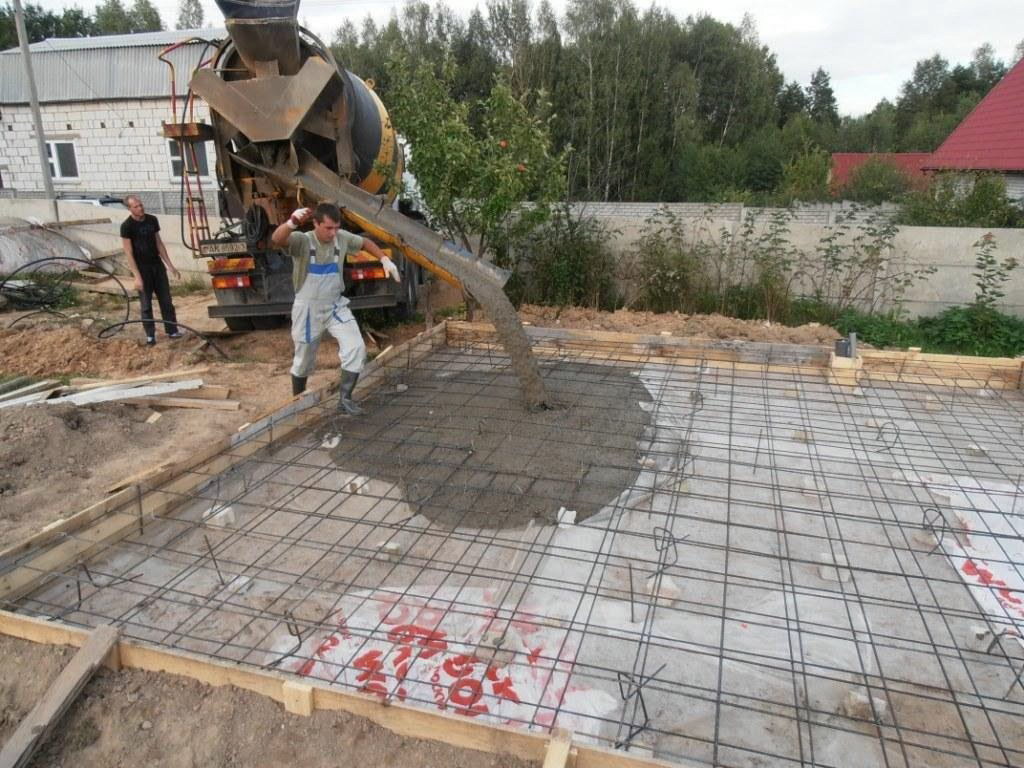
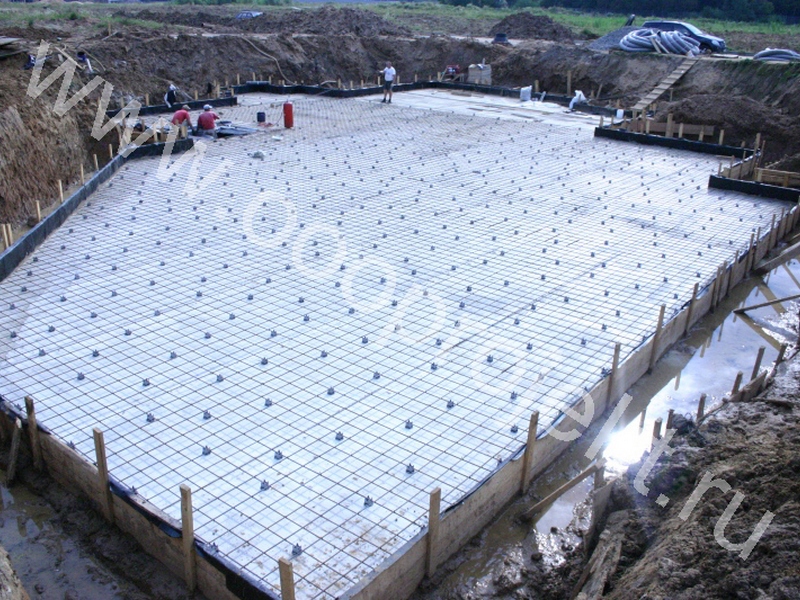
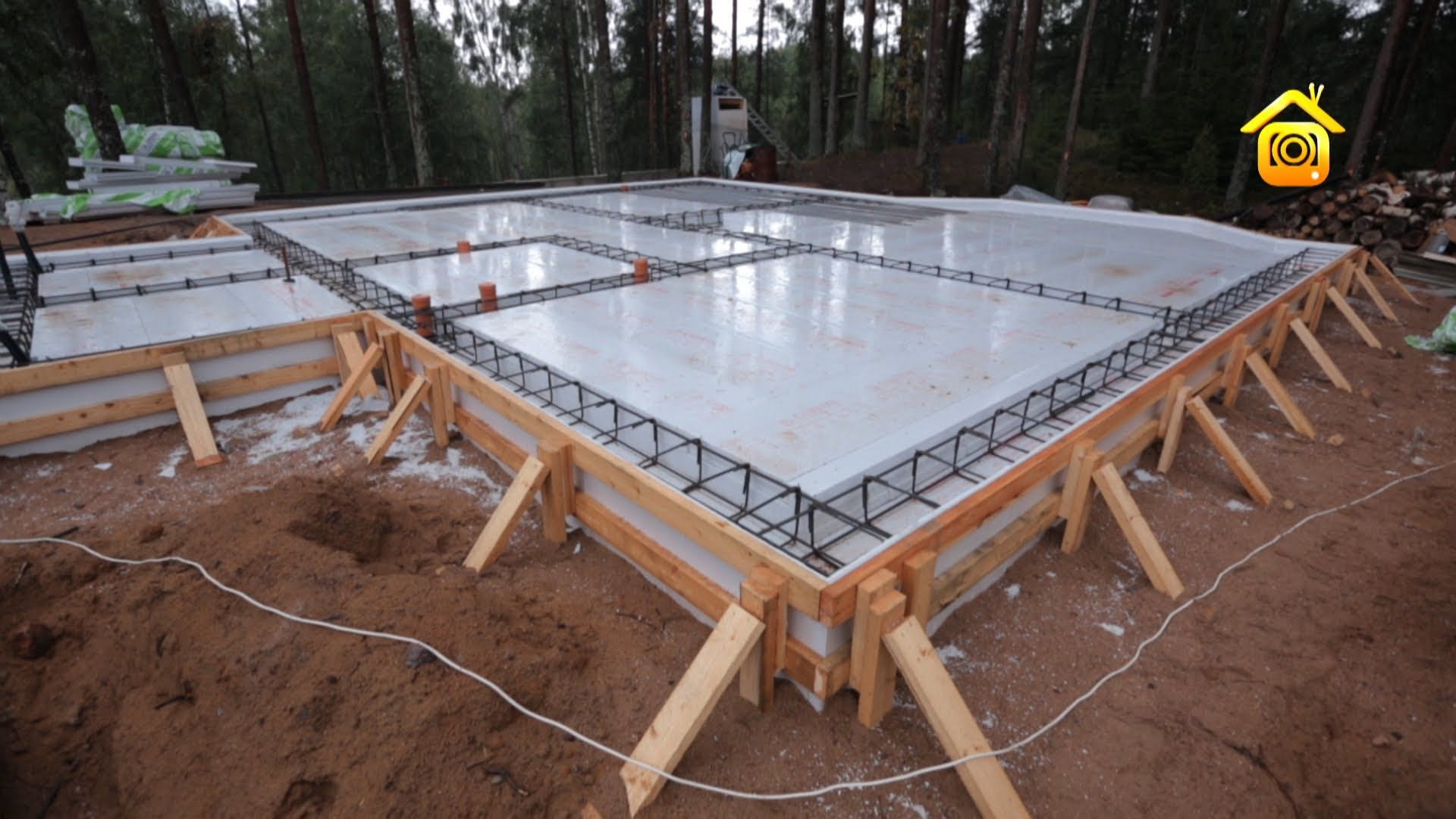
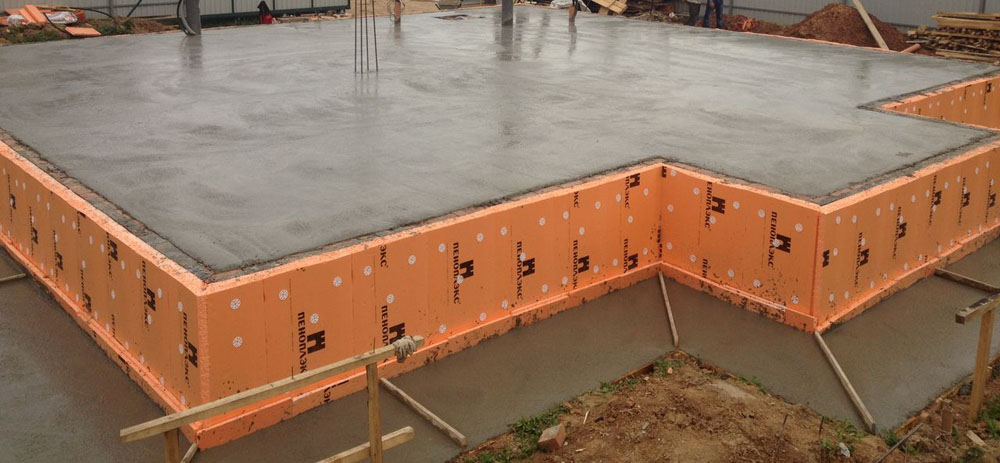
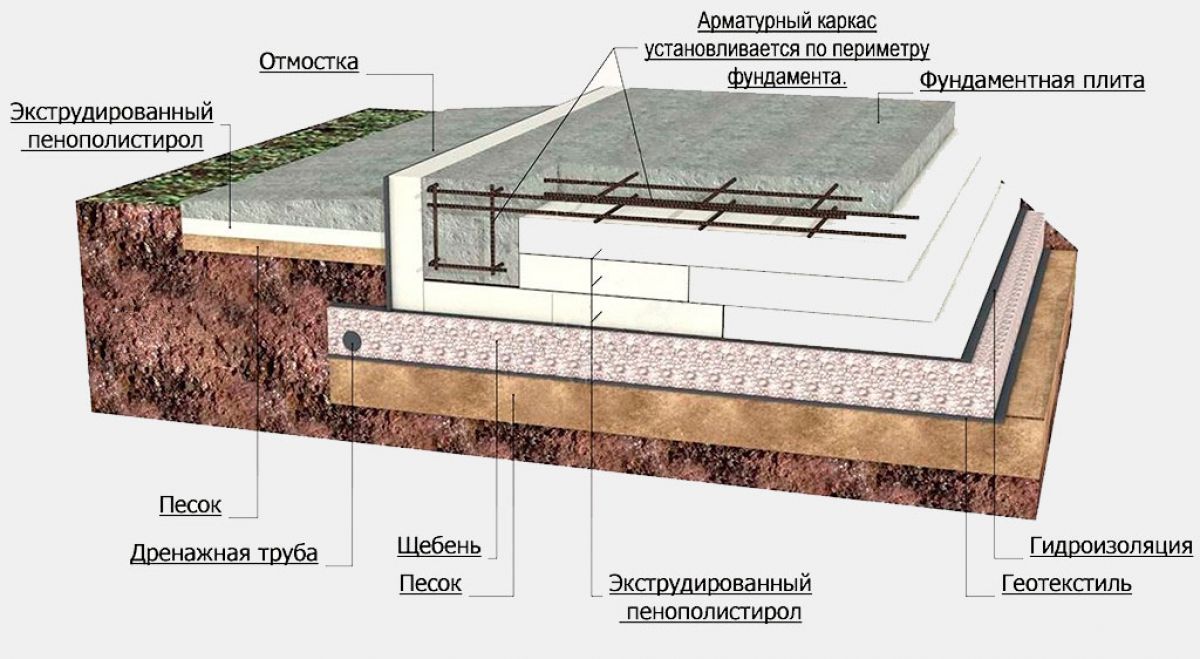
