20-30% of the height (usually 40-70 centimeters), ideal for buildings made of timber, reinforced concrete slabs, bricks, foam / aerated blocks. High bearing capacity, reliability, minimal labor costs are the main advantages. Assumes that the groundwater level lies deeper than a meter.
- Shallow - involves raising the belt of the base, demonstrates considerable bending strength. Usually the height is greater than the width, suitable for log cabins, baths, sheds, summer cottages.
- T-shaped monolithic strip foundation (reinforced concrete) - involves broadening the sole in order to compensate for lateral displacements. The design is relevant for light buildings, fences, terraces. Backfilling is done with sand.
- The belt is of the belt type - without deepening, it is used for panel board, frame buildings, in order to increase the supporting surface, the width is made greater than the height.
The construction of a monolithic strip foundation can be carried out on any type of soil. On sandy loams, dry sands, loams, the structure is designed above the freezing level. Medium / high-loamy soils suggest deepening 20-30 centimeters below the freezing line without drainage. In the case when they decide to replace the heaving soil with non-heaving soil and carry out drainage, the foundation is allowed to be buried above the freezing line.

If a high groundwater level is noted on the site, drainage measures are first carried out, since hydrostatic pressure will deform the foundation. In this case, you can also use the pile technology for arranging the base.
Device
It is not enough just to choose the right type of slabs. It is necessary to carefully evaluate their required dimensions, and first of all, the thickness. The calculation of these parameters is based on the design loads.
The main focus is on:
- pushing loads;
- bending forces;
- the effects of frost heaving of the soil.
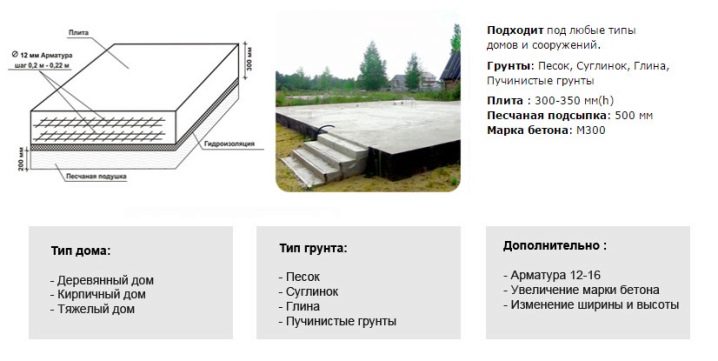
An analysis of long-term practice shows that for a frame house of two floors, the floors in which are made of reinforced concrete, it is necessary to put 200 mm thick slabs in the base. If the construction of the house is lighter, you can get by with a 150 mm slab
Important: these numbers apply only to the simplest cases with minimum load. As the weight of the house grows and its dimensions increase, the required thickness of the slab also increases
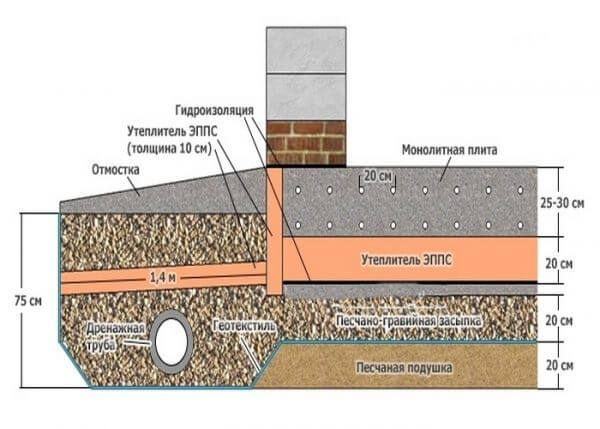
When it is known in advance that the house will be operated all year round, it is recommended to carry out thermal insulation.


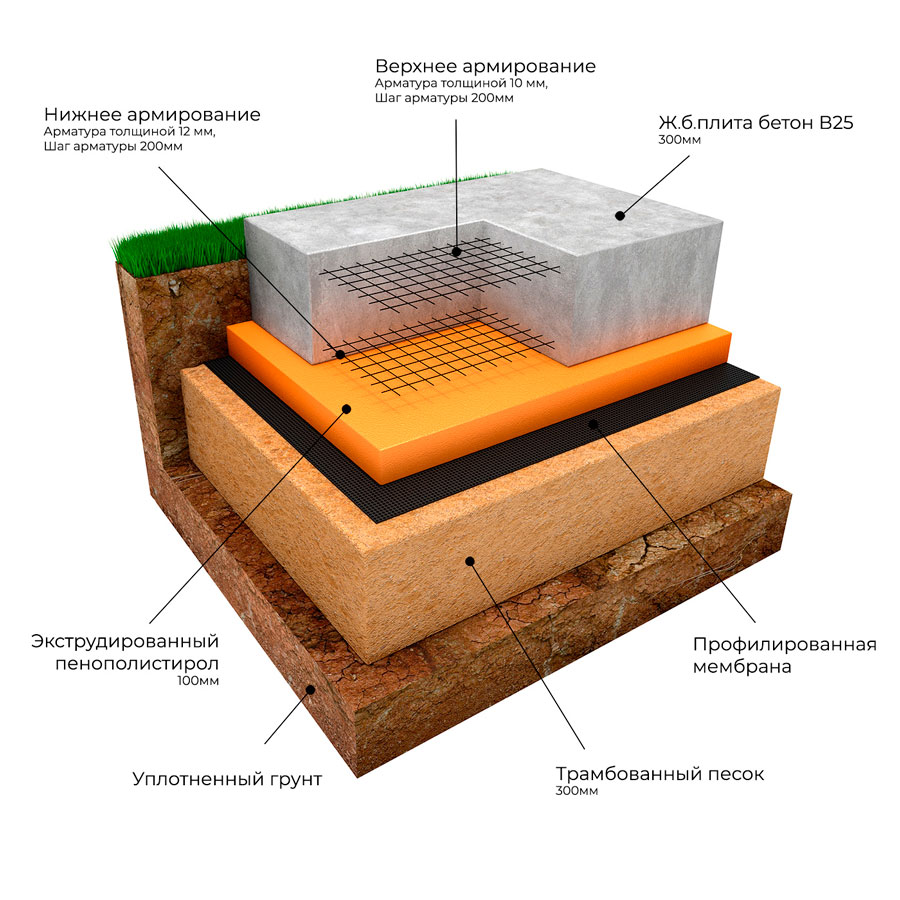
The thermal protection layer is formed both below the slab and above it. These materials should also be taken into account in order to make the right choice. Hydraulic protection in areas where groundwater is separated from the surface of 1 m of soil or more is performed in a simplified format. But with a high level of soil fluid, this practice is contraindicated. The reliability and strength of the slab foundation largely depends on how well the sand cushion is made under it.


There is gravel at the top.This material prevents moisture from concentrating under the sole of the base. The diverted water falls into a layer of sand, through which it passes even further. Additionally, the sand mass ensures uniform pressure distribution, dampens the effect of heaving forces. Under the garages where the car has to be repaired (and not just stored), the depth of the foundation is made deeper than usual, and the complexity of the work increases.

Most often, a monolithic slab is mounted under the garages according to a floating scheme. It is suitable for absolutely any soil and effectively suppresses the destruction of the garage during ground movements. As with home construction, there is no need to fill in an additional floor screed. Arrangement of underfloor heating with the rejection of classic radiator heating or in addition to it does not pose any particular problems
Attention: the secondary importance of the structure in comparison with the house does not allow it to be considered a less significant or secondary object