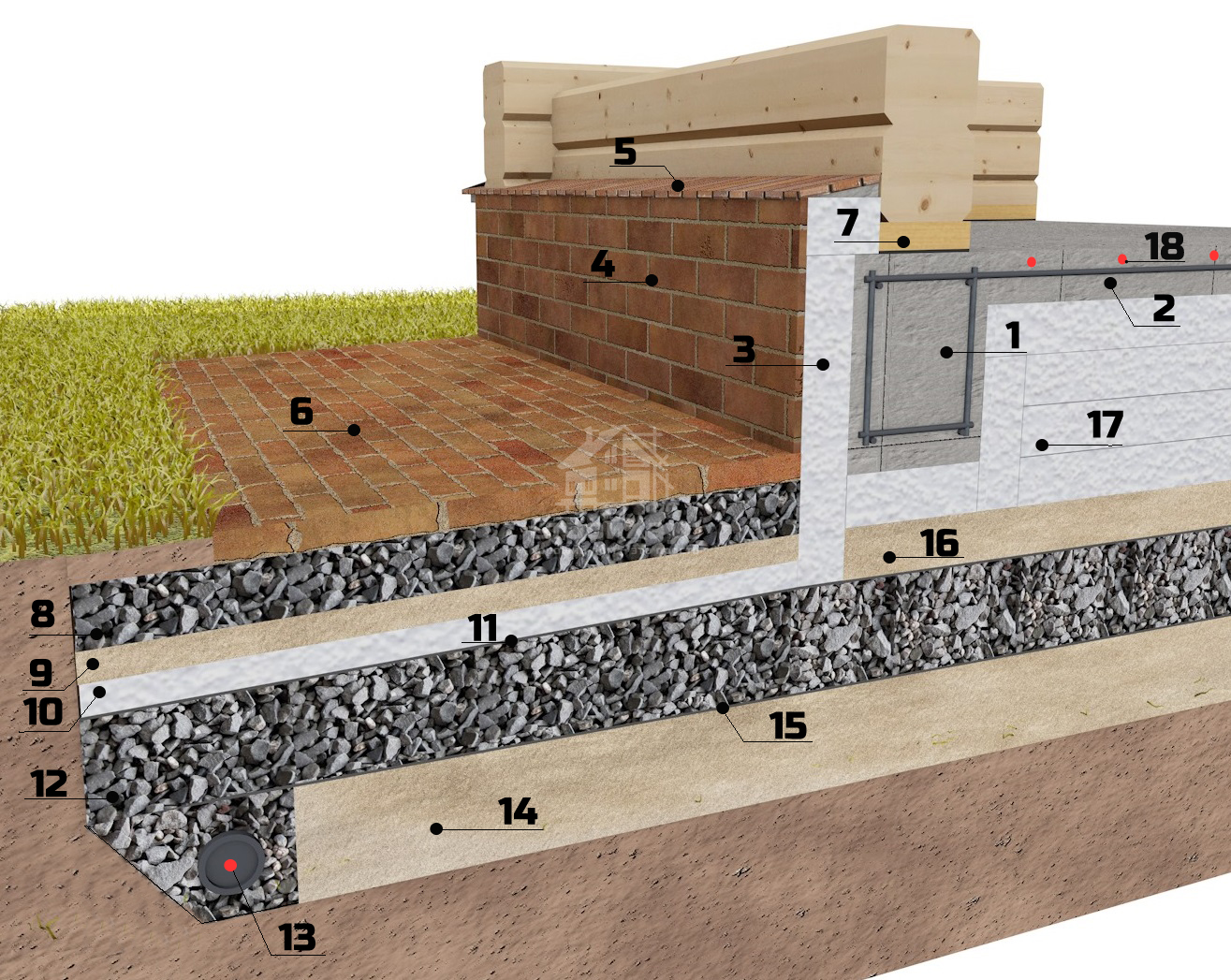
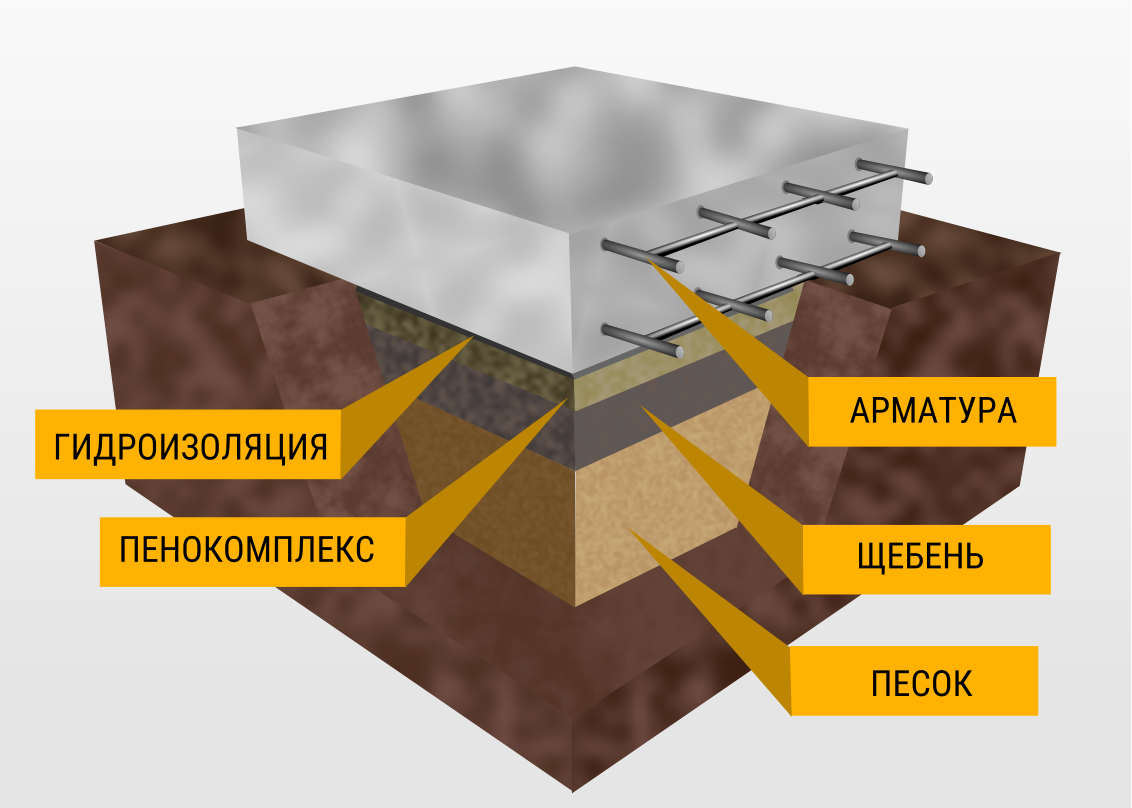
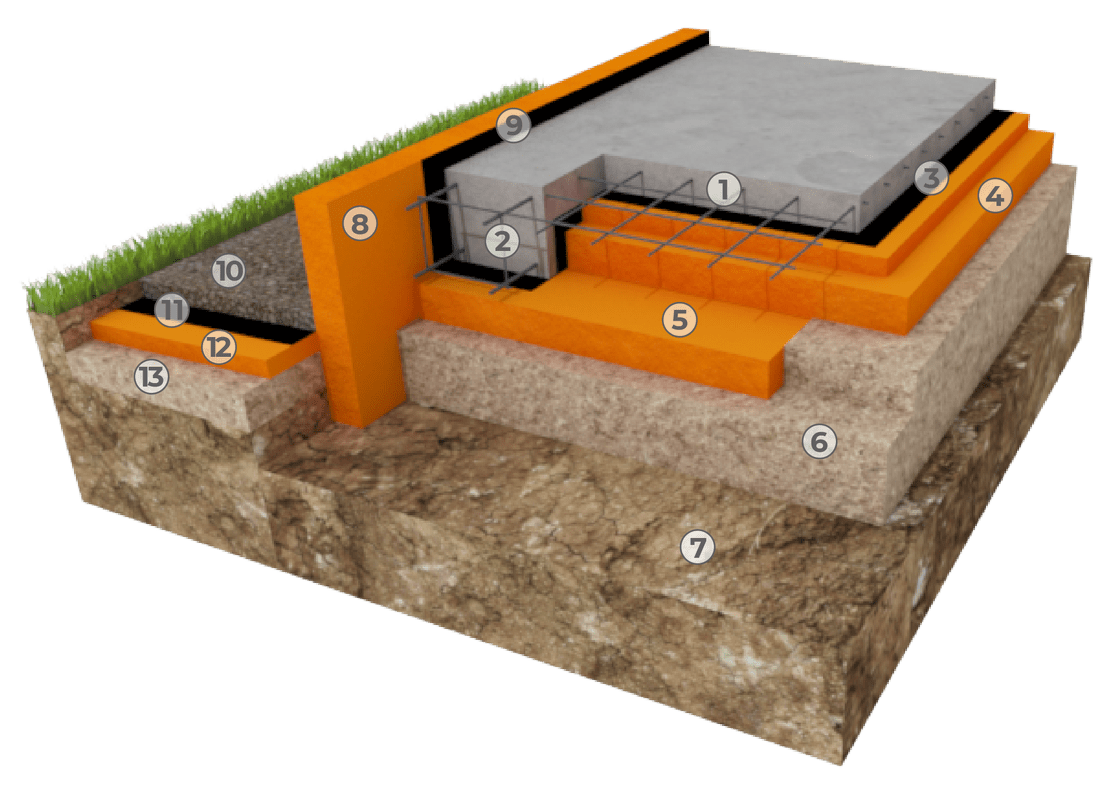
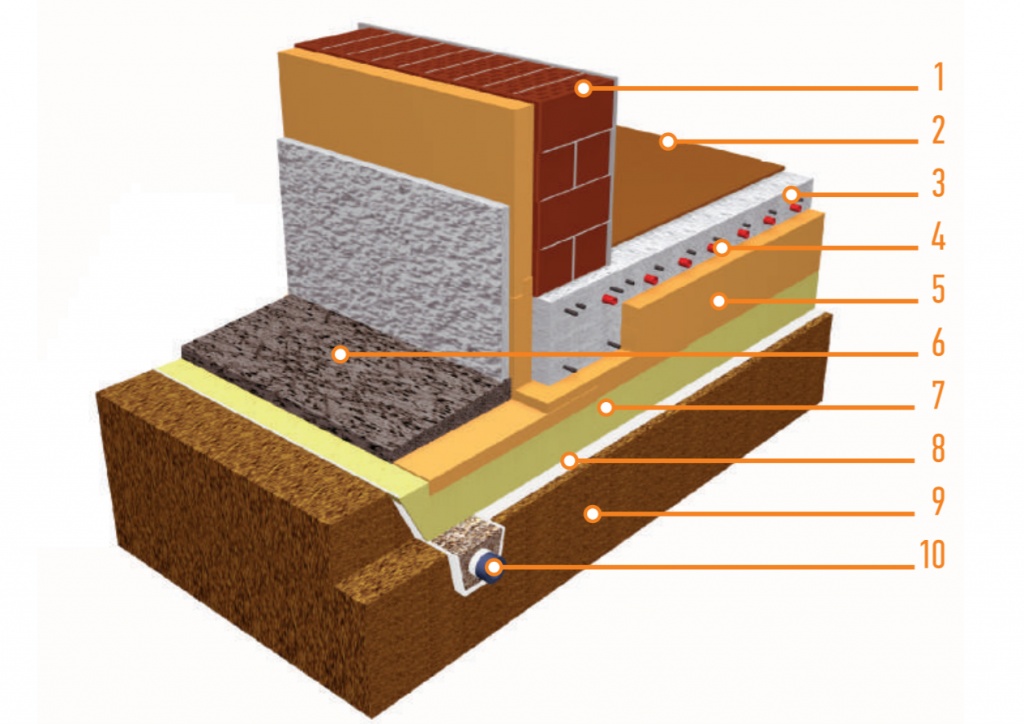
How to insulate a slab foundation with expanded polystyrene?