Formwork and metal frame construction
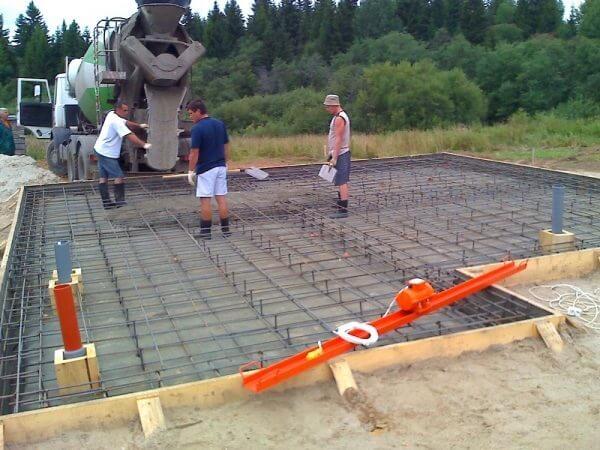
Before the monolithic reinforced concrete slab is poured, the developer must build a formwork for it:
- For the installation of such a structure, elements of natural solid wood (40mm) or plywood (up to 21mm) are usually used. A box is assembled from such material, the individual elements of which are fixed to each other by means of fasteners.
- The height of the formwork should slightly exceed the thickness of the future slab.
- Outside, the formwork (if it is removable) must be supported by the builder with jibs and stops. This is done to stiffen the box so that it can withstand the mass of the concrete mix.
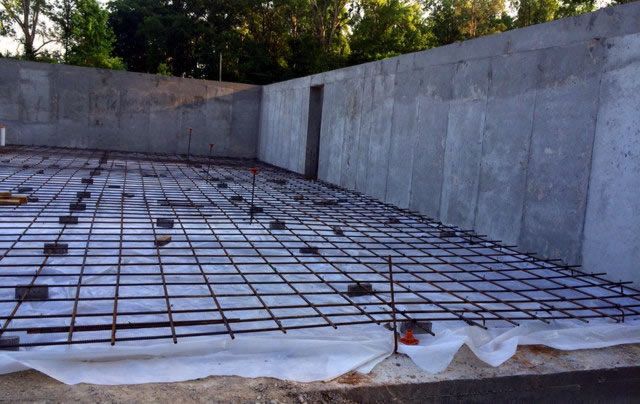
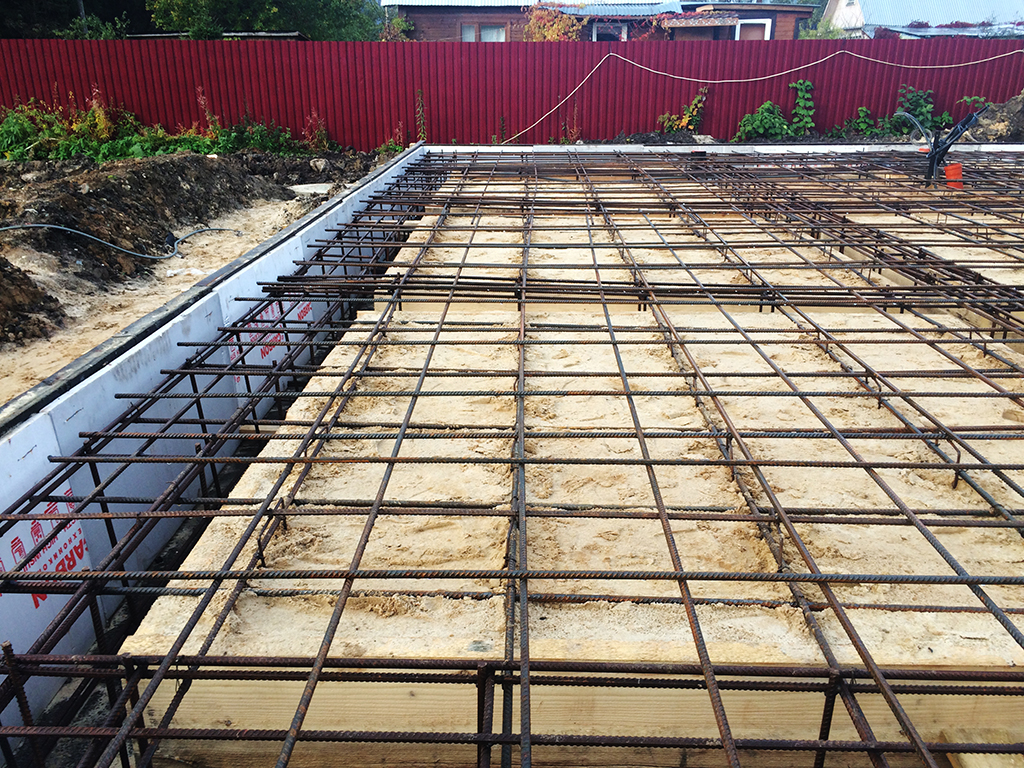
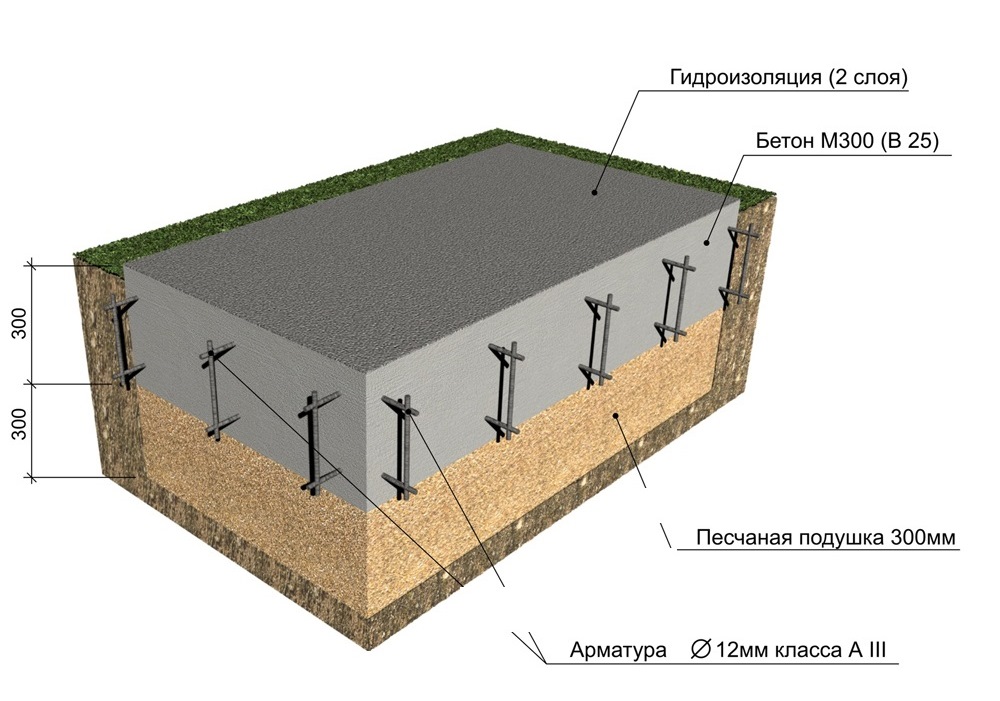
- Reinforcement (it is customary to use rods with a diameter of up to 14 mm) is laid on the compacted sand and crushed stone pillow, across and along. Make sure that the step does not exceed 30cm. Since the reinforcement should be located at a distance of 5 cm from the edge of the slab, special supports are placed under it, through which the necessary clearance is provided. If you plan to create a powerful foundation structure, then experts recommend laying the reinforcement in two or three layers. It should be tied together so that the metal frame is as strong as possible. Welding is not used in this case, since the resulting seam will be exposed to moisture during the operation of the building, which can provoke corrosion.
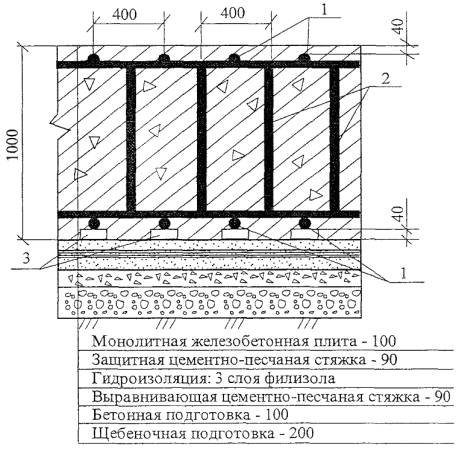
- Once the process of creating the formwork and metal cage has been completed, you can start pouring the concrete. Initially, a layer 100 mm thick is created, on the surface of which waterproofing material and insulation will be laid.
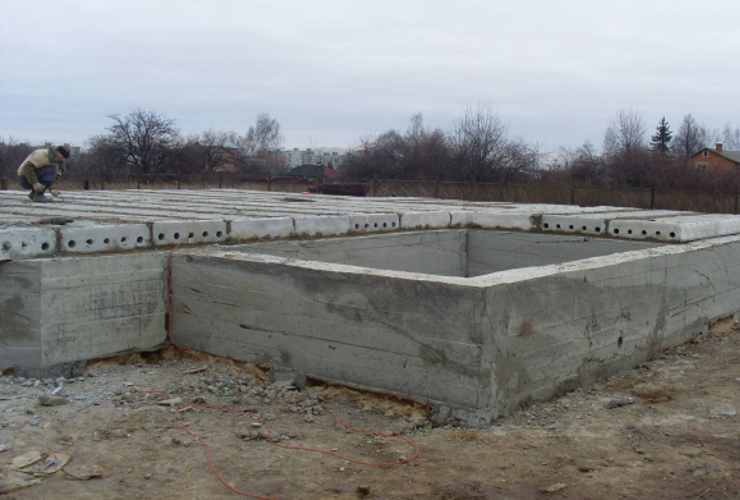
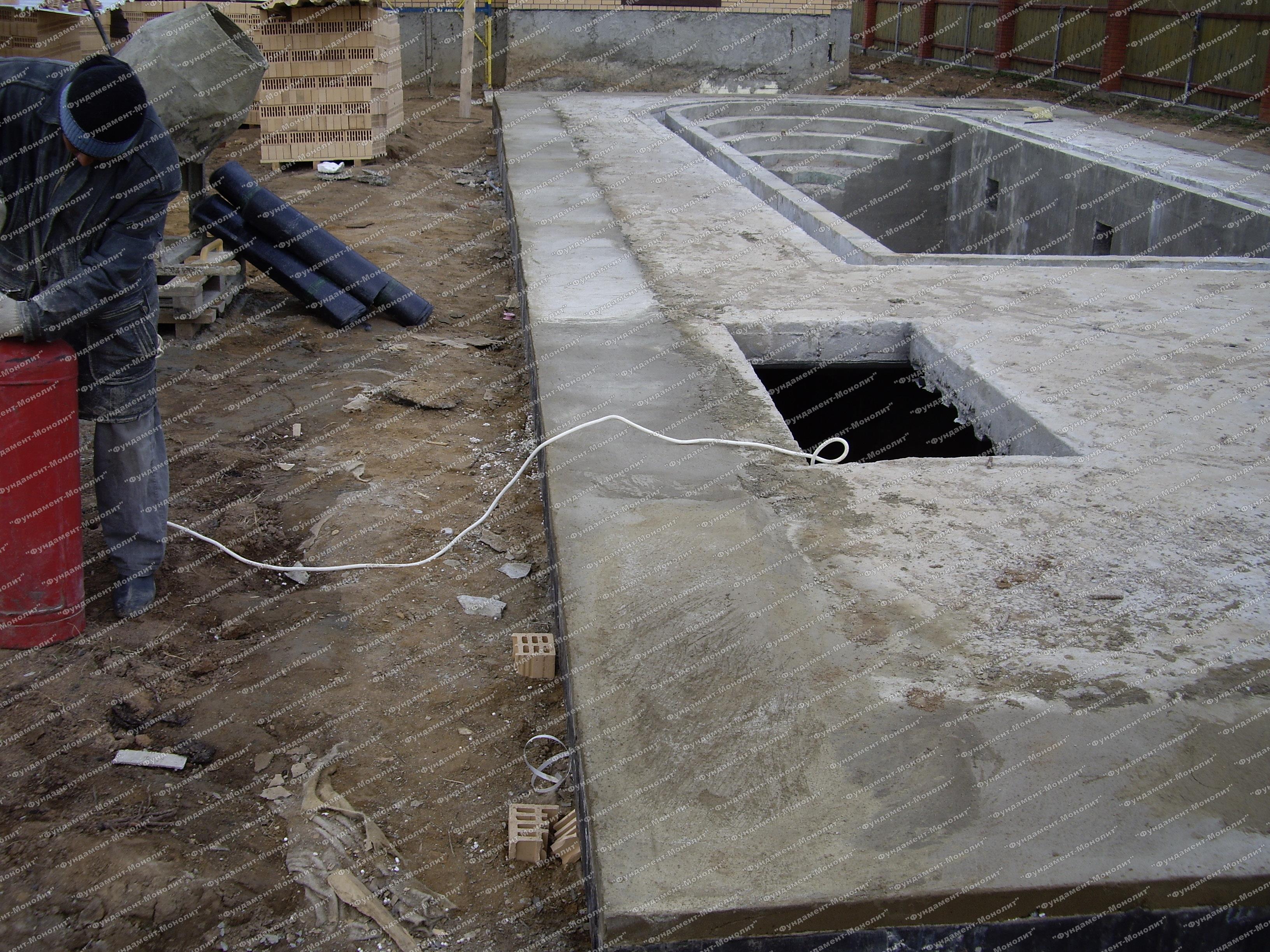
Construction of a monolithic reinforced concrete strip foundation.
To build such a foundation, you must start with a frame. For this, we prepare reinforcing "rings" with a thickness of 8 mm. We take a section of the channel, rigidly fix it and with the help of a grinder we make grooves on its two edges. We insert an eight-millimeter reinforcement into these grooves, put on a metal pipe at its other end. As a result, we get a kind of lever, which we will use to make identical rectangles, which will be our "rings".
We use the wire for knitting the reinforcement, we connect the ready-made "rings" and begin the installation of the frame. We will need 4 reinforcing rods 12 mm thick. and a length that is equal to the length of the side of the base. Using a wire, we pass the pieces of reinforcement through the "rings", and then attach them to the corners. In the middle of the upper edge of the resulting rectangle, we attach the fifth rod.
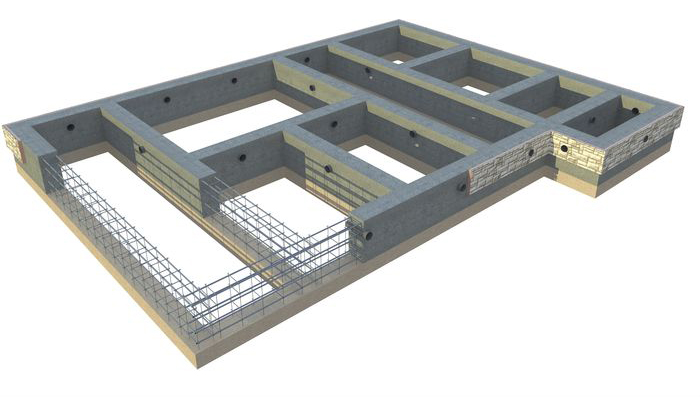
After the reinforcement cage for the entire base is ready, we lower it on the bricks laid at the bottom of the trench, and then fasten it with wire in the corners. When laying, be sure to use a level so that the structure is installed as evenly as possible. After all the above steps, we tie the frame to the pins driven into the walls.
A monolithic foundation on a reinforced concrete slab is built in about the same way; there is only one difference - concrete is poured over the entire area of the building. Often, such a base serves as a floor for the basement floor.
How to do it yourself?
Preparation
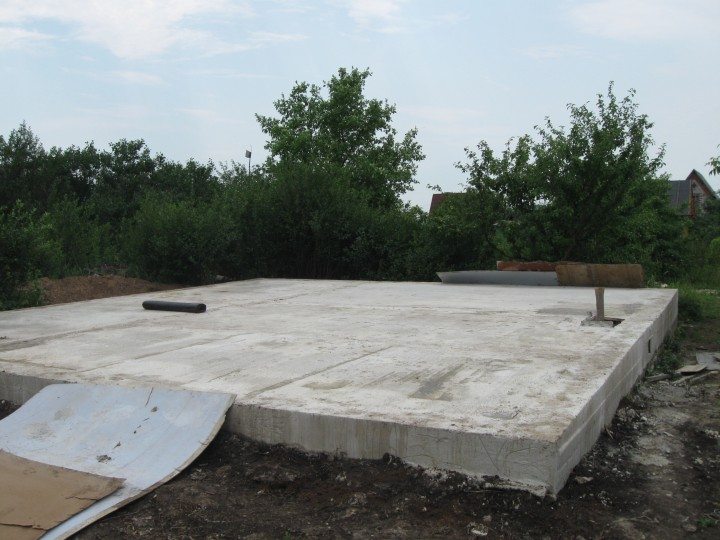
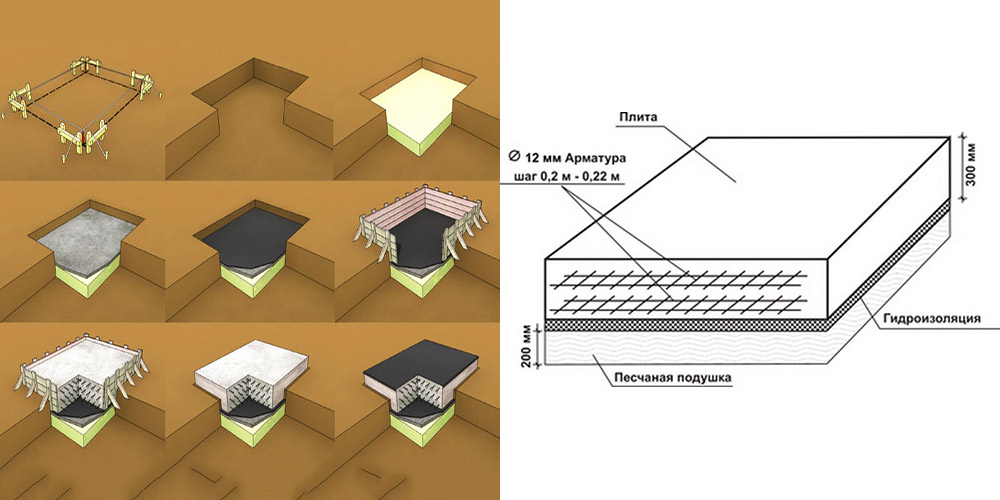
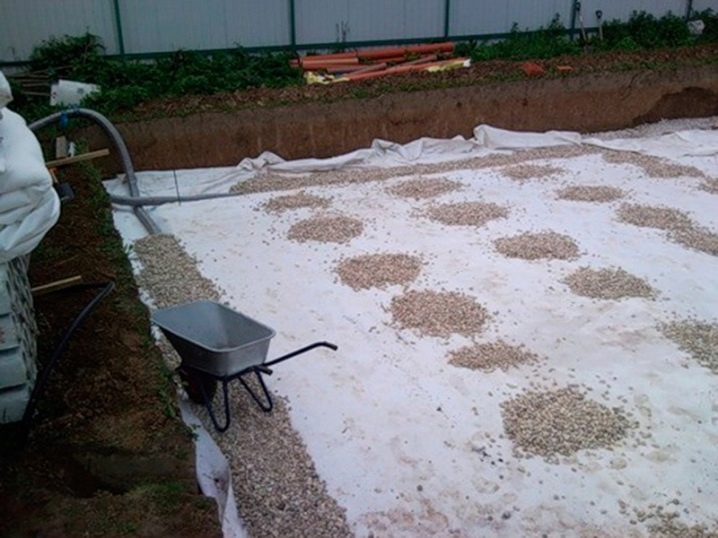
The foundation under consideration requires extensive preparatory work. The foundation slab must be perfectly level. For this, a thorough leveling of the site is carried out. All vegetation is removed, and the stumps are uprooted without residue.
The pit is dug over the entire area of the building up to 50 cm deep (taking into account the pillow and the thickness of the slab). At its bottom, a cushion of sand and gravel is poured with a total thickness of 15-30 cm, depending on the heaving of the soil. Backfilling is done in layers 8-12 cm thick with careful compaction of each layer.
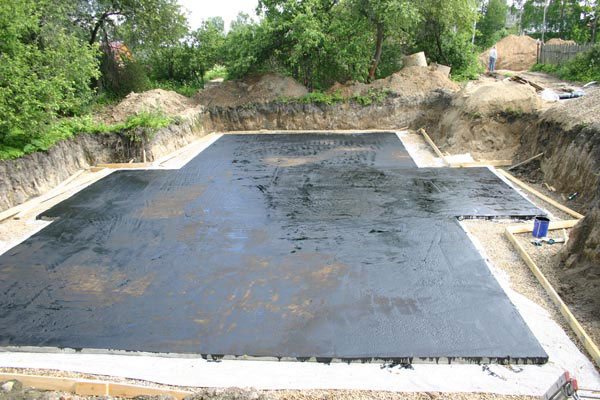