Scheme of a slab foundation with stiffeners.
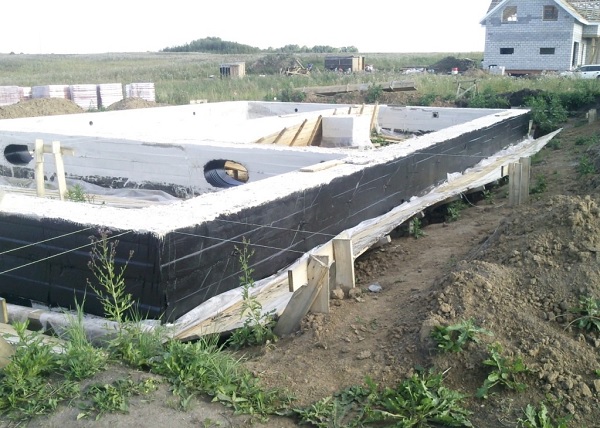
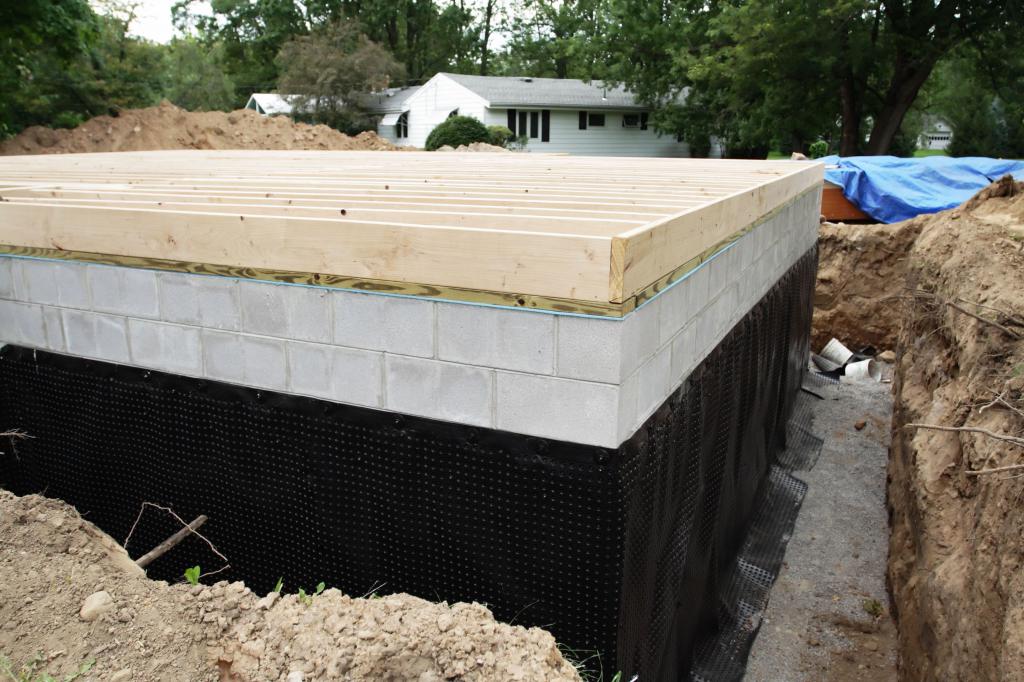
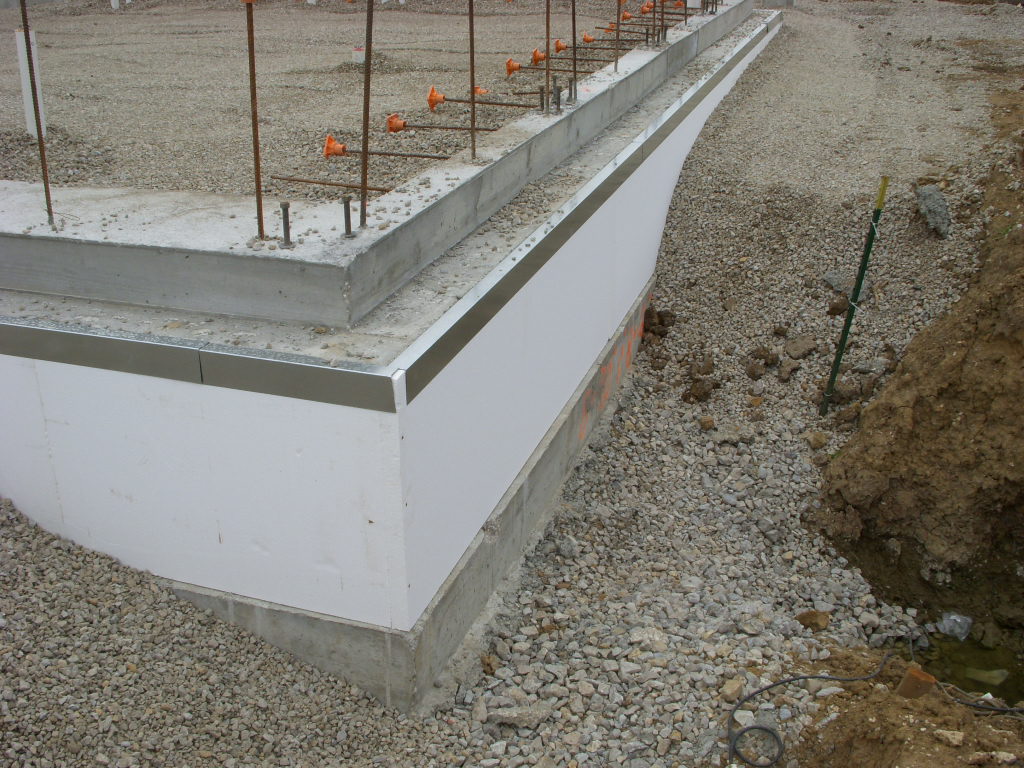
Insulating the vertical part of the foundation, polystyrene foam is installed at the depth of soil freezing, which is determined individually for each region. If you install the insulation deeper, the effectiveness of this will sharply decrease.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer in the corners should be increased by one and a half times with an indent in both directions of at least 1.5 m.
To insulate the slab foundation from the outside is a more rational way, since this way the level of heat loss will be lower.
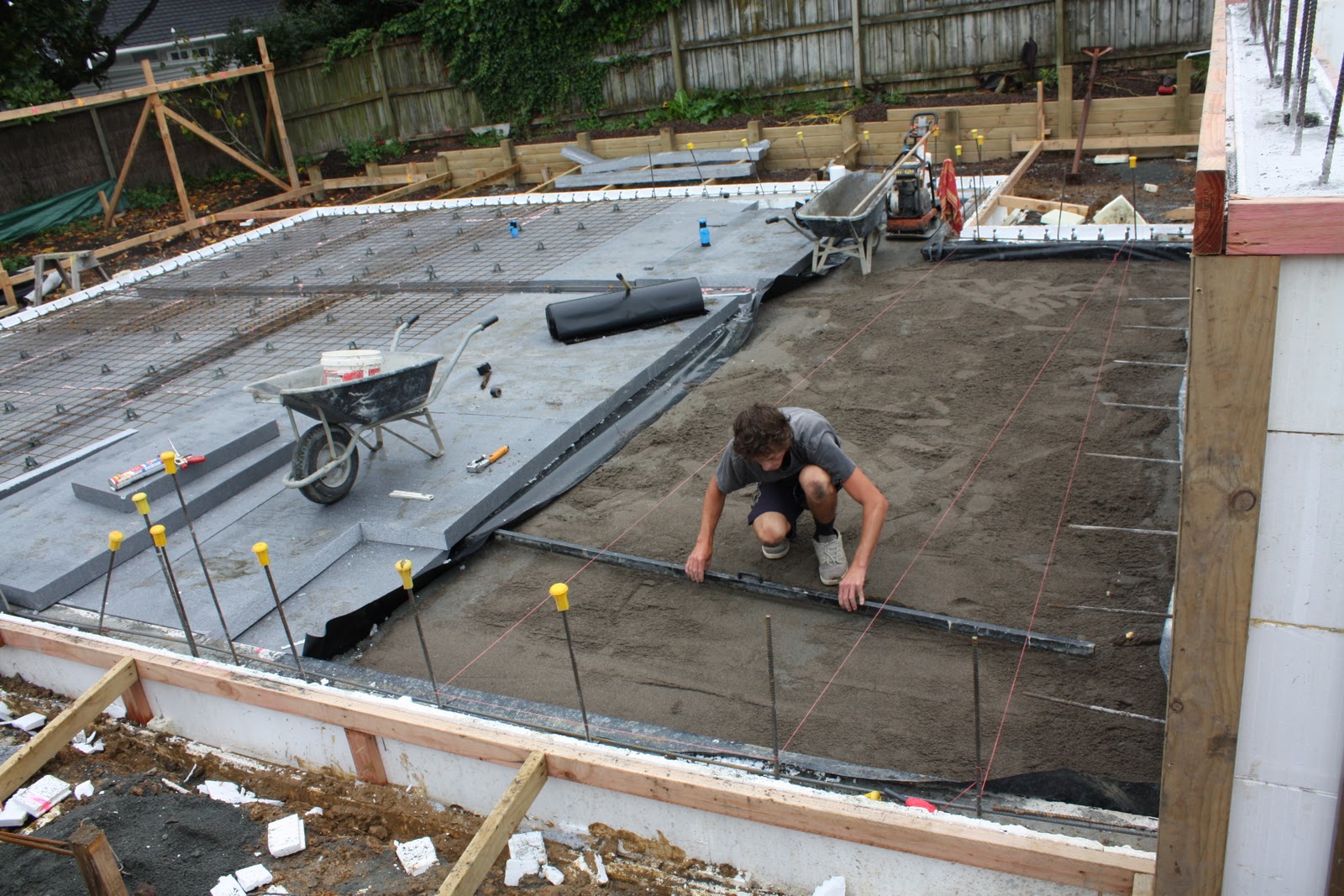
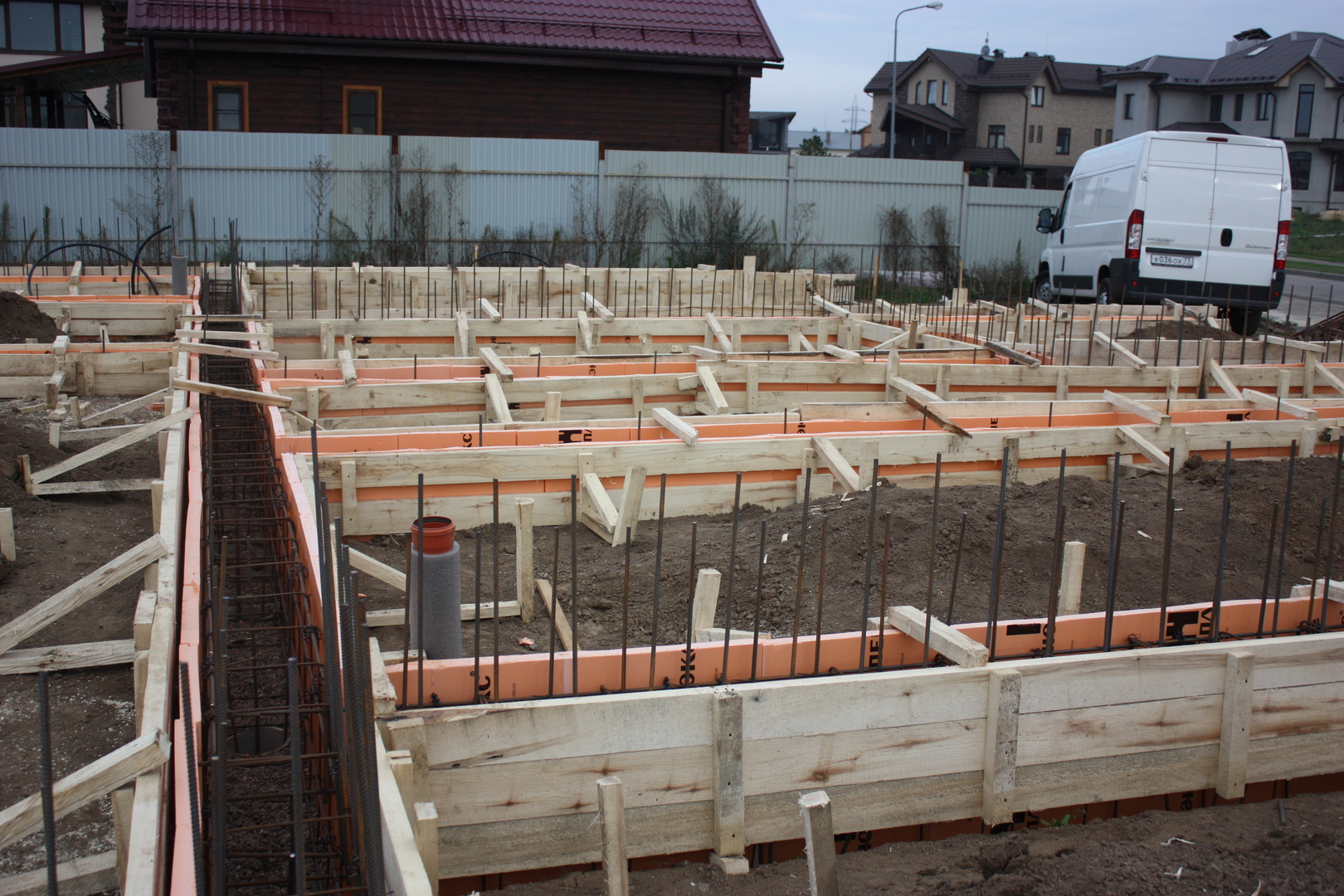
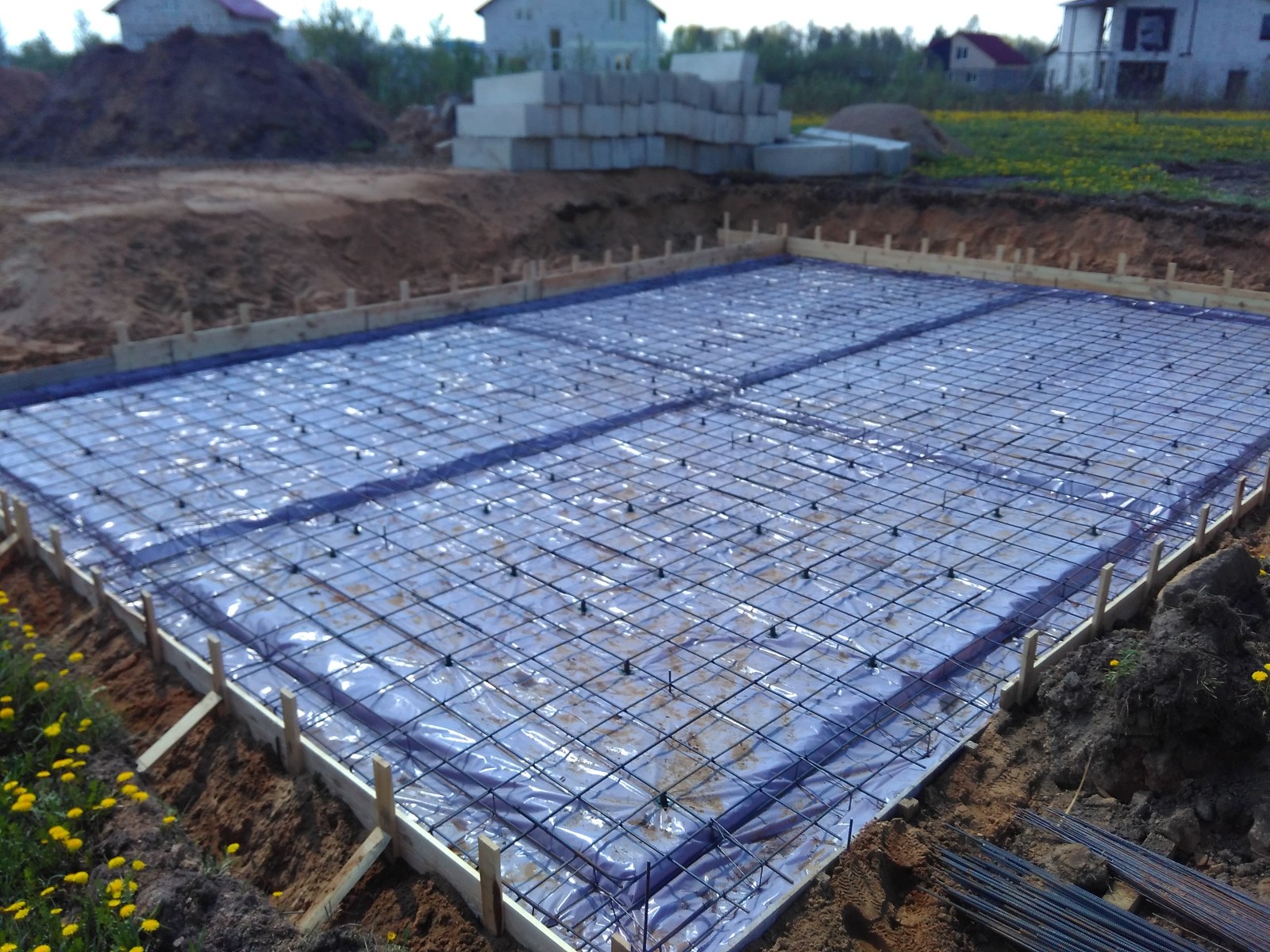
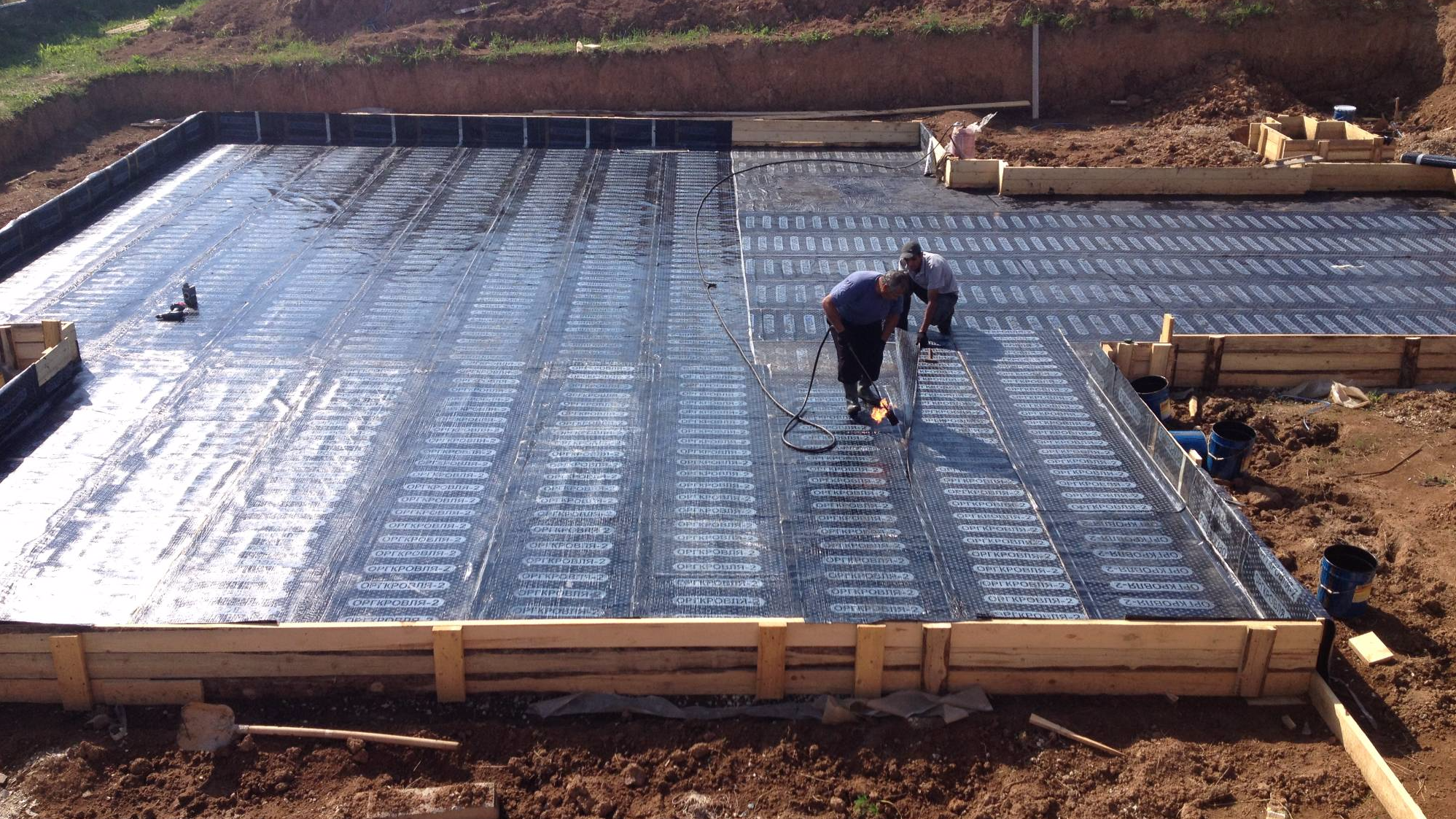
Thermal insulation boards are placed on the waterproofing layer. If you plan to use knitted reinforcement for reinforcing a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation slab or load-bearing floor, then for expanded polystyrene slabs it is necessary to arrange protection from liquid concrete components. To do this, use a polyethylene film (150-200 microns), which is laid in one layer. If the reinforcement work involves the use of welding, then a screed of low-grade concrete or cement mortar must be made over the film to protect it. Polyethylene is laid with an overlap of 100-150 mm on double-sided tape.