Applying waterproofing and insulation
After carefully leveling the pillow, a waterproofing layer of roll material is laid on top. Roofing material is most often used, which spreads in 2-3 layers with overlapping stripes in each layer of at least 15-20 cm.
Thermal insulation is formed along the waterproofing. For insulation, you can use polypropylene foam or foam. The main advantage of such a material is its high thermal insulation characteristics with increased resistance to moisture and low temperatures. Expanded clay can be used as insulation, which is covered with a layer of about 10 cm.
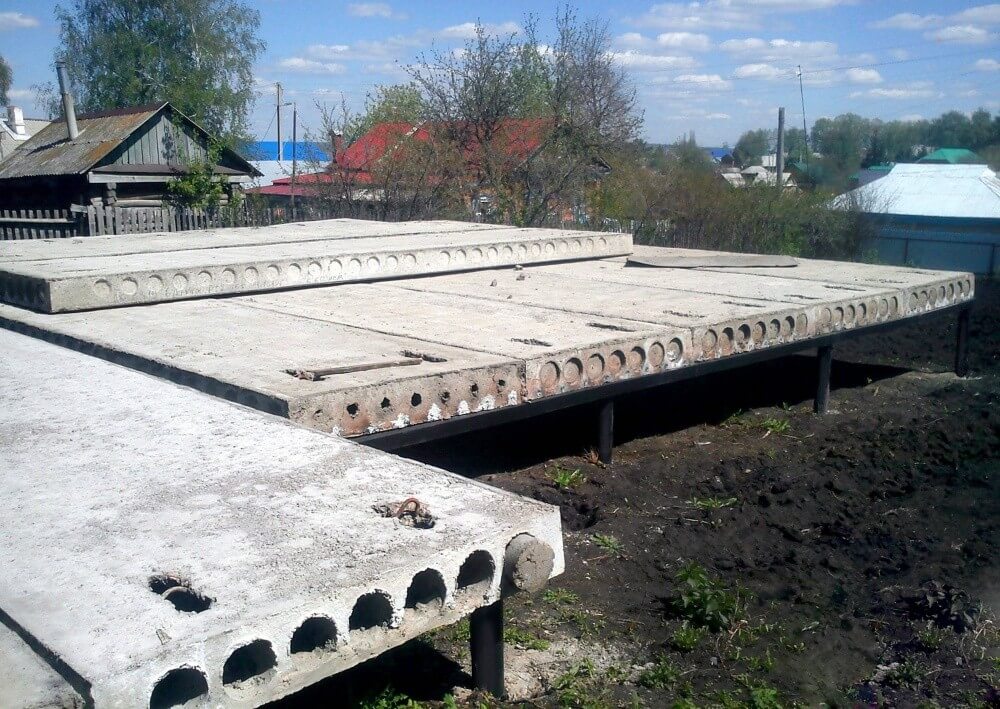
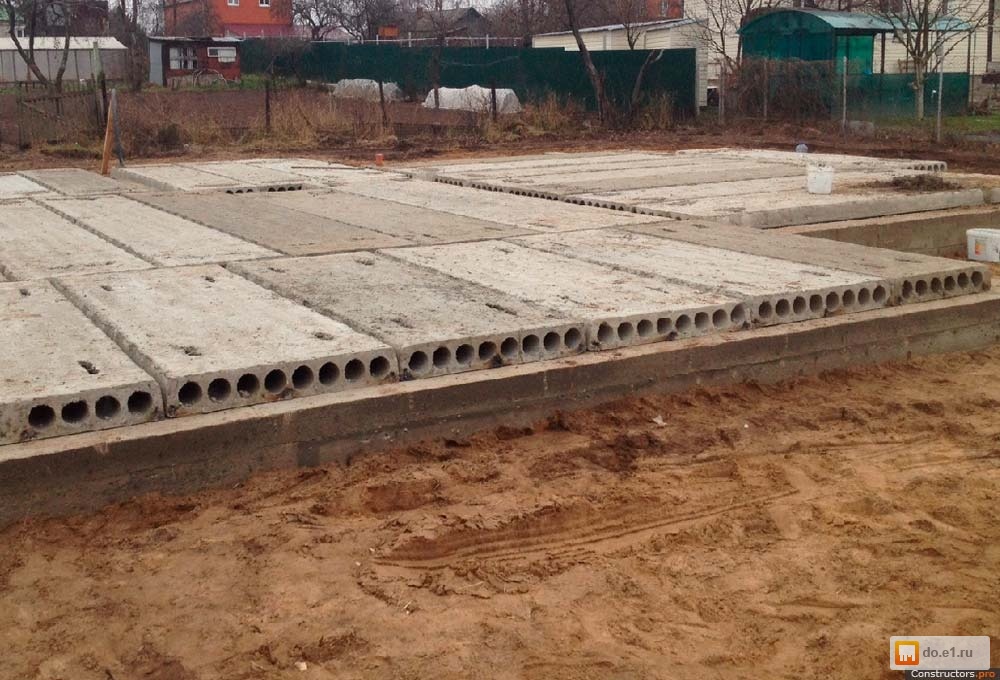
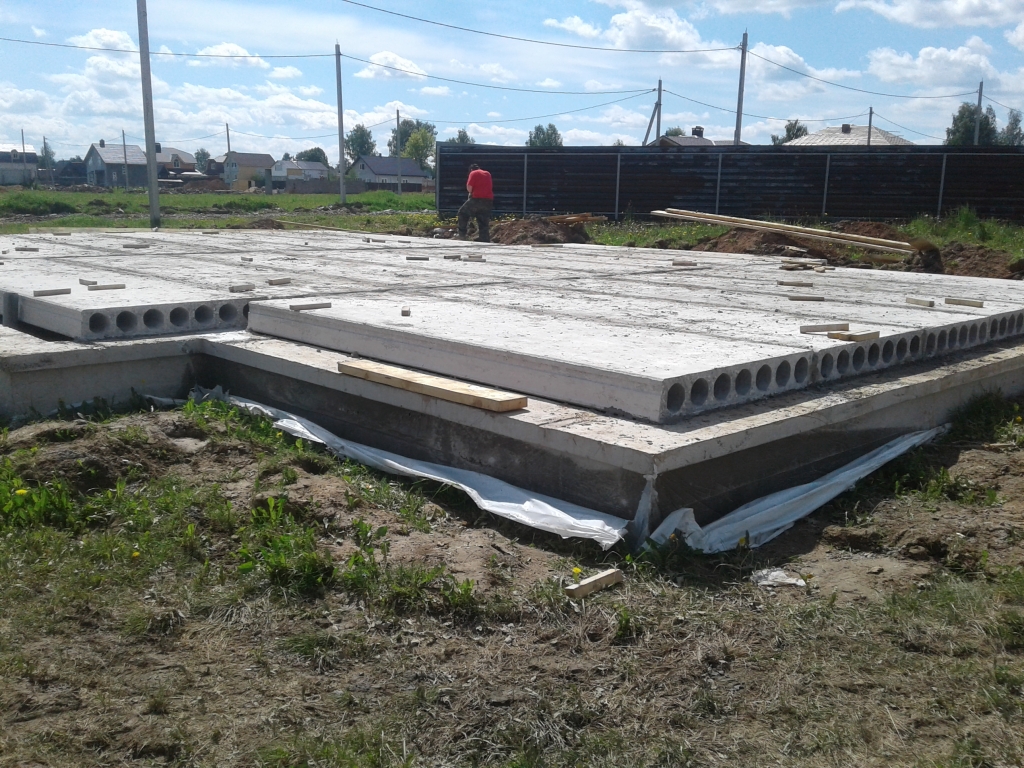
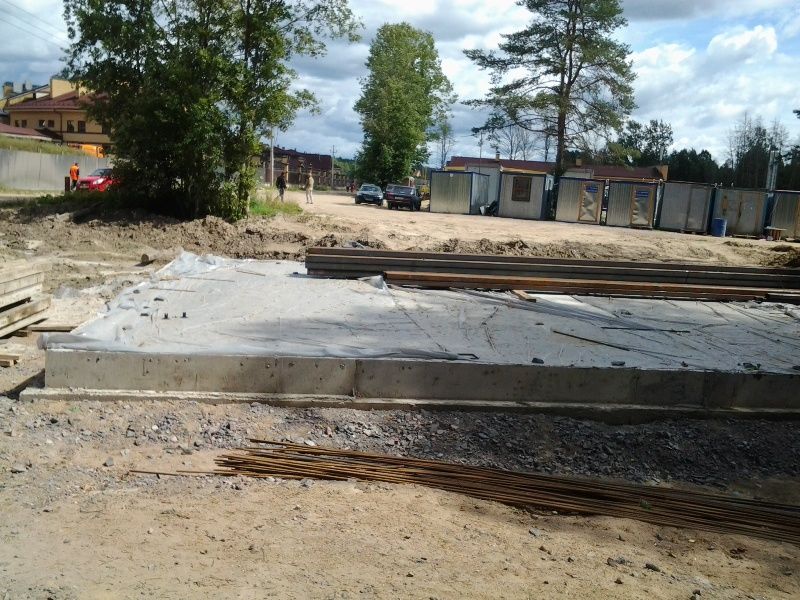
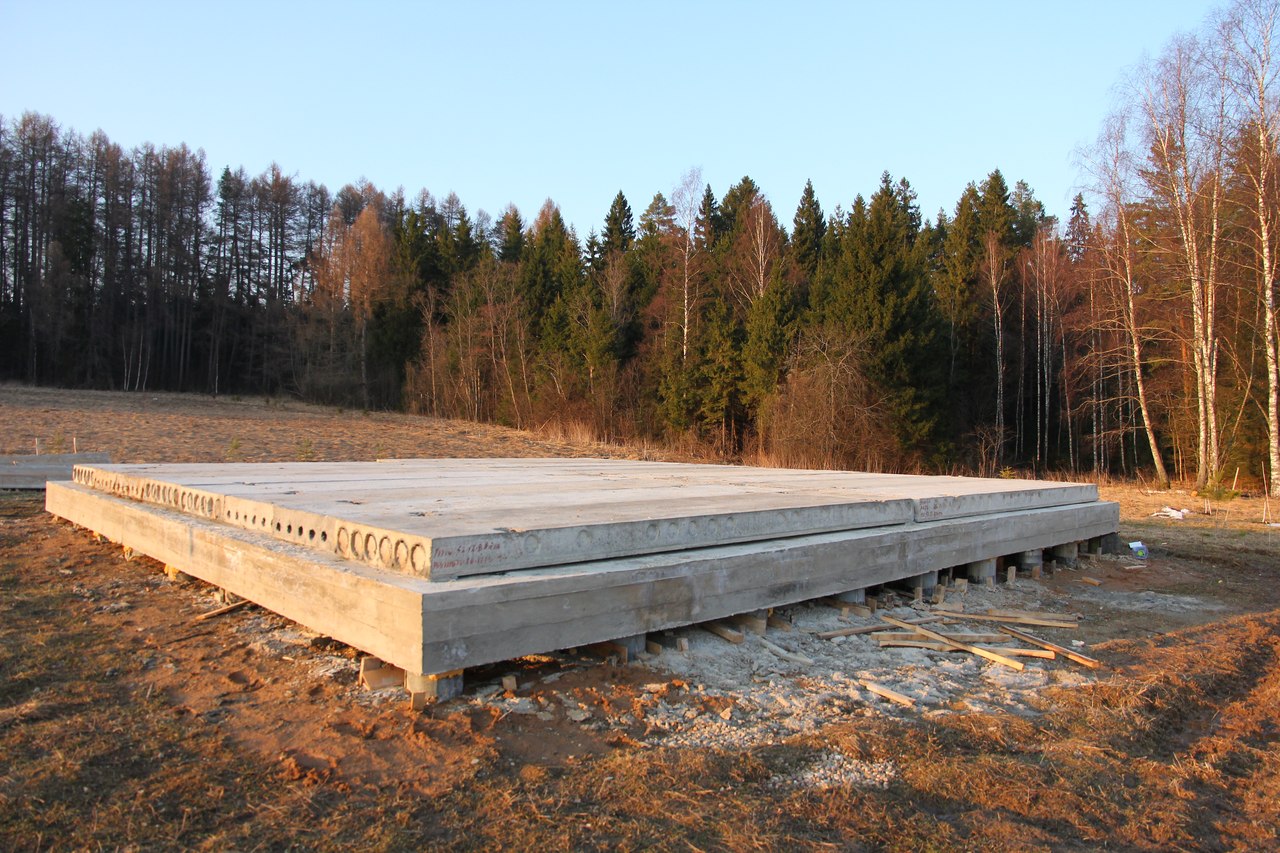
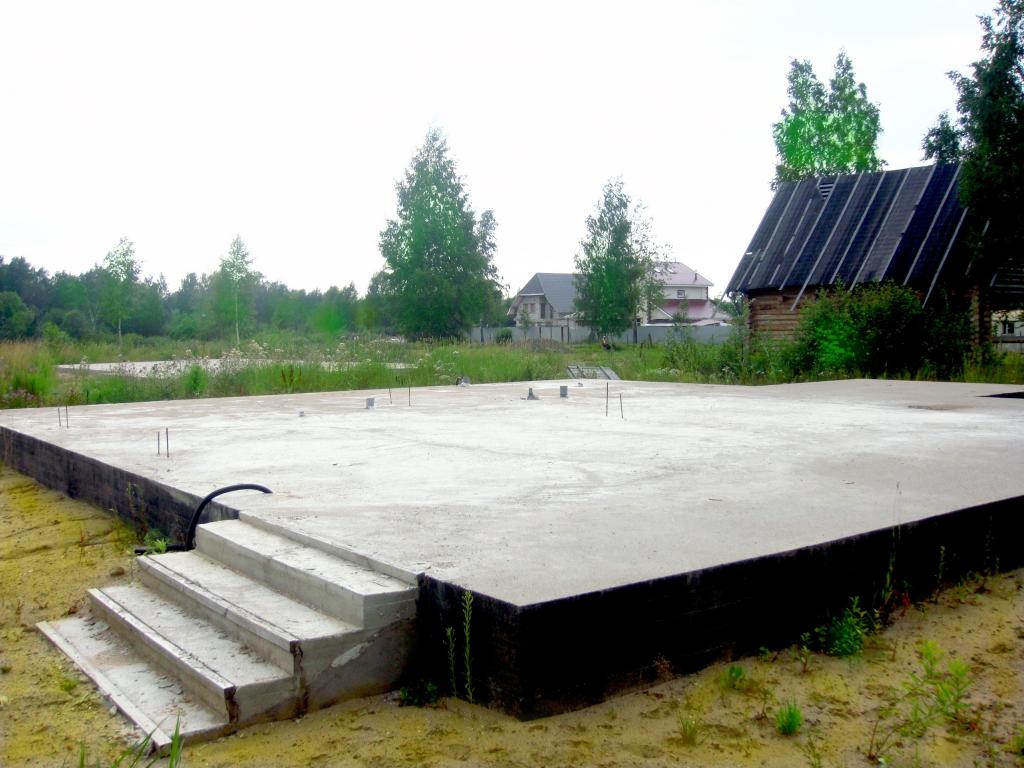
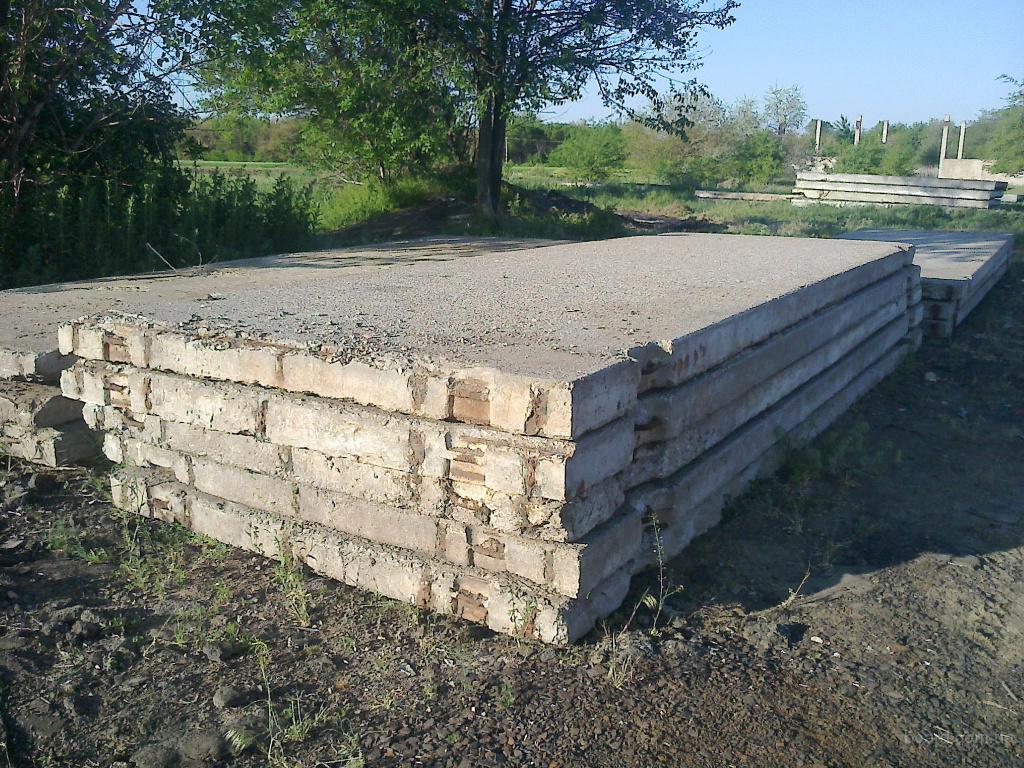
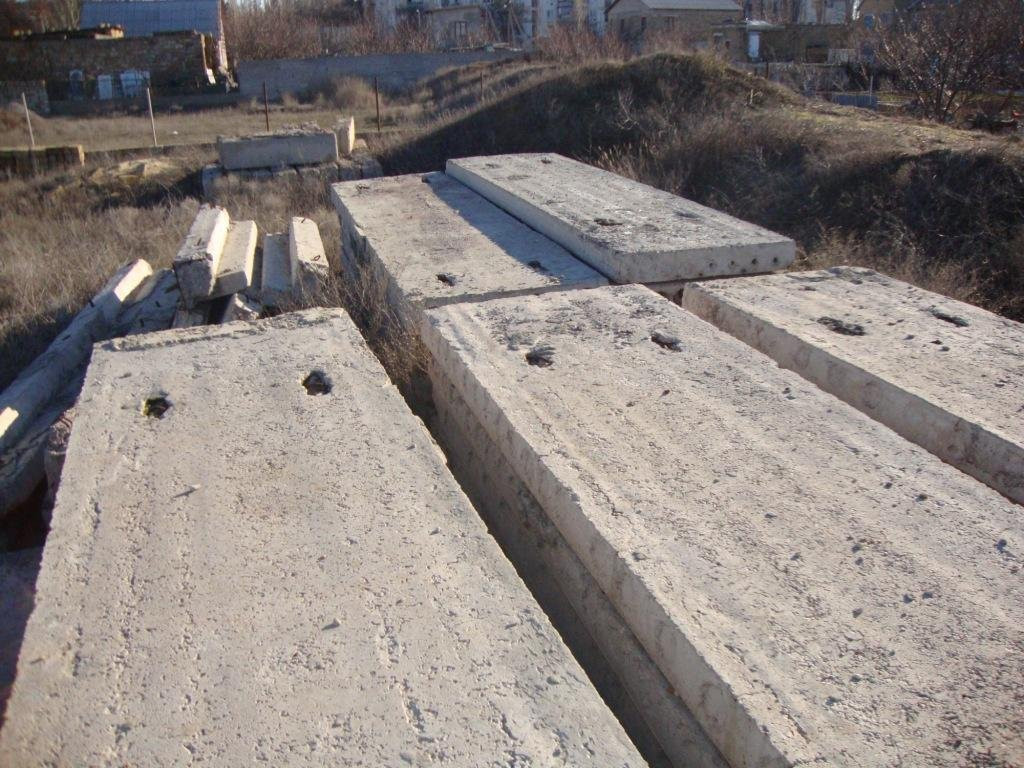
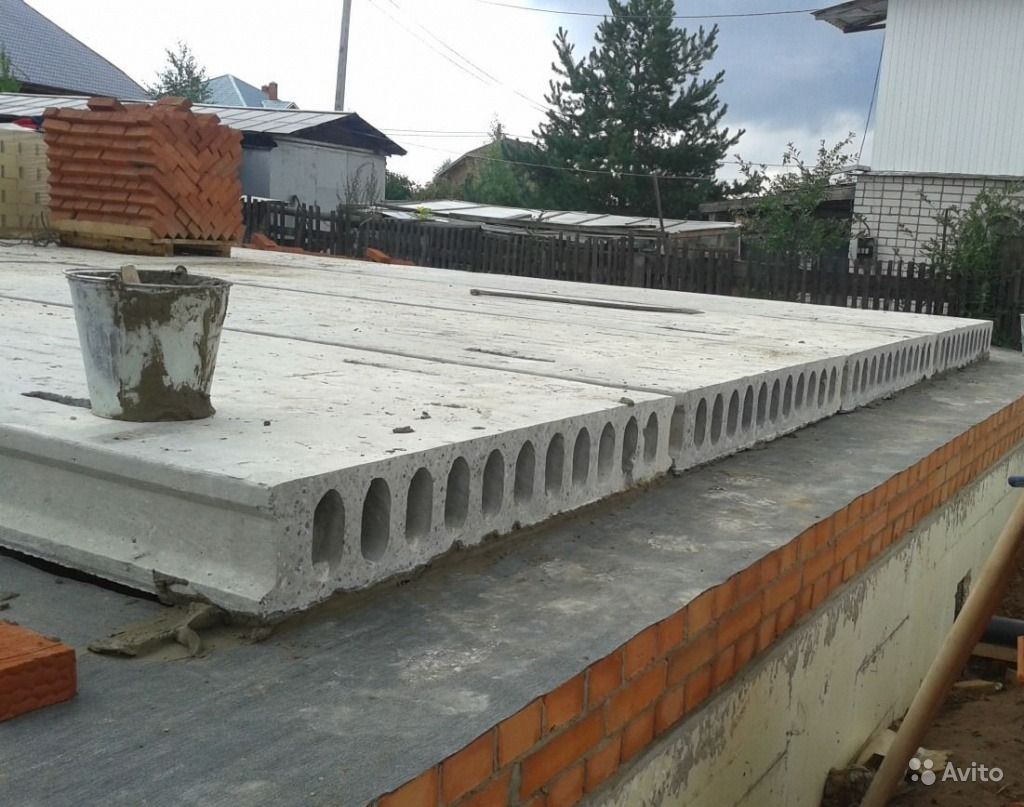
Installation of slabs
To cover the entire surface of the foundation, several ready-made reinforced concrete slabs will be required. They are stacked using a lifting mechanism as close to each other as possible. The thickness of the products is selected taking into account the loads arising from the weight of the structure.
For light, auxiliary buildings, it is sufficient to use standard slabs with a thickness of 12-15 cm. Heavier structures require the installation of slabs with a thickness of 25-30 cm. When installing the products, their steel rods are joined. They must create a single reinforcing system
It is very important to carefully align the surface of all elements with respect to each other.
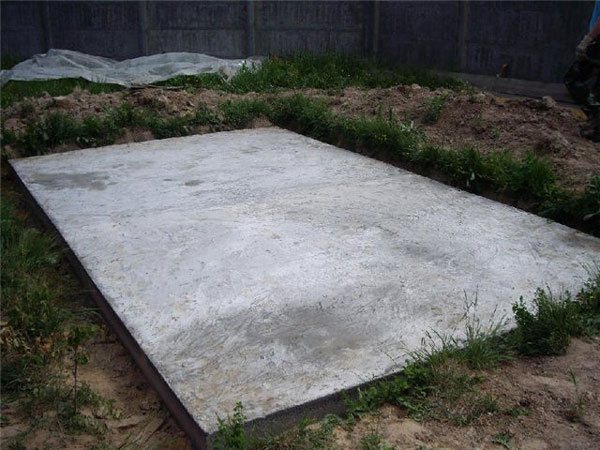