External insulation of the foundation
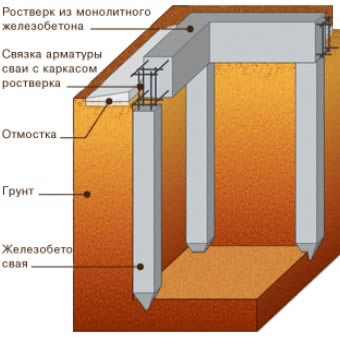
Pile foundation diagram.
To reduce the depth of freezing of walls and the base of the foundation, to keep the border of freezing in the thickness of non-porous soil - a sand and gravel cushion and backfilling will help warming the soil around the entire perimeter of the house under the construction of the blind area.
When laying polystyrene foam, it is important to take into account the given slope of the blind area - about 2% from the house. The width of the extruded polystyrene foam insulation around the perimeter should be no less than the depth of seasonal soil freezing.
The horizontal thickness of the insulation must be no less than the vertical thickness of the foundation insulation.
Internal insulation of the foundation
If it is impossible to insulate the slab foundation from the outside, it is allowed to install thermal insulation from the inside of the walls of the foundation.
Laying of thermal insulation from the side of the walls of the room is carried out either by gluing extruded polystyrene foam to the surface of the walls with solvent-free compositions (it is possible on a cement basis), or by mechanically fixing the insulation plates with a subsequent finishing device.
Types of waterproofing
If you nevertheless come to the conclusion that there is a need to provide waterproofing, the following points should be taken into account at the initial stage of the construction of the base and the use of moisture-proof materials:
- Before arranging the slab itself, the fertile layer is preliminarily destroyed on the site.
- For a more stable position of the structure, a pillow is made under the base from a layer of sand and gravel.
- Coarse gravel can easily damage the moisture-proof film or roll materials, so it is better to use small fractions of it. If the crushed stone is not evenly located, it will be simply impossible to ensure the tightness of the overlaps or joints of the material.
 Due to these reasons, builders often first pour concrete on the surface of the site to get an even layer, and then make a pillow. To ensure waterproofing of the foundation, the following materials are used:
Due to these reasons, builders often first pour concrete on the surface of the site to get an even layer, and then make a pillow. To ensure waterproofing of the foundation, the following materials are used:
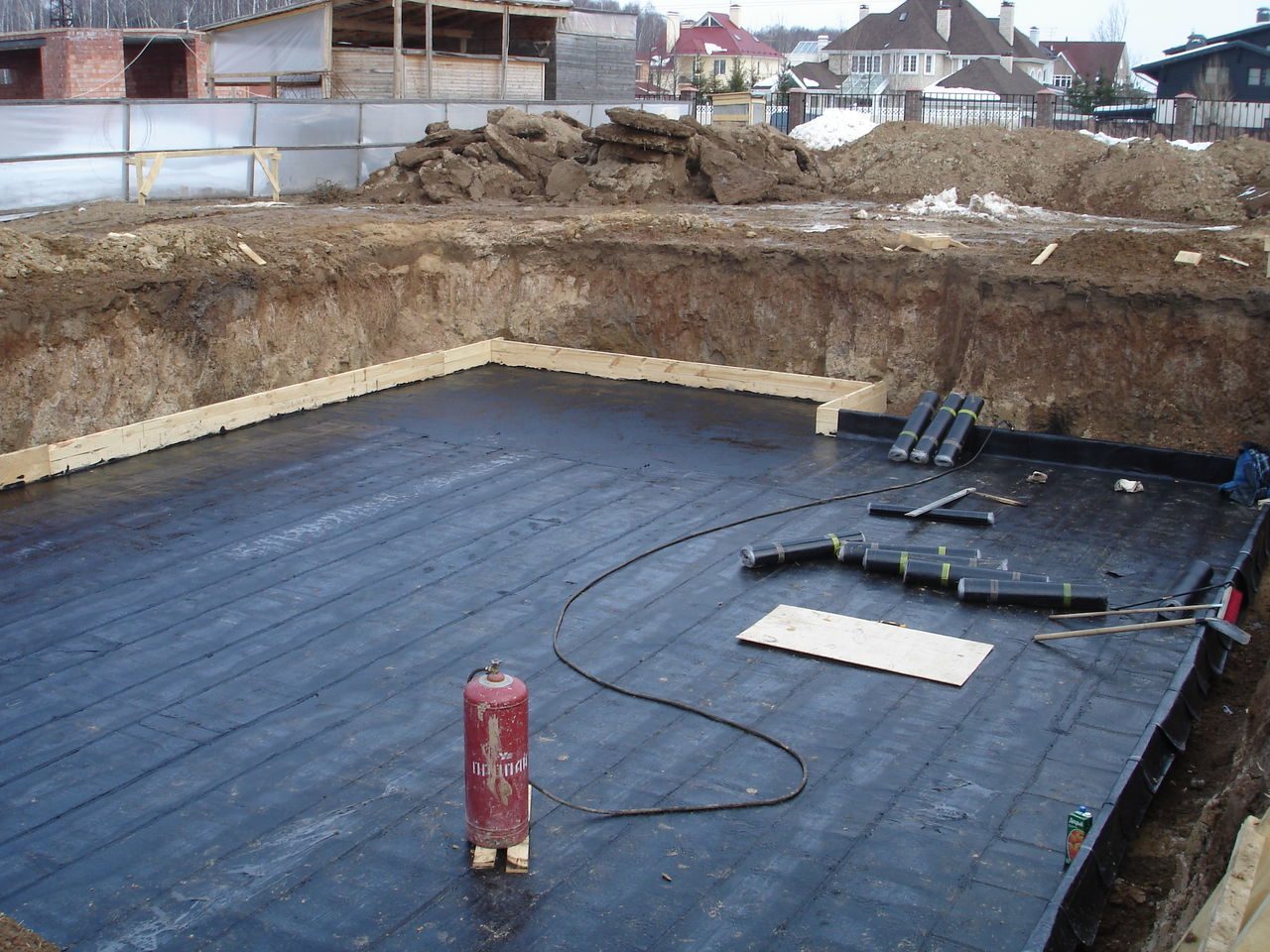
- Roll materials are the most common option. Also, this group often includes various moisture-proof films. The most popular representative is roofing material.
- Penetrating compounds. After being applied to concrete, the substances create a potential difference, which changes its structure.
- Concrete additives. Today there are many substances that are introduced into the concrete solution, and then the base is poured.
- Lubricants.They are mainly used for waterproofing strip foundations; they are not particularly suitable for slabs, since there is no possibility to coat the base sole.
For waterproofing monolithic slabs, roll materials, additives and compositions are the most suitable option. The last two options significantly reduce costs and time losses. Roll materials can be more expensive depending on prices in the region. In addition, laying roofing material or other materials of this group can take a lot of time. However, at the same time, roll materials are considered one of the most reliable.
What materials can be used to insulate a slab foundation?
Currently, a huge range of materials is presented on the domestic construction market that developers can use when carrying out insulation measures:
- Polyurethane foam. This material is made of foamed plastic, which has a porous structure filled with air bubbles. This insulating mixture is created directly at the construction site and applied to the foundation structures using special equipment. The components, which have entered into a chemical reaction, already on concrete surfaces form a durable foam that hardens almost instantly. This material helps to minimize heat loss, prevents extraneous noise from the street from entering the premises, does not undergo putrefactive changes in constant contact with a humid environment, and is highly resistant to ignition.
- Styrofoam. This material has been used for decades in the construction industry as insulation. Its main disadvantage is its low mechanical strength, which is why it needs additional cladding.
- Extruded expanded polystyrene. This material has a fine-mesh structure and is supplied to the construction market in the form of rectangular sheets. It has excellent technical properties, is able to withstand high loads, without changing either the internal structure or the geometric shape. In recent years, developers have used extruded polystyrene foam when insulating slab foundation structures, since it does not need additional protection and can perform the functions assigned to it for decades.
In what cases is it worth using a slab foundation for a house and types of slab foundations
This type of foundation is laid under the entire area of the future building and is characterized by maximum resistance to bending and breaking loads and pushing forces of the soil. As a result, such a foundation is suitable for construction on any flat areas, including sandy, peaty, swampy, often flooded, heaving and weak soils (sandy loam and loam with a bearing capacity within 2.5 kg / cm2).
The exact parameters of the slab are justified by calculation, but in general, it can easily withstand the weight of houses made of heavy building materials with a number of storeys within 3.
The maximum economic effect from the laying of the slab is achieved when building on unstable or heaving soils with a large freezing depth (in especially difficult cases, there are no alternatives to it). This type of foundation does not belong to the budget, but the investment in its construction pays off with a long service life and reliability. Limitations are manifested only in the impossibility of arranging basements near shallow slabs and in strict requirements for the evenness of the site.
Despite the uniform requirements of the technology (the presence of a dense cushion of sand and crushed stone, mandatory waterproofing of the sole and reinforcement of the structure, the choice of a slab thickness within 10-40 cm, compliance with GOST R 54257-2010 and other building codes), foundations of this type can have different depths and other differences.
Depending on the design features and the method of arrangement, the following are distinguished:
• Shallow, shallow and deeply buried foundation slabs. The former are ideal for construction on any soils other than highly heaving, the latter are laid after removing a small layer of fertile soil and have universal performance characteristics, the third are the most expensive and are chosen if there is a basement or underground floors in the project.
• Monolithic, prefabricated or prefabricated monolithic structures... In most cases, such a foundation is poured directly on site, but sometimes the functions of the foundation are performed by a solid reinforced concrete product of factory quality or prefabricated structures from floor slabs.
• Conventional flat slabs and structures reinforced with additional stiffeners or piles.
Plain and insulated
Depending on the type of cake, all slab foundations are divided into ordinary and insulated ones.
The placement of an insulating layer is not a prerequisite for the construction of a slab, but its presence significantly reduces heat losses through the bottom of the building and extends the service life of the base.
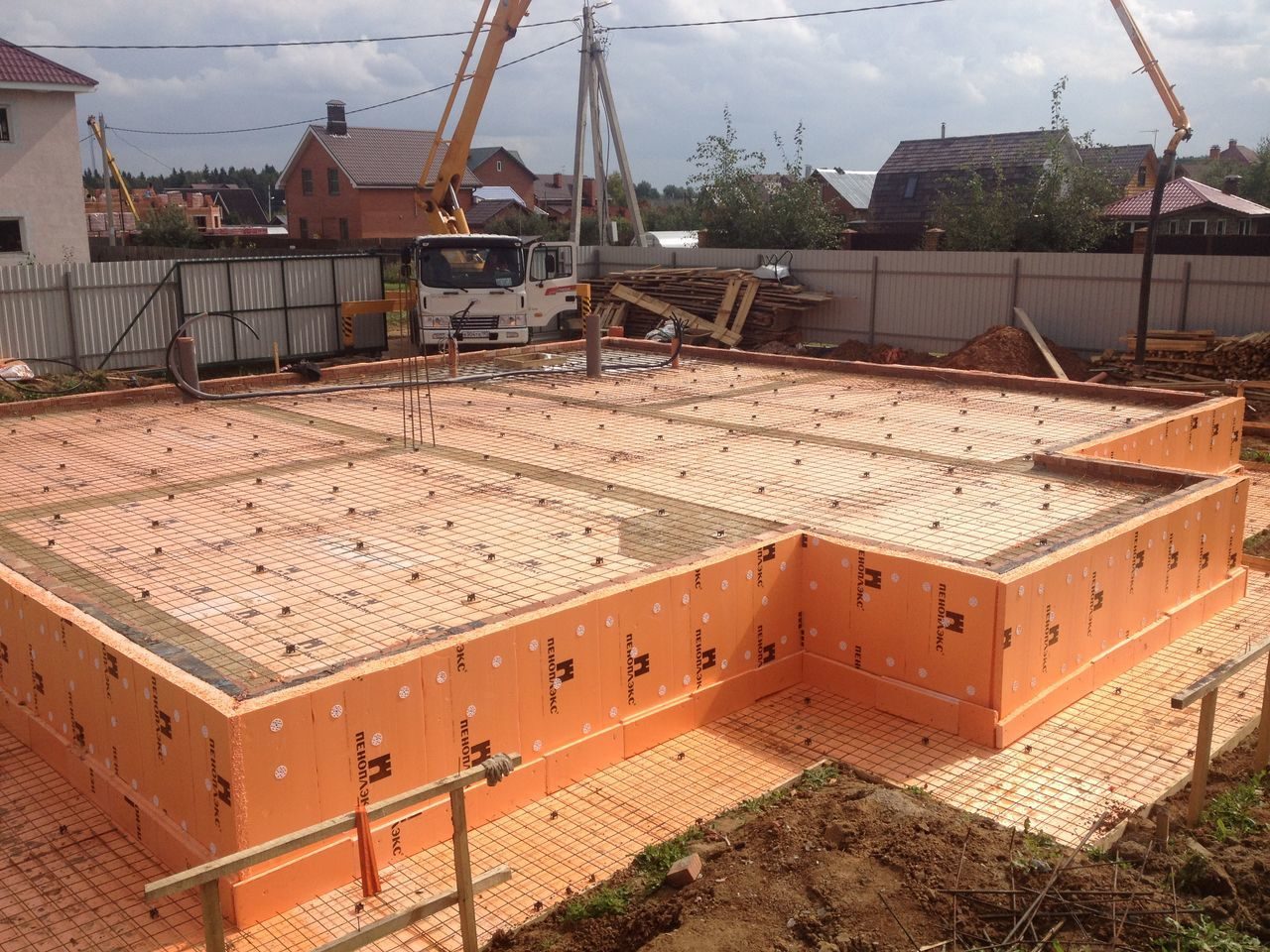
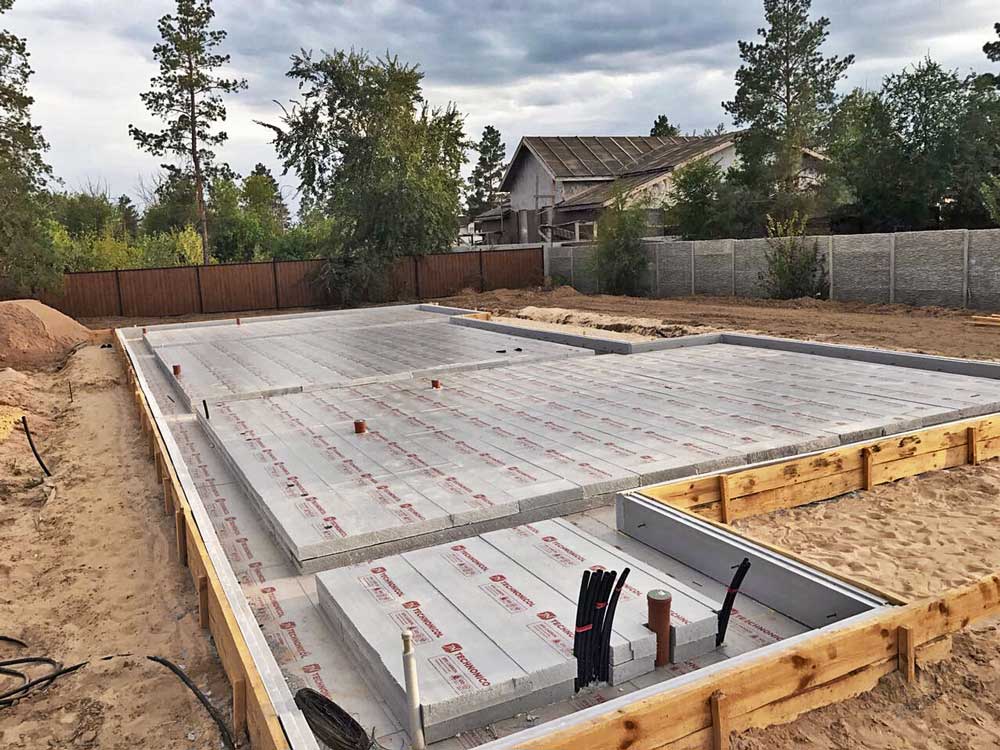
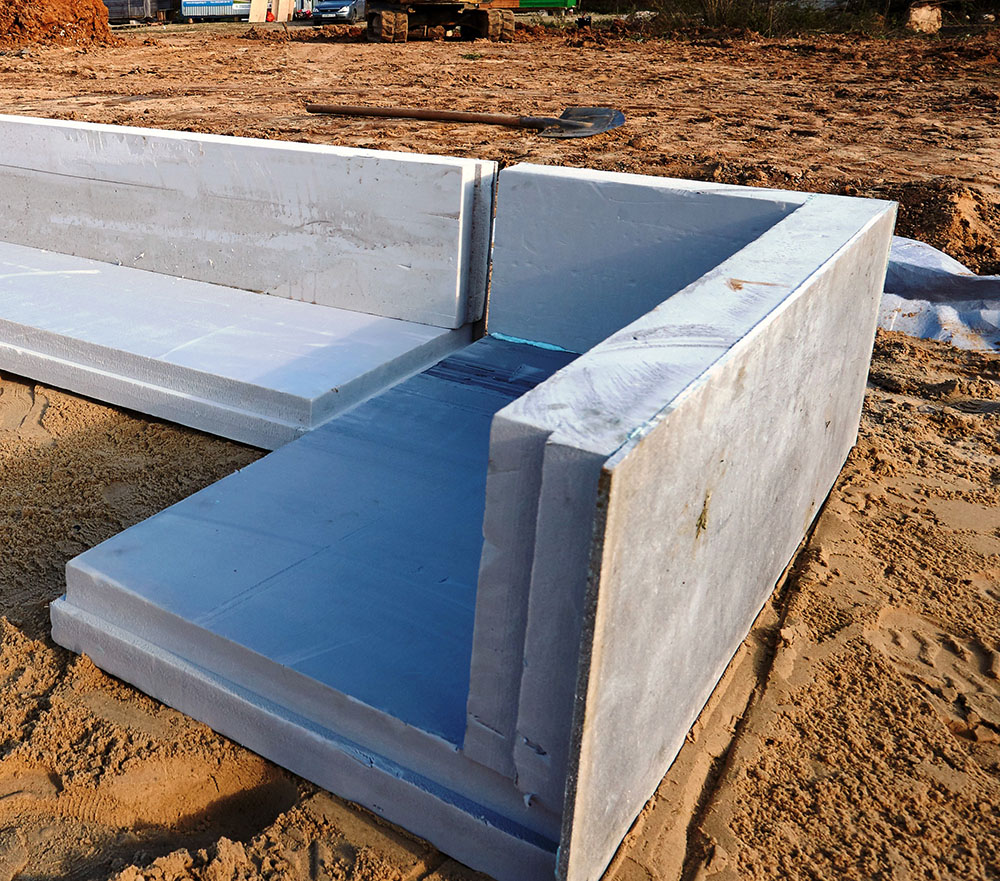
The best suited for these purposes are specialized boards of compacted polystyrene foam, laid in at least 2 layers with the usual shape of the edges, or in 1 layer or more when using sheets with an L-edge or locking systems.
The total thickness of the insulating layer depends on the operating conditions and the tasks set and is 10-15 cm for conventional foundations and at least 20 cm for foundations laid using the "Swedish plate" technology (USHP).
The latter, in turn, belong to shallow structures and are recognized as optimal for construction on heaving and flooded soils.
With and without underfloor heating
In the absence of an insulating layer in the cake of the slab foundation, laying underfloor heating elements during concreting does not make sense. The lion's share of heat in such systems goes to heating concrete and soil, their efficiency is significantly reduced.
In USP and their analogues, on the contrary, complex actions are only welcomed. In particular, in such structures, in addition to the main engineering communications, pipes of a water-heated floor are successfully placed. After the completion of the concreting and grinding stage, the surface of the slab is suitable for the installation of floor coverings, the construction time for a private house and the cost of heating it are reduced.
Recipe two: waterproofing tape, monolithic foundation
The tape base is insulated in a slightly different way. Firstly, in this case, all work is carried out on a ready-made basis. And, secondly, the waterproofing agent is applied on both sides of the foundation wall: along the outer and inner parts of the base of the structure.
Well, the process itself is as follows:
- After dismantling the wall formwork, the foundation is prepared for the installation of a waterproofer. To do this, they clean off the remnants of the soil from the wall, exposing the plane of the base to the very sole, and scrape off the unhardened areas that have not had time to transform into cement stone.
- Further, a layer of liquid rubber is sprayed over the cleaned surface using a special device, which covers both the inner and outer parts of the foundation wall, and its grillage.
- After the rubber has hardened, the foundation is wrapped with geotextiles oriented towards permeability in the direction "from the wall to the ground", and the sinuses between the base and the boundaries of the excavation are covered with selected soil.
Well, the basement part, open to any misfortunes, can, from time to time, be repaired, restoring the integrity of the waterproofing layer.