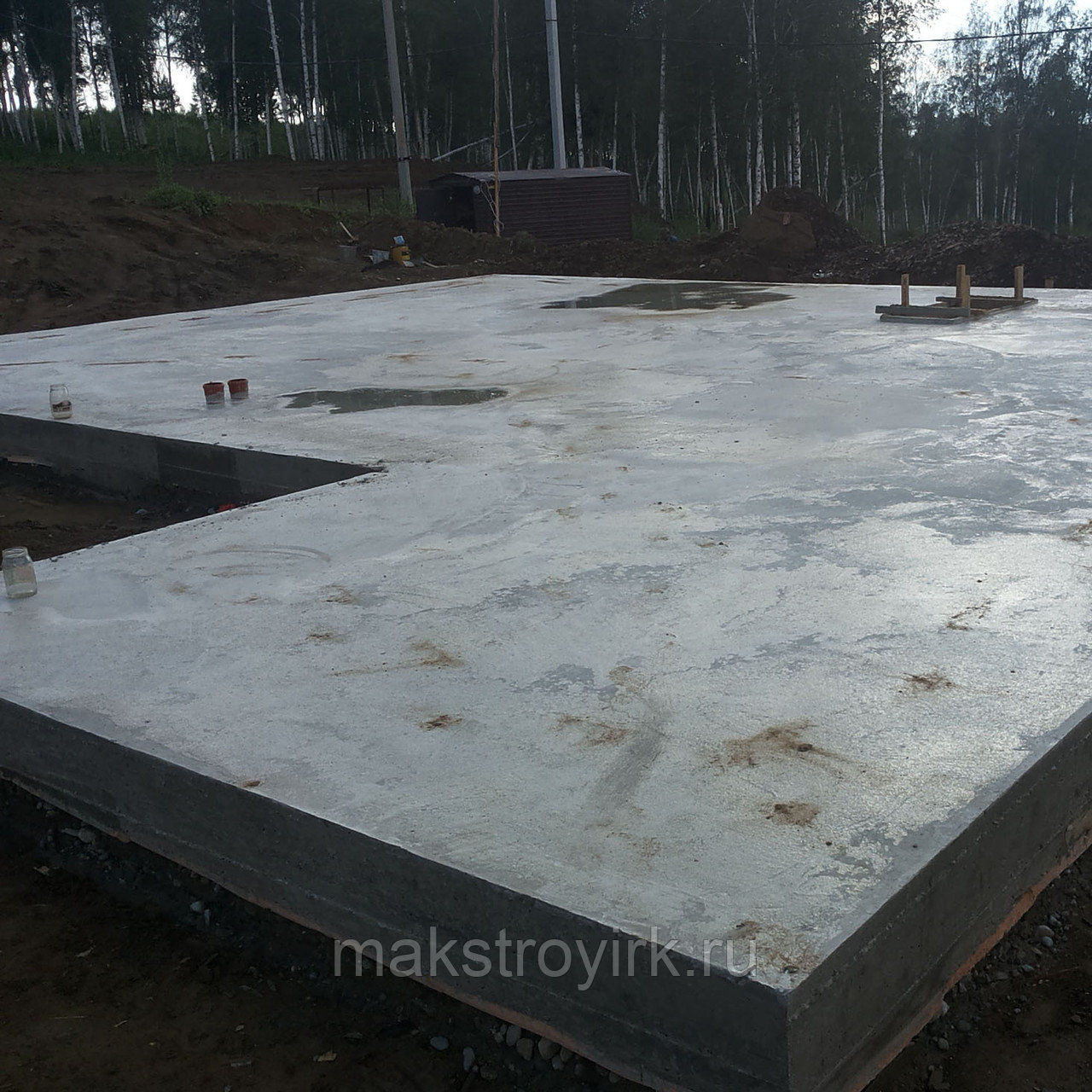
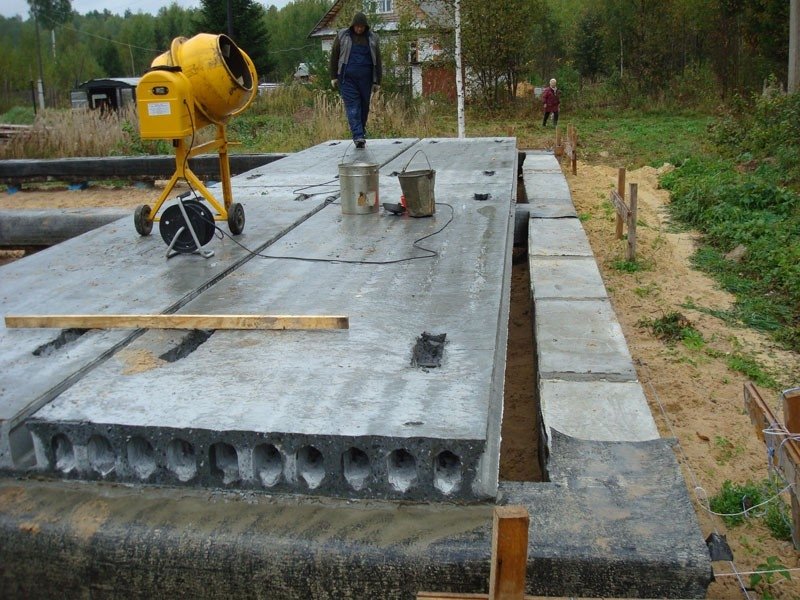
Concreting
After laying the slabs, gaps appear at the joints between them. They must be filled with cement-sand mortar. For this purpose, a mixture of cement (grade not lower than M300) and sand in a ratio of 1: 3 is used. After the mortar has dried, apply a leveling screed over the entire surface of the foundation.
It is carried out with the same mortar and reaches a thickness of 3-5 cm. The main task is to form a perfectly flat surface, which is controlled by the building level. Alignment is done using a rule.
Next, ensure proper drying of the screed to prevent cracking. To avoid sharp shrinkage of the material, the surface layer is periodically moistened for 8-10 days. For long-term preservation of moisture, it is recommended to cover the foundation with plastic wrap.
When erecting a slab foundation with your own hands, in addition to lifting mechanisms, you will need the following tool:
- preparatory work - shovel, scrap, pick, tamping device;
- installation of plates and laying of protective materials - a grinder for cutting reinforcement, a hammer or sledgehammer for leveling, scissors, a knife, pliers;
- concreting - a trowel or trowel, a spatula, as a rule, a grater and a half-trowel, a construction mixer for preparing a solution.
The quality control of the foundation is ensured using the building level. For measurements, you need a tape measure and a metal ruler.
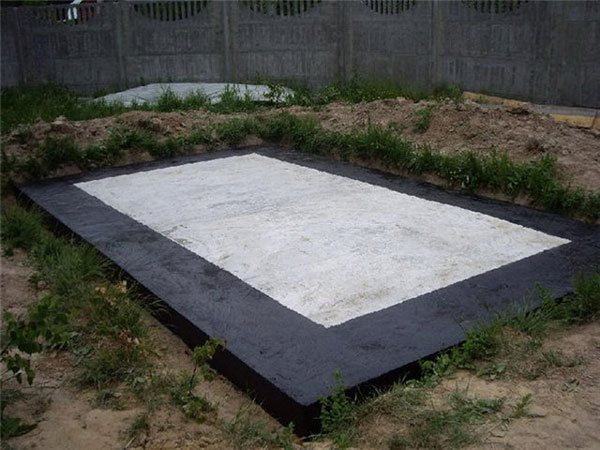