In the inner part of the base wall, on top of the rubber coating, a brickwork is equipped - a protector that will protect the soft insulator from mechanical damage.However, a similar system can be built on the basement level on the outside of the foundation, protecting the waterproofer with a brick or stone cladding.
About the site
zalman
Insulation of the foundation of a monolithic type with expanded polystyrene
Thermal insulation of base plates in this way is a relatively young form of modification of private houses. It began to be used in the 50s - 60s of the XX century. This type of slab insulation is durable and has a long service life. According to statistics, the popularity of expanded polystyrene is growing steadily every day.
Strengthening monolithic slabs with expanded polystyrene proved to be a very successful solution in the construction of houses, because their service life is more than 50 years. After carrying out various tests and checks, it became clear that the material did not change during the entire period of operation.
It follows from this that the growing popularity and steady increase in the consumption of expanded polystyrene is a regularity. Over the past 20 years, its use has increased tenfold. The main consumers of this material are Europe and North America.
Comparison of thermal insulation materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam for insulating a monolithic base plate is a material with a uniform structure, consisting of closed cells. Due to the low density of the material, its thermal insulation properties increase. You should also know that expanded polystyrene has increased strength characteristics and is able to withstand rather heavy loads.
Expanded polystyrene practically does not allow water to pass through and is not afraid of the effects of chemically aggressive environments. Thermal insulation with this material is done in regions with harsh winters and very cold weather. Expanded polystyrene copes well with repeated cycles of freezing and defrosting, while its performance does not change at all. Expanded polystyrene is usually sold in the form of slabs.
Monolithic foundation device
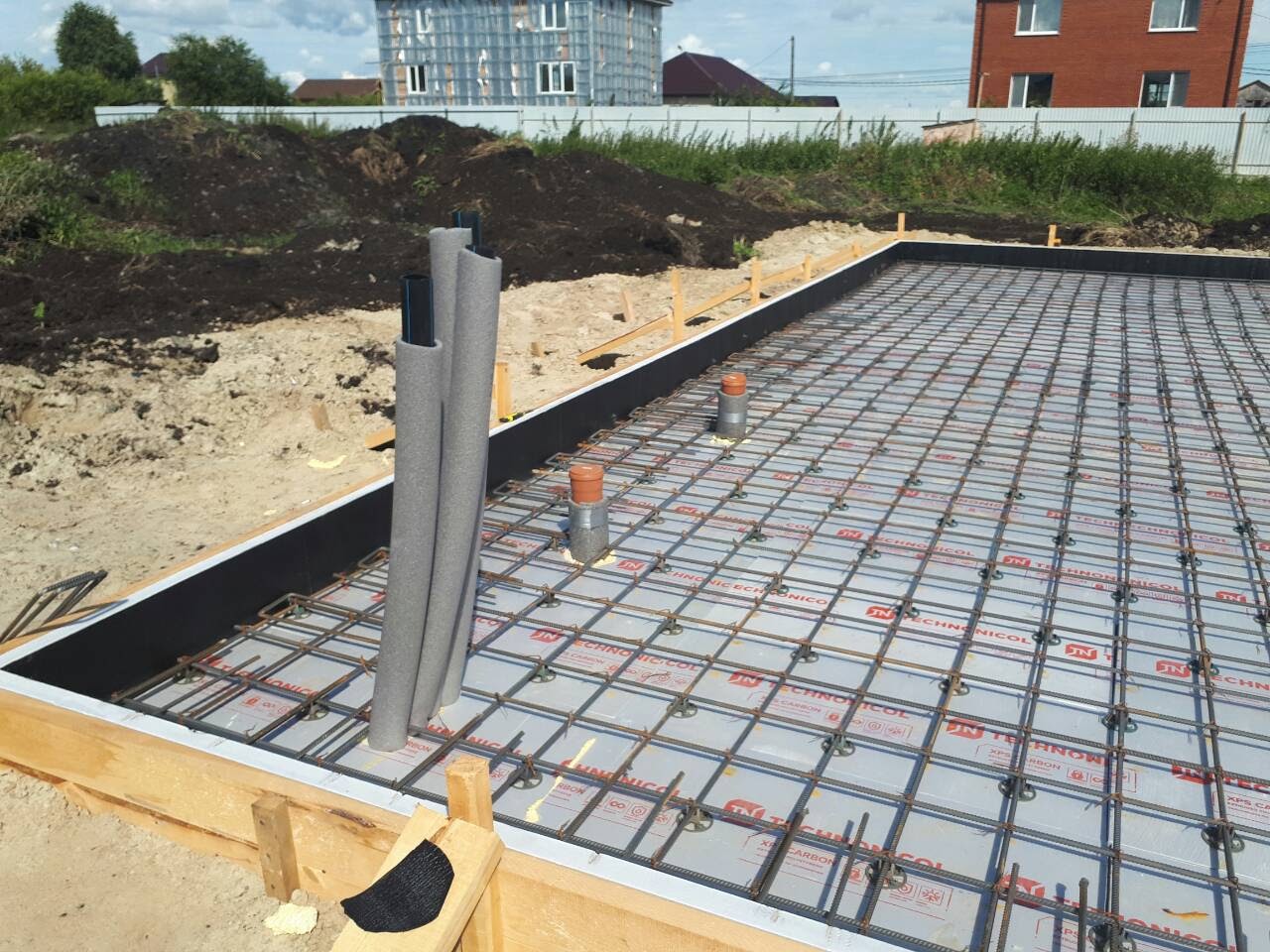
In terms of its composition, a monolithic foundation can be characterized as concrete, in the body of which there is metal reinforcement. You can also use iron rods, thick steel wire or small steel pipes as reinforcing elements. The reinforcement of a monolithic foundation performs the function of a skeleton, a power frame. Thanks to her, the loads are distributed equally to any points of the concrete pour.
It is recommended to construct the reinforcing frame in such a way that the load-bearing elements are located close to the foundation surfaces. This will reduce tensile loads. The thickness of the reinforcement or rods is not very important, but usually it is in the range of 5-15 mm.
In some cases, drawings of a monolithic foundation are drawn up. They indicate the dimensions, depth and width of the foundation, the presence of inter-wall partitions, under which pouring will also be performed. Drawings are performed in several views, that is, top view, side view and front view. In some cases, it is very difficult to do without a drawing. For example, when constructing a pile foundation, pile locations are marked on the drawing. Then the piles are driven or screwed into the ground according to the calculation data. This avoids mistakes when pouring a monolithic foundation.
Which foundation option should you prefer?
When intending to fill a monolithic foundation, you must decide in advance which type of foundation to give preference to.
The choice depends on the type of soil on the site and the weight load of the building:
On heaving soils, a slab foundation will have an advantage
It does not matter to what depth it will be laid, it is enough just to ensure its correct arrangement. Monolithic reinforced concrete slab will distribute all loads evenly over its area
A building on such a foundation, even in the case of winter swelling, will not give cracks or deformations, since all heaving forces will act equally on the entire area of the foundation. A significant disadvantage of a poured reinforced concrete slab is its high cost. Especially if the building is planned to be built large enough.
If the soil is heaving, it is not possible to apply a slab foundation, then you can equip a strip and pile monolithic foundation. The strip foundation must necessarily be deepened so deep that the depth of freezing of the soil is higher than the base of such a foundation. In this case, you can not worry about the safety of the building. The monolithic pile foundation has a special feature. Its piles must also be sunk deep enough into the soil, 20-30 centimeters below the level of soil freezing.
On non-rocky ground, it is recommended to use a strip foundation. It can be buried or shallow. If you prefer the second option, then keep in mind that the shallow foundation must be insulated. To insulate a monolithic foundation, sheets of extruded polystyrene foam are used, laid on top of the ground, along the outer perimeter of the foundation.
Materials for thermal insulation of the foundation

Insulation of the base of the house
Insulation of the foundation is a mandatory measure to protect the base of the building from adverse external influences.
When choosing a heater, it is important to proceed from indicators such as:
- high mechanical strength;
- waterproofness;
- low vapor absorption.
How to insulate the base of the house? Today, the market offers several suitable materials for insulating the foundation from the outside with your own hands. We will consider each of these materials in more detail.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam has recently been used as the optimal insulation for the foundation.
It has the following properties:
- resistance to biological influences;
- complete safety for human health;
- high moisture resistance;
- frost resistance.
Water absorption during prolonged wetting is practically zero. Basement insulation - expanded polystyrene has standard dimensions and high mechanical strength. This determines its use as an insulating material for floors, walls, roofs and concrete foundations of buildings.
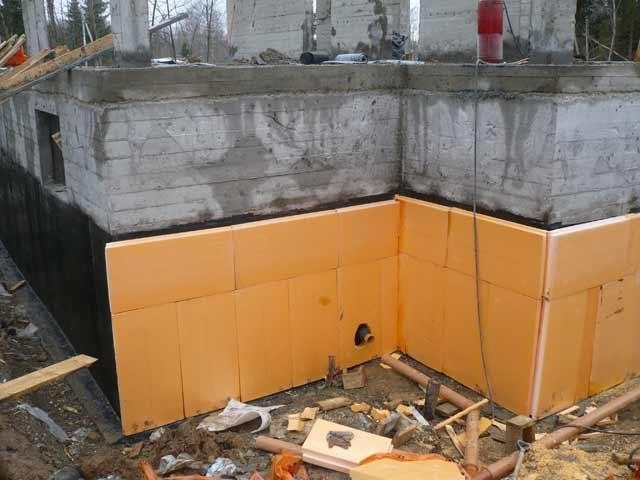

Thermal insulation of the base with extruded polystyrene foam
Installation instructions for extruded polystyrene foam:
- Insulation of foundations with extruded polystyrene foam should be carried out at a height of at least 50 cm above ground level.
- It is advisable to carry out installation after applying a waterproofing layer. To do this, you can use a water-based bitumen solution.
- If waterproof cement-based mortars are used as waterproofing, the material can be glued to the base with a special adhesive for thermal insulation.
- After the slab foundation has been insulated, the thermal insulation is covered with a protective geotextile fabric.
- Then drainage pipes are laid, and the base from the outside is covered with rubble or other material.
Polyurethane foam

Spraying polyurethane foam
Another effective material used as foundation insulation is polyurethane foam. It has the following properties:
- retains its qualities in soil saturated with moisture;
- thanks to spraying, it adheres tightly to the foundation, has no seams and "cold bridges";
- some types of this material have waterproofing properties;
- resistant to chemicals.
Polyurethane foam is not only a thermal insulation material. It also protects against moisture and absorbs noise. Installation of this material is carried out by spraying on the foundation in layers, using special equipment.
Thus, it is possible to insulate the foundation slab, as well as other types of bases.
Another advantage of the polyurethane foam coating is its solidity. With uniform spraying, no seams or gaps are formed, that is, no cold bridges are formed.
Plain foam
Thermal insulation of the plinth with foam
Do I need to insulate the base? Of course, yes, because due to the possible formation of numerous cold bridges when connecting the foundation with the walls, optimal thermal insulation is required.
Some homeowners, when deciding how to insulate the foundation for the winter, traditionally opt for ordinary foam. This material can be used only if there is no danger of flooding.