A slab foundation made of ready-made concrete products can significantly simplify and speed up construction work. It is able to provide a sufficiently reliable and durable foundation for lightweight buildings, moreover, when erecting them on difficult soils. The work can be done by hand, but for laying the slabs, you will have to attract lifting mechanisms of the required power.
The construction of frame houses is gaining more and more popularity.
Moreover, if a few years ago this technology was used exclusively for the construction of seasonal out-of-town buildings, now it is widely used in capital residential construction.
In the process of planning work, the first step is the choice of a reliable and inexpensive foundation. Of the large variety of types of foundations for a frame house, it is worth highlighting the foundation of which is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. This option is economical, fast and relatively easy to build.
The article contains information on how foundation slabs are used: sizes and prices for them.
Views
When building houses, the concrete slab base is not always the same.
The monolithic schema is divided into three subtypes:
- without deepening (with pouring directly on the surface);
- with shallow penetration (0.5-0.6 m);
- with deep penetration (up to 150 cm, that is, to the greatest depth of soil freezing).
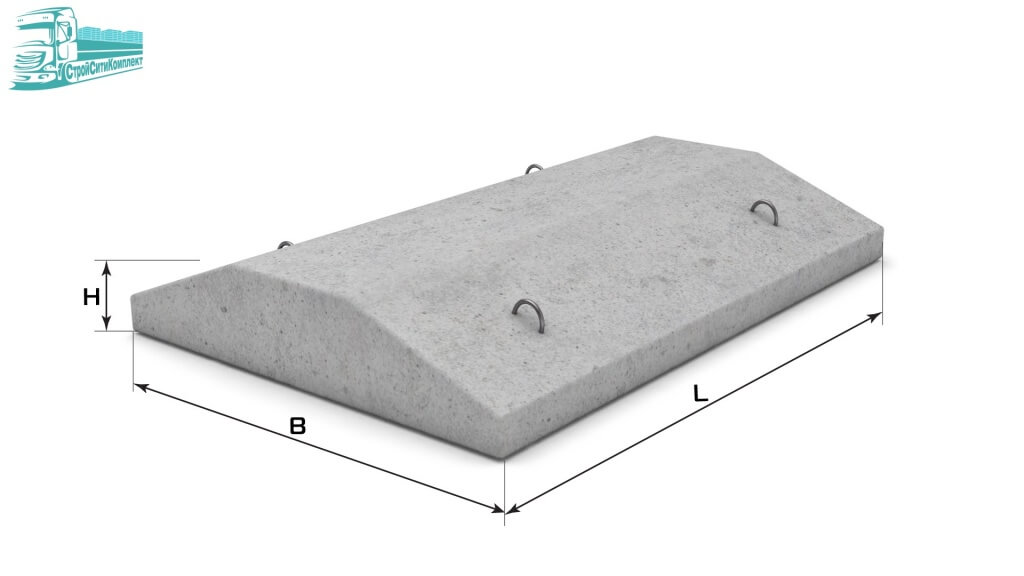
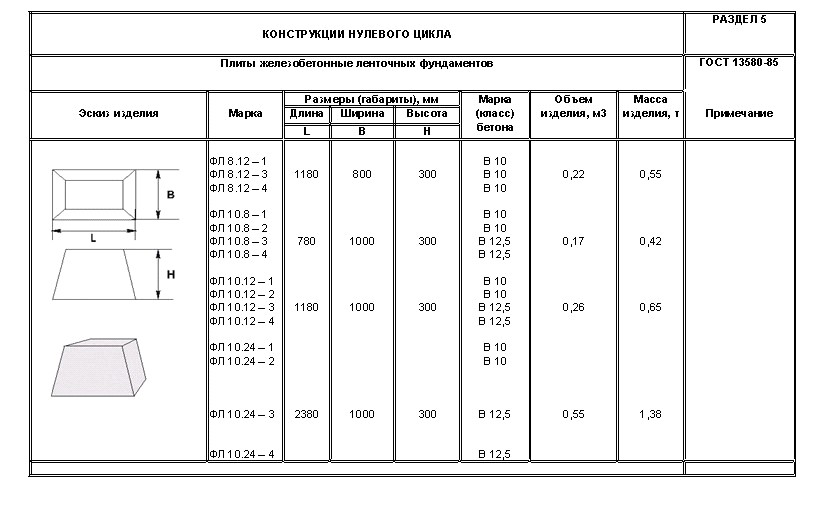
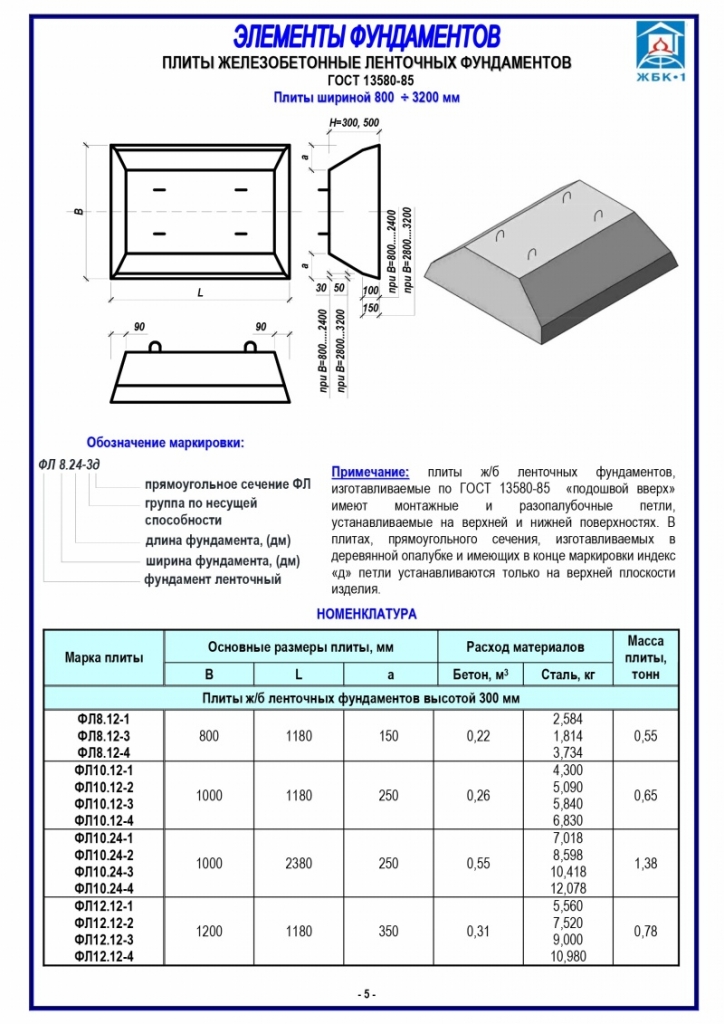
Industrial construction sometimes implies large depths of laying slabs, but they will not be required for the construction of residential buildings. A solid concrete slab is much better than a chain of prefabricated blocks connected with cement mortar. The combination of even strictly homogeneous parts is not durable enough, and the joints are the main problem. Another problem is that the RC slab can only be delivered and installed on site using expensive machines. Directly on site, you can use both plain concrete and reinforced concrete; the width of the surfaces to which the load is applied is 160 mm as standard.
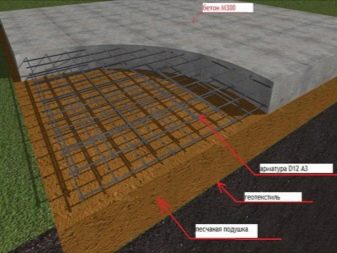

The slab foundation can be poured properly only with special heavy concrete. The choice of his brand in each specific situation is strictly individual.
Developers must take into account both the future operation of the structure and the climatic characteristics of the construction area. When making a final decision, you must first make sure that it guarantees resistance to getting wet and freezing.
Reinforced foundation blocks are supposed to be stuffed with either steel rods or reinforcing wire of strictly defined sections.


Road concrete products are attractive for their good climatic characteristics. Suffice it to say that they are used for their intended purpose even in the Far North and in other regions with severe weather conditions. With strength, too, everything is in order - on the roads where such plates are used, it is allowed to pass heavy equipment. Previously used road blocks are not always of good quality. If you buy brand new ones, you will need to pay a noticeably larger amount.

Experience has shown that paving slabs are best placed where there is no need for a high plinth. This is a garage, an outbuilding or a summer kitchen. In the case of a country house or suburban building, the owner is limited to two floors. Some people are also interested in slab foundations made of aerated concrete.
According to the regulations in force in the Russian Federation, it is strictly forbidden to use for foundation construction:
- fired stoneware containing a void or gap;
- silicate brick and materials based on it;
- concrete blocks with cracks or voids;
- ceramic bricks produced by the semi-dry pressing method;
- all aerated concrete in any form.




Aerated concrete belongs to the last category of materials, for the same reason the foam block is also prohibited. There are a number of reasons why the drafters of the regulations introduced such a strict ban. So, aerated concrete blocks are designed to reduce the mass of the enclosing structures, and their specific gravity is three times or even four times lower than that of heavy concrete. Therefore, the strength and bearing capacity are insufficient to solve the problem.Air filling, improving acoustic and thermal properties, reduces strength.

In terms of mechanical strength, ready-mixed concrete is ahead of aerated concrete, because crushed stone from gravel or granite acts as fillers.
If there is still any doubt, it is enough to take into account that the load-bearing walls made of gas blocks are not designed to support the floor slabs. Given this, aerated concrete and aerated concrete are unacceptable even for above-ground parts of foundation structures.
Aerated concrete blocks laid in walls must be covered with a layer of waterproofing from the outside and a vapor barrier must be created from the inside. The statements of any teams and contractors about the construction of aerated concrete foundation testify only to their low professionalism.

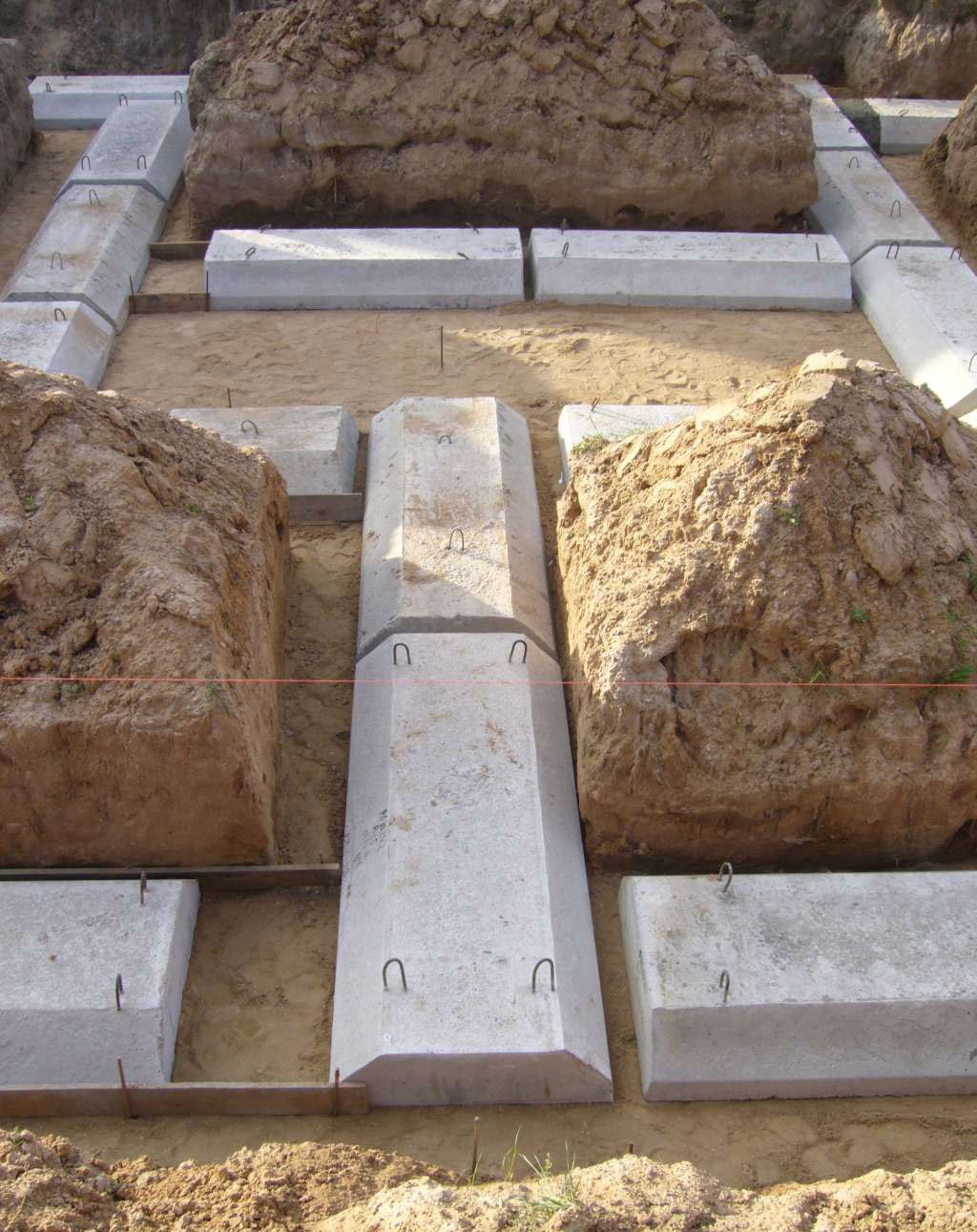
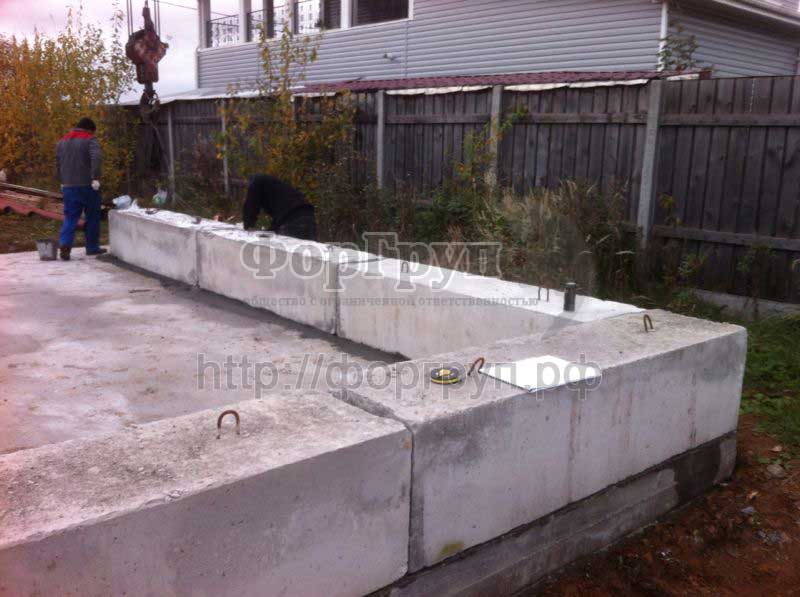
Prefabricated foundation from blocks.
Modern construction provides various options that will help to install reliable and durable load-bearing foundations of structures.
The foundation of FBS blocks enjoys well-deserved attention - it is used by many in the construction of houses. Such a structure is erected when there is a need to build a foundation quickly and without the invitation of qualified workers.