People are attracted by the price of this option. But in the matter of thermal insulation of the foundation, it is better not to save. It is wiser to choose a more practical, moisture resistant, homogeneous, strong material that will last for many years.
Regular foam is more suitable for interior insulation, for example, as insulation of a loggia or a glazed balcony.
What are the advantages of UWB?
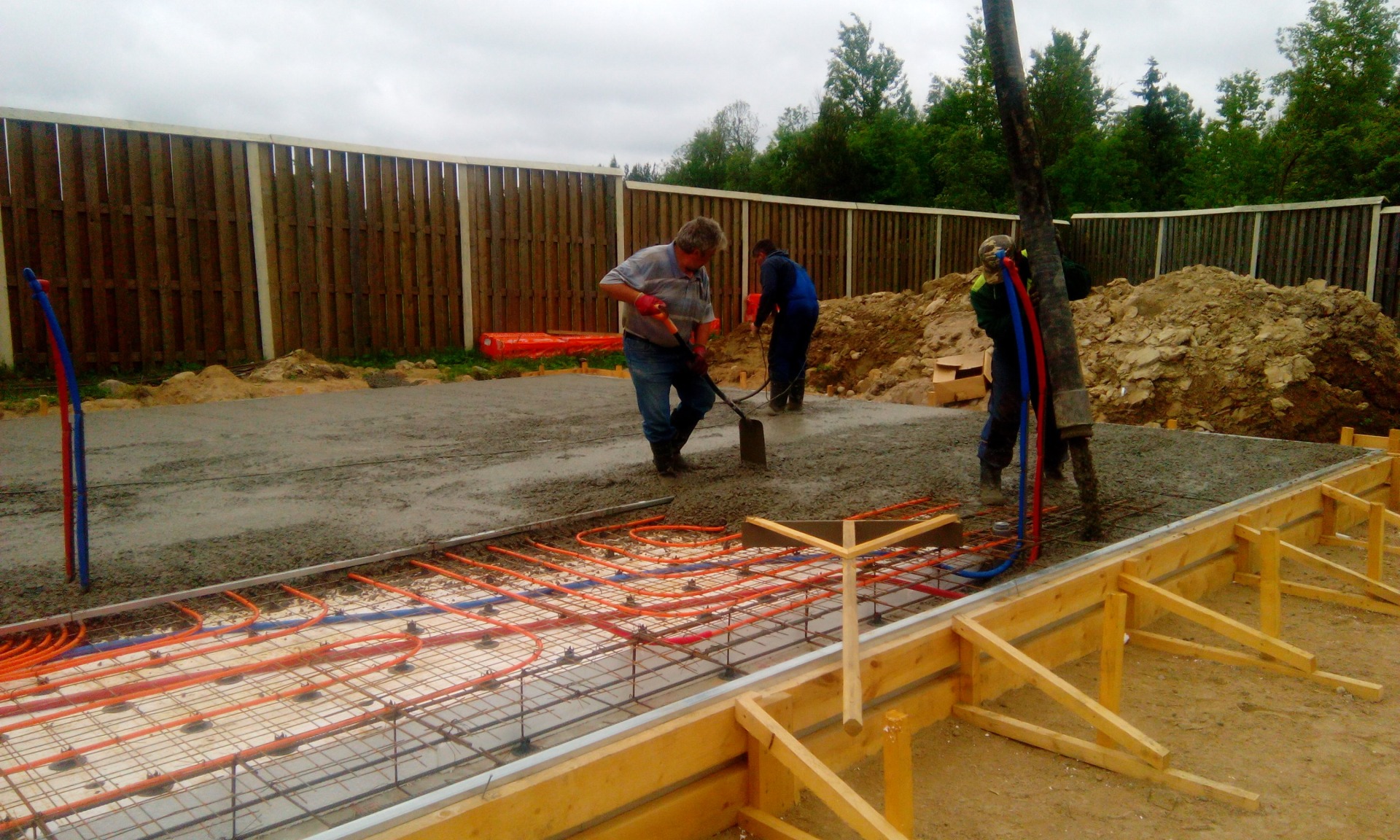
High speed of construction in 2-3 weeks. The duration of the work depends on the area and geometry of the slab: the larger in size and more complex in shape the foundation, the longer it will take to build. Weather conditions also play a role: it is better not to pour concrete during heavy rain. The possibility of the device on almost any soil, including those with a high level of groundwater and heaving - clays, loams. Thanks to the insulation, the ground does not freeze, which means that the foundation is protected from deformations due to frost heaving of the soil. However, UWB cannot be done on soils with very low bearing capacity, for example, peat bogs. In this case, foundation settlement is possible. No deep excavation required: saving on earthwork. The readiness of all communications at the stage of foundation construction. This significantly speeds up the construction of a house. High energy efficiency thanks to thermal insulation layer. This means that the cost of heating the building is low. USB with 200 mm thick insulation has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.17 W / (m • ° С). For comparison: the coefficient of thermal conductivity of a conventional monolithic concrete slab, as a rule, exceeds 0.40 W / (m • ° C)

There are no cold bridges in the structure of the slab and freezing of the lower corners of the building due to the continuous layer of thermal insulation under the foundation and the insulated blind area. Heating with a water-heated floor is 20-30% more economical than radiator heating, since the heat carrier is supplied to the radiators with a temperature of about 70 ° C, and into the warm floors - with a temperature of about 40 ° C. In addition, the warm floor warms up the room evenly, creating very comfortable temperature conditions for the inhabitants of the house. Finally, the absence of radiators improves the appearance of the premises. There is no need to put a screed on top of the slab: the surface of the foundation is leveled and sanded, it serves as a ready-made base for laying the floor covering. This means that when finishing the premises, you can refuse additional wet work.

There are no seams in the slab (expansion gaps are required in the screed), which simplifies the installation of the floor covering.
Swedish stove technology

Operating procedure:
- A pit is pulled out over the area of the future building with a depth of 40 cm.
- A gravel-sand cushion is laid with compaction and laying of intermediate geotextiles.
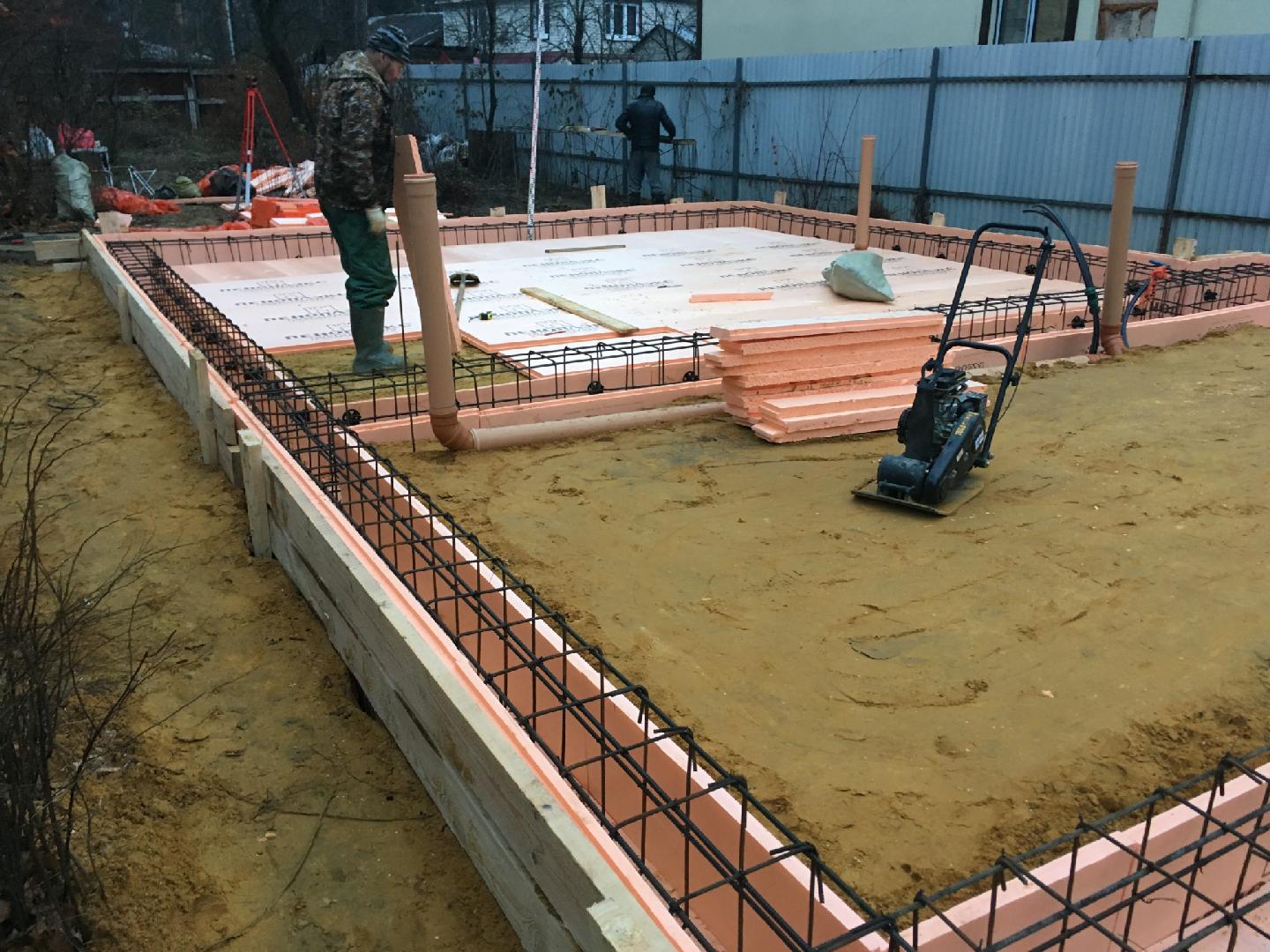
- The formwork is assembled from expanded polystyrene plates with sides using metal fasteners. The entire area is covered with ordinary polyurethane foam boards 10 cm thick. The side elements are of the same thickness. If ordinary slabs are used along the perimeter, then a formwork made of film faced plywood is additionally mounted along the outer edge.
- The bottom and walls of expanded polystyrene plates are lined with roofing material.
- Lay another layer of expanded polystyrene (also 10 cm).
- Lay communications (water supply, drainage, electricity, etc.) and floor heating.
- Reinforcement mesh is installed.
- Everything is poured with concrete using a vibrator.
So, in a short time, a super warm foundation structure is obtained. Although there is an opinion that UWB is beneficial primarily for producers of expanded polystyrene.
This technology still has disadvantages:
- A monolithic slab is prone to uneven shrinkage due to shallow deepening, and laying polystyrene foam under it can further aggravate this process. Despite the fact that the manufacturer guarantees the ability of the expanded polystyrene board to withstand maximum loads, this technology is not suitable for heavy and multi-storey buildings.
- In cases where a mistake was made in laying communications, in order to fix poorly performed work, the entire foundation will have to be dismantled. It will be extremely difficult to repair water supply and electrical communications with such a laying.
There are many ways to insulate a monolithic slab. In each case, this or that option is most suitable. Each builder must choose an option based on the type of soil, the type of structure and its future load.