It only takes a couple of days to lay this foundation. First, blocks are installed at all corners of the outer walls. Then proceed to the installation of ordinary blocks of all other walls. All rows should be connected with a solution about two centimeters wide. The joints between the blocks should not coincide in height.
In order for the foundation not to collapse from moisture and low temperatures and to serve for a long time, it is imperative to carry out work on waterproofing and insulation of the foundation. For this, you can use a variety of materials. For example, rolled hydroglass, which is thermally attached to the blocks using a special mastic and resin.
Technology
1. Preparation of the territory. The area of the proposed construction is cleared of debris, grass, if there are trees, they must be uprooted. Free passage is provided for the supply and unloading of slabs.
2. Marking the territory. First, the extreme corner point of the future foundation is marked. The required length of the future building is measured from it. At both points, metal or wooden stakes are driven in and a construction cord is pulled between them. Further, with the help of elementary mathematical measurements, the next angle is found, and then the last, fourth. We connect all the stakes with a rope. The final measurement is made by measuring the diagonals of the resulting quadrangle. They must be equal.
3. Earthwork. First of all, a pit is pulled out to the lower level of groundwater. This is approximately 1 - 1.5 meters, depending on the terrain.
The bottom of the pit is leveled and sand is poured on top, in a layer of 40-50 cm. Every 20 cm of the layer must be watered and carefully tamped with a vibrating plate or rammer. At the same stage, all underground communications are being assembled.
A layer of geotextile is spread over the sand with an overlap of layers on top of each other by 20 cm, to prevent mixing of sand and gravel. A layer of fine and medium crushed stone, 30-40 cm thick, is poured onto the geotextile. It serves as a waterproofing agent and distributes the load from the slabs.
From above, the crushed stone is spilled with cement milk until the gaps between the individual stones are completely filled. From above, the mortar should cover the crushed stone with a layer of 2-3 cm. This is the so-called. foundation.
4. After complete solidification of the concrete, it is necessary to apply layers of waterproofing. Usually, roofing material is used in 2 layers, but other materials can also be used. The strips of roofing material are overlapped by 5-10 cm and soldered with a torch or blowtorch.
Important! Waterproofing should be larger than the base area and extend beyond it by 40-50 cm. 5
Insulation is laid on the waterproofing layer. It is preferable to use polystyrene or penoplex.The thickness of the layer can vary from 10 to 15 cm, depending on the climatic zone, but, at the same time, the insulation should not be higher than the soil level. The joints of the sheets of material are carefully coated with mastic or foamed with polyurethane foam
5. Insulation is placed on the waterproofing layer. It is preferable to use polystyrene or penoplex. The thickness of the layer can vary from 10 to 15 cm, depending on the climatic zone, but, at the same time, the insulation should not be higher than the soil level. The joints of the sheets of material are carefully coated with mastic or foamed with polyurethane foam.
Important! The heat-insulating material must have an increased density, since it is the basis for laying reinforced concrete road slabs. 6
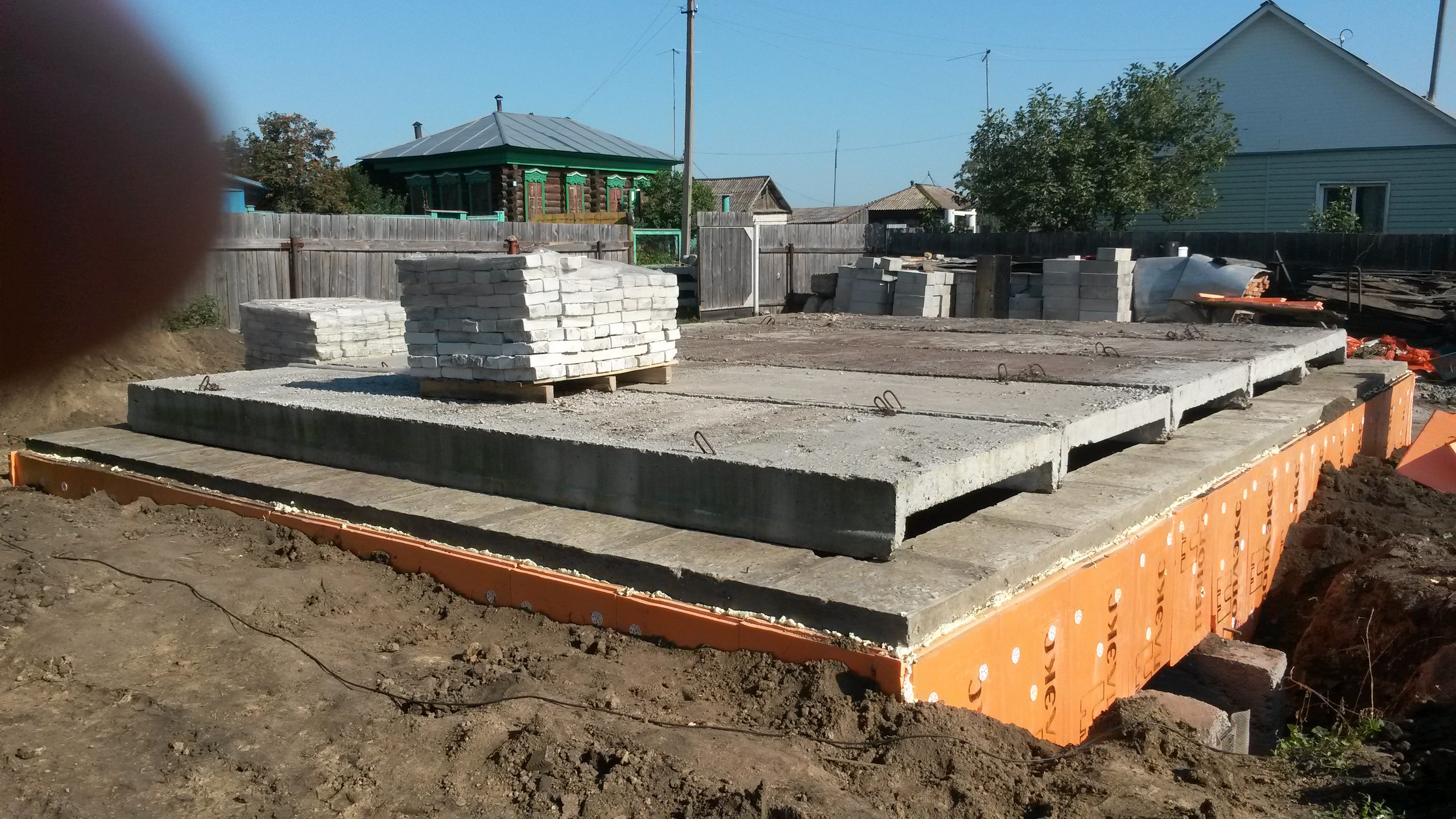
Formwork installation. You can use ready-made formwork, or make it on site from boards with a thickness of at least 2.5 cm.The height of the formwork should be equal to the height of the slabs in the laid state plus 5 cm. Boards or shields are mounted around the entire perimeter of the foundation and carefully fixed with self-tapping screws or nails
6. Installation of formwork. You can use ready-made formwork, or make it on site from boards with a thickness of at least 2.5 cm.The height of the formwork should be equal to the height of the slabs in the laid state plus 5 cm. Boards or shields are mounted around the entire perimeter of the foundation and carefully fixed with self-tapping screws or nails.
If desired, you can put a polymer insulation inside the formwork and the ends of the waterproofing remaining when it was laid under the insulation. This will save in the future from the need to carry out earthworks in order to insulate the foundation.
7. Laying of road slabs. Slabs are laid on the prepared base using construction equipment. They fit tightly to each other, a gap of 10 cm must be left only between the formwork and the edges of the elements.
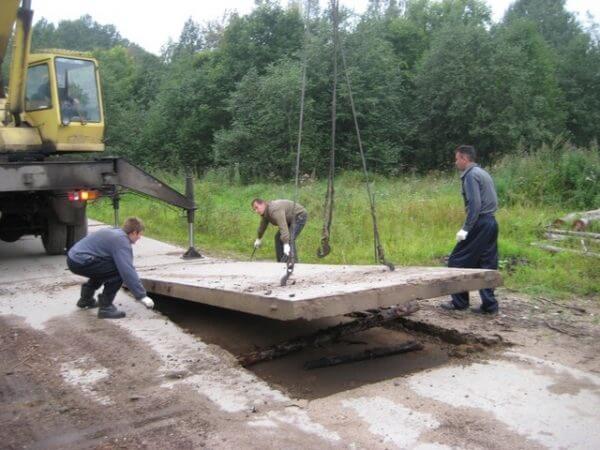

8. After laying all the elements of the foundation, the surface is poured with concrete, grade not lower than M300. All joints between the slabs are carefully spilled, a screed is made above the slabs, 5 cm thick using a reinforcing mesh, with a section of 5 mm and a step of 10 cm. The surface is carefully leveled.
9. After complete solidification (under the foundation, the reinforced concrete slab solidifies for about a month), the formwork is dismantled and the foundation surface is re-waterproofed over the entire area.
We also have step-by-step instructions on how to build a slab base on our website.
A house made of concrete panels and its layout
The choice in favor of a house made of reinforced concrete is influenced by the presence near the construction site of a plant of reinforced concrete products (concrete goods) or a house-building plant (DSK), producing parts for individual construction. You can, of course, apply standard designs, but this will impose certain restrictions on the layout of the house.
Panels are different
When choosing panels for building a house, you need to know and understand what differences exist between them.
Reinforced concrete factories, for example, often manufactured parts for industrial facilities and social facilities of typical construction - kindergartens, schools, cultural centers, shops ... The use of these structures for the construction of a residential building involves the use of such details as columns, crossbars, beams. And this, in turn, causes not entirely justified, unnecessary volumes of interior finishing work, and for the interior, concrete panels of such series are not the best choice.
The fact is that panels from a precast concrete plant are usually not self-supporting. They are intended for "sheathing" the frame of a building made of columns, crossbars or beams. Thus, outside the building is obtained with smooth walls, and the columns and crossbars "stick out" inside the premises and they have to somehow "hide".
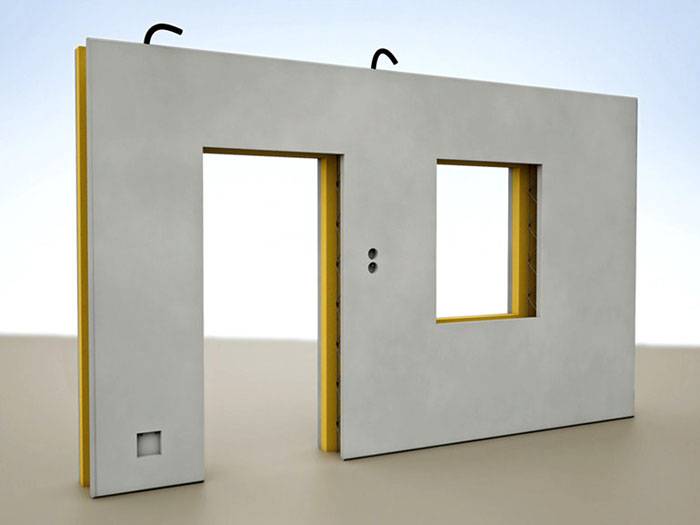

Panels for "covering" the frame of the building
DSK produce products directly intended for the construction of residential buildings. As a result, the house gets smooth walls, ceilings and right angles without protrusions and drops.This greatly simplifies the finishing work and, subsequently, the placement of furniture.

Products for the construction of the building
House layout
The most significant drawback of typical reinforced concrete parts in the construction of residential buildings is their rigidly specified dimensions. Reinforced concrete products may not be sawed, cut or chopped. Any rough forceful intervention aimed at changing the size of a part will inevitably lead to a violation of its integrity, to the appearance of cracks, and, ultimately, can cause the destruction of an already constructed building.
Therefore, before drawing up a project of a house, you need to familiarize yourself with the dimensions of the parts offered for sale from a supplier of components for houses made of concrete panels.
The location of door and window openings in walls and partitions, as well as technological holes in floor slabs, is of great importance. Only knowing these parameters, it is worth starting to draw up a plan for the placement of premises in the house
Especially if the house is planned to be built on two or three floors.
The easiest way, of course, is to develop a house project based on the availability of parts, taking into account their sizes and openings in them. But you can try to select the details, focusing on the desired layout of the future home. Or look for a manufacturer willing and able to manufacture reinforced concrete parts for a new house project.
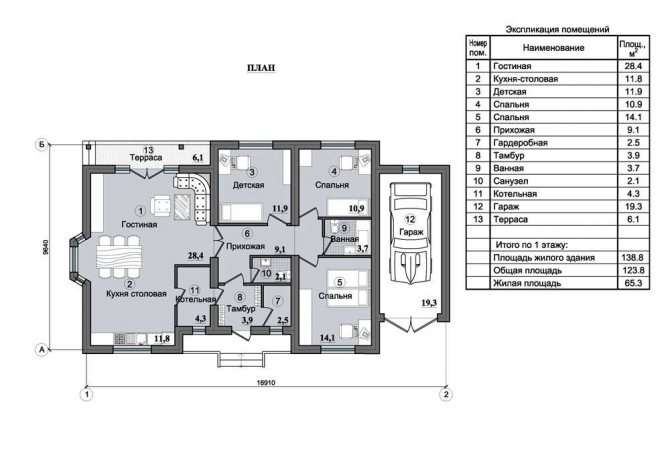
One-story house plan
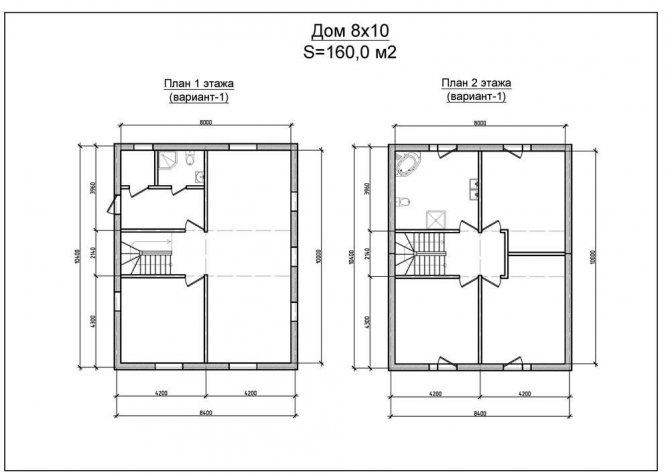
Plan of a two-storey house 8 x 10 m
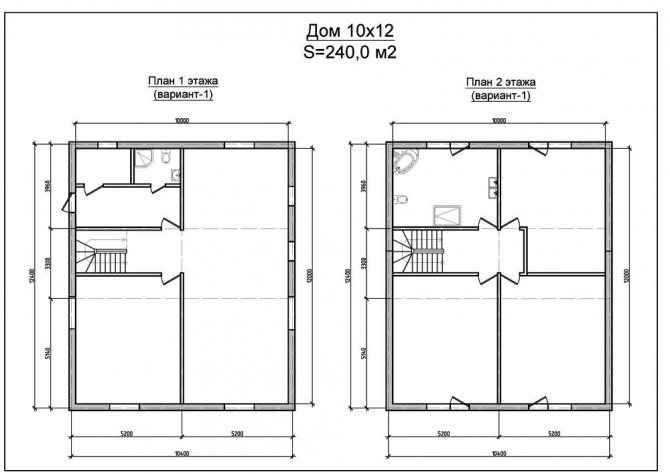
Two-storey house plan 10 x 12 m